Confederation (Canada) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Canadian Confederation () was the process by which three
 Following the
Following the
 There is extensive scholarly debate on the role of political ideas in Canadian Confederation. Traditionally, historians regarded Canadian Confederation an exercise in political pragmatism that was essentially non-ideological. In the 1960s, historian Peter Waite derided the references to political philosophers in the legislative debates on Confederation as "hot air". In Waite's view, Confederation was driven by pragmatic brokerage politics and competing interest groups.
In 1987, political scientist Peter J. Smith challenged the view Canadian Confederation was non-ideological. Smith argued Confederation was motivated by new political ideologies as much as the American and French Revolutions and Canadian Confederation was driven by a Court Party ideology. Smith traces the origins of this ideology to eighteenth and nineteenth-century Britain, where political life was polarized between defenders of classical republican values of the Country Party and proponents of a new pro-capitalist ideology of the Court Party, which believed in centralizing political power. In British North America in the late 1860s, the Court Party tradition was represented by the supporters of Confederation, whereas the anti-capitalist and agrarian Country Party tradition was embodied by the Anti-Confederates.
In a 2000 journal article, historian Ian McKay argued Canadian Confederation was motivated by the ideology of liberalism and the belief in the supremacy of individual rights. McKay described Confederation as part of the classical liberal project of creating a "liberal order" in northern North America. Many Canadian historians have adopted McKay's liberal order framework as a paradigm for understanding Canadian history.
In 2008, historian Andrew Smith advanced a very different view of Confederation's ideological origins. He argues that in the four original Canadian provinces, the politics of taxation were a central issue in the debate about Confederation. Taxation was also central to the debate in Newfoundland, the tax-averse colony that rejected it. Smith argued Confederation was supported by many colonists who were sympathetic to a relatively interventionist, or statist, approach to capitalist development. Most classical liberals, who believed in free trade and low taxes, opposed Confederation because they feared it would result in Big Government. The struggle over Confederation involved a battle between a staunch individualist economic philosophy and a comparatively collectivist view of the state's proper role in the economy. According to Smith, the victory of the
There is extensive scholarly debate on the role of political ideas in Canadian Confederation. Traditionally, historians regarded Canadian Confederation an exercise in political pragmatism that was essentially non-ideological. In the 1960s, historian Peter Waite derided the references to political philosophers in the legislative debates on Confederation as "hot air". In Waite's view, Confederation was driven by pragmatic brokerage politics and competing interest groups.
In 1987, political scientist Peter J. Smith challenged the view Canadian Confederation was non-ideological. Smith argued Confederation was motivated by new political ideologies as much as the American and French Revolutions and Canadian Confederation was driven by a Court Party ideology. Smith traces the origins of this ideology to eighteenth and nineteenth-century Britain, where political life was polarized between defenders of classical republican values of the Country Party and proponents of a new pro-capitalist ideology of the Court Party, which believed in centralizing political power. In British North America in the late 1860s, the Court Party tradition was represented by the supporters of Confederation, whereas the anti-capitalist and agrarian Country Party tradition was embodied by the Anti-Confederates.
In a 2000 journal article, historian Ian McKay argued Canadian Confederation was motivated by the ideology of liberalism and the belief in the supremacy of individual rights. McKay described Confederation as part of the classical liberal project of creating a "liberal order" in northern North America. Many Canadian historians have adopted McKay's liberal order framework as a paradigm for understanding Canadian history.
In 2008, historian Andrew Smith advanced a very different view of Confederation's ideological origins. He argues that in the four original Canadian provinces, the politics of taxation were a central issue in the debate about Confederation. Taxation was also central to the debate in Newfoundland, the tax-averse colony that rejected it. Smith argued Confederation was supported by many colonists who were sympathetic to a relatively interventionist, or statist, approach to capitalist development. Most classical liberals, who believed in free trade and low taxes, opposed Confederation because they feared it would result in Big Government. The struggle over Confederation involved a battle between a staunch individualist economic philosophy and a comparatively collectivist view of the state's proper role in the economy. According to Smith, the victory of the

 The Conference began on October 10, 1864, on the site of present-day Montmorency Park. The Conference elected
The Conference began on October 10, 1864, on the site of present-day Montmorency Park. The Conference elected
 Following the Quebec Conference, the Province of Canada's legislature passed a bill approving the union. The union proved more controversial in the Maritime provinces, however, and it was not until 1866 that New Brunswick and Nova Scotia passed union resolutions, while Prince Edward Island and Newfoundland continued to opt against joining.
In December 1866, sixteen delegates from the Province of Canada, New Brunswick, and Nova Scotia travelled to London, where the Earl of Carnarvon presented each to
Following the Quebec Conference, the Province of Canada's legislature passed a bill approving the union. The union proved more controversial in the Maritime provinces, however, and it was not until 1866 that New Brunswick and Nova Scotia passed union resolutions, while Prince Edward Island and Newfoundland continued to opt against joining.
In December 1866, sixteen delegates from the Province of Canada, New Brunswick, and Nova Scotia travelled to London, where the Earl of Carnarvon presented each to
 Confederation was accomplished when the Queen gave royal assent to the ''British North America Act'' (''BNA Act'') on March 29, 1867, followed by a royal proclamation stating, "we do ordain, declare, and command that, on and after the first day of July, one thousand eight hundred and sixty-seven, the provinces of Canada, Nova Scotia, and New Brunswick shall form and be One Dominion, under the name of Canada." The act replaced the Act of Union 1840, which had unified Upper Canada and Lower Canada into the united Province of Canada; separate provinces were established under their current names of Ontario and Quebec, respectively. July 1 is now celebrated as
Confederation was accomplished when the Queen gave royal assent to the ''British North America Act'' (''BNA Act'') on March 29, 1867, followed by a royal proclamation stating, "we do ordain, declare, and command that, on and after the first day of July, one thousand eight hundred and sixty-seven, the provinces of Canada, Nova Scotia, and New Brunswick shall form and be One Dominion, under the name of Canada." The act replaced the Act of Union 1840, which had unified Upper Canada and Lower Canada into the united Province of Canada; separate provinces were established under their current names of Ontario and Quebec, respectively. July 1 is now celebrated as
/ref> The act also details how power is distributed in both the provincial and federal jurisdictions. Two of the most important sections are 91 and 92. Section 91 gives Parliament jurisdiction over banking, interest rates, criminal law, the postal system, and the armed forces. Section 92 gives the provinces jurisdiction over property, contracts and torts, local works, and general business. Still, federal and provincial law may occasionally interfere with each other, in which case federal law prevails.
 Dominion elections were held in August and September, 1867, to elect the first
Dominion elections were held in August and September, 1867, to elect the first
''Constitution Act, 1867''
* * .
online
* Careless, J.M.C. "George Brown and Confederation", ''Manitoba Historical Society Transactions'', Series 3, Number 26, 1969–7
online
* Creighton, Donald Grant. ''The Road to Confederation: The Emergence of Canada, 1863–1867'' (1965) a standard histor
online
* Creighton, Donald Grant. ''John A. Macdonald: The Young Politician. Vol. 1'' (1952) vol 1 of biography of Macdonald * Gwyn, Richard. ''John A: The Man Who Made Us'' (2008) vol 1 of biography of Macdonald *Knox, Bruce A. "Conservative Imperialism 1858–1874: Bulwer Lytton, Lord Carnarvon, and Canadian Confederation." ''International History Review'' (1984) 6#3 pp: 333–357. * Martin, Ged. ''Britain and the origins of Canadian confederation, 1837–67'' (UBC Press, 1995). * Martin, Ged, ed. ''The Causes of Canadian confederation'' (Acadiensis Press, 1990). * Moore, Christopher. ''1867: How the Fathers Made a Deal'' (McClelland & Stewart, 2011) * Morton, William Lewis. ''The critical years: the union of British North America, 1857–1873'' (McClelland & Stewart, 1964) a standard history * Smith, Andrew. '' British Businessmen and Canadian Confederation Constitution-Making in an Era of Anglo-Globalization'' (McGill-Queen's University Press, 2008) * Smith, Andrew. "Toryism, Classical Liberalism, and Capitalism: The Politics of Taxation and the Struggle for Canadian Confederation." ''Canadian Historical Review'' 89#1 (2008): 1–25. * Smith, Jennifer. "Canadian confederation and the influence of American federalism." ''Canadian Journal of Political Science'' 21#3 (1988): 443–464. * Smith, Peter J. "The Ideological Origins of Canadian Confederation". ''Canadian Journal of Political Science'' 1987. 20#1 pp : 3–29. * Vronsky, Peter. ''Ridgeway: The American Fenian Invasion and the 1866 Battle That Made Canada'' (Penguin Canada, 2011) * Waite, Peter B. ''The life and times of Confederation, 1864–1867: politics, newspapers, and the union of British North America'' (Robin Brass Studio, 2001). * White, Walter Leroy, and W. C. Soderlund. ''Canadian Confederation: A Decision-making Analysis'' (McGill-Queen's Press-MQUP, 1979) * Wilson, David A. ''Thomas D'Arcy McGee: The Extreme Moderate, 1857–1868. Vol. 2'' (McGill-Queen's Press-MQUP, 2011)
*[https://web.archive.org/web/20111230022553/http://www.canadiana.ca/citm/themes/constitution/constitution12_e.html Canadiana: "On the Road to Confederation"]
McCord Museum: "Confederation: The Creation of Canada"
{{Authority control Canadian Confederation, 1840s in Canada 1850s in Canada 1860s in Canada 1867 in Canada Federalism in Canada National unifications Political history of Canada British North America Pre-Confederation Canada Post-Confederation Canada (1867–1914) 1867 establishments in Canada, * 1867 in Canadian law 1867 in politics 19th century in Canada
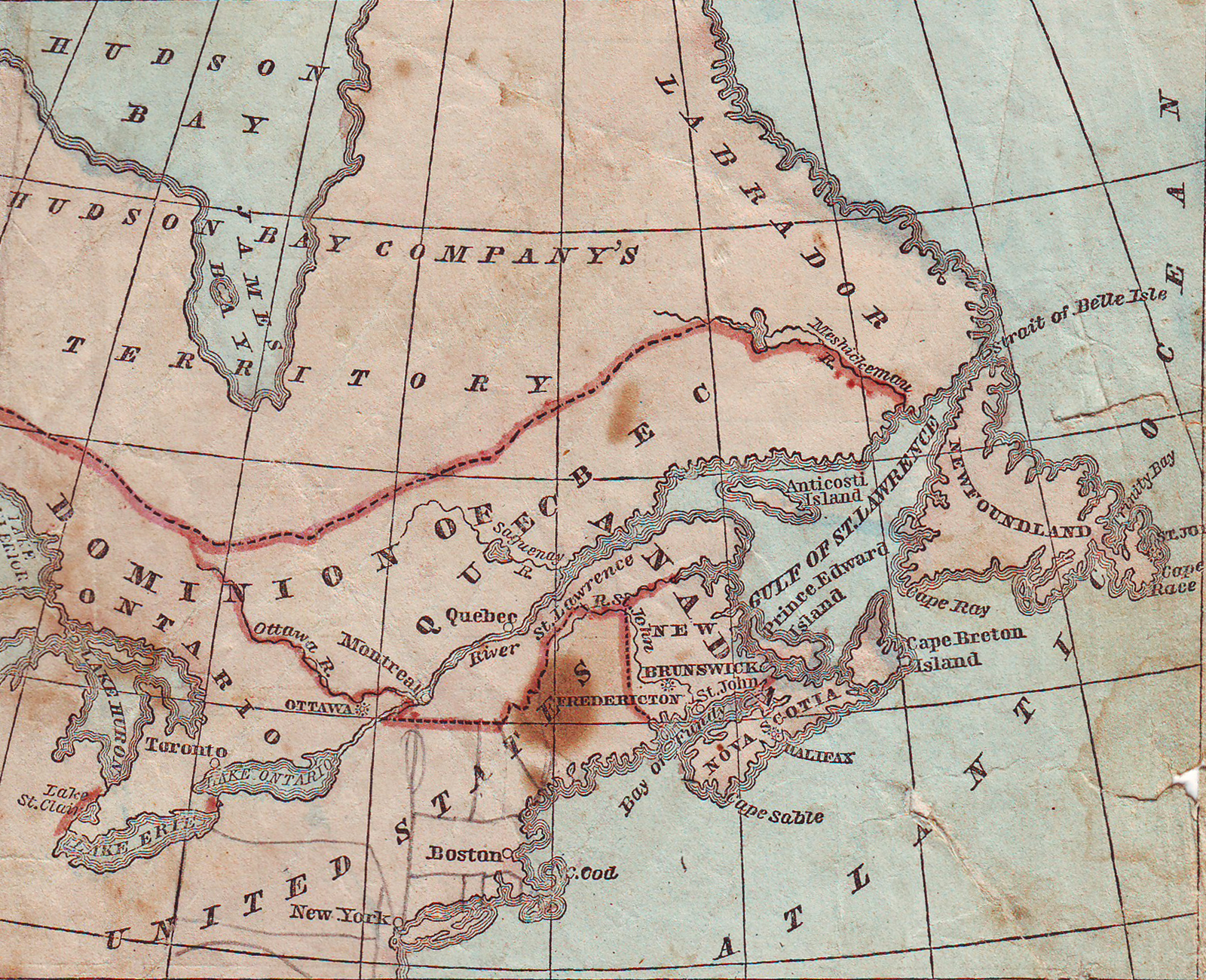
British North America
British North America comprised the colonial territories of the British Empire in North America from 1783 onwards. English colonisation of North America began in the 16th century in Newfoundland, then further south at Roanoke and Jamestown, ...
n provinces—the Province of Canada
The Province of Canada (or the United Province of Canada or the United Canadas) was a British colony in British North America from 1841 to 1867. Its formation reflected recommendations made by John Lambton, 1st Earl of Durham, in the Report ...
, Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada, located on its east coast. It is one of the three Maritime Canada, Maritime provinces and Population of Canada by province and territory, most populous province in Atlan ...
, and New Brunswick
New Brunswick is a Provinces and Territories of Canada, province of Canada, bordering Quebec to the north, Nova Scotia to the east, the Gulf of Saint Lawrence to the northeast, the Bay of Fundy to the southeast, and the U.S. state of Maine to ...
—were united into one federation
A federation (also called a federal state) is an entity characterized by a political union, union of partially federated state, self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a #Federal governments, federal government (federalism) ...
, called the Dominion
A dominion was any of several largely self-governance, self-governing countries of the British Empire, once known collectively as the ''British Commonwealth of Nations''. Progressing from colonies, their degrees of self-governing colony, colon ...
of Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
, on July 1, 1867. This process occurred in accordance with the rising tide of Canadian nationalism
Canadian nationalism () has been a significant political force since the 19th century and has typically manifested itself as seeking to advance Canada's independence from the influence of the United Kingdom and United States. Since the 1960s, m ...
that was then beginning to swell within these provinces and others. Upon Confederation, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
consisted of four provinces: Ontario
Ontario is the southernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Located in Central Canada, Ontario is the Population of Canada by province and territory, country's most populous province. As of the 2021 Canadian census, it ...
and Quebec
Quebec is Canada's List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, ...
, which had been split out from the Province of Canada, and the provinces of Nova Scotia and New Brunswick. The province of Prince Edward Island
Prince Edward Island is an island Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. While it is the smallest province by land area and population, it is the most densely populated. The island has several nicknames: "Garden of the Gulf", ...
, which had hosted the first meeting to consider Confederation, the Charlottetown Conference
The Charlottetown Conference (A Conference to discuss the Confederation of Canada) was held in Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island, for representatives from colonies of British North America to discuss Canadian Confederation. The conference to ...
, did not join Confederation until 1873. Over the years since Confederation, Canada has seen numerous territorial changes and expansions, resulting in the current number of ten provinces and three territories.
Terminology
Confederation
Canada is afederation
A federation (also called a federal state) is an entity characterized by a political union, union of partially federated state, self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a #Federal governments, federal government (federalism) ...
, rather than a confederate association of sovereign states, which is what ''confederation
A confederation (also known as a confederacy or league) is a political union of sovereign states united for purposes of common action. Usually created by a treaty, confederations of states tend to be established for dealing with critical issu ...
'' means in contemporary political theory. The country, though, is often considered to be among the world's more decentralized
Decentralization or decentralisation is the process by which the activities of an organization, particularly those related to planning and decision-making, are distributed or delegated away from a central, authoritative location or group and gi ...
federations. Use of the term ''confederation'' arose in the Province of Canada to refer to proposals beginning in the 1850s to federate all of the British North American colonies, as opposed to only Canada West (now Ontario) and Canada East (now Quebec). To contemporaries of Confederation, the ''con-'' prefix indicated a strengthening of the centrist principle compared to the American federation.
In this Canadian context, ''confederation'' describes the political process that united the colonies in 1867, events related to that process, and the subsequent incorporation of other colonies and territories. The word is now often used to describe Canada in an abstract way, such as in "the Fathers of Confederation"; provinces that became part of Canada after 1867 are also said to have joined, or entered into, Confederation (but not ''the'' Confederation). The term is also used to divide Canadian history
The history of Canada covers the period from the arrival of the Paleo-Indians to North America thousands of years ago to the present day. The lands encompassing present-day Canada have been inhabited for millennia by Indigenous peoples, with di ...
into pre-Confederation and post-Confederation periods.
Fathers of Confederation
The original Fathers of Confederation are those delegates who attended any of the conferences held at Charlottetown and Quebec in 1864 or in London, United Kingdom, in 1866, leading to Confederation. There were 36 original Fathers of Confederation; Hewitt Bernard, who was the recording secretary at theCharlottetown Conference
The Charlottetown Conference (A Conference to discuss the Confederation of Canada) was held in Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island, for representatives from colonies of British North America to discuss Canadian Confederation. The conference to ...
, is considered by some to be among them.
The individuals who brought the other provinces into Confederation after 1867 are also referred to as ''Fathers of Confederation''. In this way, Amor De Cosmos, who was instrumental both in bringing democracy to British Columbia and in bringing the province into Confederation, is considered to be a Father of Confederation. As well, Joey Smallwood
Joseph Roberts Smallwood (December 24, 1900 – December 17, 1991) was a Newfoundlander and Canadian politician. He was the main force who brought the Dominion of Newfoundland into Canadian Confederation in 1949, becoming the first premier of ...
referred to himself as "the Last Father of Confederation" because he helped lead Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region of Labrador, having a total size of . As of 2025 the population ...
into the union in 1949.
History
Colonial organization
All the former colonies and territories that became involved in the Canadian Confederation on July 1, 1867, were initially part ofNew France
New France (, ) was the territory colonized by Kingdom of France, France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Kingdom of Great Br ...
, and were once ruled by France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
. Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada, located on its east coast. It is one of the three Maritime Canada, Maritime provinces and Population of Canada by province and territory, most populous province in Atlan ...
was granted in 1621 to Sir William Alexander under charter
A charter is the grant of authority or rights, stating that the granter formally recognizes the prerogative of the recipient to exercise the rights specified. It is implicit that the granter retains superiority (or sovereignty), and that the ...
by James I. This claim overlapped the French claims to Acadia
Acadia (; ) was a colony of New France in northeastern North America which included parts of what are now the The Maritimes, Maritime provinces, the Gaspé Peninsula and Maine to the Kennebec River. The population of Acadia included the various ...
, and although the Scottish colony of Nova Scotia was short-lived, for political reasons, the conflicting imperial interests of France and the 18th century Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-west coast of continental Europe, consisting of the countries England, Scotland, and Wales. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the List of European ...
led to a long and bitter struggle for control. The British acquired present-day mainland Nova Scotia by the Treaty of Utrecht
The Peace of Utrecht was a series of peace treaty, peace treaties signed by the belligerents in the War of the Spanish Succession, in the Dutch city of Utrecht between April 1713 and February 1715. The war involved three contenders for the vac ...
of 1713 and the Acadian population was expelled by the British in 1755. They renamed Acadia "Nova Scotia", which included present-day New Brunswick
New Brunswick is a Provinces and Territories of Canada, province of Canada, bordering Quebec to the north, Nova Scotia to the east, the Gulf of Saint Lawrence to the northeast, the Bay of Fundy to the southeast, and the U.S. state of Maine to ...
. The rest of New France was acquired by the British as the result of its defeat of New France in the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War, 1756 to 1763, was a Great Power conflict fought primarily in Europe, with significant subsidiary campaigns in North America and South Asia. The protagonists were Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of Prus ...
, which ended with the Treaty of Paris in 1763. From 1763 to 1791, most of New France became the Province of Quebec
Quebec is Canada's largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, New Brunswick to the southeast and a coastal border ...
. However, in 1769 the present-day Prince Edward Island
Prince Edward Island is an island Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. While it is the smallest province by land area and population, it is the most densely populated. The island has several nicknames: "Garden of the Gulf", ...
, which had been part of Acadia, was renamed "St John's Island" and organized as a separate colony. It was renamed "Prince Edward Island" in 1798 in honour of Prince Edward, Duke of Kent and Strathearn
Prince Edward, Duke of Kent and Strathearn (Edward Augustus; 2 November 1767 – 23 January 1820) was the fourth son and fifth child of King George III and Queen Charlotte. His only child, Queen Victoria, Victoria, became Queen of the United Ki ...
.
The first English attempt at settlement on that part of the continent that would become modern Canada had been in Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region of Labrador, having a total size of . As of 2025 the population ...
which would not join Confederation until 1949. The Society of Merchant Venturers of Bristol
Bristol () is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city, unitary authority area and ceremonial county in South West England, the most populous city in the region. Built around the River Avon, Bristol, River Avon, it is bordered by t ...
began to settle Newfoundland and Labrador
Newfoundland and Labrador is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region of Labrador, having a total size of . As of 2025 the populatio ...
at Cuper's Cove as far back as 1610, and Newfoundland had also been the subject of a French colonial enterprise.
During and after the U.S. War of Independence, an estimated 50,000 United Empire Loyalist
United Empire Loyalist (UEL; or simply Loyalist) is an honorific title which was first given by the 1st Lord Dorchester, the governor of Quebec and governor general of the Canadas, to American Loyalists who resettled in British North Ameri ...
s fled to British North America
British North America comprised the colonial territories of the British Empire in North America from 1783 onwards. English colonisation of North America began in the 16th century in Newfoundland, then further south at Roanoke and Jamestown, ...
. The British created the separate province of New Brunswick in 1784 for Loyalists who settled in the western part of Nova Scotia. Nova Scotia (including New Brunswick) received slightly more than half of this influx, and many Loyalists settled in the province of Quebec, which later by the Constitutional Act 1791
The Constitutional Act 1791 (31 Geo. 3. c. 31) () was an Act of Parliament (United Kingdom), act of the Parliament of Great Britain which was passed during the reign of George III. The act divided the old Province of Quebec (1763–1791), Pro ...
was separated into a predominantly English Upper Canada
The Province of Upper Canada () was a Province, part of The Canadas, British Canada established in 1791 by the Kingdom of Great Britain, to govern the central third of the lands in British North America, formerly part of the Province of Queb ...
and a predominantly French Lower Canada
The Province of Lower Canada () was a British colonization of the Americas, British colony on the lower Saint Lawrence River and the shores of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence established in 1791 and abolished in 1841. It covered the southern portion o ...
. The War of 1812
The War of 1812 was fought by the United States and its allies against the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom and its allies in North America. It began when the United States United States declaration of war on the Uni ...
and Treaty of 1818
The Convention respecting fisheries, boundary and the restoration of slaves, also known as the London Convention, Anglo-American Convention of 1818, Convention of 1818, or simply the Treaty of 1818, is an international treaty signed in 1818 betw ...
established the border between British North America and the United States at the 49th parallel from the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes spanning the Canada–United States border. The five lakes are Lake Superior, Superior, Lake Michigan, Michigan, Lake Huron, H ...
to the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in great-circle distance, straight-line distance from the northernmost part of Western Can ...
in Western Canada.
 Following the
Following the Rebellions of 1837
Rebellion is an uprising that resists and is organized against one's government. A rebel is a person who engages in a rebellion. A rebel group is a consciously coordinated group that seeks to gain political control over an entire state or a ...
, Lord Durham in his Durham Report
The ''Report on the Affairs of British North America'', (, 1839) commonly known as the ''Durham Report'' or ''Lord Durham's Report'', is an important document in the history of Quebec, Ontario, Canada and the British Empire.
The notable Briti ...
, recommended Upper and Lower Canada be joined as the Province of Canada
The Province of Canada (or the United Province of Canada or the United Canadas) was a British colony in British North America from 1841 to 1867. Its formation reflected recommendations made by John Lambton, 1st Earl of Durham, in the Report ...
and the new province should have a responsible government
Responsible government is a conception of a system of government that embodies the principle of parliamentary accountability, the foundation of the Westminster system of parliamentary democracy. Governments (the equivalent of the executive br ...
. As a result of Durham's report, the British Parliament passed the Act of Union 1840
The ''British North America Act, 1840'' ( 3 & 4 Vict. c. 35), also known as the ''Act of Union 1840'', () was approved by Parliament in July 1840 and proclaimed February 10, 1841, in Montreal. It abolished the legislatures of Lower Canada and ...
, and the Province of Canada was formed in 1841. The new province had two parts: Canada West
The Province of Canada (or the United Province of Canada or the United Canadas) was a British colony in British North America from 1841 to 1867. Its formation reflected recommendations made by John Lambton, 1st Earl of Durham, in the Report ...
(the former Upper Canada, today's Ontario) and Canada East
Canada East () was the northeastern portion of the Province of Canada. Lord Durham's Report investigating the causes of the Upper and Lower Canada Rebellions recommended merging those two colonies. The new colony, known as the Province of ...
(the former Lower Canada, today's Quebec). Governor General Lord Elgin granted ministerial responsibility in 1848, first to Nova Scotia and then to the Province of Canada. Later, the British parliament extended responsible government to Prince Edward Island (1851), New Brunswick (1854), and Newfoundland (1855).
The area constituting modern-day British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Situated in the Pacific Northwest between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains, the province has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that ...
is the remnants of the Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC), originally the Governor and Company of Adventurers of England Trading Into Hudson’s Bay, is a Canadian holding company of department stores, and the oldest corporation in North America. It was the owner of the ...
's Columbia District
The Columbia District was a fur-trading district in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, in both the United States and British North America in the 19th century. Much of its territory overlapped with the temporarily jointly occupi ...
and New Caledonia District following the Oregon Treaty
The Oregon Treaty was a treaty between the United Kingdom and the United States that was signed on June 15, 1846, in Washington, D.C. The treaty brought an end to the Oregon boundary dispute by settling competing American and British claims to ...
. Before joining Canada in 1871, British Columbia consisted of the separate Colony of British Columbia The Colony of British Columbia refers to one of two colonies of British North America, located on the Pacific coast of modern-day Canada:
* Colony of British Columbia (1858–1866)
* Colony of British Columbia (1866–1871)
See also
* History of ...
(formed in 1858, in an area where the Crown had granted a monopoly to the Hudson's Bay Company), and the Colony of Vancouver Island
The Colony of Vancouver Island, officially known as the Island of Vancouver and its Dependencies, was a Crown colony of British North America from 1849 to 1866, after which it was united with the mainland to form the Colony of British Columbia. ...
(formed in 1849) constituting a separate crown colony
A Crown colony or royal colony was a colony governed by Kingdom of England, England, and then Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain or the United Kingdom within the English overseas possessions, English and later British Empire. There was usua ...
until it was united with the colony of British Columbia in 1866.
The remainder of modern-day Canada was made up of Rupert's Land
Rupert's Land (), or Prince Rupert's Land (), was a territory in British North America which comprised the Hudson Bay drainage basin. The right to "sole trade and commerce" over Rupert's Land was granted to Hudson's Bay Company (HBC), based a ...
and the North-Western Territory
The North-Western Territory was a region of British North America extant until 1870 and named for where it lay in relation to Rupert's Land.
Because of the lack of development, exploration, and cartographic limits of the time, the exact boun ...
(both of which were controlled by the Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC), originally the Governor and Company of Adventurers of England Trading Into Hudson’s Bay, is a Canadian holding company of department stores, and the oldest corporation in North America. It was the owner of the ...
and sold to Canada in 1870) and the Arctic Islands, which were under direct British control and became a part of Canada in 1880. Plus, Newfoundland and Labrador joined Canada in 1949.
Early attempts
The idea of joining the various colonies in North America was being floated as early as 1814. That year, Chief Justice of Lower Canada Jonathan Sewell sent a copy of his report, ''A Plan for the federal Union of British Provinces in North America'', to Prince Edward (both a son of KingGeorge III
George III (George William Frederick; 4 June 173829 January 1820) was King of Great Britain and King of Ireland, Ireland from 25 October 1760 until his death in 1820. The Acts of Union 1800 unified Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and ...
and the father of Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until Death and state funeral of Queen Victoria, her death in January 1901. Her reign of 63 year ...
), whom Sewell had befriended when they both resided in Quebec City
Quebec City is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Quebec. As of July 2021, the city had a population of 549,459, and the Census Metropolitan Area (including surrounding communities) had a populati ...
. Edward replied, "nothing can be better arranged than the whole thing is, or more perfectly", going on to suggest a unified Canada consisting of two provinces—one formed from Upper and Lower Canada and the other from the Maritime colonies—each with a lieutenant governor and executive council, one located in Montreal
Montreal is the List of towns in Quebec, largest city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Quebec, the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-largest in Canada, and the List of North American cit ...
and the other in either Annapolis Royal or Windsor. Edward said he would pass the report on to the Earl Bathurst, the then-Secretary of State for War and the Colonies
The Secretary of State for War and the Colonies was a British cabinet-level position responsible for the army and the British colonies (other than India). The Secretary was supported by an Under-Secretary of State for War and the Colonies.
Hist ...
; the Prince's comments and critiques were later cited by both the Earl of Durham and participants of the Charlottetown
Charlottetown is the capital and largest city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Prince Edward Island, and the county seat of Queens County, Prince Edward Island, Queens County. Named after Queen Charlotte, Charlott ...
and Quebec Conferences.
Lord Durham presented his idea of unification in 1839 '' Report on the Affairs of British North America'', which resulted in the Act of Union 1840. Beginning in 1857, Joseph-Charles Taché proposed a federation in a series of 33 articles published in the ''Courrier du Canada''. Two years later, Alexander Tilloch Galt
Sir Alexander Tilloch Galt, (September 6, 1817 – September 19, 1893) was a politician and Fathers of Confederation, Father of Confederation, the Canadian Confederation, union of British North American colonies into Canada.
Early life
He w ...
, George-Étienne Cartier
Sir George-Étienne Cartier, 1st Baronet, (pronounced ; September 6, 1814May 20, 1873) was a Canadians, Canadian statesman and Fathers of Confederation, Father of Confederation.
The English spelling of the name—George, instead of Georges, th ...
, and John Ross travelled to the United Kingdom to present the British Parliament with a project for confederation of the British colonies. The proposal was received by the London authorities with polite indifference.
The royal tour of British North America undertaken by Queen Victoria's son, Prince Albert Edward (later King Edward VII
Edward VII (Albert Edward; 9 November 1841 – 6 May 1910) was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 22 January 1901 until Death and state funeral of Edward VII, his death in 1910.
The second child ...
) in 1860, however, helped lead to the unification of the colonies by confirming a common bond between their inhabitants; indeed, the monarchy played a "pivotal legal and symbolic role ..in cementing the new Canadian union". Further, by 1864, it was clear that continued governance of the Province of Canada under the terms of the 1840 Act of Union had become impracticable. Therefore, a grand coalition
A grand coalition is an arrangement in a multi-party parliamentary system in which the two largest political party, political parties of opposing political spectrum, political ideologies unite in a coalition government.
Causes of a grand coali ...
of parties, the Great Coalition, formed in order to reform the political system. Queen Victoria remarked on "the impossibility of our being able to hold Canada; but, we must struggle for it; and by far the best solution would be to let it go as an independent kingdom under an English prince."
Influences leading to Confederation
Several factors influenced Confederation, caused both by internal sources and pressures from external sources. Internally, there was political deadlock resulting from the contemporary governmental structure in the Province of Canada and distrust between English Protestants and French Catholics. Further, demographic pressure from an expanding population and economic nationalism wanting economic development butted against a lack of an inter-colonial railroad, which hampered trade, military movement, and transportation in general. Externally, the Canadian–American Reciprocity Treaty (a free trade policy, starting in 1854, whereby products were allowed into the United States without taxes or tariffs, which was then considered to be beneficial for Canada) was cancelled by the United States in 1865, partly as revenge against Britain for unofficial support of the south in theAmerican Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
. Additionally, the U.S. doctrine of "manifest destiny
Manifest destiny was the belief in the 19th century in the United States, 19th-century United States that American pioneer, American settlers were destined to expand westward across North America, and that this belief was both obvious ("''m ...
" raised fears of another American invasion (Canadians had fended off American incursions during the Revolutionary War, War of 1812, Fenian raids, and St. Albans Raid), only further inflamed by the Alaska Purchase
The Alaska Purchase was the purchase of Russian colonization of North America, Alaska from the Russian Empire by the United States for a sum of $7.2 million in 1867 (equivalent to $ million in ). On May 15 of that year, the United St ...
of March 30, 1867, which had been supported in the U.S. Senate (by Charles Sumner
Charles Sumner (January 6, 1811March 11, 1874) was an American lawyer and statesman who represented Massachusetts in the United States Senate from 1851 until his death in 1874. Before and during the American Civil War, he was a leading American ...
among others) precisely in terms of taking the remainder of North America from the British. The American Civil War had also horrified Canadians and turned many from the thought of republicanism. In Britain, political pressure came from financiers who had lost money by investing in the failed Grand Trunk Railway
The Grand Trunk Railway (; ) was a Rail transport, railway system that operated in the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian provinces of Quebec and Ontario and in the List of states and territories of the United States, American sta ...
and the little Englander
The Little Englanders were a British political movement who opposed empire-building and advocated complete independence for Britain's existing colonies. The ideas of Little Englandism first began to gain popularity in the late 18th century after ...
philosophy fed a desire to withdraw troops from Britain's colonies.
Ideological origins and philosophical dimensions
 There is extensive scholarly debate on the role of political ideas in Canadian Confederation. Traditionally, historians regarded Canadian Confederation an exercise in political pragmatism that was essentially non-ideological. In the 1960s, historian Peter Waite derided the references to political philosophers in the legislative debates on Confederation as "hot air". In Waite's view, Confederation was driven by pragmatic brokerage politics and competing interest groups.
In 1987, political scientist Peter J. Smith challenged the view Canadian Confederation was non-ideological. Smith argued Confederation was motivated by new political ideologies as much as the American and French Revolutions and Canadian Confederation was driven by a Court Party ideology. Smith traces the origins of this ideology to eighteenth and nineteenth-century Britain, where political life was polarized between defenders of classical republican values of the Country Party and proponents of a new pro-capitalist ideology of the Court Party, which believed in centralizing political power. In British North America in the late 1860s, the Court Party tradition was represented by the supporters of Confederation, whereas the anti-capitalist and agrarian Country Party tradition was embodied by the Anti-Confederates.
In a 2000 journal article, historian Ian McKay argued Canadian Confederation was motivated by the ideology of liberalism and the belief in the supremacy of individual rights. McKay described Confederation as part of the classical liberal project of creating a "liberal order" in northern North America. Many Canadian historians have adopted McKay's liberal order framework as a paradigm for understanding Canadian history.
In 2008, historian Andrew Smith advanced a very different view of Confederation's ideological origins. He argues that in the four original Canadian provinces, the politics of taxation were a central issue in the debate about Confederation. Taxation was also central to the debate in Newfoundland, the tax-averse colony that rejected it. Smith argued Confederation was supported by many colonists who were sympathetic to a relatively interventionist, or statist, approach to capitalist development. Most classical liberals, who believed in free trade and low taxes, opposed Confederation because they feared it would result in Big Government. The struggle over Confederation involved a battle between a staunch individualist economic philosophy and a comparatively collectivist view of the state's proper role in the economy. According to Smith, the victory of the
There is extensive scholarly debate on the role of political ideas in Canadian Confederation. Traditionally, historians regarded Canadian Confederation an exercise in political pragmatism that was essentially non-ideological. In the 1960s, historian Peter Waite derided the references to political philosophers in the legislative debates on Confederation as "hot air". In Waite's view, Confederation was driven by pragmatic brokerage politics and competing interest groups.
In 1987, political scientist Peter J. Smith challenged the view Canadian Confederation was non-ideological. Smith argued Confederation was motivated by new political ideologies as much as the American and French Revolutions and Canadian Confederation was driven by a Court Party ideology. Smith traces the origins of this ideology to eighteenth and nineteenth-century Britain, where political life was polarized between defenders of classical republican values of the Country Party and proponents of a new pro-capitalist ideology of the Court Party, which believed in centralizing political power. In British North America in the late 1860s, the Court Party tradition was represented by the supporters of Confederation, whereas the anti-capitalist and agrarian Country Party tradition was embodied by the Anti-Confederates.
In a 2000 journal article, historian Ian McKay argued Canadian Confederation was motivated by the ideology of liberalism and the belief in the supremacy of individual rights. McKay described Confederation as part of the classical liberal project of creating a "liberal order" in northern North America. Many Canadian historians have adopted McKay's liberal order framework as a paradigm for understanding Canadian history.
In 2008, historian Andrew Smith advanced a very different view of Confederation's ideological origins. He argues that in the four original Canadian provinces, the politics of taxation were a central issue in the debate about Confederation. Taxation was also central to the debate in Newfoundland, the tax-averse colony that rejected it. Smith argued Confederation was supported by many colonists who were sympathetic to a relatively interventionist, or statist, approach to capitalist development. Most classical liberals, who believed in free trade and low taxes, opposed Confederation because they feared it would result in Big Government. The struggle over Confederation involved a battle between a staunch individualist economic philosophy and a comparatively collectivist view of the state's proper role in the economy. According to Smith, the victory of the statist
In political science, statism or etatism (from French, ''état'' 'state') is the doctrine that the political authority of the state is legitimate to some degree. This may include economic and social policy, especially in regard to taxation an ...
supporters of Confederation over their anti-statist opponents prepared the way for John A. Macdonald's government to enact the protectionist National Policy and to subsidize major infrastructure projects such as the Intercolonial and Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
Railways.
In 2007, political scientist Janet Ajzenstat connected Canadian Confederation to the individualist ideology of John Locke
John Locke (; 29 August 1632 (Old Style and New Style dates, O.S.) – 28 October 1704 (Old Style and New Style dates, O.S.)) was an English philosopher and physician, widely regarded as one of the most influential of the Enlightenment thi ...
. She argued that the union of the British North American colonies was motivated by a desire to protect individual rights, especially the rights to life, liberty, and property. She contends the Fathers of Confederation were motivated by the values of the Enlightenment of the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries. She argues their intellectual debts to Locke are most evident when one looks at the 1865 debates in the Province of Canada's legislature on whether or not union with the other British North American colonies would be desirable.
Charlottetown Conference
In the spring of 1864, New Brunswick premierSamuel Leonard Tilley
Sir Samuel Leonard Tilley (May 8, 1818June 25, 1896) was a Canadian politician and one of the Fathers of Confederation. Tilley was descended from United Empire Loyalists on both sides of his family. As a pharmacist, he went into business as ...
, Nova Scotia premier Charles Tupper
Sir Charles Tupper, 1st Baronet (July 2, 1821 – October 30, 1915) was a Canadian Father of Confederation who served as the sixth prime minister of Canada from May 1 to July 8, 1896. As the premier of Nova Scotia from 1864 to 1867, he led ...
, and Prince Edward Island premier John Hamilton Gray were contemplating the idea of a Maritime Union
Maritime Union () is a proposed political union of the three Maritime provinces of Canada – New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and Prince Edward Island – to form a single new province.Liberal-Conservative Party
The Liberal-Conservative Party () was the formal name of the Conservative Party of Canada until 1917, and again from 1922 to 1938. Prior to 1970, candidates could run under any label they chose, and in many of Canada's early elections, there wer ...
into the Great Coalition with Cartier's and George Brown George Brown may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* George Loring Brown (1814–1889), American landscape painter
* George Douglas Brown (1869–1902), Scottish novelist
* George Williams Brown (1894–1963), Canadian historian and editor
* Ge ...
's Clear Grits
Clear Grits were reformers in the Canada West district of the Province of Canada, a British colony that is now the Province of Ontario, Canada. Their name is said to have been given by George Brown, who said that only those were wanted in the p ...
. Macdonald, Cartier, and Brown felt union with the other British colonies might be a way to solve the political problems of the Province of Canada.
The Charlottetown Conference
The Charlottetown Conference (A Conference to discuss the Confederation of Canada) was held in Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island, for representatives from colonies of British North America to discuss Canadian Confederation. The conference to ...
began on September 1, 1864. Since the agenda for the meeting had already been set, the delegation from the Province of Canada was initially not an official part of the Conference. The issue of Maritime Union was deferred and the Canadians were formally allowed to join and address the Conference.
No minutes from the Charlottetown Conference survive, but it is known Cartier and Macdonald presented arguments in favour of a union of the three colonies, Alexander Tilloch Galt presented the Province of Canada's proposals on the financial arrangements of such a union, and George Brown presented a proposal for what form a united government might take. The Canadian delegation's proposal for the governmental system involved:
# preservation of ties with Great Britain
# residual jurisdiction left to a central authority
# a bicameral system including a Lower House with representation by population (rep by pop) and an Upper House with representation based on regional, rather than provincial, equality
# responsible government at the federal and provincial levels
# the appointment of a Canadian governor general by the British Crown
The Crown is a political concept used in Commonwealth realms. Depending on the context used, it generally refers to the entirety of the State (polity), state (or in federal realms, the relevant level of government in that state), the executive ...
Other proposals attractive to the politicians from the Maritime colonies were:
# assumption of provincial debt by the central government
# revenues from the central government apportioned to the provinces on the basis of population
# the building of an intercolonial railway to link Montreal and Halifax, giving Canada access to an ice-free winter port and the Maritimes easy access to Canada and Rupert's Land
Rupert's Land (), or Prince Rupert's Land (), was a territory in British North America which comprised the Hudson Bay drainage basin. The right to "sole trade and commerce" over Rupert's Land was granted to Hudson's Bay Company (HBC), based a ...
By September 7, 1864, the delegates from Nova Scotia, New Brunswick and Prince Edward Island gave a positive answer to the Canadian delegation, expressing the view the federation of all of the provinces was considered desirable if the terms of union could be made satisfactory and the question of Maritime Union was waived.
After the Conference adjourned on September 9, there were further meetings between delegates held at Halifax, Saint John, and Fredericton
Fredericton (; ) is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of New Brunswick. The city is situated in the west-central portion of the province along the Saint John River (Bay of Fundy), Saint John River, ...
. These meetings evinced enough interest that the delegates decided to hold a second Conference.

Delegates' reactions
One of the most important purposes of the Charlottetown Conference was the introduction of Canadians to the leaders from the Maritime Provinces and vice versa. At this point, there was no railway link from Quebec City to Halifax, and the people of each region had little to do with one another. Thomas D'Arcy McGee was one of the few Canadian delegates who had been to the Maritimes, when he had gone down earlier that summer with a trade mission of Canadian businessmen, journalists and politicians. George Brown remarked in a letter to his wife Anne that at a party given by the premier of PEI, Colonel John Hamilton Gray, he met a woman who had never been off the island in her entire life. Nevertheless, he found Prince Edward Islanders to be "amazingly civilized".Press and popular reaction
Reaction to the Charlottetown Conference varied among the different newspapers. In the Maritimes, there was concern that the smooth Canadians with their sparkling champagne and charming speeches were outsmarting the delegates of the smaller provinces. "From all accounts it looks as if these anadiangentlemen had it all their own way; ... and that, what with their arguments and what with their blandishments, (they gave a champagne lunch on board the ''Victoria'' where Mr. McGee's wit sparkled brightly as the wine), they carried the Lower Province delegates a little off their feet." The delegates from the Quebec conference considered if the resolutions would be better suited for acceptance if a popular vote were held on them. However, due to the divide amongst religious groups and general mistrust between areas in Canada, they believed that such a vote would be defeated. Thus, they went ahead with the resolutions on their own volition.Quebec Conference
After returning home from the Charlottetown Conference, Macdonald asked Viscount Monck, the governor general of the Province of Canada to invite delegates from the three Maritime provinces and Newfoundland to a conference with United Canada delegates. At the opening of the conference, a total of 33 delegates were included from the British North American Colonies, including Newfoundland, which had not participated in prior meetings. Monck obliged and the Conference went ahead atQuebec City
Quebec City is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Quebec. As of July 2021, the city had a population of 549,459, and the Census Metropolitan Area (including surrounding communities) had a populati ...
in October 1864.
 The Conference began on October 10, 1864, on the site of present-day Montmorency Park. The Conference elected
The Conference began on October 10, 1864, on the site of present-day Montmorency Park. The Conference elected Étienne-Paschal Taché
Sir Étienne-Paschal Taché (5 September 1795 – 30 July 1865) was a Canadian medical doctor, politician, and Father of Confederation. His family had a long history in New France, but suffered serious financial reverses due to the Seven Y ...
as its chairman, but it was dominated by Macdonald. Despite differences in the positions of some of the delegates on some issues, the Quebec Conference, following so swiftly on the success of the Charlottetown Conference, was infused with a determinative sense of purpose and nationalism
Nationalism is an idea or movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the state. As a movement, it presupposes the existence and tends to promote the interests of a particular nation, Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: Theory, I ...
. For the Reformers of Canada West, led by George Brown, the end of what they perceived as French-Canadian interference in local affairs was in sight. For Maritimers such as Tupper of Nova Scotia or Tilley of New Brunswick, horizons were suddenly broadened to take in much larger possibilities for trade and growth.
On the issue of the Senate, the Maritime Provinces pressed for as much equality as possible. With the addition of Newfoundland to the Conference, the three Maritime colonies did not wish to see the strength of their provinces in the upper chamber diluted by simply adding Newfoundland to the Atlantic category. It was the matter of the Senate that threatened to derail the entire proceedings. It was Macdonald who came up with the acceptable compromise of giving Newfoundland four senators of its own when it joined.
The delegates from the Maritimes also raised an issue with respect to the level of government—federal or provincial—that would be given the powers not otherwise specifically defined. Macdonald, who was aiming for the strongest central government possible, insisted this was to be the central government, and in this, he was supported by, among others, Tupper.
At the end of the Conference, it adopted the " seventy-two resolutions" which would form the basis of a scheduled future conference. The Conference adjourned on October 27.
Prince Edward Island emerged disappointed from the Quebec Conference. It did not receive support for a guarantee of six members in the proposed House of Commons, and was denied an appropriation of $200,000 it felt had been offered at Charlottetown to assist in buying out the holdings of absentee landlords.
Press and popular reaction
"Never was there such an opportunity as now for the birth of a nation" proclaimed a pamphlet written by S. E. Dawson and reprinted in a Quebec City newspaper during the Conference. Again, reaction to the Quebec Conference varied depending on the political views of the critic.Constitutional scheme discussed in London
George Brown was the first, in December 1864, to carry the constitutional proposals to the British government in London, where Brown received "a most gracious answer to our constitutional scheme". He also met with William Gladstone—who was then Chancellor of the Exchequer and, later, Prime Minister—"who agreed in almost everything". In April 1865, Brown, Macdonald, Cartier and Galt met with the government and found "the project of a federal union of the colonies was highly approved of by the imperial authorities". On the form of the proposed system of governance for Canada, the Fathers of Confederation were influenced by the American republic. Macdonald said in 1865:London Conference
 Following the Quebec Conference, the Province of Canada's legislature passed a bill approving the union. The union proved more controversial in the Maritime provinces, however, and it was not until 1866 that New Brunswick and Nova Scotia passed union resolutions, while Prince Edward Island and Newfoundland continued to opt against joining.
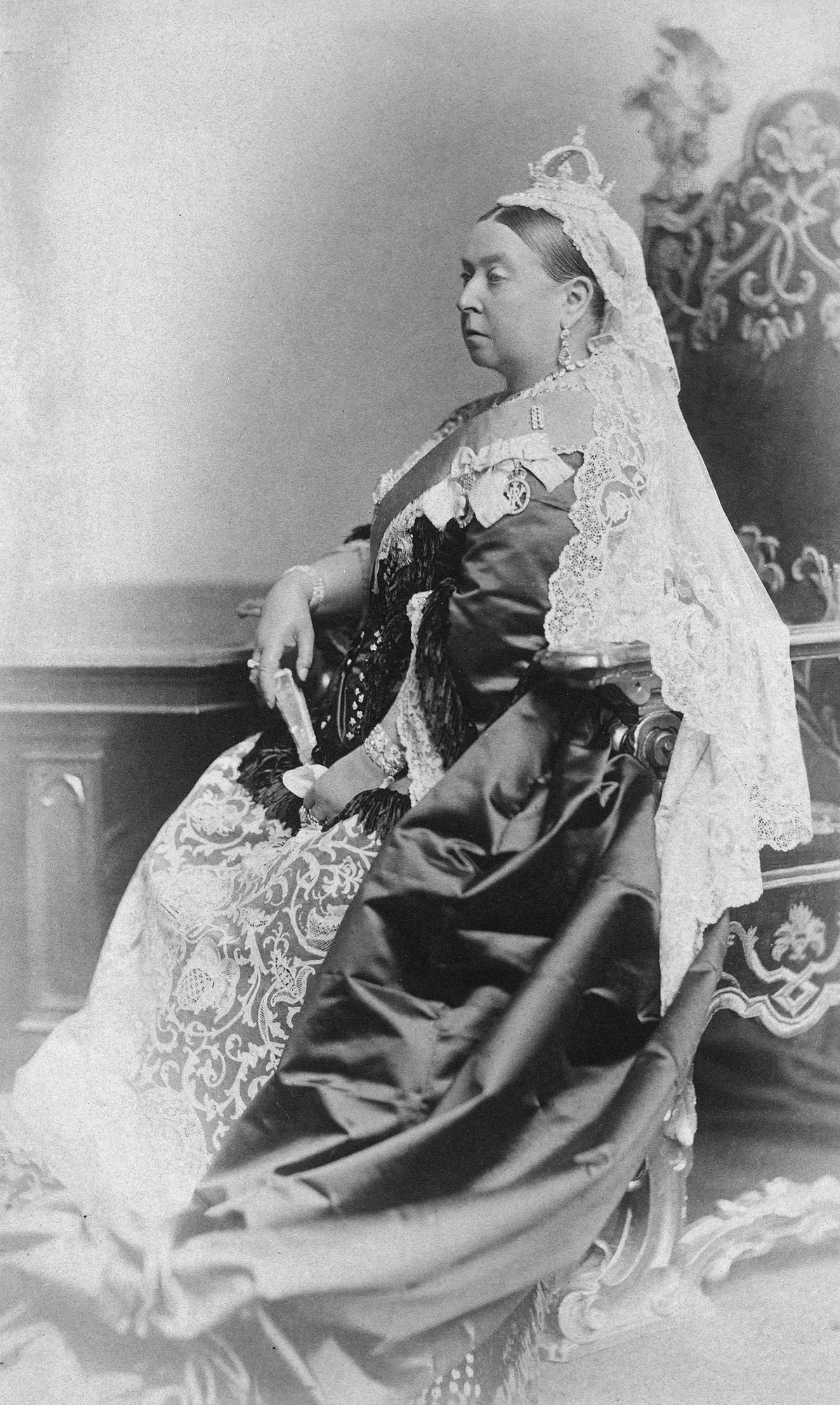
In December 1866, sixteen delegates from the Province of Canada, New Brunswick, and Nova Scotia travelled to London, where the Earl of Carnarvon presented each to
Following the Quebec Conference, the Province of Canada's legislature passed a bill approving the union. The union proved more controversial in the Maritime provinces, however, and it was not until 1866 that New Brunswick and Nova Scotia passed union resolutions, while Prince Edward Island and Newfoundland continued to opt against joining.
In December 1866, sixteen delegates from the Province of Canada, New Brunswick, and Nova Scotia travelled to London, where the Earl of Carnarvon presented each to Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until Death and state funeral of Queen Victoria, her death in January 1901. Her reign of 63 year ...
in private audience
An audience is a group of people who participate in a show or encounter a work of art, literature (in which they are called "readers"), theatre, music (in which they are called "listeners"), video games (in which they are called "players"), or ...
, as well as holding court for their wives and daughters. To the Nova Scotian delegates, the Queen said, "I take the deepest interest in onfederation for I believe it will make he provincesgreat and prosperous."
At meetings held at the Westminster Palace Hotel, the delegates reviewed and approved the 72 resolutions; although Charles Tupper had promised to anti-union forces in Nova Scotia that he would push for amendments, he was unsuccessful in getting any passed. Now known as the ''London Resolutions'', the conference's decisions were forwarded to the Colonial Office
The Colonial Office was a government department of the Kingdom of Great Britain and later of the United Kingdom, first created in 1768 from the Southern Department to deal with colonial affairs in North America (particularly the Thirteen Colo ...
.
After breaking for Christmas, the delegates reconvened in January 1867 and began drafting the ''British North America Act
The British North America Acts, 1867–1975, are a series of acts of Parliament that were at the core of the Constitution of Canada. Most were enacted by the Parliament of the United Kingdom and some by the Parliament of Canada. Some of the a ...
''. The 4th Earl of Carnarvon continued to have a central role in drafting the act at Highclere Castle
Highclere Castle is a Listed building#Categories of listed building, Grade I listed country house built in 1679 and largely renovated in the 1840s, with a park designed by Capability Brown in the 18th century. The estate is in Highclere in ...
alongside the first prime minister of Canada
The prime minister of Canada () is the head of government of Canada. Under the Westminster system, the prime minister governs with the Confidence and supply, confidence of a majority of the elected House of Commons of Canada, House of Commons ...
Macdonald, Cartier and Galt, who signed the visitor book in 1866. After suggestions of 'Franklin' and 'Guelfenland', they agreed the new country should be called ''Canada'', Canada East should be renamed ''Quebec'' and Canada West should be renamed ''Ontario''. There was, however, heated debate about how the new country should be designated. Ultimately, the delegates elected to call the new country the Dominion of Canada, after "kingdom" and "confederation", among other options, were rejected. The term ''dominion'' was allegedly suggested by Sir Samuel Leonard Tilley.
The delegates had completed their draft of the ''British North America Act'' by February 1867. The act was presented to Queen Victoria on February 11, 1867. The bill was introduced in the House of Lords
The House of Lords is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Like the lower house, the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminster in London, England. One of the oldest ext ...
the next day. The bill was quickly approved by the House of Lords, and then also quickly approved by the British House of Commons
The House of Commons is the lower house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Like the upper house, the House of Lords, it meets in the Palace of Westminster in London, England. The House of Commons is an elected body consisting of 650 memb ...
. (The Conservative
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy and ideology that seeks to promote and preserve traditional institutions, customs, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civiliza ...
Lord Derby was prime minister of the United Kingdom
The prime minister of the United Kingdom is the head of government of the United Kingdom. The prime minister Advice (constitutional law), advises the Monarchy of the United Kingdom, sovereign on the exercise of much of the Royal prerogative ...
at the time.) The act received royal assent
Royal assent is the method by which a monarch formally approves an act of the legislature, either directly or through an official acting on the monarch's behalf. In some jurisdictions, royal assent is equivalent to promulgation, while in othe ...
on March 29, 1867, and set July 1, 1867, as the date for union.
British North America Acts
 Confederation was accomplished when the Queen gave royal assent to the ''British North America Act'' (''BNA Act'') on March 29, 1867, followed by a royal proclamation stating, "we do ordain, declare, and command that, on and after the first day of July, one thousand eight hundred and sixty-seven, the provinces of Canada, Nova Scotia, and New Brunswick shall form and be One Dominion, under the name of Canada." The act replaced the Act of Union 1840, which had unified Upper Canada and Lower Canada into the united Province of Canada; separate provinces were established under their current names of Ontario and Quebec, respectively. July 1 is now celebrated as
Confederation was accomplished when the Queen gave royal assent to the ''British North America Act'' (''BNA Act'') on March 29, 1867, followed by a royal proclamation stating, "we do ordain, declare, and command that, on and after the first day of July, one thousand eight hundred and sixty-seven, the provinces of Canada, Nova Scotia, and New Brunswick shall form and be One Dominion, under the name of Canada." The act replaced the Act of Union 1840, which had unified Upper Canada and Lower Canada into the united Province of Canada; separate provinces were established under their current names of Ontario and Quebec, respectively. July 1 is now celebrated as Canada Day
Canada Day, formerly known as Dominion Day, is the national day of Canada. A Public holidays in Canada, federal statutory holiday, it celebrates the anniversary of Canadian Confederation which occurred on July 1, 1867, with the passing of the B ...
, the country's official national day.
Confederation is regarded as the creation of a kingdom in its own right and to have "successfully reconciled the physical absence of a geographically distant monarch with a continuing and pervasive presence through the medium of formal representatives and the manner and forms of legal and conventional rules and behaviour associated with British parliamentary and monarchical governance". Macdonald had spoken of "founding a great British monarchy" and wanted the newly created country to be called the ''Kingdom of Canada''. The Colonial Office
The Colonial Office was a government department of the Kingdom of Great Britain and later of the United Kingdom, first created in 1768 from the Southern Department to deal with colonial affairs in North America (particularly the Thirteen Colo ...
opposed the term ''kingdom'' as "premature" and "pretentious" and felt it might antagonize the United States. The term ''dominion
A dominion was any of several largely self-governance, self-governing countries of the British Empire, once known collectively as the ''British Commonwealth of Nations''. Progressing from colonies, their degrees of self-governing colony, colon ...
'' was chosen, instead, to indicate Canada's status as a self-governing polity of the British Empire, the first time it was used in reference to a country. When the ''British North America Act, 1867'', was passed in the Parliament in Westminster
Westminster is the main settlement of the City of Westminster in Central London, Central London, England. It extends from the River Thames to Oxford Street and has many famous landmarks, including the Palace of Westminster, Buckingham Palace, ...
, the Queen said to Macdonald, "I am very glad to see you on this mission ..It is a very important measure and you have all exhibited so much loyalty."
While the ''BNA Act'' eventually resulted in Canada having more autonomy than it had before, the country was still far from fully independent of the United Kingdom. Foreign policy remained in British hands, the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council
The Judicial Committee of the Privy Council (JCPC) is the highest court of appeal for the Crown Dependencies, the British Overseas Territories, some Commonwealth countries and a few institutions in the United Kingdom. Established on 14 August ...
remained Canada's highest court of appeal, and the constitution could be amended only in Britain. Gradually, Canada gained more autonomy; defence of British North America became a Canadian responsibility. According to the Supreme Court of Canada, Canadian "sovereignty was acquired in the period between its separate signature of the Treaty of Versailles in 1919 and the Statute of Westminster, 1931", which gave the country nearly full independence. It was only because the federal and provincial governments were unable to agree on a formula for amending the constitution that the power to do so remained with the British Parliament. Once that issue was resolved, the constitution was patriated when Elizabeth II
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; 21 April 19268 September 2022) was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until Death and state funeral of Elizabeth II, her death in 2022. ...
gave royal assent to the Canada Act, 1982.
The constitution of Canada
The Constitution of Canada () is the supreme law in Canada. It outlines Canada's system of government and the civil and human rights of those who are citizens of Canada and non-citizens in Canada. Its contents are an amalgamation of various ...
is made up of a number of codified acts and uncodified conventions; one of the principal documents is the ''Constitution Act, 1982
The ''Constitution Act, 1982'' () is a part of the Constitution of Canada.Formally enacted as Schedule B of the '' Canada Act 1982'', enacted by the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Section 60 of the ''Constitution Act, 1982'' states that t ...
'', which renamed the ''British North America Act, 1867'', to the ''Constitution Act, 1867
The ''Constitution Act, 1867'' ( 30 & 31 Vict. c. 3) (),''The Constitution Act, 1867'', 30 & 31 Victoria (U.K.), c. 3, http://canlii.ca/t/ldsw retrieved on 2019-03-14. originally enacted as the ''British North America Act, 1867'' (BNA Act), ...
''.''Constitution Act, 1982'', s. 53(1) and Schedule, Item 1./ref> The act also details how power is distributed in both the provincial and federal jurisdictions. Two of the most important sections are 91 and 92. Section 91 gives Parliament jurisdiction over banking, interest rates, criminal law, the postal system, and the armed forces. Section 92 gives the provinces jurisdiction over property, contracts and torts, local works, and general business. Still, federal and provincial law may occasionally interfere with each other, in which case federal law prevails.
Results
 Dominion elections were held in August and September, 1867, to elect the first
Dominion elections were held in August and September, 1867, to elect the first Parliament
In modern politics and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
. The governments of the Province of Canada, Nova Scotia and New Brunswick nominated the seventy-two individuals who would be named to the Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
, who were listed in the proclamation of Confederation (twenty-four each for Quebec and Ontario, twelve each for New Brunswick and Nova Scotia). They were called to the Senate by the governor general for the opening of the first Parliament.
The Anti-Confederation Party won 18 out of 19 federal Nova Scotia seats in September 1867, and in the Nova Scotia provincial election of 1868, 36 out of 38 seats in the legislature. For seven years, William Annand and Joseph Howe led the ultimately unsuccessful fight to convince British imperial authorities to release Nova Scotia from Confederation. The government was vocally against Confederation, contending it was no more than the annexation of the province to the pre-existing province of Canada.
Prior to the coming into effect of the ''Constitution Act, 1867'', there had been some concern regarding a potential "legislative vacuum" that would occur over the 15-month period between the prorogation of the Province of Canada's final Parliament in August 1866 and the opening of the now Dominion of Canada's first Parliament in November 1867. To prevent this, the ''Constitution Act, 1867'', provided for "continuance of existing laws" from the three colonies of Canada, Nova Scotia, and New Brunswick until new laws could be established in the Dominion. Thus, the "Dominion's financial systems, structures and actors were able to operate under the provisions of the old Province of Canada Acts" following confederation, and many institutions and organizations were continued and assumed "the same responsibilities for the new federal government that it had held as a provincial organization".
Joining Confederation
After the initial ''BNA Act'' in 1867,Manitoba
Manitoba is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada at the Centre of Canada, longitudinal centre of the country. It is Canada's Population of Canada by province and territory, fifth-most populous province, with a population ...
was established by an act of the Canadian Parliament on July 15, 1870, originally as an area of land much smaller than the current province. British Columbia joined Canada July 20, 1871, by an Imperial order-in-council enacted under the authority of the ''British North America Act''. The order-in-council incorporated the Terms of Union negotiated by the governments of Canada and British Columbia, including a commitment by the federal government to build a railway connecting British Columbia to the railway system of Canada within 10 years of union. Prince Edward Island (PEI) joined July 1, 1873, also by an Imperial order-in-council. One reason for joining was financial: PEI's economy was performing poorly and union would bring monetary benefits that would assist the province in avoiding bankruptcy. One of the Prince Edward Island Terms of Union was a guarantee by the federal government to operate a ferry
A ferry is a boat or ship that transports passengers, and occasionally vehicles and cargo, across a body of water. A small passenger ferry with multiple stops, like those in Venice, Italy, is sometimes referred to as a water taxi or water bus ...
link, a term deleted upon completion of the Confederation Bridge
The Confederation Bridge () is a box girder bridge carrying the Trans-Canada Highway across the Abegweit Passage of the Northumberland Strait, linking the province of Prince Edward Island with the mainland province of New Brunswick. Opened ...
in 1997. Alberta
Alberta is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Canada. It is a part of Western Canada and is one of the three Canadian Prairies, prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to its west, Saskatchewan to its east, t ...
and Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Western Canada. It is bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and to the south by the ...
were established September 1, 1905, by acts of the Canadian Parliament. Newfoundland joined on March 31, 1949, by an act of the Imperial Parliament, also with a ferry link guaranteed.
The Crown acquired Rupert's Land and the North-Western Territory from the Hudson's Bay Company in 1869 (though final payment to the Hudson's Bay Company did not occur until 1870), and then transferred jurisdiction to the Dominion on July 15, 1870, merging them and naming them North-West Territories
The Northwest Territories is a federal territory of Canada. At a land area of approximately and a 2021 census population of 41,070, it is the second-largest and the most populous of the three territories in Northern Canada. Its estimated pop ...
. In 1880, the British assigned all North American Arctic islands to Canada, right up to Ellesmere Island
Ellesmere Island (; ) is Canada's northernmost and List of Canadian islands by area, third largest island, and the List of islands by area, tenth largest in the world. It comprises an area of , slightly smaller than Great Britain, and the total ...
. From this vast swath of territory were created three provinces (Manitoba, Saskatchewan, Alberta) and two territories (Yukon Territory and North-West Territories, now Yukon and Northwest Territories), and two extensions each to Quebec, Ontario, and Manitoba. Later, the third territory of Nunavut was carved from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999. The Yukon territory was formed during the Klondike gold rush. People from all around Canada and the United States flocked to the area due to rumours of an easy way to get rich. The Canadian government sought to regulate this migration and tax gold findings, whether American or Canadian.
Below is a list of Canadian provinces and territories in the order in which they entered Confederation; territories are italicized. At formal events, representatives of the provinces and territories take Canadian order of precedence, precedence according to this ordering, except that provinces always precede territories. For provinces that entered on the same date, the order of precedence is based on the provinces' populations at the time they entered Confederation.
Legacy
The term ''confederation'' has entered into Canadian parlance both as a metaphor for the country and for the historical events that created it. It has therefore become one of the most common names for Canadian landmarks. Examples include Mount Confederation, Confederation Square, the Confederation Building (disambiguation), Confederation Building, Confederation Park (disambiguation), Confederation Park, Confederation Station (OC Transpo), Confederation Station, Confederation Heights, Confederation Bridge, and so on. This is similar to the American practices of naming things ''union'' and likewise the Australians with ''federation''. Indigenous communities were ignored in the process of Canadian confederation. As a result of Confederation, the Parliament and government of Canada assumed the responsibilities of their British counterparts in treaty dealings with the First Nations. The federal Parliament subsequently passed the ''Indian Act'' in 1876, which, in amended form, continues to govern Indigenous peoples. Confederation created conditions of colonialism, including resource grabbing, broken treaties, forced assimilation, patriarchy, and intergenerational trauma inflicted by the hegemony of the Canadian state on Indigenous nations that had been self-governing. As the 20th century progressed, attention to the conditions of Indigenous peoples in Canada increased, which included the granting of full voting rights in 1960. Treaty rights were enshrined in the Canadian constitution in 1982 and, in ''R. v. Sparrow, Sparrow v. The Queen'', the Supreme Court determined there exists a fiduciary Monarchy of Canada and the Indigenous peoples of Canada, affiliation between the Canadian Crown and Indigenous peoples in which the Crown is constitutionally charged with providing certain guarantees to the First Nations. Recognizing the principle of aboriginal title, a process of land claims settlements is ongoing. Created to resolve the effects of the residential school system, a Truth and Reconciliation Commission of Canada, Truth and Reconciliation Commission was struck to identify further measures to improve conditions.Confederation timeline
See also
* 150th anniversary of Canada * History of Canada * Territorial evolution of Canada * List of documents from the constitutional history of Canada * Acadian RenaissanceReferences
Bibliography
* * * * < * * * * *''Constitution Act, 1867''
* * .
Further reading
* Buckner, Phillip. "'British North America and a Continent in Dissolution': The American Civil War in the Making of Canadian Confederation." ''Journal of the Civil War Era'' 7.4 (2017): 512–540online
* Careless, J.M.C. "George Brown and Confederation", ''Manitoba Historical Society Transactions'', Series 3, Number 26, 1969–7
online
* Creighton, Donald Grant. ''The Road to Confederation: The Emergence of Canada, 1863–1867'' (1965) a standard histor
online
* Creighton, Donald Grant. ''John A. Macdonald: The Young Politician. Vol. 1'' (1952) vol 1 of biography of Macdonald * Gwyn, Richard. ''John A: The Man Who Made Us'' (2008) vol 1 of biography of Macdonald *Knox, Bruce A. "Conservative Imperialism 1858–1874: Bulwer Lytton, Lord Carnarvon, and Canadian Confederation." ''International History Review'' (1984) 6#3 pp: 333–357. * Martin, Ged. ''Britain and the origins of Canadian confederation, 1837–67'' (UBC Press, 1995). * Martin, Ged, ed. ''The Causes of Canadian confederation'' (Acadiensis Press, 1990). * Moore, Christopher. ''1867: How the Fathers Made a Deal'' (McClelland & Stewart, 2011) * Morton, William Lewis. ''The critical years: the union of British North America, 1857–1873'' (McClelland & Stewart, 1964) a standard history * Smith, Andrew. '' British Businessmen and Canadian Confederation Constitution-Making in an Era of Anglo-Globalization'' (McGill-Queen's University Press, 2008) * Smith, Andrew. "Toryism, Classical Liberalism, and Capitalism: The Politics of Taxation and the Struggle for Canadian Confederation." ''Canadian Historical Review'' 89#1 (2008): 1–25. * Smith, Jennifer. "Canadian confederation and the influence of American federalism." ''Canadian Journal of Political Science'' 21#3 (1988): 443–464. * Smith, Peter J. "The Ideological Origins of Canadian Confederation". ''Canadian Journal of Political Science'' 1987. 20#1 pp : 3–29. * Vronsky, Peter. ''Ridgeway: The American Fenian Invasion and the 1866 Battle That Made Canada'' (Penguin Canada, 2011) * Waite, Peter B. ''The life and times of Confederation, 1864–1867: politics, newspapers, and the union of British North America'' (Robin Brass Studio, 2001). * White, Walter Leroy, and W. C. Soderlund. ''Canadian Confederation: A Decision-making Analysis'' (McGill-Queen's Press-MQUP, 1979) * Wilson, David A. ''Thomas D'Arcy McGee: The Extreme Moderate, 1857–1868. Vol. 2'' (McGill-Queen's Press-MQUP, 2011)
Provinces and regions
* * * * * * * * * *Primary sources
* * * * *External links
*[https://web.archive.org/web/20111230022553/http://www.canadiana.ca/citm/themes/constitution/constitution12_e.html Canadiana: "On the Road to Confederation"]
McCord Museum: "Confederation: The Creation of Canada"
{{Authority control Canadian Confederation, 1840s in Canada 1850s in Canada 1860s in Canada 1867 in Canada Federalism in Canada National unifications Political history of Canada British North America Pre-Confederation Canada Post-Confederation Canada (1867–1914) 1867 establishments in Canada, * 1867 in Canadian law 1867 in politics 19th century in Canada