Corpus Cavernosum Of Clitoris on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The corpus cavernosum of the clitoris is one of a pair of sponge-like regions of
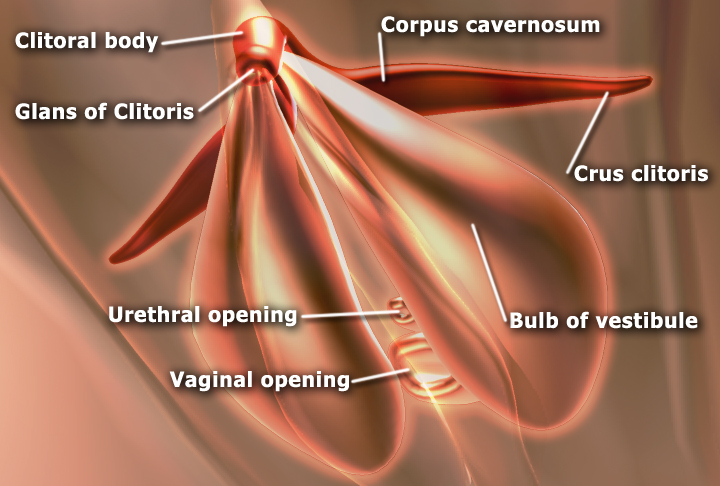 The two corpora cavernosa are expandable erectile tissues of the clitoris. They are joined together along their medial surfaces by an incomplete fibrous
The two corpora cavernosa are expandable erectile tissues of the clitoris. They are joined together along their medial surfaces by an incomplete fibrous
erectile tissue
Erectile tissue is tissue in the body with numerous vascular spaces, or cavernous tissue, that may become engorged with blood. However, tissue that is devoid of or otherwise lacking erectile tissue (such as the labia minora, vestibule, vagina and ...
that engorge with blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells.
Blood is com ...
during an erection
An erection (clinically: penile erection or penile tumescence) is a Physiology, physiological phenomenon in which the penis becomes firm, engorged, and enlarged. Penile erection is the result of a complex interaction of psychological, neural, ...
. This is homologous to the corpus cavernosum of the penis. The term ''corpora cavernosa'' literally means "cave-like bodies".
Structure
 The two corpora cavernosa are expandable erectile tissues of the clitoris. They are joined together along their medial surfaces by an incomplete fibrous
The two corpora cavernosa are expandable erectile tissues of the clitoris. They are joined together along their medial surfaces by an incomplete fibrous septum
In biology, a septum (Latin language, Latin for ''something that encloses''; septa) is a wall, dividing a Body cavity, cavity or structure into smaller ones. A cavity or structure divided in this way may be referred to as septate.
Examples
Hum ...
. Each corpus cavernosum is connected to the rami of the pubis and ischium
The ischium (; : is ...
by a clitoral crus. There is connection to the ischiocavernosus muscle
The ischiocavernosus muscle (erectores penis ''or'' erector clitoridis in older texts) is a muscle just below the surface of the perineum, present in both men and women.
Structure
It arises by tendinous and fleshy fibers from the inner surface o ...
. Each can be up to 7 cm long in an adult.
Development
The corpus cavernosum is homologous to thecorpus cavernosum penis
A corpus cavernosum penis (singular) (from Latin, characterised by "cavities/ hollows" of the penis, : corpora cavernosa) is one of a pair of sponge-like regions of erectile tissue, which contain most of the blood in the penis of several animal ...
in the male. It develops from the genital tubercle
A genital tubercle, phallic tubercle, or clitorophallic structure is a body of tissue present in the development of the reproductive system of amniotes. It forms in the ventral, caudal region of mammalian embryos of both sexes, and eventually ...
in the embryo
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sp ...
.
The clitoris also has two vestibular bulbs
In female anatomy, the vestibular bulbs, bulbs of the vestibule or clitoral bulbs are two elongated masses of erectile tissue typically described as being situated on either side of the vaginal opening. They are united to each other in front by a ...
beneath the skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different ...
of the labia minora
The labia minora (Latin for 'smaller lips', : labium minus), also known as the inner labia, inner lips, or nymphae, are two flaps of skin that are part of the primate vulva, extending outwards from the inner Vagina#Vaginal opening and hymen, vagi ...
(at the entrance to the vagina
In mammals and other animals, the vagina (: vaginas or vaginae) is the elastic, muscular sex organ, reproductive organ of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vulval vestibule to the cervix (neck of the uterus). The #Vag ...
), which expand at the same time as the glans clitoridis to cap the ends of the corpora cavernosa.Microanatomy
The corpus cavernosum is made of a sponge-like tissue. This contains irregular blood-filled spaces, lined byendothelium
The endothelium (: endothelia) is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and the r ...
, and separated by connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, a group of cells that are similar in structure, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops mostly from the mesenchyme, derived from the mesod ...
septa
SEPTA, the Southeastern Pennsylvania Transportation Authority, is a regional public transportation authority that operates bus, rapid transit, commuter rail, light rail, and electric trolleybus services for nearly four million people througho ...
.
Function
The corpora cavernosa fill withblood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells.
Blood is com ...
during clitoral erection
Clitoral erection (also known as clitoral tumescence or female erection) is a physiological phenomenon where the clitoris becomes enlarged and firm.
Clitoral erection is the result of a complex interaction of psychological, neural, vascular ...
. Their size increases 2 fold to 3 fold. In some circumstances, release of nitric oxide
Nitric oxide (nitrogen oxide, nitrogen monooxide, or nitrogen monoxide) is a colorless gas with the formula . It is one of the principal oxides of nitrogen. Nitric oxide is a free radical: it has an unpaired electron, which is sometimes den ...
precedes relaxation of the clitoral cavernosal artery and nearby muscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contra ...
, in a process similar to male arousal. More blood flows in through the clitoral cavernosal artery
An artery () is a blood vessel in humans and most other animals that takes oxygenated blood away from the heart in the systemic circulation to one or more parts of the body. Exceptions that carry deoxygenated blood are the pulmonary arteries in ...
, the pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and eve ...
in the corpora cavernosa clitoridis rises. The clitoris is engorged with blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells.
Blood is com ...
. This leads to extrusion of the glans clitoridis and enhanced sensitivity to physical contact.
Clinical significance
The corpora cavernosa can reduce in size before themenopause
Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time when Menstruation, menstrual periods permanently stop, marking the end of the Human reproduction, reproductive stage for the female human. It typically occurs between the ages of 45 and 5 ...
. This can impair sexual function in some women.
References
External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Corpus Cavernosum Of Clitoris Clitoris