Contemporary Classical Compositions on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Contemporary history, in English-language
 In 1945, the
In 1945, the 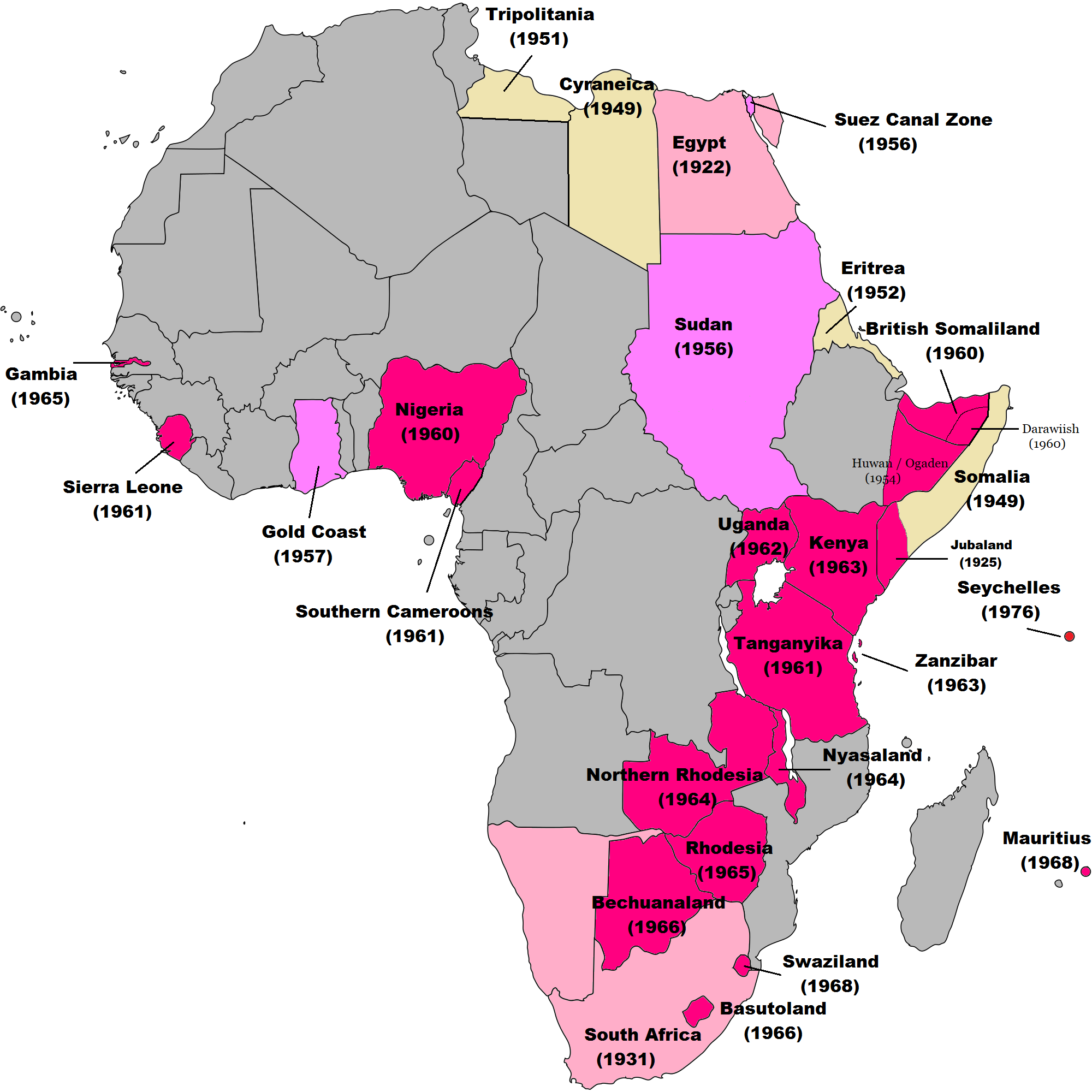
 The
The
The Global Crisis of Our Time: The Long-Term Impacts of COVID-19
, ''Oxford Research Group'' The threat of the disease caused the
ImageSize = width:1024 height:auto barincrement:27
PlotArea = top:10 bottom:20 right:130 left:70
AlignBars = justify
Colors =
id:time value:rgb(0.7,0.7,1) #
id:period value:rgb(1,0.7,0.5) #
id:age value:rgb(0.95,0.85,0.5) #
id:era value:rgb(1,0.85,0.5) #
id:eon value:rgb(1,0.85,0.7) #
id:filler value:gray(0.8) # background bar
id:black value:black
Period = from:1940 till:2025.255
TimeAxis = orientation:horizontal
ScaleMajor = unit:year increment:10 start:1940
ScaleMinor = unit:year increment:1 start:1940
PlotData =
align:center textcolor:black fontsize:8 mark:(line,black) width:11 shift:(0,-5)
bar:Tech color:era
from:1945.667 till:1948.5 text:
excerpt
* Boyd, Andrew, Joshua Comenetz. '' An atlas of world affairs'' (2007
excerpt
* Briggs, Asa, and Peter Burke. ''A Social History of the Media: From Gutenberg to the Internet'' (2002
excerpt
* * Hunt, Michael H. ''The World Transformed: 1945 to the Present'' (2nd ed. 2015) 624p
website
* Hunt, Michael H. ed., ''The World Transformed, 1945 to the Present: A Documentary Reader'' (2nd ed. 2001) primary source
excerpts
* McWilliams, Wayne C. and Harry Piotrowski. ''The World Since 1945: A History of International Relations'' (8th ed. 2014), 620pp
Internet Modern History Sourcebook
at Fordham University
''Journal of Contemporary History''
SAGE Publications. (Print )
Contemporary History Institute (CHI)
ohiou.edu (ed., Analyzes the contemporary period in world affairs—the period from World War II to the present—from an interdisciplinary historical perspective.)
Soviet Union Timeline
on ''BBC'' {{Authority control Contemporary history, Historiography Historical eras Articles which contain graphical timelines Articles containing video clips
historiography
Historiography is the study of the methods used by historians in developing history as an academic discipline. By extension, the term ":wikt:historiography, historiography" is any body of historical work on a particular subject. The historiog ...
, is a subset of modern history
The modern era or the modern period is considered the current historical period of human history. It was originally applied to the history of Europe and Western history for events that came after the Middle Ages, often from around the year 1500, ...
that describes the historical period
In historiography, periodization is the process or study of categorizing the past into discrete, quantified, and named blocks of time for the purpose of study or analysis.Adam Rabinowitz.It's about time: historical periodization and Linked Ancie ...
from about 1945 to the present. In the social sciences, contemporary history is also continuous with, and related to, the rise of postmodernity
Postmodernity (post-modernity or the postmodern condition) is the economic or cultural state or condition of society which is said to exist ''after'' modernity. Some schools of thought hold that modernity ended in the late 20th century – in th ...
.
Contemporary history is politically
Politics () is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of status or resources.
The branch of social science that studies poli ...
dominated by the Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
(1947–1991) between the Western Bloc
The Western Bloc, also known as the Capitalist Bloc, the Freedom Bloc, the Free Bloc, and the American Bloc, was an unofficial coalition of countries that were officially allied with the United States during the Cold War (1947–1991). While ...
, led by the United States, and the Eastern Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc (Combloc), the Socialist Bloc, the Workers Bloc, and the Soviet Bloc, was an unofficial coalition of communist states of Central and Eastern Europe, Asia, Africa, and Latin America that were a ...
, led by the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
. The confrontation spurred fears of a nuclear war
Nuclear warfare, also known as atomic warfare, is a War, military conflict or prepared Policy, political strategy that deploys nuclear weaponry. Nuclear weapons are Weapon of mass destruction, weapons of mass destruction; in contrast to conven ...
. An all-out "hot" war was avoided, but both sides intervened in the internal politics of smaller nations in their bid for global influence and via proxy war
In political science, a proxy war is an armed conflict where at least one of the belligerents is directed or supported by an external third-party power. In the term ''proxy war'', a belligerent with external support is the ''proxy''; both bel ...
s. The Cold War ultimately ended with the Revolutions of 1989
The revolutions of 1989, also known as the Fall of Communism, were a revolutionary wave of liberal democracy movements that resulted in the collapse of most Communist state, Marxist–Leninist governments in the Eastern Bloc and other parts ...
and the dissolution of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union was formally dissolved as a sovereign state and subject of international law on 26 December 1991 by Declaration No. 142-N of the Soviet of the Republics of the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union. Declaration No. 142-Н of ...
in 1991. The latter stages and aftermath of the Cold War enabled the democratization
Democratization, or democratisation, is the structural government transition from an democratic transition, authoritarian government to a more democratic political regime, including substantive political changes moving in a democratic direction ...
of much of Europe, Africa, and Latin America. Decolonization
Decolonization is the undoing of colonialism, the latter being the process whereby Imperialism, imperial nations establish and dominate foreign territories, often overseas. The meanings and applications of the term are disputed. Some scholar ...
was another important trend in Southeast Asia, the Middle East, and Africa as new states gained independence from European colonial empire
A colonial empire is a sovereign state, state engaging in colonization, possibly establishing or maintaining colony, colonies, infused with some form of coloniality and colonialism. Such states can expand contiguous as well as Territory#Overseas ...
s during the period from 1945–1975. The Middle East also saw a conflict involving the new state of Israel, the rise of petroleum politics
Petroleum politics have been an increasingly important aspect of diplomacy since the rise of the petroleum industry in the Middle East in the early 20th century. As competition continues for a vital resource, the strategic calculations of major ...
, the continuing prominence but later decline of Arab nationalism
Arab nationalism () is a political ideology asserting that Arabs constitute a single nation. As a traditional nationalist ideology, it promotes Arab culture and civilization, celebrates Arab history, the Arabic language and Arabic literatur ...
, and the growth of Islamism
Islamism is a range of religious and political ideological movements that believe that Islam should influence political systems. Its proponents believe Islam is innately political, and that Islam as a political system is superior to communism ...
. The first supranational organizations of government, such as the United Nations and European Union, emerged during the period after 1945.
Countercultures rose and the sexual revolution
The sexual revolution, also known as the sexual liberation, was a social movement that challenged traditional codes of behavior related to sexuality and interpersonal relationships throughout the Western world from the late 1950s to the early 1 ...
transformed social
Social organisms, including human(s), live collectively in interacting populations. This interaction is considered social whether they are aware of it or not, and whether the exchange is voluntary or not.
Etymology
The word "social" derives fro ...
relations in western countries between the 1960s and 1980s, as seen in the protests of 1968
The protests of 1968 comprised a worldwide escalation of social conflicts, which were predominantly characterized by the rise of left-wing politics, Anti-war movement, anti-war sentiment, Civil and political rights, civil rights urgency, youth C ...
. Living standards rose sharply across the developed world
A developed country, or advanced country, is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy, and advanced technological infrastructure relative to other less industrialized nations. Most commonly, the criteria for eval ...
because of the post-war economic boom. Japan and West Germany
West Germany was the common English name for the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG) from its formation on 23 May 1949 until German reunification, its reunification with East Germany on 3 October 1990. It is sometimes known as the Bonn Republi ...
both emerged as exceptionally strong economies. The culture of the United States
The culture of the United States encompasses various social behaviors, institutions, and Social norm, norms, including forms of Languages of the United States, speech, American literature, literature, Music of the United States, music, Visual a ...
spread widely, with American television and movies spreading across the world. Some Western countries began a slow process of deindustrializing in the 1970s; globalization
Globalization is the process of increasing interdependence and integration among the economies, markets, societies, and cultures of different countries worldwide. This is made possible by the reduction of barriers to international trade, th ...
led to the emergence of new financial and industrial centers in Asia. The Japanese economic miracle
The Japanese economic miracle () refers to a period of economic growth in the post–World War II Japan. It generally refers to the period from 1955, around which time the per capita gross national income of the country recovered to pre-war leve ...
was later followed by the Four Asian Tigers
The Four Asian Tigers ( the Four Asian Dragons or Four Little Dragons in Chinese and Korean) are the developed Asian economies of Hong Kong, Singapore, South Korea, and Taiwan. Between the early 1950s and 1990s, they underwent rapid industrializ ...
of Hong Kong, Singapore, South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the southern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and borders North Korea along the Korean Demilitarized Zone, with the Yellow Sea to the west and t ...
and Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
. China launched major economic reforms from 1979 onward, becoming a major exporter of consumer goods around the world.
Science
Science is a systematic discipline that builds and organises knowledge in the form of testable hypotheses and predictions about the universe. Modern science is typically divided into twoor threemajor branches: the natural sciences, which stu ...
made new advances after 1945, which included spaceflight
Spaceflight (or space flight) is an application of astronautics to fly objects, usually spacecraft, into or through outer space, either with or without humans on board. Most spaceflight is uncrewed and conducted mainly with spacecraft such ...
, nuclear technology
Nuclear technology is technology that involves the nuclear reactions of atomic nucleus, atomic nuclei. Among the notable nuclear technologies are nuclear reactors, nuclear medicine and nuclear weapons. It is also used, among other things, in s ...
, laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radi ...
s, semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity between that of a conductor and an insulator. Its conductivity can be modified by adding impurities (" doping") to its crystal structure. When two regions with different doping level ...
s, molecular biology
Molecular biology is a branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecule, molecular basis of biological activity in and between Cell (biology), cells, including biomolecule, biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactio ...
, genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinians, Augustinian ...
, particle physics
Particle physics or high-energy physics is the study of Elementary particle, fundamental particles and fundamental interaction, forces that constitute matter and radiation. The field also studies combinations of elementary particles up to the s ...
, and the Standard Model
The Standard Model of particle physics is the Scientific theory, theory describing three of the four known fundamental forces (electromagnetism, electromagnetic, weak interaction, weak and strong interactions – excluding gravity) in the unive ...
of quantum field theory
In theoretical physics, quantum field theory (QFT) is a theoretical framework that combines Field theory (physics), field theory and the principle of relativity with ideas behind quantum mechanics. QFT is used in particle physics to construct phy ...
. The first commercial computers were created, followed by the Internet, beginning the Information Age
The Information Age is a historical period that began in the mid-20th century. It is characterized by a rapid shift from traditional industries, as established during the Industrial Revolution, to an economy centered on information technology ...
.
Political history
1945–1991
Allies of World War II
The Allies, formally referred to as the United Nations from 1942, were an international Coalition#Military, military coalition formed during World War II (1939–1945) to oppose the Axis powers. Its principal members were the "Four Policeme ...
had defeated all significant opposition to them. They established the United Nations to govern international relations and disputes. A looming question was how to handle the defeated Axis nations and the shattered nations that the Axis had conquered. Following the Yalta Conference
The Yalta Conference (), held 4–11 February 1945, was the World War II meeting of the heads of government of the United States, the United Kingdom, and the Soviet Union to discuss the postwar reorganization of Germany and Europe. The three sta ...
, territory was divided into zones for which Allied country would have responsibility and manage rebuilding. While these zones were theoretically temporary (such as the eventual fate of occupied Austria, which was released to independence as a neutral country), growing tensions between the Western Bloc
The Western Bloc, also known as the Capitalist Bloc, the Freedom Bloc, the Free Bloc, and the American Bloc, was an unofficial coalition of countries that were officially allied with the United States during the Cold War (1947–1991). While ...
, led by the United States, with the Eastern Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc (Combloc), the Socialist Bloc, the Workers Bloc, and the Soviet Bloc, was an unofficial coalition of communist states of Central and Eastern Europe, Asia, Africa, and Latin America that were a ...
, led by the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
, meant that many calcified into place. Countries in Soviet zones of Eastern Europe had communist regimes installed as satellite state
A satellite state or dependent state is a country that is formally independent but under heavy political, economic, and military influence or control from another country. The term was coined by analogy to planetary objects orbiting a larger ob ...
s. The Berlin Blockade
The Berlin Blockade (24 June 1948 – 12 May 1949) was one of the first major international crises of the Cold War. During the multinational occupation of post–World War II Germany, the Soviet Union blocked the Western Allies' railway, roa ...
of 1948 led to a Western Airlift to preserve West Berlin
West Berlin ( or , ) was a political enclave which comprised the western part of Berlin from 1948 until 1990, during the Cold War. Although West Berlin lacked any sovereignty and was under military occupation until German reunification in 1 ...
and signified a cooling of East-West relations. Germany split into two countries in 1949, liberal-democratic West Germany
West Germany was the common English name for the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG) from its formation on 23 May 1949 until German reunification, its reunification with East Germany on 3 October 1990. It is sometimes known as the Bonn Republi ...
and communist East Germany
East Germany, officially known as the German Democratic Republic (GDR), was a country in Central Europe from Foundation of East Germany, its formation on 7 October 1949 until German reunification, its reunification with West Germany (FRG) on ...
. The conflict as a whole would become known as the Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
. The Western Bloc formed NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO ; , OTAN), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental Transnationalism, transnational military alliance of 32 Member states of NATO, member s ...
in 1949 while the Eastern Bloc formed the Warsaw Pact
The Warsaw Pact (WP), formally the Treaty of Friendship, Co-operation and Mutual Assistance (TFCMA), was a Collective security#Collective defense, collective defense treaty signed in Warsaw, Polish People's Republic, Poland, between the Sovi ...
in 1955. Direct combat between the new Great Powers was generally avoided, although proxy war
In political science, a proxy war is an armed conflict where at least one of the belligerents is directed or supported by an external third-party power. In the term ''proxy war'', a belligerent with external support is the ''proxy''; both bel ...
s fought in other countries by factions equipped by one side against the other side's faction occurred. An arms race
An arms race occurs when two or more groups compete in military superiority. It consists of a competition between two or more State (polity), states to have superior armed forces, concerning production of weapons, the growth of a military, and ...
to develop and build nuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission or atomic bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions (thermonuclear weapon), producing a nuclear exp ...
s happened as policymakers wanted to ensure their side had more if it came to a war.
In East Asia, Chiang Kai-shek's Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
was overthrown in the Chinese Communist Revolution
The Chinese Communist Revolution was a social revolution, social and political revolution in China that began in 1927 and culminated with the proclamation of the People's Republic of China (PRC) in 1949. The revolution was led by the Chinese C ...
from 1945–1949. His government retreated to Taiwan, but both the nationalist KMT government and the new communist mainland government under Mao Zedong
Mao Zedong pronounced ; traditionally Romanization of Chinese, romanised as Mao Tse-tung. (26December 18939September 1976) was a Chinese politician, revolutionary, and political theorist who founded the People's Republic of China (PRC) in ...
continued to claim authority over all of China. Korea was divided similarly to Germany, with the Soviet Union occupying the North and the United States occupying the South (future North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and borders China and Russia to the north at the Yalu River, Yalu (Amnok) an ...
and South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the southern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and borders North Korea along the Korean Demilitarized Zone, with the Yellow Sea to the west and t ...
). Unlike Germany, the conflict there turned hot, as the Korean War
The Korean War (25 June 1950 – 27 July 1953) was an armed conflict on the Korean Peninsula fought between North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea; DPRK) and South Korea (Republic of Korea; ROK) and their allies. North Korea was s ...
erupted from 1950–1953. Korea was not reunified under either government, however, due to strong support from both the US and China for their favored side; it became a frozen conflict
In international relations, a frozen conflict is a situation in which active armed conflict has been brought to an end, but no peace treaty or other political framework resolves the conflict to the satisfaction of the combatants. Therefore, ...
instead. Japan was given a new constitution foreswearing aggressive war in 1947, and the American occupation ended in 1952, although a treaty of mutual aid with the US was soon signed. The US also granted the Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
their independence in 1946 while keeping close relations.
The Middle East became a hotbed of instability. The new Jewish state of Israel declared its independence, recognized by both the United States and the Soviet Union, after which followed the 1948 Arab–Israeli War
The 1948 Arab–Israeli War, also known as the First Arab–Israeli War, followed the 1947–1948 civil war in Mandatory Palestine, civil war in Mandatory Palestine as the second and final stage of the 1948 Palestine war. The civil war becam ...
. Egypt's weak and ineffective king Farouk was overthrown in the 1952 Egyptian revolution
The Egyptian revolution of 1952, also known as the 1952 coup d'état () and the 23 July Revolution (), was a period of profound political, economic, and societal change in Egypt. On 23 July 1952, the revolution began with the toppling of King ...
, and replaced by General Nasser
Gamal Abdel Nasser Hussein (15 January 1918 – 28 September 1970) was an Egyptian military officer and revolutionary who served as the second president of Egypt from 1954 until his death in 1970. Nasser led the Egyptian revolution of 1952 a ...
; the 1953 Iran coup saw the American-friendly shah Mohammad Reza Pahlavi
Mohammad Reza Pahlavi (26 October 1919 – 27 July 1980) was the last List of monarchs of Iran, Shah of Iran, ruling from 1941 to 1979. He succeeded his father Reza Shah and ruled the Imperial State of Iran until he was overthrown by the ...
remove the democratic constraints on his government and take power directly; and Iraq's Western-friendly monarchy was overthrown in 1958. Nasser's Egypt would go on to face the Suez Crisis
The Suez Crisis, also known as the Second Arab–Israeli War, the Tripartite Aggression in the Arab world and the Sinai War in Israel, was a British–French–Israeli invasion of Egypt in 1956. Israel invaded on 29 October, having done so w ...
in 1956, briefly unify with Syria as the United Arab Republic
The United Arab Republic (UAR; ) was a sovereign state in the Middle East from 1958 to 1971. It was initially a short-lived political union between Republic of Egypt (1953–1958), Egypt (including Occupation of the Gaza Strip by the United Ara ...
(UAR) from 1958 to 1961, and expensively intervene in the North Yemen civil war
The North Yemen civil war, also known as the 26 September revolution, was a civil war fought in North Yemen from 1962 to 1970 between partisans of the Kingdom of Yemen, Mutawakkilite Kingdom and supporters of the Yemen Arab Republic. The war ...
from 1962 to 1970.

Decolonization
Decolonization is the undoing of colonialism, the latter being the process whereby Imperialism, imperial nations establish and dominate foreign territories, often overseas. The meanings and applications of the term are disputed. Some scholar ...
was the most important development across Southeast Asia and Africa from 1946–1975, as the old British, French, Dutch, and Portuguese colonial empires were dismantled. Many new states
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
were given their independence, but soon found themselves having to choose between allying with the Western Bloc, Eastern Bloc, or attempting to stay neutral as a member of the Non-Aligned Movement
The Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) is a forum of 121 countries that Non-belligerent, are not formally aligned with or against any major power bloc. It was founded with the view to advancing interests of developing countries in the context of Cold W ...
. British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance in South Asia. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one form or another ...
was granted independence in 1947 without an outright war of independence being required. It was partitioned into Hindu-majority India and Muslim-majority Pakistan (West Pakistan
West Pakistan was the western province of Pakistan between One Unit, 1955 and Legal Framework Order, 1970, 1970, covering the territory of present-day Pakistan. Its land borders were with Afghanistan, India and Iran, with a maritime border wit ...
and East Pakistan
East Pakistan was the eastern province of Pakistan between 1955 and 1971, restructured and renamed from the province of East Bengal and covering the territory of the modern country of Bangladesh. Its land borders were with India and Burma, wit ...
, future Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
and Bangladesh
Bangladesh, officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eighth-most populous country in the world and among the List of countries and dependencies by ...
); Indo-Pakistani wars were fought in 1947, 1965, and 1971. Sukarno
Sukarno (6 June 1901 – 21 June 1970) was an Indonesian statesman, orator, revolutionary, and nationalist who was the first president of Indonesia, serving from 1945 to 1967.
Sukarno was the leader of the Indonesian struggle for independenc ...
took control of an independent Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, ...
in 1950, as attempts to reinstate Dutch rule in 1945–1949 had largely failed, and took an independent-to-Eastern leaning stance. He would later be overthrown by Suharto
Suharto (8 June 1921 – 27 January 2008) was an Indonesian Officer (armed forces), military officer and politician, and dictator, who was the second and longest serving president of Indonesia, serving from 1967 to 1998. His 32 years rule, cha ...
in 1968, who took a pro-Western stance. The Federation of Malaya
Malaya, officially the Federation of Malaya, was a country in Southeast Asia from 1948 to 1963. It succeeded the Malayan Union and, before that, British Malaya. It comprised eleven states – nine Malay states and two of the Straits Settleme ...
was granted independence in 1957, with the concurrent fighting of the Malayan Emergency
The Malayan Emergency, also known as the Anti–British National Liberation War, was a guerrilla warfare, guerrilla war fought in Federation of Malaya, Malaya between communist pro-independence fighters of the Malayan National Liberation Arm ...
against communist forces from 1948–1960. The French unsuccessfully fought the First Indochina War
The First Indochina War (generally known as the Indochina War in France, and as the Anti-French Resistance War in Vietnam, and alternatively internationally as the French-Indochina War) was fought between French Fourth Republic, France and Việ ...
in an attempt to hold on to French Indochina
French Indochina (previously spelled as French Indo-China), officially known as the Indochinese Union and after 1941 as the Indochinese Federation, was a group of French dependent territories in Southeast Asia from 1887 to 1954. It was initial ...
; at the 1954 Geneva Conference
The Geneva Conference was intended to settle outstanding issues resulting from the Korean War and the First Indochina War and involved several nations. It took place in Geneva, Switzerland, from 26 April to 20 July 1954. The part of the confe ...
, the new states of Cambodia
Cambodia, officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. It is bordered by Thailand to the northwest, Laos to the north, and Vietnam to the east, and has a coastline ...
, Laos
Laos, officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic (LPDR), is the only landlocked country in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by Myanmar and China to the northwest, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the southeast, and Thailand to the west and ...
, the Democratic Republic of Vietnam
North Vietnam, officially the Democratic Republic of Vietnam (DRV; ; VNDCCH), was a country in Southeast Asia from 1945 to 1976, with sovereignty fully recognized in 1954. A member of the communist Eastern Bloc, it opposed the French-suppor ...
, and the eventual Republic of Vietnam
South Vietnam, officially the Republic of Vietnam (RVN; , VNCH), was a country in Southeast Asia that existed from 1955 to 1975. It first garnered international recognition in 1949 as the State of Vietnam within the French Union, with it ...
were created. The division of Indochina eventually led to the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (1 November 1955 – 30 April 1975) was an armed conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia fought between North Vietnam (Democratic Republic of Vietnam) and South Vietnam (Republic of Vietnam) and their allies. North Vietnam w ...
in the 1960s and 70s (as well as the Laotian Civil War
The Laotian Civil War was waged between the Communist Pathet Lao and the Royal Lao Government from 23 May 1959 to 2 December 1975. The Kingdom of Laos was a covert Theatre (warfare), theater during the Vietnam War with both sides receiving heavy ...
and Cambodian Civil War
The Cambodian Civil War (, Romanization of Khmer#UNGEGN, UNGEGN: ) was a civil war in Cambodia fought between the Communist Party of Kampuchea (known as the Khmer Rouge, supported by North Vietnam and China) against the government of the Ki ...
), which ended in communist North Vietnam took over Sai Gon in 1975.
In Africa, France fought the grinding Algerian War
The Algerian War (also known as the Algerian Revolution or the Algerian War of Independence) ''; '' (and sometimes in Algeria as the ''War of 1 November'') was an armed conflict between France and the Algerian National Liberation Front (Algeri ...
from 1954–1962 that saw the end of French Algeria
French Algeria ( until 1839, then afterwards; unofficially ; ), also known as Colonial Algeria, was the period of History of Algeria, Algerian history when the country was a colony and later an integral part of France. French rule lasted until ...
and the rise of a new independent Algeria
Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the northeast by Tunisia; to Algeria–Libya border, the east by Libya; to Alger ...
. The British and French both slowly released their vast holdings, leading to the creation of states such as First Nigerian Republic in 1963. Portugal, on the other hand, fiercely held onto their Empire, leading to the Portuguese Colonial War
The Portuguese Colonial War (), also known in Portugal as the Overseas War () or in the Portuguese Empire, former colonies as the War of Liberation (), and also known as the Angolan War of Independence, Angolan, Guinea-Bissau War of Independence ...
from 1961–1974 in Angola, Guinea-Bissau, and Mozambique until the '' Estado Novo'' government fell. Meanwhile, apartheid-era South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O ...
remained fiercely anti-communist, but withdrew from the British Commonwealth in 1961, and supported various pro-colonial factions across Africa that had lost support from their "home" governments in Europe. Many of the newly independent African governments struggled with the balance between being too weak and overthrown by ambitious coup-plotters, and too strong and becoming dictatorships.
Latin America saw gradual economic growth but also instability in many countries, as the threat of coups and military regimes ( juntas) were a major threat. The most famous was the Cuban Revolution
The Cuban Revolution () was the military and political movement that overthrew the dictatorship of Fulgencio Batista, who had ruled Cuba from 1952 to 1959. The revolution began after the 1952 Cuban coup d'état, in which Batista overthrew ...
that overthrew Fulgencio Batista
Fulgencio Batista y Zaldívar (born Rubén Zaldívar; January 16, 1901 – August 6, 1973) was a Cuban military officer and politician who played a dominant role in Cuban politics from his initial rise to power as part of the 1933 Revolt of t ...
's American-friendly government for Fidel Castro
Fidel Alejandro Castro Ruz (13 August 1926 – 25 November 2016) was a Cuban politician and revolutionary who was the leader of Cuba from 1959 to 2008, serving as the prime minister of Cuba from 1959 to 1976 and President of Cuba, president ...
's Soviet-aligned government. This led to the Cuban Missile Crisis
The Cuban Missile Crisis, also known as the October Crisis () in Cuba, or the Caribbean Crisis (), was a 13-day confrontation between the governments of the United States and the Soviet Union, when American deployments of Nuclear weapons d ...
in 1963, generally considered one of the incidents most dangerously close to turning the Cold War into a direct military conflict. The 1968 Peruvian coup d'état
Events January–February
* January 1968, January – The I'm Backing Britain, I'm Backing Britain campaign starts spontaneously.
* January 5 – Prague Spring: Alexander Dubček is chosen as leader of the Communist Party of Cze ...
and also installed a Soviet-friendly government. Despite this, the region ultimately leaned toward the US in this period, with the CIA
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA; ) is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States tasked with advancing national security through collecting and analyzing intelligence from around the world and ...
supporting American-friendly factions in the 1954 Guatemalan coup d'état
The 1954 Guatemalan coup d'état () deposed the democratically elected Guatemalan President Jacobo Árbenz and marked the end of the Guatemalan Revolution. The coup installed the military dictatorship of Carlos Castillo Armas, the first in ...
, the 1964 Brazilian coup d'état, the 1973 Chilean coup d'état
The 1973 Chilean coup d'état () was a military overthrow of the democratic socialist president of Chile Salvador Allende and his Popular Unity (Chile), Popular Unity coalition government. Allende, who has been described as the first Marxist ...
, and others. Nicaragua suffered the most, with the Nicaraguan Revolution
The Nicaraguan Revolution () began with rising opposition to the Somoza dictatorship in the 1960s and 1970s, the ouster of the dictatorship in 1978–79, and fighting between the government and the Contras from 1981 to 1990. The revolution r ...
seeing major military aid from both great powers to their favored factions that extended a civil war in the country for decades. Mexico escaped this unrest, although functioned largely as a one-party state dominated by the PRI. Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
had a succession of idiosyncratic governments that courted both the US and USSR, but generally mismanaged the economy.
The Middle East saw events that presaged later conflicts in the 70s and 80s. A few years after the end of the UAR's union between Egypt and Syria, Syria's government was overthrown in the 1966 Syrian coup d'état and replaced with the Neo-Baathist Party, eventually leading to the leadership of the Al-Assad family
The Assad family ruled Syria from 1971, when Hafez al-Assad became President of Syria, president under the Ba'ath Party (Syrian-dominated faction), Ba'ath Party following the Corrective Movement (Syria), 1970 coup, until Bashar al-Assad was Fal ...
. Israel and its neighbors fought the Six-Day War
The Six-Day War, also known as the June War, 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab world, Arab states, primarily United Arab Republic, Egypt, Syria, and Jordan from 5 to 10June ...
in 1967 and the Yom Kippur War
The Yom Kippur War, also known as the Ramadan War, the October War, the 1973 Arab–Israeli War, or the Fourth Arab–Israeli War, was fought from 6 to 25 October 1973 between Israel and a coalition of Arab world, Arab states led by Egypt and S ...
of 1973. Under Anwar Sadat
Muhammad Anwar es-Sadat (25 December 1918 – 6 October 1981) was an Egyptian politician and military officer who served as the third president of Egypt, from 15 October 1970 until Assassination of Anwar Sadat, his assassination by fundame ...
and later Hosni Mubarak
Muhammad Hosni El Sayed Mubarak (; 4 May 1928 – 25 February 2020) was an Egyptian politician and military officer who served as the fourth president of Egypt from 1981 to 2011 and the 41st Prime Minister of Egypt, prime minister from 1981 to ...
, Egypt switched from Nasserism
Nasserism ( ) is an Arab nationalism, Arab nationalist and Arab socialism, Arab socialist List of political ideologies, political ideology based on the thinking of Gamal Abdel Nasser, one of the two principal leaders of the Egyptian Revolution ...
to favoring the Western Bloc, and signed a peace treaty with Israel. Lebanon, once among the most prosperous countries in the region and a cultural center, collapsed into the decade-long Lebanese Civil War
The Lebanese Civil War ( ) was a multifaceted armed conflict that took place from 1975 to 1990. It resulted in an estimated 150,000 fatalities and led to the exodus of almost one million people from Lebanon.
The religious diversity of the ...
from 1975–1990. Iran's unpopular pro-American government was overthrown in the 1979 Iranian Revolution
The Iranian Revolution (, ), also known as the 1979 Revolution, or the Islamic Revolution of 1979 (, ) was a series of events that culminated in the overthrow of the Pahlavi dynasty in 1979. The revolution led to the replacement of the Impe ...
and was replaced by a new Islamic Republic headed by Ruhollah Khomeini
Ruhollah Musavi Khomeini (17 May 1900 or 24 September 19023 June 1989) was an Iranian revolutionary, politician, political theorist, and religious leader. He was the founder of the Islamic Republic of Iran and the main leader of the Iranian ...
. Iran and Baathist Iraq under Saddam Hussein
Saddam Hussein (28 April 1937 – 30 December 2006) was an Iraqi politician and revolutionary who served as the fifth president of Iraq from 1979 until Saddam Hussein statue destruction, his overthrow in 2003 during the 2003 invasion of Ira ...
then fought each other in the Iran–Iraq War
The Iran–Iraq War, also known as the First Gulf War, was an armed conflict between Iran and Iraq that lasted from September 1980 to August 1988. Active hostilities began with the Iraqi invasion of Iran and lasted for nearly eight years, unti ...
from 1980–1988, which ended inconclusively.
In East Asia, China underwent the Cultural Revolution
The Cultural Revolution, formally known as the Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution, was a Social movement, sociopolitical movement in the China, People's Republic of China (PRC). It was launched by Mao Zedong in 1966 and lasted until his de ...
from 1966 to 1976, a major internal struggle that saw an intense program of Maoism
Maoism, officially Mao Zedong Thought, is a variety of Marxism–Leninism that Mao Zedong developed while trying to realize a socialist revolution in the agricultural, pre-industrial society of the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic o ...
and persecution of perceived internal enemies. China's relations with the Soviets deteriorated in the 1960s and 70s, resulting in the Sino-Soviet split
The Sino-Soviet split was the gradual worsening of relations between the People's Republic of China (PRC) and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) during the Cold War. This was primarily caused by divergences that arose from their ...
, although the two were able to cooperate on some matters. "Ping-pong diplomacy
Ping-pong diplomacy ( zh, c=乒乓外交, p=Pīngpāng wàijiāo) refers to the exchange of table tennis (ping-pong) players between the United States and the People's Republic of China in the early 1970s. Considered a turning point in relation ...
" led to a rapprochement between the US and China and American recognition of the Chinese communist government in the 1970s. China's pro-democracy movement was suppressed after the 1989 Tiananmen Square protests
The Tiananmen Square protests, known within China as the June Fourth Incident, were student-led Demonstration (people), demonstrations held in Tiananmen Square in Beijing, China, lasting from 15 April to 4 June 1989. After weeks of unsucces ...
, and China's government survived the tensions that would roil the Soviet-aligned bloc during the 1980s. South Korea (in the June Democratic Struggle) and Taiwan (with the lifting of martial law) would take major steps toward liberalization in 1987–1988, shifting from Western-aligned one-party states to more fully participatory democracies.
The 1980s saw a general retreat for the communist bloc. The Soviet–Afghan War
The Soviet–Afghan War took place in the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan from December 1979 to February 1989. Marking the beginning of the 46-year-long Afghan conflict, it saw the Soviet Union and the Armed Forces of the Democratic Republic o ...
(1979–1989) is often called the "Soviet Union's Vietnam War" in comparison to the American defeat, being an expensive and ultimately unsuccessful war and occupation. More importantly, the intervening decades had seen that Eastern Europe was unable to compete economically with Western Europe, which undermined the promise of communist abundance compared to capitalist poverty. The Western capitalist economies had proven wealthier and stronger, which made matching the Soviet defense budget to the American one strain limited resources. The Pan-European Picnic
The Pan-European Picnic (; ; ; ) was a peace demonstration held on the Austro- Hungarian border near Sopron, Hungary on 19 August 1989. The opening of the border gate between Austria and Hungary at the Pan-European Picnic was an event in the ...
in 1989 then set in motion a peaceful chain reaction with the subsequent fall of the Berlin Wall
The fall of the Berlin Wall (, ) on 9 November in German history, 9 November 1989, during the Peaceful Revolution, marked the beginning of the destruction of the Berlin Wall and the figurative Iron Curtain, as East Berlin transit restrictions we ...
. The Revolutions of 1989
The revolutions of 1989, also known as the Fall of Communism, were a revolutionary wave of liberal democracy movements that resulted in the collapse of most Communist state, Marxist–Leninist governments in the Eastern Bloc and other parts ...
saw many countries of Eastern Europe throw off their communist governments, and the USSR declined to invade to re-establish them. East and West Germany were reunified. Client state
A client state in the context of international relations is a State (polity), state that is economically, politically, and militarily subordinated to a more powerful controlling state. Alternative terms for a ''client state'' are satellite state, ...
status for many states ended, as there was no conflict left to fund. The Malta Summit on 3 December 1989, the failure of the August Coup
The 1991 Soviet coup attempt, also known as the August Coup, was a failed attempt by hardliners of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU) to Coup d'état, forcibly seize control of the country from Mikhail Gorbachev, who was President ...
by Soviet hardliners, and the formal dissolution of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union was formally dissolved as a sovereign state and subject of international law on 26 December 1991 by Declaration No. 142-N of the Soviet of the Republics of the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union. Declaration No. 142-Н of ...
on 26 December 1991 sealed the end of the Cold War.
1991–2001
The end of the Cold War left the United States the world's sole superpower. Communism seemed discredited; while China remained an officially communist state, Deng Xiaoping's economic reforms andsocialism with Chinese characteristics
Socialism with Chinese characteristics (; ) is a set of political theories and policies of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) that are seen by their proponents as representing Marxism adapted to Chinese circumstances.
The term was first establ ...
allowed for the growth of a capitalist private sector in China. In Russia, President Boris Yeltsin
Boris Nikolayevich Yeltsin (1 February 1931 – 23 April 2007) was a Soviet and Russian politician and statesman who served as President of Russia from 1991 to 1999. He was a member of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU) from 1961 to ...
pursued a policy of privatization, spinning off former government agencies into private corporations, attempting to handle budget problems inherited from the USSR. The end of Soviet foreign aid caused a variety of changes in countries previously part of the Eastern Bloc; many officially became democratic republics, though some were more accurately described as authoritarian or oligarchic
Oligarchy (; ) is a form of government in which power rests with a small number of people. Members of this group, called oligarchs, generally hold usually hard, but sometimes soft power through nobility, fame, wealth, or education; or throug ...
republics and one-party state
A one-party state, single-party state, one-party system or single-party system is a governance structure in which only a single political party controls the ruling system. In a one-party state, all opposition parties are either outlawed or en ...
s. Many Western commentators treated the development optimistically; it was thought the world was steadily progressing toward free, liberal democracies. South Africa, no longer able to attract Western support by claiming to be anti-communist, ended apartheid in the early 1990s, and many Eastern European countries switched to stable democracies. While some Americans had anticipated a "peace dividend" from budget cuts to the Defense Department, these cuts were not as large as some had hoped. The European Economic Community
The European Economic Community (EEC) was a regional organisation created by the Treaty of Rome of 1957,Today the largely rewritten treaty continues in force as the ''Treaty on the functioning of the European Union'', as renamed by the Lisbo ...
evolved into the European Union with the signing of the Maastricht Treaty
The Treaty on European Union, commonly known as the Maastricht Treaty, is the foundation treaty of the European Union (EU). Concluded in 1992 between the then-twelve Member state of the European Union, member states of the European Communities, ...
in 1993, which integrated Europe across borders to a new degree. International coalitions continued to have a role; the Gulf War
, combatant2 =
, commander1 =
, commander2 =
, strength1 = Over 950,000 soldiers3,113 tanks1,800 aircraft2,200 artillery systems
, page = https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/GAOREPORTS-PEMD-96- ...
saw a large international coalition undo Baathist Iraq's annexation of Kuwait, but other "police" style actions were less successful. Somalia
Somalia, officially the Federal Republic of Somalia, is the easternmost country in continental Africa. The country is located in the Horn of Africa and is bordered by Ethiopia to the west, Djibouti to the northwest, Kenya to the southwest, th ...
and Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran borde ...
descended into long, bloody civil wars for almost the entirety of the decade (Somali Civil War
The Somali Civil War (; ) is an List of ongoing armed conflicts, ongoing civil war that is taking place in Somalia. It grew out of resistance to the military junta which was led by Siad Barre during the 1980s. From 1988 to 1990, the Somali Armed ...
, Afghan Civil War (1992–1996)
The 1992–1996 Afghan Civil War, also known as the Second Afghan Civil War, took place between 28 April 1992—the date a new Peshawar Accord, interim Afghan government was supposed to replace the Republic of Afghanistan (1978–1992), Republic ...
, Afghan Civil War (1996–2001)). Russia fought a brutal war in Chechnya that failed to suppress the insurgency there from 1994–1996; war would resume during the Second Chechen War
Names
The Second Chechen War is also known as the Second Chechen Campaign () or the Second Russian Invasion of Chechnya from the Chechens, Chechen insurgents' point of view.Федеральный закон № 5-ФЗ от 12 января 19 ...
in 1999–2000 that saw a resumption of Russian control after Russia successfully convinced enough rebels to join their cause with promises of autonomy. The breakup of Yugoslavia
After a period of political and economic crisis in the 1980s, the constituent republics of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia split apart in the early 1990s. Unresolved issues from the breakup caused a series of inter-ethnic Yugoslav ...
also led to a series of Yugoslav Wars
The Yugoslav Wars were a series of separate but related#Naimark, Naimark (2003), p. xvii. ethnic conflicts, wars of independence, and Insurgency, insurgencies that took place from 1991 to 2001 in what had been the Socialist Federal Republic of ...
; NATO eventually intervened in the Kosovo War
The Kosovo War (; sr-Cyrl-Latn, Косовски рат, Kosovski rat) was an armed conflict in Kosovo that lasted from 28 February 1998 until 11 June 1999. It ...
. In the Middle East, the Israeli–Palestinian peace process
Intermittent discussions are held by various parties and proposals put forward in an attempt to resolve the Israeli–Palestinian conflict through a peace process. Since the 1970s, there has been a parallel effort made to find terms upon which ...
offered the prospect of a long-term peace deal to many; the Oslo Accords
The Oslo Accords are a pair of interim agreements between Israel and the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO): the Oslo I Accord, signed in Washington, D.C., in 1993; and the Oslo II Accord, signed in Taba, Egypt, in 1995. They marked the st ...
signed in 1993 seemed to offer a "roadmap" to resolving the conflict. Despite these high hopes, they would be largely dashed in 2000–2001 after a breakdown of negotiations and the Second Intifada
The Second Intifada (; ), also known as the Al-Aqsa Intifada, was a major uprising by Palestinians against Israel and its Israeli-occupied territories, occupation from 2000. Starting as a civilian uprising in Jerusalem and October 2000 prot ...
.
2001–present
In 2001, theSeptember 11 attacks
The September 11 attacks, also known as 9/11, were four coordinated Islamist terrorist suicide attacks by al-Qaeda against the United States in 2001. Nineteen terrorists hijacked four commercial airliners, crashing the first two into ...
—the deadliest terrorist attacks in human history—were carried out by al-Qaeda
, image = Flag of Jihad.svg
, caption = Jihadist flag, Flag used by various al-Qaeda factions
, founder = Osama bin Laden{{Assassinated, Killing of Osama bin Laden
, leaders = {{Plainlist,
* Osama bin Lad ...
against the United States. In response, the United States declared the war on terror, a global conflict against Islamist terrorism. US-led coalitions launched a war in Afghanistan
War in Afghanistan, Afghan war, or Afghan civil war may refer to:
*Conquest of Afghanistan by Alexander the Great (330 BC – 327 BC), the conquest of Afghanistan by the Macedonian Empire
* Muslim conquests of Afghanistan, a series of campaigns in ...
(2001–2021) against the Taliban
, leader1_title = Supreme Leader of Afghanistan, Supreme leaders
, leader1_name = {{indented plainlist,
* Mullah Omar{{Natural Causes{{nbsp(1994–2013)
* Akhtar Mansour{{Assassinated (2015–2016)
* Hibatullah Akhundzada (2016–present) ...
-ruled Islamic Emirate and the Iraq War
The Iraq War (), also referred to as the Second Gulf War, was a prolonged conflict in Iraq lasting from 2003 to 2011. It began with 2003 invasion of Iraq, the invasion by a Multi-National Force – Iraq, United States-led coalition, which ...
(2003–2011) that deposed Iraqi leader Saddam Hussein
Saddam Hussein (28 April 1937 – 30 December 2006) was an Iraqi politician and revolutionary who served as the fifth president of Iraq from 1979 until Saddam Hussein statue destruction, his overthrow in 2003 during the 2003 invasion of Ira ...
. The US killed al-Qaeda leader Osama bin Laden
Osama bin Laden (10 March 19572 May 2011) was a militant leader who was the founder and first general emir of al-Qaeda. Ideologically a pan-Islamist, Bin Laden participated in the Afghan ''mujahideen'' against the Soviet Union, and support ...
in 2011 and withdrew from Afghanistan in 2021, after which the Taliban retook control of the country. The US also led interventions against militant groups across Africa and the Middle East, including the war against the Islamic State
Many states began to intervene against the Islamic State, in both the Syrian civil war and the War in Iraq (2013–2017), in response to its rapid territorial gains from its Northern Iraq offensive (June 2014), 2014 Northern Iraq offensives, u ...
. After the September 11 attacks, many countries expanded the powers of law enforcement to combat terrorism and several other terrorist attacks took place across the world.
China has sought to challenge the United States's global hegemony. Under Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II (born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who was the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, he was the first African American president in American history. O ...
, the US pivoted its foreign policy focus to East Asia; China–US relations deteriorated further under Xi Jinping
Xi Jinping, pronounced (born 15 June 1953) is a Chinese politician who has been the general secretary of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) and Chairman of the Central Military Commission (China), chairman of the Central Military Commission ...
in China and Donald Trump
Donald John Trump (born June 14, 1946) is an American politician, media personality, and businessman who is the 47th president of the United States. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, he served as the 45 ...
in the US. The two countries have engaged in a trade war and fought for influence in the developing world
A developing country is a sovereign state with a less-developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to developed countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreeme ...
. In later years, China escalated disputes in the South China Sea and over Taiwan and has led BRICS
BRICS is an intergovernmental organization comprising ten countriesBrazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa, Egypt, Ethiopia, Indonesia, Iran and the United Arab Emirates. The idea of a BRICS-like group can be traced back to Russian foreign ...
as forum for emerging powers, while the US formed the Quad
QUaD, an acronym for QUEST at DASI, was a ground-based cosmic microwave background (CMB) polarization experiment at the South Pole. QUEST (Q and U Extragalactic Sub-mm Telescope) was the original name attributed to the bolometer detector instrume ...
grouping with Australia, India, and Japan. Disputes between India and China led to skirmishes between the two countries (2020–2021), and after North Korea obtained nuclear weapons in 2006, the threat of their use caused the North Korean crisis (2017–2018). Elsewhere in Asia, Nepal abolished its monarchy in 2008 after the end of the Nepalese Civil War
The Nepalese Civil War was a protracted armed conflict that took place in the then Kingdom of Nepal from 1996 to 2006. It saw countrywide fighting between the Kingdom rulers and the Communist Party of Nepal (Maoist), with the latter making ...
; a 2015 nationwide ceasefire after a series of reforms (2011–2015) ended the Myanmar conflict
Myanmar has been embroiled in armed conflict since 1948, when the country, then known as Burma, Burmese Declaration of Independence, gained independence from the United Kingdom. The conflict has largely been Ethnic conflict, ethnic-based, wit ...
until a coup d'état began a new civil war in 2021; and a 2024 a pro-democracy uprising in Bangladesh overthrew Sheikh Hasina
Sheikh Hasina (''née'' Wazed; born 28 September 1947) is a Bangladeshi politician who served as the tenth prime minister of Bangladesh from June 1996 to July 2001 and again from January 2009 to August 2024. Premiership of Sheikh Hasina, Her ...
.
In the Arab world
The Arab world ( '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, comprises a large group of countries, mainly located in West Asia and North Africa. While the majority of people in ...
, a series of anti-government protests, uprisings, and armed resistances known as the Arab Spring
The Arab Spring () was a series of Nonviolent resistance, anti-government protests, Rebellion, uprisings, and Insurgency, armed rebellions that spread across much of the Arab world in the early 2010s. It began Tunisian revolution, in Tunisia ...
(2010–2012) began after a revolution in Tunisia that ended the country's dictatorship. The Egyptian revolution in 2011 led to a political crisis and a second change of power in a 2013 coup d'état; in Libya
Libya, officially the State of Libya, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to Egypt–Libya border, the east, Sudan to Libya–Sudan border, the southeast, Chad to Chad–L ...
and Yemen
Yemen, officially the Republic of Yemen, is a country in West Asia. Located in South Arabia, southern Arabia, it borders Saudi Arabia to Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, the north, Oman to Oman–Yemen border, the northeast, the south-eastern part ...
, successful revolutions gave way to protracted political crises and civil wars. Protests against Syrian leader Bashar al-Assad
Bashar al-Assad (born 11September 1965) is a Syrian politician, military officer and former dictator
Sources characterising Assad as a dictator:
who served as the president of Syria from 2000 until fall of the Assad regime, his government ...
led to a multi-sided civil war (2011–2024) that ultimately ended after the fall of the Assad regime
On 8 December 2024, the Assad regime collapsed during a 2024 Syrian opposition offensives, major offensive by Syrian opposition, opposition forces. The offensive was spearheaded by Hay'at Tahrir al-Sham (HTS) and supported mainly by the Turk ...
in 2024 amid a regional crisis triggered by the October 7 Hamas attack on Israel in 2023 and subsequent Gaza war
The Gaza war is an armed conflict in the Gaza Strip and southern Israel fought since 7 October 2023. A part of the unresolved Israeli–Palestinian conflict, Israeli–Palestinian and Gaza–Israel conflict, Gaza–Israel conflicts dating ...
. The Gaza war also led to an Israeli invasion of Lebanon that largely destroyed Hezbollah
Hezbollah ( ; , , ) is a Lebanese Shia Islamist political party and paramilitary group. Hezbollah's paramilitary wing is the Jihad Council, and its political wing is the Loyalty to the Resistance Bloc party in the Lebanese Parliament. I ...
and a significant escalation of the Iran–Israel proxy conflict
The Iran–Israel proxy conflict, also known as the Iran–Israel proxy war or Iran–Israel Cold War, is an ongoing Proxy war, proxy conflict between Iran and Israel. In the Israeli–Lebanese conflict, Iran has supported Lebanese Shia milit ...
. Fears of Iran's nuclear program
The Nuclear technology, nuclear program of Iran is one of the most scrutinized nuclear programs in the world. The military capabilities of the program are possible through its mass Enriched uranium, enrichment activities in facilities such a ...
led to a 2015 international deal to limit it and growing Arab–Israeli normalization which included the 2020 signing of the Abraham Accords.
Conflicts in the former Soviet Union continued; Russia invaded Georgia in 2008 and seized Crimea from Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
in 2014 after a pro-Western revolution in Ukraine, beginning a conflict that led to a full-scale Russian invasion of the country in 2022. The Nagorno-Karabakh conflict ended after Azerbaijan's victories in a war with Armenia (2020) and in a later offensive (2023) incorporated Artsakh into the country. Serbia and Montenegro
The State Union of Serbia and Montenegro or simply Serbia and Montenegro, known until 2003 as the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia and commonly referred to as FR Yugoslavia (FRY) or simply Yugoslavia, was a country in Southeast Europe locate ...
dissolved in 2006 and Kosovo
Kosovo, officially the Republic of Kosovo, is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe with International recognition of Kosovo, partial diplomatic recognition. It is bordered by Albania to the southwest, Montenegro to the west, Serbia to the ...
declared independence from Serbia two years later to partial recognition. NATO and the European Union continued to expand eastward; by 2024, 11 more countries had joined NATO and 13 had joined the EU, while the United Kingdom left the EU in 2020 after years of negotiations.
In Africa, the end of the Second Sudanese Civil War
The Second Sudanese Civil War was a conflict from 1983 to 2005 between the central Sudanese government and the Sudan People's Liberation Army/Movement, Sudan People's Liberation Army. It was largely a continuation of the First Sudanese Civil Wa ...
allowed South Sudan
South Sudan (), officially the Republic of South Sudan, is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered on the north by Sudan; on the east by Ethiopia; on the south by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Uganda and Kenya; and on the ...
to declare independence in 2011, and a subsequent civil war (2013–2020) ended in a ceasefire. Beginning in the 2020s, a series of coups d'état primarily in the Sahel
The Sahel region (; ), or Sahelian acacia savanna, is a Biogeography, biogeographical region in Africa. It is the Ecotone, transition zone between the more humid Sudanian savannas to its south and the drier Sahara to the north. The Sahel has a ...
installed military juntas in Mali, in Guinea, in Burkina Faso, in Niger, and in Gabon amid a regional Islamist insurgency and initiated a standoff (2023–2024) between ECOWAS
The Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS; also known as CEDEAO in French and Portuguese) is a regional political and economic union of twelve countries of West Africa. Collectively, the present and former members comprise an area ...
and juntas in Niger, Mali, and Burkina Faso, which formed the Alliance of Sahel States
The Alliance of Sahel States (, AES) is a confederation formed between Mali, Niger, and Burkina Faso. It originated as a mutual defense pact created on 16 September 2023 following the 2023 Nigerien crisis, in which the West African political bl ...
in 2023 and established a confederation in 2024. A 2021 coup in Sudan ended the country's transition to democracy and resulting political crises began a civil war in 2023. The East African Community
The East African Community (EAC) is an intergovernmental organisation in East Africa. The EAC's membership consists of eight states: Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Federal Republic of Somalia, the Republics of Burundi, Kenya, Rwanda, S ...
has developed and expanded across the continent while a military conflict between Rwanda and the Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), also known as the DR Congo, Congo-Kinshasa, or simply the Congo (the last ambiguously also referring to the neighbouring Republic of the Congo), is a country in Central Africa. By land area, it is t ...
has persisted since 2022.
Economic history
The end of World War II in 1945 saw an increase ininternational trade
International trade is the exchange of capital, goods, and services across international borders or territories because there is a need or want of goods or services. (See: World economy.)
In most countries, such trade represents a significan ...
and an interconnected system of treaties and agreements to ease its flow. In particular, the United States and the United States dollar took a pivotal role in the world economy
The world economy or global economy is the economy of all humans in the world, referring to the global economic system, which includes all economic activities conducted both within and between nations, including production (economics), producti ...
, displacing the UK. The era is sometimes called " Pax Americana" for the relative liberal peace in the Western world, resulting from the preponderance of power enjoyed by the US, as a comparison to the Pax Romana
The (Latin for ) is a roughly 200-year-long period of Roman history that is identified as a golden age of increased and sustained Roman imperialism, relative peace and order, prosperous stability, hegemonic power, and regional expansion, a ...
established at the height of the Roman Empire. New York's financial sector ("Wall Street
Wall Street is a street in the Financial District, Manhattan, Financial District of Lower Manhattan in New York City. It runs eight city blocks between Broadway (Manhattan), Broadway in the west and South Street (Manhattan), South Str ...
") was the center of the financial world from 1945–1970 in a dominant way unlikely to be seen again. Unlike the aftermath of World War I, the US strongly aided in the rebuilding of Europe, including aid to the defeated Axis nations, rather than punishment. The Marshall Plan
The Marshall Plan (officially the European Recovery Program, ERP) was an American initiative enacted in 1948 to provide foreign aid to Western Europe. The United States transferred $13.3 billion (equivalent to $ in ) in economic recovery pr ...
sent billions of dollars of aid to Western Europe to ensure its stability and ward off a potential economic downturn. The 1944 Bretton Woods Conference
The Bretton Woods Conference, formally known as the United Nations Monetary and Financial Conference, was the gathering of 730 delegates from all 44 allied nations at the Mount Washington Hotel, in Bretton Woods, New Hampshire, United States, to ...
established the Bretton Woods system
The Bretton Woods system of monetary management established the rules for commercial relations among 44 countries, including the United States, Canada, Western European countries, and Australia, after the 1944 Bretton Woods Agreement until the ...
, a set of practices that governed world trade and currencies from 1945–1971, as well as the World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and Grant (money), grants to the governments of Least developed countries, low- and Developing country, middle-income countries for the purposes of economic development ...
and the International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution funded by 191 member countries, with headquarters in Washington, D.C. It is regarded as the global lender of las ...
(IMF). Western Europe also established the European Economic Community
The European Economic Community (EEC) was a regional organisation created by the Treaty of Rome of 1957,Today the largely rewritten treaty continues in force as the ''Treaty on the functioning of the European Union'', as renamed by the Lisbo ...
in 1957 to ease customs and aid international trade. In general, vast quality of life improvements affected most every corner of the globe during this period, in both the Western and Eastern spheres. France called them '' Les Trente Glorieuses'' ("The Glorious Thirty ears). Despite being largely destroyed in the war, West Germany soon bounced back to being an economic powerhouse by the 1950s with the ''wirtschaftswunder
The ''Wirtschaftswunder'' (, "economic miracle"), also known as the Miracle on the Rhine, was the rapid reconstruction and development of the Economy, economies of West Germany and Austria after World War II. The expression was first used to re ...
''. Surprisingly, Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
followed Germany, achieving incredible economic growth and becoming the second largest economy in the world in 1968, a phenomenon called the Japanese economic miracle
The Japanese economic miracle () refers to a period of economic growth in the post–World War II Japan. It generally refers to the period from 1955, around which time the per capita gross national income of the country recovered to pre-war leve ...
. Many explanations are proffered for the enviable results of these years: relative peace (at least outside the "Third World
The term Third World arose during the Cold War to define countries that remained non-aligned with either NATO or the Warsaw Pact. The United States, Canada, Taiwan, Japan, South Korea, the Southern Cone, NATO, Western European countries and oth ...
"); a reduction in average family size; technological improvements; and others. The Eastern Bloc, meanwhile, established Comecon
The Council for Mutual Economic Assistance, often abbreviated as Comecon ( ) or CMEA, was an economic organization from 1949 to 1991 under the leadership of the Soviet Union that comprised the countries of the Eastern Bloc#List of states, Easter ...
as their equivalent to the Marshall Plan and to establish internal trading rules between communist states.
The 1970s saw economic headwinds. Notably, the price of oil
The price of oil, or the oil price, generally refers to the spot price of a barrel () of benchmark crude oil—a reference price for buyers and sellers of crude oil such as West Texas Intermediate (WTI), Brent Crude, Dubai Crude, OPEC ...
started to go up in the 1970s, as the easiest and most accessible wells had already been pumped dry in the preceding century, and oil is a non-renewable resource. Attention was drawn to the abundant oil in the Middle East, where countries in OPEC
The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC ) is an organization enabling the co-operation of leading oil-producing and oil-dependent countries in order to collectively influence the global oil market and maximize Profit (eco ...
controlled substantial untapped oil reserves. Political tensions over the Yom Kippur War
The Yom Kippur War, also known as the Ramadan War, the October War, the 1973 Arab–Israeli War, or the Fourth Arab–Israeli War, was fought from 6 to 25 October 1973 between Israel and a coalition of Arab world, Arab states led by Egypt and S ...
and the Iranian Revolution
The Iranian Revolution (, ), also known as the 1979 Revolution, or the Islamic Revolution of 1979 (, ) was a series of events that culminated in the overthrow of the Pahlavi dynasty in 1979. The revolution led to the replacement of the Impe ...
led to the 1973 oil crisis
In October 1973, the Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries (OAPEC) announced that it was implementing a total oil embargo against countries that had supported Israel at any point during the 1973 Yom Kippur War, which began after Eg ...
and 1979 oil crisis
A drop in oil production in the wake of the Iranian revolution led to an energy crisis in 1979. Although the global oil supply only decreased by approximately four percent, the oil markets' reaction raised the price of crude oil drastically ...
. The Soviet Union called it the "Era of Stagnation
The "Era of Stagnation" (, or ) is a term coined by Mikhail Gorbachev in order to describe the negative way in which he viewed the economic, political, and social policies of the Soviet Union that began during the rule of Leonid Brezhnev (1964 ...
". The 1970s and 80s also saw the rise of the Four Asian Tigers
The Four Asian Tigers ( the Four Asian Dragons or Four Little Dragons in Chinese and Korean) are the developed Asian economies of Hong Kong, Singapore, South Korea, and Taiwan. Between the early 1950s and 1990s, they underwent rapid industrializ ...
, as South Korea, Taiwan, Singapore, and Hong Kong emulated the Japanese route to prosperity with varying degree of success. In China, the leftist Gang of Four
The Gang of Four () was a Maoist political faction composed of four Chinese Communist Party (CCP) officials. They came to prominence during the Cultural Revolution (1966–1976) and were later charged with a series of treasonous crimes due to th ...
were overthrown in 1976, and Deng Xiaoping
Deng Xiaoping also Romanization of Chinese, romanised as Teng Hsiao-p'ing; born Xiansheng (). (22 August 190419 February 1997) was a Chinese statesman, revolutionary, and political theorist who served as the paramount leader of the People's R ...
pursued a policy of tentatively opening the Chinese economy to capitalist innovations throughout the 1980s, which would be continued by his successors in the 1990s. China's economy, tiny in 1976, would see tremendous growth, and eventually take the spot as second largest economy from Japan in 2010. Among Western economies, the collapse of the Bretton Woods system was replaced by a more flexible era of floating exchange rates. The Group of Seven
The Group of Seven (G7) is an Intergovernmentalism, intergovernmental political and economic forum consisting of Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom and the United States; additionally, the European Union (EU) is a "non- ...
(G7) first met in 1975 and become one of the main international forums that regulated international trade among developed country
A developed country, or advanced country, is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy, and advanced technological infrastructure relative to other less industrialized nations. Most commonly, the criteria for eval ...
. The Soviet Union implemented a policy of ''perestroika
''Perestroika'' ( ; rus, перестройка, r=perestrojka, p=pʲɪrʲɪˈstrojkə, a=ru-perestroika.ogg, links=no) was a political reform movement within the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU) during the late 1980s, widely associ ...
'' in the 1980s which allowed tentative market reforms. The fall of the USSR saw differing approaches in the 1990s in the East: some newly independent states went in a capitalist direction such as Estonia
Estonia, officially the Republic of Estonia, is a country in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and to the east by Ru ...
, some maintained a strong governmental presence in their economy, and some opted for a mix. The privatization of government firms and resources drew accusations of crony capitalism
Crony capitalism, sometimes also called simply cronyism, is a pejorative term used in political discourse to describe a situation in which businesses profit from a close relationship with state power, either through an anti-competitive regul ...
in many states, however, including the Russian Federation, the largest and most important state of the USSR; the beneficiaries of the turbulent period were often called the "Russian oligarchs
Russian oligarchs () are business oligarchs of the former Soviet republics who rapidly accumulated wealth in the 1990s via the Russian privatisation that followed the dissolution of the Soviet Union. The failing Soviet state left the ownershi ...
".
In the beginning of the 2000s, there was a global rise in prices in commodities
In economics, a commodity is an economic good, usually a resource, that specifically has full or substantial fungibility: that is, the market treats instances of the good as equivalent or nearly so with no regard to who produced them.
Th ...
and housing, marking an end to the 2000s commodities boom
The 2000s commodities boom, commodities super cycle or China boom was the rise of many physical commodity prices (such as those of food, oil, metals, chemicals and fuels) during the early 21st century (2000–2014), following the Great Commoditie ...
. The US mortgage-backed securities, which had risks that were hard to assess, were marketed around the world and a broad based credit boom fed a global speculative bubble in real estate and equities. The financial situation was also affected by a sharp increase in oil and food prices
Food prices refer to the average price level for food across countries, regions and on a global scale. Food prices affect producers and consumers of food. Price levels depend on the food production process, including food marketing and food di ...
. The collapse of the American housing bubble
A housing bubble (or housing price bubble) is one of several types of asset price bubbles which periodically occur in the market. The basic concept of a housing bubble is the same as for other asset bubbles, consisting of two main phases. First t ...
caused the values of securities
A security is a tradable financial asset. The term commonly refers to any form of financial instrument, but its legal definition varies by jurisdiction. In some countries and languages people commonly use the term "security" to refer to any for ...
tied to real estate pricing
Real estate appraisal, home appraisal, property valuation or land valuation is the process of assessing the value of real property (usually market value). The appraisal is conducted by a licensed appraiser. Real estate transactions often require ...
to plummet thereafter, damaging financial institutions. The Great Recession
The Great Recession was a period of market decline in economies around the world that occurred from late 2007 to mid-2009.
, a severe economic recession
In economics, a recession is a business cycle contraction that occurs when there is a period of broad decline in economic activity. Recessions generally occur when there is a widespread drop in spending (an adverse demand shock). This may be tr ...
which began in the United States in 2007, was sparked by the outbreak of the 2008 financial crisis
The 2008 financial crisis, also known as the global financial crisis (GFC), was a major worldwide financial crisis centered in the United States. The causes of the 2008 crisis included excessive speculation on housing values by both homeowners ...
. The 2008 financial crisis
The 2008 financial crisis, also known as the global financial crisis (GFC), was a major worldwide financial crisis centered in the United States. The causes of the 2008 crisis included excessive speculation on housing values by both homeowners ...
was linked to earlier lending practices by financial institutions and the trend of securitization
Securitization is the financial practice of pooling various types of contractual debt such as residential mortgages, commercial mortgages, auto loans, or credit card debt obligations (or other non-debt assets which generate receivables) and sellin ...
of American real estate mortgages.
The Great Recession
The Great Recession was a period of market decline in economies around the world that occurred from late 2007 to mid-2009.
spread to much of the developed country
A developed country, or advanced country, is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy, and advanced technological infrastructure relative to other less industrialized nations. Most commonly, the criteria for eval ...
, and has caused a pronounced deceleration of economic activity. The global recession
A global recession is a recession that affects many countries around the world—that is, a period of global economic slowdown or declining economic output.
Definitions
The International Monetary Fund defines a global recession as "a decline ...
occurred in an economic environment characterized by various imbalances. This global recession has resulted in a sharp drop in international trade
International trade is the exchange of capital, goods, and services across international borders or territories because there is a need or want of goods or services. (See: World economy.)
In most countries, such trade represents a significan ...
, rising unemployment and slumping commodity prices. The recession renewed interest in Keynesian economic ideas on how to combat recessionary conditions. However, various industrial countries continued to undertake austerity
In economic policy, austerity is a set of Political economy, political-economic policies that aim to reduce government budget deficits through Government spending, spending cuts, tax increases, or a combination of both. There are three prim ...
policies to cut deficits
The government budget balance, also referred to as the general government balance, public budget balance, or public fiscal balance, is the difference between government revenues and spending. For a government that uses accrual accounting (ra ...
, reduced spending, as opposed to following Keynesian theories.
From late 2009 European debt crisis
The euro area crisis, often also referred to as the eurozone crisis, European debt crisis, or European sovereign debt crisis, was a multi-year debt crisis and financial crisis in the European Union (EU) from 2009 until, in Greece, 2018. The e ...
, fears of a sovereign debt crisis developed among investors concerning rising government debt levels across the globe together with a wave of downgrading of government debt of certain European states. Concerns intensified early 2010 and thereafter making it difficult or impossible for sovereigns to re-finance their debts. On 9 May 2010, Europe's Finance Ministers approved a rescue package worth €750 billion aimed at ensuring financial stability across Europe. The European Financial Stability Facility (EFSF) was a special purpose vehicle financed by members of the eurozone
The euro area, commonly called the eurozone (EZ), is a Monetary union, currency union of 20 Member state of the European Union, member states of the European Union (EU) that have adopted the euro (Euro sign, €) as their primary currency ...
to combat the European sovereign debt crisis. In October 2011 eurozone leaders agreed on another package of measures designed to prevent the collapse of member economies. The three most affected countries, Greece, Ireland and Portugal, collectively account for six percent of eurozone's gross domestic product (GDP). In 2012, eurozone finance ministers reached an agreement on a second €130-billion Greek bailout. In 2013, the European Union agreed to a €10 billion economic bailout for Cyprus due to the 2012–2013 Cypriot financial crisis
The 2012–2013 Cypriot financial crisis was an economic crisis in the Republic of Cyprus that involved the exposure of Cypriot banks to overleveraged local property companies, the Greek government-debt crisis, the downgrading of the Government ...
. The 2020 coronavirus pandemic caused economic disruption, with wide-ranging economic impacts of COVID-19 such as supply chain changes and an increase in working-from-home, along with the COVID-19 recession
The COVID-19 recession was a global economic recession caused by COVID-19 lockdowns. The recession began in most countries in February 2020. After a year of global economic slowdown that saw stagnation of economic growth and consumer activit ...
.
Social history
Social changes since 1945 have been vast and disparate, affecting countries and subgroups within those countries in ways specific to each population, meaning there is not one single global story of social change. Despite this, one of the major trends has been an increasing interchange between cultures and a wider spread of the most successful works, enabled by new technology andglobalization
Globalization is the process of increasing interdependence and integration among the economies, markets, societies, and cultures of different countries worldwide. This is made possible by the reduction of barriers to international trade, th ...
. In earlier periods, a successful musician or theater troupe might be confined to playing in a single city at a time, limiting their reach. The spread of better recording technology, such as the magnetophon
Magnetophon was the brand or model name of the pioneering reel-to-reel tape recorder developed by engineers of the German electronics company AEG in the 1930s, based on the magnetic tape invention by Fritz Pfleumer. AEG created the world's firs ...
, meant that a musical act could have their song be played over the radio everywhere without loss of sound quality, creating international superstars such as Elvis Presley
Elvis Aaron Presley (January 8, 1935 – August 16, 1977) was an American singer and actor. Referred to as the "King of Rock and Roll", he is regarded as Cultural impact of Elvis Presley, one of the most significant cultural figures of the ...
and The Beatles
The Beatles were an English Rock music, rock band formed in Liverpool in 1960. The core lineup of the band comprised John Lennon, Paul McCartney, George Harrison and Ringo Starr. They are widely regarded as the Cultural impact of the Beatle ...
. The spread of home television set
A television set or television receiver (more commonly called TV, TV set, television, telly, or tele) is an electronic device for viewing and hearing television broadcasts, or as a computer monitor. It combines a tuner, display, and loudspeake ...
s allowed people across the globe to easily watch the same show, rather than requiring viewers to attend a local theater. Hollywood
Hollywood usually refers to:
* Hollywood, Los Angeles, a neighborhood in California
* Hollywood, a metonym for the cinema of the United States
Hollywood may also refer to:
Places United States
* Hollywood District (disambiguation)
* Hollywood ...
in California produced films that dominated cinema; while intended for the lucrative American market, these films spread across the globe, backed by their large budgets and the cinematic expertise gathered there. The rise of the Internet in the 1990s allowed both for an ever further spread of the most popular and dominant works, but the comparatively cheap cost of publishing there, whether as a personal website, blog, or YouTube video, also allowed specific niche subcultures to connect and thrive in a way that was less true in the 20th century. For example, diaspora groups of immigrants can more easily stay in contact with their family and friends in their origin region, compared to earlier eras where travel and communication was far more expensive, making a narrative of strictly increasing global homogenization incomplete. International telephone networks, and later Internet telephony, allowed cheaper and easier long-distance communication than previous eras.
Language usage in the contemporary era has seen a rise in English as a lingua franca
English as a lingua franca (ELF) is the use of the English language "as a global means of inter-community communication" and can be understood as "any use of English among speakers of different first languages for whom English is the communicativ ...
, where people across the world learn the English language as a second language
A second language (L2) is a language spoken in addition to one's first language (L1). A second language may be a neighbouring language, another language of the speaker's home country, or a foreign language.
A speaker's dominant language, which ...
. This has been both to facilitate international communication, especially in places tied to international trade or tourism, as well as to better consume widespread English-language media. This is tied to increased Americanization
Americanization or Americanisation (see spelling differences) is the influence of the American culture and economy on other countries outside the United States, including their media, cuisine, business practices, popular culture, technology ...
, as American culture has grown increasingly influential and widespread. To a lesser extent, during the Cold War, something similar happened with the Russian language in the Eastern Bloc and among communist-aligned factions; however, this status was mostly reversed after the collapse of the Soviet Union. The French and German languages saw their prestige as global language
A world language (sometimes called a global language or, rarely, an international language) is a language that is geographically widespread and makes it possible for members of different language communities to communicate. The term may also be use ...
s decline after World War II.
Religious trends have been disparate and not consistent across countries, often with sharply varying results even between similar and nearby groups. In industrialized and economically prosperous regions, there has been a loose trend toward secularization
In sociology, secularization () is a multilayered concept that generally denotes "a transition from a religious to a more worldly level." There are many types of secularization and most do not lead to atheism or irreligion, nor are they automatica ...
that deprioritized the role of religion, even among people who still identified as adherents. The decline of Christianity in the Western world
Decline may refer to:
*Decadence, involves a perceived decay in standards, morals, dignity, religious faith, or skill over time
*in marketing, the stage in the product life cycle when demand for a product begins to taper off
* "Decline" (song), 20 ...
has been perhaps the most notable of these trends, although many non-Western cultures have been affected as well, such as the rise of irreligion in China (buttressed by antireligious campaigns). As an example of how localized this process can be, during the Cold War both the Polish People's Republic
The Polish People's Republic (1952–1989), formerly the Republic of Poland (1947–1952), and also often simply known as Poland, was a country in Central Europe that existed as the predecessor of the modern-day democratic Republic of Poland. ...
and the Czechoslovak Socialist Republic
The Czechoslovak Socialist Republic, (Czech language, Czech and Slovak language, Slovak: ''Československá socialistická republika'', ČSSR) known from 1948 to 1960 as the Czechoslovak Republic (''Československá republika)'', Fourth Czecho ...
endorsed state atheism
State atheism or atheist state is the incorporation of hard atheism or non-theism into Forms of government, political regimes. It is considered the opposite of theocracy and may also refer to large-scale secularization attempts by governments ...
. However, after the fall of the Iron Curtain in 1989–1990, the people of these bordering states had radically different cultural attitudes toward religion; Poland was one of the more religious states in Europe, with 96% of its population espousing a belief in Catholic Christianity in 2011, while the Czech Republic was one of the most stridently irreligious, with only 15% of its population espousing any religious beliefs at all by 2011. In the Islamic world
The terms Islamic world and Muslim world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs, politics, and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is ...
, a notable trend has been the spread of international schools of thought into regions where belief was previously localized, such as the International propagation of Salafism and Wahhabism
Starting in the mid-1970s and 1980s (and appearing to diminish after 2017), the international propagation of Salafism and Wahhabism within Sunni Islam and throughout the Muslim world, favored by the conservative oil-exporting Saudi Arabia, Kin ...
funded by the government of Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in West Asia. Located in the centre of the Middle East, it covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula and has a land area of about , making it the List of Asian countries ...
. While regional Islamic groups remain strong, they are more contested than in the past.
Another social trend has been the rise of urbanization as a larger proportion of the world's population has moved to live in cities and urban areas, and fewer people live in rural areas. In the United States, as the overall population more than doubled from 1930 to 1990, around a third of its counties saw their population decline by around 27%, suggesting that as rural counties empty, the urban counties are where the vast majority of inhabitants are moving to. In Eastern Africa, the urban population soared from 11 million in 1920 to 77 million in 2010. Many rural Chinese people moved to large coastal cities such as Shenzhen to work in the 1990s and 2000s, leading to a sharp increase of Urbanization in China. Rural parts of Japan have seen stark population declines, especially among the young, with only the Greater Tokyo area
The Greater Tokyo Area is the most populous metropolitan area in the world, consisting of the Kantō region of Japan (including Tokyo, Tokyo Metropolis and the prefectures of Chiba Prefecture, Chiba, Gunma Prefecture, Gunma, Ibaraki Prefecture, ...
continuing to grow. How to deal with this change is a major issue, as many cities and their transportation networks were not designed to serve the larger populations that now occupy them.
A major trend in many industrialized nations was the sexual revolution
The sexual revolution, also known as the sexual liberation, was a social movement that challenged traditional codes of behavior related to sexuality and interpersonal relationships throughout the Western world from the late 1950s to the early 1 ...
, an adoption of publicly more tolerant attitudes toward sex and pre-marital sex. " The pill" was first approved for use in 1960 in the United States, and spread rapidly around the world. The pill made birth control
Birth control, also known as contraception, anticonception, and fertility control, is the use of methods or devices to prevent pregnancy. Birth control has been used since ancient times, but effective and safe methods of birth control only be ...
easier and more reliable than earlier methods. This made sex for pleasure less likely to result in unintended children. It also allowed for easier family planning
Family planning is the consideration of the number of children a person wishes to have, including the choice to have no children, and the age at which they wish to have them. Things that may play a role on family planning decisions include marit ...
, where couples could choose more specifically when to have kids compared to earlier eras. Some analysts credit this as one reason behind a decline in birth rates in the industrialized world, which had multiple second-order effects. Many regions have also made divorce much easier to officially procure. However, the decline in birth rate is not a universal trend; many nations continue to have high birth rates, and the world's overall population is still growing as of 2022.
One of the yet evolving and unknown impacts in the contemporary era has been the social effects of cheap and common Internet access. As users gradually switched from personal web page
Personal web pages are World Wide Web pages created by an individual to contain content of a personal nature rather than content pertaining to a company, organization or institution. Personal web pages are primarily used for informative or ente ...
s to blogs to social media, many surprising effects have resulted with both positive and negative assessments. Optimistic assessments often praise the decentralized nature that allows anyone to theoretically gain a platform without the need to convince a publisher or media company to back them, as well as the ease in enabling like-minded people to collaborate at long-distance, even if the digital utopianism
Cyber-utopianism, web-utopianism, digital utopianism, or utopian internet is a subcategory of technological utopianism and the belief that online communication helps bring about a more decentralized, Democracy, democratic, and libertarian society. ...
of the 1990s is less common. Pessimistic assessments worry about the effects on children such as enabling cyberbullying
Cyberbullying (cyberharassment or online bullying) is a form of bullying or harassment using electronic means. Since the 2000s, it has become increasingly common, especially among teenagers and adolescents, due to young people's increased u ...
; filter bubble
A filter bubble or ideological frame is a state of intellectual isolationTechnopediaDefinition – What does Filter Bubble mean?, Retrieved October 10, 2017, "....A filter bubble is the intellectual isolation, that can occur when websites make ...
s where Internet users are not challenged by outsider views; "cancel culture
Cancel culture is a cultural phenomenon in which an individual thought to have acted or spoken in an unacceptable manner is ostracized, boycotted, shunned or fired, often aided by social media. This shunning may extend to social or professio ...
" where people are pilloried online but sometimes disproportionately; and slacktivism
Slacktivism (a blend word, blend of ''slacker'' and ''activism'') is the practice of supporting a political or social cause by means such as social media or Online petition, online petitions, characterized as involving very little effort or comm ...
as an appealing but ineffective replacement for older forms of community work.
Contemporary science and technology
Energy
The growing world population and rising standards of living has caused a vast increase in demand forenergy development
Energy development is the field of activities focused on obtaining sources of energy from natural resources. These activities include the production of renewable, nuclear, and fossil fuel derived sources of energy, and for the recovery and re ...
, both to power vehicles such as personal cars as well as on public electrical grid
An electrical grid (or electricity network) is an interconnected network for electricity delivery from producers to consumers. Electrical grids consist of power stations, electrical substations to step voltage up or down, electric power tran ...
s. In particular, petroleum oil has been in ravenous demand across the world. Many of the cheapest and easiest sources of oil to access were largely drained in the 19th and early 20th centuries, leading to a hunt for new sources of oil. The value of oil has spilled over into politics as well, as " petrostates" with access to oil found a source of vast revenue that did not require traditional government revenue-raising measures, such as tariffs or income taxation. The rising cost of oil led to the 1970s energy crisis
The 1970s energy crisis occurred when the Western world, particularly the United States, Canada, Western Europe, Australia, and New Zealand, faced substantial petroleum shortages as well as elevated prices. The two worst crises of this period wer ...
and various adaptations in energy conservation
Energy conservation is the effort to reduce wasteful energy consumption by using fewer energy services. This can be done by using energy more effectively (using less and better sources of energy for continuous service) or changing one's behavi ...
to better conserve oil, such as more efficient engines and better insulation. It has also led to concerns of "peak oil
Peak oil is the point when global oil production reaches its maximum rate, after which it will begin to decline irreversibly. The main concern is that global transportation relies heavily on gasoline and diesel. Adoption of electric vehicles ...
," that the rising extraction costs of oil will eventually lead to massive shortages and a large disincentive to burn oil except when absolutely necessary (such as in the case of aviation fuel
Aviation fuels are either petroleum-based or blends of petroleum and synthetic fuels, used to power aircraft. They have more stringent requirements than fuels used for ground applications, such as heating and road transport, and they contain add ...
), although oil continues to be one of the most popular sources of energy.
Other fossil fuel
A fossil fuel is a flammable carbon compound- or hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the buried remains of prehistoric organisms (animals, plants or microplanktons), a process that occurs within geolog ...
s have continued a prominent role in the world's energy production. Coal energy, usually credited as helping kickstart the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succee ...
, has declined somewhat in prominence, but it started from a commanding large slice of the sources of energy. Even if diminished, coal is still a popular and common style of power plant; it made up a huge proportion of South Africa and India's power grid from 1945 to the present, for example. That said, increasing price, as well as concerns both over the air pollution generated when it is burnt and the landscape destruction when it is mined (such as mountaintop removal mining), have caused setbacks for the coal industry. Natural gas has grown in its proportion of the market, especially as Liquefied natural gas
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is natural gas (predominantly methane, CH4, with some mixture of ethane, C2H6) that has been cooled to liquid form for ease and safety of non-pressurized storage or transport. It takes up about 1/600th the volume o ...
(LNG) has enabled it to be transported over longer distances than was previously feasible.
An entirely new form of energy creation dawned in the 1950s and 1960s: nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced by ...
for peaceful purposes and the construction of nuclear power plant
A nuclear power plant (NPP), also known as a nuclear power station (NPS), nuclear generating station (NGS) or atomic power station (APS) is a thermal power station in which the heat source is a nuclear reactor. As is typical of thermal power st ...
s. Hopes that atomic energy would be " too cheap to meter" in the 1950s proved overly optimistic, however. Atomic energy grew to be a large part of several nations energy generation strategies, especially nuclear power in France
Since the mid-1980s, the largest source of Electricity sector in France, electricity in France has been nuclear power, with a generation of 379.5 terawatt-hour, TWh in 2019 and a total electricity production of . In 2018, the nuclear share was ...
. Nuclear power continues to be controversial. Concerns include its association with nuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission or atomic bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions (thermonuclear weapon), producing a nuclear exp ...
s, financial cost, disposal of radioactive nuclear waste
Radioactive waste is a type of hazardous waste that contains radioactive material. It is a result of many activities, including nuclear medicine, nuclear research, nuclear power generation, nuclear decommissioning, rare-earth mining, and nuclear ...
, and fears of safety from reactor meltdowns, especially after the 1986 Chernobyl disaster
On 26 April 1986, the no. 4 reactor of the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, located near Pripyat, Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, Ukrainian SSR, Soviet Union (now Ukraine), exploded. With dozens of direct casualties, it is one of only ...
. An anti-nuclear movement
The Anti-nuclear war movement is a new social movements, social movement that opposes various nuclear technology, nuclear technologies. Some direct action groups, environmental movements, and professional organisations have identified them ...
arose that was skeptical of atomic energy and has discouraged many projects. Nuclear proponents counter that nuclear energy produces no air pollution compared to traditional fossil fuel plants, and can provide a steady supply of energy regardless of external conditions unlike solar and wind energy. With the supply of Russian natural gas disrupted in 2022, France is looking to reactivate some of its older decommissioned nuclear plants, for example.
Various forms of renewable energy
Renewable energy (also called green energy) is energy made from renewable resource, renewable natural resources that are replenished on a human lifetime, human timescale. The most widely used renewable energy types are solar energy, wind pow ...
have grown in prominence in the contemporary era. Wind energy
Wind power is the use of wind energy to generate useful work. Historically, wind power was used by sails, windmills and windpumps, but today it is mostly used to generate electricity. This article deals only with wind power for electricity ...
, while used on a small scale for centuries, has seen growth with large distributed groups of windmill
A windmill is a machine operated by the force of wind acting on vanes or sails to mill grain (gristmills), pump water, generate electricity, or drive other machinery.
Windmills were used throughout the high medieval and early modern period ...
s used to produce energy for the grid. Solar power
Solar power, also known as solar electricity, is the conversion of energy from sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV) or indirectly using concentrated solar power. Solar panels use the photovoltaic effect to c ...
has also grown in prominence, with around 4% of the world's overall energy production in 2021 (compared to a much smaller slice before). While these energy sources are considered to be much less environmentally impactful than fossil fuels
A fossil fuel is a flammable carbon compound- or hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the buried remains of prehistoric organisms (animals, plants or microplanktons), a process that occurs within geologica ...
, concerns have been raised over the various rare earth metal
The rare-earth elements (REE), also called the rare-earth metals or rare earths, and sometimes the lanthanides or lanthanoids (although scandium and yttrium, which do not belong to this series, are usually included as rare earths), are a set o ...
s used in the production of batteries and solar, which can require destructive mining techniques to gather.
Computing and the Internet
 The
The Information Age
The Information Age is a historical period that began in the mid-20th century. It is characterized by a rapid shift from traditional industries, as established during the Industrial Revolution, to an economy centered on information technology ...
or Information Era, also commonly known as the Age of the Computer, is an idea that the current age will be characterized by the ability of individuals to transfer information freely, and to have instant access to knowledge that would have been difficult or impossible to find previously. The idea is heavily linked to the concept of a Digital Age
The Information Age is a History by period, historical period that began in the mid-20th century. It is characterized by a rapid shift from traditional industries, as established during the Industrial Revolution, to an economy centered on info ...
or Digital Revolution
The Information Age is a History by period, historical period that began in the mid-20th century. It is characterized by a rapid shift from traditional industries, as established during the Industrial Revolution, to an economy centered on info ...
, and carries the ramifications of a shift from traditional industry that the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succee ...
brought through industrialization, to an economy based around the manipulation of information. The period is generally said to have begun in the latter half of the 20th century, though the particular date varies. The term began its use around the late 1980s and early 1990s, and has been used up to the present with the availability of the Internet.
During the late 1990s, both Internet directories and search engine
A search engine is a software system that provides hyperlinks to web pages, and other relevant information on World Wide Web, the Web in response to a user's web query, query. The user enters a query in a web browser or a mobile app, and the sea ...
s were popular—Yahoo!
Yahoo (, styled yahoo''!'' in its logo) is an American web portal that provides the search engine Yahoo Search and related services including My Yahoo, Yahoo Mail, Yahoo News, Yahoo Finance, Yahoo Sports, y!entertainment, yahoo!life, and its a ...
and Altavista
AltaVista was a web search engine established in 1995. It became one of the most-used early search engines, but lost ground to Google and was purchased by Yahoo! in 2003, which retained the brand, but based all AltaVista searches on its own sear ...
(both founded 1995) were the respective industry leaders. By late 2001, the directory model had begun to give way to search engines, tracking the rise of Google (founded 1998), which had developed new approaches to relevancy ranking. Directory features, while still commonly available, became after-thoughts to search engines. Database size, which had been a significant marketing feature through the early 2000s (decade), was similarly displaced by emphasis on relevancy ranking, the methods by which search engines attempt to sort the best results first.
"Web 2.0
Web 2.0 (also known as participative (or participatory) web and social web) refers to websites that emphasize user-generated content, ease of use, participatory culture, and interoperability (i.e., compatibility with other products, systems, a ...
" is characterized as facilitating communication, information sharing
Information exchange or information sharing means that people or other entities pass information from one to another. This could be done electronically or through certain systems. These are terms that can either refer to bidirectional '' inform ...
, interoperability
Interoperability is a characteristic of a product or system to work with other products or systems. While the term was initially defined for information technology or systems engineering services to allow for information exchange, a broader de ...
, User-centered design
User-centered design (UCD) or user-driven development (UDD) is a framework of processes in which usability goals, user characteristics, environment, tasks and workflow of a product, service or brand are given extensive attention at each stag ...
and collaboration
Collaboration (from Latin ''com-'' "with" + ''laborare'' "to labor", "to work") is the process of two or more people, entities or organizations working together to complete a task or achieve a goal. Collaboration is similar to cooperation. The ...
on the World Wide Web
The World Wide Web (WWW or simply the Web) is an information system that enables Content (media), content sharing over the Internet through user-friendly ways meant to appeal to users beyond Information technology, IT specialists and hobbyis ...
. It has led to the development and evolution of web-based communities, hosted services, and web application
A web application (or web app) is application software that is created with web technologies and runs via a web browser. Web applications emerged during the late 1990s and allowed for the server to dynamically build a response to the request, ...
s. Examples include social-networking sites, video-sharing sites, wiki
A wiki ( ) is a form of hypertext publication on the internet which is collaboratively edited and managed by its audience directly through a web browser. A typical wiki contains multiple pages that can either be edited by the public or l ...
s, blogs, mashups and folksonomies. Social networking
A social network is a social structure consisting of a set of social actors (such as individuals or organizations), networks of Dyad (sociology), dyadic ties, and other Social relation, social interactions between actors. The social network per ...
emerged in the early 21st century as a popular social communication, largely replacing much of the function of email, message boards and instant messaging
Instant messaging (IM) technology is a type of synchronous computer-mediated communication involving the immediate ( real-time) transmission of messages between two or more parties over the Internet or another computer network. Originally involv ...
services. Twitter, Facebook, and YouTube are all major examples of social websites that gained widespread popularity. The information distribution continued into the early 21st century with mobile interaction and Internet access
Internet access is a facility or service that provides connectivity for a computer, a computer network, or other network device to the Internet, and for individuals or organizations to access or use applications such as email and the World Wide ...
growing massively in the early 21st century. By the 2010s, a majority of people in the developed world had Internet access and a majority of people worldwide had a mobile phone. Marking the rise of mobile computing
Mobile computing is human–computer interaction in which a computer is expected to be transported during normal usage and allow for transmission of data, which can include voice and video transmissions. Mobile computing involves mobile commun ...
, worldwide sales of personal computers fall 14% during the first quarter of 2013. The Semantic Web
The Semantic Web, sometimes known as Web 3.0, is an extension of the World Wide Web through standards set by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). The goal of the Semantic Web is to make Internet data machine-readable.
To enable the encoding o ...
(dubbed, "Web 3.0") begins the inclusion of semantic
Semantics is the study of linguistic Meaning (philosophy), meaning. It examines what meaning is, how words get their meaning, and how the meaning of a complex expression depends on its parts. Part of this process involves the distinction betwee ...
content in web pages, converting the current web dominated by unstructured and semi-structured documents into a "web of data".
With the rise of information technology, computer security
Computer security (also cybersecurity, digital security, or information technology (IT) security) is a subdiscipline within the field of information security. It consists of the protection of computer software, systems and computer network, n ...
, and information security
Information security is the practice of protecting information by mitigating information risks. It is part of information risk management. It typically involves preventing or reducing the probability of unauthorized or inappropriate access to data ...
in general, is a concern for computers and networks. Concerns include information and services which are protected from unintended or unauthorized access, change or destruction. This has also raised questions of Internet privacy
Internet privacy involves the right or mandate of personal privacy concerning the storage, re-purposing, provision to third parties, and display of information pertaining to oneself via the Internet. Internet privacy is a subset of data privacy. P ...
and personal privacy
Privacy (, ) is the ability of an individual or group to seclude themselves or information about themselves, and thereby express themselves selectively.
The domain of privacy partially overlaps with security, which can include the concepts of ...
globally.
Space exploration
TheSpace Race
The Space Race (, ) was a 20th-century competition between the Cold War rivals, the United States and the Soviet Union, to achieve superior spaceflight capability. It had its origins in the ballistic missile-based nuclear arms race between t ...
was one of the rivalries of the Cold War, with both the United States space program (NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
) and the Soviet space program
The Soviet space program () was the state space program of the Soviet Union, active from 1951 until the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. Contrary to its competitors (NASA in the United States, the European Space Agency in Western Euro ...
launching satellite
A satellite or an artificial satellite is an object, typically a spacecraft, placed into orbit around a celestial body. They have a variety of uses, including communication relay, weather forecasting, navigation ( GPS), broadcasting, scient ...
s, probes, and planning missions. While the Soviets put the first human into space with Yuri Gagarin
Yuri Alekseyevich Gagarin; Gagarin's first name is sometimes transliterated as ''Yuriy'', ''Youri'', or ''Yury''. (9 March 1934 – 27 March 1968) was a Soviet pilot and cosmonaut who, aboard the first successful Human spaceflight, crewed sp ...
, the Americans soon caught up, and the US was the first to launch a successful Moon landing mission with Apollo 11
Apollo 11 was a spaceflight conducted from July 16 to 24, 1969, by the United States and launched by NASA. It marked the first time that humans Moon landing, landed on the Moon. Commander Neil Armstrong and Lunar Module pilot Buzz Aldrin l ...
in 1969, followed by five more landings in the next few years.
In the 1970s and 80s, the US took a new approach with the Space Shuttle program
The Space Shuttle program was the fourth human spaceflight program carried out by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), which accomplished routine transportation for Earth-to-orbit crew and cargo from 1981 to 2011. Its ...
, hoping to reduce the cost of launches by creating a re-usable Space Shuttle. The first fully functional Space Shuttle orbiter
The Space Shuttle orbiter is the spaceplane component of the Space Shuttle, a partially reusable launch system, reusable orbital spaceflight, orbital spacecraft system that was part of the discontinued Space Shuttle program. Operated from 1981 ...
was Columbia (designated OV-102), launched into low Earth orbit
A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an geocentric orbit, orbit around Earth with a orbital period, period of 128 minutes or less (making at least 11.25 orbits per day) and an orbital eccentricity, eccentricity less than 0.25. Most of the artificial object ...
in April 1981. In 1996, Shuttle mission STS-75 conducted research in space with the electrodynamic tether
Electrodynamic tethers (EDTs) are long conducting wires, such as one deployed from a tether satellite, which can operate on electromagnetism, electromagnetic principles as electrical generator, generators, by converting their kinetic energy to ele ...
generator and other tether configurations. The program suffered from two incidents that destroyed a shuttle: the ''Challenger'' disaster and the ''Columbia'' disaster). The program ultimately had 135 missions. The retirement of NASA's Space Shuttle fleet took place from March to July 2011.
The end of the Cold War saw a new era of international cooperation with the International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is a large space station that was Assembly of the International Space Station, assembled and is maintained in low Earth orbit by a collaboration of five space agencies and their contractors: NASA (United ...
(ISS). Commercial spaceflight also became possible as governments loosened what had previously been their firm control over satellites, opening new possibilities, but also new risks such as light pollution from satellites. The Commercial Orbital Transportation Services
Commercial Orbital Transportation Services (COTS) was a NASA program to spur the development of Private spaceflight, private spacecraft and launch vehicles for deliveries to the International Space Station (ISS). Launched in 2006, COTS successful ...
(COTS) program began in 2006.
There are various spaceports, including spaceport
A spaceport or cosmodrome is a site for launching or receiving spacecraft, by analogy to a seaport for ships or an airport for aircraft. The word ''spaceport''—and even more so ''cosmodrome''—has traditionally referred to sites capable of ...
s of human spaceflight
Human spaceflight (also referred to as manned spaceflight or crewed spaceflight) is spaceflight with a crew or passengers aboard a spacecraft, often with the spacecraft being operated directly by the onboard human crew. Spacecraft can also be ...
and other launch system
A launch vehicle is typically a rocket-powered vehicle designed to carry a payload (a crewed spacecraft or satellites) from Earth's surface or lower atmosphere to outer space. The most common form is the ballistic missile-shaped multist ...
s (space logistics
Space logistics is "the theory and practice of driving space system design for operability and supportability, and of managing the flow of materiel, services, and information needed throughout a space system lifecycle." It includes terrestrial lo ...
). Private spaceflight
Private spaceflight is any spaceflight development that is not conducted by a government agency, such as NASA or ESA.
During the early decades of the Space Age, the government space agencies of the Soviet Union and United States pionee ...
is flight beyond the Kármán line
The Kármán line (or von Kármán line ) is a conventional definition of the Outer space#Boundary, edge of space; it is widely but not universally accepted. The international record-keeping body Fédération Aéronautique Internationale, FAI ( ...
that is conducted and paid for by an entity other than a government agency. Commercialization of space is the use of equipment sent into or through outer space to provide goods or services of commercial value, either by a corporation or state. Space trade plans and predictions began in the 1960s. Spacecraft propulsion
Spacecraft propulsion is any method used to accelerate spacecraft and artificial satellites. In-space propulsion exclusively deals with propulsion systems used in the vacuum of space and should not be confused with space launch or atmospheric e ...
is any method used to accelerate spacecraft
A spacecraft is a vehicle that is designed spaceflight, to fly and operate in outer space. Spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including Telecommunications, communications, Earth observation satellite, Earth observation, Weather s ...
and artificial satellite
A satellite or an artificial satellite is an object, typically a spacecraft, placed into orbit around a celestial body. They have a variety of uses, including communication relay, weather forecasting, navigation ( GPS), broadcasting, scient ...
s.
NASA announced in 2011 that its Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter
The ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' (''MRO'') is a spacecraft designed to search for the existence of water on Mars and provide support for missions to Mars, as part of NASA's Mars Exploration Program. It was launched from Cape Canaveral on Au ...
captured photographic evidence of possible liquid water on Mars
Although very small amounts of liquid water may occur transiently on the surface of Mars, limited to traces of dissolved moisture from the atmosphere and thin films, large quantities of ice are present on and under the surface. Small amounts of ...
during warm seasons. On 6 August 2012, the Mars Science Laboratory Curiosity
Curiosity (from Latin , from "careful, diligent, curious", akin to "care") is a quality related to inquisitive thinking, such as exploration, investigation, and learning, evident in humans and other animals. Curiosity helps Developmental psyc ...
, the most elaborate Martian exploration vehicle to date, landed on Mars. After the WMAP
The Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP), originally known as the Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP and Explorer 80), was a NASA spacecraft operating from 2001 to 2010 which measured temperature differences across the sky in the cosmic mic ...
observations of the cosmic microwave background
The cosmic microwave background (CMB, CMBR), or relic radiation, is microwave radiation that fills all space in the observable universe. With a standard optical telescope, the background space between stars and galaxies is almost completely dar ...
, information was released in 2011 of the work done by the Planck Surveyor, estimating the Age of the universe
In physical cosmology, the age of the universe is the cosmological time, time elapsed since the Big Bang: 13.79 billion years.
Astronomers have two different approaches to determine the age of the universe. One is based on a particle physics ...
to 13.8 billion years old (a 100 million years older than previously thought). Another technological advancement came in 2012 with European physicists statistically demonstrating the existence of the Higgs boson
The Higgs boson, sometimes called the Higgs particle, is an elementary particle in the Standard Model of particle physics produced by the excited state, quantum excitation of the Higgs field,
one of the field (physics), fields in particl ...
.
Challenges and problems
Climate change
Climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
and global warming
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes ...
reflects the notion of the modern climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in a region, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteoro ...
. The changes of climate over the past century, have been attributed to various factors which have resulted in a global warming. This warming is the increase in the average temperature of the Earth's near-surface air and oceans since the mid-20th century and its projected continuation. Some effects on both the natural environment
The natural environment or natural world encompasses all life, biotic and abiotic component, abiotic things occurring nature, naturally, meaning in this case not artificiality, artificial. The term is most often applied to Earth or some parts ...
and human life are, at least in part, already being attributed to global warming. A 2001 report by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is an intergovernmental body of the United Nations. Its job is to "provide governments at all levels with scientific information that they can use to develop climate policies". The World Met ...
suggests that glacier retreat, ice shelf disruption such as that of the Larsen Ice Shelf
The Larsen Ice Shelf is a long ice shelf in the northwest part of the Weddell Sea, extending along the east coast of the Antarctic Peninsula from Cape Longing to Smith Peninsula. It is named after Captain Carl Anton Larsen, the master of the ...
, sea level rise
The sea level has been rising from the end of the last ice age, which was around 20,000 years ago. Between 1901 and 2018, the average sea level rose by , with an increase of per year since the 1970s. This was faster than the sea level had e ...
, changes in rainfall patterns, and increased intensity and frequency of extreme weather
Extreme weather includes unexpected, unusual, severe weather, severe, or unseasonal weather; weather at the extremes of the historical distribution—the range that has been seen in the past. Extreme events are based on a location's recorded weat ...
events are attributable in part to global warming. Other expected effects include water scarcity
Water scarcity (closely related to water stress or water crisis) is the lack of fresh water resources to meet the standard water demand. There are two types of water scarcity. One is ''physical.'' The other is ''economic water scarcity''. Physic ...
in some regions and increased precipitation in others, changes in mountain snowpack, and adverse health effects from warmer temperatures.
It is usually impossible to connect specific weather events to human impact on the world. Instead, such impact is expected to cause changes in the overall distribution and intensity of weather events, such as changes to the frequency and intensity of heavy precipitation. Broader effects are expected to include glacial retreat, Arctic shrinkage
Sea ice in the Arctic region has declined in recent decades in area and volume due to climate change. It has been melting more in summer than it refreezes in winter. Global warming, caused by greenhouse gas forcing is responsible for the decline ...
, and worldwide sea level rise
The sea level has been rising from the end of the last ice age, which was around 20,000 years ago. Between 1901 and 2018, the average sea level rose by , with an increase of per year since the 1970s. This was faster than the sea level had e ...
. Other effects may include changes in crop yields, addition of new trade routes, species extinctions, and changes in the range of disease vectors
In epidemiology, a disease vector is any living agent that carries and transmits an infectious pathogen such as a parasite or microbe, to another living organism. Agents regarded as vectors are mostly blood-sucking ( hematophagous) arthropods such ...
. Until 2009, the Arctic ''Northwest Passage
The Northwest Passage (NWP) is the sea lane between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans through the Arctic Ocean, near the northern coast of North America via waterways through the Arctic Archipelago of Canada. The eastern route along the Arctic ...
'' pack ice
Pack or packs may refer to:
Music
* Packs (band), a Canadian indie rock band
* ''Packs'' (album), by Your Old Droog
* ''Packs'', a Berner album
Places
* Pack, Styria, defunct Austrian municipality
* Pack, Missouri, United States (US)
* ...
prevented regular marine shipping throughout most of the year in this area, but climate change has reduced the pack ice, and this Arctic shrinkage
Sea ice in the Arctic region has declined in recent decades in area and volume due to climate change. It has been melting more in summer than it refreezes in winter. Global warming, caused by greenhouse gas forcing is responsible for the decline ...
made the waterways more navigable.
Health and pandemics
Severaldisease outbreak
In epidemiology, an outbreak is a sudden increase in occurrences of a disease when cases are in excess of normal expectancy for the location or season. It may affect a small and localized group or impact upon thousands of people across an entire ...
s, epidemics, and pandemic
A pandemic ( ) is an epidemic of an infectious disease that has a sudden increase in cases and spreads across a large region, for instance multiple continents or worldwide, affecting a substantial number of individuals. Widespread endemic (epi ...
s have occurred during contemporary history. Some of these include the 1957–1958 influenza pandemic
The 1957–1958 Asian flu pandemic was a global pandemic of influenza A virus subtype H2N2 that originated in Guizhou in Northern and southern China, Southern China. The number of Excess mortality, excess deaths caused by the pandemic is estima ...
, the Hong Kong flu
The Hong Kong flu, also known as the 1968 flu pandemic, was an influenza pandemic that occurred between 1968 and 1970 and which killed between one and four million people globally. It is among the deadliest pandemics in history, and was caus ...
of 1968–1969, the 1977–1979 Russian flu, the HIV/AIDS epidemic (1981–present), the SARS outbreak of 2002–2004, the swine flu pandemic of 2009–2010, and the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December ...
(2019–2022).
COVID-19 pandemic
In 2020, an outbreak of theCOVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. In January 2020, the disease spread worldwide, resulting in the COVID-19 pandemic.
The symptoms of COVID‑19 can vary but often include fever ...
disease, first documented in late 2019 in Wuhan
Wuhan; is the capital of Hubei, China. With a population of over eleven million, it is the most populous city in Hubei and the List of cities in China by population, eighth-most-populous city in China. It is also one of the nine National cent ...
, China, spread to other countries becoming a global pandemic, which caused a major socio-economic disruption all over the world. Many countries ordered mandatory lockdowns on movement and closures of non-essential businesses., ''Oxford Research Group'' The threat of the disease caused the
COVID-19 recession
The COVID-19 recession was a global economic recession caused by COVID-19 lockdowns. The recession began in most countries in February 2020. After a year of global economic slowdown that saw stagnation of economic growth and consumer activit ...
, although the distribution of vaccines has since eased the economic impact in many countries.
More generally, COVID-19 has been held up as an example of a global catastrophic risk
A global catastrophic risk or a doomsday scenario is a hypothetical event that could damage human well-being on a global scale, endangering or even destroying modern civilization. Existential risk is a related term limited to events that co ...
unique to the modern era's ease of travel. New diseases can spread far faster and further in the contemporary era than any previous era of human history; pandemic prevention
Pandemic prevention is the organization and management of preventive measures against pandemics. Those include measures to reduce causes of new infectious diseases and measures to prevent outbreaks and epidemics from becoming pandemics. It is not ...
is one resulting field to ensure that if this happens with a sufficiently deadly virus, humanity can take measures to stop its spread.
Charts
Timeline
Tube
Tube or tubes may refer to:
* ''Tube'' (2003 film), a 2003 Korean film
* "Tubes" (Peter Dale), performer on the Soccer AM television show
* Tube (band), a Japanese rock band
* Tube & Berger, the alias of dance/electronica producers Arndt Rör ...
from:1948.5 till:1958.7 text:Transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electric power, power. It is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semicondu ...
from:1958.7 till:1970 shift:(0,2) text: Integrated
from:1958.7 till:1970 shift:(0,-8) text: circuit
from:1970 till:end text:Information Age
The Information Age is a historical period that began in the mid-20th century. It is characterized by a rapid shift from traditional industries, as established during the Industrial Revolution, to an economy centered on information technology ...
from:2010 till:end text:Big Data
Big data primarily refers to data sets that are too large or complex to be dealt with by traditional data processing, data-processing application software, software. Data with many entries (rows) offer greater statistical power, while data with ...
bar:War color:era
from:1940 till:1945.667 text:WWII
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
from:1947 till:1991.98 text:Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
from:2001.69 till:2021.56 text: War on Terror
bar:Decade color:era
from:1940 till:1946 shift:(0,5) text:Late Modernity
Late modernity (or liquid modernity) is the characterization of today's highly developed global society, societies as the continuation (or social progress, development) of modernity rather than as an element of the succeeding era known as postmo ...
from:1946 till:end shift:(0,5) text:Postmodernity
Postmodernity (post-modernity or the postmodern condition) is the economic or cultural state or condition of society which is said to exist ''after'' modernity. Some schools of thought hold that modernity ended in the late 20th century – in th ...
from:1940 till:1950 text:1940s
from:1950 till:1960 text:1950s
from:1960 till:1970 text:1960s
from:1970 till:1980 text:1970s
from:1980 till:1990 text:1980s
from:1990 till:2000 text:1990s
from:2000 till:2010 text:2000s
from:2010 till:2020 text:2010s
from:2020 till:end text:2020s
Contemporary world map
See also
General: *Modern history
The modern era or the modern period is considered the current historical period of human history. It was originally applied to the history of Europe and Western history for events that came after the Middle Ages, often from around the year 1500, ...
, Timelines of modern history, Anthropocene
''Anthropocene'' is a term that has been used to refer to the period of time during which human impact on the environment, humanity has become a planetary force of change. It appears in scientific and social discourse, especially with respect to ...
Generations:
* Generation
A generation is all of the people born and living at about the same time, regarded collectively. It also is "the average period, generally considered to be about 20–30 years, during which children are born and grow up, become adults, and b ...
, List of generations, Baby Boom Generation
Baby boomers, often shortened to boomers, are the demographic cohort preceded by the Silent Generation and followed by Generation X. The generation is often defined as people born from 1946 to 1964 during the mid-20th century baby boom that ...
, Generation X
Generation X (often shortened to Gen X) is the Demography, demographic Cohort (statistics), cohort following the Baby Boomers and preceding Millennials. Researchers and popular media often use the mid-1960s as its starting birth years and the ...
, Xennials, Generation Y
Millennials, also known as Generation Y or Gen Y, are the demographic Cohort (statistics), cohort following Generation X and preceding Generation Z. Researchers and popular media use the early 1980s as starting birth years and the mid-1990 ...
, Generation Z
Generation Z (often shortened to Gen Z), also known as zoomers, is the demographic cohort succeeding Millennials and preceding Generation Alpha. Researchers and popular media use the mid-to-late 1990s as starting birth years and the early 2 ...
, Generation Alpha
Music and arts:
* Contemporary art
Contemporary art is a term used to describe the art of today, generally referring to art produced from the 1970s onwards. Contemporary artists work in a globally influenced, culturally diverse, and technologically advancing world. Their art is a ...
, Contemporary dance
Contemporary dance is a genre of Concert dance, dance performance that developed during the mid-twentieth century and has since grown to become one of the dominant genres for formally trained dancers throughout the world, with particularly stron ...
, Contemporary literature, Contemporary music Contemporary music is whatever music is produced at the current time. Specifically, it could refer to:
Genres or audiences
* Adult contemporary music
* British contemporary R&B
* Christian adult contemporary
* Christian contemporary hit radio
* Con ...
, Contemporary hit radio, Adult contemporary music, Contemporary Christian music, Contemporary R&B, Urban contemporary, History of video games, Video games
Future:
* Future history, Futurology, Timeline of the near future], Third millennium, 21st century
References
Further reading
* Bell, P. M. H. and Mark Gilbert. ''The World Since 1945: An International History'' (2nd ed. 2017), 584pexcerpt
* Boyd, Andrew, Joshua Comenetz. '' An atlas of world affairs'' (2007
excerpt
* Briggs, Asa, and Peter Burke. ''A Social History of the Media: From Gutenberg to the Internet'' (2002
excerpt
* * Hunt, Michael H. ''The World Transformed: 1945 to the Present'' (2nd ed. 2015) 624p
website
* Hunt, Michael H. ed., ''The World Transformed, 1945 to the Present: A Documentary Reader'' (2nd ed. 2001) primary source
excerpts
* McWilliams, Wayne C. and Harry Piotrowski. ''The World Since 1945: A History of International Relations'' (8th ed. 2014), 620pp
External links
Internet Modern History Sourcebook
at Fordham University
''Journal of Contemporary History''
SAGE Publications. (Print )
Contemporary History Institute (CHI)
ohiou.edu (ed., Analyzes the contemporary period in world affairs—the period from World War II to the present—from an interdisciplinary historical perspective.)
Soviet Union Timeline
on ''BBC'' {{Authority control Contemporary history, Historiography Historical eras Articles which contain graphical timelines Articles containing video clips