Chinese Expansionism on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
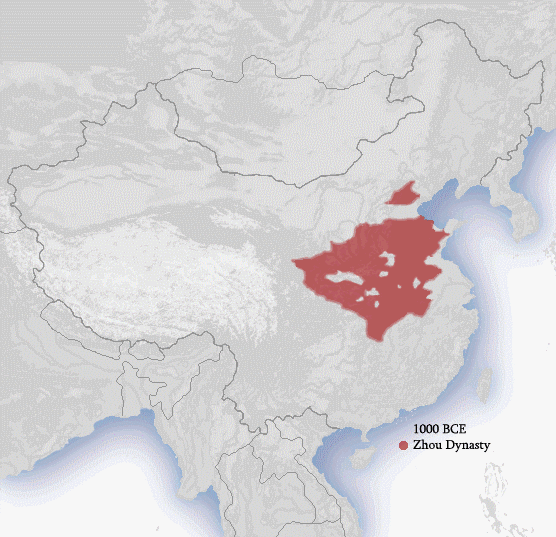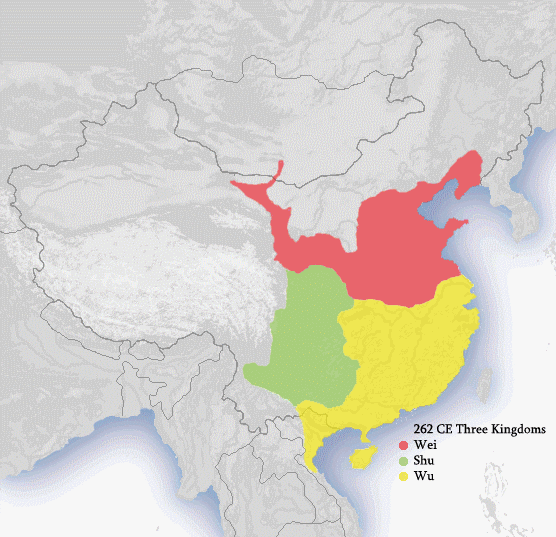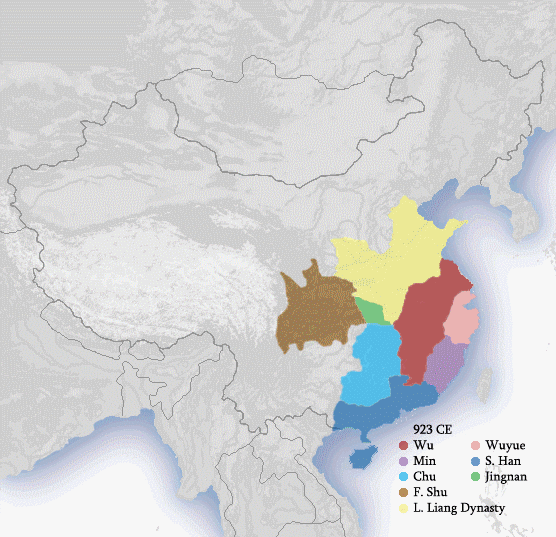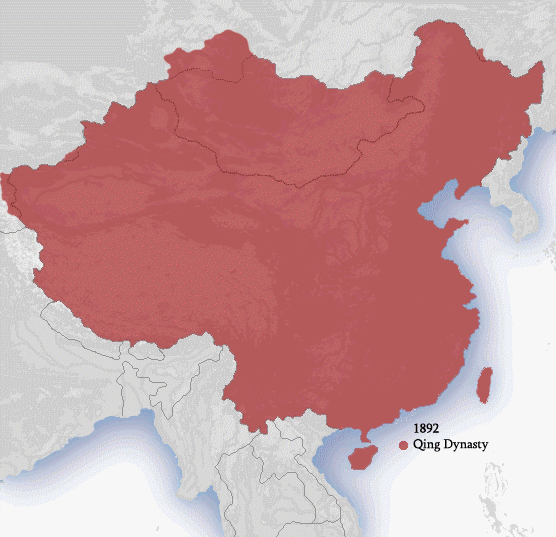 Territorial expansion took place during multiple periods of
Territorial expansion took place during multiple periods of
excerpt
* Chang, Chun-shu. ''The Rise of the Chinese Empire: Nation, State, and Imperialism in Early China, ca. 1600 B.C.–A.D. 8'' (Volume 1, University of Michigan Press, 2007). * * Hawksley, Humphrey. ''Asian Waters: The Struggle Over the South China Sea and the Strategy of Chinese Expansion'' (2018
excerpt
* Mancall, Mark. ''China at the Center: 300 Years of Foreign Policy'' (1984) * Reeves, Jeffrey. "Imperialism and the Middle Kingdom: the Xi Jinping administration's peripheral diplomacy with developing states." ''Third World Quarterly'' 39.5 (2018): 976–998. * Setzekorn, Eric. "Chinese Imperialism, Ethnic Cleansing, and Military History, 1850–1877." ''Journal of Chinese Military History'' 4.1 (2015): 80–100. * {{cite book, author=Tucker, Spencer C. , title=A Global Chronology of Conflict: From the Ancient World to the Modern Middle East , url=https://books.google.com/books?id=h5_tSnygvbIC&pg=PA419, date= 2009, publisher=ABC-CLIO, page=passim, isbn=978-1851096725 * Toje, Asle. ''Will China's Rise Be Peaceful?: Security, Stability, and Legitimacy'' (Oxford UP, 2017)
excerpt
* Westad, Odd Arne. ''Restless Empire: China and the World Since 1750'' (2012
excerpt
Empires Chinese imperialism Military history of Imperial China Neocolonialism Political history of China Settler colonialism in Asia
 Territorial expansion took place during multiple periods of
Territorial expansion took place during multiple periods of Chinese history
The history of China spans several millennia across a wide geographical area. Each region now considered part of the Chinese world has experienced periods of unity, fracture, prosperity, and strife. Chinese civilization first emerged in the Y ...
, especially under the dynasties of Han, Tang, Yuan, and Qing
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the ...
. Chinese expansionism as a motivation or even coherent phenomenon has been contentiously discussed in regard to the contemporary People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
and its territorial claims
A land claim is "the pursuit of recognized territorial ownership by a group or individual". The phrase is usually only used with respect to disputed or unresolved land claims. Some types of land claims include aboriginal land claims, Antarctic l ...
.
Historic background
Qin and Han dynasties
China slowly became a major geopolitical power center during the ancient era. Various ancient Chinese dynasties enlarged their realms. However, it was only under the unified Qin dynasty that China truly started its process of expansion into other nations. Qin's expansionism led to its first contacts with theXiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of Nomad, nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese historiography, Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, t ...
, the Yue tribes, and extended its reach to the Korean Peninsula
Korea is a peninsular region in East Asia consisting of the Korean Peninsula, Jeju Island, and smaller islands. Since the end of World War II in 1945, it has been politically divided at or near the 38th parallel between North Korea (Dem ...
.
The Han dynasty marked the height of early Chinese expansionism. Under Emperor Wu of Han
Emperor Wu of Han (156 – 29 March 87BC), born Liu Che and courtesy name Tong, was the seventh Emperor of China, emperor of the Han dynasty from 141 to 87 BC. His reign lasted 54 years – a record not broken until the reign of the Kangxi ...
, the Han China
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC ...
became the regional center of geopolitical influence in East Asia, projecting much of its imperial power on its neighbors. Han China managed to conquer northern Korea and northern Vietnam
Northern Vietnam or '' Tonkin'' () is one of three geographical regions in Vietnam. It consists of three geographic sub-regions: the Northwest (Vùng Tây Bắc), the Northeast (Vùng Đông Bắc), and the Red River Delta (Đồng Bằng Sôn ...
, annexing and incorporating several parts of these territories. The Han dynasty also managed to conquer various nomadic tribes as far north as what is now modern Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south and southeast. It covers an area of , with a population of 3.5 million, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by po ...
and Siberia
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states ...
and gained control over western regions such as modern Xinjiang
Xinjiang,; , SASM/GNC romanization, SASM/GNC: Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Sinkiang, officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People' ...
and parts of Central Asia.
Following the fall of the Han dynasty, the Korea peninsula gained political independence from The Central Plain dynasties, leaving only northern Vietnam remaining under Chinese control, and the Three Kingdoms
The Three Kingdoms of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu dominated China from AD 220 to 280 following the end of the Han dynasty. This period was preceded by the Eastern Han dynasty and followed by the Jin dynasty (266–420), Western Jin dyna ...
era temporarily halted Chinese expansionism. Nonetheless, the Cao Wei
Wei () was one of the major Dynasties in Chinese history, dynastic states in China during the Three Kingdoms period. The state was established in 220 by Cao Pi based upon the foundations laid by his father Cao Cao during the end of the Han dy ...
, Shu Han
Han (; 221–263), known in historiography as Shu Han ( ) or Ji Han ( "Junior Han"), or often shortened to Shu ( zh, t=蜀, p=Shǔ; Sichuanese Pinyin: ''Su'' < Middle Chinese: *''źjowk'' < Eastern Han Chinese: *''dźok''), was a Dynasties in ...
and Eastern Wu
Wu (Chinese language, Chinese: 吳; pinyin: ''Wú''; Middle Chinese *''ŋuo'' < Eastern Han Chinese: ''*ŋuɑ''), known in historiography as Eastern Wu or Sun Wu, was a Dynasties of China, dynastic state of China and one of the three major sta ...
managed to extend its territorial gains in some parts under their territorial control. Once the Three Kingdoms ended and establishment of the Jin dynasty, Chinese expansionism halted for four centuries, as China was in dire need to consolidate back its borderland following its significant population losses.
The Sui dynasty
The Sui dynasty ( ) was a short-lived Dynasties of China, Chinese imperial dynasty that ruled from 581 to 618. The re-unification of China proper under the Sui brought the Northern and Southern dynasties era to a close, ending a prolonged peri ...
, which reunified China after another 350 years of divisions, attempted to embark back on expansionism, but four disastrous campaigns to Goguryeo put the dynasty to an end.
Tang dynasty
The establishment of theTang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, c=唐朝), or the Tang Empire, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907, with an Wu Zhou, interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed ...
marked the comeback of Chinese expansionism. Like its Han predecessor, the Tang empire established itself as a medieval East Asian geopolitical superpower that marked another golden age for Chinese history. Tang China managed to maintain its grip over northern Vietnam and Korea
Korea is a peninsular region in East Asia consisting of the Korean Peninsula, Jeju Island, and smaller islands. Since the end of World War II in 1945, it has been politically Division of Korea, divided at or near the 38th parallel north, 3 ...
.
The Tang empire also managed to extend its control over Xinjiang and Central Asia, reaching as far west as the Aral Sea
The Aral Sea () was an endorheic lake lying between Kazakhstan to its north and Uzbekistan to its south, which began shrinking in the 1960s and had largely dried up into desert by the 2010s. It was in the Aktobe and Kyzylorda regions of Kazakhst ...
, Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, described as the List of lakes by area, world's largest lake and usually referred to as a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia: east of the Caucasus, ...
and the Lake Baikal
Lake Baikal is a rift lake and the deepest lake in the world. It is situated in southern Siberia, Russia between the Federal subjects of Russia, federal subjects of Irkutsk Oblast, Irkutsk Oblasts of Russia, Oblast to the northwest and the Repu ...
for several decades. China also gained loyalty from the Turkic and Sogdian tribes at the northern and western borders. The Tang managed to encroach into the Tibetan territory and occupy Lhasa
Lhasa, officially the Chengguan District of Lhasa City, is the inner urban district of Lhasa (city), Lhasa City, Tibet Autonomous Region, Southwestern China.
Lhasa is the second most populous urban area on the Tibetan Plateau after Xining ...
, until they had to abandon such expansionist pursuits due to difficult climate.
The Tang Chinese expansion was checked following the Battle of Talas
The Battle of Talas (; ) was an armed confrontation between the Abbasid Caliphate along with the Tibetan Empire against the Tang dynasty in 751. In July of that year, the Tang and Abbasid armies clashed at the Talas River over control of the r ...
in modern-day Kyrgyzstan, when the Tang was defeated by the Arabs. However, China remained strong enough to process a significant weight until the An Lushan Rebellion which crippled the Tang. The rebellion partly led to the collapse and implosion of the Tang into several warring states and kingdoms. After the Tang collapse, China would be divided into several smaller nations until the unification during the Yuan dynasty and Mongol empire.
Fragmentation during Song, Jin, Liao dynasties
When the Tang dynasty collapsed, China entered the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. After this period, China remained fragmented and was divided into a number of smaller countries that emerged from the turmoil. These included the Song dynasty to the south and the Liao and Jin dynasties to the north. The Song, Liao, and Jin would continue to fight each other for centuries. As a result of perpetual instability, the Vietnamese eventually seceded from the union in the Battle of Bạch Đằng in 938,Song dynasty
The Song dynasty ( ) was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 960 to 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song, who usurped the throne of the Later Zhou dynasty and went on to conquer the rest of the Fiv ...
, unified much of China's south and launched an invasion of northern Vietnam in the process, but was repelled by Lê Hoàn
Lê Hoàn (10 August 941 – 18 March 1005), posthumously title Lê Đại Hành, was the third ruler of Đại Việt kingdom, ruling from 981 to 1005, and founder of the Early Lê dynasty. He first served as the generalissimo commanding ...
. From then, the Song dynasty had struggled to reconsolidate back the borderland and inner territories, as well as repeated wars with Vietnam, the Liao dynasty, the Jin dynasty and the Western Xia
The Western Xia or the Xi Xia ( zh, c=, w=Hsi1 Hsia4, p=Xī Xià), officially the Great Xia ( zh, c=大夏, w=Ta4 Hsia4, p=Dà Xià, labels=no), also known as the Tangut Empire, and known as Stein (1972), pp. 70–71. to the Tanguts ...
. This had prevented the Song dynasty from ever taking any serious military expeditions. These various kingdoms (Song, Liao, Jin, Xia) would fight each other until they were all conquered and unified by the Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty ( ; zh, c=元朝, p=Yuáncháo), officially the Great Yuan (; Mongolian language, Mongolian: , , literally 'Great Yuan State'), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after Div ...
in 1279.
Yuan dynasty
TheYuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty ( ; zh, c=元朝, p=Yuáncháo), officially the Great Yuan (; Mongolian language, Mongolian: , , literally 'Great Yuan State'), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after Div ...
, as a Khagan
Khagan or Qaghan (Middle Mongol:; or ''Khagan''; ) or zh, c=大汗, p=Dàhán; ''Khāqān'', alternatively spelled Kağan, Kagan, Khaghan, Kaghan, Khakan, Khakhan, Khaqan, Xagahn, Qaghan, Chagan, Қан, or Kha'an is a title of empire, im ...
-ruled division of the Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire was the List of largest empires, largest contiguous empire in human history, history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Euro ...
and an imperial Chinese dynasty, was founded by the Mongols
Mongols are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, China ( Inner Mongolia and other 11 autonomous territories), as well as the republics of Buryatia and Kalmykia in Russia. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family o ...
in the traditional Chinese style in 1271. The Mongol Empire was characterized by unprecedented territorial expansionism north and west, reaching as far as Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural and socio-economic connotations. Its eastern boundary is marked by the Ural Mountain ...
and the Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western Eur ...
, although the Yuan dynasty based in China was unable to exert actual power over the west khanates due to the disintegrated nature of the Mongol Empire. The Yuan dynasty in China undertook attempts to conquer other territories further east and south too. It launched two invasions of Burma, with the first invasion delivering a devastating blow to the Pagan Kingdom and effectively resulted in its collapse. The Yuan dynasty also managed to conquer Korea and Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ), or Greater Tibet, is a region in the western part of East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are other ethnic groups s ...
, thereby incorporating Tibet into Chinese territory for the first time in history. However, the Yuan dynasty had been unsuccessful in its attempt to conquer Vietnam, with the Mongols being repelled by Trần Thái Tông
Trần Thái Tông (17 July 1218 – 5 May 1277), Vietnamese name, personal name Trần Cảnh or Trần Nhật Cảnh, temple name Thái Tông, was the first emperor of the Trần dynasty, reigned Đại Việt for 33 years (1226–58), being R ...
. Furthermore, The Yuan's naval expeditions to invade Java
Java is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea (a part of Pacific Ocean) to the north. With a population of 156.9 million people (including Madura) in mid 2024, proje ...
and Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
yielded disastrous results, eventually leading to the end of Sino-Mongol expansionist desires.
Decline during Ming dynasty
Following the collapse of the Yuan dynasty, the newly establishedMing dynasty
The Ming dynasty, officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming was the last imperial dynasty of ...
was initially reluctant to embark on expansionism due to destruction from rebellions in the waning years of the Yuan dynasty. The first Ming emperor, Hongwu, was openly against expansionism and was more concerned with killing his internal political opponents than dealing with outside threats. He specifically warned future Emperors only to defend against foreign barbarians, and not engage in military campaigns for glory and conquest. However, once Hongwu died, the reign of Yongle saw the Ming attempt to expand its territories. The Ming launched an invasion to Vietnam, eventually leading to the fourth Chinese domination. However, the Ming was defeated in the Battle of Tốt Động – Chúc Động 20 years later. Moreover, the Ming launched an attack on the Mongols and Northern Yuan to the north, but the Ming failed, and their emperors were even captured by the Mongols in the Tumu Crisis. Following its failures in Vietnam and the north, the Ming dynasty started to concentrate only in internal affairs, and refused to make further interventions or expeditions, except for naval expeditions and trades such as the Ming treasure voyages
The Ming treasure voyages were maritime expeditions undertaken by Ming China's treasure fleet between 1405 and 1433. The Yongle Emperor ordered the construction of the fleet in 1403. The grand project resulted in seven far-reaching ocean voy ...
by Zheng He
Zheng He (also romanized Cheng Ho; 1371–1433/1435) was a Chinese eunuch, admiral and diplomat from the early Ming dynasty, who is often regarded as the greatest admiral in History of China, Chinese history. Born into a Muslims, Muslim famil ...
. Rather than expanding, the Ming was more defensive in nature and faced internal rebellions such as the Rebellion of Cao Qin and Bozhou rebellion
The Bozhou rebellion, or the Yang Yinglong rebellion, refers to the uprising led by Yang Yinglong, a chieftain of the Miao people, Miao tribes located on the border of the Ming provinces of Huguang, Guizhou, and Sichuan in southwestern China. Thi ...
as well as invasions from the north such as from the Later Jin (eventually the Qing) and the Japanese under Toyotomi Hideyoshi
, otherwise known as and , was a Japanese samurai and ''daimyō'' (feudal lord) of the late Sengoku period, Sengoku and Azuchi-Momoyama periods and regarded as the second "Great Unifier" of Japan.Richard Holmes, The World Atlas of Warfare: ...
in the Imjin war
The Imjin War () was a series of two Japanese invasions of Korea: an initial invasion in 1592 also individually called the "Imjin War", a brief truce in 1596, and a second invasion in 1597 called the Chŏngyu War (). The conflict ended in 159 ...
.
Qing dynasty
TheQing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the ...
was a Manchu
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic peoples, Tungusic East Asian people, East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized Ethnic minorities in China, ethnic minority in China and the people from wh ...
-ruled dynasty, descended from the Jurchens
Jurchen (, ; , ) is a term used to collectively describe a number of East Asian people, East Asian Tungusic languages, Tungusic-speaking people. They lived in northeastern China, also known as Manchuria, before the 18th century. The Jurchens wer ...
which founded the Jin dynasty earlier. The dynasty embraced Chinese expansionism. By the late 19th century, in response to competition with other states, the Qing government of China attempted to exert direct control of its frontier areas by conquest or, if already under military control, conversion into provinces.
The ability of Qing China to project power into Central Asia came about because of two changes, one social and one technological. The social change was that under the Qing dynasty, from 1642, the Chinese military forces were organized around cavalry which was more suited for power projection than prior Chinese infantry. The technological change was advances in artillery which negated the military advantage that the people of the steppe had with their cavalry. The Dzungar Khanate
The Dzungar Khanate ( Mongolian: ), also known as the Zunghar Khanate or Junggar Khanate, was an Inner Asian khanate of Oirat Mongol origin. At its greatest extent, it covered an area from southern Siberia in the north to present-day Kyrgyz ...
was the last great independent nomadic power on the steppe of Central Asia. The Dzungars were deliberately exterminated in a brutal campaign during the Dzungar genocide by Manchu Bannermen and Khalkha Mongols. It has been estimated that more than a million people were slaughtered, and it took generations for it to recover. The Qing ruling family Aisin Gioro
The House of Aisin-Gioro is a Manchu clan that ruled the Later Jin dynasty (1616–1636), the Qing dynasty (1636–1912), and Manchukuo (1932–1945) in the history of China. Under the Ming dynasty, members of the Aisin Gioro clan served as chie ...
was supportive of Tibetan Buddhism and many in the ruling class adopted the religion.
The Qing dynasty was seen to be the return of Chinese expansionist policies. Under the Qing rule, China expanded beyond the Great Wall
The Great Wall of China (, literally "ten thousand Li (unit), ''li'' long wall") is a series of fortifications in China. They were built across the historical northern borders of ancient Chinese states and Imperial China as protection agains ...
and started to annex more territories in the process. The Qing invaded Korea
Korea is a peninsular region in East Asia consisting of the Korean Peninsula, Jeju Island, and smaller islands. Since the end of World War II in 1945, it has been politically Division of Korea, divided at or near the 38th parallel north, 3 ...
, managed to conquer Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south and southeast. It covers an area of , with a population of 3.5 million, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by po ...
, and also annexed modern territories of Xinjiang
Xinjiang,; , SASM/GNC romanization, SASM/GNC: Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Sinkiang, officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People' ...
and Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ), or Greater Tibet, is a region in the western part of East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are other ethnic groups s ...
as well. The Qing also managed to extend its control into Central Asia for once more, mostly concentrated in what would be today Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan. The Qing also destroyed the Kingdom of Tungning
The Kingdom of Tungning, also known as Tywan, was a dynastic maritime state that ruled part of southwestern Taiwan and the Penghu islands between 1661 and 1683. It is the first predominantly ethnic Han state in Taiwanese history. At its z ...
of Koxinga
Zheng Chenggong (; 27 August 1624 – 23 June 1662), born Zheng Sen () and better known internationally by his honorific title Koxinga (, from Taiwanese: ''kok sèⁿ iâ''), was a Southern Ming general who resisted the Qing conquest of Chin ...
, and annexed Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
as well. This marked for the first time, China managed to directly control Xinjiang, Taiwan, Tibet, Central Asia and Mongolia. China also marked its claims far to Sakhalin
Sakhalin ( rus, Сахали́н, p=səxɐˈlʲin) is an island in Northeast Asia. Its north coast lies off the southeastern coast of Khabarovsk Krai in Russia, while its southern tip lies north of the Japanese island of Hokkaido. An islan ...
, even though the Qing didn't manage to control it; or even to Kashmir
Kashmir ( or ) is the Northwestern Indian subcontinent, northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term ''Kashmir'' denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir P ...
where it fought a bitter war against the Sikhs
Sikhs (singular Sikh: or ; , ) are an ethnoreligious group who adhere to Sikhism, a religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak. The term ''Sikh'' ...
.
Ming loyalists led by Koxinga
Zheng Chenggong (; 27 August 1624 – 23 June 1662), born Zheng Sen () and better known internationally by his honorific title Koxinga (, from Taiwanese: ''kok sèⁿ iâ''), was a Southern Ming general who resisted the Qing conquest of Chin ...
invaded Taiwan and expelled Dutch colonialists from the island during the Siege of Fort Zeelandia and founded the Chinese Kingdom of Tungning
The Kingdom of Tungning, also known as Tywan, was a dynastic maritime state that ruled part of southwestern Taiwan and the Penghu islands between 1661 and 1683. It is the first predominantly ethnic Han state in Taiwanese history. At its z ...
. The Ming loyalists quickly moved to replace the institutions and culture of Dutch colonial rule with Han Chinese colonial rule. Language and religious institutions left by the Dutch were closed and replaced with Confucian temples and Chinese language schools for both Han Chinese and aboriginals. Officials encouraged new immigration of Han Chinese from China into territory further inland, turning aboriginal lands into new farmland. After fighting between the Ming loyalists and the Qing
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the ...
during the Revolt of the Three Feudatories
The Revolt of the Three Feudatories, () also known as the Rebellion of Wu Sangui, was a rebellion lasting from 1673 to 1681 in the early Qing dynasty of China, during the reign of the Kangxi Emperor (r. 1661–1722). The revolt was led by Wu San ...
, the Qing attacked the Kingdom of Tungning. the Qing won the Battle of Penghu and the Ming loyalists submitted to Qing rule. Tungning was annexed as part of Fujian
Fujian is a provinces of China, province in East China, southeastern China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its capital is Fuzhou and its largest prefe ...
. The Qing were "reluctant colonizers" but became convinced of Taiwan's value to their empire due to the threat the island posed if used as a base by rival powers, and by its abundant resources. The Qing turned Taiwan into its own province in 1885, after Japanese interest and a defeated French invasion attempt.
After the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
expedition to Tibet in the waning days of the Qing dynasty, the Qing responded by sending Zhao Erfeng to further integrate Tibet into China. He succeeded in abolishing the powers of the Tibetan local leaders in Kham
Kham (; ) is one of the three traditional Tibet, Tibetan regions, the others being Domey also known as Amdo in the northeast, and Ü-Tsang in central Tibet. The official name of this Tibetan region/province is Dotoe (). The original residents of ...
and appointing Chinese magistrates in their places by 1909–1910. Qing forces were also sent to Ü-Tsang
Ü-Tsang (དབུས་གཙང་། Wylie; dbus gtsang) is one of the three Tibetan regions, the others being Amdo to the northeast and Kham to the east. Geographically Ü-Tsang covers the Yarlung Tsanpo drainage basin, the western dist ...
in 1910 to establish a direct control over Tibet proper, though a province was never established in this area.
The Qing campaign against Burma (Myanmar) (1765–1769) was its most disastrous and costly frontier war. It ended in a military defeat but the Qing rulers could not accept Burma as an equal, and when diplomatic relations were resumed in 1790, the Qing court considered it a restoration of Chinese suzerainty.
The Qing dynasty established a tributary relationship with Joseon dynasty
Joseon ( ; ; also romanized as ''Chosun''), officially Great Joseon (), was a dynastic kingdom of Korea that existed for 505 years. It was founded by Taejo of Joseon in July 1392 and replaced by the Korean Empire in October 1897. The kingdom w ...
Korea following the Qing invasion of Joseon
The Qing invasion of Joseon () occurred in the winter of 1636 when the newly established Qing dynasty invaded the Joseon, Joseon dynasty, establishing the former's status as the hegemon in the Tributary system of China, Imperial Chinese Tributa ...
in 1636. In 1882, China and Korea signed the China–Korea Treaty of 1882
The China–Korea Treaty of 1882 (; ) was negotiated between representatives of the Qing dynasty China and the Joseon dynastyMoon, Myungki"Korea-China Treaty System in the 1880s and the Opening of Seoul: Review of the Joseon-Qing Communication and ...
stipulating that Korea was a dependency of China and granted Chinese merchants the right to conduct overland and maritime business freely within Korean borders as well as the Chinese unilateral extraterritoriality privileges in civil and criminal cases. China also obtained concessions in Korea, such as the Chinese concession of Incheon. However, Qing China lost its influence over Korea following the First Sino-Japanese War
The First Sino-Japanese War (25 July 189417 April 1895), or the First China–Japan War, was a conflict between the Qing dynasty of China and the Empire of Japan primarily over influence in Joseon, Korea. In Chinese it is commonly known as th ...
in 1895.
Republic of China
When the Qing collapsed in 1912, the newly establishedRepublic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
(ROC) claimed inheritance of all territories held by the Qing dynasty. When both Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ), or Greater Tibet, is a region in the western part of East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are other ethnic groups s ...
and Outer Mongolia
Outer Mongolia was the name of a territory in the Manchu-led Qing dynasty of China from 1691 to 1911. It corresponds to the modern-day independent state of Mongolia and the Russian republic of Tuva. The historical region gained ''de facto'' ...
declared their independence, they were not recognized by the Republic of China. Most of the area comprising the present-day Tibet Autonomous Region (TAR) became a ''de facto'' independent polity except for border areas such as Amdo and Eastern Kham
Kham (; ) is one of the three traditional Tibet, Tibetan regions, the others being Domey also known as Amdo in the northeast, and Ü-Tsang in central Tibet. The official name of this Tibetan region/province is Dotoe (). The original residents of ...
.
The Republic of China focused its efforts on consolidating their control over Chinese territories and refused to embrace expansionist policy. Republic of China, however, faced numerous pressure from the expansionist Empire of Japan
The Empire of Japan, also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was the Japanese nation state that existed from the Meiji Restoration on January 3, 1868, until the Constitution of Japan took effect on May 3, 1947. From Japan–Kor ...
in 1915, with the Twenty-One Demands
The Twenty-One Demands (; ) was a set of demands made during the World War I, First World War by the Empire of Japan under Prime Minister of Japan, Prime Minister Ōkuma Shigenobu to the Government of the Chinese Republic, government of the Re ...
caused public uproars. It also faced strong opposition from the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
, which also embraced expansionist policy, leading to the border conflict of 1929. The Soviets and Japanese meddling into Chinese affairs and the lack of compromises from Western leaders over Japanese and Russian expansionism made the work difficult, as Russia had interests with regard to Xinjiang, and Japanese invasion in northeast China at 1931. On the same time, the Chinese Civil War
The Chinese Civil War was fought between the Kuomintang-led Nationalist government, government of the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China and the forces of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). Armed conflict continued intermitt ...
also prevented any attempts of a possible Chinese expansion.
When World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
broke out, nonetheless Chiang Kai-shek had sought to restore Chinese influence. Being a major ally and one of the Big Four, Chiang wanted to restore Chinese influence in Korea and Southeast Asia, in a vision for a new Asia under Chiang's command. Once the World War II ended, Chiang Kai-shek started trying to implement the project, by sending troops to occupy northern Vietnam. Later, as the Chinese Civil War resumed, Chiang had to redeploy most of his army to fight the now-stronger communist force inside the border. In 1949, the government of Republic of China lost the war and was forced to retreat to Taiwan where it continues to rule today.
People's Republic of China
Following the ''de facto'' end of the Chinese Civil War,Chairman of the Chinese Communist Party
The chairman of the Central Committee of the Chinese Communist Party ( zh, s=中国共产党中央委员会主席, p=Zhōngguó Gòngchǎndǎng Zhōngyāng Wěiyuánhuì Zhǔxí) was the party leader, leader of the Chinese Communist Party. The ...
Mao Zedong
Mao Zedong pronounced ; traditionally Romanization of Chinese, romanised as Mao Tse-tung. (26December 18939September 1976) was a Chinese politician, revolutionary, and political theorist who founded the People's Republic of China (PRC) in ...
proclaimed the People's Republic of China (PRC) in 1949 and incorporated Xinjiang after absorbing the Second East Turkestan Republic, which had rebelled against the ROC with help from the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
before the latter switched side. The PRC annexed Tibet through a series of events that involved negotiations with the Government of Tibet, a military conflict in the Chamdo area of western Kham
Kham (; ) is one of the three traditional Tibet, Tibetan regions, the others being Domey also known as Amdo in the northeast, and Ü-Tsang in central Tibet. The official name of this Tibetan region/province is Dotoe (). The original residents of ...
in October 1950, and the Seventeen Point Agreement
The Seventeen-Point Agreement, officially the Agreement of the Central People's Government and the Local Government of Tibet on Measures for the Peaceful Liberation of Tibet, was an agreement between the Local Government of Tibet and the Centr ...
, which was ratified by the 14th Dalai Lama
The 14th Dalai Lama (born 6 July 1935; full spiritual name: Jetsun Jamphel Ngawang Lobsang Yeshe Tenzin Gyatso, shortened as Tenzin Gyatso; ) is the incumbent Dalai Lama, the highest spiritual leader and head of Tibetan Buddhism. He served a ...
in October 1951 but later repudiated.
The Five Fingers of Tibet
The Five Fingers of Tibet () was a Chinese territorial claim to the Himalayan region bordering India attributed to Mao Zedong. It considers Tibet to be China's right hand palm, with five fingers on its periphery: Ladakh, Nepal, Sikkim, Bhutan, an ...
was a territorial claim attributed to Mao Zedong
Mao Zedong pronounced ; traditionally Romanization of Chinese, romanised as Mao Tse-tung. (26December 18939September 1976) was a Chinese politician, revolutionary, and political theorist who founded the People's Republic of China (PRC) in ...
that considers Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ), or Greater Tibet, is a region in the western part of East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are other ethnic groups s ...
to be China's right hand palm, with five fingers on its periphery: Ladakh
Ladakh () is a region administered by India as a union territory and constitutes an eastern portion of the larger Kashmir region that has been the subject of a Kashmir#Kashmir dispute, dispute between India and Pakistan since 1947 and India an ...
, Nepal
Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China Ch ...
, Sikkim
Sikkim ( ; ) is a States and union territories of India, state in northeastern India. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China in the north and northeast, Bhutan in the east, Koshi Province of Nepal in the west, and West Bengal in the ...
, Bhutan
Bhutan, officially the Kingdom of Bhutan, is a landlocked country in South Asia, in the Eastern Himalayas between China to the north and northwest and India to the south and southeast. With a population of over 727,145 and a territory of , ...
, and North-East Frontier Agency
The North–East Frontier Agency (NEFA), originally known as the North-East Frontier Tracts (NEFT), was one of the political divisions in British India, and later the Republic of India until 20 January 1972, when it became the Union territory, U ...
(now known as Arunachal Pradesh
Arunachal Pradesh (; ) is a States and union territories of India, state in northeast India. It was formed from the North-East Frontier Agency (NEFA) region, and India declared it as a state on 20 February 1987. Itanagar is its capital and la ...
) that are considered China's responsibility to "liberate". The policy has never been discussed in official Chinese public statements and is now dormant, but concerns have often been raised over its possible continued existence or revival.
Following Dalai Lama
The Dalai Lama (, ; ) is the head of the Gelug school of Tibetan Buddhism. The term is part of the full title "Holiness Knowing Everything Vajradhara Dalai Lama" (圣 识一切 瓦齐尔达喇 达赖 喇嘛) given by Altan Khan, the first Shu ...
's escape to India, China and India fought a border war in 1962, where China gained Aksai Chin
Aksai Chin is a region administered by China partly in Hotan County, Hotan Prefecture, Xinjiang, and partly in Rutog County, Ngari Prefecture, Tibet Autonomous Region, Tibet, and constituting the easternmost portion of the larger Kashmir regio ...
and stampeded into Arunachal Pradesh
Arunachal Pradesh (; ) is a States and union territories of India, state in northeast India. It was formed from the North-East Frontier Agency (NEFA) region, and India declared it as a state on 20 February 1987. Itanagar is its capital and la ...
(called South Tibet in China), before retreating from the latter over increasing turmoil. Before that, China also sought to take over Taiwan, then under the authority of the rival Republic of China, causing the Second Taiwan Strait Crisis
The Second Taiwan Strait Crisis, also known as the 1958 Taiwan Strait Crisis, was a conflict between the People's Republic of China (PRC) and the Taiwan, Republic of China (ROC). The PRC shelled the islands of Kinmen (Quemoy) and the Matsu Is ...
, but was unsuccessful due to American threats in response. China also sought to take over Sikkim in 1967, but it was unsuccessful. A Chinese map published in 1961 showed China claiming territories in Bhutan, Nepal
Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China Ch ...
and the Kingdom of Sikkim. Incursions by Chinese soldiers and Tibetan herdsmen allying with the Chinese government also provoked tensions in Bhutan.
In 1974, China launched its first naval expedition to reclaim the Paracel Islands
The Paracel Islands, also known as the Xisha Islands () and the Hoàng Sa Archipelago (), are a disputed archipelago in the South China Sea and currently controlled by the People's Republic of China.
The word ''paracel'' is of Portuguese origi ...
and defeated the 50-strong South Vietnamese occupation force. Tensions triggered between China and later unified communist Vietnam led to the Sino-Vietnamese War of 1979. China and Vietnam later fought another bitter skirmish
Skirmishers are light infantry or light cavalry soldiers deployed as a vanguard, flank guard or rearguard to Screening (tactical), screen a tactical position or a larger body of friendly troops from enemy advances. They may be deployed in a sk ...
in the South China Sea in 1988, resulting in China's consolidation of some disputed islands.
In the opening speech at the 19th National Congress of the Chinese Communist Party
19 (nineteen) is the natural number following 18 and preceding 20. It is a prime number.
Mathematics
Nineteen is the eighth prime number.
Number theory
19 forms a twin prime with 17, a cousin prime with 23, and a sexy prime with 13 ...
(CCP), CCP General Secretary
The general secretary of the Central Committee of the Chinese Communist Party ( zh, s=中国共产党中央委员会总书记, p=Zhōngguó Gòngchǎndǎng Zhōngyāng Wěiyuánhuì Zǒngshūjì) is the leader of the Chinese Communist Party ...
Xi Jinping
Xi Jinping, pronounced (born 15 June 1953) is a Chinese politician who has been the general secretary of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) and Chairman of the Central Military Commission (China), chairman of the Central Military Commission ...
emphasized the PRC's sovereignty over Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
, stating that "We have sufficient abilities to thwart any form of Taiwan independence
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of Chi ...
attempts."
See also
* Chinese Empire * Chinese imperialism * Chinese irredentism **Annexation of Tibet by the People's Republic of China
Tibet came under the control of China, People's Republic of China (PRC) after the Ganden Phodrang, Government of Tibet signed the Seventeen Point Agreement which the 14th Dalai Lama ratified on 24 October 1951, but later repudiated on the grou ...
** Senkaku Islands dispute
* Chinese salami slicing strategy
* East China Sea EEZ disputes
* Territorial disputes in the South China Sea
* Territorial disputes of the People's Republic of China
This article is about territorial disputes of the People's Republic of China (PRC). A territorial dispute is a disagreement over the possession or control of land between two or more political entities. Many of China's territorial disputes resul ...
References
Further reading
* Chan, Steve. ''China's Troubled Waters: Maritime Disputes in Theoretical Perspective'' (Cambridge UP, 2016excerpt
* Chang, Chun-shu. ''The Rise of the Chinese Empire: Nation, State, and Imperialism in Early China, ca. 1600 B.C.–A.D. 8'' (Volume 1, University of Michigan Press, 2007). * * Hawksley, Humphrey. ''Asian Waters: The Struggle Over the South China Sea and the Strategy of Chinese Expansion'' (2018
excerpt
* Mancall, Mark. ''China at the Center: 300 Years of Foreign Policy'' (1984) * Reeves, Jeffrey. "Imperialism and the Middle Kingdom: the Xi Jinping administration's peripheral diplomacy with developing states." ''Third World Quarterly'' 39.5 (2018): 976–998. * Setzekorn, Eric. "Chinese Imperialism, Ethnic Cleansing, and Military History, 1850–1877." ''Journal of Chinese Military History'' 4.1 (2015): 80–100. * {{cite book, author=Tucker, Spencer C. , title=A Global Chronology of Conflict: From the Ancient World to the Modern Middle East , url=https://books.google.com/books?id=h5_tSnygvbIC&pg=PA419, date= 2009, publisher=ABC-CLIO, page=passim, isbn=978-1851096725 * Toje, Asle. ''Will China's Rise Be Peaceful?: Security, Stability, and Legitimacy'' (Oxford UP, 2017)
excerpt
* Westad, Odd Arne. ''Restless Empire: China and the World Since 1750'' (2012
excerpt
Empires Chinese imperialism Military history of Imperial China Neocolonialism Political history of China Settler colonialism in Asia