cloud atlas on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
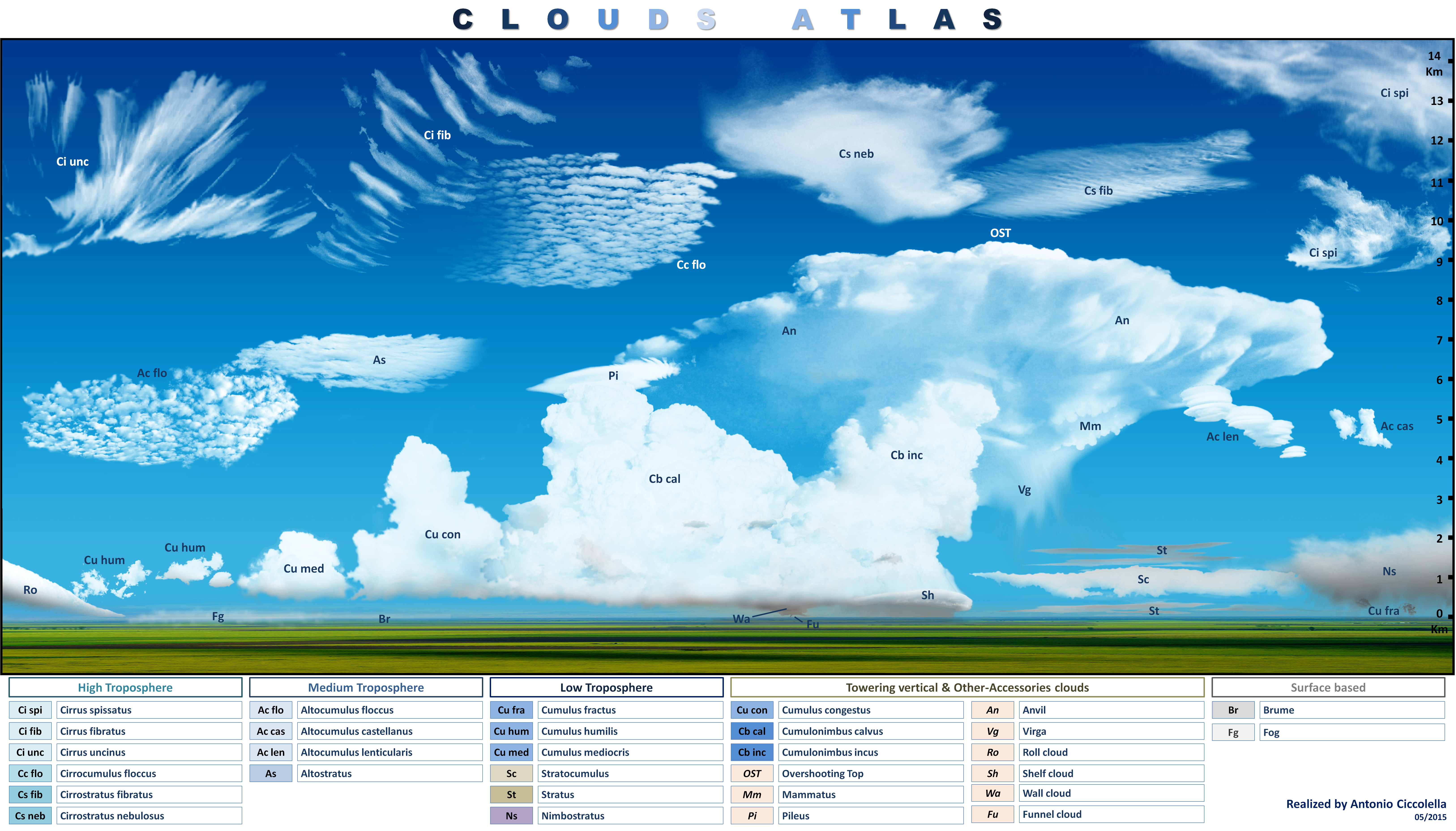 A cloud atlas is a pictorial key (or an
A cloud atlas is a pictorial key (or an
WMO International Cloud Atlas 2017Cloud Atlas at Clouds-Online.comHouze'sCloud Atlas at University of Washington Online Cloud Atlas at University of Missouri-Columbia
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20121110220538/https://itunes.apple.com/hu/app/cloud-atlas-for-in-flight/id409717141?mt=8 Cloud Atlas For In-Flight Spotters {{DEFAULTSORT:Cloud Atlas Clouds Atlases
 A cloud atlas is a pictorial key (or an
A cloud atlas is a pictorial key (or an atlas
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of world map, maps of Earth or of a continent or region of Earth. Advances in astronomy have also resulted in atlases of the celestial sphere or of other planets.
Atlases have traditio ...
) to the nomenclature
Nomenclature (, ) is a system of names or terms, or the rules for forming these terms in a particular field of arts or sciences. (The theoretical field studying nomenclature is sometimes referred to as ''onymology'' or ''taxonymy'' ). The principl ...
of cloud
In meteorology, a cloud is an aerosol consisting of a visible mass of miniature liquid droplets, frozen crystals, or other particles, suspended in the atmosphere of a planetary body or similar space. Water or various other chemicals may ...
s. Early cloud atlases were an important element in the training of meteorologist
A meteorologist is a scientist who studies and works in the field of meteorology aiming to understand or predict Earth's atmosphere of Earth, atmospheric phenomena including the weather. Those who study meteorological phenomena are meteorologists ...
s and in weather forecasting
Weather forecasting or weather prediction is the application of science and technology forecasting, to predict the conditions of the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere for a given location and time. People have attempted to predict the weather info ...
, and the author of a 1923 atlas stated that "increasing use of the air as a means of transportation will require and lead to a detailed knowledge of all the secrets of cloud building." page 3
History
Throughout the 19th century, nomenclatures and classifications of cloud types were developed, followed late in the century by cloud atlases. The firstnomenclature
Nomenclature (, ) is a system of names or terms, or the rules for forming these terms in a particular field of arts or sciences. (The theoretical field studying nomenclature is sometimes referred to as ''onymology'' or ''taxonymy'' ). The principl ...
of clouds in English was published by Luke Howard
Luke Howard (28 November 1772 – 21 March 1864) was a British manufacturing chemist and an amateur meteorologist with broad interests in science. His lasting contribution to science is a nomenclature system for clouds, which he proposed in ...
in 1802. It followed a similar effort in French by Jean-Baptiste Lamarck
Jean-Baptiste Pierre Antoine de Monet, chevalier de Lamarck (1 August 1744 – 18 December 1829), often known simply as Lamarck (; ), was a French naturalist, biologist, academic, and soldier. He was an early proponent of the idea that biologi ...
in 1801. Howard's nomenclature defined four fundamental types of clouds: cirrus or thread-cloud, cumulus or heap-cloud, stratus or flat cloud (level sheet), and nimbus or rain-cloud (see List of cloud types
The list of cloud types groups all genera as ''high'' (cirro-, cirrus), ''middle'' (alto-), ''multi-level'' (nimbo-, cumulo-, cumulus), and ''low'' (strato-, stratus). These groupings are determined by the altitude level or levels in the troposphe ...
).
There followed a long period of development of the field of meteorology
Meteorology is the scientific study of the Earth's atmosphere and short-term atmospheric phenomena (i.e. weather), with a focus on weather forecasting. It has applications in the military, aviation, energy production, transport, agricultur ...
and the classification of clouds. In the late 19th century, Clement Ley and Ralph Abercromby
Lieutenant-general (United Kingdom), Lieutenant-General Sir Ralph Abercromby, (7 October 173428 March 1801) was a British Army officer, politician and colonial administrator who served as the governor of Trinidad in 1797. Rising to the rank ...
contributed to building a classification for clouds.. Ley's book, ''Cloudland'', was influential among meteorologists, while Abercromby wrote scientific paper
Scientific literature encompasses a vast body of academic papers that spans various disciplines within the natural and social sciences. It primarily consists of academic papers that present original empirical research and theoretical ...
s on the subject, stressing that clouds are the same everywhere in the world (a novel observation at the time). Abercromby also collaborated with Hugo Hildebrand Hildebrandsson to propose a detailed classification of clouds, which was adopted in Hildebrandsson's 1890 ''Cloud Atlas''. In 1891 the International Meteorological Conference at Munich recommended the general adoption of Abercromby and Hildebrandsson's classification system. The year 1896 was declared International Year of Clouds.
The first ''International Cloud Atlas
The ''International Cloud Atlas'' or simply the ''Cloud Atlas'', is a cloud atlas that was first published in 1896 and has remained in print since. Its initial purposes included aiding the training of meteorologists and promoting more consisten ...
'' was published in 1896, to coincide with another International Meteorological Conference. It was a political and technical triumph, and an immediate de facto standard
A ''de facto'' standard is a custom or convention that is commonly used even though its use is not required.
is a Latin phrase (literally " of fact"), here meaning "in practice but not necessarily ordained by law" or "in practice or actuality, ...
. The scientific photography of clouds required several technical advances, including faster films (shorter exposures), color, and sufficient contrast between cloud and sky. Albert Riggenbach used a Nicol prism to filter polarized light, thereby increasing the contrast. Other researchers achieved similar results using mirrors or lake surfaces, and selectively photographing in certain parts of the sky.
Many subsequent editions of ''International Cloud Atlas'' were published, including editions in 1906 and 1911. Several other cloud atlases appeared, including in 1908 M. J. Vincent's ''Atlas des Nuages'' (known in English as Vincent's Cloud Atlas), which was based on the 1906 ''International Cloud Atlas'', but with additions, and it classified the clouds into three group by height of the cloud base above ground: lower, middle, upper.
Notable cloud atlases
The 1890 ''Cloud Atlas'' is the first known cloud atlas and book of this title, by Hildebrandsson, Wladimir Köppen, and Georg von Neumayer. It was an expensivequarto
Quarto (abbreviated Qto, 4to or 4º) is the format of a book or pamphlet produced from full sheets printed with eight pages of text, four to a side, then folded twice to produce four leaves. The leaves are then trimmed along the folds to produc ...
book of chromolithographs reproducing 10 color oil paintings and 12 photographs for comparison, and was designed to explore the advantages and disadvantages of photography for the scientific illustration of cloud forms. Its printing was limited but as a proof of concept it was a great success, leading directly to the ''International Cloud Atlas''.
The first ''International Cloud Atlas
The ''International Cloud Atlas'' or simply the ''Cloud Atlas'', is a cloud atlas that was first published in 1896 and has remained in print since. Its initial purposes included aiding the training of meteorologists and promoting more consisten ...
'' was published in 1896. This was prepared by Hildebrandsson, Riggenbach, and Leon Teisserenc de Bort, members of the Clouds Commission of the International Meteorological Committee. It consists of color plates of clouds, mostly photographs but some paintings, and text in French, English, and German. The plates were selected from among 300 of the best color photographs of clouds provided by members of the commission. The atlas has remained in print since then, in multiple editions.
See also
*Classification
Classification is the activity of assigning objects to some pre-existing classes or categories. This is distinct from the task of establishing the classes themselves (for example through cluster analysis). Examples include diagnostic tests, identif ...
*List of cloud types
The list of cloud types groups all genera as ''high'' (cirro-, cirrus), ''middle'' (alto-), ''multi-level'' (nimbo-, cumulo-, cumulus), and ''low'' (strato-, stratus). These groupings are determined by the altitude level or levels in the troposphe ...
* Timeline of meteorology
References
External links
WMO International Cloud Atlas 2017
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20121110220538/https://itunes.apple.com/hu/app/cloud-atlas-for-in-flight/id409717141?mt=8 Cloud Atlas For In-Flight Spotters {{DEFAULTSORT:Cloud Atlas Clouds Atlases