Chordal Style on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In music, homophony (;, Greek: ὁμόφωνος, ''homóphōnos'', from ὁμός, ''homós'', "same" and φωνή, ''phōnē'', "sound, tone") is a
In music, homophony (;, Greek: ὁμόφωνος, ''homóphōnos'', from ὁμός, ''homós'', "same" and φωνή, ''phōnē'', "sound, tone") is a
homophonic form of accompaniment/nowiki> have largely disappeared from usage and, rather than the traditional interdependence of melodic and chordal pitches sharing the same tonal basis, a clear distinction may exist between the pitch materials of the melody and harmony, commonly avoiding duplication. However, some traditional devices, such as repeated chords, are still used.
Melody dominated homophony in Chopin's Nocturne in E Op. 62 No. 2. The left hand (
 In music, homophony (;, Greek: ὁμόφωνος, ''homóphōnos'', from ὁμός, ''homós'', "same" and φωνή, ''phōnē'', "sound, tone") is a
In music, homophony (;, Greek: ὁμόφωνος, ''homóphōnos'', from ὁμός, ''homós'', "same" and φωνή, ''phōnē'', "sound, tone") is a texture
Texture may refer to:
Science and technology
* Image texture, the spatial arrangement of color or intensities in an image
* Surface texture, the smoothness, roughness, or bumpiness of the surface of an object
* Texture (roads), road surface c ...
in which a primary part
Part, parts or PART may refer to:
People
*Part (surname)
*Parts (surname)
Arts, entertainment, and media
*Part (music), a single strand or melody or harmony of music within a larger ensemble or a polyphonic musical composition
*Part (bibliograph ...
is supported by one or more additional strands that provide the harmony
In music, harmony is the concept of combining different sounds in order to create new, distinct musical ideas. Theories of harmony seek to describe or explain the effects created by distinct pitches or tones coinciding with one another; harm ...
. One melody predominates while the other parts play either single notes or an elaborate accompaniment. This differentiation of roles contrasts with equal-voice polyphony
Polyphony ( ) is a type of musical texture consisting of two or more simultaneous lines of independent melody, as opposed to a musical texture with just one voice ( monophony) or a texture with one dominant melodic voice accompanied by chord ...
(in which similar lines move with rhythmic and melodic independence to form an even texture) and monophony
In music, monophony is the simplest of texture (music), musical textures, consisting of a melody (or "tune"), typically sung by a single singer or played by a single instrument player (e.g., a flute player) without accompaniment, accompanying har ...
(in which all parts move in unison or octaves). Historically, homophony and its differentiated roles for parts emerged in tandem with tonality
Tonality is the arrangement of pitch (music), pitches and / or chord (music), chords of a musical work in a hierarchy of perceived ''relations'', ''stabilities'', ''attractions'', and ''directionality''.
In this hierarchy, the single pitch or ...
, which gave distinct harmonic functions to the soprano, bass and inner voices.
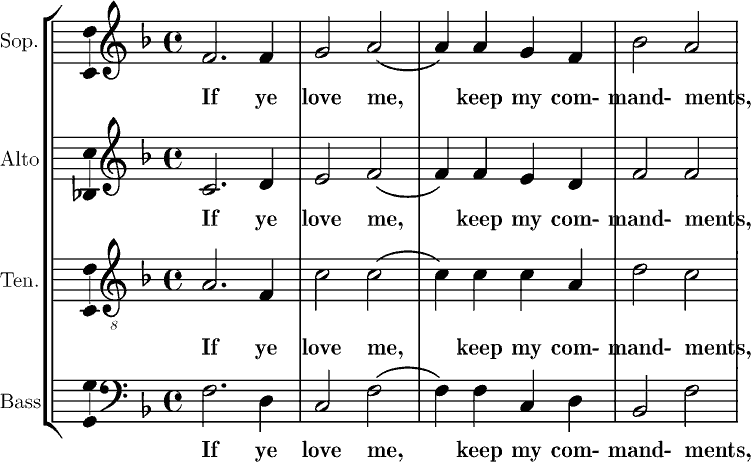
A homophonic texture may be homorhythm
In music, a homorhythm or homometer is a texture having a "similarity of rhythm in all parts"Griffiths, Paul (2005). ''The Penguin Companion to Classical Music'', p.375. . or "very similar rhythm" as would be used in simple hymn or chorale settin ...
ic, which means that all parts have the same rhythm. Chorale
A chorale is the name of several related musical forms originating in the music genre of the Lutheran chorale:
* Hymn tune of a Lutheran hymn (e.g. the melody of " Wachet auf, ruft uns die Stimme"), or a tune in a similar format (e.g. one o ...
texture is another variant of homophony. The most common type of homophony is melody-dominated homophony, in which one voice, often the highest, plays a distinct melody, and the accompanying voices work together to articulate an underlying harmony.Hyer, Brian. "Homophony", ''Grove Music Online
''The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians'' is an encyclopedic dictionary of music and musicians. Along with the German-language '' Die Musik in Geschichte und Gegenwart'', it is one of the largest reference works on the history and t ...
'', ed. L. Macy (accessed September 24, 2006) (Subscription required).
Initially, in Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece () was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity (), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically r ...
, homophony indicated music in which a single melody is performed by two or more voices in unison
Unison (stylised as UNISON) is a Great Britain, British trade union. Along with Unite the Union, Unite, Unison is one of the two largest trade unions in the United Kingdom, with over 1.2 million members who work predominantly in public servic ...
or octave
In music, an octave (: eighth) or perfect octave (sometimes called the diapason) is an interval between two notes, one having twice the frequency of vibration of the other. The octave relationship is a natural phenomenon that has been referr ...
s, i.e. monophony with multiple voices. Homophony as a term first appeared in English with Charles Burney
Charles Burney (7 April 1726 – 12 April 1814) was an English music historian, composer and musician. He was the father of the writers Frances Burney and Sarah Burney, of the explorer James Burney, and of Charles Burney, a classicis ...
in 1776, emphasizing the concord of harmonized melody.
History
European music
Homophony first appeared as one of the predominant textures inWestern classical music
Classical music generally refers to the art music of the Western world, considered to be #Relationship to other music traditions, distinct from Western folk music or popular music traditions. It is sometimes distinguished as Western classical mu ...
during the Baroque
The Baroque ( , , ) is a Western Style (visual arts), style of Baroque architecture, architecture, Baroque music, music, Baroque dance, dance, Baroque painting, painting, Baroque sculpture, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished from ...
period in the early 17th century, when composers began to commonly compose with vertical harmony in mind, the homophonic basso continuo
Basso continuo parts, almost universal in the Baroque era (1600–1750), provided the harmonic structure of the music by supplying a bassline and a chord progression. The phrase is often shortened to continuo, and the instrumentalists playing th ...
becoming a definitive feature of the style. In Western music, homophony may have originated in dance music, in which a simple and direct rhythmic style was needed for the prescribed bodily movements of individual dances. Homophony and polyphony coexisted in the 1600s and 1700s. Polyphony was the common melody during the Renaissance period. During the Baroque period, monophony became the new modern style. The choral arrangement of four voices (soprano
A soprano () is a type of classical singing voice and has the highest vocal range of all voice types. The soprano's vocal range (using scientific pitch notation) is from approximately middle C (C4) = 261 Hertz, Hz to A5 in Choir, choral ...
, alto
The musical term alto, meaning "high" in Italian (Latin: '' altus''), historically refers to the contrapuntal part higher than the tenor and its associated vocal range. In four-part voice leading alto is the second-highest part, sung in ch ...
, tenor
A tenor is a type of male singing voice whose vocal range lies between the countertenor and baritone voice types. It is the highest male chest voice type. Composers typically write music for this voice in the range from the second B below m ...
, and bass
Bass or Basses may refer to:
Fish
* Bass (fish), various saltwater and freshwater species
Wood
* Bass or basswood, the wood of the tilia americana tree
Music
* Bass (sound), describing low-frequency sound or one of several instruments in th ...
) has since become common in Western classical music. Homophony began by appearing in sacred music
Religious music (also sacred music) is a type of music that is performed or composed for religious use or through religious influence. It may overlap with ritual music, which is music, sacred or not, performed or composed for or as a ritual. Reli ...
, replacing polyphony and monophony as the dominant form, but spread to secular music, for which it is one of the standard forms today.
Composers known for their homophonic work during the Baroque period include Claudio Monteverdi, Antonio Vivaldi, George Frideric Handel, and Johann Sebastian Bach.
In 20th-century classical music
20th-century classical music is Western art music that was written between the years 1901 and 2000, inclusive. Musical style diverged during the 20th century as it never had previously, so this century was without a dominant style. Modernism, i ...
some of the "triad-oriented accompanimental figures such as the Alberti bass Jazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Its roots are in blues, ragtime, European harmony, African rhythmic rituals, spirituals, h ...
and other forms of modern popular music generally feature homophonic influences, following chord progression
In a musical composition, a chord progression or harmonic progression (informally chord changes, used as a plural, or simply changes) is a succession of chords. Chord progressions are the foundation of harmony in Western musical tradition from ...
s over which musicians play a melody or improvise.
African and Asian music
Homophony has appeared in several non-Western cultures, perhaps particularly in regions where communal vocal music has been cultivated. When explorerVasco da Gama
Vasco da Gama ( , ; – 24 December 1524), was a Portuguese explorer and nobleman who was the Portuguese discovery of the sea route to India, first European to reach India by sea.
Da Gama's first voyage (1497–1499) was the first to link ...
landed in West Africa in 1497, he referred to the music he heard there as being in "sweet harmony".Annan Mensah, Atta. "The Polyphony of Gyil-gu, Kudzo and Awutu Sakumo," '' Journal of the International Folk Music Council'', vol. 19. (1967), pp. 75–79. While the concept of harmony in that time was not necessarily the same as the concept of homophony as understood by modern scholars, it is generally accepted that homophonic voice harmonies were commonplace in African music
The continent of Africa is vast and its music is diverse, with different regions and nations having many distinct musical traditions. African music includes the genres like makwaya, highlife, mbube, township music, jùjú, fuji, jaiva ...
for centuries before contact with Europeans and is common in African music today. Singers normally harmonize voices in homophonic parallelism moving in parallel
Parallel may refer to:
Mathematics
* Parallel (geometry), two lines in the Euclidean plane which never intersect
* Parallel (operator), mathematical operation named after the composition of electrical resistance in parallel circuits
Science a ...
thirds or fourths. This type of harmonic model is also implemented in instrumental music where voices are stacked in thirds or fourths. Homophonic Parallelism is not restricted to thirds and fourths, however all harmonic material adheres to the scalar system the particular tune or song is based on. The use of harmony in sixths is common in areas where a hexatonic scale system is used . For instance, the Fang
A fang is a long, pointed tooth. In mammals, a fang is a modified maxillary tooth, used for biting and tearing flesh. In snakes, it is a specialized tooth that is associated with a venom gland (see snake venom). Spiders also have external fangs, ...
people of Gabon
Gabon ( ; ), officially the Gabonese Republic (), is a country on the Atlantic coast of Central Africa, on the equator, bordered by Equatorial Guinea to the northwest, Cameroon to the north, the Republic of the Congo to the east and south, and ...
use homophony in their music.
In eastern Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, ...
(i.e. in the music of the Toraja
The Torajan are an ethnic group indigenous people, indigenous to a mountainous region of South Sulawesi, Indonesia. Their population is approximately 1,100,000, of whom 450,000 live in the List of regencies and cities of Indonesia, regency of T ...
in South Sulawesi
South Sulawesi () is a Provinces of Indonesia, province in the South Peninsula, Sulawesi, southern peninsula of Sulawesi, Indonesia. The Selayar Islands archipelago to the south of Sulawesi is also part of the province. The capital and largest ci ...
, in Flores
Flores is one of the Lesser Sunda Islands, a group of islands in the eastern half of Indonesia. Administratively, it forms the largest island in the East Nusa Tenggara Province. The area is 14,250 km2. Including Komodo and Rinca islands ...
, in East Kalimantan
East Kalimantan (Indonesian language, Indonesian: ) is a Provinces of Indonesia, province of Indonesia. Its territory comprises the eastern portion of Borneo/Kalimantan. It had a population of about 3.03 million at the 2010 census (within the cu ...
and in North Sulawesi
North Sulawesi () is a Provinces of Indonesia, province of Indonesia. It is mainly located on the Minahasa Peninsula of the island of Sulawesi, south of the Philippines and southeast of Sabah, Malaysia, but also includes various small archipel ...
), two-part harmonies are common, usually in intervals of thirds, fourths or fifths. Additionally, Chinese music
The music of China consists of many distinct traditions, often specifically originating with one of the country's various ethnic groups. It is produced within and without the country, involving either people of Chinese origin, the use of tradit ...
is generally thought to be homophonic, since instruments typically provide accompaniment in parallel fourths and fifths and often double the voice in vocal music, heterophony
In music, heterophony is a type of texture characterized by the simultaneous variation of a single melodic line. Such a texture can be regarded as a kind of complex monophony in which there is only one basic melody, but realized at the same time ...
also being common in China.
Melody-dominated homophony
In melody-dominated homophony, accompanying voices provide chordal support for the lead voice, which assumes the melody. Somepopular music
Popular music is music with wide appeal that is typically distributed to large audiences through the music industry. These forms and styles can be enjoyed and performed by people with little or no musical training.Popular Music. (2015). ''Fun ...
today might be considered melody-dominated homophony, voice typically taking on the lead role, while instruments like piano, guitar and bass guitar normally accompany the voice. In many cases, instruments also take on the lead role, and often the role switches between parts, voice taking the lead during a verse and instruments subsequently taking solos, during which the other instruments provide chordal support.
Monody
In music, monody refers to a solo vocal style distinguished by having a single melody, melodic line and instrumental accompaniment. Although such music is found in various cultures throughout history, the term is specifically applied to Italy, ...
is similar to melody-dominated homophony in that one voice becomes the melody, while another voice assumes the underlying harmony. Monody, however, is characterized by a single voice with instrumental accompaniment, whereas melody-dominated homophony refers to a broader category of homophonic music, which includes works for multiple voices, not just works for solo voice, as was the tradition with early 17th-century Italian monody.Nigel Fortune
Nigel Cameron Fortune (5 December 1924 – 10 April 2009) was an English musicologist and political activist. Along with Thurston Dart, Oliver Neighbour and Stanley Sadie he was one of Britain's leading musicologists of the post-World War II ...
and Tim Carter. "Monody", ''Grove Music Online'', ed. L. Macy (accessed September 24, 2006) (Subscription required)
:bass clef
A clef (from French: 'key') is a musical symbol used to indicate which notes are represented by the lines and spaces on a musical staff. Placing a clef on a staff assigns a particular pitch to one of the five lines or four spaces, whi ...
) provides chordal support for the melody played by the right hand (treble clef).
See also
*Counterpoint
In music theory, counterpoint is the relationship of two or more simultaneous musical lines (also called voices) that are harmonically dependent on each other, yet independent in rhythm and melodic contour. The term originates from the Latin ...
References
{{Texture (music) Musical texture Harmony fr:Homophonie#Musique