Clonality on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
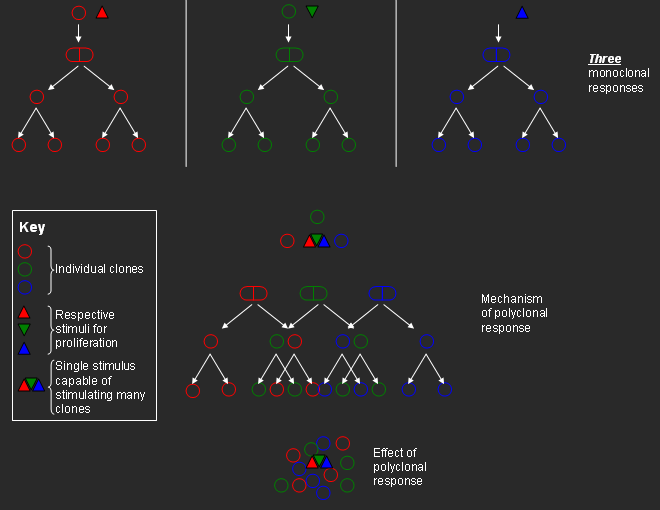 A clone is a group of ''identical'' cells that share a ''common ancestry'', meaning they are derived from the same cell.
Clonality implies the state of a cell or a substance being derived from one source or the other. Thus there are terms like ''polyclonal''—derived from many clones; ''oligoclonal''—derived from a few clones; and ''monoclonal''—derived from one clone. These terms are most commonly used in context of
A clone is a group of ''identical'' cells that share a ''common ancestry'', meaning they are derived from the same cell.
Clonality implies the state of a cell or a substance being derived from one source or the other. Thus there are terms like ''polyclonal''—derived from many clones; ''oligoclonal''—derived from a few clones; and ''monoclonal''—derived from one clone. These terms are most commonly used in context of
antibodies
An antibody (Ab) or immunoglobulin (Ig) is a large, Y-shaped protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as bacteria and viruses, including those that caus ...
or immunocytes.
Contexts
This concept of clone assumes importance as all the cells that form a clone share common ancestry, which has a very significant consequence: sharedgenotype
The genotype of an organism is its complete set of genetic material. Genotype can also be used to refer to the alleles or variants an individual carries in a particular gene or genetic location. The number of alleles an individual can have in a ...
.
# One of the most prominent usage is in describing a clone of B cell
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or inserted into the plasm ...
s. The B cells in the body have two important phenotypes
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology (physical form and structure), its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological properti ...
(functional forms)—the antibody secreting, terminally differentiated (that is, they cannot divide further) plasma cells, and the memory and the naive cells—both of which retain their proliferative potential.
# Another important area where one can talk of "clones" of cells is neoplasm
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
s. Many of the tumors derive from one
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sp ...
(sufficiently) mutated cell, so they are technically a single clone of cells. However, during course of cell division, one of the cells can get mutated further and acquire new characteristics to diverge as a new clone. However, this view of cancer onset has been challenged in recent years and many tumors have been argued to have polyclonal origin, i.e. derived from two or more cells or clones, including malignant mesothelioma.
# All the granulosa cells
A granulosa cell or follicular cell is a somatic cell of the sex cord that is closely associated with the developing female gamete (called an oocyte or egg) in the ovary of mammals.
Structure and function
In the primordial ovarian follicle, and ...
in a Graafian follicle
An ovarian follicle is a roughly spheroid cellular aggregation set found in the ovaries. It secretes hormones that influence stages of the menstrual cycle. In humans, women have approximately 200,000 to 300,000 follicles at the time of puberty, ea ...
are in fact clones.
# Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) is a rare, acquired, life-threatening disease of the blood characterized by destruction of red blood cells by the complement system, a part of the body's innate immune system. This destructive process ...
is a disorder of bone marrow cells resulting in shortened life of red blood cells, which is also a result of clonal expansion, i.e., all the altered cells are originally derived from a single cell, which also somewhat compromises the functioning of other "normal" bone marrow cells.
Basis of clonal proliferation
Most other cells cannot divide indefinitely as after a few cycles of cell division the cells stop expressing an enzymetelomerase
Telomerase, also called terminal transferase, is a ribonucleoprotein that adds a species-dependent telomere repeat sequence to the 3' end of telomeres. A telomere is a region of repetitive sequences at each end of the chromosomes of most euka ...
. The genetic material, in the form of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), continues to shorten with each cell division, and cells eventually stop dividing when they sense that their DNA is critically shortened. However, this enzyme in "youthful" cells replaces these lost bits (nucleotides
Nucleotides are Organic compound, organic molecules composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both o ...
) of DNA, thus making almost unlimited cycles of cell division possible. It is believed that the above-mentioned tissues have a constitutional elevated expression of telomerase. When ultimately many cells are produced by a single cell, ''clonal expansion'' is said to have taken place.
Concept of clonal colony
A somewhat similar concept is that of a ''clonal colony
A clonal colony or genet is a group of genetically identical individuals, such as plants, fungi, or bacteria, that have grown in a given location, all originating vegetatively, not sexually, from a single ancestor. In plants, an individual in ...
'' (also called a ''genet''), wherein the cells (usually unicellular) also share a common ancestry, but which also requires the products of clonal expansion to reside at "one place", or in close proximity. A clonal colony would be well exemplified by a bacterial culture
A microbiological culture, or microbial culture, is a method of multiplying microbial organisms by letting them reproduce in predetermined culture medium under controlled laboratory conditions. Microbial cultures are foundational and basic diag ...
colony, or the bacterial films that are more likely to be found ''in vivo'' (e.g., in infected multicellular hosts). Whereas, the cells of clones dealt with here are specialized cells of a multicellular organism (usually vertebrates), and reside at quite distant places. For instance, two plasma cells belonging to the same clone could be derived from different memory cells (in turn with shared clonality) and could be residing in quite distant locations, such as the cervical (in the neck) and inguinal (in the groin) lymph node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that includ ...
s.
Paramecium clonal reproduction and aging
The single-celleukaryote
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms ...
''Paramecium
''Paramecium'' ( , , plural "paramecia" only when used as a Common name, vernacular name) is a genus of eukaryotic, unicellular ciliates, widespread in freshwater, brackish, and Ocean, marine environments. Paramecia are often abundant in stagna ...
tetraurelia'' can undergo both asexual and sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves a complex life cycle in which a gamete ( haploid reproductive cells, such as a sperm or egg cell) with a single set of chromosomes combines with another gamete to produce a zygote tha ...
. Asexual or clonal reproduction occurs by binary fission
Binary may refer to:
Science and technology Mathematics
* Binary number, a representation of numbers using only two values (0 and 1) for each digit
* Binary function, a function that takes two arguments
* Binary operation, a mathematical o ...
. Binary fission involves mitosis
Mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new Cell nucleus, nuclei. Cell division by mitosis is an equational division which gives rise to genetically identic ...
-like behavior of the chromosomes similar to that of cells in higher organisms. The sexual forms of reproduction are autogamy
Autogamy or self-fertilization refers to the Cell fusion, fusion of two gametes that come from one individual. Autogamy is predominantly observed in the form of self-pollination, a Reproduction, reproductive mechanism employed by many flowering pl ...
, a kind of self-fertilization, and conjugation
Conjugation or conjugate may refer to:
Linguistics
*Grammatical conjugation, the modification of a verb from its basic form
*Emotive conjugation or Russell's conjugation, the use of loaded language
Mathematics
*Complex conjugation, the change o ...
, a kind of sexual interation between different cells. Clonal asexual reproduction can be initiated after completion of autogamy or conjugation. ''P. tetraurelia'' is able to replicate asexually for many generations but the dividing cells gradually age and after about 200 cell divisions, if the cells fail to undergo another autogamy or conjugation, they lose vitality and expire. This process is referred to as clonal aging. Experiments by Smith-Sonneborn, Holmes and Holmes and Gilley and BlackburnGilley, David; Blackburn, Elizabeth H. (1994). "Lack of telomere shortening during senescence in Paramecium" (PDF). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 91 (5): 1955–1958. Bibcode:1994PNAS...91.1955G. doi:10.1073/pnas.91.5.1955. PMC 43283. PMID 8127914 showed that accumulation of DNA damage
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. A weakened capacity for DNA repair is a risk factor for the development of cancer. DNA is constantly modified ...
is the likely cause of clonal aging in ''P. tetraurelia''. This aging process has similarities to the aging process in multicellular eukaryotes (See DNA damage theory of aging
The DNA damage theory of aging proposes that aging is a consequence of unrepaired accumulation of DNA damage (naturally occurring), naturally occurring DNA damage. Damage in this context is a DNA alteration that has an abnormal structure. Although ...
).
See also
*Clone (B-cell biology)
The process of immunological B-cell maturation involves transformation from an undifferentiated B cell to one that secretes antibodies with particular specificity. This differentiation and activation of the B cell occurs most rapidly after exposu ...
* Cloning
Cloning is the process of producing individual organisms with identical genomes, either by natural or artificial means. In nature, some organisms produce clones through asexual reproduction; this reproduction of an organism by itself without ...
* List of animals that have been cloned Banteng
*A Javan banteng calf was cloned from frozen cells using a cow as a surrogate, delivered via c-section on April 1, 2003, then hand raised at the San Diego Wild Animal Parks Infant Isolation Unit. It died due to an injury when it was less t ...
* Polyclonal antibodies
Polyclonal antibodies (pAbs) are antibodies that are secreted by different B cell lineages within the body (whereas monoclonal antibodies come from a single cell lineage). They are a collection of immunoglobulin molecules that react against a s ...
* Polyclonal response
Polyclonal B cell response is a natural mode of immune response exhibited by the adaptive immune system of mammals. It ensures that a single antigen is recognized and attacked through its overlapping parts, called epitopes, by multiple Clone (B-c ...
* Tumour heterogeneity
Tumour heterogeneity describes the observation that different tumour cells can show distinct morphological and phenotypic profiles, including cellular morphology, gene expression, metabolism, motility, proliferation, and metastatic potential. Th ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Clone (Cell Biology) Cell biology Cloning Immunology