Climate Of New York (state) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The climate of

 Winter temperatures vary just like the summer temperatures. The Adirondacks are the coldest in New York and are almost always below freezing for almost 3 straight months. The temps are between . Nights are cold and frigid, between . Most of Central New York, Mid Hudson Valley, and the Catskills have moderate temperatures that are not very cold but not mild, Between . Nights are cold but not frigid, between .
New York City, Hudson Valley, and Long Island are the warmest in New York State because of warmer ocean temperatures which keep these area between , warmer than locations upstate. Downstate nights typically range between 27 and 31 °F. The record low for New York state is , set at Stillwater Reservoir on February 9, 1934, and at Old Forge on February 18, 1979. In February 2015, Rochester experienced its coldest month ever, with an average temperature of . Later, 2015 had a near-record warm November and a record-breaking December. December 2015 was about 12 degrees F warmer than average, and several degrees over the previous record.
Winter temperatures vary just like the summer temperatures. The Adirondacks are the coldest in New York and are almost always below freezing for almost 3 straight months. The temps are between . Nights are cold and frigid, between . Most of Central New York, Mid Hudson Valley, and the Catskills have moderate temperatures that are not very cold but not mild, Between . Nights are cold but not frigid, between .
New York City, Hudson Valley, and Long Island are the warmest in New York State because of warmer ocean temperatures which keep these area between , warmer than locations upstate. Downstate nights typically range between 27 and 31 °F. The record low for New York state is , set at Stillwater Reservoir on February 9, 1934, and at Old Forge on February 18, 1979. In February 2015, Rochester experienced its coldest month ever, with an average temperature of . Later, 2015 had a near-record warm November and a record-breaking December. December 2015 was about 12 degrees F warmer than average, and several degrees over the previous record.
 Coastal extratropical cyclones, known as
Coastal extratropical cyclones, known as
Current Climate of the New England Region: New England Regional Assessment.
New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
New York may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* ...
(state) is generally humid continental
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation, dew, or fog to be present.
Humidity depe ...
, transitioning to the warmer humid subtropical
A humid subtropical climate is a subtropical -temperate climate type, characterized by long and hot summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between la ...
climate zone in the southeast part of the state. Winter temperatures average below freezing during January and February in much of the state of New York, but several degrees above freezing along the Atlantic coastline, including New York City and Long Island.
Seasonally, summer-like conditions prevail from May to early September statewide, while areas in far southern New York and New York City have summer conditions from late May through early-mid October. Due to frequent stormy weather and Lake Effect precipitation, the area of New York near the Great Lakes is much more cloudy than southernmost New York and Long Island. Winter-like conditions prevail from November through April in northern New York, and from December through March in southern New York. Greenhouse gas emission
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activities intensify the greenhouse effect. This contributes to climate change. Carbon dioxide (), from burning fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum, oil, and natural gas, is the main cause of climate chan ...
is low on a per-capita basis when compared to most other states due to the extensive use of mass transit, particularly across New York City. The significant urbanization within New York City has led to an urban heat island
Urban areas usually experience the urban heat island (UHI) effect; that is, they are significantly warmer than surrounding rural areas. The temperature difference is usually larger at night than during the day, and is most apparent when winds ar ...
, which causes temperatures to be warmer overnight in all seasons.
Annual precipitation is fairly even throughout the year across the state of New York. The Great Lakes region of New York sees the highest annual rain and snow amounts in the state of New York, and heavy lake-effect snow
Lake-effect snow is produced during cooler atmospheric conditions when a cold air mass moves across long expanses of warmer lake water. The lower layer of air, heated by the lake water, picks up water vapor from the lake and rises through colde ...
is common in both western and central New York in winter. In the hotter months, large, long-lived complexes of thunderstorms can invade the state from points to the west, while tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system with a low-pressure area, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its locat ...
s can bring rains and winds from the south during the summer and fall. Hurricane impacts on the state occur once every 15 years, with major hurricane impacts every 35 years. An average of ten tornado
A tornado is a violently rotating column of air that is in contact with the surface of Earth and a cumulonimbus cloud or, in rare cases, the base of a cumulus cloud. It is often referred to as a twister, whirlwind or cyclone, although the ...
es touch down in New York annually. Governors Island, Manhattan, in New York Harbor
New York Harbor is a bay that covers all of the Upper Bay. It is at the mouth of the Hudson River near the East River tidal estuary on the East Coast of the United States.
New York Harbor is generally synonymous with Upper New York Bay, ...
, is planned to host a US$1 billion research and education center poised to make New York City the global leader in addressing the climate crisis
''Climate crisis'' is a term that is used to describe global warming and climate change and their effects. This term and the term ''climate emergency'' have been used to emphasize the threat of global warming to Earth's natural environment an ...
.
Temperatures
The annual average temperature across the state ranges from around over the Adirondack Mountains to near across the Hudson Valley andLong Island
Long Island is a densely populated continental island in southeastern New York (state), New York state, extending into the Atlantic Ocean. It constitutes a significant share of the New York metropolitan area in both population and land are ...
, to around within New York City. Weather in New York is heavily influenced by two air masses: a warm, humid one from the southwest and a cold, dry one from the northwest. A cool, humid northeast airflow from the North Atlantic is much less common, and results in a persistent cloud deck with associated precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls from clouds due to gravitational pull. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, rain and snow mixed ("sleet" in Commonwe ...
which linger across the region for prolonged periods of time. Temperature differences between the warmer coast and far northern inland sections can exceed 36 degrees Fahrenheit (20 degrees Celsius), with rain near the coast and frozen precipitation, such as sleet and freezing rain, falling inland. Two-thirds of such events occur between November and April. which moves from northeast to southwest.
Unlike the vast majority of the state, New York City features a humid subtropical climate
A humid subtropical climate is a subtropical -temperate climate type, characterized by long and hot summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between ...
(Koppen ''Cfa''). New York City is an urban heat island, with temperatures 5–7 degrees Fahrenheit (3–4 degrees Celsius) warmer overnight than surrounding areas. In an effort to fight this warming, roofs of buildings are being painted white across the city in an effort to increase the reflection of solar energy, or albedo
Albedo ( ; ) is the fraction of sunlight that is Diffuse reflection, diffusely reflected by a body. It is measured on a scale from 0 (corresponding to a black body that absorbs all incident radiation) to 1 (corresponding to a body that reflects ...
.
Summer
Summers in New York State significantly vary by region. The summer climate is cooler in the Adirondacks due to higher elevation. The Adirondacks typically experience pleasant dry weather in the summer, with average daily maximum temperatures in the range of . Evenings in the Adirondacks are chilly, with average daily minimum temperatures ranging on average between . Most of Western New York, Central New York, the mid-Hudson Valley and the Catskills have moderate temperatures but are usually humid, with average maximum temperatures ranging . Nights in central New York state are often muggy, minimums averaging between . The New York City area and the Lower Hudson Valley in contrast feature more sultry and tropical summers with frequent and often long lasting bouts of high temperatures and dew points. Average maximum temperatures in this area are usually between but slightly cooler by the ocean and south-facing shorelines of Long Island average closer to . Nights are warm and muggy, dropping to an average of between . The record high for New York state is , set atTroy
Troy (/; ; ) or Ilion (; ) was an ancient city located in present-day Hisarlik, Turkey. It is best known as the setting for the Greek mythology, Greek myth of the Trojan War. The archaeological site is open to the public as a tourist destina ...
on July 22, 1926.
Heat waves
Heat wave
A heat wave or heatwave, sometimes described as extreme heat, is a period of abnormally hot weather generally considered to be at least ''five consecutive days''. A heat wave is usually measured relative to the usual climate in the area and ...
s are common in New York State which bring high heat and humidity. Heat waves occurs at least two times each summer and are an average of 3–5 days. Only the Adirondacks does not see oppressive temperatures during most heat waves in New York State. The Adirondacks have warm to hot temperatures with some humidity during a heat wave, but not to the extent of elsewhere in the state.
Winter snowfall
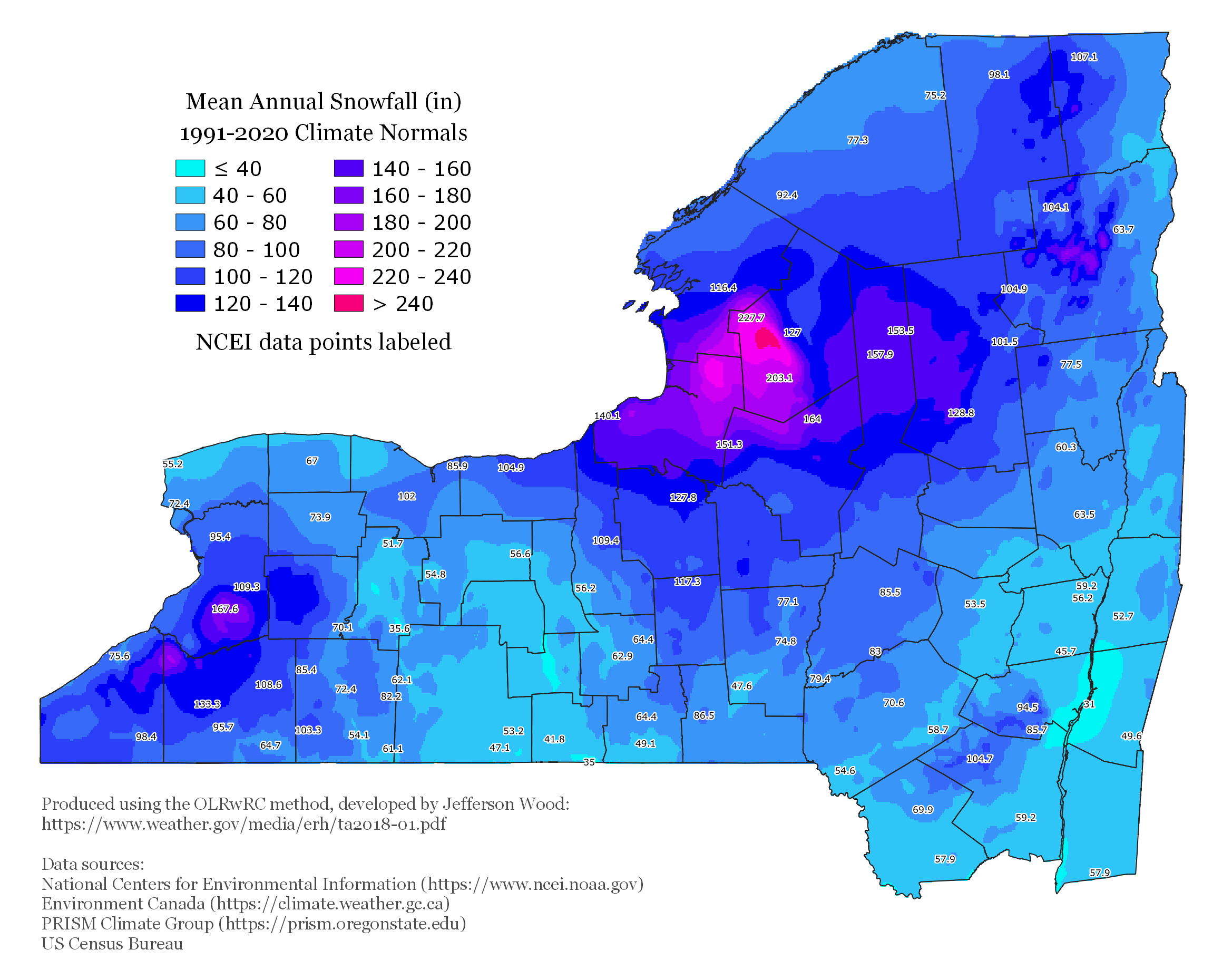
Snowfall in New York State also significantly varies by region. Lake-effect snow takes place in Western New York and the Adirondacks with Lake Ontario and Lake Erie. Lake-effect snow is very localized and areas may see feet of snow while others see only an inch or none at all. The Adirondacks see the most snowfall because of lake-effect snowfall and higher elevations which see between 100 and 200 inches per year and some may see more than 200 inches per year, especially western parts of the Adirondacks. Western and Central New York see between 75 and 150 inches per year depending on your location and where the bands hit. The Catskills see an average snowfall, between 25 and 50 inches and most of it is from nor-easters which are almost always snow. New York City, Long Island, and the Hudson Valley see the least amount of snowfall because they see warmer temperatures from the warmer ocean temperatures and the nor-easters there are mixed with rain, between 10 and 25 inches.Winter temperatures

 Winter temperatures vary just like the summer temperatures. The Adirondacks are the coldest in New York and are almost always below freezing for almost 3 straight months. The temps are between . Nights are cold and frigid, between . Most of Central New York, Mid Hudson Valley, and the Catskills have moderate temperatures that are not very cold but not mild, Between . Nights are cold but not frigid, between .
New York City, Hudson Valley, and Long Island are the warmest in New York State because of warmer ocean temperatures which keep these area between , warmer than locations upstate. Downstate nights typically range between 27 and 31 °F. The record low for New York state is , set at Stillwater Reservoir on February 9, 1934, and at Old Forge on February 18, 1979. In February 2015, Rochester experienced its coldest month ever, with an average temperature of . Later, 2015 had a near-record warm November and a record-breaking December. December 2015 was about 12 degrees F warmer than average, and several degrees over the previous record.
Winter temperatures vary just like the summer temperatures. The Adirondacks are the coldest in New York and are almost always below freezing for almost 3 straight months. The temps are between . Nights are cold and frigid, between . Most of Central New York, Mid Hudson Valley, and the Catskills have moderate temperatures that are not very cold but not mild, Between . Nights are cold but not frigid, between .
New York City, Hudson Valley, and Long Island are the warmest in New York State because of warmer ocean temperatures which keep these area between , warmer than locations upstate. Downstate nights typically range between 27 and 31 °F. The record low for New York state is , set at Stillwater Reservoir on February 9, 1934, and at Old Forge on February 18, 1979. In February 2015, Rochester experienced its coldest month ever, with an average temperature of . Later, 2015 had a near-record warm November and a record-breaking December. December 2015 was about 12 degrees F warmer than average, and several degrees over the previous record.
Records
Plant hardiness growing zones
New York State growing seasons have significant variations depending on the region. The Adirondacks, which encompasseshardiness zone
A hardiness zone is a geographic area defined as having a certain average annual minimum temperature, a factor relevant to the survival of many plants. In some systems other statistics are included in the calculations. The original and most widely ...
s 3 to 4, have the shortest growing season. Central New York, Western New York, the Catskills, and Mid-Hudson Valley encompass growing zones 5 to 6 and have much longer growing seasons and therefore more agriculture. Lower Hudson Valley, New York City, and Long Island, in growing zones 6 to 7, have the longest growing season in the state, and some areas of New York City, encompass growing zone 8, with it being due to the impact of the Atlantic and the urban heat island effect.
Cloudiness
Southeastern sections of the state near New York City have an average annual cloud cover of 59-62%, while areas of western New York around Buffalo average 71–75% cloud cover annually.Precipitation
Average precipitation across the region show maxima within the mountains of the Appalachians. Between of precipitation falls annually across the Northeastern United States, and New York's averages are similar, with maxima of over falling across southwestern Lewis County, northern Oneida County, central and southern Hamilton County, as well as northwesternUlster County
Ulster County is a county in the U.S. state of New York. It is situated along the Hudson River. As of the 2020 census, the population was 181,851. The county seat is Kingston. The county is named after the Irish province of Ulster. The count ...
. The lowest amounts occur near the northern borders with Vermont
Vermont () is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, New York (state), New York to the west, and the Provinces and territories of Ca ...
and Ontario
Ontario is the southernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Located in Central Canada, Ontario is the Population of Canada by province and territory, country's most populous province. As of the 2021 Canadian census, it ...
, as well as much of southwestern sections of the state. Temporally, a maximum in precipitation is seen around three peak times: 3 a.m., 10 a.m., and 6 p.m. During the summer, the 6 p.m. peak is most pronounced.
 Coastal extratropical cyclones, known as
Coastal extratropical cyclones, known as nor'easter
A nor'easter (also northeaster; see below) is a large-scale extratropical cyclone in the western North Atlantic Ocean. The name derives from the direction of the winds that blow from the northeast. Typically, such storms originate as a low ...
s, bring a bulk of the wintry precipitation to the region during the cold season as they track parallel to the coastline, forming along the natural temperature gradient of the Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream is a warm and swift Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows through the Straits of Florida and up the eastern coastline of the United States, then veers east near 36°N latitude (North Carolin ...
before moving up the coastline. The Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, are a mountain range in eastern to northeastern North America. The term "Appalachian" refers to several different regions associated with the mountain range, and its surrounding terrain ...
largely shield New York City from picking up any lake-effect snow, which develops in the wake of extratropical cyclones downwind of the Great Lakes. The Finger Lakes
The Finger Lakes are a group of eleven long, narrow, roughly north–south lakes located directly south of Lake Ontario in an area called the ''Finger Lakes region'' in New York (state), New York, in the United States. This region straddles th ...
of New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
New York may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* ...
are long enough for lake-effect precipitation. Lake-effect snow from the Finger Lakes (like elsewhere) occurs in upstate New York until those lakes freeze over. Annual average lake-effect snows exceed downwind of Lake Erie and downwind of Lake Ontario.
During the summer and early fall, mesoscale convective systems can move into the area from Canada and the Great Lakes. Tropical cyclones and their remains occasionally move into the region from the south and southwest. The region has experienced a couple heavy rainfall events that exceeded the 50-year return period, during October 1996 and October 1998, which suggest an increase in heavy rainfall along the coast. Barry Keim (June 1999)Current Climate of the New England Region: New England Regional Assessment.
University of New Hampshire
The University of New Hampshire (UNH) is a Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university with its main campus in Durham, New Hampshire, United States. It was founded and incorporated in 1866 as a land grant coll ...
. Retrieved on 2008-03-19.
Records
Air pollution
In terms of emissions, New York ranks 46th among the 50 states in the amount ofgreenhouse gas
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are the gases in the atmosphere that raise the surface temperature of planets such as the Earth. Unlike other gases, greenhouse gases absorb the radiations that a planet emits, resulting in the greenhouse effect. T ...
es generated per person. This efficiency is primarily due to the state's higher rate of mass transit use in and around New York City.
However, New York City (particularly Manhattan) has extremely high rates of air pollution, with high particle pollution and high cancer rates, which can be explained by extreme population density, despite low per-capita emissions rates.
Severe weather
New York experiences an average of tentornado
A tornado is a violently rotating column of air that is in contact with the surface of Earth and a cumulonimbus cloud or, in rare cases, the base of a cumulus cloud. It is often referred to as a twister, whirlwind or cyclone, although the ...
es per year, with one tornado every five years considered strong or violent (EF2-EF5). The return period for hurricane impacts on the state is 18–19 years, with major hurricane return periods between 70 and 74 years. In 2016, much of New York experienced a severe drought, including the Finger Lakes
The Finger Lakes are a group of eleven long, narrow, roughly north–south lakes located directly south of Lake Ontario in an area called the ''Finger Lakes region'' in New York (state), New York, in the United States. This region straddles th ...
region, where the drought was preceded by a very mild winter with minimal snow pack.
Climate data for select cities
See also
* Climate change in New York (state) * List of New York hurricanesReferences
Notes
{{North America topic, Climate ofNew York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
New York may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* ...
Environment of New York (state)