Coast Range Arc on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Coast Range Arc was a large
The Coast Range Arc was a large
 Volcanism in the arc began during the
Volcanism in the arc began during the 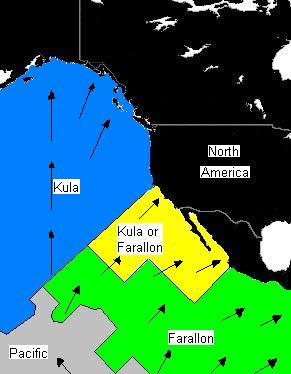 One of the major events during the Coast Range Arc was about 85 million years ago when a huge
One of the major events during the Coast Range Arc was about 85 million years ago when a huge  Since the end of the Coast Range Arc about 50 million years ago, many volcanoes have disappeared from
Since the end of the Coast Range Arc about 50 million years ago, many volcanoes have disappeared from
 Intrusions of the Coast Range Arc are intruded by widespread
Intrusions of the Coast Range Arc are intruded by widespread
 The Coast Range Arc was a large
The Coast Range Arc was a large volcanic arc
A volcanic arc (also known as a magmatic arc) is a belt of volcanoes formed above a subducting oceanic tectonic plate, with the belt arranged in an arc shape as seen from above. Volcanic arcs typically parallel an oceanic trench, with the arc ...
system, extending from northern Washington
Washington most commonly refers to:
* George Washington (1732–1799), the first president of the United States
* Washington (state), a state in the Pacific Northwest of the United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A ...
through British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Situated in the Pacific Northwest between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains, the province has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that ...
and the Alaska Panhandle
Southeast Alaska, often abbreviated to southeast or southeastern, and sometimes called the Alaska(n) panhandle, is the southeastern portion of the U.S. state of Alaska, bordered to the east and north by the northern half of the Canadian provi ...
to southwestern Yukon
Yukon () is a Provinces and territories of Canada, territory of Canada, bordering British Columbia to the south, the Northwest Territories to the east, the Beaufort Sea to the north, and the U.S. state of Alaska to the west. It is Canada’s we ...
. The Coast Range Arc lies along the western margin of the North American Plate in the Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (PNW; ) is a geographic region in Western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Though no official boundary exists, the most common ...
of western North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
. Although taking its name from the Coast Mountains
The Coast Mountains () are a major mountain range in the Pacific Coast Ranges of western North America, extending from southwestern Yukon through the Alaska Panhandle and virtually all of the British Columbia Coast, Coast of British Columbia sout ...
, this term is a geologic grouping rather than a geographic one, and the Coast Range Arc extended south into the High Cascades of the Cascade Range
The Cascade Range or Cascades is a major mountain range of western North America, extending from southern British Columbia through Washington (state), Washington and Oregon to Northern California. It includes both non-volcanic mountains, such as m ...
, past the Fraser River
The Fraser River () is the longest river within British Columbia, Canada, rising at Fraser Pass near Blackrock Mountain (Canada), Blackrock Mountain in the Rocky Mountains and flowing for , into the Strait of Georgia just south of the City of V ...
which is the northward limit of the Cascade Range proper.
The Coast Range Arc formed as a result of subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere and some continental lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at the convergent boundaries between tectonic plates. Where one tectonic plate converges with a second p ...
of the Kula and pre-existing Farallon Plates. It is most famous for being the largest single body of granitic
A granitoid is a broad term referring to a diverse group of coarse-grained igneous rocks that are widely distributed across the globe, covering a significant portion of the Earth's exposed surface and constituting a large part of the continental ...
rock in North America, which is usually referred to as the Coast Plutonic Complex or the Coast Mountains Batholith. It is a coast-parallel continental volcanic arc similar to the Andes
The Andes ( ), Andes Mountains or Andean Mountain Range (; ) are the List of longest mountain chains on Earth, longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range ...
of South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion o ...
and the largest continent
A continent is any of several large geographical regions. Continents are generally identified by convention (norm), convention rather than any strict criteria. A continent could be a single large landmass, a part of a very large landmass, as ...
al volcanic arc fossil in the world.
Geology
Evolution
 Volcanism in the arc began during the
Volcanism in the arc began during the Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the more recent of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''cre ...
period 100 million years ago based on andesitic
Andesite () is a volcanic rock of intermediate composition. In a general sense, it is the intermediate type between silica-poor basalt and silica-rich rhyolite. It is fine-grained (aphanitic) to porphyritic in texture, and is composed predomina ...
composition of the Early Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous (geochronology, geochronological name) or the Lower Cretaceous (chronostratigraphy, chronostratigraphic name) is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 143.1 ...
volcanic sections and their close temporal and spatial association with masses of felsic
In geology, felsic is a grammatical modifier, modifier describing igneous rocks that are relatively rich in elements that form feldspar and quartz.Marshak, Stephen, 2009, ''Essentials of Geology,'' W. W. Norton & Company, 3rd ed. It is contrasted ...
intrusive igneous rock
Igneous rock ( ), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rocks are formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava.
The magma can be derived from partial ...
with phaneritic
A phanerite is an igneous rock whose microstructure is made up of crystals large enough to be distinguished with the unaided human eye. In contrast, the crystals in an aphanitic rock are too fine-grained to be identifiable. Phaneritic texture fo ...
texture called tonalite
Tonalite is an igneous rock, igneous, plutonic (Intrusive rock, intrusive) rock (geology), rock, of felsic composition, with phaneritic (coarse-grained) texture. Feldspar is present as plagioclase (typically oligoclase or andesine) with alkali fe ...
. The basement of the Coast Range Arc was likely Early Cretaceous and Late Jurassic
The Late Jurassic is the third Epoch (geology), epoch of the Jurassic Period, and it spans the geologic time scale, geologic time from 161.5 ± 1.0 to 143.1 ± 0.8 million years ago (Ma), which is preserved in Upper Jurassic stratum, strata.Owen ...
intrusions. Stratigraphic and field relations in the arc suggest that the Coast Range Arc was created on Stikinia, a geologic feature that formed in an older volcanic arc environment during the Paleozoic
The Paleozoic ( , , ; or Palaeozoic) Era is the first of three Era (geology), geological eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. Beginning 538.8 million years ago (Ma), it succeeds the Neoproterozoic (the last era of the Proterozoic Eon) and ends 251.9 Ma a ...
and Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era is the Era (geology), era of Earth's Geologic time scale, geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous Period (geology), Periods. It is characterized by the dominance of archosaurian r ...
periods.
 One of the major events during the Coast Range Arc was about 85 million years ago when a huge
One of the major events during the Coast Range Arc was about 85 million years ago when a huge rift
In geology, a rift is a linear zone where the lithosphere is being pulled apart and is an example of extensional tectonics. Typical rift features are a central linear downfaulted depression, called a graben, or more commonly a half-graben ...
developed near the center of the oceanic Farallon Plate. This rifting event created the oceanic Kula Plate. It is unknown why such a large rupture of the Farallon Plate occurred. Some geologists believe some fundamental change in convection within the Earth's mantle caused the rifting event, while others believe the huge oceanic plate became mechanically unstable as it continued to subduct beneath the Pacific Northwest. The Kula Plate once again continued to subduct beneath the continental margin, supporting the Coast Range Arc.
Volcanism began to decline along the length of the arc about 60 million years ago during the early Paleogene
The Paleogene Period ( ; also spelled Palaeogene or Palæogene) is a geologic period and system that spans 43 million years from the end of the Cretaceous Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Neogene Period Ma. It is the fir ...
period of the Cenozoic
The Cenozoic Era ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterized by the dominance of mammals, insects, birds and angiosperms (flowering plants). It is the latest of three g ...
era as the rapid northern movement of the Kula Plate became parallel with the Pacific Northwest, creating a transform fault plate boundary similar to the Queen Charlotte Fault. During this passive plate boundary, the Kula Plate began subducting underneath Alaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the north ...
and southwestern Yukon
Yukon () is a Provinces and territories of Canada, territory of Canada, bordering British Columbia to the south, the Northwest Territories to the east, the Beaufort Sea to the north, and the U.S. state of Alaska to the west. It is Canada’s we ...
at the northern end of the arc during the early Eocene
The Eocene ( ) is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (Ma). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes ...
period.
The Coast Range Arc was home to some of the world's most dangerous and explosive volcanoes. Cataclysmic eruptions at the British Columbia–Yukon border created a huge nested caldera
A caldera ( ) is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcanic eruption. An eruption that ejects large volumes of magma over a short period of time can cause significant detriment to the str ...
called the Bennett Lake Volcanic Complex about 50 million years ago during the early Eocene
The Eocene ( ) is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (Ma). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes ...
period. These eruptions were from vents along arcuate fracture systems associated with the caldera, which discharged about of pyroclastic material. This volcanic event occurred shortly before nearly all the Kula Plate had been subducted beneath the North American Plate about 40 million years ago.
 Since the end of the Coast Range Arc about 50 million years ago, many volcanoes have disappeared from
Since the end of the Coast Range Arc about 50 million years ago, many volcanoes have disappeared from erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as Surface runoff, water flow or wind) that removes soil, Rock (geology), rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust#Crust, Earth's crust and then sediment transport, tran ...
. What remains of the Coast Range Arc to this day are granitic
A granitoid is a broad term referring to a diverse group of coarse-grained igneous rocks that are widely distributed across the globe, covering a significant portion of the Earth's exposed surface and constituting a large part of the continental ...
intrusion
In geology, an igneous intrusion (or intrusive body or simply intrusion) is a body of intrusive igneous rock that forms by crystallization of magma slowly cooling below the surface of the Earth. Intrusions have a wide variety of forms and com ...
s, which were formed when magma intruded and cooled at depth beneath the volcanoes. However, remnants of some volcanoes exist in southwestern Yukon, including Montana Mountain, Mount Nansen, and the Bennett Lake, Mount Skukum and Sifton Range volcanic complexes.
Many granitic rocks of the Coast Range Arc are plentiful in the North Cascades of the Cascade Range, which is the southernmost boundary of the arc. Here, these granites intruded highly deformed ocean rocks and assorted fragments from pre-existing island arcs, largely remnants of the ancient Bridge River Ocean which lay between North America and the pre-existing Insular Islands. Massive amounts of molten granite injected over this period, burning the old oceanic sediments into a glittering medium-grade metamorphic rock
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock ( protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, caus ...
called schist
Schist ( ) is a medium-grained metamorphic rock generally derived from fine-grained sedimentary rock, like shale. It shows pronounced ''schistosity'' (named for the rock). This means that the rock is composed of mineral grains easily seen with a l ...
.
The older intrusions of the Coast Range Arc were then deformed under the heat and pressure of later intrusions, turning them into a layered metamorphic rock known as gneiss
Gneiss (pronounced ) is a common and widely distributed type of metamorphic rock. It is formed by high-temperature and high-pressure metamorphic processes acting on formations composed of igneous or sedimentary rocks. This rock is formed under p ...
. In some places, mixtures of older intrusive rocks and the original oceanic rocks have been distorted and warped under intense heat, weight and stress to create unusual swirled patterns known as migmatite
Migmatite is a composite rock (geology), rock found in medium and high-grade metamorphic environments, commonly within Precambrian craton, cratonic blocks. It consists of two or more constituents often layered repetitively: one layer is an old ...
, appearing to have been nearly melted in the procedure. The remarkable migmatite of the Chelan and Skagit areas in Washington
Washington most commonly refers to:
* George Washington (1732–1799), the first president of the United States
* Washington (state), a state in the Pacific Northwest of the United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A ...
are well known in geologic circles. During construction of intrusions 70 and 57 million years ago, the northern motion of the Kula Plate might have been between per year. However, other geologic studies determined the Kula Plate moved at a rate as fast as per year.
Geological importance
 Intrusions of the Coast Range Arc are intruded by widespread
Intrusions of the Coast Range Arc are intruded by widespread basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial ...
ic dikes
Dyke or dike may refer to:
General uses
* Dyke (slang), a slang word meaning "lesbian"
* Dike (geology), formations of magma or sediment that cut through and across the layering of adjacent rocks
* Dike (mythology), ''Dikē'', the Greek goddess ...
. These dikes, although not voluminous, provide an important sampling of the post-arc lithosphere
A lithosphere () is the rigid, outermost rocky shell of a terrestrial planet or natural satellite. On Earth, it is composed of the crust and the lithospheric mantle, the topmost portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time ...
. Additionally, widespread volcanic belt
A volcanic belt is a large volcanically active region. Other terms are used for smaller areas of activity, such as volcanic fields or volcanic systems. Volcanic belts are found above zones of unusually high temperature () where magma is created ...
s, such as the Anahim Volcanic Belt, lie in the middle of the Coast Range Arc. Volcanics that form the Anahim Volcanic Belt are not strictly related to Coast Range Arc subduction, but might have formed as a result of the North American Plate sliding over a place that has experienced active volcanism for a long period of time which is described as the Anahim hotspot. During its formation, it lay beneath granitic intrusions of the Coast Range Arc. The approximately long Bella Bella and approximately long Gale Passage dike swarm
A dike swarm (American English, American spelling) or dyke swarm (British English, British spelling) is a large Geology, geological structure consisting of a major group of parallel, linear, or radially oriented Magma, magmatic dike (geolo ...
s lie in granitic intrusions of the Coast Range Arc and are used to calculate the first appearance of the Anahim hotspot about 13 and 12 million years ago.
See also
*Coast Mountains
The Coast Mountains () are a major mountain range in the Pacific Coast Ranges of western North America, extending from southwestern Yukon through the Alaska Panhandle and virtually all of the British Columbia Coast, Coast of British Columbia sout ...
*Geology of British Columbia
The geology of British Columbia is a function of its location on the leading edge of the North American continent. The mountainous physiography and the diversity of the different types and ages of rock hint at the complex geology, which is st ...
* Geology of the Pacific Northwest
* Cascade Volcanoes
*Cascadia subduction zone
The Cascadia subduction zone is a convergent plate boundary, about off the Pacific coast of North America, that stretches from northern Vancouver Island in Canada to Northern California in the United States. It is capable of producing 9.0+ m ...
* Volcanism in Canada
*Pacific Ring of Fire
The Ring of Fire (also known as the Pacific Ring of Fire, the Rim of Fire, the Girdle of Fire or the Circum-Pacific belt) is a tectonic belt of volcanoes and earthquakes.
It is about long and up to about wide, and surrounds most of the Pa ...
References
{{reflist Volcanic arcs Cascade Range Coast Mountains Volcanism of British Columbia Volcanism of Washington (state) Volcanism of Yukon Volcanism of Alaska Cretaceous System of North America Cretaceous volcanism Eocene volcanism