Climate Change In Argentina on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Climate change is predicted to have significant effects on the living conditions in
Climate change is predicted to have significant effects on the living conditions in
 There has been an increase in annual
There has been an increase in annual

 Agriculture will be affected by climate change. The decrease in precipitation that has been observed in the Andes will be predicted to continue to decrease, affecting hydroelectric energy even more. Glaciers are predicted to continue to recede and melt or in some areas, disappear. It is predicted that the Cuyo region could face a potential water crisis due to an increase in water demand owing to a reduction in river streamflows and higher
Agriculture will be affected by climate change. The decrease in precipitation that has been observed in the Andes will be predicted to continue to decrease, affecting hydroelectric energy even more. Glaciers are predicted to continue to recede and melt or in some areas, disappear. It is predicted that the Cuyo region could face a potential water crisis due to an increase in water demand owing to a reduction in river streamflows and higher
Centro de Investigaciones del Mar y la Atmósfera
Third National Communication of Argentina for Climate Change
Second National Communication of Argentina for Climate Change
{{Climate change Climate of Argentina
 Climate change is predicted to have significant effects on the living conditions in
Climate change is predicted to have significant effects on the living conditions in Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
. The climate of Argentina is changing with regards to precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls from clouds due to gravitational pull. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, rain and snow mixed ("sleet" in Commonwe ...
patterns and temperatures. The highest increase in the precipitation (from the period 1960–2010) has occurred in the eastern parts of the country. The increase in precipitation has led to more variability in precipitation from year to year in the northern parts of the country, with a higher risk of prolonged droughts
A drought is a period of drier-than-normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, ...
, limiting agriculture in these regions
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as areas, zones, lands or territories, are portions of the Earth's surface that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and ...
.
Though temperatures
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making up a subst ...
have increased at a slower rate than the global average, nonetheless, these impacts have occurred in many areas. Higher temperatures can reduce winter
Winter is the coldest and darkest season of the year in temperate and polar climates. It occurs after autumn and before spring. The tilt of Earth's axis causes seasons; winter occurs when a hemisphere is oriented away from the Sun. Dif ...
snowfall
Snow consists of individual ice crystals that grow while suspended in the atmosphere—usually within clouds—and then fall, accumulating on the ground where they undergo further changes.
It consists of frozen crystalline water througho ...
, causing river flow to decrease (less water available), which can reduce hydroelectric energy production. Again, losses of up to 40% had been observed. If these trends continue, it is predicted that climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
will exacerbate existing natural disaster
A natural disaster is the very harmful impact on a society or community brought by natural phenomenon or Hazard#Natural hazard, hazard. Some examples of natural hazards include avalanches, droughts, earthquakes, floods, heat waves, landslides ...
s such as increasing the intensity and frequency of floods
A flood is an overflow of water (list of non-water floods, or rarely other fluids) that submerges land that is usually dry. In the sense of "flowing water", the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide. Floods are of significant con ...
or create new ones. By 2050, Argentina is predicted to see a 65% increase in drought frequency while heatwaves will last 6247% longer.
The country has received a very low rating from the Climate Change Performance Index
The Climate Change Performance Index (CCPI) is a scoring system designed by the Germany, German environmental and development organisation Germanwatch Registered association (Germany), e.V. to enhance transparency in international Politics of cli ...
, as of April 2025.
Impacts on the environment
Greenhouse gas emissions
In 2023 Argentina emitted approximately 422 million tonnes ofgreenhouse gases
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are the gases in the atmosphere that raise the surface temperature of planets such as the Earth. Unlike other gases, greenhouse gases absorb the radiations that a planet emits, resulting in the greenhouse effect. T ...
, making it around the 22nd highest emitting country in the world. This is equivalent to around 9.3 tonnes emitted per person.
Temperature and weather changes
Mean temperatures have increased by from 1901–2012, which is slightly lower than the global average. Temperatures in the Andean part ofPatagonia
Patagonia () is a geographical region that includes parts of Argentina and Chile at the southern end of South America. The region includes the southern section of the Andes mountain chain with lakes, fjords, temperate rainforests, and glaciers ...
have increased by more than , which has caused the retreat of almost all of the glaciers
A glacier (; or ) is a persistent body of dense ice, a form of rock, that is constantly moving downhill under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires ...
. This affects water availability to arid
Aridity is the condition of geographical regions which make up approximately 43% of total global available land area, characterized by low annual precipitation, increased temperatures, and limited water availability.Perez-Aguilar, L. Y., Plata ...
areas of the country that depend on it.
Higher temperatures can reduce winter
Winter is the coldest and darkest season of the year in temperate and polar climates. It occurs after autumn and before spring. The tilt of Earth's axis causes seasons; winter occurs when a hemisphere is oriented away from the Sun. Dif ...
snowfall
Snow consists of individual ice crystals that grow while suspended in the atmosphere—usually within clouds—and then fall, accumulating on the ground where they undergo further changes.
It consists of frozen crystalline water througho ...
, causing river flow to decrease (less water available), which can reduce hydroelectric energy production; losses of up to 40% had been observed. Outside Patagonia, mean temperatures have increased at a smaller rate since the increase in minimum temperatures is counteracted by the decrease in maximum temperatures.
The increase in minimum temperatures in much of Argentina outside Patagonia is attributed to the increase in the concentration
In chemistry, concentration is the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Several types of mathematical description can be distinguished: '' mass concentration'', '' molar concentration'', '' number concentration'', ...
of greenhouse gases
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are the gases in the atmosphere that raise the surface temperature of planets such as the Earth. Unlike other gases, greenhouse gases absorb the radiations that a planet emits, resulting in the greenhouse effect. T ...
in the atmosphere. The decrease in maximum temperatures is a consequence of higher precipitation, which is associated with higher cloud coverage and evaporation, processes that tend to reduce maximum temperatures north of 40oS. In Patagonia, the increase in mean temperatures is higher than the increase in minimum temperatures and is due to the change in atmospheric circulation
Atmospheric circulation is the large-scale movement of Atmosphere of Earth, air and together with ocean circulation is the means by which thermal energy is redistributed on the surface of the Earth. The Earth's atmospheric circulation varies fro ...
, not just only the increase in greenhouse effect
The greenhouse effect occurs when greenhouse gases in a planet's atmosphere insulate the planet from losing heat to space, raising its surface temperature. Surface heating can happen from an internal heat source (as in the case of Jupiter) or ...
.
Ozone depletion
Ozone depletion consists of two related events observed since the late 1970s: a lowered total amount of ozone in Earth, Earth's upper atmosphere, and a much larger springtime decrease in stratospheric ozone (the ozone layer) around Earth's polar ...
has played a major role in changing the atmospheric circulation patterns. There has been a decrease in the days with frost, and increases in the number of hot nights throughout the country. Heat waves
"Heat Waves" is a song by British indie rock band Glass Animals released as a single from their third studio album ''Dreamland (Glass Animals album), Dreamland'' on 29 June 2020. A sleeper hit, it is the band's signature song and biggest hit sing ...
, which is defined as 3 consecutive days in which the temperature exceeds the 90th percentile
In statistics, a ''k''-th percentile, also known as percentile score or centile, is a score (e.g., a data point) a given percentage ''k'' of all scores in its frequency distribution exists ("exclusive" definition) or a score a given percentage ...
with respect to the 1961–1990 period have become more common and intense between 1961–2010.
Within the next 2 or 3 decades
A decade (from , , ) is a period of 10 years. Decades may describe any 10-year period, such as those of a person's life, or refer to specific groupings of calendar years.
Usage
Any period of ten years is a "decade". For example, the statement t ...
(2016–2035), mean temperatures are predicted to increase by under the two scenarios ( RCP 4.5 and RCP 8.5) from the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report
The Fifth Assessment Report (AR5) of the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is the fifth in IPCC#Assessment reports, a series of such reports and was completed in 2014.IPCC (2014The IPCC's Fifth Assessment Report (A ...
. Under the RCP 4.5 scenario, temperatures will increase by throughout the country, though this increase will be more pronounced in the northwest where temperatures would increase by . In the more severe RCP 8.5 scenario
In the performing arts, a scenario (, ; ; from Italian , "that which is pinned to the scenery") is a synoptical collage of an event or series of actions and events. In the ''commedia dell'arte'', it was an outline of entrances, exits, and actio ...
, the projected increased in temperatures will be higher, reaching in the northwest. In both scenarios, the projected warming will be more pronounced during the summer months. The predicted trend for precipitation is not as clear as the one for temperature. In the northern and central regions, precipitation is predicted to increase while in much of central–western Argentina and Patagonia, precipitation is predicted to decrease. Because Argentina is potentially vulnerable to climate change, such projected changes based on the models could enhance current or create new problems associated with climate change on Argentina.
The following images show the projected changes in the types of climate according to the Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification divides Earth climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on patterns of seasonal precipitation and temperature. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (te ...
.
Precipitation and extreme weather events
 There has been an increase in annual
There has been an increase in annual precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls from clouds due to gravitational pull. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, rain and snow mixed ("sleet" in Commonwe ...
in almost all of Argentina, particularly in the northeast and central parts of the country
A country is a distinct part of the world, such as a state, nation, or other political entity. When referring to a specific polity, the term "country" may refer to a sovereign state, state with limited recognition, constituent country, ...
. Since 1970, precipitation has increased by 10% in the northeast while in parts of La Pampa Province
La Pampa () is a sparsely populated province of Argentina, located in the Pampas in the center of the country. Neighboring provinces are from the north clockwise San Luis, Córdoba, Buenos Aires, Río Negro, Neuquén and Mendoza.
History
In ...
and western parts of Buenos Aires province
Buenos Aires, officially the Buenos Aires Province, is the largest and most populous Provinces of Argentina, Argentine province. It takes its name from the city of Buenos Aires, the capital of the country, which used to be part of the province an ...
, it has increased by 40%. The highest increases in the precipitation (from the period 1960–2010) have occurred in the eastern parts of the country. In contrast, the Andean part of Patagonia along with the Cuyo region has seen a decrease in precipitation, leading to a reduction in river flow in the last 100 years. Some parts of Patagonia in the Andes have seen a 30%–50% reduction in precipitation since the middle of the 20th century.
In March 2025, catastrophic flooding in Bahia Blanca
Bahia () is one of the 26 Federative units of Brazil, states of Brazil, located in the Northeast Region, Brazil, Northeast Region of the country. It is the fourth-largest Brazilian state by population (after São Paulo (state), São Paulo, Mina ...
, Argentina, killed 16 people and was linked to climate change. Scientists from the World Weather Attribution
World Weather Attribution is an academic collaboration studying extreme event attribution, calculations of the impact of climate change on extreme weather, extreme meteorological events such as heat waves, droughts, and storms. When an extreme eve ...
found that extreme heat and humidity, exacerbated by climate change, contributed to the heavy rains. Prior to the floods, temperatures in central Argentina exceeded 40°C, and a humid heatwave combined with moisture from the Amazon
Amazon most often refers to:
* Amazon River, in South America
* Amazon rainforest, a rainforest covering most of the Amazon basin
* Amazon (company), an American multinational technology company
* Amazons, a tribe of female warriors in Greek myth ...
, resulting in 300 mm of rain in just six hours. These conditions, which would have been nearly impossible without climate change, made the floods unprecedented. While extreme heat events remain rare, occurring every 50 to 100 years, climate change is making them more frequent. Rapid urbanization in Bahia Blanca, coupled with insufficient infrastructure, worsened the impact.
Sea level rise
In much of the coastal regions of Argentina, it will not suffer permanent flooding and loss of land associated withsea level rise
The sea level has been rising from the end of the last ice age, which was around 20,000 years ago. Between 1901 and 2018, the average sea level rose by , with an increase of per year since the 1970s. This was faster than the sea level had e ...
since much of the coastal regions are high cliffs. Nonetheless, potential agricultural land could be lost if sea levels rise by . Sea level rise will impact the country through an increase in the frequency of storm surges in coastal areas, including Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires, controlled by the government of the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires, is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Argentina. It is located on the southwest of the Río de la Plata. Buenos Aires is classified as an Alpha− glob ...
and a study has suggested that Buenos Aires could be impacted significantly by sea level rise.
Impacts on people
Economic impacts

Agriculture
 Agriculture will be affected by climate change. The decrease in precipitation that has been observed in the Andes will be predicted to continue to decrease, affecting hydroelectric energy even more. Glaciers are predicted to continue to recede and melt or in some areas, disappear. It is predicted that the Cuyo region could face a potential water crisis due to an increase in water demand owing to a reduction in river streamflows and higher
Agriculture will be affected by climate change. The decrease in precipitation that has been observed in the Andes will be predicted to continue to decrease, affecting hydroelectric energy even more. Glaciers are predicted to continue to recede and melt or in some areas, disappear. It is predicted that the Cuyo region could face a potential water crisis due to an increase in water demand owing to a reduction in river streamflows and higher evapotranspiration
Evapotranspiration (ET) refers to the combined processes which move water from the Earth's surface (open water and ice surfaces, bare soil and vegetation) into the Atmosphere of Earth, atmosphere. It covers both water evaporation (movement of w ...
from a combination of lower precipitation and higher temperatures. Higher temperatures will cause the snow cover to melt earlier in the year, causing a rise in river flow in the spring months and a drop in summer, which is when water demand is the highest for agriculture. The higher water demand would lead to higher groundwater use for irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering of plants) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has bee ...
which drives up the costs for irrigation, cause the deterioration in the water quality, and lead to the eventual depletion of aquifers
An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing material, consisting of permeability (Earth sciences), permeable or fractured rock, or of unconsolidated materials (gravel, sand, or silt). Aquifers vary greatly in their characteristics. The s ...
. In northern Patagonia
Patagonia () is a geographical region that includes parts of Argentina and Chile at the southern end of South America. The region includes the southern section of the Andes mountain chain with lakes, fjords, temperate rainforests, and glaciers ...
, a similar situation is projected in which negative impacts can occur in the future for fruit and vegetable growing owing to a reduction in available water. It is predicted that between 2020–2040, the river flow in the Colorado River
The Colorado River () is one of the principal rivers (along with the Rio Grande) in the Southwestern United States and in northern Mexico. The river, the List of longest rivers of the United States (by main stem), 5th longest in the United St ...
and the Chubut river
The Chubut River (; ; ) is located in the Patagonia region of southern Argentina. Its name comes from the Tehuelche word , which means 'transparent'. The Argentine Chubut Province, through which the river flows, is named after it. Welsh settle ...
would decrease by 20% due to more irrigation.
In the last half of the 20th century, the lack of snow at the highest peaks in the Cuyo region has impacted agriculture and viticulture
Viticulture (, "vine-growing"), viniculture (, "wine-growing"), or winegrowing is the cultivation and harvesting of grapes. It is a branch of the science of horticulture. While the native territory of ''Vitis vinifera'', the common grape vine ...
production due to less water available in the rivers (a reduction in 50% of river flow).
Numerous studies have indicated that the productivity of wheat
Wheat is a group of wild and crop domestication, domesticated Poaceae, grasses of the genus ''Triticum'' (). They are Agriculture, cultivated for their cereal grains, which are staple foods around the world. Well-known Taxonomy of wheat, whe ...
, soybean
The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean (''Glycine max'') is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean. Soy is a staple crop, the world's most grown legume, and an important animal feed.
Soy is a key source o ...
and maize
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago from wild teosinte. Native American ...
will not change that much by the middle of the 21st century. This is because while crop production
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food ...
may increase in the southern and western parts of the Pampas, it will decrease in the northern parts. In the north and central parts of the country, the higher temperatures projected for this region leads to higher evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization that occurs on the Interface (chemistry), surface of a liquid as it changes into the gas phase. A high concentration of the evaporating substance in the surrounding gas significantly slows down evapora ...
. Combined with little precipitation change for this region, it is probable that it would become more arid
Aridity is the condition of geographical regions which make up approximately 43% of total global available land area, characterized by low annual precipitation, increased temperatures, and limited water availability.Perez-Aguilar, L. Y., Plata ...
, leading to desertification
Desertification is a type of gradual land degradation of Soil fertility, fertile land into arid desert due to a combination of natural processes and human activities.
The immediate cause of desertification is the loss of most vegetation. This i ...
. In areas that normally have a dry winter, a higher evaporation would intensify droughts which would disfavor agriculture.
Since the middle of the 20th century, the isohyet in the south and the isohyet in the north, which approximately form the boundaries in which agricultural production
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food ...
is possible had moved more than to the west, expanding possible agricultural production to these areas.
Although an increase in precipitation will expand agricultural production to the west in areas that were previously too dry and will benefit hydroelectric energy owing to the increase in river flow, there will be an increase the frequency of extreme precipitation events such as flooding, hail and strong winds, which can destroy these agricultural fields. These trends were observed with an increase in the river–stream flows in most of the country excluding rivers
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of its course if it run ...
originating from the Andes
The Andes ( ), Andes Mountains or Andean Mountain Range (; ) are the List of longest mountain chains on Earth, longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range ...
, and increase in extreme precipitation events that led to considerable socioeconomic
Economics () is a behavioral science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goods and services.
Economics focuses on the behaviour and interac ...
losses. These extreme precipitation events such as flooding, and hail have occurred more frequently in the east, leading to the destruction of agricultural land in these areas. The increase in precipitation has led to more variability in precipitation from year to year in the northern parts of the country, with a higher risk of prolonged droughts
A drought is a period of drier-than-normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, ...
, disfavoring agriculture in these regions
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as areas, zones, lands or territories, are portions of the Earth's surface that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and ...
.
Health impacts
Climate change could extend thehabitats
In ecology, habitat refers to the array of resources, biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species' habitat can be seen as the physical manifestation of its ...
of vectors carrying tropical diseases such as malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomitin ...
, Chagas disease, and dengue, as they spread southwards.
Impacts on housing
Higher temperatures can negatively affecturban area
An urban area is a human settlement with a high population density and an infrastructure of built environment. Urban areas originate through urbanization, and researchers categorize them as cities, towns, conurbations or suburbs. In urbani ...
s by affecting the provision of services such as water and energy
Energy () is the physical quantity, quantitative physical property, property that is transferred to a physical body, body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of Work (thermodynamics), work and in the form of heat and l ...
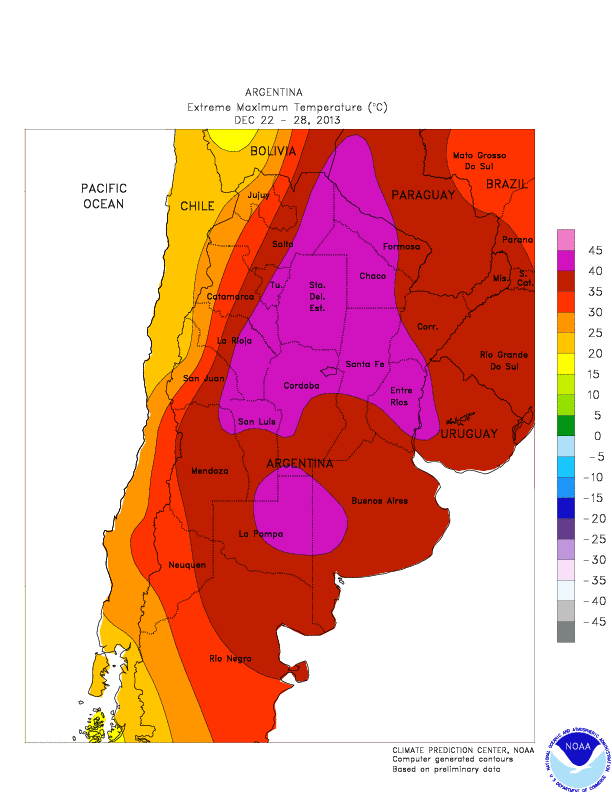
by increasing the demand for these services. Heat waves, such as the one in 2013–2014 during the summer
Summer or summertime is the hottest and brightest of the four temperate seasons, occurring after spring and before autumn. At or centred on the summer solstice, daylight hours are the longest and darkness hours are the shortest, with day ...
could become more frequent and intense. These heat waves can impact agricultural production while in urban areas, it places more demand on energy needs. Intense precipitation events could become more common, leading to negative consequences.
Argentina, with much of its population
Population is a set of humans or other organisms in a given region or area. Governments conduct a census to quantify the resident population size within a given jurisdiction. The term is also applied to non-human animals, microorganisms, and pl ...
living in urban areas
An urban area is a human settlement with a high population density and an infrastructure of built environment. Urban areas originate through urbanization, and researchers categorize them as cities, towns, conurbations or suburbs. In urbani ...
is vulnerable to intense precipitation events since many cities are located near a body of water (rivers, lakes and oceans
The ocean is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of Earth. The ocean is conventionally divided into large bodies of water, which are also referred to as ''oceans'' (the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Antarctic/Southern, and ...
), which increases the likelihood of suffering from these intense precipitation events such as flooding
A flood is an overflow of water ( or rarely other fluids) that submerges land that is usually dry. In the sense of "flowing water", the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide. Floods are of significant concern in agriculture, civi ...
.
Mitigation and adaptation
In Argentina'sNationally Determined Contribution
The nationally determined contributions (NDCs) are commitments that countries make to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions as part of climate change mitigation. These commitments include the necessary policies and measures for achieving the glob ...
it has committed to capping net greenhouse gas emissions across its economy to 349 million tonnes by 2030. Argentina has also committed to net zero
Global net-zero emissions is reached when greenhouse gas emissions and removals due to human activities are in balance. It is often called simply net zero. ''Emissions'' can refer to all greenhouse gases or only carbon dioxide (). Reaching net ze ...
and carbon neutrality by 2050.
See also
* Climate of Argentina * 2022 Southern Cone heat waveReferences
Further reading
*External links
Centro de Investigaciones del Mar y la Atmósfera
Third National Communication of Argentina for Climate Change
Second National Communication of Argentina for Climate Change
{{Climate change Climate of Argentina
Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...