Cierva C.30A Autogiro on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Cierva C.30 is an
 The production model, called the C.30A by
The production model, called the C.30A by
 ;Argentina
*Cierva C.30A ''LV-FBL'' is on display at the
;Argentina
*Cierva C.30A ''LV-FBL'' is on display at the
Spanish reproduction maiden flight
{{RLM aircraft designations C30 Single-engined tractor autogyros 1930s British military utility aircraft 1930s British civil utility aircraft Aircraft first flown in 1933
autogyro
An autogyro (from Greek and , "self-turning"), gyroscope, gyrocopter or gyroplane, is a class of rotorcraft that uses an unpowered rotor in free autorotation to develop lift. A gyroplane "means a rotorcraft whose rotors are not engine-d ...
designed by Juan de la Cierva
Juan de la Cierva y Codorníu, 1st Count of la Cierva (; 21 September 1895 – 9 December 1936), was a Spanish civil engineer, pilot and a self-taught aeronautical engineer. His most famous accomplishment was the invention in 1920 of a rotorcr ...
and built under licence from the Cierva Autogiro Company
The Cierva Autogiro Company was a British firm established in 1926 to develop the autogyro.
The company was set up to further the designs of Juan de la Cierva, a Spanish engineer and pilot, with the financial backing of James George Weir, a Scot ...
by A V Roe & Co Ltd (Avro) as the Avro 671, Lioré-et-Olivier as the LeO C.301, and Focke-Wulf
Focke-Wulf Flugzeugbau AG () was a German manufacturer of civil and military aircraft before and during World War II. Many of the company's successful fighter aircraft designs were slight modifications of the Focke-Wulf Fw 190. It is one of the ...
.
Design and Development
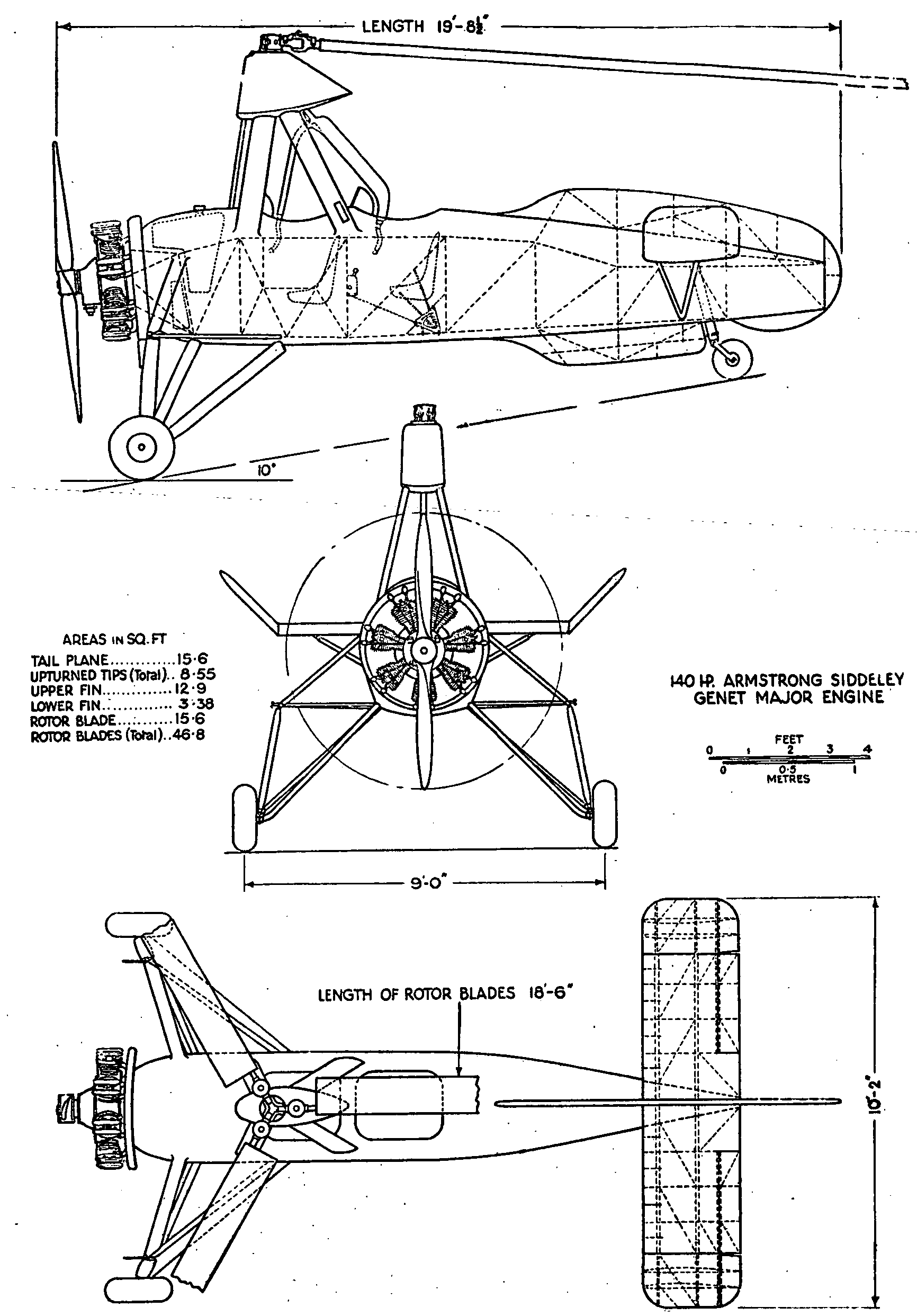
Before the experimental Cierva C.19 Mk V, autogyros had been controlled in the same way as fixed-wing aircraft, that is by deflecting the air flowing over moving surfaces such as ailerons, elevators and rudder. At the very low speeds encountered in autogyro flight, particularly during landing, these controls became ineffective. The experimental machine showed that the way forward was a tilting rotor hub fitted with a hanging stick extending to the pilot's cockpit with which he could change the rotor plane. This was known as direct control and was fitted to the C.30. The production variant, called C.30A in England, was preceded by several development machines. The first production design in the series was the C.30, a radial-engined autogyro with a three-blade, 37 ft (11.3 m) rotor mounted on an aft-leaning tripod, the control column extending into the rear of the two cockpits. The engine was the five-cylinder, 105 hp (78 kW) Armstrong Siddeley Genet Major I used in the C.19 series. The fabric-covered fuselage carried an unbraced tailplane, without elevators but with turned-up tips. The port side of the tailplane had an inverted aerofoil section to counter roll-axis torque produced by the propeller. As with most autogyros, a high vertical tail was precluded by the sagging resting rotor, so the dorsal fin was long and low, extending well aft of the tailplane like a fixed rudder and augmented by a ventral fin. The wide-track undercarriage had a pair of single, wire-braced legs and a small tail wheel was fitted. This model flew in April 1933. It was followed by four improved machines designated C.30P (P here for pre-production) which differed in having a four-legged pyramid rotor mounting and a reinforced undercarriage with three struts per side. The rotor could be folded rearwards for transport. The C.30P used the more powerful (140 hp, 104 kW) seven-cylinder Armstrong Siddeley Genet Major IA radial engine. The production model, called the C.30A by
The production model, called the C.30A by Avro
Avro (an initialism of the founder's name) was a British aircraft manufacturer. Its designs include the Avro 504, used as a trainer in the First World War, the Avro Lancaster, one of the pre-eminent bombers of the Second World War, and the d ...
, was built under licence in Britain, France and Germany and was similar to the C.30P. The main alteration was a further increase in undercarriage track with revised strutting, the uppermost leg having a pronounced knee with wire bracing. There was additional bracing to the tailplane
A tailplane, also known as a horizontal stabilizer, is a small lift (force), lifting surface located on the tail (empennage) behind the main lifting surfaces of a fixed-wing aircraft as well as other non-fixed-wing aircraft such as helicopters ...
and both it and the fin carried small movable trimming surfaces. Each licensee used nationally built engines and used slightly different names. In all, 143 production C.30s were built, making it by far the most numerous pre-war autogyro.
Between 1933 and 1936, de la Cierva used one C.30A (''G-ACWF'') to test his last contribution to autogyro development before his death in the crash of a KLM
KLM Royal Dutch Airlines, or simply KLM (an abbreviation for their official name Koninklijke Luchtvaart Maatschappij N.V. , ),
Douglas DC-2
The Douglas DC-2 is a retired 14-passenger, twin-engined airliner that was produced by the American company Douglas Aircraft Company starting in 1934. It competed with the Boeing 247. In 1935, Douglas produced a larger version called the DC-3 ...
airliner when taking off at Croydon Airfield in England on 9 December 1936. To enable the autogyro to take off without forward ground travel, Cierva produced the "autodynamic" rotor head, which allowed the rotor to be spun up by the engine in the usual way but to higher than take-off r.p.m at zero rotor incidence and then to reach operational positive pitch suddenly enough to jump some 20 ft (6 m) upwards.
At least one Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the Air force, air and space force of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies. It was formed towards the end of the World War I, First World War on 1 April 1918, on the merger of t ...
(RAF) C.30A was on floats as a Sea Rota in January 1935.
Production
;Avro Avro obtained the licence in 1934 and subsequently built 78 examples, under their model designation, fitted with an Armstrong Siddeley Genet Major IA (known in the RAF as the Civet 1) 7-cylinder radial engine producing . The first production C.30A was delivered in July 1934. ;Lioré-et-Olivier Twenty-five aircraft were built in France by Lioré-et-Olivier as the LeO C.301 with a 175 hp (130 kW) Salmson 9NE 9-cylinder radial engine. ;Focke-Wulf Forty aircraft were built in Germany as the Focke-Wulf Fw 30 Heuschrecke (Grasshopper) with a 140 hp (105 kW) Siemens Sh 14A 7-cylinder radial engine.Operational history
Of the 66 non-RAF aircraft built in the UK by Avro, 37 appeared at least for a while on the UK register. Some (maybe a dozen) were sold abroad, but others were flown by wealthy enthusiasts and by flying clubs who offered autogyro training. By the end of the decade, private flyers were moving back to the comforts and economies of fixed-wing aircraft and more C.30s moved abroad leaving the Autogyro Flying Club at London Air Park, Hanworth as the major UK user. 26 aircraft were directly exported by Avro. These went both to private owners and to foreign air forces who wish to investigate the autogyro's potential. In 1934, one Spanish Navy C.30 piloted by Cierva landed on the SpanishSeaplane tender
A seaplane tender is a boat or ship that supports the operation of seaplanes. Some of these vessels, known as seaplane carriers, could not only carry seaplanes but also provided all the facilities needed for their operation; these ships are rega ...
''Dedalo'' anchored in Valencia
Valencia ( , ), formally València (), is the capital of the Province of Valencia, province and Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Valencian Community, the same name in Spain. It is located on the banks of the Turia (r ...
harbour and later made a takeoff.
In September 1935, five members of the Lithuanian Aero Club flew C.30A in the "air train" together with the glider Schneider Grunau Baby
The Schneider Grunau Baby is a single-seat sailplane first built in Germany in 1931, with some 6,000 examples constructed in some 20 countries. It was relatively easy to build from plans, it flew well, and the aircraft was strong enough to hand ...
and the airplane de Havilland DH.60 Moth
The de Havilland DH.60 Moth is a 1920s British two-seat touring and training aircraft that was developed into a series of aircraft by the de Havilland Aircraft Company.
Development
The DH.60 was developed from the larger DH.51 biplane. T ...
over the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the ...
states: Kaunas
Kaunas (; ) is the second-largest city in Lithuania after Vilnius, the fourth largest List of cities in the Baltic states by population, city in the Baltic States and an important centre of Lithuanian economic, academic, and cultural life. Kaun ...
, Riga
Riga ( ) is the capital, Primate city, primate, and List of cities and towns in Latvia, largest city of Latvia. Home to 591,882 inhabitants (as of 2025), the city accounts for a third of Latvia's total population. The population of Riga Planni ...
, Tallinn
Tallinn is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Estonia, most populous city of Estonia. Situated on a Tallinn Bay, bay in north Estonia, on the shore of the Gulf of Finland of the Baltic Sea, it has a population of (as of 2025) and ...
, Helsinki
Helsinki () is the Capital city, capital and most populous List of cities and towns in Finland, city in Finland. It is on the shore of the Gulf of Finland and is the seat of southern Finland's Uusimaa region. About people live in the municipali ...
.
Twelve C.30As built by Avro for the Royal Air Force (RAF) entered service as the Avro 671 Rota Mk 1 ( Serials ''K4230'' to ''K4239'' and ''K4296'' & ''K4775''). The twelve were delivered between 1934 and 1935. They equipped the School of Army Co-operation
The School of Land/Air Warfare was a Royal Air Force school based at Old Sarum in Wiltshire. Its purpose was to encourage greater co-operation between officers in the air and those on the ground.
History
The School was originally established at ...
at RAF Old Sarum
Old Sarum Airfield is a grass strip airfield north-north-east of Salisbury, in Laverstock parish, Wiltshire, England.
The adjacent areas are a mix of vacant land, residential and industrial sites. Residential areas lie to the south and east ...
near Salisbury.
Many of the surviving civil aircraft were also taken into RAF service between 1939 and 1940. In 1940, they equipped 1448 Flt. at RAF Duxford
Duxford is a village in Cambridgeshire, England, about south of Cambridge. It is part of the Hundred Parishes area.
History
The village formed on the banks of the River Cam, a little below its emergence from the hills of north Essex. One of t ...
. Later they equipped 529 Sqn. at RAF Halton
Royal Air Force Halton, or more simply RAF Halton, is one of the largest Royal Air Force stations in the United Kingdom. It is located near the village of Halton near Wendover, Buckinghamshire. The site has been in use since the First World ...
on radar
Radar is a system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), direction ( azimuth and elevation angles), and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It is a radiodetermination method used to detect and track ...
calibration work: disbanded in October 1945, the twelve survivors were sold on to civilian owners.
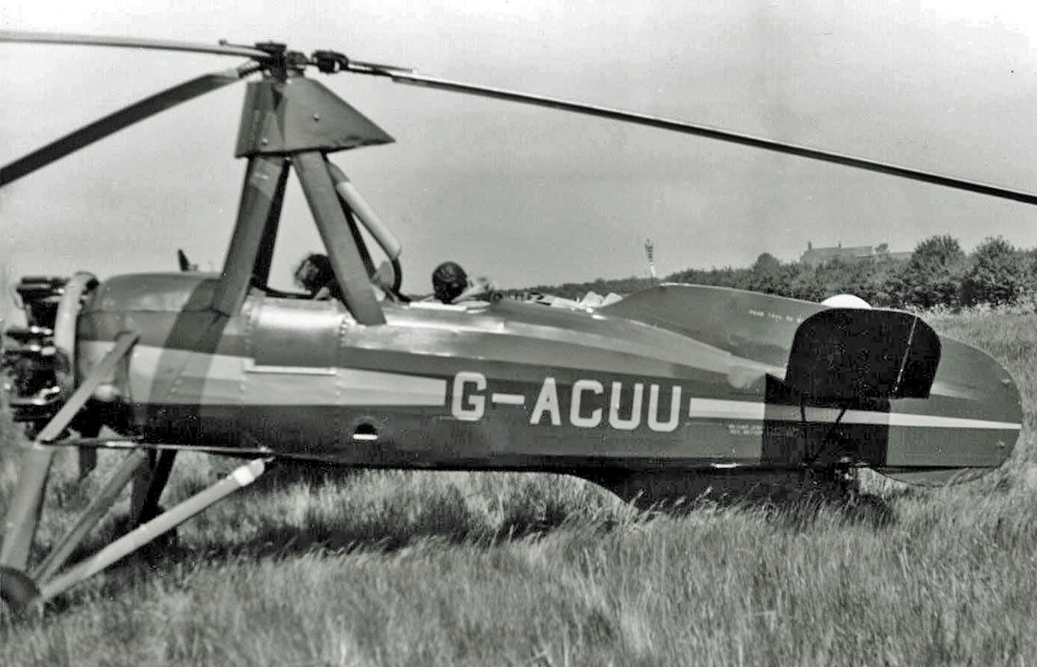
Most of these did not last long, although two were used for pilot rotary wing experience by Fairey in their Fairey Gyrodyne helicopter programme. Rota Towels kept one ex-RAF Rota airworthy ''G-AHTZ'' until an accident in 1958. ''G-ACUU'', the Imperial War Museum's C.30A exhibit at Duxford
Duxford is a village in Cambridgeshire, England, about south of Cambridge. It is part of the Hundred Parishes area.
History
The village formed on the banks of the River Cam, a little below its emergence from the hills of north Essex. One of t ...
had one of the longest active lives. It joined Air Service Training Ltd in 1934, was impressed (as Rota ''HM580'') in 1942, serving with 529 Squadron and returning to civil use by G.S. Baker based at Birmingham's Elmdon Airport with its original registration plus the nickname ''Billy Boy'' and was not withdrawn from use until 1960.
After several years of work at the Maestranza Aérea de Albacete, on 15 January 1998, a C.30 was flown again. It was piloted by Lieutenant Colonel Fernando Iglesia. After an accident in June 2000, which almost left the pilot without an arm, the aircraft was handed over to the Museum of Aeronautics and Astronautics, located at the Cuatro Vientos air base (Madrid).
Variants
;C.30: Powered by a Armstrong Siddeley Genet Major I radial piston engine. ;C.30P: Improved model, powered by a Armstrong Siddeley Genet Major IA radial piston engines ;C.30A: Main production model, powered by a Armstrong Siddeley Genet Major IA radial piston engine. ;Rota Mk I: RAF designation of the Cierva C.30A. ;Lioré et Olivier LeO C-30: 59 license built Cierva C.30, powered by Salmson 9Ne engines, were supplied to theFrench Air Force
The French Air and Space Force (, , ) is the air force, air and space force of the French Armed Forces. Formed in 1909 as the ("Aeronautical Service"), a service arm of the French Army, it became an independent military branch in 1934 as the Fr ...
and French Navy
The French Navy (, , ), informally (, ), is the Navy, maritime arm of the French Armed Forces and one of the four military service branches of History of France, France. It is among the largest and most powerful List of navies, naval forces i ...
. All LeO C-30 autogyros were destroyed or captured by German forces during the invasion of France in 1940.
;Lioré et Olivier LeO C-30S: Construction number 26 was completed as the sole C-30S.
;Lioré-et-Olivier LeO C-301: Improved C-30s with uprated Messier Messier may refer to:
People with the surname
*Ashley Messier (born 2002), Canadian ice hockey player
*Charles Messier (1730–1817), French astronomer
* Doug Messier (born 1936), Canadian ice hockey player and coach
* Éric Messier (born 1973), Ca ...
oleo-pneumatic shock absorbers, flotation devices to facilitate ditching at sea and tripod main rotor support. Six aircraft were delivered to the French Navy by early June 1940.
;Lioré et Olivier LeO C-302:Early autogyros suffered from relatively long take-off runs. To reduce the take-off length two C-301 aircraft were fitted with the equivalent of Cierva's "Jump" head allowing the aircraft to leap vertically after only a very short run. The C-302s were used extensively for testing rotor and undercarriage components but development was eventually abandoned in 1949/1950.
;Focke-Wulf C 30 Heuschrecke: (''Heuschrecke'' (Grasshopper)): 40 aircraft built, each with a Siemens Sh 14A 7-cylinder radial engine.
Aircraft on display
Museo Nacional de Aeronáutica de Argentina
The National Aeronautics Museum "Brigadier Edmundo Civati Bernasconi" () is an Argentine museum located in the city of Morón, Buenos Aires. Established in 1960, the museum is dedicated to the history of aviation, in particular the Argentine Air ...
.
;Australia
*Cierva C.30A ''VH-USR'' is on display at the Powerhouse Museum
The Powerhouse Museum, formerly known as the Museum of Applied Arts & Sciences (MAAS), is a collection of 4 museums in Sydney, owned by the Government of New South Wales. Powerhouse is a contemporary museum of applied arts and sciences, explori ...
, Sydney.
;France
*Leo C-302 ''F-BDAD'' is on display at the Musée de l'Air et de l'Espace
The Musée de l'air et de l'espace (, ) is a French aerospace museum, located at the south-eastern edge of Paris–Le Bourget Airport, north of Paris, and in the Communes of France, commune of Le Bourget. It was inaugurated in 1919 after a propo ...
, Paris.
;Italy
*Cierva C.30 ''I-CIER'' is on display at the Museo della Scienza e della Tecnologia "Leonardo da Vinci"
Museo Nazionale Scienza e Tecnologia Leonardo da Vinci in Milan, dedicated to painter and scientist Leonardo da Vinci, is the largest science and technology museum in Italy. It was opened on 15 February 1953 and inaugurated by prime minister of ...
, Milan.
;Netherlands
*Cierva C.30A ''SE-AFI'' is on display at the Aviodrome
The Nationaal Luchtvaart-Themapark Aviodrome (also known simply as Aviodrome) is a large aerospace museum in the Netherlands that has been located on Lelystad Airport since 2003. Previously the museum was located at Schiphol Airport.
.
;Spain
*Cierva C.30A ''XVU.1-1'' flyable reproduction with a Siemens engine is on display at Museo del Aire, Madrid.
;United Kingdom
*Avro Rota I ''K4232'' on display at the Royal Air Force Museum
The Royal Air Force Museum is a museum dedicated to the Royal Air Force in the United Kingdom. The museum is a non-departmental public body and is a registered charity. It has two public sites, Royal Air Force Museum London and Royal Air Fo ...
, London, England.
*Cierva C.30A ''AP506'' (smashed wreck) on display at the Helicopter Museum, Weston-super-Mare
Weston-super-Mare ( ) is a seaside town and civil parish in the North Somerset unitary district, in the county of Somerset, England. It lies by the Bristol Channel south-west of Bristol between Worlebury Hill and Bleadon Hill. Its population ...
, England.
*Cierva C.30A ''AP507'' on display at the Science Museum
A science museum is a museum devoted primarily to science. Older science museums tended to concentrate on static displays of objects related to natural history, paleontology, geology, Industry (manufacturing), industry and Outline of industrial ...
in London, England.
*Avro Rota I ''HM580'' the former ''G-ACUU'' is on display at the Imperial War Museum Duxford
Imperial War Museum Duxford, also known as IWM Duxford or simply Duxford, is a branch of the Imperial War Museum near Duxford in Cambridgeshire, England. Duxford, Britain's largest aviation museum, houses exhibits, including nearly 200 aircraf ...
, England.
;United States
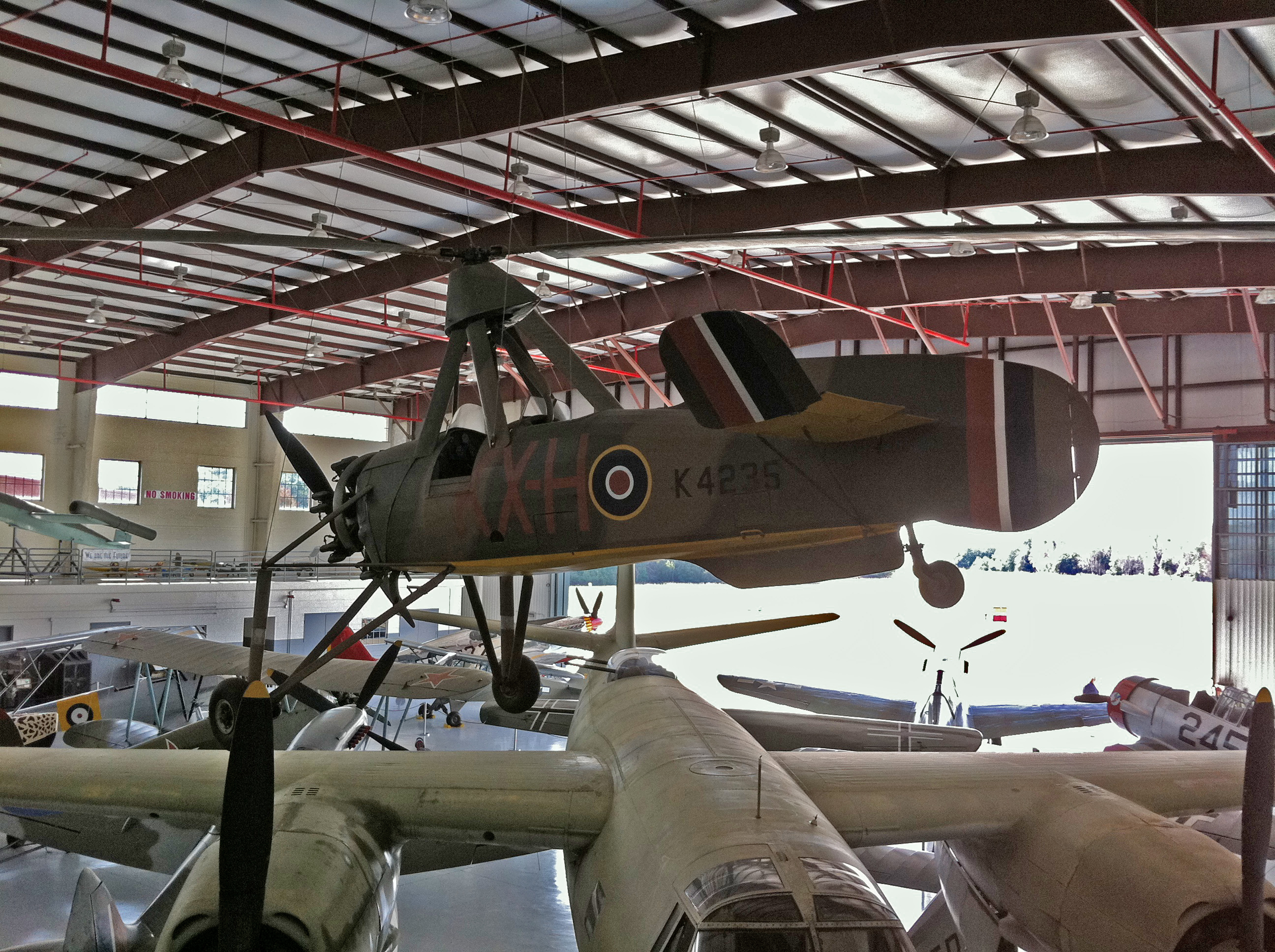
*Cierva C.30A ''K4235'' on display at Fantasy of Flight
Fantasy of Flight is an aviation museum in Polk City, Florida.
It opened in November 1995, to house Kermit Weeks' collection of aircraft that, until Hurricane Andrew damaged many in 1992, were housed at the Weeks Air Museum in Kendall-Tamiami E ...
, Polk City, Florida.
Military operators
; *Royal Danish Air Force
The Royal Danish Air Force () (RDAF) is the aerial warfare force of the Kingdom of Denmark and one of the four branches of the Danish Armed Forces. Initially being components of the Army and the Navy, it was made a separate service in 1950. I ...
;
*French Air Force
The French Air and Space Force (, , ) is the air force, air and space force of the French Armed Forces. Formed in 1909 as the ("Aeronautical Service"), a service arm of the French Army, it became an independent military branch in 1934 as the Fr ...
*French Naval Aviation
French Naval Aviation (often abbreviated in French to: (contraction of ), or , or more simply ) is the naval air arm of the French Navy. The long-form official designation is . Born as a fusion of aircraft carrier squadrons and the naval pat ...
;
*Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the Air force, air and space force of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies. It was formed towards the end of the World War I, First World War on 1 April 1918, on the merger of t ...
**No. 80 Squadron RAF
Number 80 Squadron is a squadron of the Royal Air Force. It was reformed on 15 April 2024 at Eglin Air Force Base, Florida, after the numberplate was awarded to the British team at the Australia, Canada and United Kingdom Reprogramming Laborato ...
** No. 529 Squadron RAF
Civil operators
; * Aero Club of Lithuania - single Avro-built C.30A, acquired in 1934Specifications (C.30A)

References
Notes
Bibliography
* Barratt, M. "Talkback". ''Air Enthusiast
''Air Enthusiast'' was a British, bi-monthly, aviation magazine, published by the Key Publishing group. Initially begun in 1974 as ''Air Enthusiast Quarterly'', the magazine was conceived as a historical adjunct to ''Air International'' magaz ...
'' No. 107, September/October 2003. p. 75.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
Spanish reproduction maiden flight
{{RLM aircraft designations C30 Single-engined tractor autogyros 1930s British military utility aircraft 1930s British civil utility aircraft Aircraft first flown in 1933