cities of the ancient near east on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The earliest cities in history were in the
 (ordered from north to south)
(ordered from north to south)
 (ordered from north to south)
(ordered from north to south)

Geospatial: Mapping Iraq's Ancient Cities
Ancient cities grew pretty much like modern ones, say scientists
(February 2015), ''
ancient Near East
The ancient Near East was home to many cradles of civilization, spanning Mesopotamia, Egypt, Iran (or Persia), Anatolia and the Armenian highlands, the Levant, and the Arabian Peninsula. As such, the fields of ancient Near East studies and Nea ...
, an area covering roughly that of the modern Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western Eur ...
: its history began in the 4th millennium BC and ended, depending on the interpretation of the term, either with the conquest by the Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian peoples, Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, i ...
in the 6th century BC or with that by Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
in the 4th century BC.
The largest cities of the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
Near East
The Near East () is a transcontinental region around the Eastern Mediterranean encompassing the historical Fertile Crescent, the Levant, Anatolia, Egypt, Mesopotamia, and coastal areas of the Arabian Peninsula. The term was invented in the 20th ...
housed several tens of thousands of people. Memphis in the Early Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
, with some 30,000 inhabitants, was the largest city of the time by far. Ebla
Ebla (Sumerian language, Sumerian: ''eb₂-la'', , modern: , Tell Mardikh) was one of the earliest kingdoms in Syria. Its remains constitute a Tell (archaeology), tell located about southwest of Aleppo near the village of Mardikh. Ebla was ...
is estimated to have had a population of 40,000 inhabitants in the Intermediate Bronze age. Ur in the Middle Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
is estimated to have had some 65,000 inhabitants; Babylon
Babylon ( ) was an ancient city located on the lower Euphrates river in southern Mesopotamia, within modern-day Hillah, Iraq, about south of modern-day Baghdad. Babylon functioned as the main cultural and political centre of the Akkadian-s ...
in the Late Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
similarly had a population of some 50,000–60,000. Niniveh had some 20,000–30,000, reaching 100,000 only in the Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
(around 700 BC).
In Akkadian and Hittite orthography, URU became a determinative sign denoting a city, or combined with KUR
The ancient Mesopotamian underworld (known in Sumerian language, Sumerian as ''Kur'', ''Irkalla'', ''Kukku'', ''Arali'', or ''Kigal'', and in Akkadian language, Akkadian as ''Erṣetu''), was the lowermost part of the Ancient near eastern cosmol ...
"land" the kingdom or territory controlled by a city, e.g. "the king of the country of (the city of) Ḫattuša
Hattusa, also Hattuşa, Ḫattuša, Hattusas, or Hattusha, was the capital of the Hittites, Hittite Empire in the late Bronze Age during two distinct periods. Its ruins lie near modern Boğazkale, Turkey (originally Boğazköy) within the great ...
". The KI determinative is used following place names (toponyms) in both Sumerian and Akkadian.
Mesopotamia
Lower Mesopotamia
Upper Mesopotamia
(ordered from north to south) * Urfa * Shanidar cave * Urkesh (Urkish) (''Tell Mozan'') * Tell Leilan (''Shekhna'', ''Shubat-Enlil'') * Tell Halaf *Tell Arbid
Tell Arbid is an ancient Near East archaeological site in the Khabur (Euphrates), Khabur River Basin region of Al-Hasakah Governorate, Syria, about 50 kilometers north northeast of modern Al-Hasakah. It is located 45 kilometers south of Tell Mozan ...
* Harran
Harran is a municipality and Districts of Turkey, district of Şanlıurfa Province, Turkey. Its area is 904 km2, and its population is 96,072 (2022). It is approximately southeast of Urfa and from the Syrian border crossing at Akçakale.
...
* Chagar Bazar
* Mardaman ('' Bassetki'')
* Kahat (''Tell Barri'')
* Tell Fekheriye ('' Washukanni?'')
* Hadatu (''Arslan Tash'')
* Carchemish (''Djerabis'')
* Til Barsip (''Tell Ahmar'')
* Tell Chuera
Tell Chuera (also Tell Ḫuera and Tall Ḥuwaira and Tall Chuera and Tell Khuera) is an ancient Near Eastern Tell (archaeology), tell site in Raqqa Governorate, northern Syria. It lies between the Balikh River, Balikh and Khabur (Euphrates), Khab ...
* Al-Rawda
* Nabada (''Tell Beydar'')
* Nagar (''Tell Brak'')
* Hamazi
Hamazi or Khamazi ( Sumerian: , ''ha-ma-zi''ki, or ''Ḫa-ma-zi2''ki) was an ancient kingdom or city-state which became prominent during the Early Dynastic period. Its exact location is unknown.
History
In the early days of archaeology two pot ...
* Yarim Tepe
* Telul eth-Thalathat
* Tepe Gawra
* Tell Arpachiyah (''Tepe Reshwa'')
* Tell Maghzaliyah
* Shibaniba (''Tell Billa'')
* Tarbisu (''Sherif Khan'')
* Nineveh
Nineveh ( ; , ''URUNI.NU.A, Ninua''; , ''Nīnəwē''; , ''Nīnawā''; , ''Nīnwē''), was an ancient Assyrian city of Upper Mesopotamia, located in the modern-day city of Mosul (itself built out of the Assyrian town of Mepsila) in northern ...
(''Ninua'')
* Qatara or Karana (''Tell al-Rimah'')
* Tell Hamoukar
* Dur Sharrukin (''Khorsabad'')
* Tell Shemshara
Tell Shemshāra (ancient Shusharra) (also Tell Shimshara) is an archaeological site located along the Little Zab in Sulaymaniyah Governorate, in the Iraqi Kurdistan autonomous administrative division of Iraq. The site was inundated by Lake Dukan ...
(''Shusharra'')
* Bestansur
* Tell Bazmusian
* Erbil
Erbil (, ; , ), also called Hawler (, ), is the capital and most populated city in the Kurdistan Region of Iraq. The city is the capital of the Erbil Governorate.
Human settlement at Erbil may be dated back to the 5th millennium BC. At the h ...
(''Urbilim'', ''Arba-Ilu'')
* Kurd Qaburstan (''Qabra?'')
* Qasr Shemamok (''Kilizu/Kilizi/Kakzu'')
* Qal'at Jarmo
* Tell Taya
* Tell Hassuna
* Balawat (Imgur-Enlil)
* Tell es-Sweyhat
* Tell Hadidi (''Azu'')
* Mumbaqat (''Tall Munbāqa, Ekalte'')
* Nimrud
Nimrud (; ) is an ancient Assyrian people, Assyrian city (original Assyrian name Kalḫu, biblical name Calah) located in Iraq, south of the city of Mosul, and south of the village of Selamiyah (), in the Nineveh Plains in Upper Mesopotamia. ...
* Emar (''Tell Meskene'')
* Tall Bazi
Tall Bazi, is an ancient Near East archaeological site in Raqqa Governorate of Syria in the same general area as Mari and Ebla. It is located on the east bank of Euphrates river in upper Syria, about 60 kilometers south of Turkey border. It is c ...
(''Baṣīru'', '' Armanum?'')
* Arrapha
* Kar-Tukulti-Ninurta
* Assur
* Ekallatum
* Nuzi (''Yorghan Tepe'', ''Gasur'')
* Tell al-Fakhar (''Kurruhanni?'')
* Tell Taban (''Ṭābetu'', ''Ṭābatum'')
* Terqa (''Tell Ashara'')
* Doura Europos
* Mari (''Tell Hariri'')
* Tuttul
Tuttul (Akkadian language, Akkadian: tu-ut-tu-ulki, Ugaritic: 𐎚𐎚𐎍 – ) was an ancient Near East city. Tuttul is identified with the archaeological site of Tell Bi'a (also Tall Bi'a) in Raqqa Governorate, Syria. Tell Bi'a is located near t ...
(''Tell Bi'a'')
* Haradum (''Khirbet ed-Diniyeh'')
* Tell es-Sawwan
* Nerebtum or Kiti (''Tell Ishchali'')
* Tell Agrab
* Dur-Kurigalzu (''Aqar Quf'')
* Shaduppum (''Tell Harmal'')
* Tell al-Dhiba'i
* Tell Muhammad
* Seleucia
Seleucia (; ), also known as or or Seleucia ad Tigrim, was a major Mesopotamian city, located on the west bank of the Tigris River within the present-day Baghdad Governorate in Iraq. It was founded around 305 BC by Seleucus I Nicator as th ...
* Ctesiphon
Ctesiphon ( ; , ''Tyspwn'' or ''Tysfwn''; ; , ; Thomas A. Carlson et al., “Ctesiphon — ܩܛܝܣܦܘܢ ” in The Syriac Gazetteer last modified July 28, 2014, http://syriaca.org/place/58.) was an ancient city in modern Iraq, on the eastern ba ...
(''Taq Kisra'')
* Zenobia (''Halabiye'')
* Hatra
Hatra (; (); ) was an ancient Arab city in Upper Mesopotamia located in present-day eastern Nineveh Governorate in northern Iraq. The ruins of the city lie northwest of Baghdad and southwest of Mosul. It is considered the richest archaeologi ...
* Idu
* Rabana-Merquly (''Natounia?'')
Iran
Anatolia (Turkey)
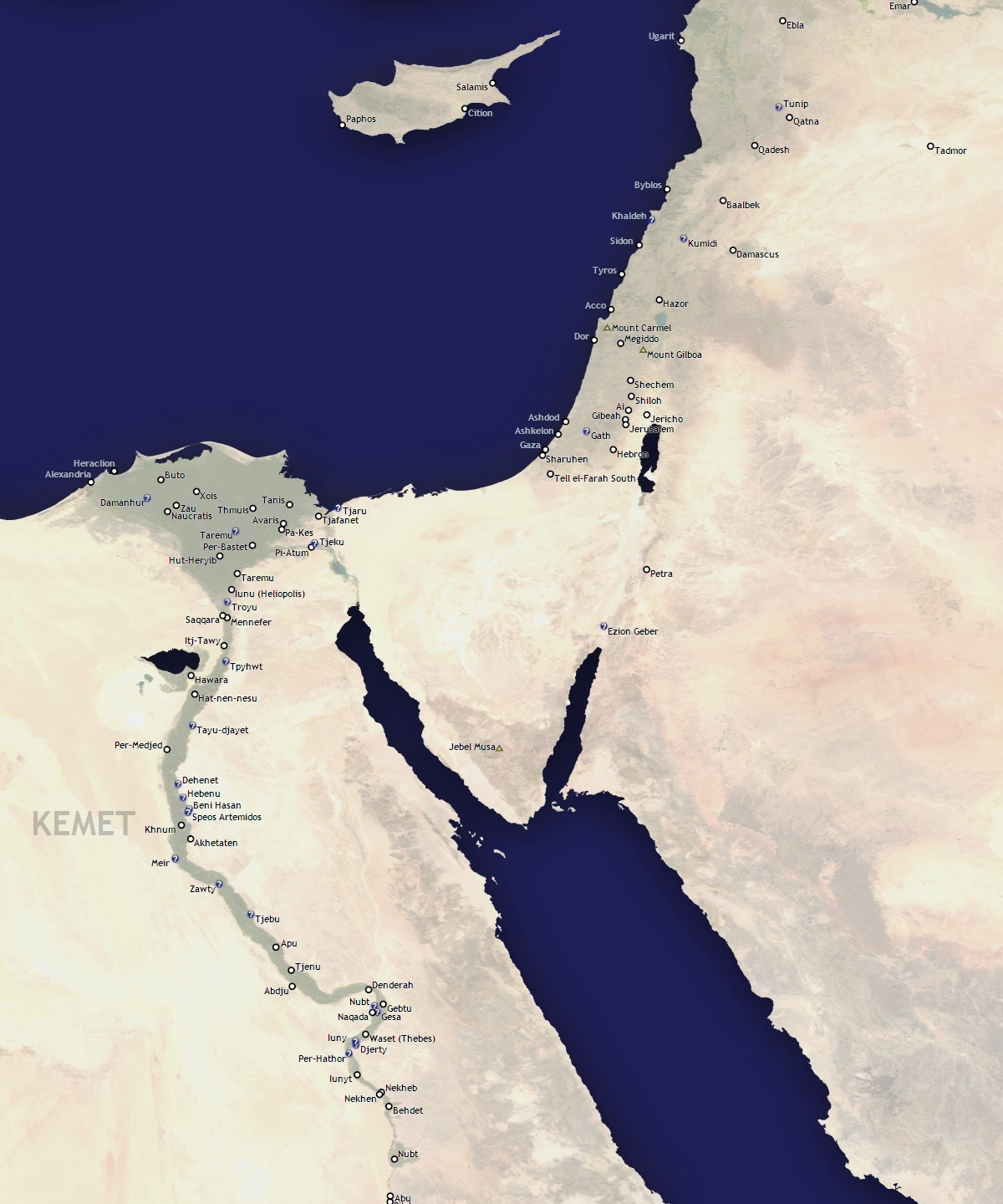
Egypt
Levant

Arabian Peninsula

Cyprus
* Enkomi * Idalion * Kition *Kourion
Kourion (; ) was an important ancient Greek city-state on the southwestern coast of the island of Cyprus. In the twelfth century BCE, after the Mycenaean Greece#Collapse or Postpalatial Bronze Age (c. 1200–1050 BC), collapse of the Mycenaean p ...
(''Koύριov'', ''Curium'')
Nubia
*Jebel Barkal
Jebel Barkal or Gebel Barkal () is a mesa or large rock outcrop located 400 km north of Khartoum, next to Karima in Northern State in Sudan, on the Nile River, in the region that is sometimes called Nubia. The jebel is 104 m tall, has a f ...
* Kerma
Kerma was the capital city of the Kerma culture, which was founded in present-day Sudan before 3500 BC. Kerma is one of the largest archaeological sites in ancient Nubia. It has produced decades of extensive excavations and research, including t ...
* Meroë
* Napata
Napata
(2020). (Old Egyptian ''Npt'', ''Npy''; Meroitic language, Meroitic ''Napa''; and Ναπάται) was a city of ...
(2020). (Old Egyptian ''Npt'', ''Npy''; Meroitic language, Meroitic ''Napa''; and Ναπάται) was a city of ...
Horn of Africa
*Adulis
Adulis (Sabaic, Sabaean: 𐩱 𐩵 𐩡 𐩪, , ) was an ancient city along the Red Sea in the Gulf of Zula, about south of Massawa. Its ruins lie within the modern Eritrean list of cities in Eritrea, city of Zula. It was the emporium (antiquit ...
* Aksum (Axum)
* Keskese
* Matara
* Qohaito
* Sembel
* Yeha
See also
*City-state
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world throughout history, including cities such as Rome, ...
* Sumerian King List
The ''Sumerian King List'' (abbreviated ''SKL'') or ''Chronicle of the One Monarchy'' is an ancient Composition (language), literary composition written in Sumerian language, Sumerian that was likely created and redacted to legitimize the claims ...
* Historical urban community sizes
* Short chronology timeline
* List of oldest continuously inhabited cities
This is a list of present-day cities by the time period over which they have been continuously inhabited as a city. The age claims listed are generally disputed. Differences in opinion can result from different definitions of "city" as well as "c ...
* Ancient towns in Saudi Arabia
* List of Ancient Settlements in the UAE
*List of largest metropolitan areas of the Middle East
This is a list of metropolitan areas in the Middle East, with their population according to different sources. The list includes metropolitan areas that have a population of over 1.5 million.
List
See also
*List of cities of the ancien ...
References
External links
Geospatial: Mapping Iraq's Ancient Cities
Ancient cities grew pretty much like modern ones, say scientists
(February 2015), ''
Christian Science Monitor
''The Christian Science Monitor'' (''CSM''), commonly known as ''The Monitor'', is a nonprofit news organization that publishes daily articles both in electronic format and a weekly print edition. It was founded in 1908 as a daily newspaper b ...
''
{{DEFAULTSORT:Cities Of The ancient Near East
Near East
The Near East () is a transcontinental region around the Eastern Mediterranean encompassing the historical Fertile Crescent, the Levant, Anatolia, Egypt, Mesopotamia, and coastal areas of the Arabian Peninsula. The term was invented in the 20th ...
Ancient Near East
Lists of cities
Ancient history-related lists