Chord Substitution on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
 Chord quality alteration is when the quality of a chord is changed, and the new chord of similar root and construction, but with one pitch different, is substituted for the original chord, for example the minor sixth for the major seventh, or the major seventh for the minor.
Chord quality alteration is when the quality of a chord is changed, and the new chord of similar root and construction, but with one pitch different, is substituted for the original chord, for example the minor sixth for the major seventh, or the major seventh for the minor.
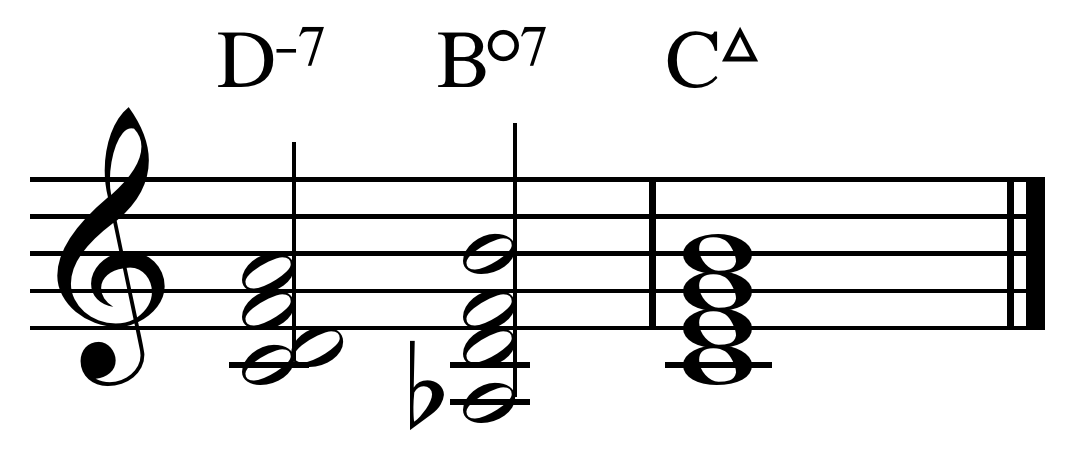
 The ''
The ''
 In a ''
In a ''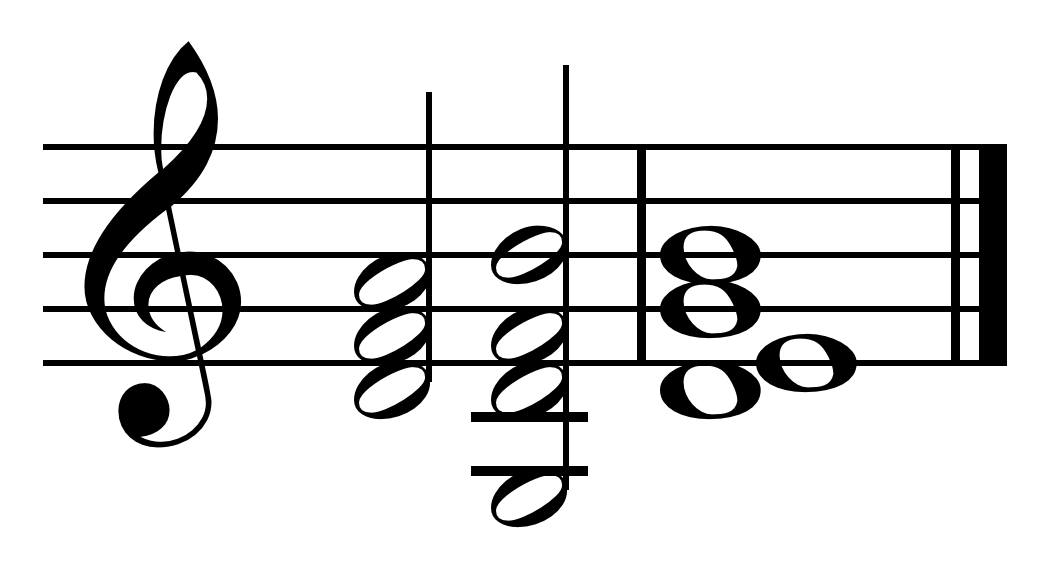 Tonic substitution is the use of chords that sound similar to the tonic chord (or I chord) in place of the tonic. In major keys, the chords iii and vi are often substituted for the I chord, to add interest. In the key of C major, the I major 7 chord is "C, E, G, B," the iii chord ("III–7") is E minor 7 ("E, G, B, D") and the vi minor 7 chord is A minor 7 ("A, C, E, G"). Both of the tonic substitute chords use notes from the tonic chord, which means that they usually support a melody originally designed for the tonic (I) chord.
Tonic substitution is the use of chords that sound similar to the tonic chord (or I chord) in place of the tonic. In major keys, the chords iii and vi are often substituted for the I chord, to add interest. In the key of C major, the I major 7 chord is "C, E, G, B," the iii chord ("III–7") is E minor 7 ("E, G, B, D") and the vi minor 7 chord is A minor 7 ("A, C, E, G"). Both of the tonic substitute chords use notes from the tonic chord, which means that they usually support a melody originally designed for the tonic (I) chord.
 The relative major/minor substitution shares two common tones and is so called because it involves the relation between major and minor keys with the same key signatures, such as C major and A minor.
The
The relative major/minor substitution shares two common tones and is so called because it involves the relation between major and minor keys with the same key signatures, such as C major and A minor.
The  The chord a minor third above, VII7, may be substituted for the dominant, and may be preceded by its ii: iv7.Richard Lawn, Jeffrey L. Hellmer (1996). ''Jazz: Theory and Practice'', p. 124. . Due to common use the two chords of the backdoor progression (IV7-VII7) may be substituted for the dominant chord. In C major the dominant would be G7: GB''DF'', sharing two common tones with B7: B''DF''A. A and F serve as upper leading-tones back to G and E, respectively, rather than B and F serving as the lower and upper leading-tones to C and E.
The chord a minor third above, VII7, may be substituted for the dominant, and may be preceded by its ii: iv7.Richard Lawn, Jeffrey L. Hellmer (1996). ''Jazz: Theory and Practice'', p. 124. . Due to common use the two chords of the backdoor progression (IV7-VII7) may be substituted for the dominant chord. In C major the dominant would be G7: GB''DF'', sharing two common tones with B7: B''DF''A. A and F serve as upper leading-tones back to G and E, respectively, rather than B and F serving as the lower and upper leading-tones to C and E.
 In
In music theory
Music theory is the study of theoretical frameworks for understanding the practices and possibilities of music. ''The Oxford Companion to Music'' describes three interrelated uses of the term "music theory": The first is the "Elements of music, ...
, chord substitution is the technique of using a chord in place of another in a progression of chords, or a chord progression
In a musical composition, a chord progression or harmonic progression (informally chord changes, used as a plural, or simply changes) is a succession of chords. Chord progressions are the foundation of harmony in Western musical tradition from ...
. Much of the European classical repertoire and the vast majority of blues
Blues is a music genre and musical form that originated among African Americans in the Deep South of the United States around the 1860s. Blues has incorporated spiritual (music), spirituals, work songs, field hollers, Ring shout, shouts, cha ...
, jazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Its roots are in blues, ragtime, European harmony, African rhythmic rituals, spirituals, h ...
and rock music
Rock is a Music genre, genre of popular music that originated in the United States as "rock and roll" in the late 1940s and early 1950s, developing into a range of styles from the mid-1960s, primarily in the United States and the United Kingdo ...
songs are based on chord progressions. "A chord substitution occurs when a chord is replaced by another that is made to function like the original. Usually substituted chords possess two pitches in common with the triad that they are replacing."
A chord progression may be repeated to form a song or tune. Composers, songwriters and arrangers have developed a number of ways to add variety to a repeated chord progression. There are many ways to add variety to music, including changing the dynamics (loudness and softness).
Use in classical music
In J. S. Bach's ''St Matthew Passion
The ''St Matthew Passion'' (), BWV 244, is a '' Passion'', a sacred oratorio written by Johann Sebastian Bach in 1727 for solo voices, double choir and double orchestra, with libretto by Picander. It sets the 26th and 27th chapters of th ...
'', the chorale
A chorale is the name of several related musical forms originating in the music genre of the Lutheran chorale:
* Hymn tune of a Lutheran hymn (e.g. the melody of " Wachet auf, ruft uns die Stimme"), or a tune in a similar format (e.g. one o ...
" Herzliebster Jesu" makes its first appearance in a straightforward harmonisation:
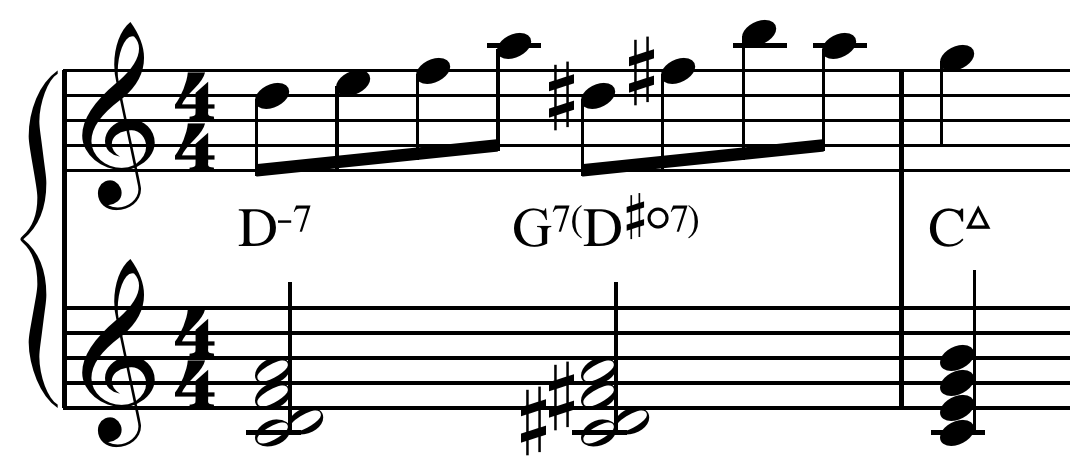
Later, as the Passion Story draws towards its sombre conclusion, we find "a more chromatic and emotional setting of the melody" that passes through "no less than ten chords with grinding chromatic
Diatonic and chromatic are terms in music theory that are used to characterize scales. The terms are also applied to musical instruments, intervals, chords, notes, musical styles, and kinds of harmony. They are very often used as a pair, es ...
steps in the bass":
The well-known theme of the second movement of Joseph Haydn
Franz Joseph Haydn ( ; ; 31 March 173231 May 1809) was an Austrian composer of the Classical period (music), Classical period. He was instrumental in the development of chamber music such as the string quartet and piano trio. His contributions ...
's String Quartet, Op. 76 No. 3 is harmonized simply at the start:
Haydn later "reharmonizes the theme". Hans Keller calls this "the fullest and richest statement" of the famous melody: "In the second bar, for instance, there even is a turn to the relative minor":
The diminished triad
In music theory, a diminished triad is a triad (music), triad consisting of two minor thirds above the root (chord), root. It is a Minor chord, minor triad with a lowered (flat (music), flattened) Fifth (chord), fifth. When using Chord names and ...
can be used to substitute for the dominant seventh
Domination or dominant may refer to:
Society
* World domination, structure where one dominant power governs the planet
* Colonialism in which one group (usually a nation) invades another region for material gain or to eliminate competition
* Ch ...
chord. In major scales
Major most commonly refers to:
* Major (rank), a military rank
* Academic major, an academic discipline to which an undergraduate student formally commits
* People named Major, including given names, surnames, nicknames
* Major and minor in music ...
, a diminished triad occurs only on the seventh scale degree
In music theory, the scale degree is the position of a particular note on a scale relative to the tonic—the first and main note of the scale from which each octave is assumed to begin. Degrees are useful for indicating the size of intervals ...
. For instance, in the key of C, this is a B diminished triad (B, D, F). Since the triad is built on the seventh scale degree, it is also called the ''leading-tone triad
In music theory, a leading tone (also called subsemitone or leading note in the UK) is a note or pitch which resolves or "leads" to a note one semitone higher or lower, being a lower and upper leading tone, respectively. Typically, leading to ...
''. This chord has a dominant function. Unlike the dominant triad or dominant seventh
Domination or dominant may refer to:
Society
* World domination, structure where one dominant power governs the planet
* Colonialism in which one group (usually a nation) invades another region for material gain or to eliminate competition
* Ch ...
, the leading-tone triad functions as a prolongation
In music theory, prolongation is the process in tonality, tonal music through which a pitch (music), pitch, interval (music), interval, or triad (music), consonant triad is considered to govern spans of music when not physically sounding. It is a ...
al chord rather than a structural chord since the strong root motion by fifth is absent.
Use in blues, jazz and rock music
Jazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Its roots are in blues, ragtime, European harmony, African rhythmic rituals, spirituals, h ...
musicians
A musician is someone who Composer, composes, Conducting, conducts, or Performing arts#Performers, performs music. According to the United States Employment Service, "musician" is a general Terminology, term used to designate a person who fol ...
often substitute chords in the original progression to create variety and add interest to a piece.
The substitute chord must have some harmonic
In physics, acoustics, and telecommunications, a harmonic is a sinusoidal wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the ''fundamental frequency'' of a periodic signal. The fundamental frequency is also called the ''1st har ...
quality and degree of function
Function or functionality may refer to:
Computing
* Function key, a type of key on computer keyboards
* Function model, a structured representation of processes in a system
* Function object or functor or functionoid, a concept of object-orie ...
in common with the original chord, and often only differs by one or two note
Note, notes, or NOTE may refer to:
Music and entertainment
* Musical note, a pitched sound (or a symbol for a sound) in music
* ''Notes'' (album), a 1987 album by Paul Bley and Paul Motian
* ''Notes'', a common (yet unofficial) shortened versi ...
s. Scott DeVeaux describes a "penchant in modern jazz for harmonic substitution."
One simple type of chord substitution is to replace a given chord with a chord that has the same function. Thus, in the simple chord progression I–ii–V–I, which in the key of C major would be the chords C Major–D minor–G Major–C Major, a musician could replace the I chords with "tonic substitutes". The most widely used substitutes are iii and vi (in a Major key), which in this case would be the chords "E minor" and "A minor".
This simple chord progression with tonic substitutes could become iii–ii–V–vi or, with chord names, "E minor–D minor–G Major–A minor". Given the overlap in notes between the original tonic chords and the chord substitutes (for example, C major is the notes "C, E, and G", and "E minor" is the notes "E, G and B"), the melody is likely to be supported by the new chords. The musician typically applies a sense of the musical style and harmonic suitability to determine if the chord substitution works with the melody.
There are also subdominant substitutes and dominant substitutes. For subdominant chords, in the key of C major, in the chord progression C major/F major/G7/C major (a simple I /IV/V7/I progression), the notes of the subdominant chord, F major, are "F, A, and C". As such, a performer or arranger who wished to add variety to the song could try using a chord substitution for a repetition of this progression. One simple chord substitute for IV is the "ii" chord, a minor chord built on the second scale degree. In the key of C major, the "ii" chord is "D minor", which is the notes "D, F, and A". As there are two shared notes between the IV and "ii" chords, a melody that works well over IV is likely to be supported by the "ii" chord.
Types
The ii–V substitution is when a chord or each chord in a progression is preceded by itssupertonic
In music, the supertonic is the second degree () of a diatonic scale, one whole step above the tonic. In the movable do solfège system, the supertonic note is sung as ''re''.
The triad built on the supertonic note is called the supertonic ...
(ii7) and dominant (V7), or simply its dominant. For example, a C major chord would be preceded by Dm7 and G7. Since secondary dominant
A secondary chord is an analytical label for a specific harmonic device that is prevalent in the tonal idiom of Western music beginning in the common practice period: the use of diatonic functions for tonicization.
Secondary chords are a ...
chords are often inserted between the chords of a progression rather than replacing one, this may be considered as 'addition' rather than 'substitution'.
 Chord quality alteration is when the quality of a chord is changed, and the new chord of similar root and construction, but with one pitch different, is substituted for the original chord, for example the minor sixth for the major seventh, or the major seventh for the minor.
Chord quality alteration is when the quality of a chord is changed, and the new chord of similar root and construction, but with one pitch different, is substituted for the original chord, for example the minor sixth for the major seventh, or the major seventh for the minor.

 The ''
The ''diminished seventh chord
The diminished seventh chord is a four-note chord (a seventh chord) composed of a Root (chord), root note, together with a minor third, a diminished fifth, and a diminished seventh above the root: (1, 3, 5, 7). For example, the dim ...
'' is often used in place of a dominant 7th chord. In the key of A Major the V chord, E dominant 7th (which is made up the notes E, G, B, and D) can be replaced with a G diminished seventh chord (G, B, D, F). If the diminished seventh chord (G) is followed by the I chord (A), this creates chromatic
Diatonic and chromatic are terms in music theory that are used to characterize scales. The terms are also applied to musical instruments, intervals, chords, notes, musical styles, and kinds of harmony. They are very often used as a pair, es ...
( stepwise semitonal) root
In vascular plants, the roots are the plant organ, organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often bel ...
movement, which can add musical interest in a song mainly constructed around the interval of the fourth or fifth. The diminished seventh chord
The diminished seventh chord is a four-note chord (a seventh chord) composed of a Root (chord), root note, together with a minor third, a diminished fifth, and a diminished seventh above the root: (1, 3, 5, 7). For example, the dim ...
on the sharpened second
The second (symbol: s) is a unit of time derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes, and finally to 60 seconds each (24 × 60 × 60 = 86400). The current and formal definition in the International System of U ...
scale degree, II7, may be used as a substitute dominant, Coker, Jerry (1997). ''Elements of the Jazz Language for the Developing Improvisor'', p. 82. . for example in C: II7 = D–F–A–C ↔ B–D–F–A = VII7.

 In a ''
In a ''tritone substitution
The tritone substitution is a common chord substitution found in both jazz and classical music. Where jazz is concerned, it was the precursor to more complex substitution patterns like Coltrane changes. Tritone substitutions are sometimes used ...
'', the substitute chord only differs slightly from the original chord. If the original chord in a song is G7 (G, B, D, F), the tritone substitution would be D7 (D, F, A, C). Note that the 3rd and 7th notes of the G7 chord are found in the D7 chord (albeit with a change of role
A role (also rôle or social role) is a set of connected behaviors, rights, obligations, beliefs, and norms as conceptualized by people in a social situation. It is an
expected or free or continuously changing behavior and may have a given indi ...
). The tritone substitution is widely used for V7 chords in the popular jazz chord progression "ii-V-I". In the key of C, this progression is "d minor, G7, C Major". With tritone substitution, this progression would become "d minor, D7, C Major," which contains chromatic root movement. When performed by the bass player, this chromatic root movement creates a smooth-sounding progression. "Tritone substitutions and altered dominants are nearly identical...Good improvisers will liberally sprinkle their solos with both devices. A simple comparison of the notes generally used with the given chord otationand the notes used in tri-tone substitution or altered dominants will reveal a rather stunning contrast, and could cause the unknowledgeable analyzer to suspect errors. ...(the distinction between the two ri-tone substitution and altered dominantis usually a moot point).".Coker (1997), p. 81.
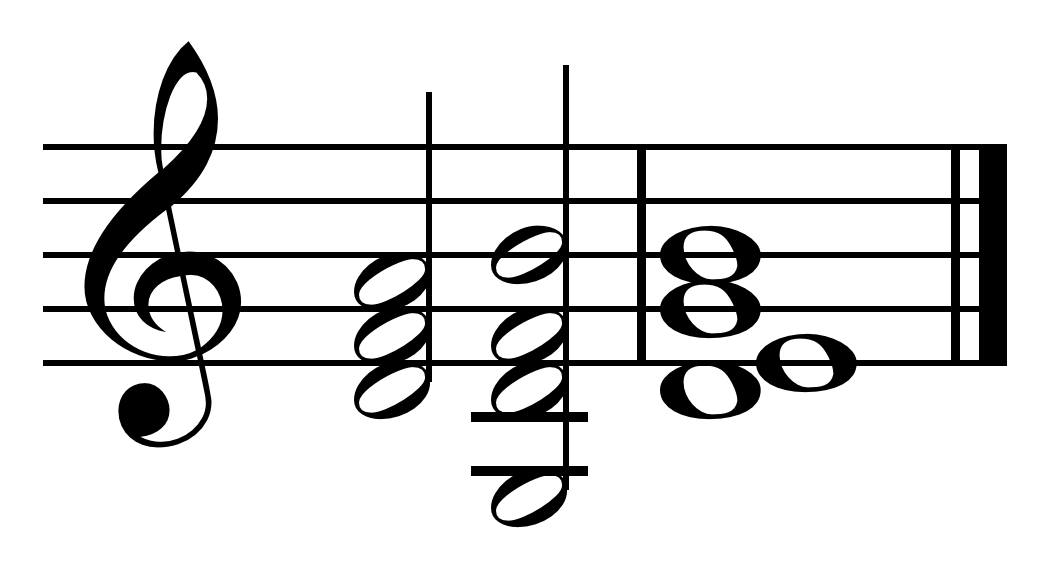 Tonic substitution is the use of chords that sound similar to the tonic chord (or I chord) in place of the tonic. In major keys, the chords iii and vi are often substituted for the I chord, to add interest. In the key of C major, the I major 7 chord is "C, E, G, B," the iii chord ("III–7") is E minor 7 ("E, G, B, D") and the vi minor 7 chord is A minor 7 ("A, C, E, G"). Both of the tonic substitute chords use notes from the tonic chord, which means that they usually support a melody originally designed for the tonic (I) chord.
Tonic substitution is the use of chords that sound similar to the tonic chord (or I chord) in place of the tonic. In major keys, the chords iii and vi are often substituted for the I chord, to add interest. In the key of C major, the I major 7 chord is "C, E, G, B," the iii chord ("III–7") is E minor 7 ("E, G, B, D") and the vi minor 7 chord is A minor 7 ("A, C, E, G"). Both of the tonic substitute chords use notes from the tonic chord, which means that they usually support a melody originally designed for the tonic (I) chord.
 The relative major/minor substitution shares two common tones and is so called because it involves the relation between major and minor keys with the same key signatures, such as C major and A minor.
The
The relative major/minor substitution shares two common tones and is so called because it involves the relation between major and minor keys with the same key signatures, such as C major and A minor.
The augmented triad
An augmented triad is a chord, made up of two major thirds (an augmented fifth). The term ''augmented triad'' arises from an augmented triad being considered a major chord whose top note (fifth) is raised. When using popular-music symbols, i ...
on the fifth scale degree may be used as a substitute dominant, and may also be considered as III+, for example in C: V+ = G–B–D, III+ = E–G–B, and since in every key: D = E.
 The chord a minor third above, VII7, may be substituted for the dominant, and may be preceded by its ii: iv7.Richard Lawn, Jeffrey L. Hellmer (1996). ''Jazz: Theory and Practice'', p. 124. . Due to common use the two chords of the backdoor progression (IV7-VII7) may be substituted for the dominant chord. In C major the dominant would be G7: GB''DF'', sharing two common tones with B7: B''DF''A. A and F serve as upper leading-tones back to G and E, respectively, rather than B and F serving as the lower and upper leading-tones to C and E.
The chord a minor third above, VII7, may be substituted for the dominant, and may be preceded by its ii: iv7.Richard Lawn, Jeffrey L. Hellmer (1996). ''Jazz: Theory and Practice'', p. 124. . Due to common use the two chords of the backdoor progression (IV7-VII7) may be substituted for the dominant chord. In C major the dominant would be G7: GB''DF'', sharing two common tones with B7: B''DF''A. A and F serve as upper leading-tones back to G and E, respectively, rather than B and F serving as the lower and upper leading-tones to C and E.
Application
In jazz, chord substitutions can be applied bycomposer
A composer is a person who writes music. The term is especially used to indicate composers of Western classical music, or those who are composers by occupation. Many composers are, or were, also skilled performers of music.
Etymology and def ...
s, arranger
In music, an arrangement is a musical adaptation of an existing composition. Differences from the original composition may include reharmonization, melodic paraphrasing, orchestration, or formal development. Arranging differs from orchestrat ...
s, or performers. Composers may use chord substitutions when they are basing a new jazz tune on an existing chord progression from an old jazz standard
Jazz standards are musical compositions that are an important part of the musical repertoire of jazz musicians, in that they are widely known, performed, and recorded by jazz musicians, and widely known by listeners. There is no definitive List ...
or a song from a musical; arrangers for a big band
A big band or jazz orchestra is a type of musical ensemble of jazz music that usually consists of ten or more musicians with four sections: saxophones, trumpets, trombones, and a rhythm section. Big bands originated during the early 1910s and ...
or jazz orchestra may use chord substitutions in their arrangement of a tune, to add harmonic interest or give a different "feel" to a song; and instrumentalists may use chord substitutions in their performance of a song. Given that many jazz songs have repetition of internal sections, such as with a 32-bar AABA song form, performers or arrangers may use chord substitution within the A sections to add variety to the song.
Jazz '' comping'' instruments (piano, guitar, organ, vibes) often use chord substitution to add harmonic interest to a jazz tune with slow harmonic change. For example, the jazz standard chord progression of "rhythm changes
The Rhythm changes is a common 32-Bar (music), bar jazz chord progression derived from George Gershwin's "I Got Rhythm". The progression is in Thirty-two-bar form, AABA form, with each A section based on repetitions of the ubiquitous I–vi–ii� ...
" uses a simple eight bar chord progression in the bridge with the chords III7, VI7, II7, V7; in the key of B, these chords are D7, G7, C7, and F7 (each for two bars). A jazz guitarist might add a ''ii–V7'' aspect to each chord, which would make the progression: "a minor, D7, d minor, G7, g minor, C7, c minor, F7. Alternatively, tritone substitutions could be applied to the progression.
Theoretically, any chord can substitute for any other chord, as long as the new chord supports the melody. In practice, though, only a few options sound musically and stylistically appropriate to a given melody. This technique is used in music such as bebop
Bebop or bop is a style of jazz developed in the early to mid-1940s in the United States. The style features compositions characterized by a fast tempo (usually exceeding 200 bpm), complex chord progressions with rapid chord changes and numerou ...
or fusion to provide more sophisticated harmony, or to create a new-sounding re-harmonization of an old jazz standard
Jazz standards are musical compositions that are an important part of the musical repertoire of jazz musicians, in that they are widely known, performed, and recorded by jazz musicians, and widely known by listeners. There is no definitive List ...
.
Jazz soloists and improvisers also use chord substitutions to help them add interest to their improvised solos. Jazz soloing instruments that can play chords, such as jazz guitar, piano, and organ players may use substitute chords to develop a chord solo over an existing jazz tune with slow-moving harmonies. Also, jazz improvisers may use chord substitution as a mental framework to help them create more interesting-sounding solos. For example, a saxophonist playing an improvised solo over the basic "rhythm changes" bridge (in B, this is "D7, G7, C7, and F7", each for two bars) might think of a more complex progression that uses substitute chords (e.g., "a minor, D7, d minor, G7, g minor, C7, c minor, F7). In doing so, this implies the substitute chords over the original progression, which adds interest for listeners.
See also
* Coltrane changes *Passing chord
In music, a passing chord is a chord that connects, or passes between, the notes of two diatonic chords. "Any chord that moves between one diatonic chord and another one nearby may be loosely termed a passing chord. A diatonic passing chord m ...
References
Further reading
*R., Ken (2012). ''DOG EAR Tritone Substitution for Jazz Guitar'', Amazon, {{Chord progressions, state=expanded