Clean Energy Technology on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Clean technology, also called cleantech or climatetech, is any process, product, or service that reduces negative environmental impacts through significant
Clean technology, also called cleantech or climatetech, is any process, product, or service that reduces negative environmental impacts through significant 
 Investments in clean technology have grown considerably since coming into the spotlight around 2000. According to the
Investments in clean technology have grown considerably since coming into the spotlight around 2000. According to the
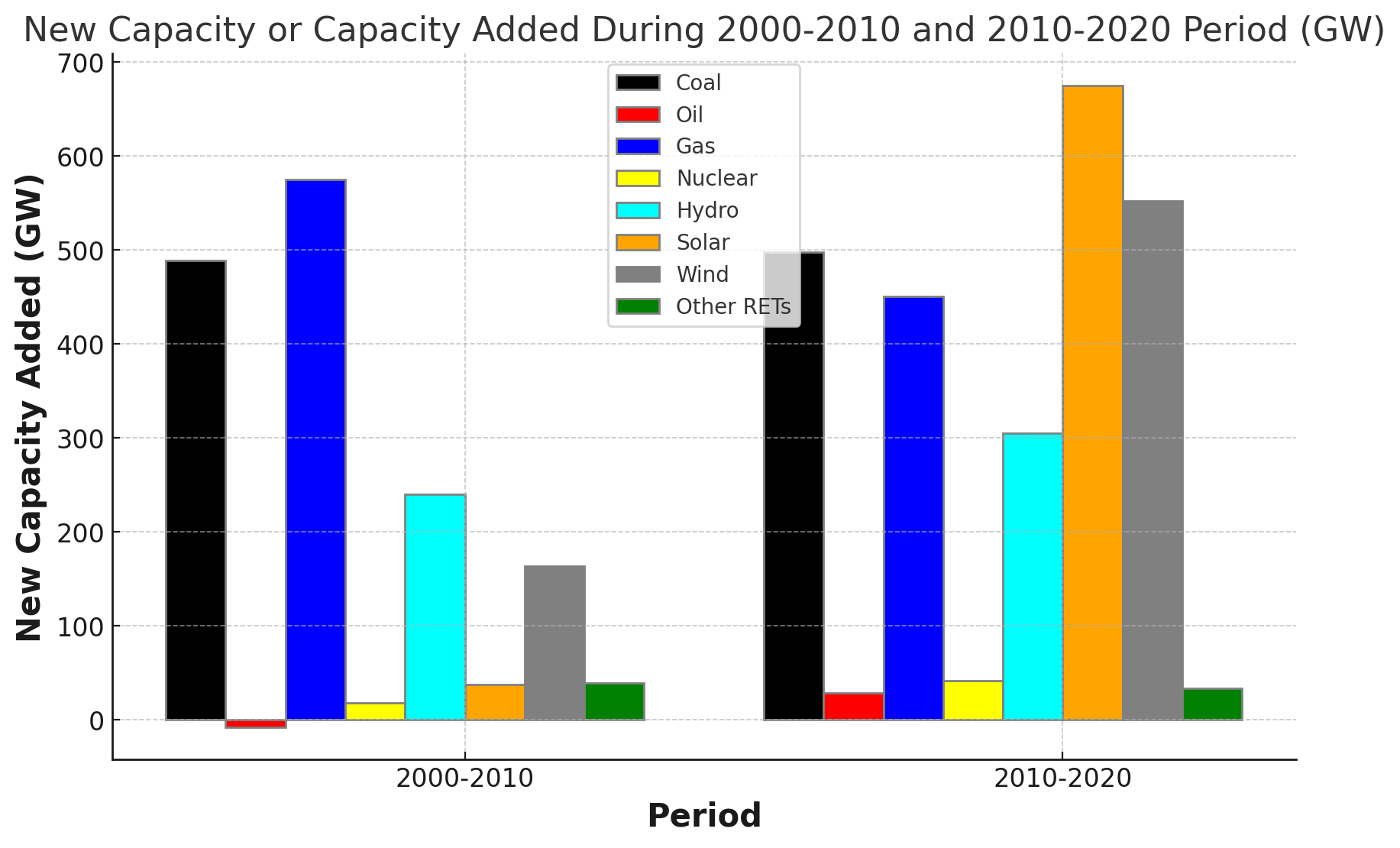 The
The
 The
The
Investing: Green technology has big growth potential
''
The Global Cleantech Innovation Index 2014
by Cleantech Group and WWF {{DEFAULTSORT:Clean Technology Economics of sustainability Environmental technology

energy efficiency
Energy efficiency may refer to:
* Energy efficiency (physics), the ratio between the useful output and input of an energy conversion process
** Electrical efficiency, useful power output per electrical power consumed
** Mechanical efficiency, a ra ...
improvements, the sustainable use of resources, or environmental protection activities. Clean technology includes a broad range of technology related to recycling
Recycling is the process of converting waste materials into new materials and objects. The Energy recycling, recovery of energy from waste materials is often included in this concept. The recyclability of a material depends on its ability t ...
, renewable energy, information technology
Information technology (IT) is the use of computers to create, process, store, retrieve, and exchange all kinds of data . and information. IT forms part of information and communications technology (ICT). An information technology system ...
, green transport
Sustainable transport refers to ways of transportation that are sustainable in terms of their social and environmental impacts. Components for evaluating sustainability include the particular vehicles used for road, water or air transport; the ...
ation, electric motor
An electric motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a wire winding to generate forc ...
s, green chemistry
Green chemistry, also called sustainable chemistry, is an area of chemistry and chemical engineering focused on the design of products and processes that minimize or eliminate the use and generation of hazardous substances. While environmental ch ...
, lighting
Lighting or illumination is the deliberate use of light to achieve practical or aesthetic effects. Lighting includes the use of both artificial light sources like lamps and light fixtures, as well as natural illumination by capturing dayli ...
, grey water
Greywater (or grey water, sullage, spelling differences, also spelled gray water in the United States) refers to domestic wastewater generated in households or office buildings from streams without fecal contamination, i.e., all streams except fo ...
, and more. Environmental finance
Environmental finance is a field within finance that employs market-based environmental policy instruments to improve the ecological impact of investment strategies. The primary objective of environmental finance is to regress the negative impac ...
is a method by which new clean technology projects can obtain financing through the generation of carbon credits
A carbon credit is a generic term for any tradable certificate or permit representing the right to emit a set amount of carbon dioxide or the equivalent amount of a different greenhouse gas (tCO2e).
Carbon credits and carbon markets are a compo ...
. A project that is developed with concern for climate change mitigation
Climate change mitigation is action to limit climate change by reducing emissions of greenhouse gases or removing those gases from the atmosphere. The recent rise in global average temperature is mostly caused by emissions from fossil fuels bu ...
is also known as a carbon project
Business action on climate change includes a range of activities relating to climate change, and to influencing political decisions on climate change-related regulation, such as the Kyoto Protocol. Major multinationals have played and to some exte ...
.
Clean Edge
Clean Edge, Inc., founded in 2000, is a U.S.-based developer and publisher of thematic stock indexes tracking clean energy, transportation, water, and the grid. The firm's first index, the Nasdaq Clean Edge Green Energy Index (CELS), was launched ...
, a clean technology research firm, describes clean technology "a diverse range of products, services, and processes that harness renewable materials and energy sources, dramatically reduce the use of natural resources, and cut or eliminate emissions and wastes." Clean Edge notes that, "Clean technologies are competitive with, if not superior to, their conventional counterparts. Many also offer significant additional benefits, notably their ability to improve the lives of those in both developed and developing countries."
 Investments in clean technology have grown considerably since coming into the spotlight around 2000. According to the
Investments in clean technology have grown considerably since coming into the spotlight around 2000. According to the United Nations Environment Program
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) is responsible for coordinating responses to environmental issues within the United Nations system. It was established by Maurice Strong, its first director, after the United Nations Conference on ...
, wind, solar, and biofuel companies received a record $148 billion in new funding in 2007 as rising oil prices and climate change policies encouraged investment in renewable energy. $50 billion of that funding went to wind power
Wind power or wind energy is mostly the use of wind turbines to generate electricity. Wind power is a popular, sustainable, renewable energy source that has a much smaller impact on the environment than burning fossil fuels. Historicall ...
. Overall, investment in clean-energy and energy-efficiency industries rose 60 percent from 2006 to 2007. In 2009, Clean Edge forecasted that the three main clean technology sectors, solar photovoltaics
Photovoltaics (PV) is the conversion of light into electricity using semiconducting materials that exhibit the photovoltaic effect, a phenomenon studied in physics, photochemistry, and electrochemistry. The photovoltaic effect is commercial ...
, wind power, and biofuels, would have revenues of $325.1 billion by 2018.
According to an MIT Energy Initiative Working Paper published in July 2016, about a half of over $25 billion funding provided by venture capital
Venture capital (often abbreviated as VC) is a form of private equity financing that is provided by venture capital firms or funds to start-up company, startups, early-stage, and emerging companies that have been deemed to have high growth poten ...
to cleantech from 2006 to 2011 was never recovered. The report cited cleantech's dismal risk/return profiles and the inability of companies developing new materials, chemistries, or processes to achieve manufacturing scale as contributing factors to its flop.
Clean technology has also emerged as an essential topic among businesses and companies. It can reduce pollutants and dirty fuels for every company, regardless of which industry they are in, and using clean technology has become a competitive advantage. Through building their Corporate Social Responsibility
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) is a form of international private business self-regulation which aims to contribute to societal goals of a philanthropic, activist, or charitable nature by engaging in or supporting volunteering or ethicall ...
(CSR) goals, they participate in using clean technology and other means by promoting Sustainability. Fortune Global 500
The ''Fortune'' Global 500, also known as Global 500, is an annual ranking of the top 500 corporations worldwide as measured by revenue. The list is compiled and published annually by '' Fortune'' magazine.
Methodology
Until 1989, it listed o ...
firms spend around $20 billion a year on CSR activities in 2018.
Silicon Valley
Silicon Valley is a region in Northern California that serves as a global center for high technology and innovation. Located in the southern part of the San Francisco Bay Area, it corresponds roughly to the geographical areas San Mateo Count ...
, Tel Aviv
Tel Aviv-Yafo ( he, תֵּל־אָבִיב-יָפוֹ, translit=Tēl-ʾĀvīv-Yāfō ; ar, تَلّ أَبِيب – يَافَا, translit=Tall ʾAbīb-Yāfā, links=no), often referred to as just Tel Aviv, is the most populous city in the G ...
and Stockholm were ranked as leading ecosystystems in the field of clean technology. According to data in 2024, there are over 750,000 international patent families (IPFs) focused on clean and sustainable technologies worldwide. This represents approximately 12% of the total number of IPFs globally. From 1997 to 2021, over 750,000 patents for clean and sustainable technologies were published, making up almost 15% of all patents in 2021, compared to just under 8% in 1997. Japan and the US each account for over 20% of clean technology patents, though their annual numbers have stabilized at around 10,000.
Between 2017 and 2021, European countries accounted for over 27% of international patent families (IPFs) in clean technology globally. This places Europe ahead of other major innovators, such as Japan (21%), the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
(20%), and China (15%).
There are two major stages when cleantech patenting has advanced. The first is from 2006 to 2021, driven by the EU and Japan (27% and 26% of overall increase in IPFs). The next stage is from 2017 to 2021, led by China, which accounted for 70% of the increase in IPFs.
Definition
Cleantech products or services are those that improve operational performance,productivity
Productivity is the efficiency of production of goods or services expressed by some measure. Measurements of productivity are often expressed as a ratio of an aggregate output to a single input or an aggregate input used in a production proce ...
, or efficiency while reducing costs, inputs, energy consumption
Energy consumption is the amount of energy used.
Biology
In the body, energy consumption is part of energy homeostasis. It derived from food energy. Energy consumption in the body is a product of the basal metabolic rate and the physical activi ...
, waste
Waste (or wastes) are unwanted or unusable materials. Waste is any substance discarded after primary use, or is worthless, defective and of no use. A by-product, by contrast is a joint product of relatively minor economic value. A waste pr ...
, or environmental pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause adverse change. Pollution can take the form of any substance (solid, liquid, or gas) or energy (such as radioactivity, heat, sound, or light). Pollutants, the ...
. Its origin is the increased consumer, regulatory, and industry interest in clean forms of energy generation—specifically, perhaps, the rise in awareness of global warming
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in a broader sense also includes ...
, climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
, and the impact on the natural environment
The natural environment or natural world encompasses all living and non-living things occurring naturally, meaning in this case not artificial. The term is most often applied to the Earth or some parts of Earth. This environment encompasses ...
from the burning of fossil fuels. Cleantech is often associated with venture capital
Venture capital (often abbreviated as VC) is a form of private equity financing that is provided by venture capital firms or funds to start-up company, startups, early-stage, and emerging companies that have been deemed to have high growth poten ...
funds and land use organizations. The term has historically been differentiated from various definitions of green business, sustainability, or triple bottom line industries by its origins in the venture capital investment community and has grown to define a business sector that includes significant and high growth industries such as solar, wind, water purification, and biofuels.
Nomenclature
While the expanding industry has grown rapidly in recent years and attracted billions of dollars of capital, the clean technology space has not settled on an agreed-upon term. ''Cleantech'', is used fairly widely, although variant spellings include and . In recent years, some clean technology companies have de-emphasized that aspect of their business to tap into broader trends, such assmart cities
A smart city is a technologically modern urban area that uses different types of electronic methods and sensors to collect specific data. Information gained from that data is used to manage assets, resources and services efficiently; in return ...
.
Origins of the concept
The idea of cleantech first emerged among a group of emerging technologies and industries, based on principles ofbiology
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditar ...
, resource efficiency Resource efficiency is the maximising of the supply of money, materials, staff, and other assets that can be drawn on by a person or organization in order to function effectively, with minimum wasted (natural) resource expenses. It means using the ...
, and second-generation production concepts in basic industries. Examples include: energy efficiency
Energy efficiency may refer to:
* Energy efficiency (physics), the ratio between the useful output and input of an energy conversion process
** Electrical efficiency, useful power output per electrical power consumed
** Mechanical efficiency, a ra ...
, selective catalytic reduction
Selective catalytic reduction (SCR) is a means of converting nitrogen oxides, also referred to as with the aid of a catalyst into diatomic nitrogen (), and water (). A reductant, typically anhydrous ammonia (), aqueous ammonia (), or a urea ...
, non-toxic
Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a subs ...
materials, water purification
Water purification is the process of removing undesirable chemicals, biological contaminants, suspended solids, and gases from water. The goal is to produce water that is fit for specific purposes. Most water is purified and disinfected for hu ...
, solar energy
Solar energy is radiant light and heat from the Sun that is harnessed using a range of technologies such as solar power to generate electricity, solar thermal energy (including solar water heating), and solar architecture. It is an ...
, wind energy
Wind power or wind energy is mostly the use of wind turbines to generate electricity. Wind power is a popular, sustainable, renewable energy source that has a much smaller impact on the environment than burning fossil fuels. Historically, ...
, and new paradigms in energy conservation. Since the 1990s, interest in these technologies has increased with two trends: a decline in the relative cost of these technologies and a growing understanding of the link between industrial design used in the 19th century and early 20th century, such as fossil fuel power plants, the internal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal co ...
, and chemical manufacturing
The chemical industry comprises the companies that produce industrial chemicals. Central to the modern world economy, it converts raw materials (oil, natural gas, air, water, metals, and minerals) into more than 70,000 different products. The p ...
, and an emerging understanding of human-caused impact on earth systems resulting from their use (see articles: ozone hole
Ozone depletion consists of two related events observed since the late 1970s: a steady lowering of about four percent in the total amount of ozone in Earth's atmosphere, and a much larger springtime decrease in stratospheric ozone (the ozone lay ...
, acid rain, desertification
Desertification is a type of land degradation in drylands in which biological productivity is lost due to natural processes or induced by human activities whereby fertile areas become increasingly arid. It is the spread of arid areas caused b ...
, climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
, and global warming
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in a broader sense also includes ...
).
Investment worldwide
During the last twenty years, regulatory schemes and international treaties have been the main factors that defined the investment environment of clean technologies. Investments in renewable sources as well as the technologies for energy efficiency represent a determining factor in the investments made under the context of the Paris Agreement and the fight against climate change and air pollution. Among financing of the public sector, the government has been using financial incentives and regulations that are targeted at the private sector. This collectively move is the cause of the continued increase in the clean energy capacity. The investments in renewable electricity generation technologies in 2015 were over $308 billion USD and in 2019 this figure rose to $311 billion USD. Startups with new technology based innovation are considered to be an attractive investment in a clean technology sector. Venture capital and crowdfunding platforms are crucial sources for developing ventures that lead to the introduction of new technologies. In the last decade, startups have significantly contributed to the increase in installed capacity for solar and wind power. The trendsetting firms that design new technologies and devise strategies for the industry to excel and to be more resilient in the face of threats. In 2008, clean technology venture investments in North America, Europe, China, and India totaled a record $8.4 billion. Cleantech Venture Capital firms include NTEC,Cleantech Ventures
MoreVC, formerly known as Israel Cleantech Ventures, is a venture capital firm founded in 2006 by Glen Schwaber, Jack Levy, and Meir Ukeles. It is a clean technology venture capital fund intent on providing growth capital to Israel's energy, wa ...
, and Foundation Capital
Foundation Capital is a venture capital firm located in Silicon Valley. The firm was founded in 1995, and in 2012 managed more than $2.4 billion in investment capital.
History
Foundation Capital was founded in 1995.
The firm raised its sevent ...
. The preliminary 2008 total represents the seventh consecutive year of growth in venture investing, widely recognized as a leading indicator of overall investment patterns. Investment in clean technology has grown significantly, with a considerable impact on production costs and productivity, especially, within energy intensive industries. The World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Inte ...
notes that these investments are enhancing economic efficiency, supporting sustainable development objectives, and promoting energy security by decreasing dependence on fossil fuel. China is seen as a major growth market for cleantech investments currently, with a focus on renewable energy technologies. In 2014, Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
, Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bo ...
and the US were leading the Global Cleantech Innovation Index, out of 40 countries assessed, while Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eigh ...
and Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wit ...
were last. Renewable energy investment has achieved substantial scale with annual investments around $300 billion. This volume of investment is fundamental to the global energy transition and remains in spite of an R&D funding plateau, representing the sector's healthy expansion and appreciation of renewable technology's promise. Several journals offer in-depth analyses and forecasts of this investment trend, stressing its significant role in attainment of the world energy and climate targets. With regards to private investments, the investment group Element 8 has received the 2014 CleanTech Achievement award from the CleanTech Alliance, a trade association focused on clean tech in the State of Washington, for its contribution in Washington State's cleantech industry. Strategic investments in clean technologies within supply chains are increasingly influenced by sustainable market forces. These investments are vital for manufacturers, enhancing not only the sustainability of production processes, but, also encouraging a comprehensive transition towards sustainability across the entire supply chain. Detailed case studies and industry analyses highlight the economic and environmental benefits of such strategic investments. According to the published research, the top clean technology sectors in 2008 were solar, biofuels, transportation, and wind. Solar accounted for almost 40% of total clean technology investment dollars in 2008, followed by biofuels at 11%. In 2019, sovereign wealth funds directly invested just under US$3 billion in renewable energy .
 The
The 2009 United Nations Climate Change Conference
The 2009 United Nations Climate Change Conference, commonly known as the Copenhagen Summit, was held at the Bella Center in Copenhagen, Denmark, between 7 and 18 December. The conference included the 15th session of the Conference of the Partie ...
in Copenhagen
Copenhagen ( or .; da, København ) is the capital and most populous city of Denmark, with a proper population of around 815.000 in the last quarter of 2022; and some 1.370,000 in the urban area; and the wider Copenhagen metropolitan ar ...
, Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establishe ...
was expected to create a framework whereby limits would eventually be placed on greenhouse gas emissions. Many proponents of the cleantech industry hoped for an agreement to be established there to replace the Kyoto Protocol
The Kyoto Protocol was an international treaty which extended the 1992 United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) that commits state parties to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, based on the scientific consensus that (par ...
. As this treaty was expected, scholars had suggested a profound and inevitable shift from "business as usual
Business as usual may refer to:
* Business as usual (business), the normal execution of operations within an organization
* Business as usual (policy), policy of the British government in World War I
Film, television and theatre
* ''Business as ...
." However, the participating States failed to provide a global framework for clean technologies. The outburst of the 2008 economic crisis then hampered private investments in clean technologies, which were back at their 2007 level only in 2014. The 2015 United Nations Climate Change Conference
The 2015 United Nations Climate Change Conference, COP 21 or CMP 11 was held in Paris, France, from 30 November to 12 December 2015. It was the 21st yearly session of the Conference of the Parties (COP) to the 1992 United Nations Framework Con ...
in Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. ...
is expected to achieve a universal agreement on climate, which would foster clean technologies development. On 23 September 2019, the Secretary-General of the United Nations hosted a Climate Action Summit in New York.
In 2022 the investment in cleantech (also called climatetech) boomed. "In fact, climate tech investment in the 12 months to Q3 2022 represented more than a quarter of every venture dollar invested, a greater proportion than 12 of the prior 16 quarters."
US leads in carbon capture technologies, with nearly 30% of patents. It also leads in plastic recycling and climate change adaptation
Climate change adaptation is the process of adjusting to current or expected effects of climate change.IPCC, 2022Annex II: Glossary öller, V., R. van Diemen, J.B.R. Matthews, C. Méndez, S. Semenov, J.S. Fuglestvedt, A. Reisinger (eds.) InClimat ...
technologies, but has a lower share in low-carbon energy (13%). Japan excels in hydrogen-related (29.3%) and low-carbon energy technologies (26.2%). Chinese applicants dominate the field of ICT-related clean technologies, accounting for more than 37% of patents between 2017 and 2021. Meanwhile, South Korean applicants make notable contributions in ICT with 12.6%, in hydrogen technologies with 13%, and in low-carbon energy with 15.5%.
About half of the EU's clean technologies are in the launch or early revenue stage, 22% are in the scale-up stage, and 10% are mature or consolidating.
Cleantech innovation hubs
Israel
Israel has 600 companies in the Cleantech sector. The Tel Aviv region was ranked second in the world by StartUp Genome for Cleantech ecosystems. Israel due to its geopolitical situation and harsh climate was forced to adopt technologies considered today as part of the cleantech sector. Following the scarcity of oil after the 1973 embargo on Israel, Israel switched to renewable energy in the 1970s and in 1976 all resedential buildings built from that year onward were forced to have such heating. As of 2020, 85% of water heating in Israel is done through renewable energy. Water scarcity led Israelis developed the modern drip irrigations system.Netafim
Netafim is an Israeli manufacturer of irrigation equipment. The company produces drippers, dripperlines, sprinklers and micro-emitters. Netafim also manufactures and distributes crop management technologies, including monitoring and control syste ...
, created in 1965 was the company that developed the technology and is now valued at about $1.85 billion. Israel also operates Israel Cleantech Ventures
MoreVC, formerly known as Israel Cleantech Ventures, is a venture capital firm founded in 2006 by Glen Schwaber, Jack Levy, and Meir Ukeles. It is a clean technology venture capital fund intent on providing growth capital to Israel's energy, wat ...
which funds cleantech startups. In Jerusalem there is a yearly Cleantech conference. UBQ, an Israeli startup which converts waste into friendly plastic secured $70 million in funding in 2023.
Silicon Valley
Silicon Valley
Silicon Valley is a region in Northern California that serves as a global center for high technology and innovation. Located in the southern part of the San Francisco Bay Area, it corresponds roughly to the geographical areas San Mateo Count ...
is the world's leading cleantech ecosystem according to StartUp Gencome's ranking. In 2020, investments in cleantech reached $17 billion.
Implementation worldwide
India
is one of the countries that have achieved remarkable success in sustainable development by implementing clean technology, and it became a global clean energy powerhouse. India, who was the third-largest emitter of greenhouse gases, advanced a scheme of converting to renewable energy with sun and wind from fossil fuels. This continuous effort has created an increase in the country's renewable energy capacity (around 80 gigawatts of installed renewable energy capacity, 2019), with a compound annual growth rate of over 20%. India's ambitious renewable energy targets have become the model for a swift clean energy shift. The government aimed to reach a 175 GW capacity of renewable energy up to 2022. Thus, included a big contribution from wind (60 GW) and solar energy (100 GW). By steadily increasing India's renewable capacity, India is achieving the Paris Agreement with a significant reduction in producing carbon emissions. Adopting renewable energy not only brought technological advances to India, but it also impacted employment by creating around 330,000 new jobs by 2022 and more than 24 million new jobs by 2030, according to theInternational Labour Organization
The International Labour Organization (ILO) is a United Nations agency whose mandate is to advance social and economic justice by setting international labour standards. Founded in October 1919 under the League of Nations, it is the first and o ...
in the renewable energy sector.
In spite of the global successes, the introduction of renewable energy is confronted with hurdles specific to the country or the region. These challenges encompass social, economic, technological, and regulatory. Research shows that social and regulatory barriers are direct factors affecting the deployment of renewable energy, economic barriers however have a more indirect, yet substantial effect. The study emphasises the need for removing these obstacles for renewable energy to become more available and attractive thus benefiting all parties such as local communities and producers.
Despite the prevalence of obstacles, emerging economy countries have formulated creative approaches to deal with the challenges. For example, India, has shown significant progress in the sector of renewable energy, a trend showing the adoption of clean technologies from other countries. The special approaches and problems that every country experiences in the course of the sustainable growth promote useful ideas for further development.
The creation of clean technologies such as battery storage, CCS, and advanced biofuels is important for the achievement of sustainable energy systems. Uninterrupted research and development is critical in improving the productivity of renewable energy sources and in making them more attractive for investment. These developments are a part of the wider goals related to sustainability and addressing climate change.
A further factor that determine the success of clean technology is how it is perceived by public and its social impact. Community involvement and observable benefits of these technologies can influence their adoption and popularity. The idea of shared benefits is created by making the renewable energy solutions environmentally friendly, cost-effective, and beneficial to producers.
Germany
has been one of the renewable energy leaders in the world, and their efforts have expedited the progress after the nuclear power plant meltdown in Japan in 2011, by deciding to switch off all 17 reactors by 2022. Still, this is just one of Germany's ultimate goals; and Germany is aiming to set the usage of renewable energy at 80% by 2050, which is currently 47% (2020). Energiewende in Germany is a model of a devoted effort to renewable energy aimed at decreasing the greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by 80% by 2050 through the rushed adoption of renewable resources. This policy, aimed at addressing the environmental issues and the nationwide agreement on nuclear power abolition, illustrates the essential role of government policy and investment in directing technological adoption and providing a pathway towards the usage of sustainable energy. Obstacles to making the Energiewende a model for the transportation and heating sectors include the integration of renewable energies into existing infrastructure, the economic costs associated with transitioning technologies, and the need for widespread consumer adoption of new energy solutions. Also, Germany is investing in renewable energy from offshore wind and anticipating its investment to result in one-third of total wind energy in Germany. The importance of clean technology also impacted the transportation sector of Germany, which produces 17 percent of its emission. The famous car-producing companies, Mercedes-Benz, BMW, Volkswagen, and Audi, in Germany, are also providing new electric cars to meet Germany's energy transition movement.Africa and the Middle East
has drawn worldwide attention for its potential share and new market of solar electricity. Notably, the countries in the Middle East have been utilizing their natural resources, an abundant amount of oil and gas, to develop solar electricity. Also, to practice the renewable energy, the energy ministers from 14 Arab countries signed a Memorandum of Understanding for an Arab Common Market for electricity by committing to the development of the electricity supply system with renewable energy. Sustainability when combined with clean technology focuses on the central environmental issues of learning how to fulfill the need of Earth's resources and the requirement for fast industrialization and consuming of the energy. The role of the technological innovations in the development of sustainable development across different fields, such as energy, agriculture, and infrastructure is paramount. The sustainability initiatives utilize contemporary science as well as green technologies of renewable energy sources and efficient energy conversion systems to minimize the environmental effects and promote economic and social welfare. This approach is consistent with sustainable development objectives since it offers measures that do not deplete natural resources but, instead, supply low-emission forms of energy.List of Clean Tech hubs
The following is a 2021 ranking of clean technology ecosystems.United Nations: Sustainable Development Goals
 The
The United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmonizi ...
has set goals for the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, which is called " Sustainable Development Goals" composed of 17 goals and 232 indicators total. These goals are designed to build a sustainable future and to implement in the countries (member states) in the UN. Many parts of the 17 goals are related to the usage of clean technology since it is eventually an essential part of designing a sustainable future in various areas such as land, cities, industries, climate, etc.
* Goal 6: "Ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all"
** Various kinds of clean water technology are used to fulfill this goal, such as filters, technology for desalination, filtered water fountains for communities, etc.
* Goal 7: "Ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all"
** Promoting countries for implementing renewable energy is making remarkable progress, such as:
*** "From 2012 to 2014, three quarters of the world's 20 largest energy-consuming countries had reduced their energy intensity — the ratio of energy used per unit of GDP. The reduction was driven mainly by greater efficiencies in the industry and transport sectors. However, that progress is still not sufficient to meet the target of doubling the global rate of improvement in energy efficiency."
* Goal 11: "Make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable"
** By designing sustainable cities and communities, clean technology takes parts in the architectural aspect, transportation, and city environment. For example:
*** Global Fuel Economy Initiative (GFEI) - Relaunched to accelerate progress on decarbonizing road transport. Its main goal for passenger vehicles, in line with SDG 7.3, is to double the energy efficiency of new vehicles by 2030. This will also help mitigate climate change by reducing harmful emissions.
* Goal 13: "Take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts*"
** Greenhouse gas emissions have significantly impacted the climate, and this results in a rapid solution for consistently increasing emission levels. United Nations held the " Paris Agreement" for dealing with greenhouse gas emissions mainly within countries and for finding solutions and setting goals.
See also
*Environmental science
Environmental science is an interdisciplinary academic field that integrates physics, biology, and geography (including ecology, chemistry, plant science, zoology, mineralogy, oceanography, limnology, soil science, geology and physical ...
*Greentech (disambiguation) Greentech could refer to:
* Cleantech
* Green technology, also called environmental technology
* GreenTech ITM, a U.S.-based company that creates modular turf systems
* GreenTech Automotive
GreenTech Automotive (GTA) was a U.S.-based automotiv ...
*Sustainable engineering
Sustainable engineering is the process of designing or operating systems such that they use energy and resources sustainably, in other words, at a rate that does not compromise the natural environment, or the ability of future generations to meet ...
* WIPO GREEN
WIPO GREEN is a World Intellectual Property Organization program that supports global efforts to address climate change and food security through sharing of sustainable technology innovations . Established in 2013, WIPO GREEN is a free online mar ...
References
External links
Investing: Green technology has big growth potential
''
Los Angeles Times
The ''Los Angeles Times'' (abbreviated as ''LA Times'') is a daily newspaper that started publishing in Los Angeles in 1881. Based in the LA-adjacent suburb of El Segundo since 2018, it is the sixth-largest newspaper by circulation in the ...
'', 2011The Global Cleantech Innovation Index 2014
by Cleantech Group and WWF {{DEFAULTSORT:Clean Technology Economics of sustainability Environmental technology