Controlled Mines on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A controlled mine was a circuit fired weapon used in coastal defenses with ancestry going back to 1805 when
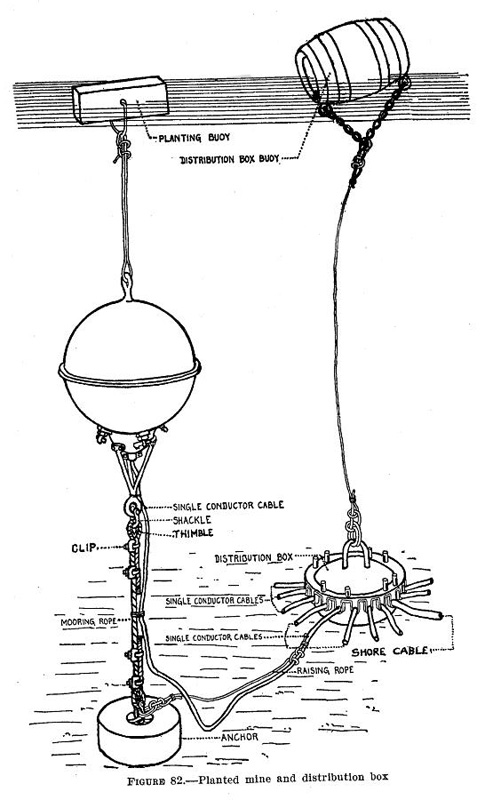 Unlike
Unlike Indicator loops website
/ref> A dozen specialized vessels known as "Indicator Loop Mine Layers"—including three ''Linnet''-class minelayers and nine smaller vessels—much like the U.S. mine planters, were built for the Royal Navy immediately before and during WWII. Similarly in Japan four Hashima-class cable layers were built between 1939 and 1941 for mine planting duties.
U.S. National Park Service; Torpedo Defense - COAST DEFENSE OF THE POTOMAC
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20110604224519/http://www.dtic.mil/cgi-bin/GetTRDoc?AD=ADA502616&Location=U2&doc=GetTRDoc.pdf Mine Defense -Today and Tomorrow; ''Coast Artillery Journal'', Vol. 71, No. 3, September 1929] - .pdf from DTIC with technical information and illustrations of equipment of the day.
Shore and Underwater Elements - Mine Facilities - Fort Miles, Del.
{{DEFAULTSORT:Controlled Mines Anti-ship weapons Explosive weapons Coastal fortifications
Robert Fulton
Robert Fulton (November 14, 1765 – February 24, 1815) was an American engineer and inventor who is widely credited with developing the world's first commercially successful steamboat, the (also known as ''Clermont''). In 1807, that steamboat ...
termed his underwater explosive device a torpedo:
Robert Fulton invented the word torpedo to describe his underwater explosive device and successfully destroyed a ship in 1805. In the 1840s Samuel Colt began experimenting with underwater mines fired by electric current and in 1842, he blew up an old schooner in the Potomac River from a shore station five miles away.
History
"Torpedoes" were in use during theAmerican Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
when such devices were made famous with the order given by David Farragut
David Glasgow Farragut (; also spelled Glascoe; July 5, 1801 – August 14, 1870) was a flag officer of the United States Navy during the American Civil War. He was the first Rear admiral (United States), rear admiral, Vice admiral (United State ...
at Mobile Bay. After that war similar mines were being contemplated or put into use by other nations.
In 1869 the United States Army Corps of Engineers
The United States Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) is the military engineering branch of the United States Army. A direct reporting unit (DRU), it has three primary mission areas: Engineer Regiment, military construction, and civil wo ...
was directed by Secretary of War
The secretary of war was a member of the U.S. president's Cabinet, beginning with George Washington's administration. A similar position, called either "Secretary at War" or "Secretary of War", had been appointed to serve the Congress of the ...
William Belknap to assume responsibility for torpedoes for coastal defense. That responsibility continued through the formation of the U.S. Torpedo Service as part of the United States' seacoast defenses. In the United States, modern naval mine development began in 1869 at the Engineer School of Application under Major Henry Larcom Abbot
Henry Larcom Abbot (August 13, 1831 – October 1, 1927) was a military engineer and career officer in the United States Army. He served in the Union Army during the American Civil War and was appointed brevet brigadier general of volunteers ...
at Willets Point, New York. Eventually, after calls for "rifled cannon" to cover the torpedo fields became reality, that service and the Corps of Engineers turned over responsibility to the newly formed coast artillery branch in 1901, which became the U.S. Army Coast Artillery Corps in 1907.
The terms "mine" and "torpedo" were used interchangeably until modern usage began separating the term with "mine" applied to static explosive devices and "torpedo" to self-propelled or "locomotive torpedo" weapons. Even during the Spanish–American War
The Spanish–American War (April 21 – August 13, 1898) was fought between Restoration (Spain), Spain and the United States in 1898. It began with the sinking of the USS Maine (1889), USS ''Maine'' in Havana Harbor in Cuba, and resulted in the ...
the interchangeable terms caused confusion.
In Britain controlled mines were termed submarine mines. Fixed minefields to defend harbours were the responsibility of the Royal Engineers
The Corps of Royal Engineers, usually called the Royal Engineers (RE), and commonly known as the ''Sappers'', is the engineering arm of the British Army. It provides military engineering and other technical support to the British Armed Forces ...
(RE), which formed special companies of Submarine Miners to maintain them. Lieutenant-General Sir Andrew Clarke, Inspector-General of Fortifications 1882–86, found that he did not have enough Regular Army engineers to man all the minefields being installed so he decided to utilise the part-time soldiers of the Volunteer Force
The Volunteer Force was a citizen army of part-time rifle, artillery and engineer corps, created as a Social movement, popular movement throughout the British Empire in 1859. Originally highly autonomous, the units of volunteers became increa ...
. After successful trials the system was rolled out to ports around the country, where the Submarine Miners might be drawn from the Regular RE, the Militia
A militia ( ) is a military or paramilitary force that comprises civilian members, as opposed to a professional standing army of regular, full-time military personnel. Militias may be raised in times of need to support regular troops or se ...
, or the Volunteers.Westlake, pp. 15–16. The Submarine Miners were also to the fore in developing searchlights to illuminate the minefields. By 1907 the War Office
The War Office has referred to several British government organisations throughout history, all relating to the army. It was a department of the British Government responsible for the administration of the British Army between 1857 and 1964, at ...
had decided to hand responsibility for the minefields to the Militia, but several Volunteer units were converted to Electrical Engineer Companies employing their lights for coastal artillery control and, eventually, anti-aircraft defences.
Operation
 Unlike
Unlike naval mines
A naval mine is a self-contained explosive weapon placed in water to damage or destroy surface ships or submarines. Similar to anti-personnel and other land mines, and unlike purpose launched naval depth charges, they are deposited and le ...
that are dispersed at sea, the controlled mine field location is chosen so that it could be under observation. The exact location of the mines was required so that they could be fired from the mine casemate when a target vessel was plotted by observers to be within the mine's effective range. For this reason the mines were "planted" in predetermined locations with electrical connection through cables to the firing location. The complex of mines, cables and junction boxes required maintenance. Specialized vessels to undertake the hazards of planting mines and maintaining the electrical cables were used.
In the United States a type of vessel termed mine planter was developed, built and deployed in 1904. By 1909 more mine planters were under construction and deployment had reached the San Francisco fortifications. These were assisted by smaller vessels. In the last stages of such coastal defenses during the Second World War the U.S. Army Mine Planter Service (USAMPS) mine flotilla usually consisted of two planters, four Distribution Box Boats and a small fleet of yawls and launches.
In the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom ...
controlled mines were often laid alongside anti-submarine indicator loops during both World Wars; the US Navy used a similar strategy in at least World War II./ref> A dozen specialized vessels known as "Indicator Loop Mine Layers"—including three ''Linnet''-class minelayers and nine smaller vessels—much like the U.S. mine planters, were built for the Royal Navy immediately before and during WWII. Similarly in Japan four Hashima-class cable layers were built between 1939 and 1941 for mine planting duties.
See also
*Naval mine
A naval mine is a self-contained explosive weapon placed in water to damage or destroy surface ships or submarines. Similar to anti-personnel mine, anti-personnel and other land mines, and unlike purpose launched naval depth charges, they are ...
* Submarine mines in United States harbor defense
References
Bibliography
* Ian F.W. Beckett, ''Riflemen Form: A study of the Rifle Volunteer Movement 1859–1908'', Aldershot: Ogilby Trusts, 1982, . * * * Maj O.M. Short, Maj H. Sherlock, Capt L.E.C.M. Perowne and Lt M.A. Fraser, ''The History of the Tyne Electrical Engineers, Royal Engineers, 1884–1933'', 1933/Uckfield: Naval & Military, nd, . * R.A. Westlake, ''Royal Engineers (Volunteers) 1859–1908'', Wembley: R.A. Westlake, 1983, .External links
U.S. National Park Service; Torpedo Defense - COAST DEFENSE OF THE POTOMAC
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20110604224519/http://www.dtic.mil/cgi-bin/GetTRDoc?AD=ADA502616&Location=U2&doc=GetTRDoc.pdf Mine Defense -Today and Tomorrow; ''Coast Artillery Journal'', Vol. 71, No. 3, September 1929] - .pdf from DTIC with technical information and illustrations of equipment of the day.
Shore and Underwater Elements - Mine Facilities - Fort Miles, Del.
{{DEFAULTSORT:Controlled Mines Anti-ship weapons Explosive weapons Coastal fortifications