Circulatory System Of Gastropods on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
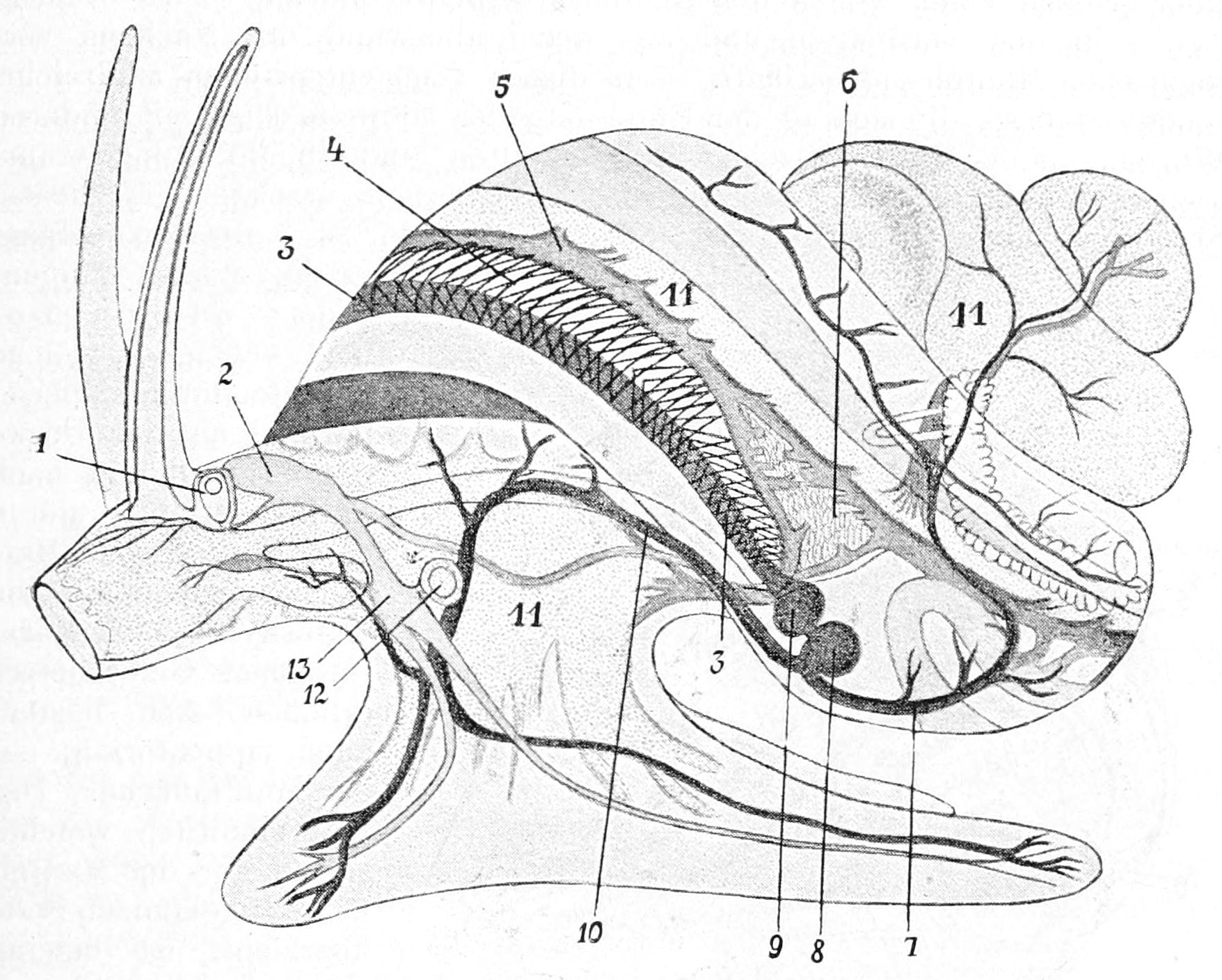 As in other
As in other
 As in other
As in other mollusc
Mollusca is a phylum of protostome, protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum ...
s, the circulatory system of gastropod
Gastropods (), commonly known as slugs and snails, belong to a large Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic class of invertebrates within the phylum Mollusca called Gastropoda ().
This class comprises snails and slugs from saltwater, freshwater, and fro ...
s is open
Open or OPEN may refer to:
Music
* Open (band), Australian pop/rock band
* The Open (band), English indie rock band
* ''Open'' (Blues Image album), 1969
* ''Open'' (Gerd Dudek, Buschi Niebergall, and Edward Vesala album), 1979
* ''Open'' (Go ...
, with the fluid, or haemolymph
Hemolymph, or haemolymph, is a fluid, similar to the blood in invertebrates, that circulates in the inside of the arthropod's body, remaining in direct contact with the animal's tissues. It is composed of a fluid plasma in which hemolymph ce ...
, flowing through sinuses
Paranasal sinuses are a group of four paired air-filled spaces that surround the nasal cavity. The maxillary sinuses are located under the eyes; the frontal sinuses are above the eyes; the ethmoidal sinuses are between the eyes and the sphenoi ...
and bathing the tissues directly. The haemolymph typically contains haemocyanin, and is blue in colour.
Circulation
Theheart
The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ found in humans and other animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. The heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrie ...
is muscular and located in the anterior part of the viscera
In a multicellular organism, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the hierarchy of life, an organ lies between tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type cells to a ...
l mass. In the great majority of species, it has two chambers; an auricle, which receives haemolymph from the gill
A gill () is a respiration organ, respiratory organ that many aquatic ecosystem, aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow r ...
or lung
The lungs are the primary Organ (biology), organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the Vertebral column, backbone on either side of the heart. Their ...
, and a ventricle, which pumps it into the aorta
The aorta ( ; : aortas or aortae) is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the Ventricle (heart), left ventricle of the heart, branching upwards immediately after, and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits at ...
. However, some primitive gastropods possess two gills, each supplying its own auricle, so that their heart has three chambers.
The aorta is relatively short, and soon divides into two main vessels, one supplying the visceral mass, and the other supplying the head and foot. In some groups, these two vessels arise directly from the heart, so that the animal may be said to have two aortas. These two vessels in turn divide into many finer vessels throughout the body, and deliver haemolymph to open arterial sinuses where it bathes and oxygenates the tissues.
De-oxygenated haemolymph drains into a large venous sinus within the head and foot, which contains the nephridium
The nephridium (: nephridia) is an invertebrate organ, found in pairs and performing a function similar to the vertebrate kidneys (which originated from the chordate nephridia). Nephridia remove metabolic wastes from an animal's body. Nephridia co ...
, an excretory organ with a function similar to that of the vertebrate kidney
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organ (anatomy), organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and rig ...
. From here it passes into vessels within the gill, or into the capillary network of the pulmonate
Pulmonata or pulmonates is an informal group (previously an order, and before that, a subclass) of snails and slugs characterized by the ability to breathe air, by virtue of having a pallial lung instead of a gill, or gills. The group inclu ...
lung, before returning to the heart.
In some genera, such as the large marine snail ''Busycon
''Busycon'' is a genus of very large edible sea snails in the subfamily Busyconinae. These snails are commonly known in the United States as ''whelks'' or ''Busycon whelks''. Less commonly they are loosely, and somewhat misleadingly, called "conc ...
'', the main anterior artery (which supplies the head and foot) includes an enlarged muscular region. This structure is effectively a secondary heart, and probably helps to maintain blood pressure in the vessels of the head.
Haemolymph
Because of the open circulatory system of gastropods and other molluscs, there is no clear distinction between theblood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells.
Blood is com ...
and the lymph
Lymph () is the fluid that flows through the lymphatic system, a system composed of lymph vessels (channels) and intervening lymph nodes whose function, like the venous system, is to return fluid from the tissues to be recirculated. At the ori ...
, or interstitial fluid. As a result, the circulatory fluid is commonly referred to as haemolymph
Hemolymph, or haemolymph, is a fluid, similar to the blood in invertebrates, that circulates in the inside of the arthropod's body, remaining in direct contact with the animal's tissues. It is composed of a fluid plasma in which hemolymph ce ...
, rather than blood.
The majority of gastropods have haemolymph containing the respiratory pigment haemocyanin. This is a copper-containing protein that helps to carry oxygen, and gives the haemolymph a pale blue colour. In the freshwater Planorbid snails, however, the haemocyanin is replaced by haemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin, Hb or Hgb) is a protein containing iron that facilitates the transportation of oxygen in red blood cells. Almost all vertebrates contain hemoglobin, with the sole exception of the fish family Channichthyidae. Hemoglobi ...
, and thus their haemolymph is red rather than blue. Some gastropods, such as the sea hare ''Aplysia
''Aplysia'' () is a genus of medium-sized to extremely large sea slugs, specifically sea hares, which are a kind of marine gastropod mollusk.
These benthic herbivorous creatures can become rather large compared with most other mollusks. They ...
'', appear to lack respiratory pigments altogether.
Regardless of whether they employ haemocyanin or haemoglobin, the pigments are dissolved directly in the serum
Serum may refer to:
Biology and pharmacology
*Serum (blood), plasma from which the clotting proteins have been removed
**Antiserum, blood serum with specific antibodies for passive immunity
*Serous fluid, any clear bodily fluid
Places
*Serum, Ind ...
, with no equivalent of the red blood cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), referred to as erythrocytes (, with -''cyte'' translated as 'cell' in modern usage) in academia and medical publishing, also known as red cells, erythroid cells, and rarely haematids, are the most common type of blood cel ...
s found in mammals. However, the haemolymph does contain amoebocyte
An amebocyte or amoebocyte () is a motile cell (moving like an amoeba) in the bodies of invertebrates including cnidaria, echinoderms, mollusca, molluscs, tunicates, sponges, and some chelicerata, chelicerates.
Moving by pseudopodia, amebocytes c ...
s, which may have a role in the immune system
The immune system is a network of biological systems that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to bacteria, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells, Parasitic worm, parasitic ...
.
See also
*Keyhole limpet hemocyanin
Keyhole limpet hemocyanin (KLH) is a large, multisubunit, oxygen-carrying, metalloprotein that is found in the hemolymph of the giant keyhole limpet, ''Megathura crenulata'', a species of keyhole limpet that lives off the coast of California, fr ...
References
* {{Gastropod anatomy Circulatory system Gastropod anatomy