Content-addressable Memory on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Content-addressable memory (CAM) is a special type of
Content-addressable memory (CAM) is a special type of
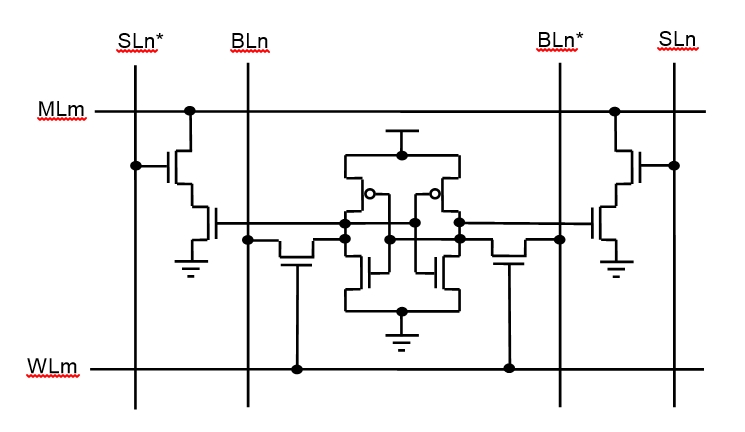 CAM is much faster than RAM in data search applications. There are cost disadvantages to CAM, however. Unlike a RAM chip, which has simple storage cells, each individual memory
CAM is much faster than RAM in data search applications. There are cost disadvantages to CAM, however. Unlike a RAM chip, which has simple storage cells, each individual memory
 Binary CAM is the simplest type of CAM and uses data search words consisting entirely of 1s and 0s. Ternary CAM (TCAM) allows a third matching state of ''X'' or ''don't care'' for one or more bits in the stored word, thus adding flexibility to the search. For example, a stored word of ''10XX0'' in a ternary CAM will match any of the four search words ''10000'', ''10010'', ''10100'', or ''10110''. The added search flexibility comes at an additional cost over binary CAM as the internal memory cell must now encode three possible states instead of the two for the binary CAM. This additional state is typically implemented by adding a mask bit (''care'' or ''don't care'' bit) to every memory cell.
In 2013,
Binary CAM is the simplest type of CAM and uses data search words consisting entirely of 1s and 0s. Ternary CAM (TCAM) allows a third matching state of ''X'' or ''don't care'' for one or more bits in the stored word, thus adding flexibility to the search. For example, a stored word of ''10XX0'' in a ternary CAM will match any of the four search words ''10000'', ''10010'', ''10100'', or ''10110''. The added search flexibility comes at an additional cost over binary CAM as the internal memory cell must now encode three possible states instead of the two for the binary CAM. This additional state is typically implemented by adding a mask bit (''care'' or ''don't care'' bit) to every memory cell.
In 2013,
CAM PrimerArithmetic Processing using Associative memory
{{Authority control Associative arrays Computer memory Computer networking
 Content-addressable memory (CAM) is a special type of
Content-addressable memory (CAM) is a special type of computer memory
Computer memory stores information, such as data and programs, for immediate use in the computer. The term ''memory'' is often synonymous with the terms ''RAM,'' ''main memory,'' or ''primary storage.'' Archaic synonyms for main memory include ...
used in certain very-high-speed searching applications. It is also known as associative memory or associative storage and compares input search data against a table of stored data, and returns the address of matching data.
CAM is frequently used in networking devices where it speeds up forwarding information base and routing table
In computer networking, a routing table, or routing information base (RIB), is a data table stored in a router or a network host that lists the routes to particular network destinations, and in some cases, metrics (distances) associated wi ...
operations. This kind of associative memory is also used in cache memory. In associative cache memory, both address and content is stored side by side. When the address matches, the corresponding content is fetched from cache memory.
History
Dudley Allen Buck invented the concept of content-addressable memory in 1955. Buck is credited with the idea of ''recognition unit''.Hardware associative array
Unlike standard computer memory,random-access memory
Random-access memory (RAM; ) is a form of Computer memory, electronic computer memory that can be read and changed in any order, typically used to store working Data (computing), data and machine code. A random-access memory device allows ...
(RAM), in which the user supplies a memory address and the RAM returns the data word stored at that address, a CAM is designed such that the user supplies a data word and the CAM searches its entire memory to see if that data word is stored anywhere in it. If the data word is found, the CAM returns a list of one or more storage addresses where the word was found. Thus, a CAM is the hardware embodiment of what in software terms would be called an associative array
In computer science, an associative array, key-value store, map, symbol table, or dictionary is an abstract data type that stores a collection of (key, value) pairs, such that each possible key appears at most once in the collection. In math ...
.
A similar concept can be found in the ''data word recognition unit'', as proposed by Dudley Allen Buck in 1955.
Standards
A major interface definition for CAMs and othernetwork search engine Computer networks are connected together to form larger networks such as campus networks, corporate networks, or the Internet. Routers are network devices that may be used to connect these networks (e.g., a home network connected to the network o ...
s was specified in an interoperability agreement called the Look-Aside Interface (LA-1 and LA-1B) developed by the Network Processing Forum. Numerous devices conforming to the interoperability agreement have been produced by Integrated Device Technology
Integrated Device Technology, Inc. (IDT), was an American semiconductor company headquartered in San Jose, California. The company designed, manufactured, and marketed low-power, high-performance mixed-signal semiconductor products for the adva ...
, Cypress Semiconductor
Cypress Semiconductor Corporation was an American semiconductor design and manufacturing company. It offered NOR flash memories, F-RAM and SRAM Traveo microcontrollers, PSoCs, PMICs, capacitive touch-sensing controllers, Wireless BLE Bluet ...
, IBM
International Business Machines Corporation (using the trademark IBM), nicknamed Big Blue, is an American Multinational corporation, multinational technology company headquartered in Armonk, New York, and present in over 175 countries. It is ...
, Broadcom
Broadcom Inc. is an American multinational corporation, multinational designer, developer, manufacturer, and global supplier of a wide range of semiconductor and infrastructure software products. Broadcom's product offerings serve the data cen ...
and others. On December 11, 2007, the OIF published the serial look-aside (SLA) interface agreement.
Semiconductor implementations
 CAM is much faster than RAM in data search applications. There are cost disadvantages to CAM, however. Unlike a RAM chip, which has simple storage cells, each individual memory
CAM is much faster than RAM in data search applications. There are cost disadvantages to CAM, however. Unlike a RAM chip, which has simple storage cells, each individual memory bit
The bit is the most basic unit of information in computing and digital communication. The name is a portmanteau of binary digit. The bit represents a logical state with one of two possible values. These values are most commonly represented as ...
in a fully parallel CAM must have its own associated comparison circuit to detect a match between the stored bit and the input bit. Additionally, match outputs from each cell in the data word must be combined to yield a complete data word match signal. The additional circuitry increases the physical size and manufacturing cost of the CAM chip. The extra circuitry also increases power dissipation since every comparison circuit is active on every clock cycle. Consequently, CAM is used only in specialized applications where searching speed cannot be accomplished using a less costly method. One successful early implementation was a General Purpose Associative Processor IC and System.
In the early 2000s several semiconductor companies including Cypress
Cypress is a common name for various coniferous trees or shrubs from the ''Cupressus'' genus of the '' Cupressaceae'' family, typically found in temperate climates and subtropical regions of Asia, Europe, and North America.
The word ''cypress'' ...
, IDT, Netlogic, Sibercore, and MOSAID
MOSAID is a semiconductor technology company incorporated in Ottawa, Canada. It was founded in 1975 as a Dynamic random-access memory, DRAM design company, and later branched out into other areas including EDA software, semiconductor reverse engine ...
introduced CAM products targeting networking applications. These products were labelled Network Search Engines (NSE), Network Search Accelerators (NSA), and Knowledge-based Processors (KBP) but were essentially CAM with specialized interfaces and features optimized for networking. Currently Broadcom
Broadcom Inc. is an American multinational corporation, multinational designer, developer, manufacturer, and global supplier of a wide range of semiconductor and infrastructure software products. Broadcom's product offerings serve the data cen ...
offers several families of KBPs.
Alternative implementations
To achieve a different balance between speed, memory size and cost, some implementations emulate the function of CAM by using standard tree search or hashing designs in hardware, using hardware tricks like replication or pipelining to speed up effective performance. These designs are often used in routers. The Luleå algorithm is an efficient implementation for longest prefix match searches as required in internet routing tables.Ternary CAMs
 Binary CAM is the simplest type of CAM and uses data search words consisting entirely of 1s and 0s. Ternary CAM (TCAM) allows a third matching state of ''X'' or ''don't care'' for one or more bits in the stored word, thus adding flexibility to the search. For example, a stored word of ''10XX0'' in a ternary CAM will match any of the four search words ''10000'', ''10010'', ''10100'', or ''10110''. The added search flexibility comes at an additional cost over binary CAM as the internal memory cell must now encode three possible states instead of the two for the binary CAM. This additional state is typically implemented by adding a mask bit (''care'' or ''don't care'' bit) to every memory cell.
In 2013,
Binary CAM is the simplest type of CAM and uses data search words consisting entirely of 1s and 0s. Ternary CAM (TCAM) allows a third matching state of ''X'' or ''don't care'' for one or more bits in the stored word, thus adding flexibility to the search. For example, a stored word of ''10XX0'' in a ternary CAM will match any of the four search words ''10000'', ''10010'', ''10100'', or ''10110''. The added search flexibility comes at an additional cost over binary CAM as the internal memory cell must now encode three possible states instead of the two for the binary CAM. This additional state is typically implemented by adding a mask bit (''care'' or ''don't care'' bit) to every memory cell.
In 2013, IBM
International Business Machines Corporation (using the trademark IBM), nicknamed Big Blue, is an American Multinational corporation, multinational technology company headquartered in Armonk, New York, and present in over 175 countries. It is ...
fabricated a nonvolatile TCAM using 2-transistor/2-resistive-storage (2T-2R) cells. A design of TCAM using hybrid Ferroelectric FeFET was recently published by a group of International scientists.
Example applications
Content-addressable memory is often used incomputer networking device
Networking hardware, also known as network equipment or computer networking devices, are electronic devices that are required for communication and interaction between devices on a computer network. Specifically, they mediate data transmission in ...
s. For example, when a network switch
A network switch (also called switching hub, bridging hub, Ethernet switch, and, by the IEEE, MAC bridge) is networking hardware that connects devices on a computer network by using packet switching to receive and forward data to the destinat ...
receives a data frame
A frame is a digital data transmission unit in computer networking and telecommunications. In packet switched systems, a frame is a simple container for a single network packet. In other telecommunications systems, a frame is a repeating structure ...
from one of its ports, it updates an internal table with the frame's source MAC address
A MAC address (short for medium access control address or media access control address) is a unique identifier assigned to a network interface controller (NIC) for use as a network address in communications within a network segment. This use i ...
and the port it was received on. It then looks up the destination MAC address in the table to determine what port the frame needs to be forwarded to, and sends it out on that port. The MAC address table is usually implemented with a binary CAM so the destination port can be found very quickly, reducing the switch's latency.
Ternary CAMs are often used in network routers, where each address has two parts: the network prefix, which can vary in size depending on the subnet
A subnet, or subnetwork, is a logical subdivision of an IP network. Updated by RFC 6918. The practice of dividing a network into two or more networks is called subnetting.
Computers that belong to the same subnet are addressed with an identica ...
configuration, and the host address, which occupies the remaining bits. Each subnet has a network mask that specifies which bits of the address are the network prefix and which bits are the host address. Routing
Routing is the process of selecting a path for traffic in a Network theory, network or between or across multiple networks. Broadly, routing is performed in many types of networks, including circuit-switched networks, such as the public switched ...
is done by consulting a routing table maintained by the router which contains each known destination network prefix, the associated network mask, and the information needed to route packets to that destination. In a simple software implementation, the router compares the destination address of the packet to be routed with each entry in the routing table, performing a bitwise AND
In computer programming, a bitwise operation operates on a bit string, a bit array or a binary numeral (considered as a bit string) at the level of its individual bits. It is a fast and simple action, basic to the higher-level arithmetic operat ...
with the network mask and comparing it with the network prefix. If they are equal, the corresponding routing information is used to forward the packet. Using a ternary CAM for the routing table makes the lookup process very efficient. The addresses are stored using ''don't care'' for the host part of the address, so looking up the destination address in the CAM immediately retrieves the correct routing entry; both the masking and comparison are done by the CAM hardware. This works if (a) the entries are stored in order of decreasing network mask length, and (b) the hardware returns only the first matching entry; thus, the match with the longest network mask (longest prefix match
Longest prefix match (also called Maximum prefix length match) refers to an algorithm used by routers in Internet Protocol (IP) networking to select an entry from a routing table.
Because each entry in a forwarding table may specify a sub-netwo ...
) is used.
Other CAM applications include:
* Fully associative cache controllers and translation lookaside buffer
A translation lookaside buffer (TLB) is a memory CPU cache, cache that stores the recent translations of virtual memory address to a physical memory Memory_address, location. It is used to reduce the time taken to access a user memory location. It ...
s
*Database
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data or a type of data store based on the use of a database management system (DBMS), the software that interacts with end users, applications, and the database itself to capture and a ...
engines
*Data compression
In information theory, data compression, source coding, or bit-rate reduction is the process of encoding information using fewer bits than the original representation. Any particular compression is either lossy or lossless. Lossless compressi ...
hardware
*Artificial neural networks
In machine learning, a neural network (also artificial neural network or neural net, abbreviated ANN or NN) is a computational model inspired by the structure and functions of biological neural networks.
A neural network consists of connected ...
*Intrusion prevention system
An intrusion detection system (IDS) is a device or software application that monitors a network or systems for malicious activity or policy violations. Any intrusion activity or violation is typically either reported to an administrator or collec ...
s
*Network processor
A network processor is an integrated circuit which has a feature set specifically targeted at the Computer networking, networking application domain.
Network processors are typically software programmable devices and would have generic characteri ...
s
*Several custom computers, like the Goodyear STARAN, were built to implement CAM.
See also
* Content-addressable network * Content-addressable parallel processor *Content-addressable storage The content-addressable network (CAN) is a distributed, decentralized Peer-to-peer, P2P infrastructure that provides hash table functionality on an Internet-like scale. CAN was one of the original four distributed hash table proposals, introduced c ...
, or file system
* Sparse distributed memory
* Tuple space
References
Bibliography
*Anargyros Krikelis, Charles C. Weems (editors) (1997). ''Associative Processing and Processors'', IEEE Computer Science Press. * * * Stormon, C.D.; Troullinos, N.B.; Saleh, E.M.; Chavan, A.V.; Brule, M.R.; Oldfield, J.V.; A general-purpose CMOS associative processor IC and system, Coherent Research Inc., East Syracuse, NY, USA, IEEE Micro, Dec. 1992, Volume: 12 Issue:6.External links
CAM Primer
{{Authority control Associative arrays Computer memory Computer networking