Commercial Crew Development on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Development of the  SpaceX's Crew Dragon Demo-1 2019 flight of Dragon 2 arrived at the International Space Station in March 2019 and returned via splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. After completion of its test series, a Crew Dragon spacecraft made its first operational Commercial Crew Program flight, SpaceX Crew-1. The flight launched on November 16, 2020. SpaceX has completed seven successful CCP flights with another, SpaceX Crew-8, currently in progress. It is contracted with NASA for fourteen operational flights total to the ISS.
The 2019 Boeing Orbital Flight Test of the CST-100 Starliner spacecraft failed to reach the ISS in December 2019. The second test flight,
SpaceX's Crew Dragon Demo-1 2019 flight of Dragon 2 arrived at the International Space Station in March 2019 and returned via splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. After completion of its test series, a Crew Dragon spacecraft made its first operational Commercial Crew Program flight, SpaceX Crew-1. The flight launched on November 16, 2020. SpaceX has completed seven successful CCP flights with another, SpaceX Crew-8, currently in progress. It is contracted with NASA for fourteen operational flights total to the ISS.
The 2019 Boeing Orbital Flight Test of the CST-100 Starliner spacecraft failed to reach the ISS in December 2019. The second test flight, 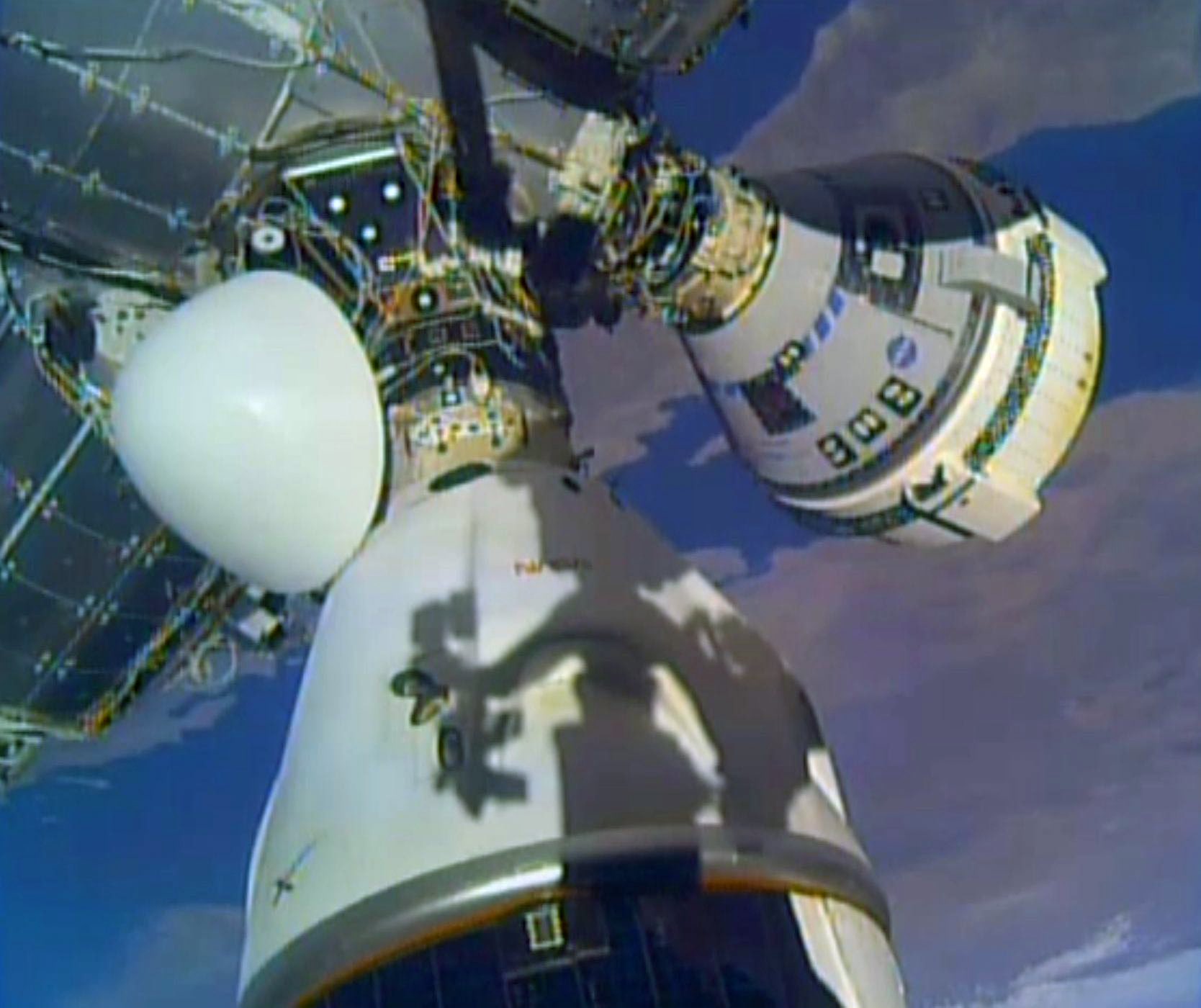
 Commercial Crew Development (CCDev 1) consisted of $50 million awarded in 2010 to five US companies to develop human spaceflight concepts and technologies. NASA awarded development funds to five companies under CCDev 1:
*
Commercial Crew Development (CCDev 1) consisted of $50 million awarded in 2010 to five US companies to develop human spaceflight concepts and technologies. NASA awarded development funds to five companies under CCDev 1:
*
 On April 18, 2011, NASA awarded nearly $270 million to four companies for developing U.S. vehicles that could fly astronauts after the Space Shuttle fleet's retirement.Dean, James
On April 18, 2011, NASA awarded nearly $270 million to four companies for developing U.S. vehicles that could fly astronauts after the Space Shuttle fleet's retirement.Dean, James
"NASA awards $270 million for commercial crew efforts"
space.com, April 18, 2011. Funded proposals: *
. ''moonandback.com'' spaceflight news, December 14, 2010, accessed December 27, 2010. Proposals selected without NASA funding: * United Launch Alliance: extend development work on human-rating the
 Commercial Crew integrated Capability (CCiCap) was originally called CCDev 3. For this phase of the program, NASA wanted proposals to be complete, end-to-end concepts of operation, including spacecraft, launch vehicles, launch services, ground and mission operations, and recovery. In September 2011, NASA released a draft request for proposals (RFP). The final RFP was released on February 7, 2012, with proposals due on March 23, 2012. The funded Space Act Agreements were awarded on August 3, 2012, and amended on August 15, 2013.
The selected proposals were announced August 3, 2012:
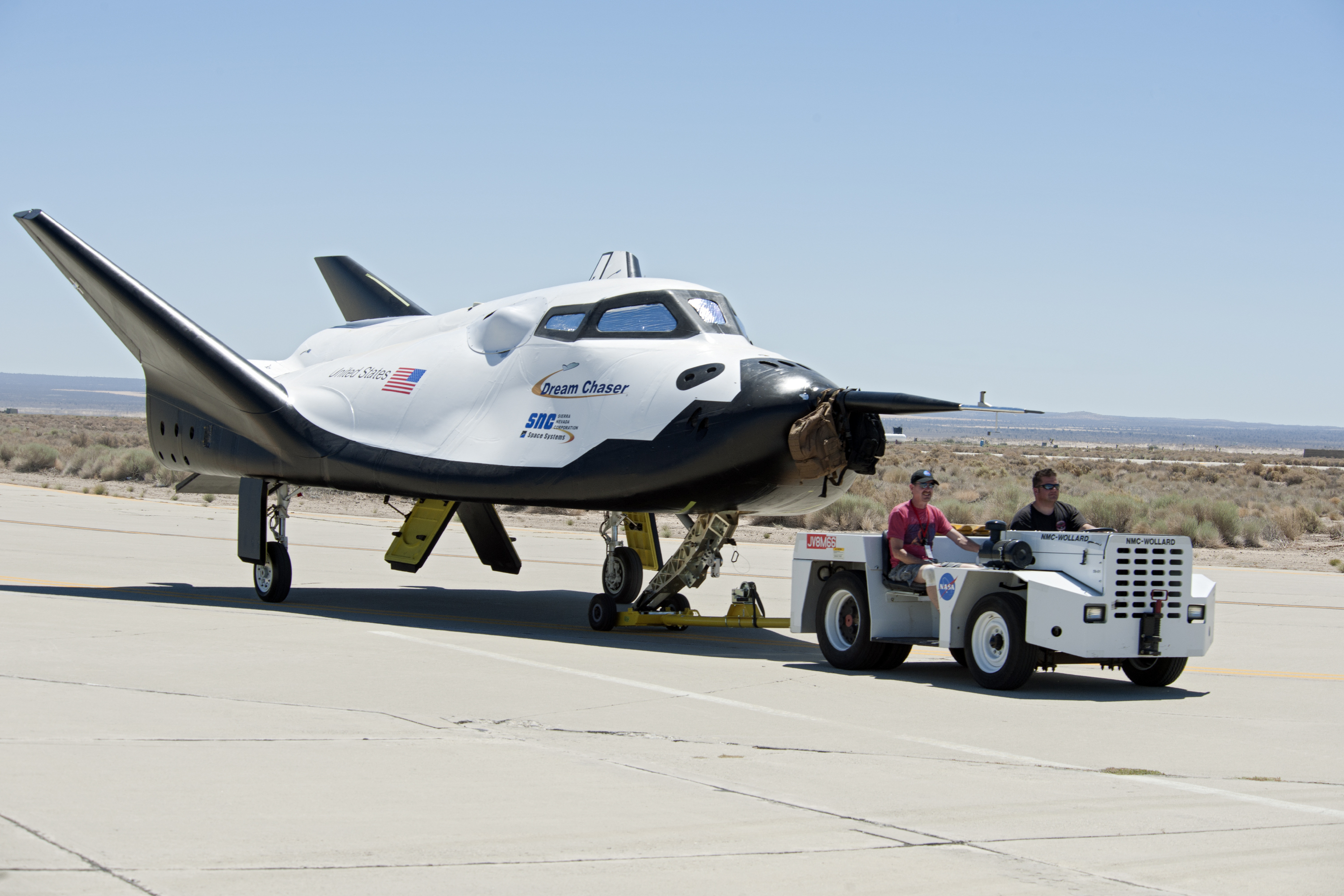
* Sierra Nevada Corporation: $212.5 million. Dream Chaser/
Commercial Crew integrated Capability (CCiCap) was originally called CCDev 3. For this phase of the program, NASA wanted proposals to be complete, end-to-end concepts of operation, including spacecraft, launch vehicles, launch services, ground and mission operations, and recovery. In September 2011, NASA released a draft request for proposals (RFP). The final RFP was released on February 7, 2012, with proposals due on March 23, 2012. The funded Space Act Agreements were awarded on August 3, 2012, and amended on August 15, 2013.
The selected proposals were announced August 3, 2012:
* Sierra Nevada Corporation: $212.5 million. Dream Chaser/

 The first flight of the Commercial Crew Program was planned to occur in 2015, but insufficient funding caused delays. For the fiscal year (FY) 2011 budget, US$500 million was requested for the CCDev program, but Congress granted only $270 million. For the FY 2012 budget, $850 million was requested and $406 million approved. For the FY 2013 budget, 830 million was requested and $488 million approved. For the FY 2014 budget, $821 million was requested and $696 million approved. In FY 2015, $848 million was requested and $805 million, or 95%, was approved. On November 14, 2019, NASA's inspector general published an auditing report listing per-seat prices of $90 million for Starliner and $55 million for Dragon Crew. With these, Boeing's price is higher than what NASA has paid the Russian space corporation, Roscosmos, for Soyuz spacecraft seats to fly US and partner-nation astronauts to the space station. The report also states that NASA agreed to pay an additional $287.2 million above Boeing's fixed prices to mitigate a perceived 18-month gap in ISS flights anticipated in 2019 and to ensure the contractor continued as a second commercial crew provider, without offering similar opportunities to SpaceX. On November 18, 2019, Boeing's Jim Chilton replied that the inspector general's report failed to list Starliner’s positive features and objected to the per seat pricing as they believe the cost is lower than $90 million given its cargo capacity. Boeing's reasoning for the extra funding was due to a later start to its development than SpaceX with comparable deadlines. Boeing also stated it committed to the program. The funding of all commercial crew contractors for each phase of the CCP program is as follows—CCtCap values are maxima and include six post-development operational flights for each vendor.
The first flight of the Commercial Crew Program was planned to occur in 2015, but insufficient funding caused delays. For the fiscal year (FY) 2011 budget, US$500 million was requested for the CCDev program, but Congress granted only $270 million. For the FY 2012 budget, $850 million was requested and $406 million approved. For the FY 2013 budget, 830 million was requested and $488 million approved. For the FY 2014 budget, $821 million was requested and $696 million approved. In FY 2015, $848 million was requested and $805 million, or 95%, was approved. On November 14, 2019, NASA's inspector general published an auditing report listing per-seat prices of $90 million for Starliner and $55 million for Dragon Crew. With these, Boeing's price is higher than what NASA has paid the Russian space corporation, Roscosmos, for Soyuz spacecraft seats to fly US and partner-nation astronauts to the space station. The report also states that NASA agreed to pay an additional $287.2 million above Boeing's fixed prices to mitigate a perceived 18-month gap in ISS flights anticipated in 2019 and to ensure the contractor continued as a second commercial crew provider, without offering similar opportunities to SpaceX. On November 18, 2019, Boeing's Jim Chilton replied that the inspector general's report failed to list Starliner’s positive features and objected to the per seat pricing as they believe the cost is lower than $90 million given its cargo capacity. Boeing's reasoning for the extra funding was due to a later start to its development than SpaceX with comparable deadlines. Boeing also stated it committed to the program. The funding of all commercial crew contractors for each phase of the CCP program is as follows—CCtCap values are maxima and include six post-development operational flights for each vendor.
Official NASA Commercial Crew Program page
* ttp://www.nasa.gov/exploration/commercial/document_library.html Commercial Crew & Cargo Document Library on NASA.gov
CCDev 1 Space Act agreements
Partners Mature Spacecraft Designs
NASA video update, January 14, 2014.
Boeing CCtCap Contract (redacted)
SpaceX CCtCap Contract (redacted)
{{NASA navbox Human spaceflight programs Space Act Agreement companies NASA programs Private spaceflight International Space Station
Commercial Crew Program
The Commercial Crew Program (CCP) provides Private spaceflight, commercially operated human spaceflight, crew transportation service to and from the International Space Station (ISS) under contract to NASA, conducting crew rotations between t ...
(CCDev) began in the second round of the program, which was rescoped from a smaller technology development program for human spaceflight
Human spaceflight (also referred to as manned spaceflight or crewed spaceflight) is spaceflight with a crew or passengers aboard a spacecraft, often with the spacecraft being operated directly by the onboard human crew. Spacecraft can also be ...
to a competitive development program that would produce the spacecraft to be used to provide crew transportation services to and from the International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is a large space station that was Assembly of the International Space Station, assembled and is maintained in low Earth orbit by a collaboration of five space agencies and their contractors: NASA (United ...
(ISS). To implement the program, NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
awarded a series of competitive fixed-price contracts to private vendors starting in 2011. Operational contracts to fly astronauts were awarded in September 2014 to SpaceX
Space Exploration Technologies Corp., commonly referred to as SpaceX, is an America, American space technology company headquartered at the SpaceX Starbase, Starbase development site in Starbase, Texas. Since its founding in 2002, the compa ...
and Boeing
The Boeing Company, or simply Boeing (), is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and product support s ...
, and NASA expected each company to complete development and achieve crew rating in 2017. Each company performed an uncrewed orbital test flight in 2019.
 SpaceX's Crew Dragon Demo-1 2019 flight of Dragon 2 arrived at the International Space Station in March 2019 and returned via splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. After completion of its test series, a Crew Dragon spacecraft made its first operational Commercial Crew Program flight, SpaceX Crew-1. The flight launched on November 16, 2020. SpaceX has completed seven successful CCP flights with another, SpaceX Crew-8, currently in progress. It is contracted with NASA for fourteen operational flights total to the ISS.
The 2019 Boeing Orbital Flight Test of the CST-100 Starliner spacecraft failed to reach the ISS in December 2019. The second test flight,
SpaceX's Crew Dragon Demo-1 2019 flight of Dragon 2 arrived at the International Space Station in March 2019 and returned via splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. After completion of its test series, a Crew Dragon spacecraft made its first operational Commercial Crew Program flight, SpaceX Crew-1. The flight launched on November 16, 2020. SpaceX has completed seven successful CCP flights with another, SpaceX Crew-8, currently in progress. It is contracted with NASA for fourteen operational flights total to the ISS.
The 2019 Boeing Orbital Flight Test of the CST-100 Starliner spacecraft failed to reach the ISS in December 2019. The second test flight, Boeing Orbital Flight Test 2
The Boeing Orbital Flight Test-2 (also known as Boe-OFT-2) was a repeat of Boeing's unsuccessful Boeing Orbital Flight Test, first Orbital Flight Test (Boe-OFT) of its Boeing Starliner, Starliner spacecraft. The uncrewed mission was part of NA ...
, occurred successfully in May 2022. Pending completion of its demonstration flights, Boeing is contracted to supply six operational flights to the ISS. The first group of astronauts was announced on August 3, 2018. The first Starliner crewed flight test launched on June 5, 2024. Starliner successfully docked with the station on June 6, 2024, after suffering several helium leaks and thruster malfunctions. Due to these issues Starliner’s return to earth was delayed initially to June 26, 2024, then indefinitely. On August 24, 2024 NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
administrator Bill Nelson
Clarence William Nelson II (born September 29, 1942) is an American politician, attorney, and former astronaut who served from 2001 to 2019 as a United States Senate, United States senator from Florida and from 2021 to 2025 as the Administrator ...
made the decision to send the Starliner crew back home on SpaceX’s Crew Dragon.

Requirements
Key high-level requirements for the Commercial Crew vehicles include: *Safely deliver and return four crew members and their equipment to theInternational Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is a large space station that was Assembly of the International Space Station, assembled and is maintained in low Earth orbit by a collaboration of five space agencies and their contractors: NASA (United ...
(ISS)
*Provide assured crew return in the event of an emergency
*Serve as a 24-hour safe haven in the event of an emergency
*Capable of remaining docked to the station for 210 days
Background
After the retirement of STS in 2011 and the cancellation of theConstellation program
The Constellation program (abbreviated CxP) was a crewed spaceflight program developed by NASA, the space agency of the United States, from 2005 to 2009. The major goals of the program were "completion of the International Space Station" and a " ...
, NASA had no domestic vehicles capable of launching astronauts to space. Artemis
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, Artemis (; ) is the goddess of the hunting, hunt, the wilderness, wild animals, transitions, nature, vegetation, childbirth, Kourotrophos, care of children, and chastity. In later tim ...
, NASA's next major human spaceflight initiative, was scheduled to launch an uncrewed qualification flight in 2016, with an Orion spacecraft atop a Space Launch System
The Space Launch System (SLS) is an American Super heavy-lift launch vehicle, super heavy-lift Expendable launch system, expendable launch vehicle used by NASA. As the primary launch vehicle of the Artemis program, Artemis Moon landing progra ...
(SLS) booster. The NASA had no human-qualified spacecraft available, and in any event SLS/Orion would be too expensive for routine flights to the ISS. In the meantime, NASA continued to send astronauts to the ISS on Soyuz
Soyuz is a transliteration of the Cyrillic text Союз (Russian language, Russian and Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, 'Union'). It can refer to any union, such as a trade union (''profsoyuz'') or the Soviet Union, Union of Soviet Socialist Republi ...
spacecraft seats purchased from Russia. The price varied over time, with the batch of seats from 2016 to 2017 costing $70.7 million per passenger per flight. Artemis continued to slip, with the first uncrewed test flight scheduled for 2022.
Development Program
The CCDev program was initiated to develop safe and reliable commercial ISS crew launch capabilities to replace the Soyuz flights. CCDev followedCommercial Orbital Transportation Services
Commercial Orbital Transportation Services (COTS) was a NASA program to spur the development of Private spaceflight, private spacecraft and launch vehicles for deliveries to the International Space Station (ISS). Launched in 2006, COTS successful ...
(COTS), an ISS commercial cargo program. CCDev contracts were issued for fixed-price, pay-for-performance milestones. CCDev was implemented in several phases. CCDev 1 contracts were for development of concepts and technologies. CCDev 2 contracts were for actual vehicle designs. CCiCap contracts were for designs of complete end-to-end crew transportation hardware and services. CPC phase 1 contracts were for the development of a full certification plan. Finally CCtCap contracts were awarded for actual demonstration of crewed transportation services, which included development, testing, and production of the required hardware followed by operational flights to the ISS.CCDev 1
 Commercial Crew Development (CCDev 1) consisted of $50 million awarded in 2010 to five US companies to develop human spaceflight concepts and technologies. NASA awarded development funds to five companies under CCDev 1:
*
Commercial Crew Development (CCDev 1) consisted of $50 million awarded in 2010 to five US companies to develop human spaceflight concepts and technologies. NASA awarded development funds to five companies under CCDev 1:
* Blue Origin
Blue Origin Enterprises, L.P. is an American space technology company headquartered in Kent, Washington. The company operates the suborbital New Shepard rocket and the heavy-lift New Glenn rocket. In addition to producing engines for its own ...
: $3.7M for a 'pusher' Launch Abort System (LAS) and composite pressure vessel
A pressure vessel is a container designed to hold gases or liquids at a pressure substantially different from the ambient pressure.
Construction methods and materials may be chosen to suit the pressure application, and will depend on the size o ...
s.
* Boeing
The Boeing Company, or simply Boeing (), is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and product support s ...
: $18M for development of the CST-100 Starliner
* Paragon Space Development Corporation: $1.4M for a plug-and-play environmental control and life support system (ECLSS) Air Revitalization System (ARS) Engineering Development Unit.
* Sierra Nevada Corporation: $20M for development of the Dream Chaser
* United Launch Alliance: $6.7M for an Emergency Detection System (EDS) for human-rating Atlas V
Atlas V is an expendable launch system and the fifth major version in the Atlas (rocket family), Atlas launch vehicle family. It was developed by Lockheed Martin and has been operated by United Launch Alliance (ULA) since 2006. Primarily used to ...
CCDev 2
 On April 18, 2011, NASA awarded nearly $270 million to four companies for developing U.S. vehicles that could fly astronauts after the Space Shuttle fleet's retirement.Dean, James
On April 18, 2011, NASA awarded nearly $270 million to four companies for developing U.S. vehicles that could fly astronauts after the Space Shuttle fleet's retirement.Dean, James"NASA awards $270 million for commercial crew efforts"
space.com, April 18, 2011. Funded proposals: *
Blue Origin
Blue Origin Enterprises, L.P. is an American space technology company headquartered in Kent, Washington. The company operates the suborbital New Shepard rocket and the heavy-lift New Glenn rocket. In addition to producing engines for its own ...
: $22 million. Technologies in support of a biconic nose cone design orbital vehicle, including launch abort system liquid oxygen
Liquid oxygen, sometimes abbreviated as LOX or LOXygen, is a clear cyan liquid form of dioxygen . It was used as the oxidizer in the first liquid-fueled rocket invented in 1926 by Robert H. Goddard, an application which is ongoing.
Physical ...
/liquid hydrogen
Liquid hydrogen () is the liquid state of the element hydrogen. Hydrogen is found naturally in the molecule, molecular H2 form.
To exist as a liquid, H2 must be cooled below its critical point (thermodynamics), critical point of 33 Kelvins, ...
engines.
* Sierra Nevada Corporation: $80 million. Dream Chaser
* SpaceX
Space Exploration Technologies Corp., commonly referred to as SpaceX, is an America, American space technology company headquartered at the SpaceX Starbase, Starbase development site in Starbase, Texas. Since its founding in 2002, the compa ...
: $75 million. Dragon 2 integrated launch abort system
* Boeing
The Boeing Company, or simply Boeing (), is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and product support s ...
: $92.3 million. Additional CST-100 Starliner developmentBoeing Submits Proposal for 2nd Round Of Commercial Crew Dev. ''moonandback.com'' spaceflight news, December 14, 2010, accessed December 27, 2010. Proposals selected without NASA funding: * United Launch Alliance: extend development work on human-rating the
Atlas V
Atlas V is an expendable launch system and the fifth major version in the Atlas (rocket family), Atlas launch vehicle family. It was developed by Lockheed Martin and has been operated by United Launch Alliance (ULA) since 2006. Primarily used to ...
* Alliant Techsystems
Alliant Techsystems Inc. (ATK) was an American Aerospace manufacturer, aerospace and arms industry, arms manufacturer headquartered in Arlington County, Virginia. The company operated across 22 states, Puerto Rico, and internationally. ATK reven ...
(ATK) and Astrium
Astrium was a European aerospace company and subsidiary of the European Aeronautic Defence and Space Company (EADS), headquartered in Paris. It designed, developed and manufactured civil and military space systems and provided related services ...
proposed development of Liberty
Liberty is the state of being free within society from oppressive restrictions imposed by authority on one's way of life, behavior, or political views. The concept of liberty can vary depending on perspective and context. In the Constitutional ...
. NASA was to share expertise and technology.
* Excalibur Almaz Inc. was developing a crewed system with modernized Soviet-era hardware intended for tourism flights to orbit. An unfunded Space Act Agreement to establish a framework to further develop EAI's spacecraft concept for low Earth orbit crew transportation.
Proposals not selected:
* Orbital Sciences
Orbital Sciences Corporation (commonly referred to as Orbital) was an American company specializing in the design, manufacture, and launch of small- and medium- class space and launch vehicle systems for commercial, military and other governmen ...
proposed the Prometheus
In Greek mythology, Prometheus (; , , possibly meaning "forethought")Smith"Prometheus". is a Titans, Titan. He is best known for defying the Olympian gods by taking theft of fire, fire from them and giving it to humanity in the form of technol ...
lifting-body spaceplane vehicle
* Paragon Space Development Corporation proposed additional development of the Commercial Crew Transport-Air Revitalization System.
* t/Space proposed a reusable eight-person crew or cargo transfer spacecraft
*United Space Alliance
United Space Alliance (USA) was a spaceflight operations company. USA was established in August 1995 as joint venture of Rockwell International and Lockheed Martin, primarily to support operations of the Space Shuttle. The sale of Rockwell's a ...
proposed to commercially fly the two remaining Space Shuttle vehicles.
CCiCap
 Commercial Crew integrated Capability (CCiCap) was originally called CCDev 3. For this phase of the program, NASA wanted proposals to be complete, end-to-end concepts of operation, including spacecraft, launch vehicles, launch services, ground and mission operations, and recovery. In September 2011, NASA released a draft request for proposals (RFP). The final RFP was released on February 7, 2012, with proposals due on March 23, 2012. The funded Space Act Agreements were awarded on August 3, 2012, and amended on August 15, 2013.
The selected proposals were announced August 3, 2012:
* Sierra Nevada Corporation: $212.5 million. Dream Chaser/
Commercial Crew integrated Capability (CCiCap) was originally called CCDev 3. For this phase of the program, NASA wanted proposals to be complete, end-to-end concepts of operation, including spacecraft, launch vehicles, launch services, ground and mission operations, and recovery. In September 2011, NASA released a draft request for proposals (RFP). The final RFP was released on February 7, 2012, with proposals due on March 23, 2012. The funded Space Act Agreements were awarded on August 3, 2012, and amended on August 15, 2013.
The selected proposals were announced August 3, 2012:
* Sierra Nevada Corporation: $212.5 million. Dream Chaser/Atlas V
Atlas V is an expendable launch system and the fifth major version in the Atlas (rocket family), Atlas launch vehicle family. It was developed by Lockheed Martin and has been operated by United Launch Alliance (ULA) since 2006. Primarily used to ...
* SpaceX: $440 million. Dragon 2/Falcon 9
Falcon 9 is a Reusable launch system#Partial reusable launch systems, partially reusable, two-stage-to-orbit, medium-lift launch vehicle designed and manufactured in the United States by SpaceX. The first Falcon 9 launch was on June 4, 2010, an ...
* Boeing: $460 million. CST-100 Starliner/Atlas V
CPC phase 1
The first phase of the Certification Products Contract (CPC) involved the development of a certification plan with engineering standards, tests, and analyses. Winners of funding of phase 1 of the CPC, announced on December 10, 2012, were: * Sierra Nevada Corporation: $10 million * SpaceX: $9.6 million * Boeing: $9.9 millionCCtCap – crew flights awarded
The Commercial Crew Transportation Capability (CCtCap) is the second phase of the CPC and included the final development, testing and verifications to allow crewed demonstration flights to the ISS. NASA issued the draft CCtCap contract's Request For Proposals (RFP) on July 19, 2013, with a response date of August 15, 2013. On September 16, 2014, NASA announced that Boeing and SpaceX had received contracts to provide crewed launch services to the ISS. Boeing could receive up to US$4.2 billion, while SpaceX could receive up to US$2.6 billion. Dragon was the less expensive proposal, but NASA's William H. Gerstenmaier considered theBoeing Starliner
The Boeing Starliner (or CST-100) is a spacecraft designed to transport crew to and from the International Space Station (ISS) and other low-Earth-orbit destinations. Developed by Boeing under NASA's Commercial Crew Program (CCP), it consists o ...
proposal the stronger of the two. In November 2019 NASA published a first cost per seat estimate: US$55 million for SpaceX's Dragon and US$90 million for Boeing's Starliner. Boeing was also granted an additional $287.2 million above the fixed price contract. Seats on Soyuz had an average cost of US$80 million. However, adjusting for the additional cargo carried by Boeing's Starliner inside its crew capsule, the adjusted cost per seat figure is approximately $70 million, which is still higher than SpaceX's Crew Dragon even if the Dragon does not carry the equivalent of a fifth passenger in cargo. Both the CST-100 Starliner and Crew Dragon
Dragon 2 is a class of partially reusable spacecraft developed, manufactured, and operated by the American space company SpaceX for flights to the International Space Station (ISS) and private spaceflight missions. The spacecraft, which consi ...
were to fly an uncrewed flight, then a crewed certification flight, then up to six operational flights to the ISS.
Timeline

Ongoing delays
The first flight of the Commercial Crew Program was planned to occur in 2015, but insufficient funding caused delays. As the spacecraft entered the testing and production phase, technical issues also caused delays, especially the parachute system, propulsion, and the launch abort system of both capsules.Starliner 2018 valve issue
In July 2018, a test anomaly was reported in which there was a hypergolic propellant leak due to several faulty abort system valves. Consequentially, the first unpiloted orbital mission was delayed to April 2019, and the first crew launch rescheduled to August 2019. In March 2019,Reuters
Reuters ( ) is a news agency owned by Thomson Reuters. It employs around 2,500 journalists and 600 photojournalists in about 200 locations worldwide writing in 16 languages. Reuters is one of the largest news agencies in the world.
The agency ...
reported these test flights had been delayed by at least three months, and in April 2019 Boeing announced that the unpiloted orbital mission was scheduled for August 2019.
Crew Dragon explosion
On April 20, 2019, an issue arose during a static fire test of Crew Dragon. The accident destroyed the capsule which was planned to be used for the In-Flight Abort Test (IFAT). SpaceX confirmed that the capsule exploded. NASA stated that the explosion would delay the planned in-flight abort and crewed orbital tests.Starliner Orbital Flight Test failure
During the first orbital flight test of Starliner in December 2019, the spacecraft reached orbit but was unable to dock with ISS due to a critical software error. Subsequent analysis revealed a second critical software error that could cause the service module to collide with the capsule after separation during the de-orbiting sequence.Crew Dragon crewed flight
On May 30, 2020, two astronauts were launched to the ISS with a Crew Dragon as part of Crew Dragon Demo-2. The end and safe landing of Demo-2 on August 2, 2020, marked the first splashdown in 45 years for NASA astronauts since the firstApollo–Soyuz
Apollo–Soyuz was the first crewed international Space exploration, space mission, carried out jointly by the United States and the Soviet Union in July 1975. Millions of people around the world watched on television as an American Apollo comm ...
U.S./U.S.S.R international space mission in July 1975, as well as the first splashdown of a crew spacecraft in the Gulf of Mexico.
Starliner 2021 valve issue
Shortly before the scheduled launch of the second orbital flight test in August 2021, routine pre-launch testing showed that thirteen valves in the propulsion system were inoperable and the launch was scrubbed. The problem required extensive analysis that was still ongoing in October 2021, and NASA and Boeing estimated that a new launch date would be scheduled in the first half of 2022.Starliner Orbital Flight Test 2
Boeing Starliner Spacecraft 2 launched as part of theBoeing Orbital Flight Test 2
The Boeing Orbital Flight Test-2 (also known as Boe-OFT-2) was a repeat of Boeing's unsuccessful Boeing Orbital Flight Test, first Orbital Flight Test (Boe-OFT) of its Boeing Starliner, Starliner spacecraft. The uncrewed mission was part of NA ...
, on May 19, 2022. It successfully docked on May 21, where it stayed for four days. On May 25, the spacecraft undocked and landed successfully in the White Sands Missile Range
White Sands Missile Range (WSMR) is a United States Army military testing area and firing range located in the US state of New Mexico. The range was originally established in 1941 as the Alamogordo Bombing and Gunnery Range, where the Trinity t ...
.
Starliner Crewed Flight Test
Days before a planned launch, Boeing announced in June 2023 that it would delay the Crewed Flight Test indefinitely due to issues with the parachute system and wiring harnesses. The mission entails flying a crew of two NASA astronauts to theInternational Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is a large space station that was Assembly of the International Space Station, assembled and is maintained in low Earth orbit by a collaboration of five space agencies and their contractors: NASA (United ...
for a one-week test flight. The Crewed Flight Test successfully launched on June 5, 2024. The Starliner spacecraft docked to the International Space Station the next day after troubleshooting issues with the thrusters on the vehicle. After more thruster testing, both in space and using another Starliner vehicle on Earth, NASA announced on August 24, 2024, that the two astronauts on the mission, Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams, would not return to Earth on Starliner, but instead fly back on Crew Dragon
Dragon 2 is a class of partially reusable spacecraft developed, manufactured, and operated by the American space company SpaceX for flights to the International Space Station (ISS) and private spaceflight missions. The spacecraft, which consi ...
with the SpaceX Crew-9 mission. The Starliner spacecraft successfully landed on the September 7, 2024. NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
confirmed on October 15, 2024 that Starliner would not be used for the following two crew rotation missions. In October 2024, Boeing
The Boeing Company, or simply Boeing (), is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and product support s ...
started exploring part of it’s space business.
Funding
 The first flight of the Commercial Crew Program was planned to occur in 2015, but insufficient funding caused delays. For the fiscal year (FY) 2011 budget, US$500 million was requested for the CCDev program, but Congress granted only $270 million. For the FY 2012 budget, $850 million was requested and $406 million approved. For the FY 2013 budget, 830 million was requested and $488 million approved. For the FY 2014 budget, $821 million was requested and $696 million approved. In FY 2015, $848 million was requested and $805 million, or 95%, was approved. On November 14, 2019, NASA's inspector general published an auditing report listing per-seat prices of $90 million for Starliner and $55 million for Dragon Crew. With these, Boeing's price is higher than what NASA has paid the Russian space corporation, Roscosmos, for Soyuz spacecraft seats to fly US and partner-nation astronauts to the space station. The report also states that NASA agreed to pay an additional $287.2 million above Boeing's fixed prices to mitigate a perceived 18-month gap in ISS flights anticipated in 2019 and to ensure the contractor continued as a second commercial crew provider, without offering similar opportunities to SpaceX. On November 18, 2019, Boeing's Jim Chilton replied that the inspector general's report failed to list Starliner’s positive features and objected to the per seat pricing as they believe the cost is lower than $90 million given its cargo capacity. Boeing's reasoning for the extra funding was due to a later start to its development than SpaceX with comparable deadlines. Boeing also stated it committed to the program. The funding of all commercial crew contractors for each phase of the CCP program is as follows—CCtCap values are maxima and include six post-development operational flights for each vendor.
The first flight of the Commercial Crew Program was planned to occur in 2015, but insufficient funding caused delays. For the fiscal year (FY) 2011 budget, US$500 million was requested for the CCDev program, but Congress granted only $270 million. For the FY 2012 budget, $850 million was requested and $406 million approved. For the FY 2013 budget, 830 million was requested and $488 million approved. For the FY 2014 budget, $821 million was requested and $696 million approved. In FY 2015, $848 million was requested and $805 million, or 95%, was approved. On November 14, 2019, NASA's inspector general published an auditing report listing per-seat prices of $90 million for Starliner and $55 million for Dragon Crew. With these, Boeing's price is higher than what NASA has paid the Russian space corporation, Roscosmos, for Soyuz spacecraft seats to fly US and partner-nation astronauts to the space station. The report also states that NASA agreed to pay an additional $287.2 million above Boeing's fixed prices to mitigate a perceived 18-month gap in ISS flights anticipated in 2019 and to ensure the contractor continued as a second commercial crew provider, without offering similar opportunities to SpaceX. On November 18, 2019, Boeing's Jim Chilton replied that the inspector general's report failed to list Starliner’s positive features and objected to the per seat pricing as they believe the cost is lower than $90 million given its cargo capacity. Boeing's reasoning for the extra funding was due to a later start to its development than SpaceX with comparable deadlines. Boeing also stated it committed to the program. The funding of all commercial crew contractors for each phase of the CCP program is as follows—CCtCap values are maxima and include six post-development operational flights for each vendor.
Test Missions
Each system is required to successfully complete abort testing, an uncrewed orbital flight test, and a crewed orbital flight test to meet NASA's requirements for human-rating certification. The agency did allow the companies to propose how they would complete the required tests, with Boeing opting not to perform an in-flight abort test, which NASA approved. Crew Dragon completed its flight tests in mid-2020 and began operational flights in November 2020. NASA will decide after September 2024 if Boeing has met its certification requirements after the problems experienced on its crew flight test.Operational missions
See also
*Commercial Orbital Transportation Services
Commercial Orbital Transportation Services (COTS) was a NASA program to spur the development of Private spaceflight, private spacecraft and launch vehicles for deliveries to the International Space Station (ISS). Launched in 2006, COTS successful ...
* Commercial Resupply Services
Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) are a series of flights awarded by NASA for the delivery of cargo and supplies to the International Space Station (ISS) on commercially operated spacecraft.
The first phase of CRS contracts (CRS-1) were sign ...
* NASA Docking System
The NASA Docking System is NASA's implementation of the International Docking System Standard (IDSS), an international spacecraft docking standard promulgated by the International Space Station Multilateral Coordination Board. NDS is a Docking an ...
* Private spaceflight
Private spaceflight is any spaceflight development that is not conducted by a government agency, such as NASA or ESA.
During the early decades of the Space Age, the government space agencies of the Soviet Union and United States pionee ...
* Review of United States Human Space Flight Plans Committee
The Review of United States Human Space Flight Plans Committee, better known as the HSF Committee, Augustine Commission, or Augustine Committee, was a group convened by NASA at the request of the Office of Science and Technology Policy (OSTP), to ...
* Space Shuttle successors
References
External links
Official NASA Commercial Crew Program page
* ttp://www.nasa.gov/exploration/commercial/document_library.html Commercial Crew & Cargo Document Library on NASA.gov
CCDev 1 Space Act agreements
Partners Mature Spacecraft Designs
NASA video update, January 14, 2014.
Boeing CCtCap Contract (redacted)
SpaceX CCtCap Contract (redacted)
{{NASA navbox Human spaceflight programs Space Act Agreement companies NASA programs Private spaceflight International Space Station