Cod Omelette on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
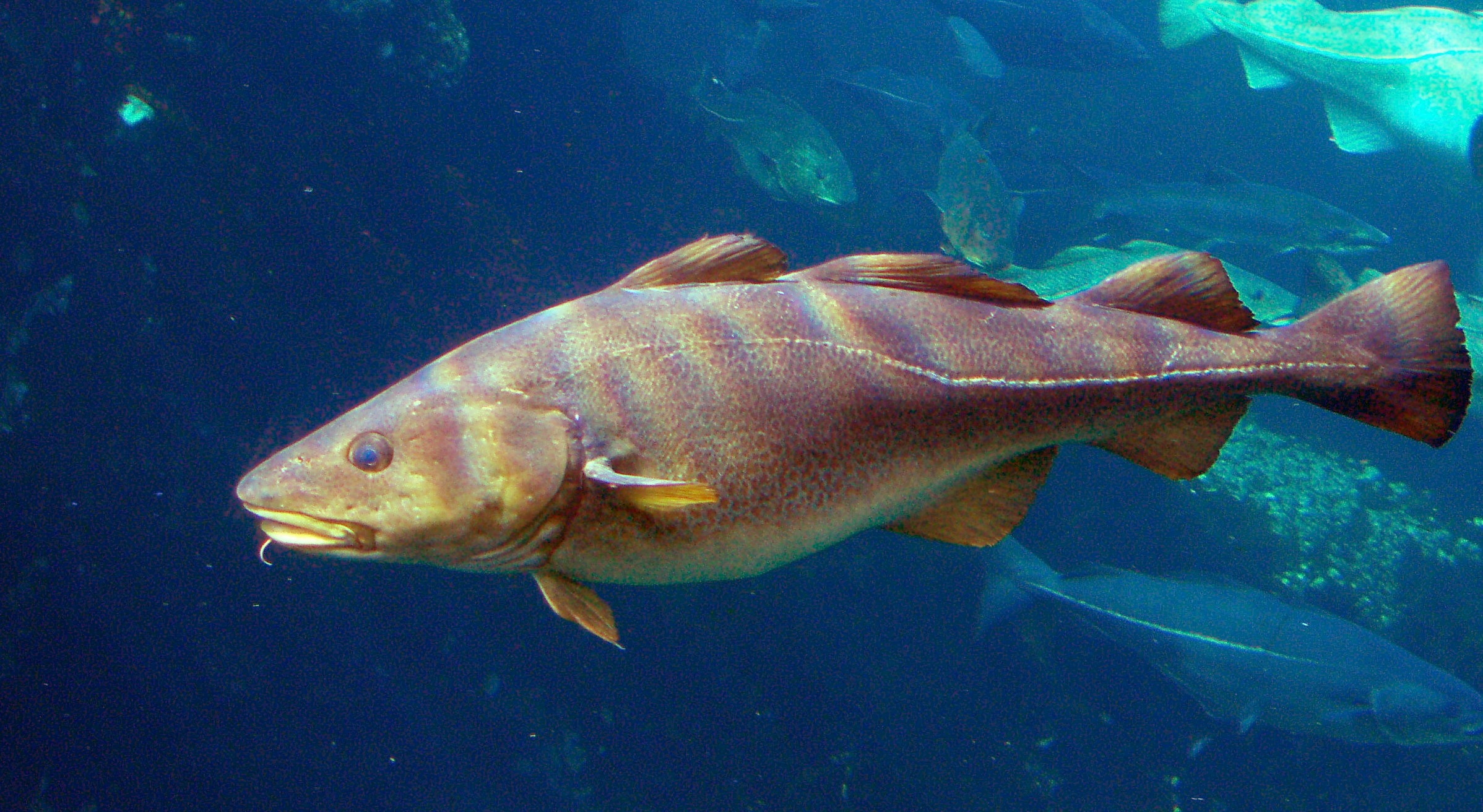 Cod (: cod) is the
Cod (: cod) is the
Alaska pollock
''. or ''bigeye cod''.
 Cods of the genus ''Gadus'' have three rounded
Cods of the genus ''Gadus'' have three rounded
, ''Encyclopædia Britannica online'' 2008 Atlantic cod could be further divided into several
 Adult cod are active hunters, feeding on
Adult cod are active hunters, feeding on
 Cod is popular as a
Cod is popular as a
 Cod has been an important economic commodity in
Cod has been an important economic commodity in
Codtrace
.
fishbase.org – Scientific Names for Gadus
Fisheries Heritage website, Newfoundland and Labrador
(archived)
Species factsheet on cod from the UK Sea Fish Industry Authority
(PDF, 2MB) * {{Authority control Commercial fish Gadidae Fish common names
common name
In biology, a common name of a taxon or organism (also known as a vernacular name, English name, colloquial name, country name, popular name, or farmer's name) is a name that is based on the normal language of everyday life; and is often con ...
for the demersal fish
Demersal fish, also known as groundfish, live and feed on or near the bottom of seas or lakes (the demersal zone).Walrond Carl . "Coastal fish - Fish of the open sea floor"Te Ara - the Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Updated 2 March 2009 They oc ...
genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ...
''Gadus
''Gadus'' is a genus of demersal fish in the family Gadidae, commonly known as cod, although there are additional cod species in other genera. The best known member of the genus is the Atlantic cod
The Atlantic cod (: cod; ''Gadus morhua'') ...
'', belonging to the family
Family (from ) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). It forms the basis for social order. Ideally, families offer predictabili ...
Gadidae
The Gadidae are a family of marine fish, included in the order Gadiformes, known as the cods, codfishes, or true cods. It contains several commercially important fishes, including the cod, haddock, whiting, and pollock.
Most gadid species ar ...
. Cod is also used as part of the common name for a number of other fish species, and one species that belongs to genus ''Gadus'' is commonly not called cod (Alaska pollock
The Alaska pollock or walleye pollock (''Gadus chalcogrammus'') is a marine fish species of the cod genus ''Gadus'' and family Gadidae.
It is a semi-pelagic Shoaling and schooling, schooling fish widely distributed in the North Pacific Ocean, No ...
, ''Gadus chalcogrammus'').
The two most common species of cod are the Atlantic cod
The Atlantic cod (: cod; ''Gadus morhua'') is a fish of the family Gadidae, widely consumed by humans. It is also commercially known as '' cod'' or ''codling''.North Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the Age of Discovery, it was known for ...
, and the Pacific cod
The Pacific cod (''Gadus macrocephalus)'' is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Gadidae. It is a bottom-dwelling fish found in the northern Pacific Ocean, mainly on the continental shelf and upper slopes, to depths of about . It can grow ...
(''Gadus macrocephalus''), which is found in both eastern and western regions of the northern Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
. ''Gadus morhua'' was named by Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné,#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. was a Swedish biologist and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming o ...
in 1758
Events
January–March
* January 1 – Swedish biologist Carl Linnaeus (Carl von Linné) publishes in Stockholm the first volume (''Animalia'') of the 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae'', the starting point of modern zoologic ...
. (However, ''G. morhua callarias'', a low-salinity, nonmigratory race restricted to parts of the Baltic, was originally described as ''Gadus callarias'' by Linnaeus.)
Cod as food
Cod and other cod-like fish have been widely used as food through history. Other cod-like fish come from the same family (Gadidae) that cod belong to, such as haddock, pollock, and Merlangius, whiting.
Cod
Cod is popular as a food with a mild f ...
is popular in several parts of the world. It has a mild flavour and a dense, flaky, white flesh. Cod livers are processed to make cod liver oil
Cod liver oil is a dietary supplement derived from liver of Atlantic cod (''Gadus morhua''). As with most fish oils, it contains the omega-3 fatty acids eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), and also vitamin A and vita ...
, a common source of vitamin A
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin that is an essential nutrient. The term "vitamin A" encompasses a group of chemically related organic compounds that includes retinol, retinyl esters, and several provitamin (precursor) carotenoids, most not ...
, vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of structurally related, fat-soluble compounds responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, along with numerous other biological functions. In humans, the most important compo ...
, vitamin E
Vitamin E is a group of eight compounds related in molecular structure that includes four tocopherols and four tocotrienols. The tocopherols function as fat-soluble antioxidants which may help protect cell membranes from reactive oxygen speci ...
, and omega-3 fatty acid
Omega−3 fatty acids, also called omega−3 oils, ω−3 fatty acids or ''n''−3 fatty acids, are polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) characterized by the presence of a double bond three atoms away from the terminal methyl group in their ...
s ( EPA and DHA). Young Atlantic cod or haddock
The haddock (''Melanogrammus aeglefinus'') is a saltwater ray-finned fish from the Family (biology), family Gadidae, the true cods. It is the only species in the Monotypy, monotypic genus ''Melanogrammus''. It is found in the North Atlantic Oce ...
prepared in strips for cooking is called scrod
Scrod or schrod () is a small cod or haddock, and sometimes other whitefish (fisheries term), whitefish, used as food. It is usually served as a fish fillet, fillet, though formerly it was often split instead.
In the wholesale fish business, scr ...
. In the United Kingdom, Atlantic cod
The Atlantic cod (: cod; ''Gadus morhua'') is a fish of the family Gadidae, widely consumed by humans. It is also commercially known as '' cod'' or ''codling''.fish and chips
Fish and chips is a hot dish consisting of batter (cooking), battered and fried fish, served with French fries, chips. Often considered the national dish of the United Kingdom, fish and chips originated in England in the 19th century. Today, ...
, along with haddock
The haddock (''Melanogrammus aeglefinus'') is a saltwater ray-finned fish from the Family (biology), family Gadidae, the true cods. It is the only species in the Monotypy, monotypic genus ''Melanogrammus''. It is found in the North Atlantic Oce ...
and plaice
Plaice is a common name for a group of flatfish that comprises four species: the European, American, Alaskan and scale-eye plaice.
Commercially, the most important plaice is the European. The principal commercial flatfish in Europe, it is ...
.
Species
At various times in the past, taxonomists included many species in the genus ''Gadus
''Gadus'' is a genus of demersal fish in the family Gadidae, commonly known as cod, although there are additional cod species in other genera. The best known member of the genus is the Atlantic cod
The Atlantic cod (: cod; ''Gadus morhua'') ...
''. Most of these are now either classified in other genera, or have been recognized as forms of one of three species. All these species have a number of common name
In biology, a common name of a taxon or organism (also known as a vernacular name, English name, colloquial name, country name, popular name, or farmer's name) is a name that is based on the normal language of everyday life; and is often con ...
s, most of them ending with the word "cod", whereas other species, as closely related, have other common names (such as pollock
Pollock or pollack (pronounced ) is the common name used for either of the two species of North Atlantic ocean, marine fish in the genus ''Pollachius''. ''Pollachius pollachius'' is referred to as "pollock" in North America, Ireland and the Unit ...
and haddock
The haddock (''Melanogrammus aeglefinus'') is a saltwater ray-finned fish from the Family (biology), family Gadidae, the true cods. It is the only species in the Monotypy, monotypic genus ''Melanogrammus''. It is found in the North Atlantic Oce ...
). However, many other, unrelated species also have common names ending with cod. The usage often changes with different localities and at different times.
Cod in the genus ''Gadus''/True cod
Three species in the genus ''Gadus'' are currently called cod: The fourth species of genus Gadus, ''Gadus chalcogrammus
The Alaska pollock or walleye pollock (''Gadus chalcogrammus'') is a marine fish species of the cod genus ''Gadus'' and family Gadidae.
It is a semi-pelagic schooling fish widely distributed in the North Pacific, with largest concentrations foun ...
'', is commonly called ''Alaska pollock'' or ''walleye pollock''. But there are also less widespread alternative trade names highlighting the fish's belonging to the cod genus, like ''snow cod''SeafoodSource.com (23 January 2014): Alaska pollock
''. or ''bigeye cod''.
Related species
''Cod'' forms part of thecommon name
In biology, a common name of a taxon or organism (also known as a vernacular name, English name, colloquial name, country name, popular name, or farmer's name) is a name that is based on the normal language of everyday life; and is often con ...
of many other fish no longer classified in the genus ''Gadus''. Many are members of the family Gadidae
The Gadidae are a family of marine fish, included in the order Gadiformes, known as the cods, codfishes, or true cods. It contains several commercially important fishes, including the cod, haddock, whiting, and pollock.
Most gadid species ar ...
; others are members of three related families within the order Gadiformes
Gadiformes , also called the Anacanthini, are an order of ray-finned fish that include the cod, hakes, pollock, haddock, burbot, rocklings and moras, many of which are food fish of major commercial value. They are mostly marine fish found thr ...
whose names include the word "cod": the morid cod
The Moridae are a family of cod-like fishes, known as codlings, hakelings, and moras.
Morids are marine fishes found throughout the world, and may be found at depths to , although most prefer shallower waters. In appearance, they greatly resemb ...
s, Moridae
The Moridae are a family of cod-like fishes, known as codlings, hakelings, and moras.
Morids are marine fishes found throughout the world, and may be found at depths to , although most prefer shallower waters. In appearance, they greatly resembl ...
(100 or so species); the eel cods, Muraenolepididae
The Muraenolepididae is a family of cod-like fish, known as eel cods, found in southern oceans.
References
Gadiformes
Euteleostei families
{{Gadiformes-stub ...
(four species); and the Eucla cod, Euclichthyidae (one species). The tadpole cod family ( Ranicipitidae) has now been placed in Gadidae.
Some fish have common names derived from "cod", such as codling, codlet
Codlets are a family, Bregmacerotidae, of cod-like fishes, containing the single genus ''Bregmaceros'' found in tropical and subtropical waters throughout the world. They are very small fishes and even the largest, ''B. lanceolatus'', reaches onl ...
, or tomcod. ("Codling" is also used as a name for a young cod.)
Other species
Some fish commonly known as cod are unrelated to ''Gadus''. Part of this name confusion is market-driven. Severely shrunken Atlantic cod stocks have led to the marketing of cod replacements usingculinary name
Culinary names, menu names, or kitchen names are names of foods used in the preparation or selling of food, as opposed to their names in agriculture or in scientific nomenclature. The menu name may even be different from the kitchen name. For exa ...
s of the form "''x'' cod", according to culinary rather than phyletic similarity. The common names for the following species have become well established; note that all inhabit the Southern Hemisphere.
Perciformes
Fish of theorder
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* A socio-political or established or existing order, e.g. World order, Ancien Regime, Pax Britannica
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
...
Perciformes
Perciformes (), also called the Acanthopteri, is an order or superorder of ray-finned fish in the clade Percomorpha. ''Perciformes'' means " perch-like". Among the well-known members of this group are perches and darters ( Percidae), and als ...
that are commonly called "cod" include:
*Blue cod
The New Zealand blue cod (''Parapercis colias'') is a temperate Marine (ocean), marine ray-finned fish of the family (biology), family Pinguipedidae. It is also known by its Māori language, Māori names, rāwaru, pākirikiri and patutuki, and ...
''Parapercis colias''
* Eastern freshwater cod ''Maccullochella ikei''
*Mary River cod
The Mary River cod (''Maccullochella mariensis'') is a species of temperate perch native to the coastal Mary River system of southern Queensland, Australia. Mary River cod are one of Australia's most endangered freshwater fishes and are nota ...
''Maccullochella mariensis''
*Murray cod
The Murray cod (''Maccullochella peelii'') is a large Australian predatory freshwater fish of the genus '' Maccullochella'' in the family Percichthyidae.Dianne J. Bray & Vanessa J. Thompson (2011Murray Cod, Maccullochella peelii Fishes of Au ...
''Maccullochella peelii''
* Potato cod ''Epinephelus tukula''
* Sleepy cod ''Oxyeleotris lineolatus''
* Trout cod ''Maccullochella macquariensis''
*The notothen family, Nototheniidae
: ''In some scientific literature, the term "cod icefish" is used to identify members of this family. This should not be confused with the term "icefish," which refers to the "white-blooded" fishes of the family Channichthyidae. See Icefish (disam ...
, including:
** Antarctic cod ''Dissostichus mawsoni''
***''Dissostichus eliginoides'', the Patagonian toothfish, is also marketed as "cod"
** Black cod ''Notothenia microlepidota''
** Maori cod ''Paranotothenia magellanica''
Rock cod, reef cod, and coral cod
Almost all coral cod, reef cod or rock cod are also in orderPerciformes
Perciformes (), also called the Acanthopteri, is an order or superorder of ray-finned fish in the clade Percomorpha. ''Perciformes'' means " perch-like". Among the well-known members of this group are perches and darters ( Percidae), and als ...
. Most are better known as grouper
Groupers are a diverse group of marine ray-finned fish in the family Epinephelidae, in the order Perciformes.
Groupers were long considered a subfamily of the seabasses in Serranidae, but are now treated as distinct. Not all members of this f ...
s, and belong to the family Serranidae
Serranidae is a large family (biology), family of fishes belonging to the order Perciformes. The family contains about 450 species in 65 genera, including the sea basses and the groupers (subfamily Epinephelinae). Although many species are small, ...
. Others belong to the Nototheniidae
: ''In some scientific literature, the term "cod icefish" is used to identify members of this family. This should not be confused with the term "icefish," which refers to the "white-blooded" fishes of the family Channichthyidae. See Icefish (disam ...
. Two exceptions are the Australasia
Australasia is a subregion of Oceania, comprising Australia, New Zealand (overlapping with Polynesia), and sometimes including New Guinea and surrounding islands (overlapping with Melanesia). The term is used in a number of different context ...
n red rock cod, which belongs to a different order (see below), and the fish known simply as the rock cod and as soft cod
Soft may refer to:
* Softness
In materials science, hardness (antonym: softness) is a measure of the resistance to plastic deformation, such as an indentation (over an area) or a scratch (linear), induced mechanically either by Pressing (meta ...
in New Zealand, '' Lotella rhacina'', which as noted above actually is related to the true cod (it is a morid cod).
Scorpaeniformes
From the orderScorpaeniformes
The Scorpaeniformes are a diverse Order (biology), order of Actinopterygii, ray-finned fish, including the lionfishes and sculpins, but have also been called the Scleroparei. It is one of the five largest orders of bony fishes by number of spec ...
:
*Ling cod
The lingcod or ling cod (''Ophiodon elongatus'') is a fish of the greenling family Hexagrammidae. Despite its name, the lingcod is neither a cod nor a ling. It is also known as the buffalo cod, cultus cod, or Buckethead. It is the only extant me ...
''Ophiodon elongatus''
* Red rock cod ''Scorpaena papillosa''
*Rock cod ''Sebastes
''Sebastes'' is a genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the subfamily Sebastinae part of the family Scorpaenidae, most of which have the common name of rockfish. A few are called ocean perch, sea perch or redfish instead. They are found ...
''
Ophidiiformes
The tadpole cod family, Ranicipitidae, and the Eucla cod family, Euclichthyidae, were formerly classified in the orderOphidiiformes
Ophidiiformes is an order of ray-finned fish that includes the cusk-eels (family Ophidiidae), pearlfishes (family Carapidae), viviparous brotulas (family Bythitidae), and others. Members of this order have small heads and long slender bodies. ...
, but are now grouped with the Gadiformes
Gadiformes , also called the Anacanthini, are an order of ray-finned fish that include the cod, hakes, pollock, haddock, burbot, rocklings and moras, many of which are food fish of major commercial value. They are mostly marine fish found thr ...
.
Marketed as cod
Some fish that do not have "cod" in their names are sometimes sold as cod. Haddock and whiting belong to the same family, the Gadidae, as cod. *Haddock
The haddock (''Melanogrammus aeglefinus'') is a saltwater ray-finned fish from the Family (biology), family Gadidae, the true cods. It is the only species in the Monotypy, monotypic genus ''Melanogrammus''. It is found in the North Atlantic Oce ...
''Melanogrammus aeglefinus''
* Whiting ''Merlangius merlangus''
Characteristics
 Cods of the genus ''Gadus'' have three rounded
Cods of the genus ''Gadus'' have three rounded dorsal
Dorsal (from Latin ''dorsum'' ‘back’) may refer to:
* Dorsal (anatomy), an anatomical term of location referring to the back or upper side of an organism or parts of an organism
* Dorsal, positioned on top of an aircraft's fuselage
The fus ...
and two anal fin
Fins are moving appendages protruding from the body of fish that interact with water to generate thrust and help the fish swim. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the back bone and are supported o ...
s. The pelvic fin
Pelvic fins or ventral fins are paired fins located on the ventral (belly) surface of fish, and are the lower of the only two sets of paired fins (the other being the laterally positioned pectoral fins). The pelvic fins are homologous to the hi ...
s are small, with the first ray extended, and are set under the gill
A gill () is a respiration organ, respiratory organ that many aquatic ecosystem, aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow r ...
cover (i.e. the throat region), in front of the pectoral fin
Fins are moving appendages protruding from the body of fish that interact with water to generate thrust and help the fish aquatic locomotion, swim. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the vertebral column ...
s. The upper jaw extends over the lower jaw, which has a well-developed chin barbel. The eyes are medium-sized, approximately the same as the length of the chin barbel. Cod have a distinct white lateral line
The lateral line, also called the lateral line organ (LLO), is a system of sensory organs found in fish, used to detect movement, vibration, and pressure gradients in the surrounding water. The sensory ability is achieved via modified epithelia ...
running from the gill slit above the pectoral fin, to the base of the caudal or tail fin. The back tends to be a greenish to sandy brown, and shows extensive mottling, especially towards the lighter sides and white belly. Dark brown colouration of the back and sides is not uncommon, especially for individuals that have resided in rocky inshore regions.
The Atlantic cod
The Atlantic cod (: cod; ''Gadus morhua'') is a fish of the family Gadidae, widely consumed by humans. It is also commercially known as '' cod'' or ''codling''.Atlantic cod
The Atlantic cod (: cod; ''Gadus morhua'') is a fish of the family Gadidae, widely consumed by humans. It is also commercially known as '' cod'' or ''codling''.Pacific cod
The Pacific cod (''Gadus macrocephalus)'' is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Gadidae. It is a bottom-dwelling fish found in the northern Pacific Ocean, mainly on the continental shelf and upper slopes, to depths of about . It can grow ...
(''Gadus macrocephalus'') is found in both eastern and western regions of the Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
."Cod", ''Encyclopædia Britannica online'' 2008 Atlantic cod could be further divided into several
stocks
Stocks are feet and hand restraining devices that were used as a form of corporal punishment and public humiliation. The use of stocks is seen as early as Ancient Greece, where they are described as being in use in Solon's law code. The law de ...
, including the Arcto-Norwegian, North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Denmark, Norway, Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium, and France. A sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian Se ...
, Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the ...
, Faroe, Iceland
Iceland is a Nordic countries, Nordic island country between the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic and Arctic Oceans, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge between North America and Europe. It is culturally and politically linked with Europe and is the regi ...
, East Greenland
Tunu, in Danish Østgrønland ("East Greenland"), was one of the three counties (''amter'') of Greenland until 31 December 2008. The county seat was at the main settlement, Tasiilaq. The county's population in 2005 was around 3,800.
The county ...
, West Greenland
Kitaa, originally Vestgrønland ("West Greenland"), is a former administrative division of Greenland. It was by far the most populated of the divisions, being home to almost 90% of the total population. The divisions were de facto replaced by s ...
, Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region of Labrador, having a total size of . As of 2025 the population ...
, and Labrador
Labrador () is a geographic and cultural region within the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. It is the primarily continental portion of the province and constitutes 71% of the province's area but is home to only 6% of its populatio ...
stocks. There seems to be little interchange between the stocks, although migrations to their individual breeding grounds may involve distances of or more. For instance, eastern Baltic cod shows specific reproductive adaptations to low salinity compared to Western Baltic and Atlantic cod.
Atlantic cod occupy varied habitats, favouring rough ground, especially inshore, and are demersal
The demersal zone is the part of the sea or ocean (or deep lake) consisting of the part of the water column near to (and significantly affected by) the seabed and the benthos. The demersal zone is just above the benthic zone and forms a layer o ...
in depths between , on average, although not uncommonly to depths of . Off the Norwegian and New England coasts and on the Grand Banks of Newfoundland
The Grand Banks of Newfoundland are a series of underwater plateaus south-east of the island of Newfoundland on the North American continental shelf. The Grand Banks are one of the world's richest fishing grounds, supporting Atlantic cod, swordf ...
, cod congregate at certain seasons in water of depth. Cod are gregarious and form schools, although shoaling
In biology, any group of fish that stay together for social reasons are shoaling, and if the group is swimming in the same direction in a coordinated manner, they are schooling. In common usage, the terms are sometimes used rather loosely. Ab ...
tends to be a feature of the spawning season.
Life cycle
Spawning of northeastern Atlantic cod occurs between January and April (March and April are the peak months), at a depth of in specific spawning grounds at water temperatures between . Around the UK, the major spawning grounds are in the middle to southern North Sea, the start of theBristol Channel
The Bristol Channel (, literal translation: "Severn Sea") is a major inlet in the island of Great Britain, separating South Wales (from Pembrokeshire to the Vale of Glamorgan) and South West England (from Devon to North Somerset). It extends ...
(north of Newquay
Newquay ( ; ) is a town on the north coast in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is a civil parishes in England, civil parish, seaside resort, regional centre for aerospace industries with an airport and a spaceport, and a fishing port on t ...
), the Irish Channel (both east and west of the Isle of Man
The Isle of Man ( , also ), or Mann ( ), is a self-governing British Crown Dependency in the Irish Sea, between Great Britain and Ireland. As head of state, Charles III holds the title Lord of Mann and is represented by a Lieutenant Govern ...
), around Stornoway
Stornoway (; ) is the main town, and by far the largest, of the Outer Hebrides (or Western Isles), and the capital of Lewis and Harris in Scotland.
The town's population is around 6,953, making it the third-largest island town in Scotlan ...
, and east of Helmsdale.
Prespawning courtship involves fin displays and male grunting, which leads to pairing. The male inverts himself beneath the female, and the pair swim in circles while spawning. The eggs are planktonic and hatch between eight and 23 days, with larva reaching in length. This planktonic phase lasts some ten weeks, enabling the young cod to increase its body weight by 40-fold, and growing to about . The young cod then move to the seabed and change their diet to small benthic
The benthic zone is the ecological region at the lowest level of a body of water such as an ocean, lake, or stream, including the sediment surface and some sub-surface layers. The name comes from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning "the depths". ...
crustaceans
Crustaceans (from Latin meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of Arthropod, arthropods that are traditionally a part of the subphylum Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquat ...
, such as isopods
Isopoda is an Order (biology), order of crustaceans. Members of this group are called isopods and include both Aquatic animal, aquatic species and Terrestrial animal, terrestrial species such as woodlice. All have rigid, segmented exoskeletons ...
and small crabs. They increase in size to in the first six months, by the end of their first year, and to by the end of the second. Growth tends to be less at higher latitudes. Cod reach maturity at about at about 3 to 4 years of age. Changes in growth rate over decades of particular stocks have been reported, current eastern Baltic cod shows the lowest growth observed since 1955.
Ecology
 Adult cod are active hunters, feeding on
Adult cod are active hunters, feeding on sand eel
Sand eel or sandeel is the common name used for a considerable number of species of fish. While they are not true eels, they are eel-like in their appearance and can grow up to in length. Many species are found off the western coasts of Europe ...
s, whiting, haddock
The haddock (''Melanogrammus aeglefinus'') is a saltwater ray-finned fish from the Family (biology), family Gadidae, the true cods. It is the only species in the Monotypy, monotypic genus ''Melanogrammus''. It is found in the North Atlantic Oce ...
, small cod, squid
A squid (: squid) is a mollusc with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight cephalopod limb, arms, and two tentacles in the orders Myopsida, Oegopsida, and Bathyteuthida (though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also ...
, crab
Crabs are decapod crustaceans of the infraorder Brachyura (meaning "short tailed" in Greek language, Greek), which typically have a very short projecting tail-like abdomen#Arthropoda, abdomen, usually hidden entirely under the Thorax (arthropo ...
s, lobster
Lobsters are Malacostraca, malacostracans Decapoda, decapod crustaceans of the family (biology), family Nephropidae or its Synonym (taxonomy), synonym Homaridae. They have long bodies with muscular tails and live in crevices or burrows on th ...
s, mussel
Mussel () is the common name used for members of several families of bivalve molluscs, from saltwater and Freshwater bivalve, freshwater habitats. These groups have in common a shell whose outline is elongated and asymmetrical compared with other ...
s, worm
Worms are many different distantly related bilateria, bilateral animals that typically have a long cylindrical tube-like body, no limb (anatomy), limbs, and usually no eyes.
Worms vary in size from microscopic to over in length for marine ...
s, mackerel
Mackerel is a common name applied to a number of different species of pelagic fish, mostly from the family Scombridae. They are found in both temperate and tropical seas, mostly living along the coast or offshore in the oceanic environment.
...
, and mollusc
Mollusca is a phylum of protostome, protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum ...
s.
In the Baltic Sea the most important prey species are herring
Herring are various species of forage fish, belonging to the Order (biology), order Clupeiformes.
Herring often move in large Shoaling and schooling, schools around fishing banks and near the coast, found particularly in shallow, temperate wate ...
and sprat
Sprat is the common name applied to a group of forage fish belonging to the genus ''Sprattus'' in the Family (biology), family Clupeidae. The term also is applied to a number of other small sprat-like forage fish (''Clupeoides'', ''Clupeonella ...
. Many studies that analyze the stomach contents of these fish indicate that cod is the top predator, preying on the herring and sprat. Sprat form particularly high concentrations in the Bornholm
Bornholm () is a List of islands of Denmark, Danish island in the Baltic Sea, to the east of the rest of Denmark, south of Sweden, northeast of Germany and north of Poland.
Strategically located, Bornholm has been fought over for centuries. I ...
Basin in the southern Baltic Sea. Although cod feed primarily on adult sprat, sprat tend to prey on the cod eggs and larvae.
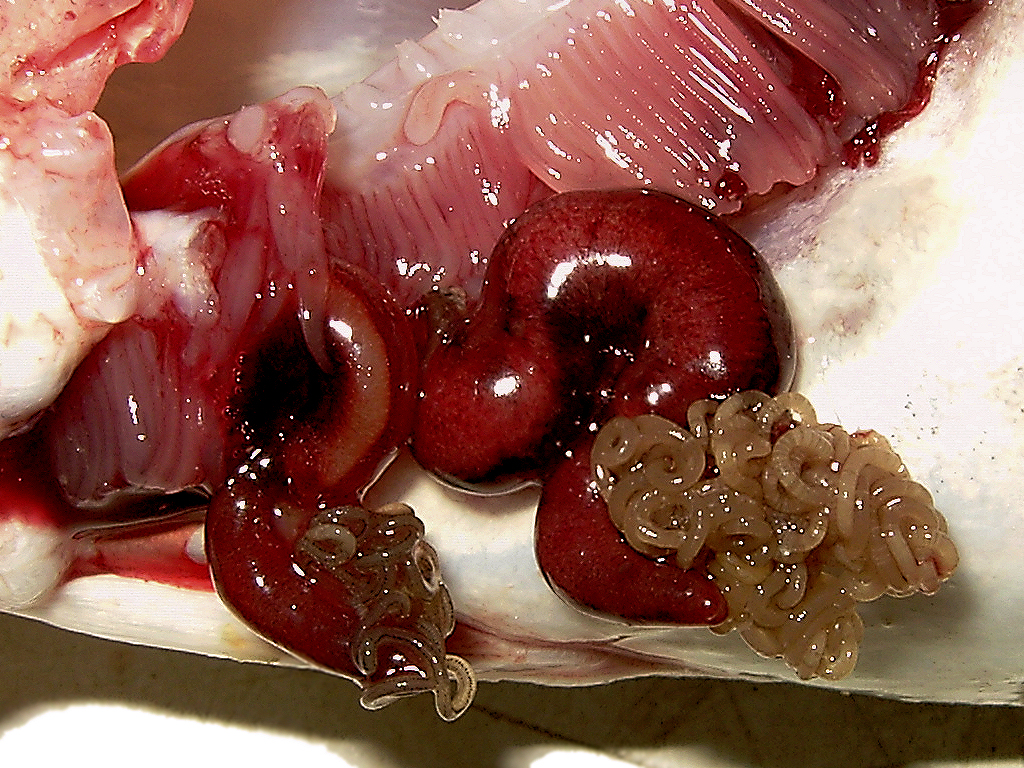
Cod and related species are plagued by parasites. For example, the cod worm
''Lernaeocera branchialis'', sometimes called cod worm, is a parasite of marine fish, found mainly in the North Atlantic. It is a marine copepod which starts life as a small pelagic crustacean larva. It is among the largest of copepods, ranging ...
, ''Lernaeocera branchialis'', starts life as a copepod
Copepods (; meaning 'oar-feet') are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat (ecology), habitat. Some species are planktonic (living in the water column), some are benthos, benthic (living on the sedimen ...
-like larva, a small free-swimming crustacean. The first host used by the larva is a flatfish
A flatfish is a member of the Ray-finned fish, ray-finned demersal fish Order (biology), suborder Pleuronectoidei, also called the Heterosomata. In many species, both eyes lie on one side of the head, one or the other migrating through or around ...
or lumpsucker
The Cyclopteridae are a family of marine fishes, commonly known as lumpsuckers or lumpfish, in the order Scorpaeniformes. They are found in the cold waters of the Arctic Ocean, Arctic, Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic, and Pacific Ocean, North Paci ...
, which it captures with grasping hooks at the front of its body. It penetrates the fish with a thin filament
The word filament, which is descended from Latin ''filum'' meaning " thread", is used in English for a variety of thread-like structures, including:
Astronomy
* Galaxy filament, the largest known cosmic structures in the universe
* Solar filament ...
, which it uses to suck the fish's blood. The nourished larvae then mate on the fish. The female larva, with her now fertilized eggs, then finds a cod, or a cod-like fish such as a haddock
The haddock (''Melanogrammus aeglefinus'') is a saltwater ray-finned fish from the Family (biology), family Gadidae, the true cods. It is the only species in the Monotypy, monotypic genus ''Melanogrammus''. It is found in the North Atlantic Oce ...
or whiting. There the larva clings to the gill
A gill () is a respiration organ, respiratory organ that many aquatic ecosystem, aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow r ...
s while it metamorphoses into a plump sinusoidal wormlike body with a coiled mass of egg strings at the rear. The front part of the worm's body penetrates the body of the cod until it enters the rear bulb of the host's heart
The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ found in humans and other animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. The heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrie ...
. There, firmly rooted in the cod's circulatory system, the front part of the parasite develops like the branches of a tree, reaching into the main artery
An artery () is a blood vessel in humans and most other animals that takes oxygenated blood away from the heart in the systemic circulation to one or more parts of the body. Exceptions that carry deoxygenated blood are the pulmonary arteries in ...
. In this way, the worm extracts nutrients from the cod's blood, remaining safely tucked beneath the cod's gill cover until it releases a new generation of offspring into the water.
Fisheries
The 2006 northwest Atlantic cod quota is 23,000 tons, representing half the available stocks, while the northeast Atlantic quota is 473,000 tons. Pacific cod is currently enjoying strong global demand. The 2006total allowable catch
The Common Fisheries Policy (CFP) is the fisheries policy of the European Union (EU). It sets quotas for which member states are allowed to catch each type of fish, as well as encouraging the fishing industry by various market interventions. ...
(TAC) for the Gulf of Alaska
The Gulf of Alaska ( Tlingit: ''Yéil T'ooch’'') is an arm of the Pacific Ocean defined by the curve of the southern coast of Alaska, stretching from the Alaska Peninsula and Kodiak Island in the west to the Alexander Archipelago in the ...
and Aleutian Islands
The Aleutian Islands ( ; ; , "land of the Aleuts"; possibly from the Chukchi language, Chukchi ''aliat'', or "island")—also called the Aleut Islands, Aleutic Islands, or, before Alaska Purchase, 1867, the Catherine Archipelago—are a chain ...
was 260,000 tons.
Aquaculture
Farming of Atlantic cod has received a significant amount of interest due to the overall trend of increasing cod prices alongside reduced wild catches. However, progress in creating large scale farming of cod has been slow, mainly due to bottlenecks in the larval production stage, where survival and growth are often unpredictable. It has been suggested that this bottleneck may be overcome by ensuring cod larvae are fed diets with similar nutritional content as the copepods they feed on in the wild Recent examples have shown that increasing dietary levels of minerals such as selenium, iodine and zinc may improve survival and/or biomarkers for health in aquaculture reared cod larvae.As food
 Cod is popular as a
Cod is popular as a food
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for Nutrient, nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or Fungus, fungal origin and contains essential nutrients such as carbohydrates, fats, protein (nutrient), proteins, vitamins, ...
with a mild flavour and a dense, flaky white flesh. Cod livers are processed to make cod liver oil
Cod liver oil is a dietary supplement derived from liver of Atlantic cod (''Gadus morhua''). As with most fish oils, it contains the omega-3 fatty acids eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), and also vitamin A and vita ...
, an important source of vitamin A
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin that is an essential nutrient. The term "vitamin A" encompasses a group of chemically related organic compounds that includes retinol, retinyl esters, and several provitamin (precursor) carotenoids, most not ...
, vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of structurally related, fat-soluble compounds responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, along with numerous other biological functions. In humans, the most important compo ...
, vitamin E
Vitamin E is a group of eight compounds related in molecular structure that includes four tocopherols and four tocotrienols. The tocopherols function as fat-soluble antioxidants which may help protect cell membranes from reactive oxygen speci ...
and omega-3 fatty acid
Omega−3 fatty acids, also called omega−3 oils, ω−3 fatty acids or ''n''−3 fatty acids, are polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) characterized by the presence of a double bond three atoms away from the terminal methyl group in their ...
s ( EPA and DHA).
Young Atlantic cod or haddock
The haddock (''Melanogrammus aeglefinus'') is a saltwater ray-finned fish from the Family (biology), family Gadidae, the true cods. It is the only species in the Monotypy, monotypic genus ''Melanogrammus''. It is found in the North Atlantic Oce ...
prepared in strips for cooking is called scrod
Scrod or schrod () is a small cod or haddock, and sometimes other whitefish (fisheries term), whitefish, used as food. It is usually served as a fish fillet, fillet, though formerly it was often split instead.
In the wholesale fish business, scr ...
. In the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, Atlantic cod
The Atlantic cod (: cod; ''Gadus morhua'') is a fish of the family Gadidae, widely consumed by humans. It is also commercially known as '' cod'' or ''codling''.fish and chips
Fish and chips is a hot dish consisting of batter (cooking), battered and fried fish, served with French fries, chips. Often considered the national dish of the United Kingdom, fish and chips originated in England in the 19th century. Today, ...
, along with haddock
The haddock (''Melanogrammus aeglefinus'') is a saltwater ray-finned fish from the Family (biology), family Gadidae, the true cods. It is the only species in the Monotypy, monotypic genus ''Melanogrammus''. It is found in the North Atlantic Oce ...
and plaice
Plaice is a common name for a group of flatfish that comprises four species: the European, American, Alaskan and scale-eye plaice.
Commercially, the most important plaice is the European. The principal commercial flatfish in Europe, it is ...
. Cod's soft liver can be tinned (canned) and eaten.
History
 Cod has been an important economic commodity in
Cod has been an important economic commodity in international market
Global marketing is defined as “marketing on a worldwide scale reconciling or taking global operational differences, similarities and opportunities to reach global objectives".
Global marketing is also a field of study in general business mana ...
s since the Viking
Vikings were seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway, and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded, and settled throughout parts of Europe.Roesdahl, pp. 9� ...
period (around 800 AD). Norwegians
Norwegians () are an ethnic group and nation native to Norway, where they form the vast majority of the population. They share a common culture and speak the Norwegian language. Norwegians are descended from the Norsemen, Norse of the Early ...
travelled with dried cod and soon a dried cod market developed in southern Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
. This market has lasted for more than 1,000 years, enduring the Black Death
The Black Death was a bubonic plague pandemic that occurred in Europe from 1346 to 1353. It was one of the list of epidemics, most fatal pandemics in human history; as many as people perished, perhaps 50% of Europe's 14th century population. ...
, wars and other crises, and is still an important Norwegian fish trade. The Portuguese began fishing cod in the 15th century. Clipfish
Dried and salted cod, sometimes referred to as salt cod or saltfish or salt dolly, is cod which has been preserved by drying after salting. Cod which has been dried without the addition of salt is stockfish. Salt cod was long a major export of ...
is widely enjoyed in Portugal. The Basques
The Basques ( or ; ; ; ) are a Southwestern European ethnic group, characterised by the Basque language, a Basque culture, common culture and shared genetic ancestry to the ancient Vascones and Aquitanians. Basques are indigenous peoples, ...
played an important role in the cod trade, and allegedly found the Canadian fishing banks before Columbus' discovery of America.
The North American east coast developed in part due to the vast cod stocks. Many cities in the New England area are located near cod fishing grounds. The fish was so important to the history and development of Massachusetts
Massachusetts ( ; ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Maine to its east, Connecticut and Rhode ...
, the state's House of Representatives hung a wood carving of a codfish, known as the Sacred Cod of Massachusetts
The Sacred Cod is a carved-wood effigy of an Atlantic codfish, painted to the life, hanging in the House of Representatives chamber of Boston's Massachusetts State House"a memorial of the importance of the Cod-Fishery to the welfare of this C ...
, in its chambers.
Apart from the long history, cod differ from most fish because the fishing grounds are far from population centres. The large cod fisheries along the coast of North Norway
Northern Norway (, , ; ) is a geographical region of Norway, consisting of the three northernmost counties Nordland, Troms and Finnmark, in total about 35% of the Norwegian mainland. Some of the largest towns in Northern Norway (from south to no ...
(and in particular close to the Lofoten
Lofoten ( , ; ; ) is an archipelago and a Districts of Norway, traditional district in the county of Nordland, Norway. Lofoten has distinctive scenery with dramatic mountains and peaks, open sea and sheltered bays, beaches, and untouched lands. T ...
islands) have been developed almost uniquely for export
An export in international trade is a good produced in one country that is sold into another country or a service provided in one country for a national or resident of another country. The seller of such goods or the service provider is a ...
, depending on sea transport of stockfish
Stockfish is unsalted fish, especially cod, dried by cold air and wind on wooden racks (which are called "hjell" in Norway) on the foreshore. The drying of food is the world's oldest known preservation method, and dried fish has a storage li ...
over large distances. Since the introduction of salt, dried and salted cod
Dried and salted cod, sometimes referred to as salt cod or saltfish or salt dolly, is cod which has been preserved by drying after salting. Cod which has been dried without the addition of salt is stockfish. Salt cod was long a major export of ...
(clipfish or 'klippfisk' in Norwegian) has also been exported. By the end of the 14th century, the Hanseatic League
The Hanseatic League was a Middle Ages, medieval commercial and defensive network of merchant guilds and market towns in Central Europe, Central and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Growing from a few Northern Germany, North German towns in the ...
dominated trade operations and sea transport, with Bergen
Bergen (, ) is a city and municipalities of Norway, municipality in Vestland county on the Western Norway, west coast of Norway. Bergen is the list of towns and cities in Norway, second-largest city in Norway after the capital Oslo.
By May 20 ...
as the most important port.
William Pitt the Elder
William Pitt, 1st Earl of Chatham (15 November 170811 May 1778) was a British Whig statesman who served as Prime Minister of Great Britain from 1766 to 1768. Historians call him "Chatham" or "Pitt the Elder" to distinguish him from his son ...
, criticizing the Treaty of Paris in Parliament
In modern politics and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
, claimed cod was "British gold"; and that it was folly to restore Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region of Labrador, having a total size of . As of 2025 the population ...
fishing rights to the French.
In the 17th and 18th centuries in the New World, especially in Massachusetts
Massachusetts ( ; ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Maine to its east, Connecticut and Rhode ...
and Newfoundland, cod became a major commodity, creating trade networks and cross-cultural exchanges. In 1733, Britain tried to gain control over trade between New England and the British Caribbean
The Caribbean ( , ; ; ; ) is a region in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, mostly overlapping with the West Indies. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America ...
by imposing the Molasses Act
The Molasses Act 1733 ( 6 Geo. 2. c. 13), also known as the Trade of Sugar Colonies Act 1732, was an act of the Parliament of Great Britain that imposed a tax of six pence per gallon on imports of molasses from non-British colonies. Parliament ...
, which they believed would eliminate the trade by making it unprofitable. The cod trade grew instead, because the "French were eager to work with the New Englanders in a lucrative contraband arrangement". In addition to increasing trade, the New England settlers organized into a "codfish aristocracy". The colonists rose up against Britain's "tariff on an import".
In the 20th century, Iceland
Iceland is a Nordic countries, Nordic island country between the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic and Arctic Oceans, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge between North America and Europe. It is culturally and politically linked with Europe and is the regi ...
re-emerged as a fishing power and entered the Cod Wars
The Cod Wars (; also known as , ; ) were a series of 20th-century confrontations between the United Kingdom (with aid from West Germany) and Iceland about Exclusive economic zone, fishing rights in the North Atlantic. Each of the disputes ended ...
. In the late 20th and early 21st centuries, fishing off the European and American coasts severely depleted stocks and become a major political issue. The necessity of restricting catches to allow stocks to recover upset the fishing industry and politicians who are reluctant to hurt employment.
Collapse of the Atlantic northwest cod fishery
On July 2, 1992, the HonourableJohn Crosbie
John Carnell Crosbie (January 30, 1931 – January 10, 2020) was a Canadian provincial and federal politician who served as the 12th lieutenant governor of Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada. Prior to being lieutenant governor, he served as a ...
, Canadian Federal Minister of Fisheries and Oceans, declared a two-year moratorium on the Northern Cod fishery, a designated fishing region off the coast of Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region of Labrador, having a total size of . As of 2025 the population ...
, after data showed that the total cod biomass had suffered a collapse to less than 1% of its normal value.Hamilton and Butler, 1. The minister championed the measure as a temporary solution, allowing the cod population time to recover. The fisheries had long shaped the lives and communities on Canada's Atlantic eastern coast for the preceding five centuries. Societies which are dependent on fishing have a strong mutual relationship with them: the act of fishing changes the ecosystems' balance, which forces the fishery and, in turn, the fishing societies to adapt to new ecological conditions.
The near-complete destruction of the Atlantic northwest cod biomass off the shores devastated coastal communities, which had been overexploiting the same cod population for decades. The fishermen along the Atlantic northwest had employed modern fishing technologies, including the ecologically-devastating practice of trawling
Trawling is an industrial method of fishing that involves pulling a fishing net through the water behind one or more boats. The net used for trawling is called a trawl. This principle requires netting bags which are towed through water to catch di ...
, especially in the years leading up to the 1990s, in the misguided belief that fishing stocks are perpetually plentiful and unable to be depleted. After this assumption was empirically and abruptly shown to be incorrect, to the dismay of government officials and rural workers, some 19,000 fishermen and cod processing plant workers in Newfoundland lost their employment. Nearly 40,000 workers and harvesters in the provinces of Newfoundland and Labrador applied for the federal relief program TAGS (the Atlantic Groundfish Strategy). Abandoned and rusting fishing boats still litter the coasts of Newfoundland and the Canadian northwest to this day.
The fishery minister, John Crosbie, after delivering a speech on the day before the declaration of the moratorium, or July 1, 1992, was publicly heckled and verbally harassed by disgruntled locals at a fishing village. The moratorium, initially lasting for only two years, was indefinitely extended after it became evident that cod populations had not recovered at all but, instead, had continued to spiral downward in both size and numbers, due to the damage caused by decades of horrible fishing practices, and the fact that the moratorium had permitted exceptions for food fisheries for "personal consumption" purposes to this very day. Some 12,000 tons of Northwest cod are still being caught every year along the Newfoundland coast by local fishermen.
The collapse of the four-million ton biomass, which had persevered through several previous marine extinctions over tens of millions of years, in a timespan of no more than 20 years, is oft-cited by researchers as one of the most visible examples of the phenomenon of the "Tragedy of the Commons." Factors which had been implicated as contributing to the collapse include: overfishing; government mismanagement; the disregard of scientific uncertainty; warming habitat waters; declining reproduction; and plain human ignorance. The Northern Cod biomass has been recovering slowly since the imposition of the moratorium. However, as of 2021, the growth of the cod population has been stagnant since 2017, and some scientists argue that the population will not rebound unless the Fisheries Department of Canada lower its yearly quota to 5,000 tons.
See also
* '' The Cod Fisheries: The History of an International Economy'', for the Canadian industryReferences
Further reading
* Bavington, Dean L. Y. ''Managed Annihilation: An Unnatural History of the Newfoundland Cod Collapse'' (University of British Columbia Press; 2010) 224 pages. Links the collapse of Newfoundland and Labrador cod fishing to state management of the resource. * * *Mark Kurlansky
Mark Kurlansky (December 7, 1948) is an American journalist and author who has written a number of books of fiction and nonfiction. His 1997 book, ''Cod: A Biography of the Fish That Changed the World'' (1997), was an international bestseller a ...
(1997). ''Cod: A Biography of the Fish That Changed the World''.
*
External links
Codtrace
.
fishbase.org – Scientific Names for Gadus
Fisheries Heritage website, Newfoundland and Labrador
(archived)
Species factsheet on cod from the UK Sea Fish Industry Authority
(PDF, 2MB) * {{Authority control Commercial fish Gadidae Fish common names