Ciociaria on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Ciociaria () is the name commonly used, in modern times, for some impoverished territories southeast of Rome, without defined geographical limits. Starting from the Fascist period and the creation of the
Ciociaria () is the name commonly used, in modern times, for some impoverished territories southeast of Rome, without defined geographical limits. Starting from the Fascist period and the creation of the
 Even the local artisanal production, which has historical roots in the much older craftsmanship of
Even the local artisanal production, which has historical roots in the much older craftsmanship of
Two Women (La Ciociara) - premiered at San Francisco Opera - Composer: Marco Tutino
Accessed 9 December 2017 This further contributed to the spread of the term that is indeed often associated with these war crimes.
CiociariaTurismo
tourist organization
Keepers of a dying dialect: Italian immigrants in Sarnia, Ontario, still speak an ancient language
{{Authority control

 Ciociaria () is the name commonly used, in modern times, for some impoverished territories southeast of Rome, without defined geographical limits. Starting from the Fascist period and the creation of the
Ciociaria () is the name commonly used, in modern times, for some impoverished territories southeast of Rome, without defined geographical limits. Starting from the Fascist period and the creation of the province of Frosinone
The province of Frosinone () is a province in the Lazio region of Italy. Its capital is the city of Frosinone. It has an area of and a total population of 493,605 (2016). The province contains 91 ''comuni'' (: ''comune''), listed in the ...
, the same name was arbitrarily imposed by the local fascist organizations and then misused by the local press, by promotional associations and folkloristic events as a synonym for Frosinone and all the popular traditions of its territory.
The local dialect is referred to as ''campanino'' in old literature. It is merely a local variants of Central-Italian Latian but is improperly indicated as " ciociaro dialect", although the linguistic and scientific definition is Central-Northern Latian. In more recent times, the term ''Campagna Romana'', or Roman Campagna, a favorite subject of countless painters from all over Europe, has referred to the adjoining region to the north of ''Ciociaria'', but part of the Province of Rome
The province of Rome () was one of the five provinces that formed part of the Lazio region of Italy. It was established in 1870 and disestablished in 2014. It was essentially coterminous with the Rome metropolitan area. The city of Rome was t ...
.
Origin of the name
The term first appears in a map of thePapal States
The Papal States ( ; ; ), officially the State of the Church, were a conglomeration of territories on the Italian peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope from 756 to 1870. They were among the major states of Italy from the 8th c ...
, in which a land in ''Campagna e Marittima
The Campagna and Marittima Province (Latin ''Campaniæ Maritimæque Provincia'', Italian ''Provincia di Campagna e Marittima'') was one of the seven provinces of the Papal States from the 12th century to the end of the 18th.
The province was esta ...
'' province is named ''Ciociarìa''. The variant ''Cioceria'' has been used since the 18th century.
The name comes from the derogatory term, in Roman dialect
Romanesco () is one of the Central Italian dialects spoken in the Metropolitan City of Rome Capital, especially in the Rome, core city. It is linguistically close to Tuscan dialect, Tuscan and Italian language, Standard Italian, with some notable ...
applied to some poor shepherds, because of their footwear, called in Roman dialect '' ciocie''. These shoes, which were widespread among the poorest shepherds of much of Southern and Southeast Europe, are used today in the province of Frosinone only by folklore groups and for touristic initiatives.
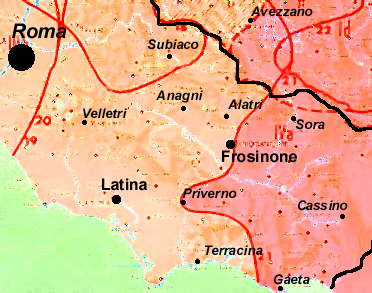
Geography
Since, until the Fascist era, there were no official publications that imposed the term on the territories of the current province of Frosinone, the term, however rare, was used during the nineteenth century in a rather varied way with respect to geographical areas. In 1861, Franco Mistrali applied the term for example to the brigands of Sabina and not of Lazio.Historical names
The correct geographic term for the northern area of the province of Frosinone is Valle del Sacco (or MiddleValle Latina
Valle Latina (English: "Latin Valley") is an Italian geographical and historical region that extends from the south of Rome to Cassino, corresponding to the eastern area of ancient Roman Latium.
The valley's principal cities are Frosinone, Cassi ...
(Latin Valley)). The area inhabited by the Hernici
The Hernici were an Italic tribe of ancient Italy, whose territory was in Latium between the Fucine Lake and the Sacco River (''Trerus''), bounded by the Volsci on the south, and by the Aequi and the Marsi on the north.
History
For many y ...
was known in Latin as ''ager Hernicus''.
Literature and clichés
Except for the fascist propaganda of the time, most scholars believe that the toponym Ciociaria was originally widespread only in Roman popular culture and among the intellectuals who disseminated its traditions, and therefore insignificant outside the borders of thePapal State
The Papal States ( ; ; ), officially the State of the Church, were a conglomeration of territories on the Italian peninsula under the direct Sovereignty, sovereign rule of the pope from 756 to 1870. They were among the major states of Italy fro ...
: the term does not appear in any document of the Kingdom of Naples
The Kingdom of Naples (; ; ), officially the Kingdom of Sicily, was a state that ruled the part of the Italian Peninsula south of the Papal States between 1282 and 1816. It was established by the War of the Sicilian Vespers (1282–1302). Until ...
or the Two Sicilies
The Kingdom of the Two Sicilies () was a kingdom in Southern Italy from 1816 to 1861 under the control of the House of Bourbon-Two Sicilies, a cadet branch of the Bourbons. The kingdom was the largest sovereign state by population and land are ...
to indicate the Liri Valley
The Valle del Liri (''Liri valley'') is a valley and a geographical region of southern Lazio and part of the larger Latin Valley, located in the province of Frosinone, crossed by the Liri river (as well as the Valle Roveto in Abruzzo, which is inc ...
or the territory of Fondi
Fondi (; Southern Laziale: ''Fùnn'') is a city and ''comune'' in the province of Latina, Lazio, central Italy, halfway between Rome and Naples. As of 2017, the city had a population of 39,800. The city has experienced steady population growth si ...
, nor is the adjective ciociaro used to designate a population or a culture in the Neapolitan state. From the second post-war period, however, the realist and neorealist literary ''topos'', the search for a common Christian Democratic political identity in southern Lazio and in part the suppression of the ecclesiastical province of Capua with the annexation of the dioceses of Monte Cassino
The Abbey of Monte Cassino (today usually spelled Montecassino) is a Catholic Church, Catholic, Benedictines, Benedictine monastery on a rocky hill about southeast of Rome, in the Valle Latina, Latin Valley. Located on the site of the ancient ...
, Aquino and Atina to the Roman ecclesiastical province, were the cultural factors that favored, in the common opinion, the spread of that point of view according to which this undefined and non-geographic term to the south reaches the Garigliano
The Garigliano () is a river in central Italy.
It forms at the confluence of the rivers Gari (also known as the Rapido) and Liri. Garigliano is actually a deformation of "Gari-Lirano" (which in Italian means something like "Gari from the Liri" ...
(including according to some even the ).
Folklore and handicraft
On the basis of the above, various local institutions periodically organize various folkloristic events that recall the aforementioned clichés with respect to the clothing, religious initiatives and traditions of the territories of the valle del Sacco, considering them as manifestations of a "''ciociaria'' tradition". These events include food fairs and music festivals, processions, performances of bands, palios and tournaments among the town's quarters. Even the local artisanal production, which has historical roots in the much older craftsmanship of
Even the local artisanal production, which has historical roots in the much older craftsmanship of Lazio
Lazio ( , ; ) or Latium ( , ; from Latium, the original Latin name, ) is one of the 20 Regions of Italy, administrative regions of Italy. Situated in the Central Italy, central peninsular section of the country, it has 5,714,882 inhabitants an ...
, Campania
Campania is an administrative Regions of Italy, region of Italy located in Southern Italy; most of it is in the south-western portion of the Italian Peninsula (with the Tyrrhenian Sea to its west), but it also includes the small Phlegraean Islan ...
and Abruzzo
Abruzzo (, ; ; , ''Abbrìzze'' or ''Abbrèzze'' ; ), historically also known as Abruzzi, is a Regions of Italy, region of Southern Italy with an area of 10,763 square km (4,156 sq mi) and a population of 1.3 million. It is divided into four ...
is often improperly associated by tourist organizations, promotional events or the press as part of this "''ciociara'' tradition". Among the best known objects in the artisanal production of the areas south east of Rome that are arbitrarily associated to this recent term there are copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
amphora
An amphora (; ; English ) is a type of container with a pointed bottom and characteristic shape and size which fit tightly (and therefore safely) against each other in storage rooms and packages, tied together with rope and delivered by land ...
s (called "conca"); wicker and "vinchio" (marshy grass that grows on the slopes of the Aurunci Mounts) woven in the shape of baskets; terracotta
Terracotta, also known as terra cotta or terra-cotta (; ; ), is a clay-based non-vitreous ceramic OED, "Terracotta""Terracotta" MFA Boston, "Cameo" database fired at relatively low temperatures. It is therefore a term used for earthenware obj ...
amphorae, called "cannate", terracotta jugs made in Aquino and Fiuggi
Fiuggi ( Central-Northern Latian dialect: ) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the province of Frosinone, in the Italian region of Latium. The town of Fiuggi became famous for its Acqua di Fiuggi (Fiuggi Water), which flows from its natural spr ...
; gold and coral
Corals are colonial marine invertebrates within the subphylum Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact Colony (biology), colonies of many identical individual polyp (zoology), polyps. Coral species include the important Coral ...
jewellery produced in Alatri
Alatri () is an Italian town and ''comune'' of the province of Frosinone in the region of Lazio, with c. 30,000 inhabitants. An ancient city of the Hernici,Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Hernici". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). it is kno ...
, Anagni
Anagni () is an ancient town and ''comune'' in the province of Frosinone, Lazio, in the hills east-southeast of Rome. It is a historical and artistic centre of the Latin Valley.
Geography Overview
Anagni still maintains the appearance of a s ...
, Fiuggi
Fiuggi ( Central-Northern Latian dialect: ) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the province of Frosinone, in the Italian region of Latium. The town of Fiuggi became famous for its Acqua di Fiuggi (Fiuggi Water), which flows from its natural spr ...
, Veroli
Veroli () is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Frosinone, Lazio, central Italy, in the Latin Valley.
History
Veroli (''Verulae'') became a Ancient Rome, Roman municipium in 90 BC. It became the seat of a bishopric in 743 AD, and was occupi ...
; works in copper and wrought iron; embroideries, like the embroidered towels and tablecloth
A tablecloth is a cloth used to cover a table. Some are mainly ornamental coverings, which may also help protect the table from scratches and stains. Other tablecloths are designed to be spread on a dining table before laying out tableware and ...
s of Veroli and Boville Ernica
Boville Ernica is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Frosinone, Lazio, Italy. It is located over the summit of a steep hill commanding the Liri, Cosa and Sacco valleys. It is one of I Borghi più belli d'Italia ("The most beautiful villages ...
and the religious vestments produced in Anagni
Anagni () is an ancient town and ''comune'' in the province of Frosinone, Lazio, in the hills east-southeast of Rome. It is a historical and artistic centre of the Latin Valley.
Geography Overview
Anagni still maintains the appearance of a s ...
.
Rapes after the battle of Monte Cassino
The day following theBattle of Monte Cassino
The Battle of Monte Cassino, also known as the Battle for Rome, was a series of four military assaults by the Allies of World War II, Allies against Nazi Germany, German forces in Kingdom of Italy, Italy during the Italian Campaign (World War ...
, '' Goumiers'' rampaged through the surrounding countryside committing mass rape
Rape is a type of sexual assault involving sexual intercourse, or other forms of sexual penetration, carried out against a person without consent. The act may be carried out by physical force, coercion, abuse of authority, or against a person ...
in Southern Lazio. Victims of such crimes became known in Italy as ', literally translatable as "Moroccaned". Alberto Moravia
Alberto Pincherle (; 28 November 1907 – 26 September 1990), known by his pseudonym Alberto Moravia ( , ), was an Italian novelist and journalist. His novels explored matters of modern sexuality, social alienation and existentialism. Moravia i ...
wrote the novel ''La ciociara
''Two Women'' ( , rough literal translation "The Woman from Ciociaria") is a 1960 war drama film directed by Vittorio De Sica from a screenplay he co-wrote with Cesare Zavattini, based on the 1957 novel of the same name by Alberto Moravia. Th ...
'' on the event, which was made into a successful 1960 movie directed by Vittorio de Sica
Vittorio De Sica ( , ; 7 July 1901 – 13 November 1974) was an Italian film director and actor, a leading figure in the neorealist movement.
Widely considered one of the most influential filmmakers in the history of cinema, four of the fil ...
starring Sophia Loren
Sofia Costanza Brigida Villani Scicolone (; born 20 September 1934), known professionally as Sophia Loren ( , ), is an Italian actress, active in her native country and the United States. With a career spanning over 70 years, she is one of the ...
and a 2015 opera by Marco Tutino.Accessed 9 December 2017 This further contributed to the spread of the term that is indeed often associated with these war crimes.
See also
* Ciociaria in cinematographyReferences
External links
CiociariaTurismo
tourist organization
Keepers of a dying dialect: Italian immigrants in Sarnia, Ontario, still speak an ancient language
{{Authority control