Comb Polymers on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In polymer chemistry, graft polymers are segmented copolymers with a linear backbone of one composite and randomly distributed branches of another composite. The picture labeled "graft polymer" shows how grafted chains of species B are covalently bonded to polymer species A. Although the side chains are structurally distinct from the main chain, the individual grafted chains may be homopolymers or copolymers.
Graft polymers have been synthesized for many decades and are especially used as impact resistant materials, thermoplastic elastomers, compatibilizers, or 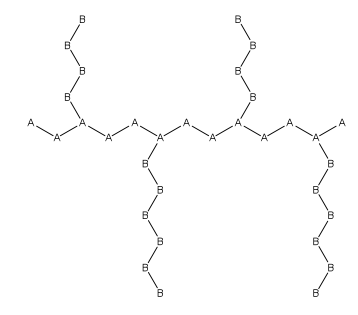


 High impact polystyrene (HIPS) was discovered by Charles F. Fryling in 1961. HIPS is a low cost, plastic material that is easy to fabricate and often used for low strength structural applications when impact resistance, machinability, and low cost are required. Its major applications include machined prototypes, low-strength structural components, housings, and covers. In order to produce the graft polymer, polybutadiene ( rubber) or any similar elastomeric polymer is dissolved in styrene and polymerized. This reaction allows for two simultaneous polymerizations, that of styrene to polystyrene and that of the graft polymerization of styrene-rubber. During commercial use, it can be prepared by graft copolymerization with additional polymer to give the product specific characteristics.
The advantages of HIPS includes:
*FDA compliant
*Good impact resistance
*Excellent machinability
*Good dimensional stability
*Easy to paint and glue
*Low cost
*Excellent aesthetic qualities
High impact polystyrene (HIPS) was discovered by Charles F. Fryling in 1961. HIPS is a low cost, plastic material that is easy to fabricate and often used for low strength structural applications when impact resistance, machinability, and low cost are required. Its major applications include machined prototypes, low-strength structural components, housings, and covers. In order to produce the graft polymer, polybutadiene ( rubber) or any similar elastomeric polymer is dissolved in styrene and polymerized. This reaction allows for two simultaneous polymerizations, that of styrene to polystyrene and that of the graft polymerization of styrene-rubber. During commercial use, it can be prepared by graft copolymerization with additional polymer to give the product specific characteristics.
The advantages of HIPS includes:
*FDA compliant
*Good impact resistance
*Excellent machinability
*Good dimensional stability
*Easy to paint and glue
*Low cost
*Excellent aesthetic qualities
emulsifier
An emulsion is a mixture of two or more liquids that are normally immiscible (unmixable or unblendable) owing to liquid-liquid phase separation. Emulsions are part of a more general class of two-phase systems of matter called colloids. Altho ...
s for the preparation of stable blends or alloys. One of the better-known examples of a graft polymer is a component used in high impact polystyrene, consisting of a polystyrene backbone with polybutadiene
Polybutadiene utadiene rubber BRis a synthetic rubber. Polybutadiene rubber is a polymer formed from the polymerization of the monomer 1,3-butadiene. Polybutadiene has a high resistance to wear and is used especially in the manufacture of tir ...
grafted chains.

General properties
Graft copolymers are a branched copolymer where the components of the side chain are structurally different than that of the main chain. Graft copolymers containing a larger quantity of side chains are capable of wormlike conformation, compact molecular dimension, and notable chain end effects due to their confined and tight fit structures. The preparation of graft copolymers has been around for decades. All synthesis methods can be employed to create general physical properties of graft copolymers. They can be used for materials that are impact resistant, and are often used as thermoplastics elastomers, compatibilizers or emulsifiers for the preparation of stable blends or alloys. Generally, grafting methods for copolymer synthesis results in materials that are more thermostable than their homopolymer counterparts. There are three methods of synthesis, grafting to, grafting from, and grafting through, that are used to construct a graft polymer.Synthesis methods
There are many different approaches to synthesizing graft copolymers. Usually they employ familiar polymerization techniques that are commonly used such asatom transfer radical polymerization Atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) is an example of a reversible-deactivation radical polymerization. Like its counterpart, ATRA, or atom transfer radical addition, ATRP is a means of forming a carbon-carbon bond with a transition metal cat ...
(ATRP), ring-opening metathesis polymerization
Ring-opening metathesis polymerization (ROMP) is a type of olefin metathesis chain-growth polymerization. The driving force of the reaction is relief of ring strain in cyclic olefins (e.g. norbornene or cyclopentene). A variety of heterogeneous ...
(ROMP), anionic and cationic polymerizations, and free radical living polymerization. Some other less common polymerization include radiation-induced polymerization, ring-opening olefin metathesis polymerization, polycondensation reactions, and iniferter-induced polymerization.

Grafting to
The grafting to method involves the use of a backbone chain with functional groups A that are distributed randomly along the chain.Hadjichristidis, N., S. Pispas, H. Iatrou, and D. J. Lohse. "Graft Copolymers." Graft Copolymers. John Wiley and Sons Inc, 15 July 2002. Web. 14 Feb. 2014. The formation of the graft copolymer originates from the coupling reaction between the functional backbone and the end-groups of the branches that are reactive. These coupling reactions are made possible by modifying the backbone chemically. Common reaction mechanisms used to synthesize these copolymers include free- radical polymerization, anionic polymerization, atom-transfer radical-polymerization, and living polymerization techniques. Copolymers that are prepared with the grafting-to method often utilize anionic polymerization techniques. This method uses a coupling reaction of the electrophilic groups of the backbone polymer and the propagation site of an anionic living polymer. This method would not be possible without the generation of a backbone polymer that has reactive groups. This method has become more popular with the rise ofclick chemistry
In chemical synthesis, click chemistry is a class of biocompatible small molecule reactions commonly used in bioconjugation, allowing the joining of substrates of choice with specific biomolecules. Click chemistry is not a single specific reaction ...
. A high yield chemical reaction called atom transfer nitroxide radical coupling chemistry is for the grafting-to method for polymerization.
Grafting from
In the grafting-from method, the macromolecular backbone is chemically modified in order to introduce active sites capable of initiating functionality. The initiating sites can be incorporated by copolymerization, can be incorporated in a post-polymerization reaction, or can already be a part of the polymer. If the number of active sites along the backbone participates in the formation of one branch, then the number of chains grafted to the macromolecule can be controlled by the number of active sites. Even though the number of grafted chains can be controlled, there may be a difference in the lengths of each grafted chain due to kinetic and steric hindrance effects. Grafting from reactions have been conducted from polyethylene, polyvinylchloride, and polyisobutylene. Different techniques such as anionic grafting, cationic grafting, atom-transfer radical polymerization, andfree-radical polymerization
In polymer chemistry, free-radical polymerization (FRP) is a method of polymerization by which a polymer forms by the successive addition of free-radical building blocks (repeat units). Free radicals can be formed by a number of different mechanis ...
have been used in the synthesis of grafting from copolymers.
Graft copolymers that are employed with the grafting-from method are often synthesized with ATRP reactions and anionic and cationic grafting techniques.
Grafting through
The grafting through, also known as the macromonomer method, is one of the simpler ways of synthesizing a graft polymer with well defined side chains. Typically a monomer of a lower molecular weight is copolymerized with free radicals with an acrylate functionalized macromonomer. The ratio of monomer to macromonomer molar concentrations as well as their copolymerization behavior determines the number of chains that are grafted. As the reaction proceeds, the concentrations of monomer to macromonomer change causing random placement of branches and formation of graft copolymers with different number of branches. This method allows for branches to be added heterogeneously or homogeneously based on the reactivity ratio of the terminal functional group on the macromolecular to the monomer. The difference in distribution of grafts has significant effects on the physical properties of the grafted copolymer. Polyethylene, polysiloxanes and poly(ethylene oxide) are all macromonomers that have been incorporated in apolystyrene
Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or foamed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. It is an inexpensive resin per unit weight. It is a ...
or poly(methyl acrylate)
Poly(methyl acrylate) (PMA) is a family of organic polymers with the formula ()n. It is a synthetic acrylate polymer derived from methyl acrylate monomer. The polymers are colorless. This homopolymer is far less important than copolymers derived ...
backbone.
The macromonomer (grafting through) method can be employed using any known polymerization technique. Living polymerizations give special control over the molecular weight, molecular weight distribution, and chain-end functionalization.
Applications
Graft copolymers became widely studied due to their increased number of applications like in drug delivery vehicles, surfactants,water filtration
A water filter removes impurities by lowering contamination of water using a fine physical barrier, a chemical process, or a biological process. Filters cleanse water to different extents, for purposes such as: providing agricultural irrigation ...
, rheology modifiers, etc. It is their unique structures relative to other copolymers such as alternating, periodic, statistical, and block copolymers.
Some common applications of graft copolymers include:
*Membranes for the separation of gases or liquids
* Hydrogels
*Drug deliverers
* Thermoplastic elastomers
*Compatibilizers for polymer blends
*Polymeric emulsifiers
*Impact resistant plastics

High impact polystyrene
New properties as a result of grafting
By grafting polymers onto polymer backbones, the final grafted copolymers gain new properties from their parent polymers. Specifically, cellulose graft copolymers have various different applications that are dependent on the structure of the polymer grafted onto the cellulose. Some of the new properties that cellulose gains from different monomers grafted onto it include: * Absorption of water *Improvedelasticity
Elasticity often refers to:
*Elasticity (physics), continuum mechanics of bodies that deform reversibly under stress
Elasticity may also refer to:
Information technology
* Elasticity (data store), the flexibility of the data model and the cl ...
*Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic character
*Ion-exchange
Ion exchange is a reversible interchange of one kind of ion present in an insoluble solid with another of like charge present in a solution surrounding the solid with the reaction being used especially for softening or making water demineralised, ...
*Dye adsorption capabilities
*Heat Resistance
*Thermosensitivity
* pH sensitivity
* Antibacterial effect
These properties give new application to the ungrafted cellulose polymers that include:
*Medical body fluid absorbent materials
*Enhanced moisture absorbing ability in fabrics
*Permselective membranes
*Stronger nucleating properties than ungrafted cellulose, and adsorption of hazardous contaminants like heavy metal ions or dyes from aqueous solutions by temperature swing adsorption
*Sensors and optical materials
*Reducing agents for various carbonyl compounds
References
{{reflist Polymers