Copepoda on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Copepods (; meaning 'oar-feet') are a group of small

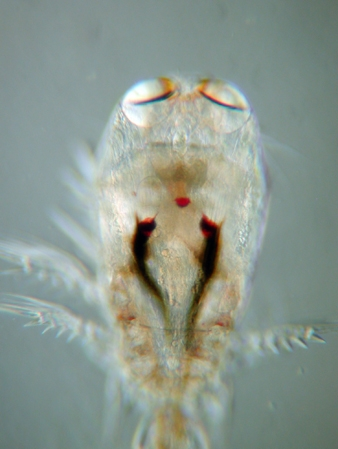 Copepods vary considerably, but are typically long, with a teardrop-shaped body and large antennae. Like other crustaceans, they have an armoured
Copepods vary considerably, but are typically long, with a teardrop-shaped body and large antennae. Like other crustaceans, they have an armoured
 Some copepods have extremely fast escape responses when a predator is sensed, and can jump with high speed over a few millimetres. Many species have
Some copepods have extremely fast escape responses when a predator is sensed, and can jump with high speed over a few millimetres. Many species have
 Most nonparasitic copepods are holoplanktonic, meaning they stay planktonic for all of their lifecycles, although harpacticoids, although free-living, tend to be benthic rather than planktonic.
During mating, the male copepod grips the female with his first pair of antennae, which is sometimes modified for this purpose. The male then produces an adhesive package of sperm and transfers it to the female's genital opening with his thoracic limbs. Eggs are sometimes laid directly into the water, but many species enclose them within a sac attached to the female's body until they hatch. In some pond-dwelling species, the eggs have a tough shell and can lie dormant for extended periods if the pond dries up.
Eggs hatch into nauplius larvae, which consist of a head with a small
Most nonparasitic copepods are holoplanktonic, meaning they stay planktonic for all of their lifecycles, although harpacticoids, although free-living, tend to be benthic rather than planktonic.
During mating, the male copepod grips the female with his first pair of antennae, which is sometimes modified for this purpose. The male then produces an adhesive package of sperm and transfers it to the female's genital opening with his thoracic limbs. Eggs are sometimes laid directly into the water, but many species enclose them within a sac attached to the female's body until they hatch. In some pond-dwelling species, the eggs have a tough shell and can lie dormant for extended periods if the pond dries up.
Eggs hatch into nauplius larvae, which consist of a head with a small
 Because of their smaller size and relatively faster growth rates, and because they are more evenly distributed throughout more of the world's oceans, copepods almost certainly contribute far more to the secondary productivity of the world's oceans, and to the global ocean
Because of their smaller size and relatively faster growth rates, and because they are more evenly distributed throughout more of the world's oceans, copepods almost certainly contribute far more to the secondary productivity of the world's oceans, and to the global ocean
 Despite their modern abundance, due to their small size and fragility, copepods are extremely rare in the fossil record. The oldest known fossils of copepods are from the late
Despite their modern abundance, due to their small size and fragility, copepods are extremely rare in the fossil record. The oldest known fossils of copepods are from the late
Drink Up NYC: Meet The Tiny Crustaceans (Not Kosher) In Your Tap Water
''. Time, September 2010, Allie Townsend. such as
Copepod fact sheet – Guide to the marine zooplankton of south eastern Australia
Diversity and geographical distribution of pelagic copepoda
Copepod World
Neotropical Copepoda Database Project
{{Authority control Bioindicators Extant Early Cretaceous first appearances Maxillopoda
crustacean
Crustaceans (from Latin meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of arthropods that are traditionally a part of the subphylum Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquatic arthrop ...
s found in nearly every freshwater
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. The term excludes seawater and brackish water, but it does include non-salty mi ...
and saltwater habitat
In ecology, habitat refers to the array of resources, biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species' habitat can be seen as the physical manifestation of its ...
. Some species are plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms that drift in Hydrosphere, water (or atmosphere, air) but are unable to actively propel themselves against ocean current, currents (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are ca ...
ic (living in the water column), some are benthic
The benthic zone is the ecological region at the lowest level of a body of water such as an ocean, lake, or stream, including the sediment surface and some sub-surface layers. The name comes from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning "the depths". ...
(living on the sediments), several species have parasitic phases, and some continental species may live in limnoterrestrial habitats and other wet terrestrial places, such as swamps, under leaf fall in wet forests, bogs, springs, ephemeral ponds, puddles, damp moss, or water-filled recesses of plants ( phytotelmata) such as bromeliad
The Bromeliaceae (the bromeliads) are a Family (biology), family of monocot flowering plants of about 80 genera and 3700 known species, native mainly to the Tropics, tropical Americas, with several species found in the American subtropics and on ...
s and pitcher plant
Pitcher plants are carnivorous plants
known as pitfall traps—a prey-trapping mechanism featuring a deep cavity filled with digestive liquid. The traps of pitcher plant are considered to be "true" pitcher plants and are formed by specialized ...
s. Many live underground in marine and freshwater caves, sinkhole
A sinkhole is a depression or hole in the ground caused by some form of collapse of the surface layer. The term is sometimes used to refer to doline, enclosed depressions that are also known as shakeholes, and to openings where surface water ...
s, or stream beds. Copepods are sometimes used as biodiversity indicators.
As with other crustaceans, copepods have a larva
A larva (; : larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into their next life stage. Animals with indirect development such as insects, some arachnids, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase ...
l form. For copepods, the egg hatches into a nauplius form, with a head and a tail but no true thorax or abdomen. The larva molts several times until it resembles the adult and then, after more molts, achieves adult development. The nauplius form is so different from the adult form that it was once thought to be a separate species. The metamorphosis had, until 1832, led to copepods being misidentified as zoophytes or insect
Insects (from Latin ') are Hexapoda, hexapod invertebrates of the class (biology), class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (Insect morphology#Head, head, ...
s (albeit aquatic ones), or, for parasitic copepods, 'fish lice
Louse (: lice) is the common name for any member of the infraorder Phthiraptera, which contains nearly 5,000 species of wingless parasitic insects. Phthiraptera was previously recognized as an order, until a 2021 genetic study determined th ...
'.
Classification and diversity
Copepods are assigned to theclass
Class, Classes, or The Class may refer to:
Common uses not otherwise categorized
* Class (biology), a taxonomic rank
* Class (knowledge representation), a collection of individuals or objects
* Class (philosophy), an analytical concept used d ...
Copepoda within the superclass Multicrustacea in the subphylum Crustacea
Crustaceans (from Latin meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of arthropods that are traditionally a part of the subphylum Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquatic arthrop ...
. An alternative treatment is as a subclass belonging to class Hexanauplia. They are divided into 10 orders. Some 13,000 species of copepods are known, and 2,800 of them live in fresh water.
Characteristics

 Copepods vary considerably, but are typically long, with a teardrop-shaped body and large antennae. Like other crustaceans, they have an armoured
Copepods vary considerably, but are typically long, with a teardrop-shaped body and large antennae. Like other crustaceans, they have an armoured exoskeleton
An exoskeleton () . is a skeleton that is on the exterior of an animal in the form of hardened integument, which both supports the body's shape and protects the internal organs, in contrast to an internal endoskeleton (e.g. human skeleton, that ...
, but they are so small that in most species, this thin armour and the entire body is almost totally transparent. Some polar copepods reach . Most copepods have a single median compound eye
A compound eye is a Eye, visual organ found in arthropods such as insects and crustaceans. It may consist of thousands of ommatidium, ommatidia, which are tiny independent photoreception units that consist of a cornea, lens (anatomy), lens, and p ...
, usually bright red and in the centre of the transparent head. Subterranean species may be eyeless, and members of the genera ''Copilia'' and ''Corycaeus'' possess two eyes, each of which has a large anterior cuticular lens paired with a posterior internal lens to form a telescope. Like other crustaceans, copepods possess two pairs of antennae; the first pair is often long and conspicuous.
Free-living copepods of the orders Calanoida, Cyclopoida, and Harpacticoida typically have a short, cylindrical body, with a rounded or beaked head, although considerable variation exists in this pattern. The head is fused with the first one or two thoracic
The thorax (: thoraces or thoraxes) or chest is a part of the anatomy of mammals and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen.
In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main ...
segments, while the remainder of the thorax has three to five segments, each with limbs. The first pair of thoracic appendages is modified to form maxilliped
An appendage (or outgrowth) is an external body part or natural prolongation that protrudes from an organism's body such as an arm or a leg. Protrusions from single-celled bacteria and archaea are known as cell-surface appendages or surface app ...
s, which assist in feeding. The abdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the gut, belly, tummy, midriff, tucky, or stomach) is the front part of the torso between the thorax (chest) and pelvis in humans and in other vertebrates. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal ...
is typically narrower than the thorax, and contains five segments without any appendages, except for some tail-like "rami" at the tip. Parasitic copepods (the other seven orders) vary widely in morphology and no generalizations are possible.
Because of their small size, copepods have no need of any heart
The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ found in humans and other animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. The heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrie ...
or circulatory system (the members of the order Calanoida have a heart, but no blood vessel
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many Animal, animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the Tissue (biology), tissues of a Body (bi ...
s), and most also lack gill
A gill () is a respiration organ, respiratory organ that many aquatic ecosystem, aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow r ...
s. Instead, they absorb oxygen directly into their bodies. Their excretory system consists of maxillary glands.
Behavior
The second pair of cephalic appendages in free-living copepods is usually the main time-averaged source of propulsion, beating like oars to pull the animal through the water. However, different groups have different modes of feeding and locomotion, ranging from almost immotile for several minutes (e.g. some harpacticoid copepods) to intermittent motion (e.g., some cyclopoid copepods) and continuous displacements with some escape reactions (e.g. most calanoid copepods). Some copepods have extremely fast escape responses when a predator is sensed, and can jump with high speed over a few millimetres. Many species have
Some copepods have extremely fast escape responses when a predator is sensed, and can jump with high speed over a few millimetres. Many species have neuron
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural net ...
s surrounded by myelin
Myelin Sheath ( ) is a lipid-rich material that in most vertebrates surrounds the axons of neurons to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) pass along the axon. The myelinated axon can be lik ...
(for increased conduction speed), which is very rare among invertebrate
Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordata, chordate s ...
s (other examples are some annelid
The annelids (), also known as the segmented worms, are animals that comprise the phylum Annelida (; ). The phylum contains over 22,000 extant species, including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. The species exist in and have adapted to vario ...
s and malacostraca
Malacostraca is the second largest of the six classes of pancrustaceans behind insects, containing about 40,000 living species, divided among 16 orders. Its members, the malacostracans, display a great diversity of body forms and include crab ...
n crustaceans like palaemonid shrimp and penaeids). Even rarer, the myelin is highly organized, resembling the well-organized wrapping found in vertebrates (Gnathostomata
Gnathostomata (; from Ancient Greek: (') 'jaw' + (') 'mouth') are jawed vertebrates. Gnathostome diversity comprises roughly 60,000 species, which accounts for 99% of all extant vertebrates, including all living bony fishes (both ray-finned ...
). Despite their fast escape response, copepods are successfully hunted by slow-swimming seahorse
A seahorse (also written ''sea-horse'' and ''sea horse'') is any of 46 species of small marine Osteichthyes, bony fish in the genus ''Hippocampus''. The genus name comes from the Ancient Greek (), itself from () meaning "horse" and () meanin ...
s, which approach their prey so gradually, it senses no turbulence, then suck the copepod into their snout too suddenly for the copepod to escape.
Several species are bioluminescent and able to produce light. It is assumed this is an antipredatory defense mechanism.
Finding a mate in the three-dimensional space
In geometry, a three-dimensional space (3D space, 3-space or, rarely, tri-dimensional space) is a mathematical space in which three values ('' coordinates'') are required to determine the position of a point. Most commonly, it is the three- ...
of open water is challenging. Some copepod females solve the problem by emitting pheromone
A pheromone () is a secreted or excreted chemical factor that triggers a social response in members of the same species. Pheromones are chemicals capable of acting like hormones outside the body of the secreting individual, to affect the behavio ...
s, which leave a trail in the water that the male can follow. Copepods experience a low Reynolds number
In fluid dynamics, the Reynolds number () is a dimensionless quantity that helps predict fluid flow patterns in different situations by measuring the ratio between Inertia, inertial and viscous forces. At low Reynolds numbers, flows tend to ...
and therefore a high relative viscosity. One foraging strategy involves chemical detection of sinking marine snow
In the deep ocean, marine snow (also known as "ocean dandruff") is a continuous shower of mostly organic detritus falling from the upper layers of the water column. It is a significant means of exporting energy from the light-rich photic zone to ...
aggregates and taking advantage of nearby low-pressure gradients to swim quickly towards food sources.
Diet
Most free-living copepods feed directly onphytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater Aquatic ecosystem, ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek language, Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), mea ...
, catching cells individually. A single copepod can consume up to 373,000 phytoplankton per day. They generally have to clear the equivalent to about a million times their own body volume of water every day to cover their nutritional needs. Some of the larger species are predators of their smaller relatives. Many benthic copepods eat organic detritus or the bacteria that grow in it, and their mouth parts are adapted for scraping and biting. Herbivorous copepods, particularly those in rich, cold seas, store up energy from their food as oil droplets while they feed in the spring and summer on plankton blooms. These droplets may take up over half of the volume of their bodies in polar species. Many copepods (e.g., fish lice like the Siphonostomatoida) are parasites, and feed on their host organisms. In fact, three of the 10 known orders of copepods are wholly or largely parasitic, with another three comprising most of the free-living species.
Life cycle
 Most nonparasitic copepods are holoplanktonic, meaning they stay planktonic for all of their lifecycles, although harpacticoids, although free-living, tend to be benthic rather than planktonic.
During mating, the male copepod grips the female with his first pair of antennae, which is sometimes modified for this purpose. The male then produces an adhesive package of sperm and transfers it to the female's genital opening with his thoracic limbs. Eggs are sometimes laid directly into the water, but many species enclose them within a sac attached to the female's body until they hatch. In some pond-dwelling species, the eggs have a tough shell and can lie dormant for extended periods if the pond dries up.
Eggs hatch into nauplius larvae, which consist of a head with a small
Most nonparasitic copepods are holoplanktonic, meaning they stay planktonic for all of their lifecycles, although harpacticoids, although free-living, tend to be benthic rather than planktonic.
During mating, the male copepod grips the female with his first pair of antennae, which is sometimes modified for this purpose. The male then produces an adhesive package of sperm and transfers it to the female's genital opening with his thoracic limbs. Eggs are sometimes laid directly into the water, but many species enclose them within a sac attached to the female's body until they hatch. In some pond-dwelling species, the eggs have a tough shell and can lie dormant for extended periods if the pond dries up.
Eggs hatch into nauplius larvae, which consist of a head with a small tail
The tail is the elongated section at the rear end of a bilaterian animal's body; in general, the term refers to a distinct, flexible appendage extending backwards from the midline of the torso. In vertebrate animals that evolution, evolved to los ...
, but no thorax or true abdomen. The nauplius moults five or six times, before emerging as a "copepodid larva". This stage resembles the adult, but has a simple, unsegmented abdomen and only three pairs of thoracic limbs. After a further five moults, the copepod takes on the adult form. The entire process from hatching to adulthood can take a week to a year, depending on the species and environmental conditions such as temperature and nutrition (e.g., egg-to-adult time in the calanoid ''Parvocalanus crassirostris'' is ~7 days at but 19 days at .
Biophysics
Copepods jump out of the water - porpoising. The biophysics of this motion has been described by Waggett and Buskey 2007 and Kim et al 2015.Ecology
Planktonic copepods are important to globalecology
Ecology () is the natural science of the relationships among living organisms and their Natural environment, environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community (ecology), community, ecosystem, and biosphere lev ...
and the carbon cycle
The carbon cycle is a part of the biogeochemical cycle where carbon is exchanged among the biosphere, pedosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere of Earth. Other major biogeochemical cycles include the nitrogen cycle and the water cycl ...
. They are usually the dominant members of the zooplankton
Zooplankton are the heterotrophic component of the planktonic community (the " zoo-" prefix comes from ), having to consume other organisms to thrive. Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents. Consequent ...
, and are major food organisms for small fish
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can ...
such as the dragonet
Dragonets are small Percomorpha, percomorph marine fish of the diverse family Callionymidae (from the Greek language, Greek ''kallis'', "beautiful" and ', "name") found mainly in the tropical waters of the western Indo-Pacific. They are Benthos, ...
, banded killifish, Alaska pollock, and other crustaceans such as krill
Krill ''(Euphausiids)'' (: krill) are small and exclusively marine crustaceans of the order (biology), order Euphausiacea, found in all of the world's oceans. The name "krill" comes from the Norwegian language, Norwegian word ', meaning "small ...
in the ocean and in fresh water. Some scientists say they form the largest animal biomass
Biomass is a term used in several contexts: in the context of ecology it means living organisms, and in the context of bioenergy it means matter from recently living (but now dead) organisms. In the latter context, there are variations in how ...
on earth. Copepods compete for this title with Antarctic krill
Antarctic krill (''Euphausia superba'') is a species of krill found in the Antarctica, Antarctic waters of the Southern Ocean. It is a small, swimming crustacean that lives in large schools, called swarms, sometimes reaching densities of 10,000� ...
(''Euphausia superba''). ''C. glacialis'' inhabits the edge of the Arctic icepack, especially in polynya
A polynya () is an area of open water surrounded by sea ice. It is now used as a geographical term for an area of unfrozen seawater within otherwise contiguous pack ice or fast ice. It is a loanword from the Russian language, Russian (), whic ...
s where light (and photosynthesis) is present, in which they alone comprise up to 80% of zooplankton biomass. They bloom as the ice recedes each spring. The ongoing large reduction in the annual ice pack minimum may force them to compete in the open ocean with the much less nourishing ''C. finmarchicus'', which is spreading from the North Sea and the Norwegian Sea into the Barents Sea.
 Because of their smaller size and relatively faster growth rates, and because they are more evenly distributed throughout more of the world's oceans, copepods almost certainly contribute far more to the secondary productivity of the world's oceans, and to the global ocean
Because of their smaller size and relatively faster growth rates, and because they are more evenly distributed throughout more of the world's oceans, copepods almost certainly contribute far more to the secondary productivity of the world's oceans, and to the global ocean carbon sink
A carbon sink is a natural or artificial carbon sequestration process that "removes a greenhouse gas, an aerosol or a precursor of a greenhouse gas from the atmosphere". These sinks form an important part of the natural carbon cycle. An overar ...
than krill, and perhaps more than all other groups of organisms together. The surface layers of the oceans are believed to be the world's largest carbon sink, absorbing about 2 billion tons of carbon a year, the equivalent to perhaps a third of human carbon emissions, thus reducing their impact. Many planktonic copepods feed near the surface at night, then sink (by changing oils into more dense fats) into deeper water during the day to avoid visual predators. Their moulted exoskeleton
An exoskeleton () . is a skeleton that is on the exterior of an animal in the form of hardened integument, which both supports the body's shape and protects the internal organs, in contrast to an internal endoskeleton (e.g. human skeleton, that ...
s, faecal pellets, and respiration at depth all bring carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
to the deep sea.
About half of the estimated 14,000 described species of copepods are parasitic
and many have adapted extremely modified bodies for their parasitic lifestyles.
They attach themselves to bony fish, sharks, marine mammals, and many kinds of invertebrates such as corals, other crustaceans, molluscs, sponges, and tunicates. They also live as ectoparasites on some freshwater fish.
Copepods as parasitic hosts
In addition to being parasites themselves, copepods are subject to parasitic infection. The most common parasites are marinedinoflagellate
The Dinoflagellates (), also called Dinophytes, are a monophyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes constituting the phylum Dinoflagellata and are usually considered protists. Dinoflagellates are mostly marine plankton, but they are also commo ...
s of the genus '' Blastodinium'', which are gut parasites of many copepod species. Twelve species of ''Blastodinium'' are described, the majority of which were discovered in the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Eur ...
. Most ''Blastodinium'' species infect several different hosts, but species-specific infection of copepods does occur. Generally, adult copepod females and juveniles are infected.
During the naupliar stage, the copepod host ingests the unicellular dinospore of the parasite. The dinospore is not digested and continues to grow inside the intestinal lumen of the copepod. Eventually, the parasite divides into a multicellular arrangement called a trophont. This trophont is considered parasitic, contains thousands of cells, and can be several hundred micrometers in length. The trophont is greenish to brownish in color as a result of well-defined chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle, organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant cell, plant and algae, algal cells. Chloroplasts have a high concentration of chlorophyll pigments which captur ...
s. At maturity, the trophont ruptures and ''Blastodinium'' spp. are released from the copepod anus as free dinospore cells. Not much is known about the dinospore stage of ''Blastodinium'' and its ability to persist outside of the copepod host in relatively high abundances.
The copepod ''Calanus finmarchicus'', which dominates the northeastern Atlantic coast, has been shown to be greatly infected by this parasite. A 2014 study in this region found up to 58% of collected ''C. finmarchicus'' females to be infected. In this study, ''Blastodinium''-infected females had no measurable feeding rate over a 24-hour period. This is compared to uninfected females which, on average, ate 2.93 × 104 cells per day. ''Blastodinium''-infected females of ''C. finmarchicus'' exhibited characteristic signs of starvation, including decreased respiration, fecundity, and fecal pellet production. Though photosynthetic
Photosynthesis ( ) is a Biological system, system of biological processes by which Photoautotrophism, photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical ener ...
, ''Blastodinium'' spp. procure most of their energy from organic material in the copepod gut, thus contributing to host starvation. Underdeveloped or disintegrated ovaries
The ovary () is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are endocr ...
and decreased fecal pellet size are a direct result of starvation in female copepods. Parasitic infection by ''Blastodinium'' spp. could have serious ramifications on the success of copepod species and the function of entire marine ecosystems. ''Blastodinium'' parasitism is not lethal, but has negative impacts on copepod physiology, which in turn may alter marine biogeochemical cycles.
Freshwater copepods of the ''Cyclops'' genus are the intermediate host of the Guinea worm ('' Dracunculus medinensis''), the nematode
The nematodes ( or ; ; ), roundworms or eelworms constitute the phylum Nematoda. Species in the phylum inhabit a broad range of environments. Most species are free-living, feeding on microorganisms, but many are parasitic. Parasitic worms (h ...
that causes dracunculiasis
Dracunculiasis, also called Guinea-worm disease, is a parasitic infection by the Guinea worm ('' Dracunculus medinensis).'' A person becomes infected by drinking water contaminated with Guinea-worm larvae that reside inside copepods (a typ ...
disease in humans. This disease may be close to being eradicated through efforts by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the National public health institutes, national public health agency of the United States. It is a Federal agencies of the United States, United States federal agency under the United S ...
, the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
, and the Carter Center
The Carter Center is a nongovernmental, nonprofit organization founded in 1982 by former U.S. president Jimmy Carter. He and his wife Rosalynn Carter partnered with Emory University after his defeat in the 1980 United States presidential ele ...
.
Copepods are known hosts of '' Vibrio'' bacteria, including pathogenic species. The ''Vibrio'' attach to the copepod's chitinous carapace, wearing it away to create a niche to stay. They are more protected from ecological stressors when attached to copepods and have an easy dispersal method. ''Vibrio'' are not known to infect copepods, but the degradation of the carapace is presumably detrimental to the copepod.
Copepods are infected by a variety of marine fungi including '' Metschnikowia'' species, and this can be lethal. They are also parasitized by tapeworms
Cestoda is a class of parasitic worms in the flatworm phylum (Platyhelminthes). Most of the species—and the best-known—are those in the subclass Eucestoda; they are ribbon-like worms as adults, commonly known as tapeworms. Their bodies con ...
, isopods
Isopoda is an Order (biology), order of crustaceans. Members of this group are called isopods and include both Aquatic animal, aquatic species and Terrestrial animal, terrestrial species such as woodlice. All have rigid, segmented exoskeletons ...
, and many kinds of protist, including Ellobiopsidae, Ciliates
The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a different ...
, and Sporozoans.
Evolution
 Despite their modern abundance, due to their small size and fragility, copepods are extremely rare in the fossil record. The oldest known fossils of copepods are from the late
Despite their modern abundance, due to their small size and fragility, copepods are extremely rare in the fossil record. The oldest known fossils of copepods are from the late Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a Geologic time scale, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era that spans 60 million years, from the end of the Devonian Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the ...
( Pennsylvanian) of Oman
Oman, officially the Sultanate of Oman, is a country located on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in West Asia and the Middle East. It shares land borders with Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. Oman’s coastline ...
, around 303 million years old, which were found in a clast of bitumen
Bitumen ( , ) is an immensely viscosity, viscous constituent of petroleum. Depending on its exact composition, it can be a sticky, black liquid or an apparently solid mass that behaves as a liquid over very large time scales. In American Engl ...
from a glacial diamictite
Diamictite (; from Ancient Greek (): 'through' and (): 'mixed') is a type of lithified sedimentary rock that consists of nonsorted to poorly sorted terrigenous sediment containing particles that range in size from clay to boulders, suspended ...
. The copepods present in the bitumen clast were likely residents of a subglacial lake
A subglacial lake is a lake that is found under a glacier, typically beneath an ice cap or ice sheet. Subglacial lakes form at the boundary between ice and the underlying bedrock, where liquid water can exist above the lower melting point of ic ...
which the bitumen had seeped upwards through while still liquid, before the clast subsequently solidified and was deposited by glaciers. Though most of the remains were undiagnostic, at least some likely belonged to the extant harpacticoid family Canthocamptidae, suggesting that copepods had already substantially diversified by this time. Possible microfossils of copepods are known from the Cambrian
The Cambrian ( ) is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 51.95 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran period 538.8 Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Ordov ...
of North America. Transitions to parasitism have occurred within copepods independently at least 14 different times, with the oldest record of this being from damage to fossil echinoids
Sea urchins or urchins () are echinoderms in the class (biology), class Echinoidea. About 950 species live on the seabed, inhabiting all oceans and depth zones from the intertidal zone to deep seas of . They typically have a globular body cove ...
done by cyclopoids from the Middle Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately 143.1 Mya. ...
of France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
, around 168 million years old.
Practical aspects
In marine aquaria
Live copepods are used in the saltwater aquarium hobby as a food source and are generally considered beneficial in most reef tanks. They are scavengers and also may feed on algae, including coralline algae. Live copepods are popular among hobbyists who are attempting to keep particularly difficult species such as the mandarin dragonet or scooter blenny. They are also popular to hobbyists who want to breed marine species in captivity. In a saltwater aquarium, copepods are typically stocked in the refugium.Water supplies
Copepods are sometimes found in public main water supplies, especially systems where the water is not mechanically filtered,Drink Up NYC: Meet The Tiny Crustaceans (Not Kosher) In Your Tap Water
''. Time, September 2010, Allie Townsend. such as
New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
, Boston
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
, and San Francisco
San Francisco, officially the City and County of San Francisco, is a commercial, Financial District, San Francisco, financial, and Culture of San Francisco, cultural center of Northern California. With a population of 827,526 residents as of ...
. This is not usually a problem in treated water supplies. In some tropical countries, such as Peru
Peru, officially the Republic of Peru, is a country in western South America. It is bordered in the north by Ecuador and Colombia, in the east by Brazil, in the southeast by Bolivia, in the south by Chile, and in the south and west by the Pac ...
and Bangladesh
Bangladesh, officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eighth-most populous country in the world and among the List of countries and dependencies by ...
, a correlation has been found between copepods' presence and cholera
Cholera () is an infection of the small intestine by some Strain (biology), strains of the Bacteria, bacterium ''Vibrio cholerae''. Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea last ...
in untreated water, because the cholera bacteria attach to the surfaces of planktonic animals. The larvae of the guinea worm must develop within a copepod's digestive tract before being transmitted to humans. The risk of infection with these diseases can be reduced by filtering out the copepods (and other matter), for example with a cloth filter
A cloth filter is a simple and cost-effective appropriate technology method for reducing the contamination of drinking water, developed for use mainly in Bangladesh. Water collected in this way has a greatly reduced pathogen count. Though not a ...
.
Copepods have been used successfully in Vietnam
Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's List of countries and depende ...
to control disease-bearing mosquitoes
Mosquitoes, the Culicidae, are a family of small flies consisting of 3,600 species. The word ''mosquito'' (formed by '' mosca'' and diminutive ''-ito'') is Spanish and Portuguese for ''little fly''. Mosquitoes have a slender segmented body, ...
such as ''Aedes aegypti
''Aedes aegypti'' ( or from Greek 'hateful' and from Latin, meaning 'of Egypt'), sometimes called the Egyptian mosquito, dengue mosquito or yellow fever mosquito, is a mosquito that spreads diseases like dengue fever, yellow fever, malar ...
'' that transmit dengue fever and other human parasitic diseases.
The copepods can be added to water-storage containers where the mosquitoes breed. Copepods, primarily of the genera '' Mesocyclops'' and ''Macrocyclops'' (such as '' Macrocyclops albidus''), can survive for periods of months in the containers, if the containers are not completely drained by their users. They attack, kill, and eat the younger first- and second-instar
An instar (, from the Latin '' īnstar'' 'form, likeness') is a developmental stage of arthropods, such as insects, which occurs between each moult (''ecdysis'') until sexual maturity is reached. Arthropods must shed the exoskeleton in order to ...
larvae of the mosquitoes. This biological control
Biological control or biocontrol is a method of controlling pests, whether pest animals such as insects and mites, weeds, or pathogens affecting animals or plants by using other organisms. It relies on predation, parasitism, herbivory, or o ...
method is complemented by community trash removal and recycling to eliminate other possible mosquito-breeding sites. Because the water in these containers is drawn from uncontaminated sources such as rainfall, the risk of contamination by cholera bacteria is small, and in fact no cases of cholera have been linked to copepods introduced into water-storage containers. Trials using copepods to control container-breeding mosquitoes are underway in several other countries, including Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
and the southern United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
. The method, though, would be very ill-advised in areas where the guinea worm is endemic.
The presence of copepods in the New York City water supply system
The New York City water supply system is a combination of Aqueduct (water supply), aqueducts, reservoirs, and tunnels which supplies fresh water to New York City. With three major water systems (New Croton Aqueduct, Croton, Catskill Aqueduct, Ca ...
has caused problems for some Jewish
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
people who observe kashrut
(also or , ) is a set of Food and drink prohibitions, dietary laws dealing with the foods that Jewish people are permitted to eat and how those foods must be prepared according to halakha, Jewish law. Food that may be consumed is deemed ko ...
. Copepods, being crustaceans, are not kosher, nor are they quite small enough to be ignored as nonfood microscopic organisms, since some specimens can be seen with the naked eye. Hence, large specimens are certainly non-Kosher. However, some species are visible to the naked eye, but are small enough that they only appear as little white specks. These are problematic, as it is a question as to whether they are considered visible enough to be non-Kosher.
When a group of rabbis
A rabbi (; ) is a spiritual leader or religious teacher in Judaism. One becomes a rabbi by being ordained by another rabbi—known as '' semikha''—following a course of study of Jewish history and texts such as the Talmud. The basic form of ...
in Brooklyn, New York
Brooklyn is a Boroughs of New York City, borough of New York City located at the westernmost end of Long Island in the New York (state), State of New York. Formerly an independent city, the borough is coextensive with Kings County, one of twelv ...
, discovered these copepods in the summer of 2004, they triggered such debate in rabbinic circles that some observant Jews felt compelled to buy and install filters for their water. The water was ruled kosher by posek
In Jewish law, a ''posek'' ( , pl. ''poskim'', ) is a legal scholar who determines the application of ''halakha'', the Jewish religious laws derived from the written and Oral Torah, in cases of Jewish law where previous authorities are incon ...
Yisrael Belsky, chief posek of the OU and one of the most scientifically literate poskim of his time. Meanwhile, Rabbi Dovid Feinstein, based on the ruling of Rabbi Yosef Shalom Elyashiv - the two widely considered to be the greatest poskim of their time - ruled it was not kosher until filtered. Several major kashrus organizations (e.g OU Kashrus and Star-K) require tap water to have filters.
In popular culture
TheNickelodeon
Nickelodeon (nicknamed Nick) is an American pay television channel and the flagship property of the Nickelodeon Group, a sub-division of the Paramount Media Networks division of Paramount Global. Launched on April 1, 1979, as the first ca ...
television series ''SpongeBob SquarePants
''SpongeBob SquarePants'' is an American animated television series, animated comedy television series created by marine science educator and animator Stephen Hillenburg for Nickelodeon. It first aired as a sneak peek after the 1999 Kids' C ...
'' features a copepod named Sheldon J. Plankton as a recurring character.
See also
* Particle (ecology) * World Association of CopepodologistsReferences
External links
Copepod fact sheet – Guide to the marine zooplankton of south eastern Australia
Diversity and geographical distribution of pelagic copepoda
Copepod World
Neotropical Copepoda Database Project
{{Authority control Bioindicators Extant Early Cretaceous first appearances Maxillopoda