Choana on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
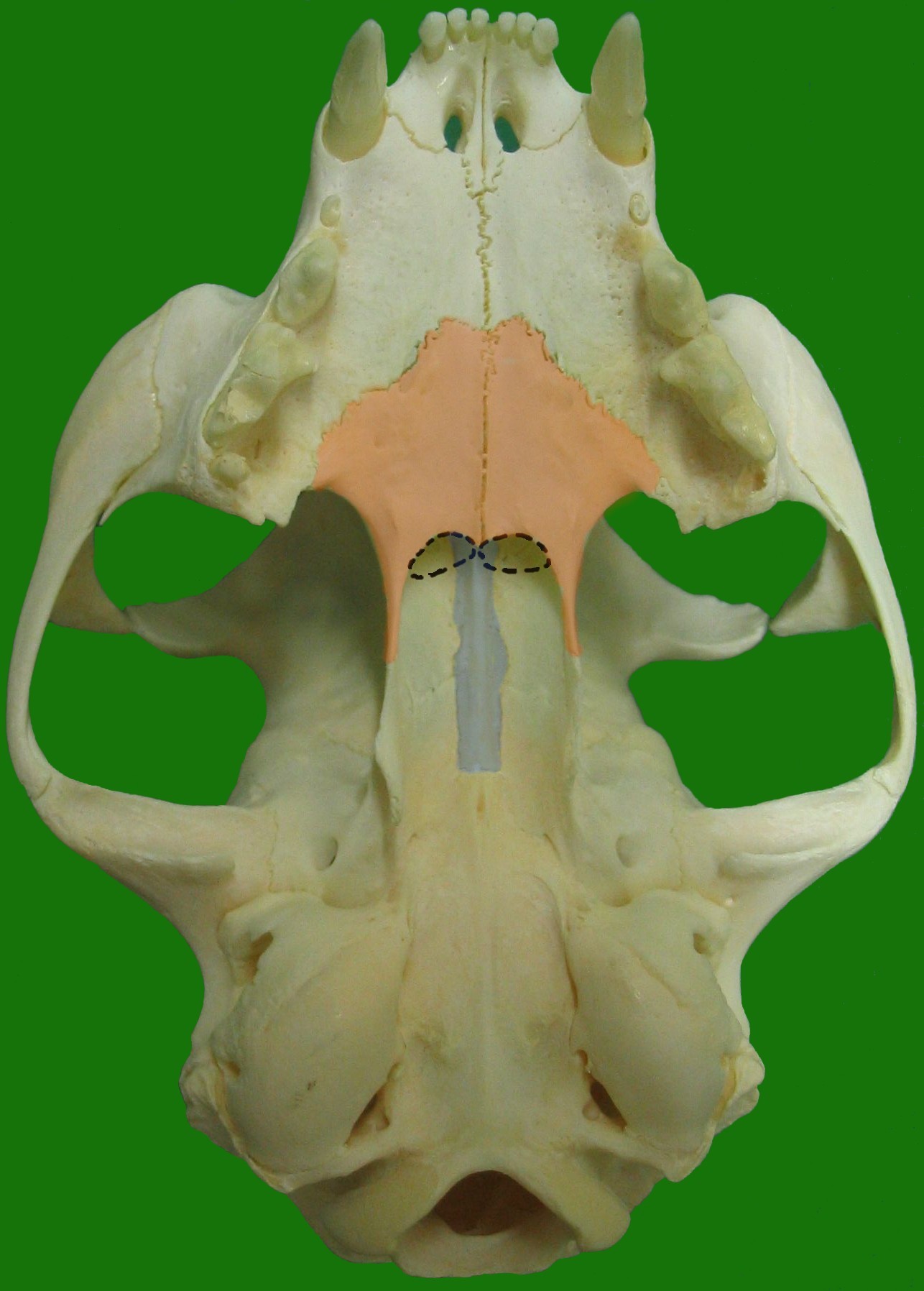 The choanae (: choana), posterior nasal apertures or internal nostrils are two openings found at the back of the nasal passage between the
The choanae (: choana), posterior nasal apertures or internal nostrils are two openings found at the back of the nasal passage between the
 The choanae (: choana), posterior nasal apertures or internal nostrils are two openings found at the back of the nasal passage between the
The choanae (: choana), posterior nasal apertures or internal nostrils are two openings found at the back of the nasal passage between the nasal cavity
The nasal cavity is a large, air-filled space above and behind the nose in the middle of the face. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. The nas ...
and the pharynx
The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the human mouth, mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates ...
, in humans and other mammals (as well as crocodilians
Crocodilia () is an order of semiaquatic, predatory reptiles that are known as crocodilians. They first appeared during the Late Cretaceous and are the closest living relatives of birds. Crocodilians are a type of crocodylomorph pseudosuchi ...
and most skinks). They are considered one of the most important synapomorphies
In phylogenetics, an apomorphy (or derived trait) is a novel character or character state that has evolved from its ancestral form (or plesiomorphy). A synapomorphy is an apomorphy shared by two or more taxa and is therefore hypothesized to ...
of tetrapodomorphs, that allowed the passage from water to land.
In animals with secondary palates, they allow breathing when the mouth is closed. Janvier, Philippe (2004) "Wandering nostrils". ''Nature'', 432 (7013): 23–24. In tetrapods without secondary palates their function relates primarily to olfaction (sense of smell).
The choanae are separated in two by the vomer
The vomer (; ) is one of the unpaired facial bones of the skull. It is located in the midsagittal line, and articulates with the sphenoid, the ethmoid, the left and right palatine bones, and the left and right maxillary bones. The vomer forms ...
.
Boundaries
A choana is the opening between thenasal cavity
The nasal cavity is a large, air-filled space above and behind the nose in the middle of the face. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. The nas ...
and the nasopharynx
The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its ...
.
It is therefore not a structure but a space bounded as follows:
* anteriorly
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek language, Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. Thi ...
and inferiorly by the horizontal plate of palatine bone
In anatomy, the palatine bones (; derived from the Latin ''palatum'') are two irregular bones of the facial skeleton in many animal species, located above the uvula in the throat. Together with the maxilla, they comprise the hard palate.
Stru ...
,
* superiorly and posteriorly by the sphenoid bone
The sphenoid bone is an unpaired bone of the neurocranium. It is situated in the middle of the skull towards the front, in front of the basilar part of occipital bone, basilar part of the occipital bone. The sphenoid bone is one of the seven bon ...
* laterally by the medial pterygoid plates.
* medially by the Vomer
Etymology
The term is a latinization from the Greek χοάνη, "choanē" meaning funnel.Choanae in different animals
Early bony fishes (~420 mya) had two pairs of nostrils, one pair for incoming water (known as the anterior or incurrent nostrils), and a second pair for outgoing water (the posterior or excurrent nostrils), with the olfactory apparatus (for sense of smell) in between. In the first tetrapodomorphs (~415 mya) the excurrent nostrils migrated to the edge of the mouth, occupying a position between the maxillary and premaxillary bones, directly below the lateral rostral (a bone that vanished in early tetrapods). In all but the most basal (primitive) tetrapodomorphs (or "choanates"), the excurrent nostrils have migrated from the edge of the mouth to the interior of the mouth. In tetrapods that lack a secondary palate (basal tetrapods and amphibians), the choanae are located forward in the roof of the mouth, just inside the upper jaw. These internal nasal passages evolved while the vertebrates still lived in water. In animals with complete secondary palates (mammals, crocodilians, most skinks) the space between the primary and secondary palates contain the nasal passages, with the choanae located above the posterior end of the secondary palate. In animals with partial secondary palates (most birds and reptiles), the median ''choanal slit'' separates the two halves of the posterior half of the palate, connecting the nasal cavity with the buccal cavity (mouth) and the pharynx (throat).Fish
Mostfish
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can ...
do not have choanae, instead they have two pairs of external nostrils: each with two tubes whose frontal openings lie close to the upper jaw, and the posterior openings further behind near the eyes. A 395-million-year-old fossil lobe-finned fish called '' Kenichthys'' ''campbelli'' has something between a choana and the external nostrils seen on other fish. The posterior opening of the external nostrils has migrated into the mouth.
In lungfish, the inner nostrils are regarded as an example of parallel evolution. The fossil lungfish '' Diabolepis'' shows an intermediate stage between posterior and interior nostril and supports the independent origin of internal nostrils in the lungfish.
Hagfish
Hagfish, of the Class (biology), class Myxini (also known as Hyperotreti) and Order (biology), order Myxiniformes , are eel-shaped Agnatha, jawless fish (occasionally called slime eels). Hagfish are the only known living Animal, animals that h ...
es have a single internal nostril that opens inside the mouth cavity, while chimaeras have open canals that leads water from their external nostrils into their mouths and through their gills.
References
{{Authority control Skull Otorhinolaryngology