Coldrum Stones on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Coldrum Long Barrow, also known as the Coldrum Stones and the Adscombe Stones, is a
 Across Western Europe, the Early Neolithic marked the first period in which humans built monumental structures in the landscape. These structures included
Across Western Europe, the Early Neolithic marked the first period in which humans built monumental structures in the landscape. These structures included  The Medway long barrows all conformed to the same general design plan, and are all aligned on an east to west axis. Each had a stone chamber at the eastern end of the mound, and they each probably had a stone facade flanking the entrance. They had internal heights of up to , making them taller than most other chambered long barrows in Britain. The chambers were constructed from
The Medway long barrows all conformed to the same general design plan, and are all aligned on an east to west axis. Each had a stone chamber at the eastern end of the mound, and they each probably had a stone facade flanking the entrance. They had internal heights of up to , making them taller than most other chambered long barrows in Britain. The chambers were constructed from
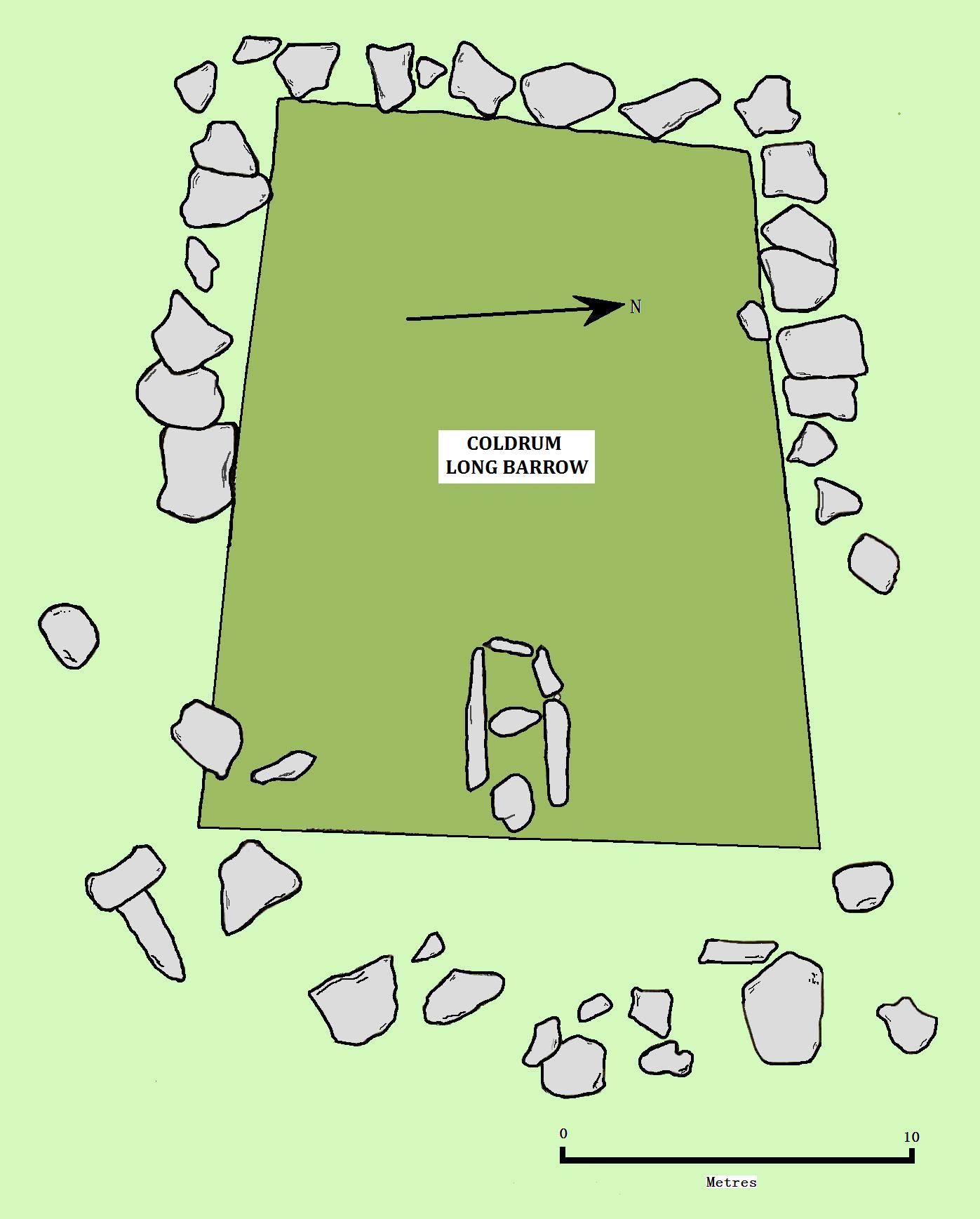 The Coldrum Long Barrow originally consisted of a sarsen stone chamber, covered by a low earthen mound, which was bounded by prostrate slabs. As such, Ashbee asserted that the monument could be divided into three particular features: the chamber, the barrow, and the sarsen stone surround. It had been built using about 50 stones. The barrow is sub-rectangular in plan, and about in length. At its broader, eastern end, where the chamber is located, the monument measures , while at the narrower, western end, it is in breadth. As such, the barrow is a "truncated wedge-shape".
The megalithic builders responsible for the Coldrum Stones positioned it on the top of a small ridge adjacent to the North Downs, and constructed it facing eastward, towards the River Medway. It is located on the edge of a large
The Coldrum Long Barrow originally consisted of a sarsen stone chamber, covered by a low earthen mound, which was bounded by prostrate slabs. As such, Ashbee asserted that the monument could be divided into three particular features: the chamber, the barrow, and the sarsen stone surround. It had been built using about 50 stones. The barrow is sub-rectangular in plan, and about in length. At its broader, eastern end, where the chamber is located, the monument measures , while at the narrower, western end, it is in breadth. As such, the barrow is a "truncated wedge-shape".
The megalithic builders responsible for the Coldrum Stones positioned it on the top of a small ridge adjacent to the North Downs, and constructed it facing eastward, towards the River Medway. It is located on the edge of a large
 The inner chamber measures in length, and in width, although it was potentially much larger when originally constructed. The chamber's internal height would have been at least . In its current state, the
northern side of the chamber is made up of two slabs. One is long, deep, and thick;
the other is long, nearly deep, and thick. Conversely, the chamber's southern side consists of a single slab, measuring in length, in depth, and in thickness at its eastern end.
The western end of the chamber is closed off with a slab measuring about wide, with a thickness of and a depth of around . A collapsed, broken slab lies at the chamber's opening, eastern end. It is also possible that a largely rectangular slab at the bottom of the slope had once been part of the chamber's eastern end. Excavation has revealed that flint masonry was used to pack around the chamber and support its sarsens; 20th-century renovation has seen this largely replaced with cement, allowing the stones to continue standing upright.
It is possible that there was a facade in front of the chamber, as is evident at other chambered tombs in Britain, such as
The inner chamber measures in length, and in width, although it was potentially much larger when originally constructed. The chamber's internal height would have been at least . In its current state, the
northern side of the chamber is made up of two slabs. One is long, deep, and thick;
the other is long, nearly deep, and thick. Conversely, the chamber's southern side consists of a single slab, measuring in length, in depth, and in thickness at its eastern end.
The western end of the chamber is closed off with a slab measuring about wide, with a thickness of and a depth of around . A collapsed, broken slab lies at the chamber's opening, eastern end. It is also possible that a largely rectangular slab at the bottom of the slope had once been part of the chamber's eastern end. Excavation has revealed that flint masonry was used to pack around the chamber and support its sarsens; 20th-century renovation has seen this largely replaced with cement, allowing the stones to continue standing upright.
It is possible that there was a facade in front of the chamber, as is evident at other chambered tombs in Britain, such as
 Keith believed that the crania he examined displayed similar features to one another, suggesting that this meant that they all belonged to "one family—or several families united by common descent." Similar observations have been made regarding the crania from other long barrows in Britain. The osteoarchaeologists Martin Smith and Megan Brickley cautioned that this did not necessarily mean that all of the individuals in any given barrow were members of a single family group, for such shared cranial traits would also be consistent with "a population that was still relatively small and scattered", in which most people were interrelated.
Wysocki's team noted that in all but one case, the fracture morphologies of the bones are consistent with dry-bone breakage.
Three of the skulls displayed evidence that they had experienced violence; a probable adult female had an unhealed injury on the left
Keith believed that the crania he examined displayed similar features to one another, suggesting that this meant that they all belonged to "one family—or several families united by common descent." Similar observations have been made regarding the crania from other long barrows in Britain. The osteoarchaeologists Martin Smith and Megan Brickley cautioned that this did not necessarily mean that all of the individuals in any given barrow were members of a single family group, for such shared cranial traits would also be consistent with "a population that was still relatively small and scattered", in which most people were interrelated.
Wysocki's team noted that in all but one case, the fracture morphologies of the bones are consistent with dry-bone breakage.
Three of the skulls displayed evidence that they had experienced violence; a probable adult female had an unhealed injury on the left
 Cut-marks were identified on some of the bones (two
Cut-marks were identified on some of the bones (two
 Pagans sometimes visit the site alone or in pairs, there to
Pagans sometimes visit the site alone or in pairs, there to
 In 1857, the antiquarian J. M. Kemble excavated at the site with the help of the Reverend Larking, providing a report of their findings to the Central Committee of the
In 1857, the antiquarian J. M. Kemble excavated at the site with the help of the Reverend Larking, providing a report of their findings to the Central Committee of the
 In his 1924 publication dealing with Kent, the archaeologist
In his 1924 publication dealing with Kent, the archaeologist
Coldrum Long Barrow
at the National Trust website
Coldrum Long Barrow
at The Megalithic Portal
Coldrum Long Barrow
at The Modern Antiquarian {{Long Barrows in Britain Archaeological sites in Kent Barrows in the United Kingdom Buildings and structures in Kent History of Kent Megalithic monuments in England National Trust properties in Kent Neo-druidism in Britain Religion in Kent Stone Age sites in Kent Tonbridge and Malling
chambered long barrow
Long barrows are a style of monument constructed across Western Europe in the fifth and fourth millennia BCE, during the Early Neolithic period. Typically constructed from earth and either timber or stone, those using the latter material repres ...
located near the village of Trottiscliffe
Trottiscliffe ( ) is an English village in the county of Kent about north west of West Malling.
It is colloquially known as ''Trosley'' after Trosley Country Park at the top of the North Downs, which was once part of the Trosley Towers Est ...
in the south-eastern English county of Kent
Kent is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South East England. It is bordered by Essex across the Thames Estuary to the north, the Strait of Dover to the south-east, East Sussex to the south-west, Surrey to the west, and Gr ...
. Probably constructed in the fourth millennium BCE, during Britain's Early Neolithic period, today it survives only in a state of ruin
Ruins () are the remains of a civilization's architecture. The term refers to formerly intact structures that have fallen into a state of partial or total disrepair over time due to a variety of factors, such as lack of maintenance, deliberate ...
.
Archaeologists
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, ...
have established that the monument was built by pastoralist communities shortly after the introduction of agriculture
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ...
to Britain from continental Europe. Part of an architectural tradition of long barrow building that was widespread across Neolithic Europe, the Coldrum Stones belong to a localised regional variant of barrows produced in the vicinity of the River Medway
The River Medway is a river in South East England. It rises in the High Weald AONB, High Weald, West Sussex and flows through Tonbridge, Maidstone and the Medway conurbation in Kent, before emptying into the Thames Estuary near Sheerness, a to ...
, now known as the Medway Megaliths. Of these, it is in the best surviving condition. It lies near to both Addington Long Barrow and Chestnuts Long Barrow on the western side of the river. Two further surviving long barrows, Kit's Coty House and Little Kit's Coty House
Little Kit's Coty House, also known as Lower Kit's Coty House and the Countless Stones, is a chambered long barrow located near to the village of Aylesford, Kent, Aylesford in the southeastern English county of Kent. Constructed ''circa'' 4000 B ...
, as well as possible survivals such as the Coffin Stone and White Horse Stone, are located on the Medway's eastern side.
Built out of earth and around fifty local sarsen
Sarsen stones are silicification, silicified sandstone blocks found extensively across southern England on the Salisbury Plain and the Marlborough Downs in Wiltshire; in Kent; and in smaller quantities in Berkshire, Essex, Oxfordshire, Dorset, an ...
-stone megalith
A megalith is a large stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. More than 35,000 megalithic structures have been identified across Europe, ranging geographically f ...
s, the long barrow consisted of a sub-rectangular earthen tumulus
A tumulus (: tumuli) is a mound of Soil, earth and Rock (geology), stones raised over a grave or graves. Tumuli are also known as barrows, burial mounds, mounds, howes, or in Siberia and Central Asia as ''kurgans'', and may be found through ...
enclosed by kerb-stones. Within the eastern end of the tumulus was a stone chamber, into which human remains were deposited on at least two separate occasions during the Early Neolithic. Osteoarchaeological analysis of these remains has shown them to be those of at least seventeen individuals, a mixture of men, women, and children. At least one of the bodies had been dismembered before burial, potentially reflecting a funerary tradition of excarnation
In archaeology and anthropology, the term excarnation (also known as defleshing) refers to the practice of removing the flesh and organs of the dead before burial. Excarnation may be achieved through natural means, such as leaving a dead body exp ...
and secondary burial
The secondary burial (German: ''Nachbestattung'' or ''Sekundärbestattung''), or “double funeral”Duday, Henri, et al. ''The Archaeology of the Dead: Lectures in Archaeothanatology''. United Kingdom, Oxbow Books, 2009. (not to be confused with ...
. As with other barrows, Coldrum has been interpreted as a tomb to house the remains of the dead, perhaps as part of a belief system involving ancestor veneration
The veneration of the dead, including one's ancestors, is based on love and respect for the deceased. In some cultures, it is related to beliefs that the dead have a continued existence, and may possess the ability to influence the fortune of t ...
, although archaeologists have suggested that it may also have had further religious, ritual, and cultural connotations and uses.
After the Early Neolithic, the long barrow fell into a state of ruined dilapidation, perhaps experiencing deliberate destruction in the Late Medieval period, either by Christian
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a Monotheism, monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the wo ...
iconoclasts or treasure hunters. In local folklore
Folklore is the body of expressive culture shared by a particular group of people, culture or subculture. This includes oral traditions such as Narrative, tales, myths, legends, proverbs, Poetry, poems, jokes, and other oral traditions. This also ...
, the site became associated with the burial of a prince and the countless stones
The countless stones is a motif that appears in English and Welsh folklore. It is associated with various megalithic monuments, including chambered long barrows from the Early Neolithic and the stones circles of the Late Neolithic and Early Bro ...
motif. The ruin attracted the interest of antiquarian
An antiquarian or antiquary () is an aficionado or student of antiquities or things of the past. More specifically, the term is used for those who study history with particular attention to ancient artefacts, archaeological and historic si ...
s in the 19th century, while archaeological excavation
In archaeology, excavation is the exposure, processing and recording of archaeological remains. An excavation site or "dig" is the area being studied. These locations range from one to several areas at a time during a project and can be condu ...
took place in the early 20th. In 1926, ownership was transferred to heritage charity the National Trust
The National Trust () is a heritage and nature conservation charity and membership organisation in England, Wales and Northern Ireland.
The Trust was founded in 1895 by Octavia Hill, Sir Robert Hunter and Hardwicke Rawnsley to "promote the ...
. Open without charge to visitors all year around, the stones are the site of a rag tree, a May Day
May Day is a European festival of ancient origins marking the beginning of summer, usually celebrated on 1 May, around halfway between the Northern Hemisphere's March equinox, spring equinox and midsummer June solstice, solstice. Festivities ma ...
morris dance
Morris dancing is a form of English folklore, English folk dance. It is based on rhythmic stepping and the execution of choreographed figures by a group of dancers in costume, usually wearing bell pads on their shins, their shoes or both. A ban ...
, and various modern Pagan
Modern paganism, also known as contemporary paganism and neopaganism, spans a range of new religious movements variously influenced by the Paganism, beliefs of pre-modern peoples across Europe, North Africa, and the Near East. Despite some comm ...
rituals.
Name and location
The Coldrum Stones are named after a nearby farm, Coldrum Lodge, which has since been demolished. The monument lies in a "rather isolated site" north-east of the nearby village ofTrottiscliffe
Trottiscliffe ( ) is an English village in the county of Kent about north west of West Malling.
It is colloquially known as ''Trosley'' after Trosley Country Park at the top of the North Downs, which was once part of the Trosley Towers Est ...
, in the south-eastern English county of Kent
Kent is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South East England. It is bordered by Essex across the Thames Estuary to the north, the Strait of Dover to the south-east, East Sussex to the south-west, Surrey to the west, and Gr ...
. The site is also positioned about from a prehistoric track known as the Pilgrims' Way
A pilgrims' way or pilgrim way is a standard route that pilgrims take when they go on a pilgrimage in order to reach their destination – usually a holy site or place of worship. These sites may be towns or cities of special significance such a ...
. The tomb can be reached along a pathway known as Coldrum Lane, which is accessible only on foot. The nearest car park to Coldrum Lane can be found off Pinesfield Lane in Trottiscliffe. The village of Addington is located
away.
Context
The Early Neolithic was a revolutionary period of British history. Between 4500 and 3800 BCE, it saw a widespread change in lifestyle as the communities living in theBritish Isles
The British Isles are an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner Hebrides, Inner and Outer Hebr ...
adopted agriculture
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ...
as their primary form of subsistence, abandoning the hunter-gatherer
A hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living in a community, or according to an ancestrally derived Lifestyle, lifestyle, in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local naturally occurring sources, esp ...
lifestyle that had characterised the preceding Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Ancient Greek language, Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic i ...
period. This came about through contact with continental Europe
Continental Europe or mainland Europe is the contiguous mainland of Europe, excluding its surrounding islands. It can also be referred to ambiguously as the European continent, – which can conversely mean the whole of Europe – and, by som ...
an societies; it is unclear to what extent this can be attributed to an influx of migrants or to indigenous Mesolithic Britons adopting agricultural technologies from the continent. The region of modern Kent would have been key for the arrival of continental European settlers and visitors, because of its position on the estuary of the River Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the The Isis, River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the Longest rivers of the United Kingdom, s ...
and its proximity to the continent.
Britain was then largely forested; widespread forest clearance did not occur in Kent until the Late Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
(c.1000 to 700 BCE). Environmental data from the vicinity of the White Horse Stone, a putatively prehistoric monolith
A monolith is a geological feature consisting of a single massive stone or rock, such as some mountains. Erosion usually exposes the geological formations, which are often made of very hard and solid igneous or metamorphic rock. Some monolit ...
near the River Medway
The River Medway is a river in South East England. It rises in the High Weald AONB, High Weald, West Sussex and flows through Tonbridge, Maidstone and the Medway conurbation in Kent, before emptying into the Thames Estuary near Sheerness, a to ...
, supports the idea that the area was still largely forested in the Early Neolithic, covered by a woodland of oak, ash, hazel/alder and amygdaloideae
Amygdaloideae is a subfamily within the flowering plant family Rosaceae. It was formerly considered by some authors to be separate from Rosaceae, and the family names Prunaceae and Amygdalaceae have been used. Reanalysis from 2007 has shown that ...
. Throughout most of Britain, there is little evidence of cereal or permanent dwellings from this period, leading archaeologists to believe that the island's Early Neolithic economy was largely pastoral
The pastoral genre of literature, art, or music depicts an idealised form of the shepherd's lifestyle – herding livestock around open areas of land according to the seasons and the changing availability of water and pasture. The target au ...
, relying on herding cattle, with people living a nomadic or semi-nomadic life.
Medway Megaliths
 Across Western Europe, the Early Neolithic marked the first period in which humans built monumental structures in the landscape. These structures included
Across Western Europe, the Early Neolithic marked the first period in which humans built monumental structures in the landscape. These structures included chambered long barrow
Long barrows are a style of monument constructed across Western Europe in the fifth and fourth millennia BCE, during the Early Neolithic period. Typically constructed from earth and either timber or stone, those using the latter material repres ...
s, rectangular or oval earthen tumuli
A tumulus (: tumuli) is a mound of Soil, earth and Rock (geology), stones raised over a grave or graves. Tumuli are also known as barrows, burial mounds, mounds, howes, or in Siberia and Central Asia as ''kurgans'', and may be found through ...
which had a chamber built into one end. Some of these chambers were constructed out of timber, while others were built using large stones, now known as "megalith
A megalith is a large stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. More than 35,000 megalithic structures have been identified across Europe, ranging geographically f ...
s". These long barrows often served as tombs, housing the physical remains of the dead within their chamber. Individuals were rarely buried alone in the Early Neolithic, instead being interred in collective burials with other members of their community. These chambered tombs were built all along the Western European seaboard during the Early Neolithic, from southeastern Spain up to southern Sweden, taking in most of the British Isles; the architectural tradition was introduced to Britain from continental Europe in the first half of the fourth millennium BCE. Although there are stone buildings—like Göbekli Tepe
Göbekli Tepe (, ; Kurdish: or , 'Wish Hill') is a Neolithic archaeological site in Upper Mesopotamia (''al-Jazira'') in modern-day Turkey. The settlement was inhabited from around to at least , during the Pre-Pottery Neolithic. It is famou ...
in modern Turkey—which predate them, the chambered long barrows constitute humanity's first widespread tradition of construction using stone.
Although now all in a ruinous state and not retaining their original appearance, at the time of construction the Medway Megaliths would have been some of the largest and most visually imposing Early Neolithic funerary monuments in Britain. Grouped along the River Medway as it cuts through the North Downs
The North Downs are a ridge of chalk hills in south east England that stretch from Farnham in Surrey to the White Cliffs of Dover in Kent. Much of the North Downs comprises two Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty, Areas of Outstanding Natural Be ...
, they constitute the most southeasterly group of megalithic monuments in the British Isles, and the only megalithic group in eastern England. The archaeologists Brian Philp and Mike Dutto deemed the Medway Megaliths to be "some of the most interesting and well known" archaeological sites in Kent, while the archaeologist Paul Ashbee described them as "the most grandiose and impressive structures of their kind in southern England".
The Medway Megaliths can be divided into two separate clusters: one to the west of the River Medway and the other on Blue Bell Hill
Blue Bell Hill is a chalk hill between Maidstone and Rochester in the English county of Kent. It overlooks the River Medway and is part of the North Downs. Settlements on the hill include the Walderslade suburb of Chatham and the villages o ...
to the east, with the distance between the two clusters measuring at between and . The western group includes Coldrum Long Barrow, Addington Long Barrow, and the Chestnuts Long Barrow. The eastern group consists of Smythe's Megalith, Kit's Coty House, and Little Kit's Coty House
Little Kit's Coty House, also known as Lower Kit's Coty House and the Countless Stones, is a chambered long barrow located near to the village of Aylesford, Kent, Aylesford in the southeastern English county of Kent. Constructed ''circa'' 4000 B ...
, while various stones on the eastern side of the river, most notably the Coffin Stone and White Horse Stone, may also have been parts of such structures. It is not known if they were all built at the same time, or whether they were constructed in succession, while similarly it is not known if they each served the same function or whether there was a hierarchy in their usage.
 The Medway long barrows all conformed to the same general design plan, and are all aligned on an east to west axis. Each had a stone chamber at the eastern end of the mound, and they each probably had a stone facade flanking the entrance. They had internal heights of up to , making them taller than most other chambered long barrows in Britain. The chambers were constructed from
The Medway long barrows all conformed to the same general design plan, and are all aligned on an east to west axis. Each had a stone chamber at the eastern end of the mound, and they each probably had a stone facade flanking the entrance. They had internal heights of up to , making them taller than most other chambered long barrows in Britain. The chambers were constructed from sarsen
Sarsen stones are silicification, silicified sandstone blocks found extensively across southern England on the Salisbury Plain and the Marlborough Downs in Wiltshire; in Kent; and in smaller quantities in Berkshire, Essex, Oxfordshire, Dorset, an ...
, a dense, hard, and durable stone that occurs naturally throughout Kent, having formed out of sand from the Eocene
The Eocene ( ) is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (Ma). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes ...
epoch. Early Neolithic builders would have selected blocks from the local area, and then transported them to the site of the monument to be erected.
These common architectural features among the Medway Megaliths indicate a strong regional cohesion with no direct parallels elsewhere in the British Isles. Nevertheless, as with other regional groupings of Early Neolithic long barrows—such as the Cotswold-Severn group in south-western Britain—there are also various idiosyncrasies in the different monuments, such as Coldrum's rectilinear shape, the Chestnut Long Barrow's facade, and the long, thin mounds at Addington and Kit's Coty. These variations might have been caused by the tombs being altered and adapted over the course of their use; in this scenario, the monuments would be composite structures.
The people who built these monuments were probably influenced by pre-existing tomb-shrines that they were already aware of. Whether those people had grown up locally, or moved into the Medway area from elsewhere is not known. Based on a stylistic analysis of their architectural designs, the archaeologist Stuart Piggott
Stuart Ernest Piggott, (28 May 1910 – 23 September 1996) was a British archaeologist, best known for his work on prehistoric Wessex.
Early life
Piggott was born in Petersfield, Hampshire, the son of G. H. O. Piggott, and was educated ...
thought that the plan behind the Medway Megaliths had originated in the area around the Low Countries
The Low Countries (; ), historically also known as the Netherlands (), is a coastal lowland region in Northwestern Europe forming the lower Drainage basin, basin of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta and consisting today of the three modern "Bene ...
, while fellow archaeologist Glyn Daniel
Glyn Edmund Daniel (23 April 1914 – 13 December 1986) was a Welsh scientist and archaeologist who taught at Cambridge University, where he specialised in the European Neolithic period. He was appointed Disney Professor of Archaeology in ...
instead believed that the same evidence showed an influence from Scandinavia. John H. Evans instead suggested an origin in Germany, and Ronald F. Jessup thought that their origins could be seen in the Cotswold-Severn megalithic group. Ashbee noted that their close clustering in the same area was reminiscent of the megalithic tomb-shrine traditions of continental Northern Europe, and emphasised that the Medway Megaliths were a regional manifestation of a tradition widespread across Early Neolithic Europe. He nevertheless stressed that a precise place of origin was "impossible to indicate" with the available evidence.
Design and construction
 The Coldrum Long Barrow originally consisted of a sarsen stone chamber, covered by a low earthen mound, which was bounded by prostrate slabs. As such, Ashbee asserted that the monument could be divided into three particular features: the chamber, the barrow, and the sarsen stone surround. It had been built using about 50 stones. The barrow is sub-rectangular in plan, and about in length. At its broader, eastern end, where the chamber is located, the monument measures , while at the narrower, western end, it is in breadth. As such, the barrow is a "truncated wedge-shape".
The megalithic builders responsible for the Coldrum Stones positioned it on the top of a small ridge adjacent to the North Downs, and constructed it facing eastward, towards the River Medway. It is located on the edge of a large
The Coldrum Long Barrow originally consisted of a sarsen stone chamber, covered by a low earthen mound, which was bounded by prostrate slabs. As such, Ashbee asserted that the monument could be divided into three particular features: the chamber, the barrow, and the sarsen stone surround. It had been built using about 50 stones. The barrow is sub-rectangular in plan, and about in length. At its broader, eastern end, where the chamber is located, the monument measures , while at the narrower, western end, it is in breadth. As such, the barrow is a "truncated wedge-shape".
The megalithic builders responsible for the Coldrum Stones positioned it on the top of a small ridge adjacent to the North Downs, and constructed it facing eastward, towards the River Medway. It is located on the edge of a large lynchet
A lynchet or linchet is an Terrace (earthworks), earth terrace found on the side of a hill. Lynchets are a feature of ancient field systems of the British Isles. They are commonly found in vertical rows and more commonly referred to as "strip lyn ...
scarp, although it is difficult to ascertain what views would have been possible from the monument at the time of construction, due to a lack of information on how densely forested the vicinity was. If the area was not highly wooded, then 360° views of the surrounding landscape would have been possible. The monument's axis points toward both the North Downs and the Medway Valley, which is similar to the other Medway Megaliths. The archaeologist Sian Killick suggested that the Coldrum Long Barrow might have been built within view of a nearby settlement, and that this "may have been a key factor in the experience of ceremonies and rituals taking place at the tombs and may also have defined a link between the tomb builders and the landscape."
Coldrum Long Barrow is comparatively isolated from the other Medway Megaliths; in this it is unique, given that the other surviving examples are clustered into two groups. It is possible that another chambered tomb was located nearby; a razed, elongated earthen mound with an east–west orientation is located in a hollow at the foot of the downs just under a quarter of a mile north of the Coldrum Stones. It may be that this represents the remnants of another such monument which has had its stones removed or buried. Several large sarsens south of the Coldrums might represent the remnants of a further such tomb, since destroyed.
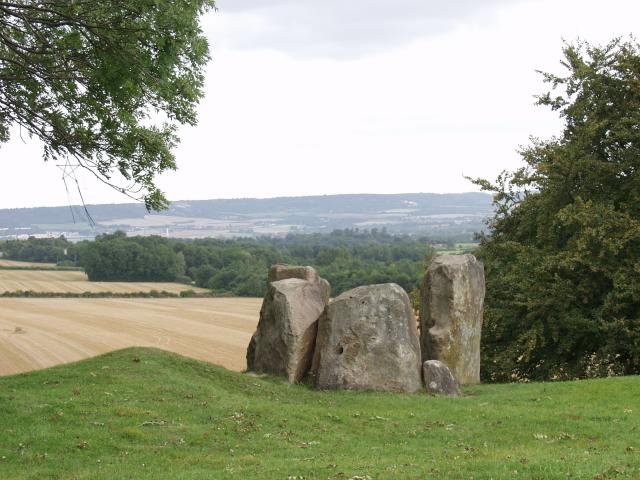
The chamber
 The inner chamber measures in length, and in width, although it was potentially much larger when originally constructed. The chamber's internal height would have been at least . In its current state, the
northern side of the chamber is made up of two slabs. One is long, deep, and thick;
the other is long, nearly deep, and thick. Conversely, the chamber's southern side consists of a single slab, measuring in length, in depth, and in thickness at its eastern end.
The western end of the chamber is closed off with a slab measuring about wide, with a thickness of and a depth of around . A collapsed, broken slab lies at the chamber's opening, eastern end. It is also possible that a largely rectangular slab at the bottom of the slope had once been part of the chamber's eastern end. Excavation has revealed that flint masonry was used to pack around the chamber and support its sarsens; 20th-century renovation has seen this largely replaced with cement, allowing the stones to continue standing upright.
It is possible that there was a facade in front of the chamber, as is evident at other chambered tombs in Britain, such as
The inner chamber measures in length, and in width, although it was potentially much larger when originally constructed. The chamber's internal height would have been at least . In its current state, the
northern side of the chamber is made up of two slabs. One is long, deep, and thick;
the other is long, nearly deep, and thick. Conversely, the chamber's southern side consists of a single slab, measuring in length, in depth, and in thickness at its eastern end.
The western end of the chamber is closed off with a slab measuring about wide, with a thickness of and a depth of around . A collapsed, broken slab lies at the chamber's opening, eastern end. It is also possible that a largely rectangular slab at the bottom of the slope had once been part of the chamber's eastern end. Excavation has revealed that flint masonry was used to pack around the chamber and support its sarsens; 20th-century renovation has seen this largely replaced with cement, allowing the stones to continue standing upright.
It is possible that there was a facade in front of the chamber, as is evident at other chambered tombs in Britain, such as West Kennet Long Barrow
The West Kennet Long Barrow, also known as South Long Barrow, is a chambered long barrow near the village of Avebury in the south-western English county of Wiltshire. Probably constructed in the thirty-seventh century BC, during Britain's Early ...
and Wayland's Smithy
Wayland's Smithy is an Early Neolithic chambered long barrow located near the village of Ashbury in the south-central English county of Oxfordshire. The barrow is believed to have been completed around 3430 BCE by pastoral communities shortl ...
. It is also possible that there was a portal stone atop the chamber, as was apparent at Kit's Coty House and Lower Kit's Coty House. Many of the larger slabs of stone that have fallen down the slope on the eastern end of the monument may have been parts of this facade or portal.
The mound and kerb-stones
The earthen mound that once covered the tomb is now visible only as an undulation approximately in height. In the 19th century, the mound was higher on the western end of the tomb, although during the 1920s this was removed by excavation to reveal the sarsens beneath. It is probable that in the Early Neolithic, the mound had a quarry ditch surrounding it, and it is inside this ditch that the kerb-stones now sit. The kerb-stones around the tomb display some patterning; those on the northern side are mostly rectilinear, while those on the southern side are smaller and largely irregular in shape. It is probable that there was an ancillary dry-stone wall constructed using blocks ofironstone
Ironstone is a sedimentary rock, either deposited directly as a ferruginous sediment or created by chemical replacement, that contains a substantial proportion of an iron ore compound from which iron (Fe) can be smelted commercially.
Not to be c ...
from the geological Folkestone beds, as is evident at Chestnuts Long Barrow. Given that such blocks of stone rarely occur naturally, it may have been quarried.
A concave line of abrasion and polishing can be found both on one of the central kerb-stones on the western end of the monument and on a kerb-stone on the south-east of the monument. These have been attributed to the sharpening of flint and other stone axe-blades on these sarsens. It is possible that these tools were sharpened for use in cutting and carving the timber levers and struts which would have been used in erecting the stones and constructing the tomb. Similar evidence for the sharpening of tools has been found at West Kennet Long Barrow, as well as later prehistoric monuments such as Stonehenge
Stonehenge is a prehistoric Megalith, megalithic structure on Salisbury Plain in Wiltshire, England, west of Amesbury. It consists of an outer ring of vertical sarsen standing stones, each around high, wide, and weighing around 25 tons, to ...
.
Meaning and purpose
Britain's Early Neolithic communities placed greater emphasis on the ritual burial of the dead than their Mesolithic forebears. Archaeologists have suggested that this is because Early Neolithic Britons adhered to an ancestor cult that venerated the spirits of the dead, believing that they could intercede with the forces of nature for the benefit of their living descendants. The archaeologist Robin Holgate stressed that rather than simply being tombs, the Medway Megaliths were "communal monuments fulfilling a social function for the communities who built and used them". Thus, it has been suggested that Early Neolithic people entered into the tombs—which doubled astemple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a place of worship, a building used for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. By convention, the specially built places of worship of some religions are commonly called "temples" in Engli ...
s or shrine
A shrine ( "case or chest for books or papers"; Old French: ''escrin'' "box or case") is a sacred space">-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ...: ''escri ...
s—to perform rituals honouring the dead and requesting their assistance. For this reason, the historian Ronald Hutton
Ronald Edmund Hutton (born 19 December 1953) is an Indian-born English historian specialising in early modern Britain, British folklore, pre-Christian religion, and modern paganism. A professor at the University of Bristol, Hutton has writte ...
termed these monuments "tomb-shrines" to reflect their dual purpose.
In Britain, these tombs were typically located on prominent hills and slopes overlooking the landscape, perhaps at the junction between different territories. The archaeologist Caroline Malone
Caroline Ann Tuke Malone (born 1957) is a British academic and archaeologist. She was Professor of Prehistory at Queen's University, Belfast from 2013 and is now emeritus professor.
Education
Malone graduated with a Bachelor of Arts (BA) de ...
noted that the tombs would have served as one of various landscape markers that conveyed information on "territory, political allegiance, ownership, and ancestors". Many archaeologists have subscribed to the idea that these tomb-shrines were territorial markers between different tribes; others have argued that such markers would be of little use to a nomadic herding society. Instead it has been suggested that they represent markers along herding pathways. The archaeologist Richard Bradley suggested that the construction of these monuments reflects an attempt to mark control and ownership over the land, thus reflecting a change in mindset brought about by the transition from the hunter-gatherer Mesolithic to the pastoralist Early Neolithic. Others have suggested that these monuments were built on sites already deemed sacred by Mesolithic hunter-gatherers.
Human remains
Within the chamber were placed human remains, which have been discovered and removed at intervals during the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. Early twentieth century excavation found two separate deposits of bone, each buried atop a stone slab, one higher than the other. Also buried within the chamber were flint tools and small quantities of pottery.Demographics
Ashbee suggested that—taking into account both its size and comparisons with other long barrows, such as Fussell's Lodge—the Coldrum tomb could have housed the remains of over a hundred individuals. Excavations conducted in the early 20th century have led to the methodical discovery and removal of what was believed to be the remains of twenty-two humans. These remains were examined by Sir Arthur Keith, the conservator of the museum at theRoyal College of Surgeons
The Royal College of Surgeons is an ancient college (a form of corporation) established in England to regulate the activity of surgeons. Derivative organisations survive in many present and former members of the Commonwealth. These organisations ...
. He published his results in 1913, in a paper largely concerned with discerning racial characteristics of the bodies. He ended his paper with the conclusion that "the people of pre-Christian Kent were physically not very different from the Kentish man of the Christian period".
In the early 21st century, these bones were re-analysed by a team led by the forensic taphonomist Michael Wysocki, the results of which were published in 2013. Wysocki's team conducted "osteological analysis, Bayesian modelling of radiocarbon dates, and carbon and nitrogen stable isotope analysis" in order to discover more about the "demography, burial practices, diet and subsistence, and chronology of the Coldrum population". Disputing earlier conclusions, their report stated that the minimum number of individuals was seventeen. These were identified as probably belonging to nine adults (probably five males and four females), two sub-adults (probably 16 to 20 years old), four older children, and two younger children (one around five years old, the other between 24 and 30 months old).
 Keith believed that the crania he examined displayed similar features to one another, suggesting that this meant that they all belonged to "one family—or several families united by common descent." Similar observations have been made regarding the crania from other long barrows in Britain. The osteoarchaeologists Martin Smith and Megan Brickley cautioned that this did not necessarily mean that all of the individuals in any given barrow were members of a single family group, for such shared cranial traits would also be consistent with "a population that was still relatively small and scattered", in which most people were interrelated.
Wysocki's team noted that in all but one case, the fracture morphologies of the bones are consistent with dry-bone breakage.
Three of the skulls displayed evidence that they had experienced violence; a probable adult female had an unhealed injury on the left
Keith believed that the crania he examined displayed similar features to one another, suggesting that this meant that they all belonged to "one family—or several families united by common descent." Similar observations have been made regarding the crania from other long barrows in Britain. The osteoarchaeologists Martin Smith and Megan Brickley cautioned that this did not necessarily mean that all of the individuals in any given barrow were members of a single family group, for such shared cranial traits would also be consistent with "a population that was still relatively small and scattered", in which most people were interrelated.
Wysocki's team noted that in all but one case, the fracture morphologies of the bones are consistent with dry-bone breakage.
Three of the skulls displayed evidence that they had experienced violence; a probable adult female had an unhealed injury on the left frontal bone
In the human skull, the frontal bone or sincipital bone is an unpaired bone which consists of two portions.'' Gray's Anatomy'' (1918) These are the vertically oriented squamous part, and the horizontally oriented orbital part, making up the bo ...
, an adult of indeterminate sex had an unhealed fracture on the left frontal, and a second adult female had a healed depressed fracture on the right frontal.
Isotope analysis
Isotope analysis is the identification of isotopic signature, abundance of certain stable isotopes of chemical elements within organic and inorganic compounds. Isotopic analysis can be used to understand the flow of energy through a food we ...
of the remains revealed that while the bones had δ13C values that were typical of those found at many other southern British Neolithic sites, they had significantly higher values of δ15N, which grew over time. Although this data is difficult to interpret, the investigative team believed that it probably reflected that these individuals had had a terrestrial diet high in animal protein that over time was increasingly supplemented with freshwater river or estuarine foods. In the case of the older individuals whose remains were interred in the tomb, the tooth enamel
Tooth enamel is one of the four major Tissue (biology), tissues that make up the tooth in humans and many animals, including some species of fish. It makes up the normally visible part of the tooth, covering the Crown (tooth), crown. The other ...
was worn away and the dentine
Dentin ( ) (American English) or dentine ( or ) (British English) () is a calcified tissue of the body and, along with enamel, cementum, and pulp, is one of the four major components of teeth. It is usually covered by enamel on the crown ...
had become exposed on the chewing area of the crowns.
Radiocarbon dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for Chronological dating, determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of carbon-14, radiocarbon, a radioactive Isotop ...
of the human remains suggested that some were brought to the site between either 3980–3800 calibrated
In measurement technology and metrology, calibration is the comparison of measurement values delivered by a device under test with those of a calibration standard of known accuracy. Such a standard could be another measurement device of known ...
BCE (95% probability) or 3960–3880 cal BCE (68% probability). It further suggested that after an interval of either 60–350 years (95% probability) or 140–290 years (68% probability), additional depositions of human remains were made inside the tomb. This second phase probably began in 3730–3540 cal BCE (95% probability) or 3670–3560 cal BCE (68% probability).
The radiocarbon dating of the human remains does not necessarily provide a date for the construction of Coldrum Long Barrow itself, because it is possible that the individuals died some time either before or after the monument's construction.
Post-mortem deposition
 Cut-marks were identified on some of the bones (two
Cut-marks were identified on some of the bones (two femora
The femur (; : femurs or femora ), or thigh bone is the only bone in the thigh — the region of the lower limb between the hip and the knee. In many four-legged animals the femur is the upper bone of the hindleg.
The top of the femur fits in ...
, two innominates, and one cranium), with osteoarchaeological specialists suggesting that these had been created post-mortem as the bodies were dismembered and the bones removed from their attached ligaments. They further suggested that the absence of cut-marks on certain bones suggested that the body had already undergone partial decomposition or the removal of soft tissues prior to dismemberment. The precision of the cut-marks suggests that this dismemberment was done carefully; "they do not suggest frenzied hacking or mutilation." None of the criteria that osteoarchaeologists deem diagnostic of cannibalism
Cannibalism is the act of consuming another individual of the same species as food. Cannibalism is a common ecological interaction in the animal kingdom and has been recorded in more than 1,500 species. Human cannibalism is also well document ...
were found on the bones.
This cut-marked human bone assemblage represented the largest yet identified from within a Neolithic long barrow in southern Britain, although similar evidence for dismemberment has been found from other Neolithic British sites, such as West Trump, Eyford, Aldestrop, and Haddenham. There are two possibilities for how this material developed. The first is that the bodies of the dead were excarnated or exposed to the elements, followed by a secondary burial within the tomb. The second is that they were placed in the tomb, where the flesh decomposed, before the bodies were then rearranged within the tomb itself. These practices may have been accompanied by other ritualistic or ceremonial practices, direct evidence for which does not survive.
The inclusion of occupational debris like ceramic sherds over the bones was not unique to the site but common in chambered tombs from southern England. On the basis of an example discovered at Kit's Coty House, Ashbee thought it apparent that the contents of the Coldrum's chamber would have been compartmentalised by medial slabs, which served the same purpose as the side chambers of West Kennet and Wayland's Smithy.
Damage and dilapidation
All the surviving megalithic tombs from the Early Neolithic period have suffered from neglect and the ravages of agriculture. Ashbee noted that the Coldrum Stones represent "Kent's least damaged megalithic long barrow", however it too has suffered considerable damage, having become dilapidated and fallen apart over the six millennia since its original construction. Most prominently, the eastern side has largely collapsed, with the stones that once helped to hold up the side of the barrow having fallen to the bottom of the slope. Conversely, it is possible that the sarsens at the bottom of the slope were not part of the original monument, but were stones found in nearby fields which were deposited there by farmers. Excavation of Chestnuts Long Barrow revealed that it had been systematically destroyed in one event, and Ashbee suggested that the same may have happened to the Coldrum Stones. He believed that the kerb-stones around the barrow were toppled, laid prostrate in the surrounding ditch, and then buried during the late 13th or early 14th century, by Christians seeking to obliterate non-Christian monuments. Conversely, the archaeologist John Alexander—who excavated Chestnuts in 1957—suggested that the Medway tombs were destroyed by robbers looking for treasure within them. As evidence, he pointed to theClose Roll
The Close Rolls () are an administrative record created in medieval England, Wales, Ireland and the Channel Islands by the royal chancery, in order to preserve a central record of all letters close issued by the chancery in the name of the Crown ...
of 1237, which ordered the opening of tumuli
A tumulus (: tumuli) is a mound of Soil, earth and Rock (geology), stones raised over a grave or graves. Tumuli are also known as barrows, burial mounds, mounds, howes, or in Siberia and Central Asia as ''kurgans'', and may be found through ...
on the Isle of Wight
The Isle of Wight (Help:IPA/English, /waɪt/ Help:Pronunciation respelling key, ''WYTE'') is an island off the south coast of England which, together with its surrounding uninhabited islets and Skerry, skerries, is also a ceremonial county. T ...
in search for treasure, a practice which may have spread to Kent around the same time. Alexander believed that the destruction in Kent may have been brought about by a special commissioner, highlighting that the "expertness and thoroughness of the robbery" at Chestnuts would have necessitated resources beyond that which a local community could probably muster. Ashbee further suggested that in subsequent centuries, locals raided the damaged Coldrum tomb for loamy chalk and stone, which was then re-used as building material.
Folklore, folk tradition, and modern Paganism
In a 1946 paper, thefolklorist
Folklore studies (also known as folkloristics, tradition studies or folk life studies in the UK) is the academic discipline devoted to the study of folklore. This term, along with its synonyms, gained currency in the 1950s to distinguish the ac ...
John H. Evans recorded the existence of a local folk belief that a battle was fought at the site of the Coldrum Stones, and that a "Black Prince" was buried within its chamber. He suggested that the tales of battles taking place at this site and at other Medway Megaliths had not developed independently among the local population but had "percolated down from the theories of antiquaries" who believed that the fifth-century Battle of Aylesford, which was recorded in the ninth-century ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' is a collection of annals in Old English, chronicling the history of the Anglo-Saxons.
The original manuscript of the ''Chronicle'' was created late in the ninth century, probably in Wessex, during the reign of ...
'', took place in the area.
Evans also recorded a local folk belief applied to all the Medway Megaliths and which had been widespread "up to the last generation"; this was that it was impossible for anyone to successfully count the number of stones in the monuments. This "countless stones
The countless stones is a motif that appears in English and Welsh folklore. It is associated with various megalithic monuments, including chambered long barrows from the Early Neolithic and the stones circles of the Late Neolithic and Early Bro ...
" motif is not unique to the Medway region, and can be found at various other megalithic monuments in Britain. The earliest textual evidence for it is found in an early 16th-century document, where it applies to the stone circle of Stonehenge in Wiltshire, although in an early 17th-century document it was applied to The Hurlers, a set of three stone circles in Cornwall
Cornwall (; or ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South West England. It is also one of the Celtic nations and the homeland of the Cornish people. The county is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, ...
. Later records reveal that it had gained widespread distribution in England, as well as a single occurrence each in Wales and Ireland. The folklorist S. P. Menefee suggested that it could be attributed to an animistic
Animism (from meaning 'breath, Soul, spirit, life') is the belief that objects, places, and creatures all possess a distinct Spirituality, spiritual essence. Animism perceives all things—animals, plants, Rock (geology), rocks, rivers, Weather, ...
understanding that these megaliths had lives of their own.
Several modern Pagan
Modern paganism, also known as contemporary paganism and neopaganism, spans a range of new religious movements variously influenced by the Paganism, beliefs of pre-modern peoples across Europe, North Africa, and the Near East. Despite some comm ...
religions are practiced at the Medway Megaliths, with Pagan activity having taken place at the Coldrum Stones from at least the late 1980s. These Pagans commonly associated the sites both with a concept of ancestry and of their being a source of "earth energy
Proponents and practitioners of various esoteric forms of spirituality and alternative medicine refer to a variety of claimed experiences and phenomena as being due to "energy" or "force" that defy measurement or experimentation, and thus are d ...
". The scholar of religion Ethan Doyle White argued that these sites in particular were interpreted as having connections to the ancestors both because they were created by Neolithic peoples whom modern Pagans view as their "own spiritual ancestors" and because the sites were once chambered tombs, and thus held the remains of the dead, who themselves may have been perceived as ancestors. On this latter point, Pagan perspectives on these sites are shaped by older archaeological interpretations. The Pagans also cited the Megaliths as spots marking sources of "earth energy", often aligned on ley lines
Ley lines () are straight alignments drawn between various historic structures, prehistoric sites and prominent landmarks. The idea was developed in early 20th-century Europe, with ley line believers arguing that these alignments were recognis ...
, an idea probably derived ultimately from the publications of Earth Mysteries
Earth mysteries are a wide range of spiritual, religious ideas focusing on cultural and religious beliefs about the Earth, generally with a regard for specific geographic locations of historic importance. Similar to modern druidry, prehistoric ...
proponents like John Michell
John Michell (; 25 December 1724 – 21 April 1793) was an English natural philosopher and clergyman who provided pioneering insights into a wide range of scientific fields including astronomy, geology, optics, and gravitation. Considered "on ...
.
 Pagans sometimes visit the site alone or in pairs, there to
Pagans sometimes visit the site alone or in pairs, there to meditate
Meditation is a practice in which an individual uses a technique to train attention and awareness and detach from reflexive, "discursive thinking", achieving a mentally clear and emotionally calm and stable state, while not judging the meditat ...
, pray
File:Prayers-collage.png, 300px, alt=Collage of various religionists praying – Clickable Image, Collage of various religionists praying ''(Clickable image – use cursor to identify.)''
rect 0 0 1000 1000 Shinto festivalgoer praying in front ...
, or perform rituals, and some have reported experiencing visions there. A modern Druidic group known as Roharn's Grove hold regular rites at the site, particularly during the eight festivals that make up the Pagan Wheel of the Year
The Wheel of the Year is an annual cycle of seasonal festivals, observed by a range of Modern paganism, modern pagans, marking the year's chief solar events (solstices and equinoxes) and the midpoints between them. Modern pagan observances are ...
. The Coldrums have also witnessed Pagan rites of passage
A rite of passage is a ceremony or ritual of the passage which occurs when an individual leaves one group to enter another. It involves a significant change of status in society. In cultural anthropology the term is the Anglicisation of ''rite ...
; circa 2000, a handfasting
Handfasting is a traditional practice that, depending on the term's usage, may define an unofficiated wedding (in which a couple marries without an officiant, usually with the intent of later undergoing a second wedding with an officiant), a ...
—or Wicca
Wicca (), also known as "The Craft", is a Modern paganism, modern pagan, syncretic, Earth religion, Earth-centred religion. Considered a new religious movement by Religious studies, scholars of religion, the path evolved from Western esote ...
n marriage ceremony—was held there. One member of the Odinic Rite
The Odinic Rite (OR) is a reconstructionist religious organisation named after the god Odin. It conceives itself as a " folkish" Heathen movement concerned with Germanic paganism, mythology, folklore, and runes. As a white supremacist organizati ...
, a Heathen organisation, gave their "oath of profession" to the group at the Coldrum Stones because they felt a particularly positive energy exists there. Politically motivated rituals have also been held at the site. In the late 1990s, the South London branch of the Paganlink organisation held a ritual at the Coldrum Stones in an unsuccessful attempt to prevent the construction of the Channel Tunnel Rail Link
High Speed 1 (HS1), officially the Channel Tunnel Rail Link (CTRL), is a high-speed railway linking London with the Channel Tunnel.
It is part of the line carrying international passenger traffic between the United Kingdom and mainland Euro ...
through the Medway Valley landscape. Another politically motivated Pagan rite was carried out there in the early 2010s by The Warrior's Call, a group seeking to prevent fracking
Fracking (also known as hydraulic fracturing, fracing, hydrofracturing, or hydrofracking) is a well stimulation technique involving the fracturing of formations in bedrock by a pressurized liquid. The process involves the high-pressure inje ...
in the United Kingdom by invoking "the traditional spirits of Albion
Albion is an alternative name for Great Britain. The oldest attestation of the toponym comes from the Greek language. It is sometimes used poetically and generally to refer to the island, but is less common than "Britain" today. The name for Scot ...
" against it.
In the early 21st century, a tradition developed in which the Hartley Morris Men, a morris dancing
Morris dancing is a form of English folk dance. It is based on rhythmic stepping and the execution of choreographed figures by a group of dancers in costume, usually wearing bell pads on their shins, their shoes or both. A band or single musi ...
side, meet at the site at dawn every May Day
May Day is a European festival of ancient origins marking the beginning of summer, usually celebrated on 1 May, around halfway between the Northern Hemisphere's March equinox, spring equinox and midsummer June solstice, solstice. Festivities ma ...
in order to "sing up the sun". This consists of dances performed within the stones on top of the barrow, followed by a song performed at the base of the monument. The trees overhanging the Coldrum Stones on its northern side have become rag trees, with hundreds of ribbons in various colours having been tied to their branches. This is a folk custom that some Pagans engage in, although it is also carried out by many other individuals; one Pagan has been recorded as saying that she tied a ribbon to the tree with her young son, both to make a wish for an improved future and as an offering to the "spirit of place". As of early 2014, runic
Runes are the letters in a set of related alphabets, known as runic rows, runic alphabets or futharks (also, see '' futhark'' vs ''runic alphabet''), native to the Germanic peoples. Runes were primarily used to represent a sound value (a ...
carvings written in the Elder Futhark
The Elder Futhark (or Fuþark, ), also known as the Older Futhark, Old Futhark, or Germanic Futhark, is the oldest form of the runic alphabets. It was a writing system used by Germanic peoples for Northwest Germanic dialects in the Migration Per ...
alphabet were also evident on the trunks of these trees, spelling the names of the Norse gods Thor
Thor (from ) is a prominent list of thunder gods, god in Germanic paganism. In Norse mythology, he is a hammer-wielding æsir, god associated with lightning, thunder, storms, sacred trees and groves in Germanic paganism and mythology, sacred g ...
and Odin
Odin (; from ) is a widely revered god in Norse mythology and Germanic paganism. Most surviving information on Odin comes from Norse mythology, but he figures prominently in the recorded history of Northern Europe. This includes the Roman Em ...
; these had probably been carved by Heathens, members of a religious movement that worships these deities.
Antiquarian and archaeological investigation
Early antiquarian descriptions
The earliest antiquarian accounts of Coldrum Long Barrow were never published. There are claims that at the start of the 19th century, the Reverend Mark Noble, Rector ofBarming
Barming is a civil parish in the Maidstone District of Kent, England. It lies to the west of Maidstone and at the 2011 census had a population of 2,690. The eastern end of the parish is part of the built-up area of Maidstone, although the remai ...
, prepared a plan of the site for ''Gentleman's Magazine
''The Gentleman's Magazine'' was a monthly magazine founded in London, England, by Edward Cave in January 1731. It ran uninterrupted for almost 200 years, until 1907, ceasing publication altogether in 1922. It was the first to use the term '' ...
'', although no copies have been produced to verify this. Between 1842 and 1844, the Reverend Beale Poste authored ''Druidical Remains at Coldrum'', in which he described the monument. This remained unpublished at the time. Associating the site with the druid
A druid was a member of the high-ranking priestly class in ancient Celtic cultures. The druids were religious leaders as well as legal authorities, adjudicators, lorekeepers, medical professionals and political advisors. Druids left no wr ...
s of Britain's Iron Age, Poste's suggestion was that the name "Coldrum" derived from the linguistically Celtic "Gael-Dun", and that Belgic chiefs were interred there. He further reported that in both 1804 and 1825, skulls had been found at the site. In 1844, an antiquarian named Thomas Wright published a note on the Coldrum Stones and other Medway Megaliths in '' The Archaeological Journal''. Wright had been alerted to their existence by a local vicar
A vicar (; Latin: '' vicarius'') is a representative, deputy or substitute; anyone acting "in the person of" or agent for a superior (compare "vicarious" in the sense of "at second hand"). Linguistically, ''vicar'' is cognate with the English p ...
, the Reverend Lambert B. Larking, and proceeded to visit them with him. Describing the Coldrums, Wright mentioned "a smaller circle of stones" to the others in the area, with "a subterranean cromlech in the middle". He further added that "it is a tradition of the peasantry that a continuous line of stones ran from Coldrum direct to the well-known monument called Kit's Cotty icHouse", attributing this belief to various megaliths scattered throughout the landscape.
 In 1857, the antiquarian J. M. Kemble excavated at the site with the help of the Reverend Larking, providing a report of their findings to the Central Committee of the
In 1857, the antiquarian J. M. Kemble excavated at the site with the help of the Reverend Larking, providing a report of their findings to the Central Committee of the British Archaeological Association
The British Archaeological Association (BAA) was founded in 1843 and aims to inspire, support and disseminate high quality research in the fields of Western archaeology, art and architecture, primarily of the mediaeval period, through lectures, co ...
. Describing the monument as a stone circle
A stone circle is a ring of megalithic standing stones. Most are found in Northwestern Europe – especially Stone circles in the British Isles and Brittany – and typically date from the Late Neolithic and Early Bronze Age, with most being ...
, they asserted that they discovered Anglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons, in some contexts simply called Saxons or the English, were a Cultural identity, cultural group who spoke Old English and inhabited much of what is now England and south-eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. They traced t ...
pottery at the site, and noted that as well as being called the Coldrum Stones, the monument also had the name of the Adscombe Stones, which Kemble believed originated with the Old English
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-S ...
word for funeral pile, ''ad''. In August 1863, members of the Archaeological Institute—which was holding its week-long meeting in Rochester—visited the site, guided by the antiquary Charles Roach Smith
Charles Roach Smith (20 August 1807 – 2 August 1890), FSA, was an English antiquarian and amateur archaeologist who was elected a fellow of the Society of Antiquaries of London, and the London Numismatic Society. He was a founding member of ...
. That year, the monument was described in a copy of ''Gentleman's Magazine'' by Yorkshire antiquary Charles Moore Jessop, who believed it to be a "Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
*Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Foot ...
" stone circle.
In 1869, the antiquarian A. L. Lewis first visited the site, and was informed by locals that several years previously a skull had been uncovered from inside or near to the chamber, but that they believed it to be that of a gypsy
{{Infobox ethnic group
, group = Romani people
, image =
, image_caption =
, flag = Roma flag.svg
, flag_caption = Romani flag created in 1933 and accepted at the 1971 World Romani Congress
, po ...
. A later account elaborated on this, stating that two individuals who excavated in the centre of the chamber without permission discovered a human skeleton, the skull of which was re-buried in the churchyard at Meopham
Meopham is a large linear village and civil parish in the Gravesham, Borough of Gravesham in north-west Kent, England, lying to the south of Gravesend. The parish covers , and comprises two villages and two smaller settlements; it had a popula ...
. In an 1878 note published in ''The Journal of the Anthropological Institute of Great Britain and Ireland
The ''Journal of the Royal Anthropological Institute'' (JRAI) is the principal journal of the oldest anthropological organization in the world, the Royal Anthropological Institute of Great Britain and Ireland. Articles, at the forefront of the dis ...
'', Lewis noted that while many tourists visited Kit's Coty House, "very few goes to or ever hears of a yet more curious collection of stones at Colderham or Coldrum Lodge". He believed that the monument consisted of both a "chamber" and an "oval" of stones, suggesting that they were "two distinct erections". In 1880, the archaeologist Flinders Petrie
Sir William Matthew Flinders Petrie ( – ), commonly known as simply Sir Flinders Petrie, was an English people, English Egyptology, Egyptologist and a pioneer of systematic methodology in archaeology and the preservation of artefacts. ...
included the existence of the stones at "Coldreham" in his list of Kentish earthworks; although noting that a previous commentator had described the stones as being in the shape of an oval, he instead described them as forming "a rectilinear enclosure" around the chamber. He then included a small, basic plan of the monument.
In August 1889, two amateur archaeologists, George Payne and A. A. Arnold, came across the monument, which they noted was known among locals as the "Coldrum Stones" and "Druid Temple"; according to Payne, "the huge stones were so overgrown with brambles and brushwood that they could not be discerned". He returned the next year, noting that the brushwood had since been cut away to reveal the megaliths. In his 1893 book ''Collectanea Cantiana'', Payne noted that although it had first been described in print in 1844, "since that time no one seems to have taken the trouble to properly record them or make a plan", an unusual claim given that a copy of Petrie's published plan existed in his library. For this reason, after gaining permission from the landowner, he convinced Major A. O. Green, Instructor in Survey at Brompton, to conduct a survey of the monument in August 1892. He also wrote to the archaeologist Augustus Pitt-Rivers
Lieutenant General Augustus Henry Lane Fox Pitt Rivers (14 April 18274 May 1900) was an English officer in the British Army, ethnologist, and archaeologist. He was noted for innovations in archaeological methodology, and in the museum display o ...
, encouraging him to schedule the Coldrum Stones as a legally protected site under the Ancient Monuments Protection Act 1882
The Ancient Monuments Protection Act 1882 ( 45 & 46 Vict. c. 73) was an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It was introduced by John Lubbock, 1st Baron Avebury, recognising the need for a governmental administration on the protection ...
. Payne described the Coldrum Stones as "the finest monument of its class in the county, and one worthy of every care and attention." Comparing it to other monuments of its type in Britain, he stated that it was undoubtedly "of sepulchral origin, belonging to a period anterior to the Roman domination of Britain." Payne also noted a folk tradition that there were stone avenues connecting Coldrum to the Addington Long Barrow, but added that he was unable to discover any physical evidence of this feature.
In 1904, George Clinch published a note on the Medway Megaliths in the Royal Anthropological Institute's journal, ''Man
A man is an adult male human. Before adulthood, a male child or adolescent is referred to as a boy.
Like most other male mammals, a man's genome usually inherits an X chromosome from the mother and a Y chromosome from the f ...
'', in which he referred to the Coldrum Stones as "at once the most remarkable and the least known of the whole series." Suggesting that its design indicates that it was built during "a late date in the neolithic age", he compared the workmanship in producing the megaliths to that at Stonehenge, although noted that they differed in that the Coldrum Stones clearly represented "a sepulchral pile". Ultimately, he ended his note by urging for the site to be protected under the Ancient Monuments Protection Act 1900. In that same issue, Lewis included an added note in which he rejected the idea that the monument had once been covered by an earthen tumulus because he could see "no evidence that anything of that kind ever existed", and instead he interpreted the site as a stone circle, comparing it to the examples at Avebury
Avebury () is a Neolithic henge monument containing three stone circles, around the village of Avebury in Wiltshire, in south-west England. One of the best-known prehistoric sites in Britain, it contains the largest megalithic stone circle in ...
, Arbor Low
Arbor Low is a well-preserved Neolithic henge in the Derbyshire Peak District, England. It lies on a Carboniferous Limestone plateau known as the White Peak area. The monument consists of a stone circle surrounded by earthworks and a ditch.
...
, and Stanton Drew
Stanton Drew is a small village and Civil parishes in England, civil parish within the Chew Valley in Somerset, England, lying north of the Mendip Hills, south of Bristol, just off the A368 road, A368 between Chelwood and Bishop Sutton in th ...
, suggesting that the central chamber was a shrine.
Archaeological excavation
The Coldrum Stones have been excavated on multiple occasions. On 16 April 1910, the amateur archaeologist F. J. Bennett began excavation at the site, having previously uncovered Neolithic stone tools from Addington Long Barrow. He soon discovered human bones "under only a few inches of chalky soil" at Coldrum. He returned to the site for further excavation in August 1910, this time with his niece and her husband, both of whom were dentists with an interest incraniology
Phrenology is a pseudoscience that involves the measurement of bumps on the skull to predict mental traits. It is based on the concept that the brain is the organ of the mind, and that certain brain areas have localized, specific functions or ...
; on that day they discovered pieces of a human skull, which they were able to largely reconstruct. A few days later he returned to excavate on the north-west corner of the chamber with the architect E. W. Filkins; that day, they found a second skull, further bones, a flint tool, and pieces of pottery. This pottery was later identified as being Anglo-Saxon in date.
Later that month, George Payne and F. W. Reader met with Bennett to discuss his finds. With the aid of two other interested amateur archaeologists, Mr Boyd and Miss Harker, both from Malling, excavation resumed in early September. In 2009, the archaeologists Martin Smith and Megan Brickley noted that Bennett's excavations had taken heed of Pitt-Rivers's advice that excavations should be recorded in full. They noted that Bennett had provided "clear plan and section drawings, photographs of the monument and careful attempts to consider site formation processes." Suggesting that the monument was constructed on agricultural land, in his published report Bennett cited the ideas of anthropologist James Frazer
Sir James George Frazer (; 1 January 1854 – 7 May 1941) was a Scottish social anthropologist and folkloristJosephson-Storm (2017), Chapter 5. influential in the early stages of the modern studies of mythology and comparative religion.
Per ...
in ''The Golden Bough
''The Golden Bough: A Study in Comparative Religion'' (retitled ''The Golden Bough: A Study in Magic and Religion'' in its second edition) is a wide-ranging, comparative study of mythology and religion, written by the Scottish anthropologist Sir ...
'' in proposing that the Coldrum Stones "may at one time have been dedicated, though not necessarily initially so, to the worship of the corn god and of agriculture." He believed that the human remains found at the site were the victims of human sacrifice
Human sacrifice is the act of killing one or more humans as part of a ritual, which is usually intended to please or appease deity, gods, a human ruler, public or jurisdictional demands for justice by capital punishment, an authoritative/prie ...
killed in fertility rites; conversely, Evans later stated that "we have no means of knowing" whether human sacrifice had taken place at the site.
In September 1922, Filkins again excavated at Coldrum, this time with the aid of Gravesend
Gravesend is a town in northwest Kent, England, situated 21 miles (35 km) east-southeast of Charing Cross (central London) on the Bank (geography), south bank of the River Thames, opposite Tilbury in Essex. Located in the diocese of Roche ...
resident Charles Gilbert. Their project was financed through grants provided by the British Association and the Society of Antiquaries, with Filkins noting that at the time of its commencement, "a miniature jungle" had grown up around the site which had to be cleared. Excavation continued sporadically until at least 1926. Human remains were discovered, and placed into the possession of Sir Arthur Keith of the Royal College of Surgeons
The Royal College of Surgeons is an ancient college (a form of corporation) established in England to regulate the activity of surgeons. Derivative organisations survive in many present and former members of the Commonwealth. These organisations ...
. It is also recorded that at some point between 1939 and 1945 human remains that had been found at the site were reburied in the churchyard at Trottiscliffe. This excavation revealed all the existing sarsens surrounding the monument, several which had previously been buried. The stones of the chamber were shored up with concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of aggregate bound together with a fluid cement that cures to a solid over time. It is the second-most-used substance (after water), the most–widely used building material, and the most-manufactur ...
foundations where Filkins deemed it necessary. Although Filkins' excavation was comprehensive, it ignored stone holes, packing stones, and their relationship to the mound. In 1998, Ashbee noted that while from "a present-day perspective, it is possible to see shortcomings n Filkins' excavation...in terms of the general standards of the early part of this century, there is much to commend."
Management by the National Trust
 In his 1924 publication dealing with Kent, the archaeologist
In his 1924 publication dealing with Kent, the archaeologist O. G. S. Crawford
Osbert Guy Stanhope Crawford (28 October 1886 – 28 November 1957) was a British archaeologist who specialised in the archaeology of prehistoric Britain and Sudan. A keen proponent of aerial archaeology, he spent most of his career as t ...
, then working as the archaeological officer for the Ordnance Survey
The Ordnance Survey (OS) is the national mapping agency for Great Britain. The agency's name indicates its original military purpose (see Artillery, ordnance and surveying), which was to map Scotland in the wake of the Jacobite rising of ...
, listed the Coldrum Stones alongside the other Medway Megaliths. In 1926, the Coldrum Stones were given to the National Trust
The National Trust () is a heritage and nature conservation charity and membership organisation in England, Wales and Northern Ireland.
The Trust was founded in 1895 by Octavia Hill, Sir Robert Hunter and Hardwicke Rawnsley to "promote the ...
, a charity which dedicated it as a memorial to the Kentish prehistorian Benjamin Harrison. A plaque was erected to mark this, which erroneously termed the monument a stone circle; in 1953, the archaeologist Leslie Grinsell
Leslie Valentine Grinsell (14 February 1907 – 28 February 1995) was an English archaeologist and museum curator. Publishing over twenty books on archaeology during his lifetime, he was renowned as a specialist on the prehistoric barrows ...
expressed the view that "it is hoped that this error may be rectified in the near future". Still owned by the Trust, the site is open to visitors all year round, free of charge. On their website, the Trust advises visitors to look for "stunning views from the top of the barrow". John H. Evans characterised the site as "the most impressive" of the Medway Megaliths, while Grinsell described it as "the finest and most complete" of the group.
Among the Pagans who use the Coldrum Stones for their ritual activities, there is general satisfaction with the Trust's management of the site, although some frustration at the poor access for disabled visitors. A patch of scorched earth exists on the grass in the centre of the monument, perhaps used by Pagans as well as non-Pagans, and the Trust warden responsible for the site has decided to leave it there rather than seeding it over, in order to encourage any who do light fires to do so in the same spot rather than nearer to the stones themselves. The site also faces a problem from litter left by visitors, with Pagans who regularly visit the site cleaning this up.
References
Footnotes
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Coldrum Long Barrow
at the National Trust website
Coldrum Long Barrow
at The Megalithic Portal
Coldrum Long Barrow
at The Modern Antiquarian {{Long Barrows in Britain Archaeological sites in Kent Barrows in the United Kingdom Buildings and structures in Kent History of Kent Megalithic monuments in England National Trust properties in Kent Neo-druidism in Britain Religion in Kent Stone Age sites in Kent Tonbridge and Malling