Civil Rights Act may refer to several
civil right acts in the United States
Civil Rights Acts have been part of the Constitution of the United States of America, but in order to be received equally by all the population required to made List of amendments to the United States Constitution, amendments to the United States ...
. These
acts of the United States Congress are meant to protect
rights
Rights are law, legal, social, or ethics, ethical principles of freedom or Entitlement (fair division), entitlement; that is, rights are the fundamental normative rules about what is allowed of people or owed to people according to some legal sy ...
to ensure
individual
An individual is one that exists as a distinct entity. Individuality (or self-hood) is the state or quality of living as an individual; particularly (in the case of humans) as a person unique from other people and possessing one's own needs or g ...
s'
freedom
Freedom is the power or right to speak, act, and change as one wants without hindrance or restraint. Freedom is often associated with liberty and autonomy in the sense of "giving oneself one's own laws".
In one definition, something is "free" i ...
from infringement by
government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a State (polity), state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive (government), execu ...
s,
social organization
In sociology, a social organization is a pattern of relationships between and among individuals and groups. Characteristics of social organization can include qualities such as sexual composition, spatiotemporal cohesion, leadership, struc ...
s, and private individuals.
The first wave of civil rights acts were passed during the
Reconstruction era
The Reconstruction era was a period in History of the United States, US history that followed the American Civil War (1861-65) and was dominated by the legal, social, and political challenges of the Abolitionism in the United States, abol ...
after the
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
. The
Civil Rights Act of 1866
The Civil Rights Act of 1866 (, enacted April 9, 1866, reenacted 1870) was the first United States federal law to define citizenship and affirm that all citizens are equally protected by the law. It was mainly intended, in the wake of the Ame ...
extends the rights of emancipated slaves by stating that any person born in the United States regardless of race is an American citizen. The
Enforcement Acts
The Enforcement Acts were three bills that were passed by the United States Congress between 1870 and 1871. They were criminal codes that protected African Americans’ right to vote, to hold office, to serve on juries, and receive equal protect ...
of 1870-1871 allows the
President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film and television
*'' Præsident ...
to protect
Black American men’s right to vote, to hold office, to serve on juries, and for Black men and women to receive
equal protection of laws, including protection from racist violence. The
Civil Rights Act of 1875
The Civil Rights Act of 1875, sometimes called the Enforcement Act or the Force Act, was a United States federal law enacted during the Reconstruction era in response to civil rights violations against African Americans. The bill was passed by the ...
prohibited discrimination in "public accommodations" until it was found unconstitutional in 1883 by the
Supreme Court of the United States
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all Federal tribunals in the United States, U.S. federal court cases, and over Stat ...
. The
Jim Crow Laws
The Jim Crow laws were U.S. state, state and local laws introduced in the Southern United States in the late 19th and early 20th centuries that enforced Racial segregation in the United States, racial segregation, "Jim Crow (character), Ji ...
were established during the 19th century and served to block African American votes, ban integration in public facilities such as schools, and forbid interracial marriage in the South. The enactment of these laws was able to vastly undermine the progress toward equality which was made during the Reconstruction era.
Civil Rights Acts would not be passed for 82 more years until the success of the
Civil rights movement which aimed to abolish legalized
racial segregation
Racial segregation is the separation of people into race (human classification), racial or other Ethnicity, ethnic groups in daily life. Segregation can involve the spatial separation of the races, and mandatory use of different institutions, ...
,
discrimination
Discrimination is the process of making unfair or prejudicial distinctions between people based on the groups, classes, or other categories to which they belong or are perceived to belong, such as race, gender, age, class, religion, or sex ...
, and
disenfranchisement
Disfranchisement, also disenfranchisement (which has become more common since 1982) or voter disqualification, is the restriction of suffrage (the right to vote) of a person or group of people, or a practice that has the effect of preventing someo ...
in the country, which was most commonly employed against
African Americans
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from any of the Black racial groups of Africa ...
. The
Civil Rights Act of 1957
The Civil Rights Act of 1957 was the first federal civil rights law passed by the United States Congress since the Civil Rights Act of 1875. The bill was passed by the 85th United States Congress and signed into law by President Dwight D. E ...
established the Civil Rights Commission and the
Civil Rights Act of 1960
The Civil Rights Act of 1960 () is a United States federal law that established federal inspection of local voter registration polls and introduced penalties for anyone who obstructed someone's attempt to register to vote. It dealt primarily wi ...
established federal inspection of local voter registration polls. The landmark
Civil Rights Act of 1964
The Civil Rights Act of 1964 () is a landmark civil rights and United States labor law, labor law in the United States that outlaws discrimination based on Race (human categorization), race, Person of color, color, religion, sex, and nationa ...
prohibits discrimination based on
race, color,
religion
Religion is a range of social system, social-cultural systems, including designated religious behaviour, behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, religious text, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics in religion, ethics, or ...
, sex, and national origin by federal and state governments as well as public places. The
Civil Rights Act of 1968
The Civil Rights Act of 1968 () is a Lists of landmark court decisions, landmark law in the United States signed into law by President of the United States, United States President Lyndon B. Johnson during the King assassination riots.
Titles ...
prohibits discrimination in sale, rental, and financing of housing based on race, creed, and national origin. The
Civil Rights Restoration Act of 1987 specifies that recipients of federal funds must comply with civil rights laws in all areas, not just in the particular program or activity that received federal funding. The
Civil Rights Act of 1990 was a bill that would have made it easier for plaintiffs to win civil rights cases which was vetoed by President
George H. W. Bush
George Herbert Walker BushBefore the outcome of the 2000 United States presidential election, he was usually referred to simply as "George Bush" but became more commonly known as "George H. W. Bush", "Bush Senior," "Bush 41," and even "Bush th ...
. The
Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990
The Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990 or ADA () is a civil rights law that prohibits discrimination based on disability. It affords similar protections against discrimination to Americans with disabilities as the Civil Rights Act of 1964, ...
prohibits discrimination based on
disability
Disability is the experience of any condition that makes it more difficult for a person to do certain activities or have equitable access within a given society. Disabilities may be Cognitive disability, cognitive, Developmental disability, d ...
. The
Civil Rights Act of 1991
The Civil Rights Act of 1991 is a United States labor law, passed in response to United States Supreme Court decisions that limited the rights of employees who had sued their employers for discrimination. The Act represented the first effort sin ...
provides the right to trial by jury on discrimination claims and introducing the possibility of emotional distress damages, while limiting the amount that a jury could award.
Background
The first shift towards equality for African Americans occurred when President
Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln (February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was the 16th president of the United States, serving from 1861 until Assassination of Abraham Lincoln, his assassination in 1865. He led the United States through the American Civil War ...
passed the
Emancipation Proclamation
The Emancipation Proclamation, officially Proclamation 95, was a presidential proclamation and executive order issued by United States President Abraham Lincoln on January 1, 1863, during the American Civil War. The Proclamation had the eff ...
in 1863, which declared that "all persons held as slaves... shall be then, thenceforward, and forever free...". As initially ratified, the
United States Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the Supremacy Clause, supreme law of the United States, United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, on March 4, 1789. Originally includi ...
granted each state complete discretion to determine voter qualifications for its residents.
In American history, the
Reconstruction era
The Reconstruction era was a period in History of the United States, US history that followed the American Civil War (1861-65) and was dominated by the legal, social, and political challenges of the Abolitionism in the United States, abol ...
was the period from 1865-1877 following the end of the
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
. This period was marked by various attempts made to redress the inequities imposed on African Americans through slavery.
Three
Reconstruction Amendments
The , or the , are the Thirteenth, Fourteenth, and Fifteenth amendments to the United States Constitution, adopted between 1865 and 1870. The amendments were a part of the implementation of the Reconstruction of the American South which oc ...
were ratified and limited this discretion. The
Thirteenth Amendment (1865) prohibits
slavery
Slavery is the ownership of a person as property, especially in regards to their labour. Slavery typically involves compulsory work, with the slave's location of work and residence dictated by the party that holds them in bondage. Enslavemen ...
"except as a punishment for crime"; the
Fourteenth Amendment (1868) grants
citizenship
Citizenship is a membership and allegiance to a sovereign state.
Though citizenship is often conflated with nationality in today's English-speaking world, international law does not usually use the term ''citizenship'' to refer to nationalit ...
to anyone "born or naturalized in the United States" and guarantees every person
due process
Due process of law is application by the state of all legal rules and principles pertaining to a case so all legal rights that are owed to a person are respected. Due process balances the power of law of the land and protects the individual p ...
and
equal protection
The Equal Protection Clause is part of the first section of the Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution. The clause, which took effect in 1868, provides "nor shall any State... deny to any person within its jurisdiction the equal pr ...
rights; and the
Fifteenth Amendment (1870) provides that "
e right of citizens of the United States to vote shall not be denied or abridged by the United States or by any State on account of race, color, or previous condition of servitude."
These amendments were established to provide African Americans the same civil rights as white Americans, and also empower
Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of ...
to
enforce their provisions through "appropriate legislation". This time period marked the beginnings of the
Civil Rights Movement.
To enforce the Reconstruction Amendments, Congress passed the
Enforcement Acts
The Enforcement Acts were three bills that were passed by the United States Congress between 1870 and 1871. They were criminal codes that protected African Americans’ right to vote, to hold office, to serve on juries, and receive equal protect ...
in the 1870s. The acts criminalized the obstruction of a citizen's
voting rights
Suffrage, political franchise, or simply franchise is the right to vote in representative democracy, public, political elections and referendums (although the term is sometimes used for any right to vote). In some languages, and occasionally in ...
and provided for federal supervision of the electoral process, including
voter registration
In electoral systems, voter registration (or enrollment) is the requirement that a person otherwise Suffrage, eligible to Voting, vote must register (or enroll) on an electoral roll, which is usually a prerequisite for being entitled or permitted ...
.
By 1873, Supreme Court decisions began to limit the scope of Reconstruction legislation, and many whites resorted to intimidation and violence to undermine African Americans' voting rights.
In 1875 the
Supreme Court
In most legal jurisdictions, a supreme court, also known as a court of last resort, apex court, high (or final) court of appeal, and court of final appeal, is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
struck down parts of the legislation as unconstitutional in ''
United States v. Cruikshank
''United States v. Cruikshank'', 92 U.S. 542 (1876), was a landmark decision of the United States Supreme Court ruling that the U.S. Bill of Rights did not limit the power of private actors or state governments despite the adoption of the Fo ...
'' and ''
United States v. Reese
''United States v. Reese'', 92 U.S. 214 (1876), was a voting rights case in which the United States Supreme Court narrowly construed the Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution
The Fifteenth Amendment (Amendment XV) to the Uni ...
''.
The
Compromise of 1877
The Compromise of 1877, also known as the Wormley Agreement, the Tilden-Hayes Compromise, the Bargain of 1877, or Corrupt bargain, the Corrupt Bargain, was a speculated unwritten political deal in the United States to settle the intense dispute ...
, an informal agreement to resolve a political dispute, marked the end of the Reconstruction era. After the
Reconstruction Era
The Reconstruction era was a period in History of the United States, US history that followed the American Civil War (1861-65) and was dominated by the legal, social, and political challenges of the Abolitionism in the United States, abol ...
ended in 1877, enforcement of these civil rights laws ceased, and in 1894, Congress repealed most of their provisions.
Southern Democrats largely stopped adhering to the provisions of Reconstruction legislation, ceasing to intervene in Southern voting practices, which prompted widespread disenfranchisement of African American voters during and after Reconstruction. From 1868 to 1888,
electoral fraud
Electoral fraud, sometimes referred to as election manipulation, voter fraud, or vote rigging, involves illegal interference with the process of an election, either by increasing the vote share of a favored candidate, depressing the vote share o ...
and violence throughout the South suppressed the
African-American
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from any of the Black racial groups of Africa. ...
vote.
From 1888 to 1908, Southern states legalized disenfranchisement by enacting
Jim Crow laws
The Jim Crow laws were U.S. state, state and local laws introduced in the Southern United States in the late 19th and early 20th centuries that enforced Racial segregation in the United States, racial segregation, "Jim Crow (character), Ji ...
; they amended their
constitutions
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organization or other type of entity, and commonly determines how that entity is to be governed.
When these princ ...
and passed legislation to impose various voting restrictions, including
literacy test
A literacy test assesses a person's literacy skills: their ability to read and write. Literacy tests have been administered by various governments, particularly to immigrants.
Between the 1850s and 1960s, literacy tests were used as an effecti ...
s,
poll taxes
A poll tax, also known as head tax or capitation, is a tax levied as a fixed sum on every liable individual (typically every adult), without reference to income or resources. ''Poll'' is an archaic term for "head" or "top of the head". The sen ...
, property-ownership requirements, moral character tests, requirements that voter registration applicants interpret particular documents, and
grandfather clauses that allowed otherwise-ineligible persons to vote if their grandfathers voted (which excluded many African Americans whose grandfathers had been slaves or otherwise ineligible).
During this period, the Supreme Court generally upheld efforts to discriminate against racial minorities. In ''
Giles v. Harris'' (1903), the court held that regardless of the Fifteenth Amendment, the
judiciary
The judiciary (also known as the judicial system, judicature, judicial branch, judiciative branch, and court or judiciary system) is the system of courts that adjudicates legal disputes/disagreements and interprets, defends, and applies the law ...
did not have the remedial power to force states to register racial minorities to vote.
The Civil Rights Act of 1866
The Civil Rights Act of 1866 (, enacted April 9, 1866, reenacted 1870) was the first
United States federal law
The law of the United States comprises many levels of Codification (law), codified and uncodified forms of law, of which the supreme law is the nation's Constitution of the United States, Constitution, which prescribes the foundation of the ...
to define citizenship and affirm that all citizens are equally protected by the law. It was mainly intended, in the wake of the
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
, to protect the
civil rights
Civil and political rights are a class of rights that protect individuals' political freedom, freedom from infringement by governments, social organizations, and private individuals. They ensure one's entitlement to participate in the civil and ...
of persons of African descent born in or brought to the
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
.
Civil Rights Act of 1866
The Civil Rights Act of 1866 (, enacted April 9, 1866, reenacted 1870) was the first United States federal law to define citizenship and affirm that all citizens are equally protected by the law. It was mainly intended, in the wake of the Ame ...
The Act was passed by
Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of ...
in 1866 and vetoed by
U.S. President
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president directs the Federal government of the United States#Executive branch, executive branch of the Federal government of t ...
Andrew Johnson
Andrew Johnson (December 29, 1808July 31, 1875) was the 17th president of the United States, serving from 1865 to 1869. The 16th vice president, he assumed the presidency following the assassination of Abraham Lincoln. Johnson was a South ...
. In April 1866, Congress again passed the bill to support the
Thirteenth Amendment, and Johnson again vetoed it, but a two-thirds majority in each chamber overrode the veto to allow it to become law without presidential signature.
John Bingham
John Armor Bingham (January 21, 1815 – March 19, 1900) was an American politician who served as a Republican representative from Ohio and as the United States ambassador to Japan. In his time as a congressman, Bingham served as both assis ...
and other congressmen argued that Congress did not yet have sufficient constitutional power to enact this law. Following passage of the
Fourteenth Amendment in 1868, Congress ratified the 1866 Act in 1870.
The act had three primary objectives for the integration of
African Americans
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from any of the Black racial groups of Africa ...
into the American society following the Civil War: 1.) a definition of American citizenship 2.) the rights which come with this citizenship and 3.) the unlawfulness to deprive any person of citizenship rights "on the basis of race, color, or prior condition of slavery or involuntary servitude."
The act accomplished these three primary objectives.
The author of the Civil Rights Act of 1866 was
United States Senator
The United States Senate consists of 100 members, two from each of the 50 U.S. state, states. This list includes all senators serving in the 119th United States Congress.
Party affiliation
Independent Senators Angus King of Maine and Berni ...
Lyman Trumbull
Lyman Trumbull (October 12, 1813 – June 25, 1896) was an American lawyer, judge, and politician who represented the state of Illinois in the United States Senate from 1855 to 1873. Trumbull was a leading abolitionist attorney and key polit ...
.
Congressman
A member of congress (MOC), also known as a congressman or congresswoman, is a person who has been appointed or elected and inducted into an official body called a congress, typically to represent a particular constituency in a legislature. The t ...
James F. Wilson summarized what he considered to be the purpose of the act as follows, when he introduced the legislation in the House of Representatives:
During the subsequent legislative process, the following key provision was deleted: "there shall be no discrimination in civil rights or immunities among the inhabitants of any State or Territory of the United States on account of race, color, or previous condition of servitude."
John Bingham
John Armor Bingham (January 21, 1815 – March 19, 1900) was an American politician who served as a Republican representative from Ohio and as the United States ambassador to Japan. In his time as a congressman, Bingham served as both assis ...
was an influential supporter of this deletion, on the ground that courts might construe the term "civil rights" more broadly than people like Wilson intended. Weeks later, Senator Trumbull described the bill's intended scope:
On April 5, 1866, the Senate overrode President Andrew Johnson's veto. This marked the first time that the U.S. Congress ever overrode a presidential veto for a major piece of legislation.
Content
With an
incipit
The incipit ( ) of a text is the first few words of the text, employed as an identifying label. In a musical composition, an incipit is an initial sequence of Musical note, notes, having the same purpose. The word ''incipit'' comes from Latin an ...
of "An Act to protect all Persons in the United States in their Civil Rights, and furnish the Means of their vindication", the act declared that all people born in the United States who are not subject to any foreign power are entitled to be citizens, without regard to race, color, or previous condition of
slavery
Slavery is the ownership of a person as property, especially in regards to their labour. Slavery typically involves compulsory work, with the slave's location of work and residence dictated by the party that holds them in bondage. Enslavemen ...
or involuntary servitude.
A similar provision (called the
Citizenship Clause
The Citizenship Clause is the first sentence of the Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, which was adopted on July 9, 1868, which states:
This clause reversed a portion of the '' Dred Scott v. Sandford'' decision, which had ...
) was written a few months later into the proposed
Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution
The Fourteenth Amendment (Amendment XIV) to the United States Constitution was adopted on July 9, 1868, as one of the Reconstruction Amendments. Considered one of the most consequential amendments, it addresses Citizenship of the United States ...
.
The Civil Rights Act of 1866 also said that any citizen has the same right that a white citizen has to make and enforce contracts, sue and be sued, give evidence in court, and inherit, purchase, lease, sell, hold, and convey real and personal property. Additionally, the act guaranteed to all citizens the "full and equal benefit of all laws and proceedings for the security of person and property, as is enjoyed by white citizens, and ... like punishment, pains, and penalties..." Persons who denied these rights on account of race or previous enslavement were guilty of a misdemeanor and upon conviction faced a fine not exceeding $1,000, or imprisonment not exceeding one year, or both.
The act used language very similar to that of the
Equal Protection Clause
The Equal Protection Clause is part of the first section of the Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution. The clause, which took effect in 1868, provides "nor shall any State... deny to any person within its jurisdiction the equal pr ...
in the newly proposed Fourteenth Amendment. In particular, the act discussed the need to provide "reasonable protection to all persons in their constitutional rights of equality before the law, without distinction of race or color, or previous condition of slavery or involuntary servitude, except as a punishment for crime, whereof the party shall have been duly convicted. ..."
This statute was a major part of general federal policy during
Reconstruction
Reconstruction may refer to:
Politics, history, and sociology
*Reconstruction (law), the transfer of a company's (or several companies') business to a new company
*''Perestroika'' (Russian for "reconstruction"), a late 20th century Soviet Union ...
, and was closely related to the
Second Freedmen's Bureau Act of 1866. According to Congressman
John Bingham
John Armor Bingham (January 21, 1815 – March 19, 1900) was an American politician who served as a Republican representative from Ohio and as the United States ambassador to Japan. In his time as a congressman, Bingham served as both assis ...
, "the seventh and eighth sections of the Freedmen's Bureau bill enumerate the same rights and all the rights and privileges that are enumerated in the first section of this
he Civil Rightsbill."
Parts of the Civil Rights Act of 1866 are enforceable into the 21st century, according to the
United States Code
The United States Code (formally The Code of Laws of the United States of America) is the official Codification (law), codification of the general and permanent Law of the United States#Federal law, federal statutes of the United States. It ...
:
One section of the United States Code (42 U.S.C. §1981), is §1 of the Civil Rights Act of 1866 as revised and amended by subsequent Acts of Congress. The Civil Rights Act of 1866 was reenacted by the
Enforcement Act of 1870
The Enforcement Act of 1870, also known as the Civil Rights Act of 1870 or First Ku Klux Klan Act, or Force Act (41st Congress, Sess. 2, ch. 114, , enacted May 31, 1870, effective 1871), is a United States federal law that empowers the Presiden ...
, ch. 114, § 18, 16 Stat. 144, codified as sections 1977 and 1978 of the Revised Statutes of 1874, and appears now as 42 U.S.C. §§ 1981–82 (1970). Section 2 of the Civil Rights Act of 1866, as subsequently revised and amended, appears in the US Code at 18 U.S.C. §242. After the fourteenth amendment became effective, the 1866 Act was reenacted as an addendum to the Enforcement Act of 1870 in order to dispel any possible doubt as to its constitutionality. Act of May 31, 1870, ch. 114, § 18, 16 Stat. 144.
Enactment, constitutionalization, and reenactment
Senator
Lyman Trumbull
Lyman Trumbull (October 12, 1813 – June 25, 1896) was an American lawyer, judge, and politician who represented the state of Illinois in the United States Senate from 1855 to 1873. Trumbull was a leading abolitionist attorney and key polit ...
was the
Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
sponsor of the Civil Rights Act of 1866, and he argued that Congress had power to enact it in order to eliminate a discriminatory "badge of servitude" prohibited by the
Thirteenth Amendment.
[Salzman, Lawrence. "Civil Rights Act of 1866" in ''Encyclopedia of American Civil Liberties'', by Paul Finkelman, Volume 1]
pp. 299–300
(CRC Press, 2006). Congressman
A member of congress (MOC), also known as a congressman or congresswoman, is a person who has been appointed or elected and inducted into an official body called a congress, typically to represent a particular constituency in a legislature. The t ...
John Bingham
John Armor Bingham (January 21, 1815 – March 19, 1900) was an American politician who served as a Republican representative from Ohio and as the United States ambassador to Japan. In his time as a congressman, Bingham served as both assis ...
, principal author of the first section of the
Fourteenth Amendment, was one of several Republicans who believed (prior to that Amendment) that Congress lacked power to pass the 1866 Act. In the 20th century, the U.S. Supreme Court ultimately adopted Trumbull's Thirteenth Amendment rationale for congressional power to ban racial discrimination by states and by private parties, as the Thirteenth Amendment does not require a
state actor
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
.
To the extent that the Civil Rights Act of 1866 may have been intended to go beyond preventing discrimination, by conferring particular rights on all citizens, the constitutional power of Congress to do that was more questionable. For example, Representative
William Lawrence argued that Congress had power to enact the statute because of the
Privileges and Immunities Clause
The Privileges and Immunities Clause (United States Constitution, U.S. Constitution, Article Four of the United States Constitution, Article IV, Section 2, Clause 1, also known as the Comity Clause) prevents a U.S. state, state of the United Stat ...
in Article IV of the original unamended Constitution, even though courts had suggested otherwise.
In any event, there is currently no consensus that the language of the Civil Rights Act of 1866 actually purports to confer any legal benefits upon white citizens. Representative
Samuel Shellabarger said that it did not.
After enactment of the Civil Rights Act of 1866 by overriding a presidential veto, some members of Congress supported the
Fourteenth Amendment in order to eliminate doubts about the constitutionality of the Civil Rights Act of 1866, or to ensure that no subsequent Congress could later repeal or alter the main provisions of that Act. Thus, the
Citizenship Clause
The Citizenship Clause is the first sentence of the Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, which was adopted on July 9, 1868, which states:
This clause reversed a portion of the '' Dred Scott v. Sandford'' decision, which had ...
in the Fourteenth Amendment parallels citizenship language in the Civil Rights Act of 1866, and likewise the
Equal Protection Clause
The Equal Protection Clause is part of the first section of the Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution. The clause, which took effect in 1868, provides "nor shall any State... deny to any person within its jurisdiction the equal pr ...
parallels nondiscrimination language in the 1866 Act; the extent to which other clauses in the Fourteenth Amendment may have incorporated elements of the Civil Rights Act of 1866 is a matter of continuing debate.
Ratification of the Fourteenth Amendment was completed in 1868, 2 years after, the 1866 Act was reenacted, as Section 18 of the
Enforcement Act of 1870
The Enforcement Act of 1870, also known as the Civil Rights Act of 1870 or First Ku Klux Klan Act, or Force Act (41st Congress, Sess. 2, ch. 114, , enacted May 31, 1870, effective 1871), is a United States federal law that empowers the Presiden ...
.
After Johnson's veto was overridden, the measure became law. Despite this victory, even some Republicans who had supported the goals of the Civil Rights Act began to doubt that Congress possessed the constitutional power to turn those goals into laws. The experience encouraged both radical and moderate Republicans to seek Constitutional guarantees for black rights, rather than relying on temporary political majorities.
The activities of groups such as the
Ku Klux Klan
The Ku Klux Klan (), commonly shortened to KKK or Klan, is an American Protestant-led Christian terrorism, Christian extremist, white supremacist, Right-wing terrorism, far-right hate group. It was founded in 1865 during Reconstruction era, ...
(KKK) undermined the act, meaning that it failed to immediately secure the civil rights of African Americans.
While it has been ''de jure'' illegal in the U.S. to
discriminate in employment and housing on the basis of race since 1866, federal penalties were not provided for until the second half of the 20th century (with the passage of related civil rights legislation), which meant remedies were left to the individuals involved: because those being discriminated against had limited or no access to legal assistance, this often left many victims of discrimination without recourse.
There have been an increasing number of remedies provided under this act since the second half of the 20th century, including the landmark ''
Jones v. Mayer'' and ''Sullivan v. Little Hunting Park, Inc.'' decisions in 1968.
Enforcement Acts of 1870-1871
The Enforcement Acts were three bills that were passed by the
United States Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature, legislative branch of the federal government of the United States. It is a Bicameralism, bicameral legislature, including a Lower house, lower body, the United States House of Representatives, ...
between 1870 and 1871. They were criminal codes that protected
African Americans
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from any of the Black racial groups of Africa ...
’ right to vote, to hold office, to serve on juries, and receive
equal protection of laws. Passed under the presidency of
Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant (born Hiram Ulysses Grant; April 27, 1822July 23, 1885) was the 18th president of the United States, serving from 1869 to 1877. In 1865, as Commanding General of the United States Army, commanding general, Grant led the Uni ...
, the laws also allowed the federal government to intervene when states did not act to protect these rights. The acts passed following the ratification of the
Fourteenth Amendment to the US Constitution, which gave full citizenship to anyone born in the United States or freed
slaves
Slavery is the ownership of a person as property, especially in regards to their labour. Slavery typically involves compulsory work, with the slave's location of work and residence dictated by the party that holds them in bondage. Enslavemen ...
, and the
Fifteenth Amendment, which banned racial discrimination in voting.
At the time, the lives of all newly freed slaves, as well as their political and economic rights, were being threatened.
This threat led to the creation of the Enforcement Acts. The main goal in creating these acts was to improve conditions for black people and freed slaves. The main target was the
Ku Klux Klan
The Ku Klux Klan (), commonly shortened to KKK or Klan, is an American Protestant-led Christian terrorism, Christian extremist, white supremacist, Right-wing terrorism, far-right hate group. It was founded in 1865 during Reconstruction era, ...
, a
white supremacy
White supremacy is the belief that white people are superior to those of other races. The belief favors the maintenance and defense of any power and privilege held by white people. White supremacy has roots in the now-discredited doctrine ...
organization, which was targeting black people, and, later, other groups. Although this act was meant to fight the KKK and help black people and freedmen, many states were reluctant to take such relatively extreme actions, for several reasons. Some
politicians
A politician is a person who participates in policy-making processes, usually holding an elective position in government. Politicians represent the people, make decisions, and influence the formulation of public policy. The roles or duties tha ...
at the state and federal levels were either members of the Klan, or did not have enough strength to fight the Klan. Another goal of these acts was to achieve national unity, by creating a country where all
races were considered equal under the law.
The Enforcement Acts did many things to help freedmen. The main purpose under the act was the prohibited use of
violence
Violence is characterized as the use of physical force by humans to cause harm to other living beings, or property, such as pain, injury, disablement, death, damage and destruction. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines violence a ...
or any form of intimidation to prevent the freedmen from voting and denying them that right. There were many provisions placed under the act, many with serious consequences. The Enforcement Acts were created as part of the
Reconstruction era
The Reconstruction era was a period in History of the United States, US history that followed the American Civil War (1861-65) and was dominated by the legal, social, and political challenges of the Abolitionism in the United States, abol ...
following the
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
. To allow full national unity, all citizens must be accepted and viewed equally, with violence prohibited.
Enforcement Act of 1870
The Enforcement Act of 1870 prohibited discrimination by state officials in voter registration on the basis of race, color, or previous condition of servitude. It established penalties for interfering with a person's right to vote and gave federal courts the power to enforce the act.
The act also authorized the President to employ the use of the army to uphold the act and the use of federal marshals to bring charges against offenders for election fraud, the bribery or intimidation of voters, and conspiracies to prevent citizens from exercising their constitutional rights.
The act banned the use of terror, force or bribery to prevent people from voting because of their race. Other laws banned the KKK entirely. Hundreds of KKK members were arrested and tried as common criminals and terrorists. The first Klan was all but eradicated within a year of federal prosecution.
Enforcement Act of 1871
The
Second Enforcement Act of 1871
The second (symbol: s) is a unit of time derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes, and finally to 60 seconds each (24 × 60 × 60 = 86400). The current and formal definition in the International System of U ...
(formally, "an Act to enforce the rights of citizens of the United States to vote in the several states of this union"), permitted federal oversight of local and state elections if any two citizens in a town with more than twenty-thousand inhabitants desired it.
The
Enforcement Act of 1871 (second act) and the
Civil Rights Act of 1875
The Civil Rights Act of 1875, sometimes called the Enforcement Act or the Force Act, was a United States federal law enacted during the Reconstruction era in response to civil rights violations against African Americans. The bill was passed by the ...
are very similar to the original act as they all have the same goal, but revised the first act with the intention of being more effective. The Act of 1871 has more severe punishments with larger fines for disregarding the regulations, and the prison sentences vary in length.
The final act, and the most effective, was also a revision. Although the fines lowered again, and the prison sentences remained approximately the same,
this act was the best enforced by the government.
Ku Klux Klan Act
The
Enforcement Act of 1871, the third Enforcement Act passed by Congress and also known as the Ku Klux Klan Act (formally, "An Act to enforce the Provisions of the Fourteenth Amendment to the Constitution of the United States, and for other Purposes"), made state officials liable in federal court for depriving anyone of their civil rights or the equal protection of the laws. It further made a number of the KKK's intimidation tactics into federal offenses, authorized the president to call out the militia to suppress conspiracies against the operation of the federal government, and prohibited those suspected of complicity in such conspiracies to serve on juries related to the Klan's activities. The Act also authorized the president to suspend the writ of ''
habeas corpus
''Habeas corpus'' (; from Medieval Latin, ) is a legal procedure invoking the jurisdiction of a court to review the unlawful detention or imprisonment of an individual, and request the individual's custodian (usually a prison official) to ...
'' if violence rendered efforts to suppress the Klan ineffective. It was passed at the request of
Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant (born Hiram Ulysses Grant; April 27, 1822July 23, 1885) was the 18th president of the United States, serving from 1869 to 1877. In 1865, as Commanding General of the United States Army, commanding general, Grant led the Uni ...
.
Aftermath
As a response to the act, Klansmen in
South Carolina
South Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders North Carolina to the north and northeast, the Atlantic Ocean to the southeast, and Georgia (U.S. state), Georg ...
were put on trial in front of juries made up of mainly African Americans.
Amos T. Akerman
Amos Tappan Akerman (February 23, 1821 – December 21, 1880) was an American politician who served as United States Attorney General under President Ulysses S. Grant from 1870 to 1871.
A native of New Hampshire, Akerman graduated from Dartmou ...
was largely involved with the prosecutions of the Klansmen. He worked to make America aware of Klan violence and how much of a problem it was becoming. His work led to trials and to jail sentences of a few hundred Klan members. Many others who were put on trial either fled or were only given a warning. By 1872, the Klan as an organization had been officially broken.
The Enforcement Acts were a series of acts, but it was not until the
Ku Klux Klan Act
The Enforcement Act of 1871 (), also known as the Ku Klux Klan Act, Third Enforcement Act, Third Ku Klux Klan Act, Civil Rights Act of 1871, or Force Act of 1871, is an Act of the United States Congress that was intended to combat the paramilit ...
of 1871, the third Enforcement Act, that their regulations to protect black Americans, and to enforce the Fourteenth and
Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution
The Fifteenth Amendment (Amendment XV) to the United States Constitution prohibits the federal government and each state from denying or abridging a citizen's right to vote "on account of race, color, or previous condition of servitude." It wa ...
were really enforced and followed. It was only after the creation of the third Enforcement Act that trials were conducted, and perpetrators were convicted for any crimes they had committed in violation of the Enforcement Acts.
Judicial interpretations
After the
Colfax massacre in Louisiana, the federal government brought a civil rights case against nine men (out of 97 indicted) who were accused of paramilitary activity intended to stop black people from voting. In ''
United States v. Cruikshank
''United States v. Cruikshank'', 92 U.S. 542 (1876), was a landmark decision of the United States Supreme Court ruling that the U.S. Bill of Rights did not limit the power of private actors or state governments despite the adoption of the Fo ...
'' (1876), the Court ruled that the federal government did not have the authority to prosecute the men because the Fourteenth and Fifteenth Amendments provide only for redress against
state actor
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
s. However, in ''
Ex Parte Yarbrough
''Ex parte Yarbrough'' (also known as the ''Ku Klux Cases''), 110 U.S. 651 (1884), was a decision of the Supreme Court of the United States involving Congress's power to punish individuals who interfere with the right to vote in federal election ...
'' (1884) the Court allowed individuals who were not state actors to be prosecuted because
Article I Section 4 of the Constitution gives Congress the power to regulate federal elections.
In ''
Hodges v. United States'' (1906) the Court addressed a possible
Thirteenth Amendment rationale for the Enforcement Acts, and found that the federal government did not have the authority to punish a group of men for interfering with black workers through
whitecapping
Whitecapping was a violent vigilante movement of farmers in the United States during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. It was originally a ritualized form of extralegal actions to enforce community standards, appropriate behavior, and tradi ...
. ''Hodges v. United States'' would be overruled in ''
Jones v. Alfred H. Mayer Co.'' some 50 years later, stating for the first time since Reconstruction that the federal government could criminalize racist acts by private actors.
Civil Rights Act of 1875
The Civil Rights Act of 1875, sometimes called the Enforcement Act or the Force Act, was a
United States federal law
The law of the United States comprises many levels of Codification (law), codified and uncodified forms of law, of which the supreme law is the nation's Constitution of the United States, Constitution, which prescribes the foundation of the ...
enacted during the
Reconstruction era
The Reconstruction era was a period in History of the United States, US history that followed the American Civil War (1861-65) and was dominated by the legal, social, and political challenges of the Abolitionism in the United States, abol ...
in response to civil rights violations against African Americans. The bill was passed by the
43rd United States Congress
The 43rd United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, consisting of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C. from March 4, 1873, ...
and signed into law by
President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film and television
*'' Præsident ...
Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant (born Hiram Ulysses Grant; April 27, 1822July 23, 1885) was the 18th president of the United States, serving from 1869 to 1877. In 1865, as Commanding General of the United States Army, commanding general, Grant led the Uni ...
on March 1, 1875. The act was designed to "protect all citizens in their civil and legal rights", providing for equal treatment in
public accommodations
In public relations and communication science, publics are groups of individual people, and the public (a.k.a. the general public) is the totality of such groupings. This is a different concept to the sociological concept of the ''Öffentlichk ...
and public transportation and prohibiting exclusion from
jury service. It was originally drafted by Senator
Charles Sumner
Charles Sumner (January 6, 1811March 11, 1874) was an American lawyer and statesman who represented Massachusetts in the United States Senate from 1851 until his death in 1874. Before and during the American Civil War, he was a leading American ...
in 1870, but was not passed until shortly after Sumner's death in 1875. The law was not effectively enforced, partly because President Grant had favored different measures to help him suppress election-related violence against blacks and
Republicans in the
Southern United States
The Southern United States (sometimes Dixie, also referred to as the Southern States, the American South, the Southland, Dixieland, or simply the South) is List of regions of the United States, census regions defined by the United States Cens ...
.
The Reconstruction era ended with the resolution of the
1876 presidential election, and the Civil Rights Act of 1875 was the last federal civil rights law enacted until the passage of the
Civil Rights Act of 1957
The Civil Rights Act of 1957 was the first federal civil rights law passed by the United States Congress since the Civil Rights Act of 1875. The bill was passed by the 85th United States Congress and signed into law by President Dwight D. E ...
. In 1883, the
Supreme Court
In most legal jurisdictions, a supreme court, also known as a court of last resort, apex court, high (or final) court of appeal, and court of final appeal, is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
ruled in the ''
Civil Rights Cases
The ''Civil Rights Cases'', 109 U.S. 3 (1883), were a group of five landmark cases in which the Supreme Court of the United States held that the Thirteenth and Fourteenth Amendments did not empower Congress to outlaw racial discrimination by ...
'' that the public accommodation sections of the act were unconstitutional, saying Congress was not afforded control over private persons or corporations under the
Equal Protection Clause
The Equal Protection Clause is part of the first section of the Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution. The clause, which took effect in 1868, provides "nor shall any State... deny to any person within its jurisdiction the equal pr ...
. Parts of the Civil Rights Act of 1875 were later re-adopted in the
Civil Rights Act of 1964
The Civil Rights Act of 1964 () is a landmark civil rights and United States labor law, labor law in the United States that outlaws discrimination based on Race (human categorization), race, Person of color, color, religion, sex, and nationa ...
and the
Civil Rights Act of 1968
The Civil Rights Act of 1968 () is a Lists of landmark court decisions, landmark law in the United States signed into law by President of the United States, United States President Lyndon B. Johnson during the King assassination riots.
Titles ...
, both of which cited the
Commerce Clause
The Commerce Clause describes an enumerated power listed in the United States Constitution ( Article I, Section 8, Clause 3). The clause states that the United States Congress shall have power "to regulate Commerce with foreign Nations, and amon ...
as the source of Congress's power to regulate private actors.
Legislative history
The drafting of the bill was performed early in 1870 by
United States Senator
The United States Senate consists of 100 members, two from each of the 50 U.S. state, states. This list includes all senators serving in the 119th United States Congress.
Party affiliation
Independent Senators Angus King of Maine and Berni ...
Charles Sumner
Charles Sumner (January 6, 1811March 11, 1874) was an American lawyer and statesman who represented Massachusetts in the United States Senate from 1851 until his death in 1874. Before and during the American Civil War, he was a leading American ...
, a dominant
Radical Republican
The Radical Republicans were a political faction within the Republican Party originating from the party's founding in 1854—some six years before the Civil War—until the Compromise of 1877, which effectively ended Reconstruction. They ca ...
in the Senate, with the assistance of
John Mercer Langston
John Mercer Langston (December 14, 1829 – November 15, 1897) was an African-American abolitionist, attorney, educator, activist, diplomat, and politician. He was the founding dean of the law school at Howard University and helped create the d ...
, a prominent African American who established the
law department at
Howard University
Howard University is a private, historically black, federally chartered research university in Washington, D.C., United States. It is classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity" and accredited by the Mid ...
. The bill was proposed by Senator Sumner and co-sponsored by
Representative Benjamin F. Butler, both
Republicans from
Massachusetts
Massachusetts ( ; ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Maine to its east, Connecticut and Rhode ...
, in the
41st Congress of the United States in 1870. Congress removed the coverage of public schools that Sumner had included. The act was passed by the 43rd Congress in February 1875 as a memorial to honor Sumner, who had just died. It was signed into law by
United States President
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president directs the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed For ...
Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant (born Hiram Ulysses Grant; April 27, 1822July 23, 1885) was the 18th president of the United States, serving from 1869 to 1877. In 1865, as Commanding General of the United States Army, commanding general, Grant led the Uni ...
on March 1, 1875.
Enforcement
President Grant had wanted an entirely different law to help him suppress election-related violence against blacks and Republicans in the South. Congress did not give him that, but instead wrote a law for equal rights to public accommodations that was passed as a memorial to Grant's bitterest enemy, the late Senator Charles Sumner. Grant never commented on the 1875 law, and did nothing to enforce it, says historian
John Hope Franklin
John Hope Franklin (January 2, 1915 – March 25, 2009) was an American historian of the United States and former president of Phi Beta Kappa, the Organization of American Historians, the American Historical Association, the American Studies ...
. Grant's Justice Department ignored it and did not send copies to US attorneys, says Franklin, while many federal judges called it unconstitutional before the Supreme Court shut it down. Franklin concludes regarding Grant and Hayes administrations, "The Civil Rights Act was never effectively enforced." Public opinion was opposed, with the black community in support. Historian Rayford Logan looking at newspaper editorials finds the press was overwhelmingly opposed.
Case law
The Supreme Court, in an 8–1 decision, declared sections of the act unconstitutional in the ''Civil Rights Cases'' on October 15, 1883, thus stripping the
Civil Rights Act of 1875
The Civil Rights Act of 1875, sometimes called the Enforcement Act or the Force Act, was a United States federal law enacted during the Reconstruction era in response to civil rights violations against African Americans. The bill was passed by the ...
of much of its ability to protect civil rights.
Justice
In its broadest sense, justice is the idea that individuals should be treated fairly. According to the ''Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy'', the most plausible candidate for a core definition comes from the ''Institutes (Justinian), Inst ...
John Marshall Harlan
John Marshall Harlan (June 1, 1833 – October 14, 1911) was an American lawyer and politician who served as an associate justice of the Supreme Court of the United States from 1877 until his death in 1911. He is often called "The Great Disse ...
provided the lone dissent. The Court held the
Equal Protection Clause
The Equal Protection Clause is part of the first section of the Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution. The clause, which took effect in 1868, provides "nor shall any State... deny to any person within its jurisdiction the equal pr ...
within the
Fourteenth Amendment prohibits discrimination by the state and local government, but it does not give the federal government the power to prohibit discrimination by private individuals and organizations. The Court also held that the
Thirteenth Amendment was meant to eliminate "the badge of slavery," but not to prohibit racial discrimination in public accommodations.
The Civil Rights Act of 1875 was the last federal civil rights bill signed into law until the
Civil Rights Act of 1957
The Civil Rights Act of 1957 was the first federal civil rights law passed by the United States Congress since the Civil Rights Act of 1875. The bill was passed by the 85th United States Congress and signed into law by President Dwight D. E ...
, enacted during the
Civil Rights Movement. In the late 19th and early 20th century, the legal justification for voiding the Civil Rights Act of 1875 was part of a larger trend by the United States Supreme Court majorities to invalidate most government regulations of the private sector, except when dealing with laws designed to protect traditional public morality. The Civil Rights Act of 1875 is notable as the last major piece of legislation related to Reconstruction that was passed by Congress during the
Reconstruction era
The Reconstruction era was a period in History of the United States, US history that followed the American Civil War (1861-65) and was dominated by the legal, social, and political challenges of the Abolitionism in the United States, abol ...
. These include the
Civil Rights Act of 1866
The Civil Rights Act of 1866 (, enacted April 9, 1866, reenacted 1870) was the first United States federal law to define citizenship and affirm that all citizens are equally protected by the law. It was mainly intended, in the wake of the Ame ...
, the four
Reconstruction Acts
The Reconstruction Acts, or the Military Reconstruction Acts, sometimes referred to collectively as the Reconstruction Act of 1867, were four landmark U.S. federal statutes enacted by the 39th and 40th United States Congresses over the veto ...
of 1867 and 1868, the three
Enforcement Acts
The Enforcement Acts were three bills that were passed by the United States Congress between 1870 and 1871. They were criminal codes that protected African Americans’ right to vote, to hold office, to serve on juries, and receive equal protect ...
of 1870 and 1871, and the three
Constitutional Amendments
A constitutional amendment (or constitutional alteration) is a modification of the constitution of a polity, organization or other type of entity. Amendments are often interwoven into the relevant sections of an existing constitution, directly alt ...
adopted between 1865 and 1870.
Provisions contained in the Civil Rights Act of 1875 were later readopted by Congress during the Civil Rights Movement as part of the
Civil Rights Act of 1964
The Civil Rights Act of 1964 () is a landmark civil rights and United States labor law, labor law in the United States that outlaws discrimination based on Race (human categorization), race, Person of color, color, religion, sex, and nationa ...
and the
Civil Rights Act of 1968
The Civil Rights Act of 1968 () is a Lists of landmark court decisions, landmark law in the United States signed into law by President of the United States, United States President Lyndon B. Johnson during the King assassination riots.
Titles ...
. The 1964 and 1968 acts relied upon the
Commerce Clause
The Commerce Clause describes an enumerated power listed in the United States Constitution ( Article I, Section 8, Clause 3). The clause states that the United States Congress shall have power "to regulate Commerce with foreign Nations, and amon ...
contained in
Article One of the
Constitution of the United States
The Constitution of the United States is the Supremacy Clause, supreme law of the United States, United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, on March 4, 1789. Originally includi ...
rather than the Equal Protection Clause within the Fourteenth Amendment.
Civil Rights Act of 1957
The
Civil Rights Act of 1957
The Civil Rights Act of 1957 was the first federal civil rights law passed by the United States Congress since the Civil Rights Act of 1875. The bill was passed by the 85th United States Congress and signed into law by President Dwight D. E ...
, signed by President
Dwight D. Eisenhower
Dwight David "Ike" Eisenhower (born David Dwight Eisenhower; October 14, 1890 – March 28, 1969) was the 34th president of the United States, serving from 1953 to 1961. During World War II, he was Supreme Commander of the Allied Expeditionar ...
on September 9, 1957, was the first federal civil rights legislation since the
Civil Rights Act of 1875
The Civil Rights Act of 1875, sometimes called the Enforcement Act or the Force Act, was a United States federal law enacted during the Reconstruction era in response to civil rights violations against African Americans. The bill was passed by the ...
to become law. After the
Supreme Court
In most legal jurisdictions, a supreme court, also known as a court of last resort, apex court, high (or final) court of appeal, and court of final appeal, is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
ruled school segregation unconstitutional in 1954 in ''
Brown v. Board of Education
''Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka'', 347 U.S. 483 (1954), was a landmark decision of the United States Supreme Court that ruled that U.S. state laws establishing racial segregation in public schools are unconstitutional, even if the ...
'', Southern Democrats began a campaign of "
massive resistance" against desegregation, and even the few moderate white leaders shifted to openly racist positions. Partly in an effort to defuse calls for more far-reaching reforms, Eisenhower proposed a civil rights bill that would increase the protection of African American voting rights.
The
Supreme Court
In most legal jurisdictions, a supreme court, also known as a court of last resort, apex court, high (or final) court of appeal, and court of final appeal, is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
's 1954 ruling in the case of ''
Brown v. Board of Education
''Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka'', 347 U.S. 483 (1954), was a landmark decision of the United States Supreme Court that ruled that U.S. state laws establishing racial segregation in public schools are unconstitutional, even if the ...
'' brought the issue of school desegregation to the fore of public attention, as Southern Democratic leaders began a campaign of "
massive resistance" against desegregation. In the midst of this campaign, President Eisenhower proposed a civil rights bill designed to provide federal protection for
African American
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an Race and ethnicity in the United States, American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from an ...
voting rights; most African Americans in the
Southern United States
The Southern United States (sometimes Dixie, also referred to as the Southern States, the American South, the Southland, Dixieland, or simply the South) is List of regions of the United States, census regions defined by the United States Cens ...
had been
disenfranchised by state and local laws. Though the civil rights bill passed Congress, opponents of the act were able to remove or weaken several provisions via the
Anderson–Aiken amendment and the
O'Mahoney jury trial amendment, significantly watering down its immediate impact. During the debate over the law, Senator
Strom Thurmond
James Strom Thurmond Sr. (December 5, 1902 – June 26, 2003) was an American politician who represented South Carolina in the United States Senate from 1954 to 2003. Before his 49 years as a senator, he served as the 103rd governor of South ...
conducted the longest one-person filibuster in Senate history. Under the direction of Senate Majority Leader
Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson (; August 27, 1908January 22, 1973), also known as LBJ, was the 36th president of the United States, serving from 1963 to 1969. He became president after the assassination of John F. Kennedy, under whom he had served a ...
of Texas, the Senate passed a watered-down, yet also passable, version of the House bill which removed stringent voting protection clauses.
Despite having a limited impact on African-American voter participation, at a time when black voter registration from 0% (in 11 counties) to less than 5% (in 97 counties) despite being majority-Black counties, the Civil Rights Act of 1957 did establish the
United States Commission on Civil Rights
The U.S. Commission on Civil Rights (CCR) is a bipartisan, independent commission of the United States federal government, created by the Civil Rights Act of 1957 during the Eisenhower administration, that is charged with the responsibility f ...
and the
United States Department of Justice Civil Rights Division
The Civil Rights Division of the United States Department of Justice enforces federal statutes prohibiting discrimination on the basis of race, sex, disability, religion, and national origin.
The division was established on December 9, 1957, b ...
. By 1960, black voting had increased by only 3%, and Congress passed the
Civil Rights Act of 1960
The Civil Rights Act of 1960 () is a United States federal law that established federal inspection of local voter registration polls and introduced penalties for anyone who obstructed someone's attempt to register to vote. It dealt primarily wi ...
, which eliminated certain loopholes left by the 1957 Act. Congress would later pass far more effective civil rights laws in the form of the
Civil Rights Act of 1964
The Civil Rights Act of 1964 () is a landmark civil rights and United States labor law, labor law in the United States that outlaws discrimination based on Race (human categorization), race, Person of color, color, religion, sex, and nationa ...
, the
Voting Rights Act of 1965
The Voting Rights Act of 1965 is a landmark piece of federal legislation in the United States that prohibits racial discrimination in voting. It was signed into law by President Lyndon B. Johnson during the height of the civil rights move ...
, and the
Civil Rights Act of 1968
The Civil Rights Act of 1968 () is a Lists of landmark court decisions, landmark law in the United States signed into law by President of the United States, United States President Lyndon B. Johnson during the King assassination riots.
Titles ...
.
Background
Following the Supreme Court ruling in ''Brown'', which eventually led to the integration of public schools,
Southern whites
White is a racial classification of people generally used for those of predominantly European ancestry. It is also a skin color specifier, although the definition can vary depending on context, nationality, ethnicity and point of view.
De ...
began a campaign of "
Massive Resistance". Violence against black people rose; in
Little Rock, Arkansas
Little Rock is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Arkansas, most populous city of the U.S. state of Arkansas. The city's population was 202,591 as of the 2020 census. The six-county Central Arkan ...
where President
Dwight D. Eisenhower
Dwight David "Ike" Eisenhower (born David Dwight Eisenhower; October 14, 1890 – March 28, 1969) was the 34th president of the United States, serving from 1953 to 1961. During World War II, he was Supreme Commander of the Allied Expeditionar ...
ordered U.S. paratroopers of the
101st Airborne Division
The 101st Airborne Division (Air Assault) ("Screaming Eagles") is a light infantry division (military), division of the United States Army that specializes in air assault military operation, operations. The 101st is designed to plan, coordinat ...
to protect
nine black teenagers integrating into a public school, the first time federal troops were deployed in the South to settle civil rights issues since the
Reconstruction Era
The Reconstruction era was a period in History of the United States, US history that followed the American Civil War (1861-65) and was dominated by the legal, social, and political challenges of the Abolitionism in the United States, abol ...
. There had been continued physical assaults against suspected activists and bombings of schools and churches in the South. Partly in an effort to defuse calls for more far-reaching reforms, President Eisenhower proposed a civil rights bill that would increase the protection of African American voting rights.
By 1957, only about 20% of black people were registered to vote. Despite being the majority in numerous counties and
congressional districts
Congressional districts, also known as electoral districts in other nations, are divisions of a larger administrative region that represent the population of a region in the larger congressional body. Countries with congressional districts includ ...
in the South, most black people had been effectively
disfranchised by discriminatory
voter registration
In electoral systems, voter registration (or enrollment) is the requirement that a person otherwise Suffrage, eligible to Voting, vote must register (or enroll) on an electoral roll, which is usually a prerequisite for being entitled or permitted ...
rules and laws in those states since the late 19th and early 20th centuries that were heavily instituted and propagated by Southern Democrats. Civil rights organizations had collected evidence of discriminatory practices, such as the administration of
literacy
Literacy is the ability to read and write, while illiteracy refers to an inability to read and write. Some researchers suggest that the study of "literacy" as a concept can be divided into two periods: the period before 1950, when literacy was ...
and comprehension tests and
poll taxes
A poll tax, also known as head tax or capitation, is a tax levied as a fixed sum on every liable individual (typically every adult), without reference to income or resources. ''Poll'' is an archaic term for "head" or "top of the head". The sen ...
. While the states had the right to establish rules for voter registration and elections, the federal government found an oversight role in ensuring that citizens could exercise the constitutional right to vote for federal officers: electors for president and
vice president
A vice president or vice-president, also director in British English, is an officer in government or business who is below the president (chief executive officer) in rank. It can also refer to executive vice presidents, signifying that the vi ...
and members of the US Congress.
Legislative history
The
Democratic Senate majority leader
The positions of majority leader and minority leader are held by two United States senators and people of the party leadership of the United States Senate. They serve as chief spokespersons for their respective political parties, holding the ...
,
Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson (; August 27, 1908January 22, 1973), also known as LBJ, was the 36th president of the United States, serving from 1963 to 1969. He became president after the assassination of John F. Kennedy, under whom he had served a ...
of
Texas
Texas ( , ; or ) is the most populous U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the we ...
, who would play a vital role in the bill's passage in the Senate, realized that the bill and its journey through Congress could tear apart his party, as southern Democrats vehemently opposed civil rights, and its northern members were strongly in favor of them. Southern Democratic senators occupied chairs of numerous important committees because of their long
seniority
Seniority is the state of being older or placed in a higher position of status relative to another individual, group, or organization. For example, one employee may be senior to another either by role or rank (such as a CEO vice a manager), or by ...
. As, in the near-century between the end of Reconstruction and the 1960s, white Southerners voted solidly as a bloc for the Democrats, Southern Democrats in Congress rarely lost their seats in elections, ensuring that they had more seniority than Democratic members of Congress from other parts of the country. Johnson sent the bill to the
Senate Judiciary Committee
The United States Senate Committee on the Judiciary, informally known as the Senate Judiciary Committee, is a Standing committee (United States Congress), standing committee of 22 U.S. senators whose role is to oversee the United States Departm ...
, led by Democratic Senator
James Eastland of
Mississippi
Mississippi ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Deep South regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Alabama to the east, the Gulf of Mexico to the south, Louisiana to the s ...
, who drastically altered the bill. Democratic Senator
Richard Russell Jr., of
Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
had denounced the bill as an example of the federal government seeking to impose its laws on states. Johnson sought recognition from civil rights advocates for passing the bill as well as recognition from the anti-civil rights Democrats for weakening the bill so much as to make it toothless.
As well as a general if vague support for civil rights as
the party of Lincoln, Republicans saw that this could be an effective way to increase the number of
Black Republican voters as the blocking of the Bill by the Democrats in the
Southern Caucus
The Southern Caucus was a Congressional caucus of Southern Democrats in the United States Senate chaired by Richard Russell, which was an effective opposition to civil rights legislation and formed a vital part of the later conservative coalit ...
would become obvious. They, like Johnson, also saw the potential for dividing the Democratic party's Northern and Southern wings. This meant that the (on this issue) liberal but hardball Republican operators like the
Vice President
A vice president or vice-president, also director in British English, is an officer in government or business who is below the president (chief executive officer) in rank. It can also refer to executive vice presidents, signifying that the vi ...
,
Richard Nixon
Richard Milhous Nixon (January 9, 1913April 22, 1994) was the 37th president of the United States, serving from 1969 until Resignation of Richard Nixon, his resignation in 1974. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican ...
, who had a constitutional right to chair the Senate took a great interest in the Bill. Conservative Republican Senators who were sympathetic to Southern arguments on
States rights
In American political discourse, states' rights are political powers held for the state governments rather than the federal government according to the United States Constitution, reflecting especially the enumerated powers of Congress and t ...
were more likely to vote on a party basis. On the other hand, the Republicans were willing to quietly allow Democratic Southern obstruction if this meant that African-American and liberal voters would be more likely to see the culprits as Democrats.
Anderson–Aiken amendment
A bipartisan group of Senators realized that Southerners would not allow passage of the act with Title III, which authorized the US Attorney General to seek preventive relief in civil rights cases. Majority Leader Johnson convinced Senator
Clinton Anderson (D-NM) to introduce an amendment to strip out the enforcement provisions of Title III.
Anderson's initial hesitancy to be associated with the anti-civil rights bloc was met with Johnson's urging to introduce the amendment along with a Republican colleague. Anderson approached
George Aiken
George David Aiken (August 20, 1892 – November 19, 1984) was an American politician and horticulturist. A member of the Republican Party, he was the 64th governor of Vermont (1937–1941) before serving in the United States Senate for 34 ye ...
(R-VT), who agreed to co-sponsor the amendment.
[
A crucial cause of the weakening of support for Title III was a speech given by the unofficial leader of the ]Southern Caucus
The Southern Caucus was a Congressional caucus of Southern Democrats in the United States Senate chaired by Richard Russell, which was an effective opposition to civil rights legislation and formed a vital part of the later conservative coalit ...
the Georgian Democrat, Richard Russell,[ who pointed out that Title III was not a new law but an amendment of Section 1985 of ]Title 42 of the United States Code
Title 42 of the United States Code is the United States Code dealing with public health, social welfare, and civil rights. Parts of Title 42 which formerly related to the US space program have been transferred to Title 51 of the United States ...
. It seems that this had not been understood previously by either the opponents or the supporters of the Civil Rights Act, including Douglas or Brownell. In his speech Russell drew out the implications of this, including the invocation of Section 1993 of Title 42 of the United States Code
Title 42 of the United States Code is the United States Code dealing with public health, social welfare, and civil rights. Parts of Title 42 which formerly related to the US space program have been transferred to Title 51 of the United States ...
, a Reconstruction era
The Reconstruction era was a period in History of the United States, US history that followed the American Civil War (1861-65) and was dominated by the legal, social, and political challenges of the Abolitionism in the United States, abol ...
law which wasn't mentioned in the bill and which authorized the President to enforce judicial decisions - which would include '' Brown v Board''. This specter of military involvement in domestic politics became a worry not just for moderate previous supporters of the bill such as Bourke Hickenlooper (R-IA) - who after Russell's speech referred to Title III as a "violation of the civil rights of the white race."[ - but also strong supporters such as Douglas. Later President Eisenhower in answer to a direct question on Russell's charges distanced himself from the "exact language" of Title III.][
President Eisenhower did not express enthusiasm for the provisions in Title III. In a press conference, he referred to it as going "too far too fast in laws", and instead placed an emphasis on the voting rights provisions in Title IV.][ This diminished the already-waning support for the title among Republicans, many of whom opposed its expansion of federal power on conservative grounds in spite of their sympathy towards civil rights causes.
The Anderson–Aiken amendment passed by a 52–38 vote. The vote on the amendment did not split purely along partisan or ideological lines; it was opposed by conservative ]William Knowland
William Fife Knowland (June 26, 1908 – February 23, 1974) was an American politician and newspaper publisher. A member of the Republican Party, he served as a United States Senator from California from 1945 to 1959. He was Senate Majority L ...
(R-CA) and supported by liberal Frank Church (D-ID).[
]
Jury trial amendment
Majority Leader Johnson, who was intent on passing a fully weakened act in contrast to overseeing a legislative graveyard at the hands of a Southern filibuster, moved to effectively weaken the voting rights-related provisions in Title IV.[
The jury trial amendment was not introduced by a Southern Democrat, instead being spearheaded by Wyoming senator Joseph C. O'Mahoney.][ The motivation for Western liberal Democrats to spearhead the cause of weakening the Civil Rights Act of 1957 was attributed to their traditional ]populist
Populism is a contested concept used to refer to a variety of political stances that emphasize the idea of the " common people" and often position this group in opposition to a perceived elite. It is frequently associated with anti-establis ...
disdain for the perceived disproportionate power wielded by judges to quell labor causes in the Western United States, thus contributing to a resonance with the expansion of jury trial rights,[ although Lyndon Johnson's biographer Robert Caro also claims that Johnson had facilitated a bargain that Western liberal Democrats would vote with the South in important votes on Civil Rights in return for Southern support for public involvement in the building of the Hells Canyon Dam.]United Mine Workers of America
The United Mine Workers of America (UMW or UMWA) is a North American labor union best known for representing coal miners. Today, the Union also represents health care workers, truck drivers, manufacturing workers and public employees in the Unit ...
who agreed that this would also stop injunctions in union cases. Their support was seen as a major reason why Senators in mining states such as West Virginia and mid western Republican senators where the railroads were strong became less hostile to the amendment.[
Several conservative Republican senators who voted for the Anderson–Aiken amendment on small-government grounds opposed the jury trial amendment for its intent of weakening civil rights efforts. ]Idaho
Idaho ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest and Mountain states, Mountain West subregions of the Western United States. It borders Montana and Wyoming to the east, Nevada and Utah to the south, and Washington (state), ...
senator Henry Dworshak decried that it "practically scuttled any hope of getting an effective civil rights bill."
Filibuster
Then-Democratic Senator Strom Thurmond
James Strom Thurmond Sr. (December 5, 1902 – June 26, 2003) was an American politician who represented South Carolina in the United States Senate from 1954 to 2003. Before his 49 years as a senator, he served as the 103rd governor of South ...
of South Carolina
South Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders North Carolina to the north and northeast, the Atlantic Ocean to the southeast, and Georgia (U.S. state), Georg ...
, an ardent racial segregation, segregationist, sustained the longest one-person filibuster in history in an attempt to keep the bill from becoming law. His one-man filibuster lasted 24 hours and 18 minutes; he began with readings of every US state's election laws in alphabetical order. He later read from the United States Declaration of Independence, Declaration of Independence, the United States Bill of Rights, Bill of Rights, and George Washington's Farewell Address.
Final passage
The bill passed 285–126 in the United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives with a majority of both parties' support (Republicans 167–19, Democrats 118–107). It then passed 72–18 in the Senate, again with a majority of both parties (Republicans 43–0, Democrats 29–18). Despite large opposition from Southern Democrats, the Democratic U.S. Senators from Tennessee and Texas would support the law.
Civil Rights Act of 1960
The Civil Rights Act of 1960 () is a United States federal law
The law of the United States comprises many levels of Codification (law), codified and uncodified forms of law, of which the supreme law is the nation's Constitution of the United States, Constitution, which prescribes the foundation of the ...
that established federal inspection of local voter registration
In electoral systems, voter registration (or enrollment) is the requirement that a person otherwise Suffrage, eligible to Voting, vote must register (or enroll) on an electoral roll, which is usually a prerequisite for being entitled or permitted ...
polls and introduced penalties for anyone who obstructed someone's attempt to register to vote. It dealt primarily with discriminatory laws and practices in the segregated Southern United States, South, by which African Americans, African-Americans and Tejanos had been effectively Disenfranchisement after the Reconstruction era, disenfranchised since the late 19th and start of the 20th century. This was the fifth Civil Rights Act to be enacted in United States history. Over an 85-year period, it was preceded only by the Civil Rights Act of 1957
The Civil Rights Act of 1957 was the first federal civil rights law passed by the United States Congress since the Civil Rights Act of 1875. The bill was passed by the 85th United States Congress and signed into law by President Dwight D. E ...
, whose shortcomings largely influenced its creation. This law served to more effectively enforce what was set forth in the 1957 act through eliminating certain loopholes in it, and to establish additional provisions. Aside from addressing voting rights, the Civil Rights Act of 1960 also imposed criminal penalties for obstruction of court orders to limit resistance to the Supreme Court's school desegregation decisions, arranged for free education for military members' children, and banned the act of fleeing to avoid prosecution for property damage. The Civil Rights Act of 1960 was signed into law by President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film and television
*'' Præsident ...
Dwight D. Eisenhower
Dwight David "Ike" Eisenhower (born David Dwight Eisenhower; October 14, 1890 – March 28, 1969) was the 34th president of the United States, serving from 1953 to 1961. During World War II, he was Supreme Commander of the Allied Expeditionar ...
.
Civil Rights Act of 1964
The Civil Rights Act of 1964 () is a landmark civil rights and United States labor law, labor law in the United States that outlaws discrimination based on race, Person of color, color, religion, sex, and national origin. It prohibits unequal application of voter registration requirements, racial segregation in schools and public accommodations
In public relations and communication science, publics are groups of individual people, and the public (a.k.a. the general public) is the totality of such groupings. This is a different concept to the sociological concept of the ''Öffentlichk ...
, and employment discrimination. The act "remains one of the most significant legislative achievements in American history".
Initially, powers given to enforce the act were weak, but these were supplemented during later years. Congress asserted its authority to legislate under several different parts of the United States Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the Supremacy Clause, supreme law of the United States, United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, on March 4, 1789. Originally includi ...
, principally its Enumerated powers (United States), enumerated power to regulate interstate commerce under the Commerce Clause
The Commerce Clause describes an enumerated power listed in the United States Constitution ( Article I, Section 8, Clause 3). The clause states that the United States Congress shall have power "to regulate Commerce with foreign Nations, and amon ...
of Article One of the United States Constitution#Section 8: Powers of Congress, Article I, Section 8, its duty to guarantee all citizens equal protection
The Equal Protection Clause is part of the first section of the Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution. The clause, which took effect in 1868, provides "nor shall any State... deny to any person within its jurisdiction the equal pr ...
of the laws under the Fourteenth Amendment to the U.S. Constitution, 14th Amendment, and its duty to protect voting rights under the Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, 15th Amendment.
The legislation was proposed by President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film and television
*'' Præsident ...
John F. Kennedy in June 1963, but it was opposed by filibuster in the Senate. After Assassination of John F. Kennedy, Kennedy was assassinated on November 22, 1963, President Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson (; August 27, 1908January 22, 1973), also known as LBJ, was the 36th president of the United States, serving from 1963 to 1969. He became president after the assassination of John F. Kennedy, under whom he had served a ...
pushed the bill forward. The United States House of Representatives passed the bill on February 10, 1964, and after a 72-day filibuster, it passed the United States Senate on June 19, 1964. The final vote was 290–130 in the House of Representatives and 73–27 in the Senate. After the House agreed to a subsequent Senate amendment, the Civil Rights Act of 1964 was signed into law by President Johnson at the White House on July 2, 1964.
Legislative history
On June 11, 1963, President Kennedy met with Republican leaders to discuss the legislation before his television address to the nation that evening. Two days later, Senate Minority Leader Everett Dirksen and Senate Majority Leader Mike Mansfield both voiced support for the president's bill, except for provisions guaranteeing equal access to places of public accommodations. This led to several Republican Representatives drafting a compromise bill to be considered. On June 19, the president sent his bill to Congress as it was originally written, saying legislative action was "imperative". The president's bill went first to the United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives, where it was referred to the United States House Committee on the Judiciary, Judiciary Committee, chaired by New York (state), New York Democrat Emanuel Celler. After a series of hearings on the bill, Celler's committee strengthened the act, adding provisions to ban racial discrimination in employment, providing greater protection to black voters, eliminating segregation in all publicly owned facilities (not just schools), and strengthening the anti-segregation clauses regarding public facilities such as lunch counters. They also added authorization for the Attorney General to file lawsuits to protect individuals against the deprivation of any rights secured by the Constitution or U.S. law. In essence, this was the controversial "Title III" that had been removed from the Civil Rights Act of 1957, 1957 Act and Civil Rights Act of 1960, 1960 Act. Civil rights organizations pressed hard for this provision because it could be used to protect peaceful protesters and black voters from police brutality and suppression of free speech rights.
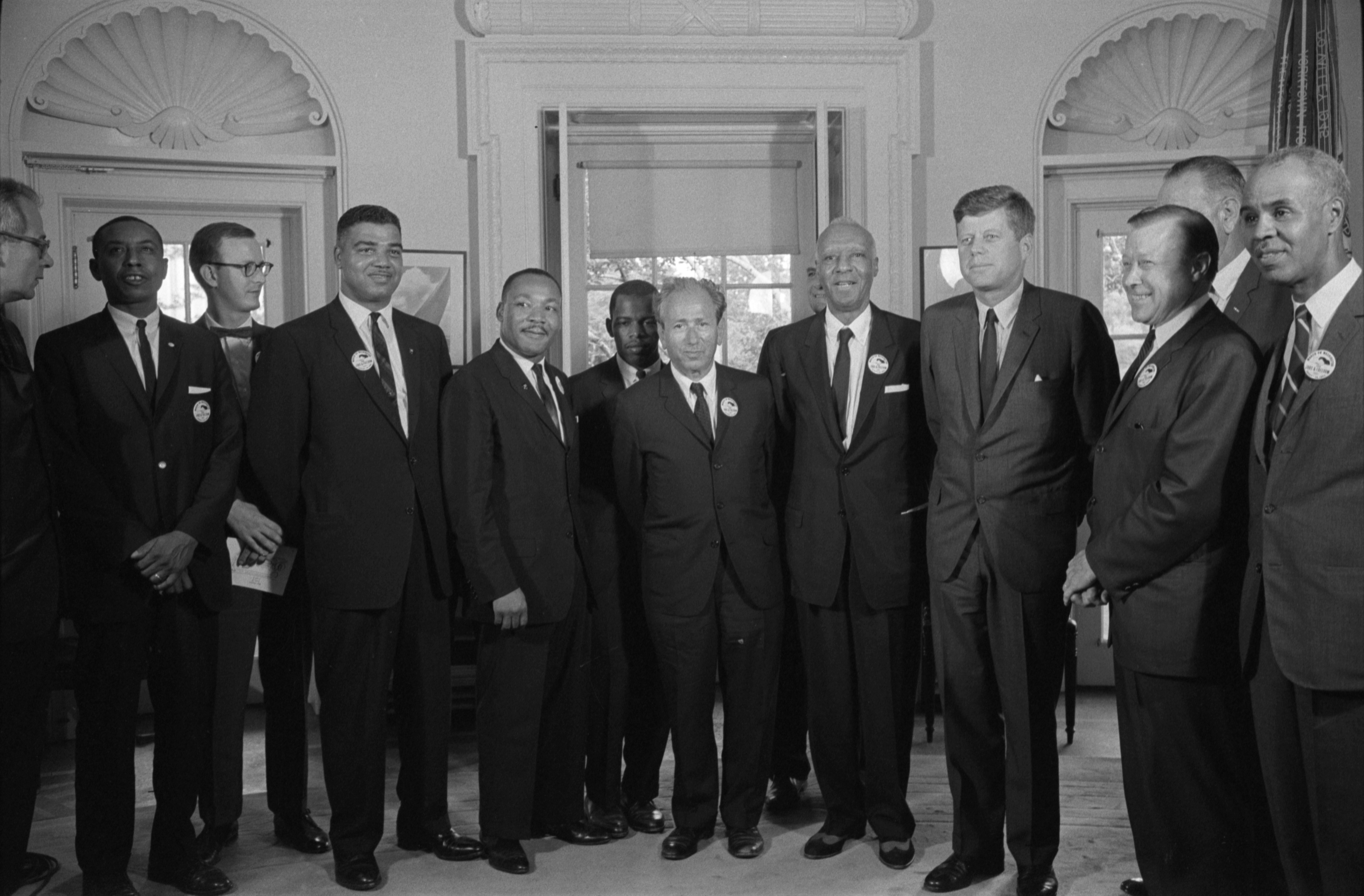 Lobbying support for the Civil Rights Act was coordinated by the Leadership Conference on Civil and Human Rights, Leadership Conference on Civil Rights, a coalition of 70 liberal and labor organizations. The principal lobbyists for the Leadership Conference were civil rights lawyer Joseph L. Rauh Jr. and Clarence Mitchell Jr. of the NAACP.
After the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom, on August 28, 1963, the organizers visited Kennedy to discuss the civil rights bill. Roy Wilkins, A. Philip Randolph, and Walter Reuther attempted to persuade him to support a provision establishing a Fair Employment Practices Commission that would ban discriminatory practices by all federal agencies, unions, and private companies.
Kennedy called the congressional leaders to the White House in late October 1963 to line up the necessary votes in the House for passage. The bill was reported out of the Judiciary Committee in November 1963 and referred to the United States House Committee on Rules, Rules Committee, whose chairman, Howard W. Smith, a Democrat and staunch segregationist from Virginia, indicated his intention to keep the bill bottled up indefinitely.
The assassination of John F. Kennedy, assassination of United States President John F. Kennedy on November 22, 1963, changed the political situation. Kennedy's successor as president,
Lobbying support for the Civil Rights Act was coordinated by the Leadership Conference on Civil and Human Rights, Leadership Conference on Civil Rights, a coalition of 70 liberal and labor organizations. The principal lobbyists for the Leadership Conference were civil rights lawyer Joseph L. Rauh Jr. and Clarence Mitchell Jr. of the NAACP.
After the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom, on August 28, 1963, the organizers visited Kennedy to discuss the civil rights bill. Roy Wilkins, A. Philip Randolph, and Walter Reuther attempted to persuade him to support a provision establishing a Fair Employment Practices Commission that would ban discriminatory practices by all federal agencies, unions, and private companies.
Kennedy called the congressional leaders to the White House in late October 1963 to line up the necessary votes in the House for passage. The bill was reported out of the Judiciary Committee in November 1963 and referred to the United States House Committee on Rules, Rules Committee, whose chairman, Howard W. Smith, a Democrat and staunch segregationist from Virginia, indicated his intention to keep the bill bottled up indefinitely.
The assassination of John F. Kennedy, assassination of United States President John F. Kennedy on November 22, 1963, changed the political situation. Kennedy's successor as president, Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson (; August 27, 1908January 22, 1973), also known as LBJ, was the 36th president of the United States, serving from 1963 to 1969. He became president after the assassination of John F. Kennedy, under whom he had served a ...
, made use of his experience in legislative politics, along with the bully pulpit he wielded as president, in support of the bill. In his first address to a Joint session of the United States Congress, joint session of Congress on November 27, 1963, Johnson told the legislators, "No memorial oration or eulogy could more eloquently honor President Kennedy's memory than the earliest possible passage of the civil rights bill for which he fought so long."
Judiciary Committee chairman Celler filed a discharge petition, petition to discharge the bill from the Rules Committee which required the support of a majority of House members to move the bill to the floor. Initially, Celler had a difficult time acquiring the signatures necessary, with many Representatives who supported the civil rights bill itself remaining cautious about violating normal House procedure with the rare use of a discharge petition. By the time of the 1963 winter recess, 50 signatures were still needed.
After the return of Congress from its winter recess, however, it was apparent that public opinion in the North favored the bill and that the petition would acquire the necessary signatures. To avert the humiliation of a successful discharge petition, Chairman Smith relented and allowed the bill to pass through the Rules Committee.
 Johnson, who wanted the bill passed as soon as possible, ensured that it would be quickly considered by the
Johnson, who wanted the bill passed as soon as possible, ensured that it would be quickly considered by the Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
.
Normally, the bill would have been referred to the Senate Judiciary Committee
The United States Senate Committee on the Judiciary, informally known as the Senate Judiciary Committee, is a Standing committee (United States Congress), standing committee of 22 U.S. senators whose role is to oversee the United States Departm ...
, which was chaired by James O. Eastland, a Democratic Party (United States), Democrat from Mississippi
Mississippi ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Deep South regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Alabama to the east, the Gulf of Mexico to the south, Louisiana to the s ...
, whose firm opposition made it seem impossible that the bill would reach the Senate floor. Senate Majority Leader Mike Mansfield took a novel approach to prevent the Judiciary Committee from keeping the bill in limbo: initially waiving a second reading immediately after the first reading, which would have sent it to the Judiciary Committee, he took the unprecedented step of giving the bill a second reading on February 26, 1964, thereby bypassing the Judiciary Committee, and sending it to the Senate floor for immediate debate.
When the bill came before the full Senate for debate on March 30, 1964, the "Solid South, Southern Bloc" of 18 southern Democratic Senators and lone Republican John Tower of Texas, led by Richard Russell Jr., Richard Russell (D-GA), launched a filibuster to prevent its passage. Russell proclaimed, "We will resist to the bitter end any measure or any movement which would tend to bring about social equality and miscegenation, intermingling and amalgamation of the races in our [Southern] states."
Strong opposition to the bill also came from Senator Strom Thurmond
James Strom Thurmond Sr. (December 5, 1902 – June 26, 2003) was an American politician who represented South Carolina in the United States Senate from 1954 to 2003. Before his 49 years as a senator, he served as the 103rd governor of South ...
, who was still a Democrat at the time: "This so-called Civil Rights Proposals [''sic''], which the President has sent to Capitol Hill for enactment into law, are unconstitutional, unnecessary, unwise and extend beyond the realm of reason. This is the worst civil-rights package ever presented to the Congress and is reminiscent of the Reconstruction era of the United States, Reconstruction proposals and actions of the Radical Republicans, radical Republican Congress."
After the filibuster had gone on for 54 days, Senators Mansfield, Hubert Humphrey, Everett Dirksen, and Thomas Kuchel introduced a substitute bill that they hoped would overcome it by combining a sufficient number of Republicans as well as core liberal Democrats. The compromise bill was weaker than the House version as to the government's power in regulating the conduct of private business, but not weak enough to make the House reconsider it.
Senator Robert Byrd ended his filibuster in opposition to the bill on the morning of June 10, 1964, after 14 hours and 13 minutes. Up to then, the measure had occupied the Senate for 60 working days, including six Saturdays. The day before, Humphrey, the bill's manager, concluded that he had the 67 votes required at that time to end the debate and the filibuster. With six wavering senators providing a four-vote victory margin, the final tally stood at 71 to 29. Never before in its entire history had the Senate been able to muster enough votes to defeat a filibuster on a civil rights bill, and only once in the 37 years since 1927 had it agreed to cloture for any measure.
The most dramatic moment during the cloture vote came when Senator Clair Engle (D-CA) was wheeled into the chamber. Suffering from terminal brain cancer, unable to speak, he pointed to his left eye, signifying his affirmative "Voice vote#United States, Aye" vote when his name was called.
Aspects
Women's rights
One year earlier, the same Congress had passed the Equal Pay Act of 1963, which prohibited wage differentials based on sex. The prohibition on sex discrimination was added to the Civil Rights Act by Howard W. Smith, a powerful Virginia Democrat who chaired the House Rules Committee and strongly opposed the legislation. Smith's amendment was passed by a teller vote of 168 to 133. Historians debate whether Smith Wrecking amendment, cynically attempted to defeat the bill because he opposed civil rights for Black people and women or attempted to support their rights by broadening the bill to include women.[Jo Freeman, Freeman, Jo. "How 'Sex' Got Into Title VII: Persistent Opportunism as a Maker of Public Policy," ''Law and Inequality: A Journal of Theory and Practice'', Vol. 9, No. 2, March 1991, pp 163–184]
online version
[Gold, Michael Evan. ''A Tale of Two Amendments: The Reasons Congress Added Sex to Title VII and Their Implication for the Issue of Comparable Worth.'' Faculty Publications – Collective Bargaining, Labor Law, and Labor History. Cornell, 198]
Smith asserted that he was not joking and sincerely supported the amendment. Along with Representative Martha Griffiths, he was the amendment's chief spokesperson.
Desegregation
One of the bill's opponents' most damaging arguments was that once passed, the bill would require desegregation busing in the United States, forced busing to achieve certain racial quotas in schools.
Aftermath
 The bill divided both major American political parties and engendered a long-term change in the demographics of the support for each. President Kennedy realized that supporting this bill would risk losing the South's overwhelming support of the Democratic Party. Both Attorney General Robert F. Kennedy and Vice President Johnson had pushed for the introduction of the civil rights legislation. Johnson told Kennedy aide Ted Sorensen that "I know the risks are great and we might lose the South, but those sorts of states may be lost anyway." Senator Richard Russell Jr., Richard Russell, Jr. later warned President Johnson that his strong support for the civil rights bill "will not only cost you the South, it will cost you the election". Johnson, however, went on to win the 1964 United States presidential election, 1964 election by one of the biggest landslides in American history. The South, which had five states swing Republican in 1964, became a stronghold of the Republican Party by the 1990s.
Although majorities in both parties voted for the bill, there were notable exceptions. Though he opposed forced segregation, Republican Party (United States), Republican 1964 presidential candidate, Senator Barry Goldwater of Arizona, voted against the bill, remarking, "You can't legislate morality." Goldwater had supported previous attempts to pass civil rights legislation in 1957 and 1960 as well as the Twenty-fourth Amendment to the United States Constitution, 24th Amendment outlawing the Poll tax (United States), poll tax. He stated that the reason for his opposition to the 1964 bill was Title II, which in his opinion violated individual liberty and states' rights. Democrats and Republicans from the Southern states opposed the bill and led an unsuccessful 60 working day filibuster, including Senators Albert Gore Sr., Albert Gore, Sr. (D-TN) and J. William Fulbright (D-AR), as well as Senator Robert Byrd (D-WV), who personally filibustered for 14 hours straight.
There were white business owners who claimed that Congress did not have the constitutional authority to ban segregation in public accommodations. For example, Moreton Rolleston, the owner of a motel in Atlanta, Georgia, said he should not be forced to serve black travelers, saying, "the fundamental question [...] is whether or not Congress has the power to take away the liberty of an individual to run his business as he sees fit in the selection and choice of his customers".
The bill divided both major American political parties and engendered a long-term change in the demographics of the support for each. President Kennedy realized that supporting this bill would risk losing the South's overwhelming support of the Democratic Party. Both Attorney General Robert F. Kennedy and Vice President Johnson had pushed for the introduction of the civil rights legislation. Johnson told Kennedy aide Ted Sorensen that "I know the risks are great and we might lose the South, but those sorts of states may be lost anyway." Senator Richard Russell Jr., Richard Russell, Jr. later warned President Johnson that his strong support for the civil rights bill "will not only cost you the South, it will cost you the election". Johnson, however, went on to win the 1964 United States presidential election, 1964 election by one of the biggest landslides in American history. The South, which had five states swing Republican in 1964, became a stronghold of the Republican Party by the 1990s.
Although majorities in both parties voted for the bill, there were notable exceptions. Though he opposed forced segregation, Republican Party (United States), Republican 1964 presidential candidate, Senator Barry Goldwater of Arizona, voted against the bill, remarking, "You can't legislate morality." Goldwater had supported previous attempts to pass civil rights legislation in 1957 and 1960 as well as the Twenty-fourth Amendment to the United States Constitution, 24th Amendment outlawing the Poll tax (United States), poll tax. He stated that the reason for his opposition to the 1964 bill was Title II, which in his opinion violated individual liberty and states' rights. Democrats and Republicans from the Southern states opposed the bill and led an unsuccessful 60 working day filibuster, including Senators Albert Gore Sr., Albert Gore, Sr. (D-TN) and J. William Fulbright (D-AR), as well as Senator Robert Byrd (D-WV), who personally filibustered for 14 hours straight.
There were white business owners who claimed that Congress did not have the constitutional authority to ban segregation in public accommodations. For example, Moreton Rolleston, the owner of a motel in Atlanta, Georgia, said he should not be forced to serve black travelers, saying, "the fundamental question [...] is whether or not Congress has the power to take away the liberty of an individual to run his business as he sees fit in the selection and choice of his customers".
Voting Rights Act of 1965
The Voting Rights Act of 1965 is a landmark piece of Federal government of the United States, federal legislation in the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
that prohibits racial discrimination in voting.President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film and television
*'' Præsident ...
Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson (; August 27, 1908January 22, 1973), also known as LBJ, was the 36th president of the United States, serving from 1963 to 1969. He became president after the assassination of John F. Kennedy, under whom he had served a ...
during the height of the civil rights movement on August 6, 1965, and United States Congress, Congress later amended the Act five times to expand its protections.United States Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the Supremacy Clause, supreme law of the United States, United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, on March 4, 1789. Originally includi ...
, the Act sought to secure the right to vote for Race and ethnicity in the United States, racial minorities throughout the country, especially in the Southern United States, South. According to the U.S. Department of Justice, the Act is considered to be the most effective piece of federal civil rights legislation ever enacted in the country.literacy test
A literacy test assesses a person's literacy skills: their ability to read and write. Literacy tests have been administered by various governments, particularly to immigrants.
Between the 1850s and 1960s, literacy tests were used as an effecti ...
s and similar devices that were historically used to disenfranchise racial minorities. The act also contains "special provisions" that apply to only certain jurisdictions. A core special provision is the Section 5 preclearance requirement, which prohibited certain jurisdictions from implementing any change affecting voting without first receiving confirmation from the U.S. attorney general or the U.S. District Court for D.C. that the change does not discriminate against protected minorities.[''Shelby County v. Holder'', ] The court did not strike down Section 5, but without a coverage formula, Section 5 is unenforceable.
Background
 Prior to the enactment of the Voting Rights Act of 1965 there were several efforts to stop the disenfranchisement of black voters by Southern states,.
Prior to the enactment of the Voting Rights Act of 1965 there were several efforts to stop the disenfranchisement of black voters by Southern states,.Civil Rights Act of 1957
The Civil Rights Act of 1957 was the first federal civil rights law passed by the United States Congress since the Civil Rights Act of 1875. The bill was passed by the 85th United States Congress and signed into law by President Dwight D. E ...
. This legislation authorized the attorney general to sue for injunctive relief on behalf of persons whose Fifteenth Amendment rights were denied, created the United States Department of Justice Civil Rights Division, Civil Rights Division within the United States Department of Justice, Department of Justice to enforce civil rights through litigation, and created the Commission on Civil Rights to investigate voting rights deprivations. Further protections were enacted in the Civil Rights Act of 1960
The Civil Rights Act of 1960 () is a United States federal law that established federal inspection of local voter registration polls and introduced penalties for anyone who obstructed someone's attempt to register to vote. It dealt primarily wi ...
, which allowed federal courts to appoint referees to conduct voter registration in jurisdictions that engaged in voting discrimination against racial minorities.public accommodations
In public relations and communication science, publics are groups of individual people, and the public (a.k.a. the general public) is the totality of such groupings. This is a different concept to the sociological concept of the ''Öffentlichk ...
and government services by passing the Civil Rights Act of 1964
The Civil Rights Act of 1964 () is a landmark civil rights and United States labor law, labor law in the United States that outlaws discrimination based on Race (human categorization), race, Person of color, color, religion, sex, and nationa ...
. The act included some voting rights protections; it required registrars to equally administer literacy tests in writing to each voter and to accept applications that contained minor errors, and it created a rebuttable presumption that persons with a sixth-grade education were sufficiently literate to vote.President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film and television
*'' Præsident ...
Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson (; August 27, 1908January 22, 1973), also known as LBJ, was the 36th president of the United States, serving from 1963 to 1969. He became president after the assassination of John F. Kennedy, under whom he had served a ...
recognized this, and shortly after the 1964 elections in which Democratic Party (United States), Democrats gained overwhelming majorities in both chambers of Congress, he privately instructed Attorney General Nicholas Katzenbach to draft "the goddamndest, toughest voting rights act that you can". Following the 1964 elections, civil rights organizations such as the Southern Christian Leadership Conference (SCLC) and the Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee (SNCC) pushed for federal action to protect the voting rights of racial minorities.
Following the 1964 elections, civil rights organizations such as the Southern Christian Leadership Conference (SCLC) and the Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee (SNCC) pushed for federal action to protect the voting rights of racial minorities.[
In January 1965, Martin Luther King Jr., James Bevel,]Ku Klux Klan
The Ku Klux Klan (), commonly shortened to KKK or Klan, is an American Protestant-led Christian terrorism, Christian extremist, white supremacist, Right-wing terrorism, far-right hate group. It was founded in 1865 during Reconstruction era, ...
members.[The March to Montgomery](_blank)
~ Civil Rights Movement Archive. The worst injured was Reverend James Reeb from Boston, who died on Thursday, March 11.
In the wake of the events in Selma, President Johnson, addressing a televised joint session of Congress on March 15, called on legislators to enact expansive voting rights legislation. In his speech, he used the words "we shall overcome", adopting the rallying cry of the civil rights movement.
Legislative history
Efforts to eliminate discriminatory election practices by litigation on a case-by-case basis by the United States Department of Justice had been unsuccessful and existing federal anti-discrimination laws were not sufficient to overcome the resistance by state officials to enforcement of the 15th Amendment. Against this backdrop Congress came to the conclusion that a new comprehensive federal bill was necessary to break the grip of state disfranchisement.
Original bill
Senate
The Voting Rights Act of 1965 was introduced in Congress on March 17, 1965, as S. 1564, and it was jointly sponsored by Senate majority leader Mike Mansfield (D-MT) and Senate minority leader Everett Dirksen (R-IL), both of whom had worked with Attorney General Katzenbach to draft the bill's language.[Voting Rights Act of 1965 § 3(c); (formerly 42 U.S.C. § 1973a(c))]Texas
Texas ( , ; or ) is the most populous U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the we ...
or Arkansas, mitigating opposition from those two states' influential congressional delegations.Mississippi
Mississippi ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Deep South regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Alabama to the east, the Gulf of Mexico to the south, Louisiana to the s ...
, passed during a committee meeting in which three liberal members were absent. Dirksen offered to drop the amendment if the poll tax ban were removed. Ultimately, the bill was reported out of committee on April 9 by a 12–4 vote without a recommendation.Strom Thurmond
James Strom Thurmond Sr. (December 5, 1902 – June 26, 2003) was an American politician who represented South Carolina in the United States Senate from 1954 to 2003. Before his 49 years as a senator, he served as the 103rd governor of South ...
(D-SC) retorted that the bill would lead to "despotism and tyranny", and Senator Sam Ervin (D-NC) argued that the bill was unconstitutional because it deprived states of their right under Article One of the United States Constitution#Section 2: House of Representatives, Article I, Section 2 of the Constitution to establish voter qualifications and because the bill's special provisions targeted only certain jurisdictions. On May 6, Ervin offered an amendment to abolish the coverage formula's automatic trigger and instead allow federal judges to appoint federal examiners to administer voter registration. This amendment overwhelmingly failed, with 42 Democrats and 22 Republicans voting against it.
House of Representatives
Emanuel Celler (D-NY), Chair of the House Judiciary Committee, introduced the Voting Rights Act in the United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives on March 19, 1965, as H.R. 6400.
Conference committee
The chambers appointed a conference committee to resolve differences between the House and Senate versions of the bill. A major contention concerned the poll tax provisions; the Senate version allowed the attorney general to sue states that used poll taxes to discriminate, while the House version outright banned all poll taxes. Initially, the committee members were stalemated. To help broker a compromise, Attorney General Katzenbach drafted legislative language explicitly asserting that poll taxes were unconstitutional and instructed the Department of Justice to sue the states that maintained poll taxes. To assuage concerns of liberal committee members that this provision was not strong enough, Katzenbach enlisted the help of Martin Luther King Jr., who gave his support to the compromise. King's endorsement ended the stalemate, and on July 29, the conference committee reported its version out of committee.
Amendments
 Congress enacted major amendments to the Act in 1970, 1975, 1982, 1992, and 2006. Each amendment coincided with an impending expiration of some or all of the Act's special provisions. Originally set to expire by 1970, Congress repeatedly reauthorized the special provisions in recognition of continuing voting discrimination.
Congress enacted major amendments to the Act in 1970, 1975, 1982, 1992, and 2006. Each amendment coincided with an impending expiration of some or all of the Act's special provisions. Originally set to expire by 1970, Congress repeatedly reauthorized the special provisions in recognition of continuing voting discrimination.[Voting Rights Act of 1965 § 14(c)(3); (formerly 42 U.S.C. § 1973l(c)(3))] Congress amended various provisions, such as the preclearance requirement and Section 2's general prohibition of discriminatory voting laws, to prohibit discrimination against language minorities.[''Reno v. Bossier Parish School Board'', ] which interpreted the Section 5 preclearance requirement to prohibit only voting changes that were enacted or maintained for a "retrogressive" discriminatory purpose instead of any discriminatory purpose, and ''Georgia v. Ashcroft'' (2003),[''Georgia v. Ashcroft'', ] which established a broader test for determining whether a redistricting plan had an impermissible effect under Section 5 than assessing only whether a minority group could elect its preferred candidates.
Provisions
The act contains two types of provisions: "general provisions", which apply nationwide, and "special provisions", which apply to only certain states and local governments.[Voting Rights Act of 1965 § 2; (formerly 42 U.S.C. § 1973)] Section 2 of the law contains two separate protections against voter discrimination for laws which, in contrast to Section 5 of the law, are already implemented.[''Mobile v. Bolden'', ]Section 2 prohibits voting practices that "result[] in a denial or abridgment of the right * * * to vote on account of race or color [or language-minority status]," and it states that such a result "is established" if a jurisdiction’s "political processes * * * are not equally open" to members of such a group "in that [they] have less opportunity * * * to participate in the political process and to elect representatives of their choice.
52 U.S.C. 10301
[...] Subsection (b) states in relevant part:
A violation of subsection (a) is established if, based on the totality of circumstances, it is shown that the political processes leading to nomination or election in the State or political subdivision are not equally open to participation by members of a class of citizens protected by subsection (a) in that its members have less opportunity than other members of the electorate to participate in the political process and to elect representatives of their choice.
The Office of the Arizona Attorney General stated with respect to the framework to determine whether a jurisdiction's election law violates the general prohibition from Section 2 in its amended form and the reason for the adoption of Section 2 in its amended form:
To establish a violation of amended Section 2, the plaintiff must prove,"based on the totality of circumstances," that the State’s "political processes" are "not equally open to participation by members" of a protected class, "in that its members have less opportunity than other members of the electorate to participate in the political process and to elect representatives of their choice." § 10301(b). That is the "result" that amended Section 2 prohibits: "less ''opportunity'' than other members of the electorate," viewing the State’s "political processes" as a whole. The new language was crafted as a compromise designed to eliminate the need for direct evidence of discriminatory intent, which is often difficult to obtain, but without embracing an unqualified "disparate impact" test that would invalidate many legitimate voting procedures. S. REP. NO. 97–417, at 28–29, 31–32, 99 (1982)
In ''Brnovich v. Democratic National Committee'' (2021) the United States Supreme Court introduced the means to review Section 2 challenges.[''Thornburg v. Gingles'', ]
The first precondition is known as the "compactness" requirement and concerns whether a majority-minority district can be created. The second and third preconditions are collectively known as the "racially polarized voting" or "racial bloc voting" requirement, and they concern whether the voting patterns of the different racial groups are different from each other. If a plaintiff proves these preconditions exist, then the plaintiff must additionally show, using the remaining Senate Factors and other evidence, that under the "totality of the circumstances", the jurisdiction's redistricting plan or use of at-large or multimember elections diminishes the ability of the minority group to elect candidates of its choice.[''Holder v. Hall'', ] the Supreme Court held that claims that minority votes are diluted by the small size of a governing body, such as a one-person county commission, may not be brought under Section 2. A plurality of the court reasoned that no uniform, non-dilutive "benchmark" size for a governing body exists, making relief under Section 2 impossible. Another type of vote dilution may result from a jurisdiction's requirement that a candidate be elected by a majority vote. A majority-vote requirement may cause a minority group's candidate of choice, who would have won the election with a simple plurality (voting), plurality of votes, to lose after a majority of voters unite behind another candidate in a two-round system, runoff election. The Supreme Court has not addressed whether such claims may be brought under Section 2, and lower courts have reached different conclusions on the issue.
In addition to claims of vote dilution, courts have considered vote denial claims brought under Section 2. The Supreme Court, in ''Richardson v. Ramirez'' (1974), held that felony disenfranchisement laws cannot violate Section 2 because, among other reasons, Section 2 of the Fourteenth Amendment permits such laws.
Specific prohibitions
The act contains several specific prohibitions on conduct that may interfere with a person's ability to cast an effective vote. One of these prohibitions is prescribed in Section 201, which prohibits any jurisdiction from requiring a person to comply with any "test or device" to register to vote or cast a ballot. The term "test or device" is defined as literacy tests, educational or knowledge requirements, proof of good moral character, and requirements that a person be vouched for when voting. Before the Act's enactment, these devices were the primary tools used by jurisdictions to prevent racial minorities from voting.disability
Disability is the experience of any condition that makes it more difficult for a person to do certain activities or have equitable access within a given society. Disabilities may be Cognitive disability, cognitive, Developmental disability, d ...
from being accompanied into the ballot box by an assistant of the person's choice. The only exceptions are that the assistant may not be an Law of agency, agent of the person's employer or union.
Bail-in
Section 3(c) contains a "bail-in" or "pocket trigger" process by which jurisdictions that fall outside the coverage formula of Section 4(b) may become subject to preclearance. Under this provision, if a jurisdiction has racially discriminated against voters in violation of the Fourteenth or Fifteenth Amendments, a court may order the jurisdiction to have future changes to its election laws preapproved by the federal government.
Special provisions
=Coverage formula
=
 Section 4(b) contains a "coverage formula" that determines which states and local governments may be subjected to the Act's other special provisions (except for the Section 203(c) bilingual election requirements, which fall under a different formula). Congress intended for the coverage formula to encompass the most pervasively discriminatory jurisdictions. A jurisdiction is covered by the formula if:
# As of November 1, 1964, 1968, or 1972, the jurisdiction used a "test or device" to restrict the opportunity to register and vote; and
# Less than half of the jurisdiction's eligible citizens were registered to vote on November 1, 1964, 1968, or 1972; or less than half of eligible citizens voted in the presidential election of November 1964, 1968, or 1972.
As originally enacted, the coverage formula contained only November 1964 triggering dates; subsequent revisions to the law supplemented it with the additional triggering dates of November 1968 and November 1972, which brought more jurisdictions into coverage.
Section 4(b) contains a "coverage formula" that determines which states and local governments may be subjected to the Act's other special provisions (except for the Section 203(c) bilingual election requirements, which fall under a different formula). Congress intended for the coverage formula to encompass the most pervasively discriminatory jurisdictions. A jurisdiction is covered by the formula if:
# As of November 1, 1964, 1968, or 1972, the jurisdiction used a "test or device" to restrict the opportunity to register and vote; and
# Less than half of the jurisdiction's eligible citizens were registered to vote on November 1, 1964, 1968, or 1972; or less than half of eligible citizens voted in the presidential election of November 1964, 1968, or 1972.
As originally enacted, the coverage formula contained only November 1964 triggering dates; subsequent revisions to the law supplemented it with the additional triggering dates of November 1968 and November 1972, which brought more jurisdictions into coverage.
=Preclearance requirement
=
Section 5[Voting Rights Act of 1965 § 5; (formerly 42 U.S.C. § 1973c)] requires that covered jurisdictions receive federal approval, known as "preclearance", before implementing changes to their election laws. A covered jurisdiction has the burden of proving that the change does not have the purpose or effect of discriminating on the basis of race or language minority status; if the jurisdiction fails to meet this burden, the federal government will deny preclearance and the jurisdiction's change will not go into effect. The Supreme Court broadly interpreted Section 5's scope in ''Allen v. State Board of Election'' (1969),[''Allen v. State Board of Elections'', ] holding that any change in a jurisdiction's voting practices, even if minor, must be submitted for preclearance.[''Lopez v. Monterey County'' (''Lopez I''), ]
Jurisdictions may seek preclearance through either an "administrative preclearance" process or a "judicial preclearance" process. If a jurisdiction seeks administrative preclearance, the attorney general will consider whether the proposed change has a discriminatory purpose or effect. After the jurisdiction submits the proposed change, the attorney general has 60 days to interpose an objection to it. The 60-day period may be extended an additional 60 days if the jurisdiction later submits additional information. If the attorney general interposes an objection, then the change is not precleared and may not be implemented.[''Beer v. United States'', ] the court held that for a voting change to have a prohibited discriminatory effect, it must result in "retrogression" (backsliding). Under this standard, a voting change that causes discrimination, but does not result in ''more'' discrimination than before the change was made, cannot be denied preclearance for having a discriminatory effect.
=Federal examiners and observers
=
Until the 2006 amendments to the Act,
=Bailout
=
Under Section 4(a), a covered jurisdiction may seek exemption from coverage through a process called "bailout."[Voting Rights Act of 1965 § 4(a); (formerly 42 U.S.C. § 1973b(a)(1)(F))]
The 1982 amendment to the bailout eligibility standard went into effect on August 5, 1984.[''Northwest Austin Municipal Utility District No. 1 v. Holder'', ] which held that local governments that do not register voters have the ability to bail out. After this ruling, jurisdictions succeeded in at least 20 bailout actions before the Supreme Court held in ''Shelby County v. Holder'' (2013) that the coverage formula was unconstitutional.
=Bilingual election requirements
=
Two provisions require certain jurisdictions to provide election materials to voters in multiple languages: Section 4(f)(4) and Section 203(c). A jurisdiction covered by either provision must provide all materials related to an election—such as voter registration materials, ballots, notices, and instructions—in the language of any applicable language minority group residing in the jurisdiction.
Impact
"The Voting Rights Act had an immediate impact. By the end of 1965, a quarter of a million new Black voters had been registered, one-third by federal examiners. By the end of 1966, only four out of 13 southern states had fewer than 50 percent of African Americans registered to vote."
Civil Rights Act of 1968
The Civil Rights Act of 1968 () is a Lists of landmark court decisions, landmark law in the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
signed into law by United States President
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president directs the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed For ...
Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson (; August 27, 1908January 22, 1973), also known as LBJ, was the 36th president of the United States, serving from 1963 to 1969. He became president after the assassination of John F. Kennedy, under whom he had served a ...
during the King assassination riots.
Titles II through VII comprise the Indian Civil Rights Act, which applies to the Native Americans in the United States, Native American tribes of the United States and makes many but not all of the guarantees of the United States Bill of Rights, U.S. Bill of Rights applicable within the tribes. (That Act appears today in Title 25, sections 1301 to 1303 of the United States Code).
Titles VIII and IX are commonly known as the Fair Housing Act, which was meant as a follow-up to the Civil Rights Act of 1964
The Civil Rights Act of 1964 () is a landmark civil rights and United States labor law, labor law in the United States that outlaws discrimination based on Race (human categorization), race, Person of color, color, religion, sex, and nationa ...
. (This is different legislation than the Housing and Urban Development Act of 1968, which expanded housing funding programs.) While the Civil Rights Act of 1866
The Civil Rights Act of 1866 (, enacted April 9, 1866, reenacted 1870) was the first United States federal law to define citizenship and affirm that all citizens are equally protected by the law. It was mainly intended, in the wake of the Ame ...
prohibited discrimination in housing, there were no federal enforcement provisions. The 1968 act expanded on previous acts and prohibited discrimination concerning the sale, rental, and financing of housing based on Race (classification of human beings), race, religion, national origin, and since 1974, sex. Since 1988, the act protects people with disabilities and families with children. Pregnant women are also protected from illegal discrimination because they have been given familial status with their unborn child being the other family member. Victims of discrimination may use both the 1968 act and the 1866 act's Civil Rights Act of 1871#As later amended and codified as section 1983, section 1983 to seek redress. The 1968 act provides for federal solutions while the 1866 act provides for private solutions (i.e., civil suits). The act also made it a federal crime to "by force or by threat of force, injure, intimidate, or interfere with anyone... by reason of their race, color, religion, or national origin, handicap or familial status."
Title X, commonly known as the Anti-Riot Act, makes it a felony to "travel in interstate commerce...with the intent to incite, promote, encourage, participate in and carry on a riot." That provision has been criticized for "equating organized political protest with organized violence."
Legislative history and components
In 1966, President Johnson proposed a new civil rights bill, but it was not passed through by the Senate. On February 17, 1967, the bill was introduced in the House by Rep. Manny Celler and in the Senate by Senator Philip A. Hart.
The House Judiciary Committee cleared HR 2516 (civil rights bill) and HR 10805 (extended life of Civil Rights Commission for another five years). House Judiciary Subcommittee No. 5 June 22 approved a package combining HR 2516 and HR 421 (Administration bill) in order to strengthen protections for civil rights workers.
The initial vote in the United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives was 327–92 (161–25 in the House Republican Conference and 166–67 in the House Democratic Caucus) with 12 members voting present or abstaining, while in the Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
the final vote with amendments was 71–20 (29–3 in the Senate Republican Conference and 42–17 in the Senate Democratic Caucus) with 5 members voting present or abstaining. The House agreed to the Senate amendments by a vote of 250–172 (100–84 in the House Republican Conference and 150–88 in the House Democratic Caucus) with 10 members voting present or abstaining.
Bill H.R. 2516 was passed by the 90th United States Congress and signed by the List of presidents of the United States, 36th President of the United States, Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson (; August 27, 1908January 22, 1973), also known as LBJ, was the 36th president of the United States, serving from 1963 to 1969. He became president after the assassination of John F. Kennedy, under whom he had served a ...
on April 11, 1968.
Title I: Hate crimes
The Civil Rights Act of 1968 also enacted (b)(2), which permits federal prosecution of anyone who "willingly injures, intimidates or interferes with another person, or attempts to do so, by force because of the other person's race, color, religion or national origin" because of the victim's attempt to engage in one of six types of federally protected activities, such as attending school, patronizing a public place/facility, applying for employment, acting as a juror in a state court or voting.
Persons violating this law face a fine or imprisonment of up to one year or both. If bodily injury results or if such acts of intimidation involve the use of firearms, explosives or fire, individuals can receive prison terms of up to 10 years, while crimes involving kidnapping, sexual assault, or murder can be punishable by life in prison or the death penalty.
Though sexual orientation and gender identity were also excluded from this law, they are included in a more recent Federal hate-crime law, the Matthew Shepard and James Byrd, Jr. Hate Crimes Prevention Act.
Title II–VII: Indian Civil Rights Act
The Indian Civil Rights Act of 1968 granted Native Americans full access to the United States Bill of Rights. The first minor section focuses on re-establishing amendments now granted to Native Americans. The main portion of the section focuses on Native Americans in the United States legal system. The last section of this act points out other materials related to more constitutional rights of Native Americans, such as the "Indian Affairs, Laws and Treaties" doctrine.
Title VIII–IX: Fair Housing Act
=Housing discrimination
=
Title VIII of the Civil Rights Act of 1968 is commonly referred to as the Fair Housing Act of 1968. Since 1968 its protections have been expanded significantly by amendment. The Office of Fair Housing and Equal Opportunity within the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development is charged with administering and enforcing this law.
=Types of banned discrimination
=
 The Civil Rights Act of 1968 prohibited the following forms of Housing discrimination in the United States, housing discrimination:
* Refusal to sell or rent a dwelling to any person because of their race, color, religion or national origin. Discrimination on the basis of sex was added in 1974, and people with disabilities and families with children were added to the list of protected classes in 1988.
The Civil Rights Act of 1968 prohibited the following forms of Housing discrimination in the United States, housing discrimination:
* Refusal to sell or rent a dwelling to any person because of their race, color, religion or national origin. Discrimination on the basis of sex was added in 1974, and people with disabilities and families with children were added to the list of protected classes in 1988.
=Types of allowed discrimination
=
Only certain kinds of discrimination are covered by fair housing laws. Landlords are not required by law to rent to any tenant who applies for a property. Landlords can select tenants based on objective business criteria, such as the applicant's ability to pay the rent and take care of the property. Landlords can lawfully discriminate against tenants with bad credit histories or low incomes, and (except in some areas) do not have to rent to tenants who will be receiving Section 8 (housing), Section 8 vouchers. Landlords must be consistent in the screening, treat tenants who are inside and outside the protected classes in the same manner, and should document any legitimate business reason for not renting to a prospective tenant.
The United States Department of Housing and Urban Development has stated that buyers and renters may discriminate and may request real estate agents representing them to limit home searches to parameters that are discriminatory. The primary purpose of the Fair Housing Act is to protect the buyer's (and renter's) right to seek a dwelling anywhere they choose. It protects the buyer's right to discriminate by prohibiting certain discriminatory acts by sellers, landlords, and real estate agents.
= People with disabilities
=
The Fair Housing Act defines a person with a disability in the same manner as the Americans with Disabilities Act – "a person with a physical or mental impairment which substantially limits one or more major life activities; a record of such an impairment; or being regarded as having such an impairment."
The Fair Housing Act provides several specific protections for buyers and tenants with disabilities. Landlords and sellers cannot make a dwelling unit unavailable or deny a dwelling to a buyer or renter because of their disability or the disability of any person who intends to reside in the dwelling or because of the disability of anyone with whom they are associated. Landlords cannot deny a person with a disability all of the privileges provided in connection with the dwelling, because of the person's disability.
The Fair Housing Act (FHA) provides some specific protections for people with disabilities that facilitate independence and community living. First, the FHA allows tenants to make reasonable modifications to the existing premises. It makes it illegal for landlords to not allow people with disabilities to make reasonable modifications to the premises, at their own expense, if they need the modification to have full enjoyment of the premises. For example, an individual with a disability may require grab bars installed in order to have access to take a shower. The landlord must allow the tenant to install the grab bars to allow access to take a shower. However, technically, the landlord may require the tenant remove the grab bars at the end of the tenancy, at the tenant's own expense. However, the regulations specify that in rental housing, a landlord may not condition widening a bathroom doorway to provide wheelchair access, to its return to its former narrow state upon the end of the tenancy, since it will not interfere with the next tenants use and enjoyment of the premises.
The second protection offered by the FHA includes the requirement that no one can refuse to make reasonable accommodations to "rules, policies, practices, or services, when the accommodation is necessary to afford" a person with a disability "equal opportunity to use and enjoy a dwelling unit," including the amenities of the dwelling, which may involve common areas. For example, a building with a "No Pets" policy would violate the FHA if it did not allow a blind person to have their seeing eye dog live with them as a reasonable accommodation to the policy. Similarly, a wheelchair user could request an assigned, accessible parking space as a reasonable accommodation in a "first come first serve" parking lot attached to an apartment complex.
Title X: Anti-Riot Act
The Act included the "Anti-Riot Act," enacted at (with its key terms, "riot" and "incite a riot," defined in ), which makes it a federal crime to use interstate or foreign commerce routes or facilities (such as by crossing state lines or through mail, use of the Internet, or phone calls) to incite a riot, organize, promote or participate in a riot or to extend activities of a riot, or to aid and abet any person performing such activities. The provision has been informally referred to as the "H. Rap Brown Law" since the arrest and trial of H. Rap Brown in 1967 for carrying a gun across state lines. Rulings by the United States Court of Appeals for the Fourth Circuit, 4th Circuit in 2020 and United States Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit, 9th Circuit in 2021 struck down in those circuits the portions of the law which prohibit "urging" a riot on the grounds of freedom of speech, leaving in place bans on inciting and participation in riots.
Civil Rights Restoration Act of 1987
The Civil Rights Restoration Act of 1987, or'Grove City Bill, is a US, United States legislative act that specifies that entities receiving federal funds must comply with civil rights legislation in all of their operations, not just in the program or activity that received the funding. The Act overturned the precedent set by the Supreme Court decision in ''Grove City College v. Bell'', 465 U.S. 555 (1984), which held that only the particular program in an educational institution receiving federal financial assistance was required to comply with the anti-discrimination provisions of Title IX of the Education Amendments of 1972, not the institution as a whole.
The Act was proposed as a response to the ''Grove City College v. Bell'' Supreme Court decision in 1984. The decision held that only the particular program in an educational institution receiving federal financial assistance was required to comply with anti-discrimination provisions of Title IX. This decision created loopholes for educational institutions to continue discriminatory practices in other areas, which had a significant impact on minority communities, women, and people with disabilities.
Legislative history
The Act was first passed by the House in June 1984 (375–32) but stalled for several years after divisions over its potential effects on Title IX regulations prohibiting discrimination relating to abortion impeded the effectiveness of a civil rights coalition.Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
accepted an amendment by Senator John Danforth (R-MO). He is described as "abortion neutral" and clarified that the Act does not impose a requirement for entities receiving federal funding to pay or provide for abortions and that it prohibits discrimination against women who use or seek abortion services. The amendment was opposed by the National Organization for Women and other pro-choice groups but ultimately resulted in passage of the bill in both the House and the Senate.
The final vote in the Senate, on January 28, 1988, was 75–14 (48–0 in the Senate Democratic Caucus and 27–14 in the Senate Republican Conference), with 11 members voting present or abstaining. The final vote in the United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives on March 2, 1988, was 315–98 (242–4 in the House Democratic Caucus and 73–94 in the House Republican Conference) with 20 members voting present or abstaining.
On March 16, 1988, President Ronald Reagan vetoed the bill by arguing that the Act represented an overexpansion of governmental power over private organizational decision-making and "would diminish substantially the freedom and independence of religious institutions in our society." On March 22, 1988, the Senate overrode Reagan's veto by a vote of 73–24 (52–0 in the Senate Democratic Caucus and 21–24 in the Senate Republican Conference) with 3 members voting present or abstaining. On the same day, the House voted in favor of the bill with a vote of 292–133 (240–10 in the House Democratic Caucus and 52–123 in the House Republican Conference), with 7 members voting present or abstaining. Reagan's veto was the first veto of a civil rights act since Andrew Johnson
Andrew Johnson (December 29, 1808July 31, 1875) was the 17th president of the United States, serving from 1865 to 1869. The 16th vice president, he assumed the presidency following the assassination of Abraham Lincoln. Johnson was a South ...
vetoed the Civil Rights Act of 1866
The Civil Rights Act of 1866 (, enacted April 9, 1866, reenacted 1870) was the first United States federal law to define citizenship and affirm that all citizens are equally protected by the law. It was mainly intended, in the wake of the Ame ...
.
Provisions
In addition to Title IX of the Education Amendments of 1972 (which prohibits sex discrimination in educational institutions), the Act applies to the Rehabilitation Act of 1973 (which prohibits discrimination on the basis of disability), Title VI of the Civil Rights Act of 1964
The Civil Rights Act of 1964 () is a landmark civil rights and United States labor law, labor law in the United States that outlaws discrimination based on Race (human categorization), race, Person of color, color, religion, sex, and nationa ...
(which prohibits racial discrimination), and the Age Discrimination in Employment Act of 1967 (which prohibits age discrimination in employment).
With the passage of the act, educational institutions receiving any federal funding were required to comply with all federal civil rights laws, including those relating to gender, race, and disability, throughout the institution (not only in the parts of the institution receiving the funding). The act also extended protection against discrimination in educational institutions to a wider range of individuals, including students, faculty, and staff.
Civil Rights Act of 1990
The Civil Rights Act of 1990' was a bill that, had it been signed into law, would have made it easier for litigants in race or sex discrimination cases to win. It was introduced into the 101st United States Congress on February 7, 1990, by Senator Edward Kennedy (D-MA) in the United States Senate, and by Augustus Hawkins (D-CA) in the United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives.[ While making its way through Congress, the bill was considered to be civil rights groups' number one legislative priority. Soon before the bill made it to the desk of then-President of the United States ]George H. W. Bush
George Herbert Walker BushBefore the outcome of the 2000 United States presidential election, he was usually referred to simply as "George Bush" but became more commonly known as "George H. W. Bush", "Bush Senior," "Bush 41," and even "Bush th ...
, it was criticized by the Harvard Law School professor Charles Fried. In a ''New York Times'' op-ed, Fried (a ranking member of the Federalist Society who served as Solicitor General of the United States, Solicitor General in the Reagan Administration from 1985-1989), wrote that descriptions of the bill as the most important civil rights legislation in a quarter-century were "a public relations flimflam perpetrated by a cabal of overzealous civil rights plaintiffs' lawyers." He concluded by saying that Bush should "veto this bill in its present form."
On October 22, 1990, President Bush vetoed the bill, claiming that it "employs a maze of highly legalistic language to introduce the destructive force of racial quota, quotas into our national employment system."[
The Civil Rights Act of 1991 is a United States labor law, passed in response to United States Supreme Court decisions that limited the rights of employees who had sued their employers for discrimination. The Act represented the first effort since the passage of the ]Civil Rights Act of 1964
The Civil Rights Act of 1964 () is a landmark civil rights and United States labor law, labor law in the United States that outlaws discrimination based on Race (human categorization), race, Person of color, color, religion, sex, and nationa ...
to modify some of the basic procedural and substantive rights provided by federal law in employment discrimination cases. It provided the right to trial by jury on discrimination claims and introduced the possibility of emotional distress damages and limited the amount that a jury could award. It added provisions to Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 protections expanding the rights of women to sue and collect compensatory and punitive damages for sexual discrimination or harassment. U.S. President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film and television
*'' Præsident ...
George H.W. Bush, George H. W. Bush had used his veto against the more comprehensive Civil Rights Act of 1990. He feared racial quotas would be imposed but later approved the 1991 version of the bill.
The 1991 Act was intended to strengthen the protections afforded by 2 different civil rights acts: the Civil Rights Act of 1866
The Civil Rights Act of 1866 (, enacted April 9, 1866, reenacted 1870) was the first United States federal law to define citizenship and affirm that all citizens are equally protected by the law. It was mainly intended, in the wake of the Ame ...
, better known by the number assigned to it in the codification of federal laws as Section 1981, and the employment-related provisions of the Civil Rights Act of 1964
The Civil Rights Act of 1964 () is a landmark civil rights and United States labor law, labor law in the United States that outlaws discrimination based on Race (human categorization), race, Person of color, color, religion, sex, and nationa ...
, generally referred to as Title VII. The two statutes, passed nearly a century apart, approached the issue of employment discrimination very differently: Section 1981 prohibited only discrimination based on race or color, but Title VII also prohibited discrimination on the basis of sex, religion, and national origin. Section 1981, which had lain dormant and unenforced for a century after its passage, allowed plaintiffs to seek compensatory damages and trial by jury. Title VII, passed in the 1960s when it was assumed that Southern juries could not render a fair verdict, allowed only trial by the court and provided for only traditional equity (law), equitable remedies: back pay, reinstatement, and injunctions against future acts of discrimination. By the time the 1991 Act was passed, both allowed for an award of attorneys' fees.[Flood, Julee Tate, "Judicial Influence on Academic Decision-Making: A Study of Tenure Denial Litigation Cases in which Higher Education Institutions Did Not Wholly Prevail. " PhD diss., University of Tennessee, 2012. https://trace.tennessee.edu/utk_graddiss/1293] The 1991 Act expanded the remedies available to victims of discrimination by amending Title VII of the 1964 Act.
Background
Congress had amended Title VII once before, in 1972, when it broadened the coverage of the Act. It was moved to overhaul Title VII in 1991 and to harmonize it with Section 1981 jurisprudence, as a result of a series of controversial Supreme Court decisions:
*''Patterson v. McLean Credit Union'', , which held that an employee could not sue for damages caused by racial harassment on the job because even if the employer's conduct were discriminatory, the employer had not denied the employee the "same right... to make and enforce contracts... as is enjoyed by white citizens," the language that Congress chose in passing the law in 1866.
*''Wards Cove Packing Co. v. Atonio'', , which made it more difficult for employees of Wards Cove Packing Company to prove that an employer's personnel practices, neutral on their face, had an unlawful disparate impact on them by requiring that they identify the particular policy or requirement that allegedly produced inequality in the workplace, inequalities in the workplace and show that it, in isolation, had that effect.
*''Price Waterhouse v. Hopkins,'' , which held that the burden of proof shifted, once an employee had proved that an unlawful consideration had played a part in the employer's personnel decision, to the employer to prove that it would have made the same decision if it had not been motivated by that unlawful factor, but such proof by the employer would constitute a complete defense for the employer.
*''Martin v. Wilks'', , which permitted white firefighters who had not been party to the litigation, establishing a consent decree governing hiring and promotion of black firefighters in the Birmingham, Alabama, Fire Department, to bring suit to challenge the decree.
*''United Automobile Workers v. Johnson Controls, Inc.'', , which held that Title VII prohibits gender-specific fetal protection policies.
Changes
''Patterson'' had attracted much criticism since it appeared to leave employees victimized by racial harassment on the job with no effective remedies, as they could not prove a violation of Section 1981 and could rarely show any wage losses that they could recover under Title VII. In addition, the Court's narrow reading of the phrase "make or enforce contracts" eliminated any liability under Section 1981 for lost promotions and most other personnel decisions that did not constitute a refusal to hire on the basis of race or color.
Congress addressed the issue by redefining the phrase "make and enforce contracts" to include "the making, performance, modification, and termination of contracts, and the enjoyment of all benefits, privileges, terms, and conditions of the contractual relationship." Congress also clarified that Section 1981 applied to both governmental and private discrimination, the issue that the Supreme Court originally announced it would decide in ''Patterson''.
Congress also believed that the ''Wards Cove'' case made it too difficult to prove disparate impact claims under Title VII. While the amended Act still generally requires that a plaintiff identify particular employment practice(s) allegedly causing a disparate impact, Congress added that an employer's decisionmaking process may be analyzed as a whole if the plaintiff can show that "the elements of [an employer's] decisionmaking process are not capable of separation for analysis." Congress also established that the employer has the burden of proof on the business necessity defense and restored the meaning of "business necessity" to how it was interpreted before ''Wards Cove''. Congress did not, however, alter the portion of ''Wards Cove'' describing the plaintiff's burden with respect to statistical proof, in which the court had held: "The mere existence of a statistical imbalance in an employer's workforce on account of race, color, religion, sex, or national origin is not alone sufficient to establish a prima facie case of disparate impact violation."
While the majority in Congress supported the burden-shifting rule in ''Price Waterhouse'', it was uncomfortable with how that case gave the employer the ability to prove that it would have made the same decision in any event, as a complete defense in a case in which it had been shown that race or gender or another unlawful factor played a significant role in its decision. Congress amended the Act to provide that the employer's proof that it would have made the same decision in any case was a defense to back pay, reinstatement and other remedies but not to liability ''per se''. The practical effect of this change was to allow a party that proved that the employer discriminated but could not show that it made any practical difference to the outcome could still recover attorney's fees after showing that the employer discriminated, even if no other remedy was awarded.
Finally, Congress limited the rights of non-parties to attack consent decrees by barring any challenges by parties who knew or should have known of the decree or who were adequately represented by the original parties. The Act also authorized jury trials on Title VII claims and allowed Title VII plaintiffs to recover emotional distress and punitive damages, while imposing caps on such relief. The 1991 Act also made technical changes affecting the length of time allowed to challenge unlawful seniority provisions, to sue the federal government for discrimination, and to bring age discrimination claims, but it allowed successful plaintiffs to recover expert witness fees as part of an award of attorney's fees and to collect interest on any judgment against the federal government.
See also
*Civil right acts in the United States
Notes
References
Bibliography
*
* {{cite book , last1=Pach , first1=Chester J. , last2=Richardson , first2=Elmo , date=1991 , title=Presidency of Dwight D. Eisenhower , publisher=University Press of Kansas , isbn=0700604367 , ref={{sfnref, Pach, Richardson
Anti-discrimination law in the United States
Post–civil rights era in African-American history
Civil Rights Acts,
Lists of legislation by short title and collective title
 Lobbying support for the Civil Rights Act was coordinated by the Leadership Conference on Civil and Human Rights, Leadership Conference on Civil Rights, a coalition of 70 liberal and labor organizations. The principal lobbyists for the Leadership Conference were civil rights lawyer Joseph L. Rauh Jr. and Clarence Mitchell Jr. of the NAACP.
After the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom, on August 28, 1963, the organizers visited Kennedy to discuss the civil rights bill. Roy Wilkins, A. Philip Randolph, and Walter Reuther attempted to persuade him to support a provision establishing a Fair Employment Practices Commission that would ban discriminatory practices by all federal agencies, unions, and private companies.
Kennedy called the congressional leaders to the White House in late October 1963 to line up the necessary votes in the House for passage. The bill was reported out of the Judiciary Committee in November 1963 and referred to the United States House Committee on Rules, Rules Committee, whose chairman, Howard W. Smith, a Democrat and staunch segregationist from Virginia, indicated his intention to keep the bill bottled up indefinitely.
The assassination of John F. Kennedy, assassination of United States President John F. Kennedy on November 22, 1963, changed the political situation. Kennedy's successor as president,
Lobbying support for the Civil Rights Act was coordinated by the Leadership Conference on Civil and Human Rights, Leadership Conference on Civil Rights, a coalition of 70 liberal and labor organizations. The principal lobbyists for the Leadership Conference were civil rights lawyer Joseph L. Rauh Jr. and Clarence Mitchell Jr. of the NAACP.
After the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom, on August 28, 1963, the organizers visited Kennedy to discuss the civil rights bill. Roy Wilkins, A. Philip Randolph, and Walter Reuther attempted to persuade him to support a provision establishing a Fair Employment Practices Commission that would ban discriminatory practices by all federal agencies, unions, and private companies.
Kennedy called the congressional leaders to the White House in late October 1963 to line up the necessary votes in the House for passage. The bill was reported out of the Judiciary Committee in November 1963 and referred to the United States House Committee on Rules, Rules Committee, whose chairman, Howard W. Smith, a Democrat and staunch segregationist from Virginia, indicated his intention to keep the bill bottled up indefinitely.
The assassination of John F. Kennedy, assassination of United States President John F. Kennedy on November 22, 1963, changed the political situation. Kennedy's successor as president,  Johnson, who wanted the bill passed as soon as possible, ensured that it would be quickly considered by the
Johnson, who wanted the bill passed as soon as possible, ensured that it would be quickly considered by the  The bill divided both major American political parties and engendered a long-term change in the demographics of the support for each. President Kennedy realized that supporting this bill would risk losing the South's overwhelming support of the Democratic Party. Both Attorney General Robert F. Kennedy and Vice President Johnson had pushed for the introduction of the civil rights legislation. Johnson told Kennedy aide Ted Sorensen that "I know the risks are great and we might lose the South, but those sorts of states may be lost anyway." Senator Richard Russell Jr., Richard Russell, Jr. later warned President Johnson that his strong support for the civil rights bill "will not only cost you the South, it will cost you the election". Johnson, however, went on to win the 1964 United States presidential election, 1964 election by one of the biggest landslides in American history. The South, which had five states swing Republican in 1964, became a stronghold of the Republican Party by the 1990s.
Although majorities in both parties voted for the bill, there were notable exceptions. Though he opposed forced segregation, Republican Party (United States), Republican 1964 presidential candidate, Senator Barry Goldwater of Arizona, voted against the bill, remarking, "You can't legislate morality." Goldwater had supported previous attempts to pass civil rights legislation in 1957 and 1960 as well as the Twenty-fourth Amendment to the United States Constitution, 24th Amendment outlawing the Poll tax (United States), poll tax. He stated that the reason for his opposition to the 1964 bill was Title II, which in his opinion violated individual liberty and states' rights. Democrats and Republicans from the Southern states opposed the bill and led an unsuccessful 60 working day filibuster, including Senators Albert Gore Sr., Albert Gore, Sr. (D-TN) and J. William Fulbright (D-AR), as well as Senator Robert Byrd (D-WV), who personally filibustered for 14 hours straight.
There were white business owners who claimed that Congress did not have the constitutional authority to ban segregation in public accommodations. For example, Moreton Rolleston, the owner of a motel in Atlanta, Georgia, said he should not be forced to serve black travelers, saying, "the fundamental question [...] is whether or not Congress has the power to take away the liberty of an individual to run his business as he sees fit in the selection and choice of his customers". Rolleston claimed that the Civil Rights Act of 1964 was a breach of the Fourteenth Amendment and also violated the Fifth Amendment to the United States Constitution, Fifth and Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, Thirteenth Amendments by depriving him of "liberty and property without due process". In ''Heart of Atlanta Motel, Inc. v. United States, Heart of Atlanta Motel v. United States'' (1964), the Supreme Court held that Congress drew its authority from the Constitution's Commerce Clause, rejecting Rolleston's claims.
Resistance to the public accommodation clause continued for years on the ground, especially in the South. When local college students in Orangeburg, South Carolina, attempted to desegregate a bowling alley in 1968, they were violently attacked, leading to rioting and what became known as the "Orangeburg massacre." Resistance by school boards continued into the next decade, with the most significant declines in black-white school segregation only occurring at the end of the 1960s and the start of the 1970s in the aftermath of the ''Green v. County School Board of New Kent County'' (1968) court decision.
In June 2020, the U.S. Supreme Court ruled in three cases (''Bostock v. Clayton County'', ''Altitude Express, Inc. v. Zarda'', and ''R.G. & G.R. Harris Funeral Homes Inc. v. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission'') that Title VII of the Civil Rights Act, which barred employers from discriminating on the basis of sex, precluded employers from discriminating on the basis of sexual orientation or gender identity. Afterward, ''USA Today'' stated that in addition to LGBTQ employment discrimination, " e court's ruling is likely to have a sweeping impact on federal civil rights laws barring sex discrimination in education, health care, housing and financial credit."
The bill divided both major American political parties and engendered a long-term change in the demographics of the support for each. President Kennedy realized that supporting this bill would risk losing the South's overwhelming support of the Democratic Party. Both Attorney General Robert F. Kennedy and Vice President Johnson had pushed for the introduction of the civil rights legislation. Johnson told Kennedy aide Ted Sorensen that "I know the risks are great and we might lose the South, but those sorts of states may be lost anyway." Senator Richard Russell Jr., Richard Russell, Jr. later warned President Johnson that his strong support for the civil rights bill "will not only cost you the South, it will cost you the election". Johnson, however, went on to win the 1964 United States presidential election, 1964 election by one of the biggest landslides in American history. The South, which had five states swing Republican in 1964, became a stronghold of the Republican Party by the 1990s.
Although majorities in both parties voted for the bill, there were notable exceptions. Though he opposed forced segregation, Republican Party (United States), Republican 1964 presidential candidate, Senator Barry Goldwater of Arizona, voted against the bill, remarking, "You can't legislate morality." Goldwater had supported previous attempts to pass civil rights legislation in 1957 and 1960 as well as the Twenty-fourth Amendment to the United States Constitution, 24th Amendment outlawing the Poll tax (United States), poll tax. He stated that the reason for his opposition to the 1964 bill was Title II, which in his opinion violated individual liberty and states' rights. Democrats and Republicans from the Southern states opposed the bill and led an unsuccessful 60 working day filibuster, including Senators Albert Gore Sr., Albert Gore, Sr. (D-TN) and J. William Fulbright (D-AR), as well as Senator Robert Byrd (D-WV), who personally filibustered for 14 hours straight.
There were white business owners who claimed that Congress did not have the constitutional authority to ban segregation in public accommodations. For example, Moreton Rolleston, the owner of a motel in Atlanta, Georgia, said he should not be forced to serve black travelers, saying, "the fundamental question [...] is whether or not Congress has the power to take away the liberty of an individual to run his business as he sees fit in the selection and choice of his customers". Rolleston claimed that the Civil Rights Act of 1964 was a breach of the Fourteenth Amendment and also violated the Fifth Amendment to the United States Constitution, Fifth and Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, Thirteenth Amendments by depriving him of "liberty and property without due process". In ''Heart of Atlanta Motel, Inc. v. United States, Heart of Atlanta Motel v. United States'' (1964), the Supreme Court held that Congress drew its authority from the Constitution's Commerce Clause, rejecting Rolleston's claims.
Resistance to the public accommodation clause continued for years on the ground, especially in the South. When local college students in Orangeburg, South Carolina, attempted to desegregate a bowling alley in 1968, they were violently attacked, leading to rioting and what became known as the "Orangeburg massacre." Resistance by school boards continued into the next decade, with the most significant declines in black-white school segregation only occurring at the end of the 1960s and the start of the 1970s in the aftermath of the ''Green v. County School Board of New Kent County'' (1968) court decision.
In June 2020, the U.S. Supreme Court ruled in three cases (''Bostock v. Clayton County'', ''Altitude Express, Inc. v. Zarda'', and ''R.G. & G.R. Harris Funeral Homes Inc. v. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission'') that Title VII of the Civil Rights Act, which barred employers from discriminating on the basis of sex, precluded employers from discriminating on the basis of sexual orientation or gender identity. Afterward, ''USA Today'' stated that in addition to LGBTQ employment discrimination, " e court's ruling is likely to have a sweeping impact on federal civil rights laws barring sex discrimination in education, health care, housing and financial credit."
 Prior to the enactment of the Voting Rights Act of 1965 there were several efforts to stop the disenfranchisement of black voters by Southern states,. Besides the above-mentioned literacy tests and poll taxes other bureaucratic restrictions were used to deny them the right to vote. African Americans also "risked harassment, intimidation, economic reprisals, and physical violence when they tried to register or vote. As a result, very few African Americans were registered voters, and they had very little, if any, political power, either locally or nationally." In the 1950s the Civil Rights Movement increased pressure on the United States federal government, federal government to protect the voting rights of racial minorities. In 1957, Congress passed the first civil rights legislation since Reconstruction: the
Prior to the enactment of the Voting Rights Act of 1965 there were several efforts to stop the disenfranchisement of black voters by Southern states,. Besides the above-mentioned literacy tests and poll taxes other bureaucratic restrictions were used to deny them the right to vote. African Americans also "risked harassment, intimidation, economic reprisals, and physical violence when they tried to register or vote. As a result, very few African Americans were registered voters, and they had very little, if any, political power, either locally or nationally." In the 1950s the Civil Rights Movement increased pressure on the United States federal government, federal government to protect the voting rights of racial minorities. In 1957, Congress passed the first civil rights legislation since Reconstruction: the  Following the 1964 elections, civil rights organizations such as the Southern Christian Leadership Conference (SCLC) and the Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee (SNCC) pushed for federal action to protect the voting rights of racial minorities. Their efforts culminated in protests in Alabama, particularly in the city of Selma, Alabama, Selma, where County Sheriff Jim Clark (sheriff), Jim Clark's police force violently resisted African-American voter registration efforts. Speaking about the voting rights push in Selma, James Forman of SNCC said: "Our strategy, as usual, was to force the U.S. government to intervene in case there were arrests—and if they did not intervene, that inaction would once again prove the government was not on our side and thus intensify the development of a mass consciousness among blacks. Our slogan for this drive was 'One Man, One Vote.
In January 1965, Martin Luther King Jr., James Bevel, and other civil rights leaders organized several Selma to Montgomery marches, peaceful demonstrations in Selma, which were violently attacked by police and white counter-protesters. Throughout January and February, these protests received national media coverage and drew attention to the issue of voting rights. King and other demonstrators were arrested during a march on February 1 for violating an anti-parade local ordinance, ordinance; this inspired similar marches in the following days, causing hundreds more to be arrested. On February 4, civil rights leader Malcolm X gave a militant speech in Selma in which he said that many African Americans did not support King's nonviolent approach; he later privately said that he wanted to frighten whites into supporting King. The next day, King was released and a letter he wrote addressing voting rights, "Letter From A Selma Jail", appeared in ''The New York Times''.
With increasing national attention focused on Selma and voting rights, President Johnson reversed his decision to delay voting rights legislation. On February 6, he announced he would send a proposal to Congress. Johnson did not reveal the proposal's content or disclose when it would come before Congress.
On February 18 in Marion, Alabama, state troopers violently broke up a nighttime voting-rights march during which officer James Bonard Fowler shot and killed young African-American protester Jimmie Lee Jackson, who was unarmed and protecting his mother. Spurred by this event, and at the initiation of Bevel, on March 7 SCLC and SNCC began the first of the Selma to Montgomery marches, in which Selma residents intended to march to Alabama's capital, Montgomery, Alabama, Montgomery, to highlight voting rights issues and present Governor George Wallace with their grievances. On the first march, demonstrators were stopped by state and county police on horseback at the Edmund Pettus Bridge near Selma. The police shot tear gas into the crowd and trampled protesters. Televised footage of the scene, which became known as Selma to Montgomery marches#"Bloody Sunday" events, "Bloody Sunday", generated outrage across the country. A second march was held on March 9, which became known as Selma to Montgomery marches#Second march: "Turnaround Tuesday", "Turnaround Tuesday". That evening, three white Unitarian Universalism, Unitarian ministers who participated in the march were attacked on the street and beaten with clubs by four
Following the 1964 elections, civil rights organizations such as the Southern Christian Leadership Conference (SCLC) and the Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee (SNCC) pushed for federal action to protect the voting rights of racial minorities. Their efforts culminated in protests in Alabama, particularly in the city of Selma, Alabama, Selma, where County Sheriff Jim Clark (sheriff), Jim Clark's police force violently resisted African-American voter registration efforts. Speaking about the voting rights push in Selma, James Forman of SNCC said: "Our strategy, as usual, was to force the U.S. government to intervene in case there were arrests—and if they did not intervene, that inaction would once again prove the government was not on our side and thus intensify the development of a mass consciousness among blacks. Our slogan for this drive was 'One Man, One Vote.
In January 1965, Martin Luther King Jr., James Bevel, and other civil rights leaders organized several Selma to Montgomery marches, peaceful demonstrations in Selma, which were violently attacked by police and white counter-protesters. Throughout January and February, these protests received national media coverage and drew attention to the issue of voting rights. King and other demonstrators were arrested during a march on February 1 for violating an anti-parade local ordinance, ordinance; this inspired similar marches in the following days, causing hundreds more to be arrested. On February 4, civil rights leader Malcolm X gave a militant speech in Selma in which he said that many African Americans did not support King's nonviolent approach; he later privately said that he wanted to frighten whites into supporting King. The next day, King was released and a letter he wrote addressing voting rights, "Letter From A Selma Jail", appeared in ''The New York Times''.
With increasing national attention focused on Selma and voting rights, President Johnson reversed his decision to delay voting rights legislation. On February 6, he announced he would send a proposal to Congress. Johnson did not reveal the proposal's content or disclose when it would come before Congress.
On February 18 in Marion, Alabama, state troopers violently broke up a nighttime voting-rights march during which officer James Bonard Fowler shot and killed young African-American protester Jimmie Lee Jackson, who was unarmed and protecting his mother. Spurred by this event, and at the initiation of Bevel, on March 7 SCLC and SNCC began the first of the Selma to Montgomery marches, in which Selma residents intended to march to Alabama's capital, Montgomery, Alabama, Montgomery, to highlight voting rights issues and present Governor George Wallace with their grievances. On the first march, demonstrators were stopped by state and county police on horseback at the Edmund Pettus Bridge near Selma. The police shot tear gas into the crowd and trampled protesters. Televised footage of the scene, which became known as Selma to Montgomery marches#"Bloody Sunday" events, "Bloody Sunday", generated outrage across the country. A second march was held on March 9, which became known as Selma to Montgomery marches#Second march: "Turnaround Tuesday", "Turnaround Tuesday". That evening, three white Unitarian Universalism, Unitarian ministers who participated in the march were attacked on the street and beaten with clubs by four  Congress enacted major amendments to the Act in 1970, 1975, 1982, 1992, and 2006. Each amendment coincided with an impending expiration of some or all of the Act's special provisions. Originally set to expire by 1970, Congress repeatedly reauthorized the special provisions in recognition of continuing voting discrimination. Congress extended the coverage formula and special provisions tied to it, such as the Section 5 preclearance requirement, for five years in 1970, seven years in 1975, and 25 years in both 1982 and 2006. In 1970 and 1975, Congress also expanded the reach of the coverage formula by supplementing it with new 1968 and 1972 trigger dates. Coverage was further enlarged in 1975 when Congress expanded the meaning of "tests or devices" to encompass any jurisdiction that provided English-only election information, such as ballots, if the jurisdiction had a single language minority group that constituted more than five percent of the jurisdiction's voting-age citizens. These expansions brought numerous jurisdictions into coverage, including many outside of the South. To ease the burdens of the reauthorized special provisions, Congress liberalized the bailout procedure in 1982 by allowing jurisdictions to escape coverage by complying with the Act and affirmatively acting to expand minority political participation.
In addition to reauthorizing the original special provisions and expanding coverage, Congress amended and added several other provisions to the Act. For instance, Congress expanded the original ban on "tests or devices" to apply nationwide in 1970, and in 1975, Congress made the ban permanent. Separately, in 1975 Congress expanded the Act's scope to protect language minorities from voting discrimination. Congress defined "language minority" to mean "persons who are American Indian, Asian American, Alaskan Natives or of Spanish heritage."Voting Rights Act of 1965 § 14(c)(3); (formerly 42 U.S.C. § 1973l(c)(3)) Congress amended various provisions, such as the preclearance requirement and Section 2's general prohibition of discriminatory voting laws, to prohibit discrimination against language minorities. Congress also enacted a bilingual election requirement in Section 203, which requires election officials in certain jurisdictions with large numbers of English-illiterate language minorities to provide ballots and voting information in the language of the language minority group. Originally set to expire after 10 years, Congress reauthorized Section 203 in 1982 for seven years, expanded and reauthorized it in 1992 for 15 years, and reauthorized it in 2006 for 25 years. The bilingual election requirements have remained controversial, with proponents arguing that bilingual assistance is necessary to enable recently naturalized citizens to vote and opponents arguing that the bilingual election requirements constitute costly unfunded mandates.
Several of the amendments responded to judicial rulings with which Congress disagreed. In 1982, Congress amended the Act to overturn the Supreme Court case ''Mobile v. Bolden'' (1980), which held that the general prohibition of voting discrimination prescribed in Section 2 prohibited only ''purposeful'' discrimination. Congress responded by expanding Section 2 to explicitly ban any voting practice that had a discriminatory ''effect'', regardless of whether the practice was enacted or operated for a discriminatory purpose. The creation of this "results test" shifted the majority of vote dilution litigation brought under the Act from preclearance lawsuits to Section 2 lawsuits. In 2006, Congress amended the Act to overturn two Supreme Court cases: ''Reno v. Bossier Parish School Board'' (2000),''Reno v. Bossier Parish School Board'', which interpreted the Section 5 preclearance requirement to prohibit only voting changes that were enacted or maintained for a "retrogressive" discriminatory purpose instead of any discriminatory purpose, and ''Georgia v. Ashcroft'' (2003),''Georgia v. Ashcroft'', which established a broader test for determining whether a redistricting plan had an impermissible effect under Section 5 than assessing only whether a minority group could elect its preferred candidates. Since the Supreme Court struck down the coverage formula as unconstitutional in ''Shelby County v. Holder'' (2013), several bills have been introduced in Congress to create a new coverage formula and amend various other provisions; none of these bills have passed.
Congress enacted major amendments to the Act in 1970, 1975, 1982, 1992, and 2006. Each amendment coincided with an impending expiration of some or all of the Act's special provisions. Originally set to expire by 1970, Congress repeatedly reauthorized the special provisions in recognition of continuing voting discrimination. Congress extended the coverage formula and special provisions tied to it, such as the Section 5 preclearance requirement, for five years in 1970, seven years in 1975, and 25 years in both 1982 and 2006. In 1970 and 1975, Congress also expanded the reach of the coverage formula by supplementing it with new 1968 and 1972 trigger dates. Coverage was further enlarged in 1975 when Congress expanded the meaning of "tests or devices" to encompass any jurisdiction that provided English-only election information, such as ballots, if the jurisdiction had a single language minority group that constituted more than five percent of the jurisdiction's voting-age citizens. These expansions brought numerous jurisdictions into coverage, including many outside of the South. To ease the burdens of the reauthorized special provisions, Congress liberalized the bailout procedure in 1982 by allowing jurisdictions to escape coverage by complying with the Act and affirmatively acting to expand minority political participation.
In addition to reauthorizing the original special provisions and expanding coverage, Congress amended and added several other provisions to the Act. For instance, Congress expanded the original ban on "tests or devices" to apply nationwide in 1970, and in 1975, Congress made the ban permanent. Separately, in 1975 Congress expanded the Act's scope to protect language minorities from voting discrimination. Congress defined "language minority" to mean "persons who are American Indian, Asian American, Alaskan Natives or of Spanish heritage."Voting Rights Act of 1965 § 14(c)(3); (formerly 42 U.S.C. § 1973l(c)(3)) Congress amended various provisions, such as the preclearance requirement and Section 2's general prohibition of discriminatory voting laws, to prohibit discrimination against language minorities. Congress also enacted a bilingual election requirement in Section 203, which requires election officials in certain jurisdictions with large numbers of English-illiterate language minorities to provide ballots and voting information in the language of the language minority group. Originally set to expire after 10 years, Congress reauthorized Section 203 in 1982 for seven years, expanded and reauthorized it in 1992 for 15 years, and reauthorized it in 2006 for 25 years. The bilingual election requirements have remained controversial, with proponents arguing that bilingual assistance is necessary to enable recently naturalized citizens to vote and opponents arguing that the bilingual election requirements constitute costly unfunded mandates.
Several of the amendments responded to judicial rulings with which Congress disagreed. In 1982, Congress amended the Act to overturn the Supreme Court case ''Mobile v. Bolden'' (1980), which held that the general prohibition of voting discrimination prescribed in Section 2 prohibited only ''purposeful'' discrimination. Congress responded by expanding Section 2 to explicitly ban any voting practice that had a discriminatory ''effect'', regardless of whether the practice was enacted or operated for a discriminatory purpose. The creation of this "results test" shifted the majority of vote dilution litigation brought under the Act from preclearance lawsuits to Section 2 lawsuits. In 2006, Congress amended the Act to overturn two Supreme Court cases: ''Reno v. Bossier Parish School Board'' (2000),''Reno v. Bossier Parish School Board'', which interpreted the Section 5 preclearance requirement to prohibit only voting changes that were enacted or maintained for a "retrogressive" discriminatory purpose instead of any discriminatory purpose, and ''Georgia v. Ashcroft'' (2003),''Georgia v. Ashcroft'', which established a broader test for determining whether a redistricting plan had an impermissible effect under Section 5 than assessing only whether a minority group could elect its preferred candidates. Since the Supreme Court struck down the coverage formula as unconstitutional in ''Shelby County v. Holder'' (2013), several bills have been introduced in Congress to create a new coverage formula and amend various other provisions; none of these bills have passed.
 The Civil Rights Act of 1968 prohibited the following forms of Housing discrimination in the United States, housing discrimination:
* Refusal to sell or rent a dwelling to any person because of their race, color, religion or national origin. Discrimination on the basis of sex was added in 1974, and people with disabilities and families with children were added to the list of protected classes in 1988.
* Discrimination against a person in the terms, conditions or privilege of the sale or rental of a dwelling.
* Advertising the sale or rental of a dwelling indicating preference of discrimination based on race, color, religion or national origin. This provision was also amended to include sex, disability, and having children.
* Coercing, threatening, intimidating, or interfering with a person's enjoyment or exercise of housing rights based on discriminatory reasons or retaliating against a person or organization that aids or encourages the exercise or enjoyment of fair housing rights.
* Neglecting maintenance and repairs of the units rented by people based on race, religion, sex, or any other discriminatory demographic.
* Restricting access to services and amenities on the basis of the renter's race, gender, religion, or nationality.
* In 2012, the United States Department of Housing and Urban Development's Office of Fair Housing and Equal Opportunity issued a regulation prohibiting LGBT discrimination in federally assisted housing programs. The Supreme Court ruled in 2020 that discrimination on the basis of "sex" includes discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation and gender identity. It was not until February 2021 that Housing and Urban Development issued a rule change under President Joe Biden to implement this decision. In addition, many states, cities and towns have passed laws prohibiting discrimination in housing based on sexual orientation and gender identity.
The Civil Rights Act of 1968 prohibited the following forms of Housing discrimination in the United States, housing discrimination:
* Refusal to sell or rent a dwelling to any person because of their race, color, religion or national origin. Discrimination on the basis of sex was added in 1974, and people with disabilities and families with children were added to the list of protected classes in 1988.
* Discrimination against a person in the terms, conditions or privilege of the sale or rental of a dwelling.
* Advertising the sale or rental of a dwelling indicating preference of discrimination based on race, color, religion or national origin. This provision was also amended to include sex, disability, and having children.
* Coercing, threatening, intimidating, or interfering with a person's enjoyment or exercise of housing rights based on discriminatory reasons or retaliating against a person or organization that aids or encourages the exercise or enjoyment of fair housing rights.
* Neglecting maintenance and repairs of the units rented by people based on race, religion, sex, or any other discriminatory demographic.
* Restricting access to services and amenities on the basis of the renter's race, gender, religion, or nationality.
* In 2012, the United States Department of Housing and Urban Development's Office of Fair Housing and Equal Opportunity issued a regulation prohibiting LGBT discrimination in federally assisted housing programs. The Supreme Court ruled in 2020 that discrimination on the basis of "sex" includes discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation and gender identity. It was not until February 2021 that Housing and Urban Development issued a rule change under President Joe Biden to implement this decision. In addition, many states, cities and towns have passed laws prohibiting discrimination in housing based on sexual orientation and gender identity.