Child Characters In Animation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A child () is a
 In the biological sciences, a child is usually defined as a person between birth and puberty, or between the developmental period of infancy and puberty. Legally, the term ''child'' may refer to anyone below the age of majority or some other age limit.
The
In the biological sciences, a child is usually defined as a person between birth and puberty, or between the developmental period of infancy and puberty. Legally, the term ''child'' may refer to anyone below the age of majority or some other age limit.
The
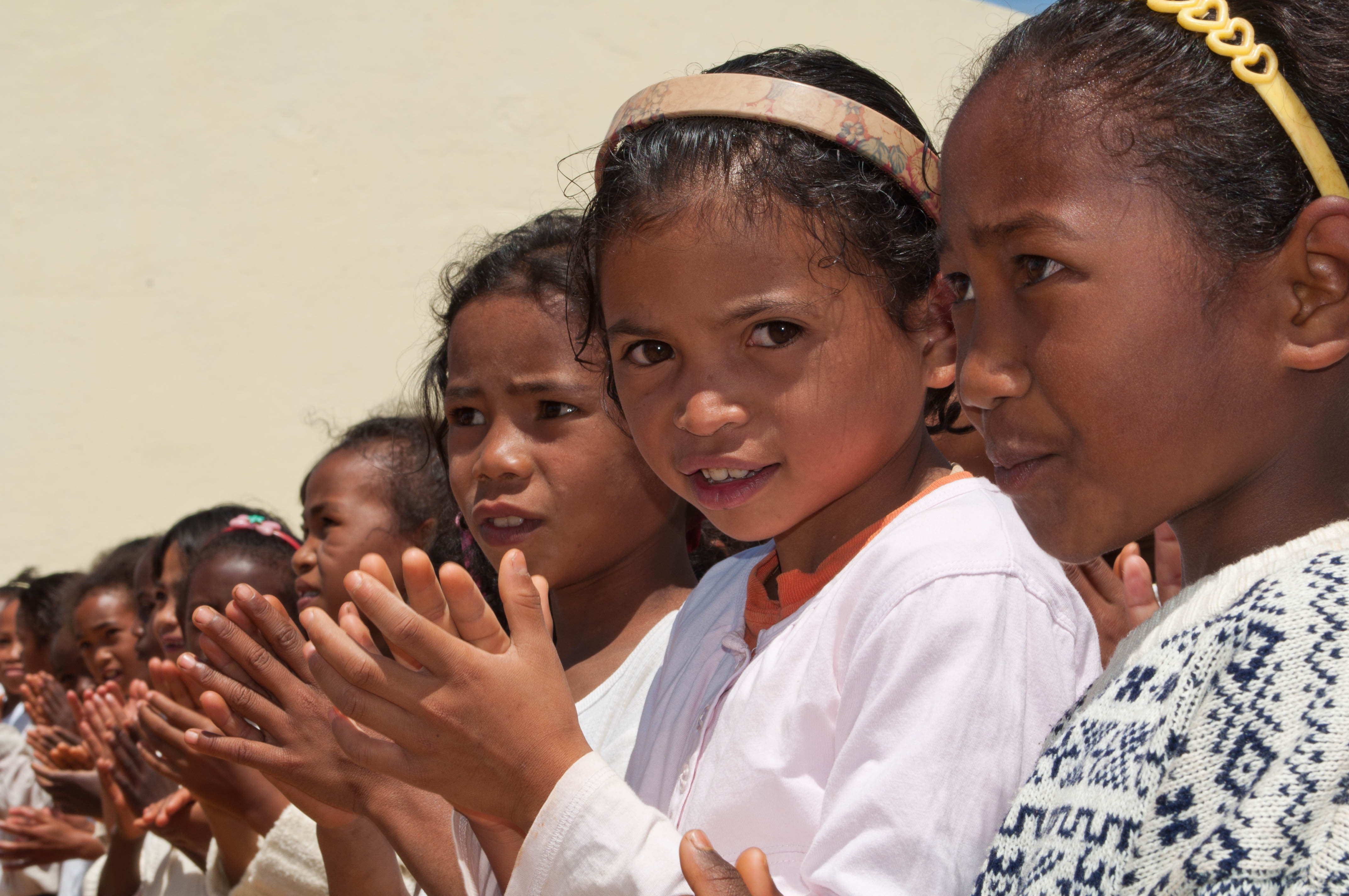


 Early childhood follows the
Early childhood follows the

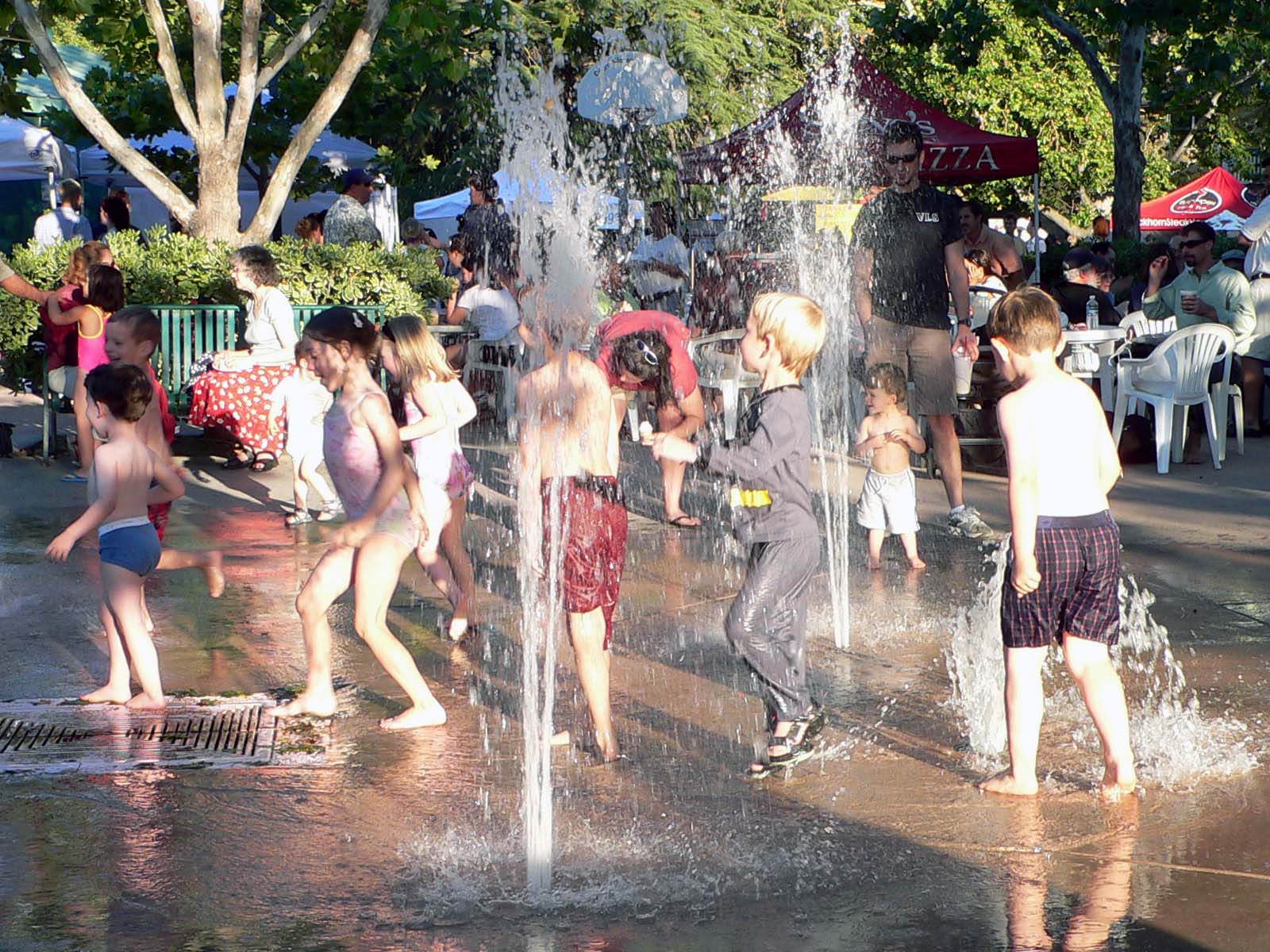

 The modern attitude to children emerged by the late 19th century; the Victorian middle and upper classes emphasized the role of the family and the sanctity of the child – an attitude that has remained dominant in Western societies ever since. The genre of
The modern attitude to children emerged by the late 19th century; the Victorian middle and upper classes emphasized the role of the family and the sanctity of the child – an attitude that has remained dominant in Western societies ever since. The genre of
 Play is essential to the cognitive, physical, social, and emotional well-being of children. It offers children opportunities for physical (running, jumping, climbing, etc.), intellectual (social skills, community norms, ethics and general knowledge) and emotional development (empathy, compassion, and friendships). Unstructured play encourages creativity and imagination. Playing and interacting with other children, as well as some adults, provides opportunities for friendships, social interactions, conflicts and resolutions. However, adults tend to (often mistakenly) assume that virtually all children's social activities can be understood as "play" and, furthermore, that children's play activities do not involve much skill or effort.
It is through play that children at a very early age engage and interact in the world around them. Play allows children to create and explore a world they can master, conquering their fears while practicing adult roles, sometimes in conjunction with other children or adult caregivers. Undirected play allows children to learn how to work in groups, to share, to negotiate, to resolve conflicts, and to learn self-advocacy skills. However, when play is controlled by adults, children acquiesce to adult rules and concerns and lose some of the benefits play offers them. This is especially true in developing creativity, leadership, and group skills.
Play is essential to the cognitive, physical, social, and emotional well-being of children. It offers children opportunities for physical (running, jumping, climbing, etc.), intellectual (social skills, community norms, ethics and general knowledge) and emotional development (empathy, compassion, and friendships). Unstructured play encourages creativity and imagination. Playing and interacting with other children, as well as some adults, provides opportunities for friendships, social interactions, conflicts and resolutions. However, adults tend to (often mistakenly) assume that virtually all children's social activities can be understood as "play" and, furthermore, that children's play activities do not involve much skill or effort.
It is through play that children at a very early age engage and interact in the world around them. Play allows children to create and explore a world they can master, conquering their fears while practicing adult roles, sometimes in conjunction with other children or adult caregivers. Undirected play allows children to learn how to work in groups, to share, to negotiate, to resolve conflicts, and to learn self-advocacy skills. However, when play is controlled by adults, children acquiesce to adult rules and concerns and lose some of the benefits play offers them. This is especially true in developing creativity, leadership, and group skills.
 Play is considered to be very important to optimal child development that it has been recognized by the
Play is considered to be very important to optimal child development that it has been recognized by the
 Children's street culture refers to the cumulative
Children's street culture refers to the cumulative
 Social attitudes toward children differ around the world in various cultures and change over time. A 1988 study on European attitudes toward the centrality of children found that Italy was more child-centric and the Netherlands less child-centric, with other countries, such as Austria, Great Britain, Ireland and
Social attitudes toward children differ around the world in various cultures and change over time. A 1988 study on European attitudes toward the centrality of children found that Italy was more child-centric and the Netherlands less child-centric, with other countries, such as Austria, Great Britain, Ireland and
online book
see also
online review
* Fawcett, Barbara, Brid Featherstone, and Jim Goddard. ''Contemporary child care policy and practice'' (Bloomsbury Publishing, 2017
online
* Hutchison, Elizabeth D., and Leanne W. Charlesworth. "Securing the welfare of children: Policies past, present, and future." ''Families in Society'' 81.6 (2000): 576–585. * Fass, Paula S. ''The end of American childhood: A history of parenting from life on the frontier to the managed child'' (Princeton University Press, 2016). * Fass, Paula S. ed. ''The Routledge History of Childhood in the Western World'' (2012
online
* Klass, Perri. ''The Best Medicine: How Science and Public Health Gave Children a Future'' (WW Norton & Company, 2020
online
* Michail, Samia. "Understanding school responses to students’ challenging behaviour: A review of literature." ''Improving schools'' 14.2 (2011): 156–171
online
* Sorin, Reesa. ''Changing images of childhood: Reconceptualising early childhood practice'' (Faculty of Education, University of Melbourne, 2005
online
* Sorin, Reesa. "Childhood through the eyes of the child and parent." ''Journal of Australian Research in Early Childhood Education'' 14.1 (2007)
online
* Vissing, Yvonne. "History of Children’s Human Rights in the USA." in ''Children's Human Rights in the USA: Challenges and Opportunities'' (Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2023) pp. 181–212. * Yuen, Francis K.O. ''Social work practice with children and families: a family health approach'' (Routledge, 2014
online
{{Authority control * Developmental psychology Kinship and descent
human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
being between the stages of birth
Birth is the act or process of bearing or bringing forth offspring, also referred to in technical contexts as parturition. In mammals, the process is initiated by hormones which cause the muscular walls of the uterus to contract, expelling the f ...
and puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a female, the testicles i ...
, or between the developmental period of infancy
In common terminology, a baby is the very young offspring of adult human beings, while infant (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'baby' or 'child') is a formal or specialised synonym. The terms may also be used to refer to juveniles of ...
and puberty. The term may also refer to an unborn human being. In English-speaking countries, the legal definition of ''child'' generally refers to a minor
Minor may refer to:
Common meanings
* Minor (law), a person not under the age of certain legal activities.
* Academic minor, a secondary field of study in undergraduate education
Mathematics
* Minor (graph theory), a relation of one graph to an ...
, in this case as a person younger than the local age of majority
The age of majority is the threshold of legal adulthood as recognized or declared in law. It is the moment when a person ceases to be considered a minor (law), minor, and assumes legal control over their person, actions, and decisions, thus te ...
(there are exceptions such as, for example, the consume and purchase of alcoholic beverage
Drinks containing alcohol (drug), alcohol are typically divided into three classes—beers, wines, and Distilled beverage, spirits—with alcohol content typically between 3% and 50%. Drinks with less than 0.5% are sometimes considered Non-al ...
even after said age of majority), regardless of their physical, mental and sexual development as biological adult
An adult is an animal that has reached full growth. The biological definition of the word means an animal reaching sexual maturity and thus capable of reproduction. In the human context, the term ''adult'' has meanings associated with social an ...
s. Children generally have fewer rights
Rights are law, legal, social, or ethics, ethical principles of freedom or Entitlement (fair division), entitlement; that is, rights are the fundamental normative rules about what is allowed of people or owed to people according to some legal sy ...
and responsibilities than adults. They are generally classed as unable to make serious decisions.
''Child'' may also describe a relationship with a parent
A parent is either the progenitor of a child or, in humans, it can refer to a caregiver or legal guardian, generally called an adoptive parent or step-parent. Parents who are progenitors are First-degree relative, first-degree relatives and have ...
(such as son
A son is a male offspring; a boy or a man in relation to his parents. The female counterpart is a daughter. From a biological perspective, a son constitutes a first degree relative.
Social issues
In pre-industrial societies and some current ...
s and daughter
A daughter is a female offspring; a girl or a woman in relation to her parents. Daughterhood is the state, condition or quality of being someone's daughter. The male counterpart is a son. Analogously the name is used in several areas to show r ...
s of any age) or, metaphorically
A metaphor is a figure of speech that, for rhetorical effect, directly refers to one thing by mentioning another. It may provide, or obscure, clarity or identify hidden similarities between two different ideas. Metaphors are usually meant to cr ...
, an authority figure
Authority is commonly understood as the legitimate power of a person or group of other people.
In a civil state, ''authority'' may be practiced by legislative, executive, and judicial branches of government,''The New Fontana Dictionary of Mo ...
, or signify group membership in a clan, tribe, or religion; it can also signify being strongly affected by a specific time, place, or circumstance, as in "a child of nature" or "a child of the Sixties."
Biological, legal and social definitions
 In the biological sciences, a child is usually defined as a person between birth and puberty, or between the developmental period of infancy and puberty. Legally, the term ''child'' may refer to anyone below the age of majority or some other age limit.
The
In the biological sciences, a child is usually defined as a person between birth and puberty, or between the developmental period of infancy and puberty. Legally, the term ''child'' may refer to anyone below the age of majority or some other age limit.
The United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
Convention on the Rights of the Child
The United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child (commonly abbreviated as the CRC or UNCRC) is an international international human rights treaty which sets out the civil, political, economic, social, health and cultural rights of ch ...
defines ''child'' as, "A human being below the age of 18 years unless under the law
Law is a set of rules that are created and are enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior, with its precise definition a matter of longstanding debate. It has been variously described as a science and as the ar ...
applicable to the child, majority
A majority is more than half of a total; however, the term is commonly used with other meanings, as explained in the "#Related terms, Related terms" section below.
It is a subset of a Set (mathematics), set consisting of more than half of the se ...
is attained earlier." This is ratified by 192 of 194 member countries. The term ''child'' may also refer to someone below another legally defined age limit unconnected to the age of majority. In Singapore
Singapore, officially the Republic of Singapore, is an island country and city-state in Southeast Asia. The country's territory comprises one main island, 63 satellite islands and islets, and one outlying islet. It is about one degree ...
, for example, a ''child'' is legally defined as someone under the age of 14 under the "Children and Young Persons Act" whereas the age of majority is 21. In U.S. Immigration Law, a child refers to anyone who is under the age of 21.
Some English definitions of the word ''child'' include the fetus
A fetus or foetus (; : fetuses, foetuses, rarely feti or foeti) is the unborn offspring of a viviparous animal that develops from an embryo. Following the embryonic development, embryonic stage, the fetal stage of development takes place. Pren ...
(sometimes termed ''the unborn'').See Shorter ''Oxford English Dictionary
The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (''OED'') is the principal historical dictionary of the English language, published by Oxford University Press (OUP), a University of Oxford publishing house. The dictionary, which published its first editio ...
'' 397 (6th ed. 2007), which's first definition is "A fetus; an infant;...". See also ‘The Compact Edition of the ''Oxford English Dictionary
The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (''OED'') is the principal historical dictionary of the English language, published by Oxford University Press (OUP), a University of Oxford publishing house. The dictionary, which published its first editio ...
'': Complete Text Reproduced Micrographically’, Vol. I (''Oxford University Press'', Oxford 1971): 396, which defines it as: ‘The unborn or newly born human being; foetus, infant’. In many cultures, a child is considered an adult after undergoing a rite of passage
A rite of passage is a ceremony or ritual of the passage which occurs when an individual leaves one group to enter another. It involves a significant change of social status, status in society. In cultural anthropology the term is the Anglicisa ...
, which may or may not correspond to the time of puberty.
Children generally have fewer rights than adults and are classed as unable to make serious decisions, and legally must always be under the care of a responsible adult or child custody
Child custody is a legal term regarding '' guardianship'' which is used to describe the legal and practical relationship between a parent or guardian and a child in that person's care. Child custody consists of ''legal custody'', which is the ri ...
, whether their parents divorce or not.
Developmental stages of childhood
Early childhood

 Early childhood follows the
Early childhood follows the infancy
In common terminology, a baby is the very young offspring of adult human beings, while infant (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'baby' or 'child') is a formal or specialised synonym. The terms may also be used to refer to juveniles of ...
stage and begins with toddler
A toddler is a child approximately 1 to 3 years old, though definitions vary. The toddler years are a time of great cognitive, emotional and social development. The word is derived from "toddle", which means to walk unsteadily, as children at thi ...
hood when the child begins speaking or taking steps independently. While toddlerhood ends around age 3 when the child becomes less dependent on parental assistance for basic needs, early childhood continues approximately until the age of 5 or 6. However, according to the National Association for the Education of Young Children
The National Association for the Education of Young Children (NAEYC) is a large nonprofit association in the United States representing early childhood education teachers, para-educators, center directors, trainers, college educators, families o ...
, early childhood also includes infancy. At this stage children are learning through observing, experimenting and communicating with others. Adults supervise and support the development process of the child, which then will lead to the child's autonomy. Also during this stage, a strong emotional bond is created between the child and the care providers. The children also start preschool and kindergarten at this age: and hence their social lives.
Middle childhood
Middle childhood begins at around age 7, and ends at around age 9 or 10. Together, early and middle childhood are called formative years. In this middle period, children develop socially and mentally. They are at a stage where they make new friends and gain new skills, which will enable them to become more independent and enhance their individuality. During middle childhood, children enter the school years, where they are presented with a different setting than they are used to. This new setting creates new challenges and faces for children. Upon the entrance of school, mental disorders that would normally not be noticed come to light. Many of these disorders include:autism
Autism, also known as autism spectrum disorder (ASD), is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by differences or difficulties in social communication and interaction, a preference for predictability and routine, sensory processing d ...
, dyslexia
Dyslexia (), previously known as word blindness, is a learning disability that affects either reading or writing. Different people are affected to different degrees. Problems may include difficulties in spelling words, reading quickly, wri ...
, dyscalculia
Dyscalculia () is a learning disability resulting in difficulty learning or comprehending arithmetic, such as difficulty in understanding numbers, numeracy, learning how to manipulate numbers, performing mathematical calculations, and learning f ...
, and ADHD
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterised by symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, impulsivity, and emotional dysregulation that are excessive and pervasive, impairing in multiple ...
. Special education
Special education (also known as special-needs education, aided education, alternative provision, exceptional student education, special ed., SDC, and SPED) is the practice of educating students in a way that accommodates their individual di ...
, least restrictive environment
In the United States, the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) is a special education law that mandates regulation for students with disabilities to protect their rights as students and the rights of their parents. The IDEA requires ...
, response to intervention and individualized education plan
An Individualized Education Program (IEP) is a legal document under United States law that is developed for each public school child in the U.S. who needs special education. IEPs must be reviewed every year to keep track of the child's educati ...
s are all specialized plans to help children with disabilities.
Middle childhood is the time when children begin to understand responsibility and are beginning to be shaped by their peers and parents. Chores and more responsible decisions come at this time, as do social comparison and social play. During social play, children learn from and teach each other, often through observation.
Late childhood
Preadolescence is a stage of human development following early childhood and precedingadolescence
Adolescence () is a transitional stage of human Developmental biology, physical and psychological Human development (biology), development that generally occurs during the period from puberty to adulthood (typically corresponding to the age o ...
. Preadolescence is commonly defined as ages 9–12, ending with the major onset of puberty, with markers such as menarche
Menarche ( ; ) is the first menstrual cycle, or first menstruation, menstrual bleeding, in female humans. From both social and medical perspectives, it is often considered the central event of female puberty, as it signals the possibility of fe ...
, spermarche
Spermarche, also known as semenarche, is the time at which a male experiences his first ejaculation. It is considered to be the counterpart of menarche in females. Depending on upbringing, cultural differences, and prior sexual knowledge, males may ...
, and the peak of height velocity occurring. These changes usually occur between ages 11 and 14. It may also be defined as the 2-year period before the major onset of puberty. Preadolescence can bring its own challenges and anxieties. Preadolescent children have a different view of the world from younger children in many significant ways. Typically, theirs is a more realistic view of life than the intense, fantasy-oriented world of earliest childhood. Preadolescents have more mature, sensible, realistic thoughts and actions: 'the most "sensible" stage of development...the child is a much ''less emotional being'' now.' Preadolescents may well view human relationships differently (e.g. they may notice the flawed, human side of authority
Authority is commonly understood as the legitimate power of a person or group of other people.
In a civil state, ''authority'' may be practiced by legislative, executive, and judicial branches of government,''The New Fontana Dictionary of M ...
figures). Alongside that, they may begin to develop a sense of self
In philosophy, the self is an individual's own being, knowledge, and values, and the relationship between these attributes.
The first-person perspective distinguishes selfhood from personal identity. Whereas "identity" is (literally) same ...
-identity
Identity may refer to:
* Identity document
* Identity (philosophy)
* Identity (social science)
* Identity (mathematics)
Arts and entertainment Film and television
* ''Identity'' (1987 film), an Iranian film
* ''Identity'' (2003 film), an ...
, and to have increased feelings of independence
Independence is a condition of a nation, country, or state, in which residents and population, or some portion thereof, exercise self-government, and usually sovereignty, over its territory. The opposite of independence is the status of ...
: 'may feel an individual, no longer "just one of the family."'
Developmental stages post-childhood
Adolescence

Adolescence
Adolescence () is a transitional stage of human Developmental biology, physical and psychological Human development (biology), development that generally occurs during the period from puberty to adulthood (typically corresponding to the age o ...
is usually determined to be between the onset of puberty and legal adulthood: mostly corresponding to the teenage years (13–19). However, puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a female, the testicles i ...
usually begins before the teenage years (10—11 for girls and 11—12 for boys). Although biologically a child is a human being between the stages of birth
Birth is the act or process of bearing or bringing forth offspring, also referred to in technical contexts as parturition. In mammals, the process is initiated by hormones which cause the muscular walls of the uterus to contract, expelling the f ...
and puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a female, the testicles i ...
, adolescents are legally considered children, as they tend to lack adult rights and are still required to attend compulsory schooling in many cultures, though this varies. The onset of adolescence brings about various physical, psychological
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Its subject matter includes the behavior of humans and nonhumans, both consciousness, conscious and Unconscious mind, unconscious phenomena, and mental processes such as thoughts, feel ...
and behavioral changes. The end of adolescence and the beginning of adulthood varies by country and by function, and even within a single nation-state or culture there may be different ages at which an individual is considered to be mature enough to be entrusted by society with certain tasks.
History
During the EuropeanRenaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
, artistic depictions of children increased dramatically, which did not have much effect on the social attitude toward children, however.
The French historian Philippe Ariès
Philippe Ariès (; 21 July 1914 – 8 February 1984) was a French medievalist and historian of the family and childhood, in the style of Georges Duby. He wrote many books on the common daily life. His most prominent works regarded the change in ...
argued that during the 1600s, the concept of childhood began to emerge in Europe, however other historians like Nicholas Orme
Nicholas Orme FSA FRHistS (born 1942) is a British historian specialising in the Middle Ages and Tudor period, focusing on the history of children, and ecclesiastical history, with a particular interest in South West England.
Orme is an eme ...
have challenged this view and argued that childhood has been seen as a separate stage since at least the medieval period. Adults saw children as separate beings, innocent and in need of protection and training by the adults around them. The English philosopher John Locke
John Locke (; 29 August 1632 (Old Style and New Style dates, O.S.) – 28 October 1704 (Old Style and New Style dates, O.S.)) was an English philosopher and physician, widely regarded as one of the most influential of the Enlightenment thi ...
was particularly influential in defining this new attitude towards children, especially with regard to his theory of the tabula rasa
''Tabula rasa'' (; Latin for "blank slate") is the idea of individuals being born empty of any built-in mental content, so that all knowledge comes from later perceptions or sensory experiences. Proponents typically form the extreme "nurture" ...
, which considered the mind at birth to be a "blank slate". A corollary of this doctrine was that the mind of the child was born blank, and that it was the duty of the parents to imbue the child with correct notions. During the early period of capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their use for the purpose of obtaining profit. This socioeconomic system has developed historically through several stages and is defined by ...
, the rise of a large, commercial middle class, mainly in the Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
countries of the Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, commonly referred to in historiography as the Dutch Republic, was a confederation that existed from 1579 until the Batavian Revolution in 1795. It was a predecessor state of the present-day Netherlands ...
and England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
, brought about a new family ideology centred around the upbringing of children. Puritanism
The Puritans were English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries who sought to rid the Church of England of what they considered to be Roman Catholic practices, maintaining that the Church of England had not been fully reformed and should ...
stressed the importance of individual salvation and concern for the spiritual welfare of children.
The modern notion of childhood with its own autonomy and goals began to emerge during the 18th-century Enlightenment
Enlightenment or enlighten may refer to:
Age of Enlightenment
* Age of Enlightenment, period in Western intellectual history from the late 17th to late 18th century, centered in France but also encompassing (alphabetically by country or culture): ...
and the Romantic period
Romanticism (also known as the Romantic movement or Romantic era) was an artistic and intellectual movement that originated in Europe towards the end of the 18th century. The purpose of the movement was to advocate for the importance of subjec ...
that followed it. Jean Jacques Rousseau
Jean-Jacques Rousseau (, ; ; 28 June 1712 – 2 July 1778) was a Genevan philosopher ('' philosophe''), writer, and composer. His political philosophy influenced the progress of the Age of Enlightenment throughout Europe, as well as aspects ...
formulated the romantic attitude towards children in his famous 1762 novel '' Emile: or, On Education''. Building on the ideas of John Locke
John Locke (; 29 August 1632 (Old Style and New Style dates, O.S.) – 28 October 1704 (Old Style and New Style dates, O.S.)) was an English philosopher and physician, widely regarded as one of the most influential of the Enlightenment thi ...
and other 17th-century thinkers, Jean-Jaques Rousseau described childhood as a brief period of sanctuary before people encounter the perils and hardships of adulthood. Sir Joshua Reynolds
Sir Joshua Reynolds (16 July 1723 – 23 February 1792) was an English painter who specialised in portraits. The art critic John Russell (art critic), John Russell called him one of the major European painters of the 18th century, while Lucy P ...
' extensive children portraiture demonstrated the new enlightened attitudes toward young children. His 1788 painting ''The Age of Innocence
''The Age of Innocence'' is a novel by American author Edith Wharton, published on 25 October 1920. It was her eighth novel, and was initially serialized in 1920 in four parts, in the magazine '' Pictorial Review''. Later that year, it was rele ...
'' emphasizes the innocence and natural grace of the posing child and soon became a public favourite. Postle, Martin. (2005) "''The Age of Innocence''" Child Portraiture in Georgian Art and Society", in ''Pictures of Innocence: Portraits of Children from Hogarth to Lawrence''. Bath: Holburne Museum of Art
The Holburne Museum (formerly known as the Holburne of Menstrie Museum and the Holburne Museum of Art) is located in Sydney Pleasure Gardens, Bath, Somerset, England. The city's first public art gallery, the Grade I listed building, is home to ...
, pp. 7–8.
The idea of childhood as a locus of divinity, purity, and innocence is further expounded upon in William Wordsworth
William Wordsworth (7 April 177023 April 1850) was an English Romantic poetry, Romantic poet who, with Samuel Taylor Coleridge, helped to launch the Romanticism, Romantic Age in English literature with their joint publication ''Lyrical Balla ...
's "Ode: Intimations of Immortality from Recollections of Early Childhood", the imagery of which he "fashioned from a complex mix of pastoral aesthetics, pantheistic views of divinity, and an idea of spiritual purity based on an Edenic notion of pastoral innocence infused with Neoplatonic notions of reincarnation". This Romantic conception of childhood, historian Margaret Reeves suggests, has a longer history than generally recognized, with its roots traceable to similarly imaginative constructions of childhood circulating, for example, in the neo-platonic poetry of seventeenth-century metaphysical poet Henry Vaughan
Henry Vaughan (17 April 1621 – 23 April 1695) was a Welsh metaphysical poet, author and translator writing in English, and a medical physician. His religious poetry appeared in ''Silex Scintillans'' in 1650, with a second part in 1655.''Oxfo ...
(e.g., "The Retreate", 1650; "Childe-hood", 1655). Such views contrasted with the stridently didactic, Calvinist views of infant depravity.
With the onset of industrialisation
Industrialisation ( UK) or industrialization ( US) is the period of social and economic change that transforms a human group from an agrarian society into an industrial society. This involves an extensive reorganisation of an economy for th ...
in England in 1760, the divergence between high-minded romantic ideals of childhood and the reality of the growing magnitude of child exploitation in the workplace, became increasingly apparent. By the late 18th century, British children were specially employed in factories and mines and as chimney sweep
A chimney sweep is a person who inspects then clears soot and creosote from chimneys. The chimney uses the pressure difference caused by a hot column of gas to create a draught and draw air over the hot coals or wood enabling continued combust ...
s, often working long hours in dangerous jobs for low pay. As the century wore on, the contradiction between the conditions on the ground for poor children and the middle-class notion of childhood as a time of simplicity and innocence led to the first campaigns for the imposition of legal protection for children.
British reformers attacked child labor
Child labour is the exploitation of children through any form of work that interferes with their ability to attend regular school, or is mentally, physically, socially and morally harmful. Such exploitation is prohibited by legislation w ...
from the 1830s onward, bolstered by the horrific descriptions of London street life by Charles Dickens
Charles John Huffam Dickens (; 7 February 1812 – 9 June 1870) was an English novelist, journalist, short story writer and Social criticism, social critic. He created some of literature's best-known fictional characters, and is regarded by ...
. The campaign eventually led to the Factory Acts
The Factory Acts were a series of acts passed by the Parliament of the United Kingdom beginning in 1802 to regulate and improve the conditions of industrial employment.
The early acts concentrated on regulating the hours of work and moral wel ...
, which mitigated the exploitation of children at the workplace
Modern concepts of childhood
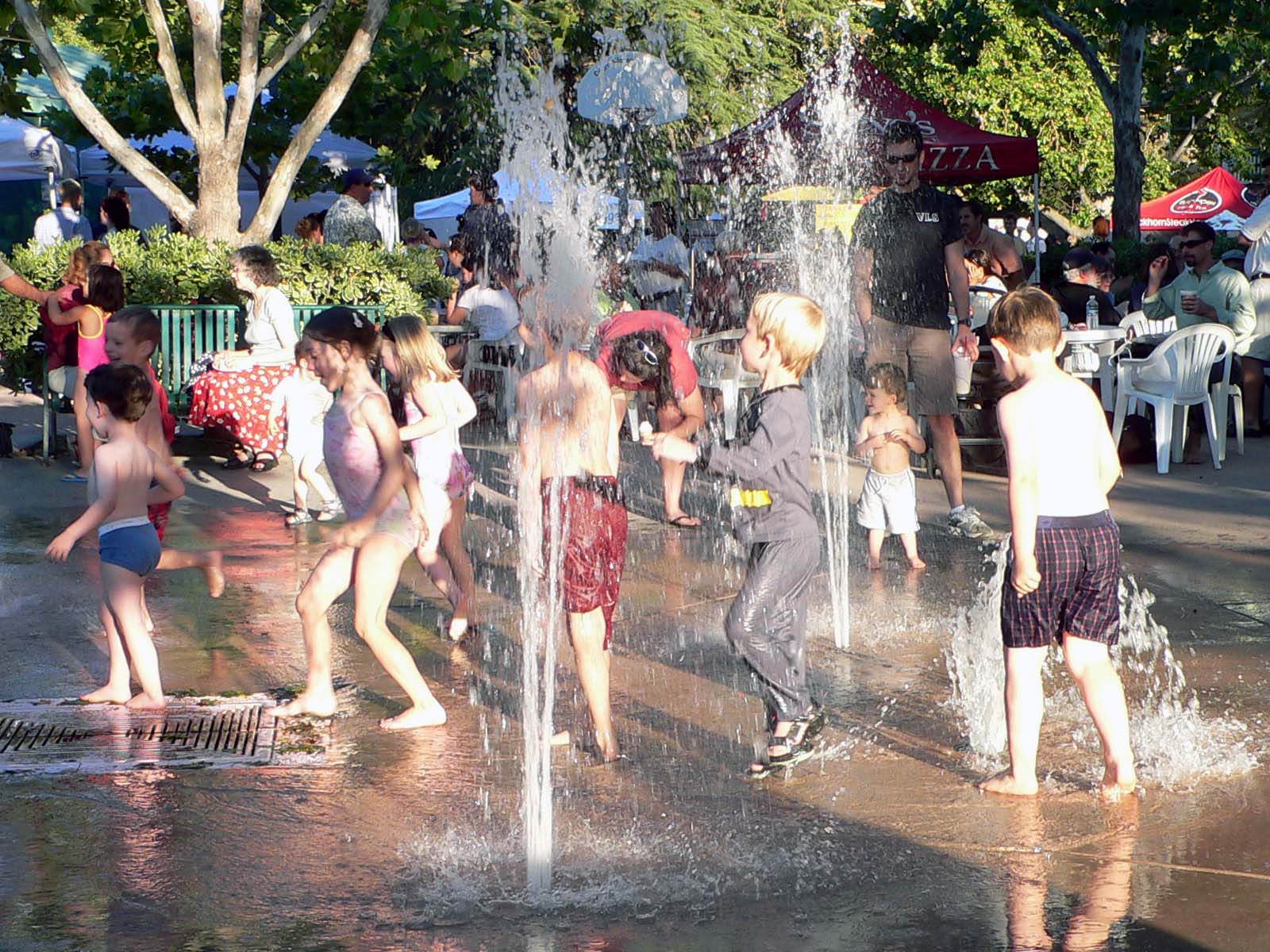

 The modern attitude to children emerged by the late 19th century; the Victorian middle and upper classes emphasized the role of the family and the sanctity of the child – an attitude that has remained dominant in Western societies ever since. The genre of
The modern attitude to children emerged by the late 19th century; the Victorian middle and upper classes emphasized the role of the family and the sanctity of the child – an attitude that has remained dominant in Western societies ever since. The genre of children's literature
Children's literature or juvenile literature includes stories, books, magazines, and poems that are created for children. In addition to conventional literary genres, modern children's literature is classified by the intended age of the reade ...
took off, with a proliferation of humorous, child-oriented books attuned to the child's imagination. Lewis Carroll
Charles Lutwidge Dodgson (27 January 1832 – 14 January 1898), better known by his pen name Lewis Carroll, was an English author, poet, mathematician, photographer and reluctant Anglicanism, Anglican deacon. His most notable works are ''Alice ...
's fantasy ''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland
''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland'' (also known as ''Alice in Wonderland'') is an 1865 English Children's literature, children's novel by Lewis Carroll, a mathematics university don, don at the University of Oxford. It details the story of a ...
'', published in 1865 in England, was a landmark in the genre; regarded as the first "English masterpiece written for children", its publication opened the "First Golden Age" of children's literature.
The latter half of the 19th century saw the introduction of compulsory state schooling of children across Europe, which decisively removed children from the workplace into schools.
The market economy of the 19th century enabled the concept of childhood as a time of fun, happiness, and imagination. Factory-made dolls and doll houses delighted the girls and organized sports and activities were played by the boys.
The Boy Scout
A Scout, Boy Scout, Girl Scout or, in some countries, a Pathfinder is a participant in the Scout Movement, usually aged 10–18 years, who engage in learning scoutcraft and outdoor and other special interest activities. Some Scout organizatio ...
s was founded by Sir Robert Baden-Powell
Lieutenant-General Robert Stephenson Smyth Baden-Powell, 1st Baron Baden-Powell, ( ; 22 February 1857 – 8 January 1941) was a British Army officer, writer, founder of The Boy Scouts Association and its first Chief Scout, and founder, with ...
in 1908, which provided young boys with outdoor activities aiming at developing character, citizenship, and personal fitness qualities.
In the 20th century, Philippe Ariès
Philippe Ariès (; 21 July 1914 – 8 February 1984) was a French medievalist and historian of the family and childhood, in the style of Georges Duby. He wrote many books on the common daily life. His most prominent works regarded the change in ...
, a French historian specializing in medieval history
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the West ...
, suggested that childhood was not a natural phenomenon, but a creation of society in his 1960 book ''Centuries of Childhood
''Centuries of Childhood: A Social History of Family Life'' ( French: ''L'enfant et la vie familiale sous l'ancien régime''; English: lit. "The Child and Family Life during the ''Ancien Régime'') is a 1960 book on the history of childhood b ...
''. In 1961 he published a study of paintings, gravestones, furniture, and school records, finding that before the 17th century, children were represented as mini-adults.
In 1966, the American philosopher George Boas
George Boas (; 28 August 1891 – 17 March 1980) was an American professor of philosophy at Johns Hopkins University.
Education
Boas received his education at Brown University, obtaining both a B.A. and M.A. in philosophy there, after whi ...
published the book ''The Cult of Childhood''. Since then, historians have increasingly researched childhood in past times.
In 2006, Hugh Cunningham published the book ''Invention of Childhood'', looking at British childhood from the year 1000, the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
, to what he refers to as the Post War Period of the 1950s, 1960s and 1970s.
Childhood evolves and changes as lifestyles change and adult expectations alter. In the modern era, many adults believe that children should not have any worries or work, as life should be happy and trouble-free. Childhood is seen as a mixture of simplicity, innocence, happiness, fun, imagination, and wonder. It is thought of as a time of playing, learning, socializing, exploring, and worrying in a world without much adult interference.
A "loss of innocence" is a common concept, and is often seen as an integral part of coming of age
Coming of age is a young person's transition from being a child to being an adult. The specific age at which this transition takes place varies between societies, as does the nature of the change. It can be a simple legal convention or can b ...
. It is usually thought of as an experience or period in a child's life that widens their awareness of evil, pain or the world around them. This theme is demonstrated in the novels ''To Kill a Mockingbird
''To Kill a Mockingbird'' is a 1960 Southern Gothic novel by American author Harper Lee. It became instantly successful after its release; in the United States, it is widely read in high schools and middle schools. ''To Kill a Mockingbird'' ...
'' and ''Lord of the Flies
''Lord of the Flies'' is the 1954 debut novel of British author William Golding. The plot concerns a group of prepubescent British boys who are stranded on an uninhabited island and their disastrous attempts to govern themselves that led to ...
''. The fictional character Peter Pan
Peter Pan is a fictional character created by Scottish novelist and playwright J. M. Barrie. A free-spirited and mischievous young boy who can fly and never grows up, Peter Pan spends his never-ending childhood having adventures on the mythical ...
was the embodiment of a childhood that never ends.
Healthy childhoods
Role of parents
Children's health
Children's health includes the physical, mental and social well-being of children. Maintaining children's health implies offering them healthy foods, insuring they get enough sleep and exercise, and protecting their safety. Children in certain parts of the world often suffer frommalnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients which adversely affects the body's tissues a ...
, which is often associated with other conditions, such diarrhea, pneumonia and malaria.
Child protection
Child protection, according to UNICEF, refers to "preventing and responding to violence, exploitation and abuse against children – including commercial sexual exploitation,trafficking
Smuggling is the illegal transportation of objects, substances, information or people, such as out of a house or buildings, into a prison, or across an international border, in violation of applicable laws or other regulations. More broadly, soc ...
, child labour
Child labour is the exploitation of children through any form of work that interferes with their ability to attend regular school, or is mentally, physically, socially and morally harmful. Such exploitation is prohibited by legislation w ...
and harmful traditional practices, such as female genital mutilation
Female genital mutilation (FGM) (also known as female genital cutting, female genital mutilation/cutting (FGM/C) and female circumcision) is the cutting or removal of some or all of the vulva for non-medical reasons. Prevalence of female ge ...
/cutting and child marriage
Child marriage is a practice involving a marriage or domestic partnership, formal or informal, that includes an individual under 18 and an adult or other child.*
*
*
*
Research has found that child marriages have many long-term negative co ...
". The
Convention on the Rights of the Child
The United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child (commonly abbreviated as the CRC or UNCRC) is an international international human rights treaty which sets out the civil, political, economic, social, health and cultural rights of ch ...
protects the fundamental rights of children.
Play
 Play is essential to the cognitive, physical, social, and emotional well-being of children. It offers children opportunities for physical (running, jumping, climbing, etc.), intellectual (social skills, community norms, ethics and general knowledge) and emotional development (empathy, compassion, and friendships). Unstructured play encourages creativity and imagination. Playing and interacting with other children, as well as some adults, provides opportunities for friendships, social interactions, conflicts and resolutions. However, adults tend to (often mistakenly) assume that virtually all children's social activities can be understood as "play" and, furthermore, that children's play activities do not involve much skill or effort.
It is through play that children at a very early age engage and interact in the world around them. Play allows children to create and explore a world they can master, conquering their fears while practicing adult roles, sometimes in conjunction with other children or adult caregivers. Undirected play allows children to learn how to work in groups, to share, to negotiate, to resolve conflicts, and to learn self-advocacy skills. However, when play is controlled by adults, children acquiesce to adult rules and concerns and lose some of the benefits play offers them. This is especially true in developing creativity, leadership, and group skills.
Play is essential to the cognitive, physical, social, and emotional well-being of children. It offers children opportunities for physical (running, jumping, climbing, etc.), intellectual (social skills, community norms, ethics and general knowledge) and emotional development (empathy, compassion, and friendships). Unstructured play encourages creativity and imagination. Playing and interacting with other children, as well as some adults, provides opportunities for friendships, social interactions, conflicts and resolutions. However, adults tend to (often mistakenly) assume that virtually all children's social activities can be understood as "play" and, furthermore, that children's play activities do not involve much skill or effort.
It is through play that children at a very early age engage and interact in the world around them. Play allows children to create and explore a world they can master, conquering their fears while practicing adult roles, sometimes in conjunction with other children or adult caregivers. Undirected play allows children to learn how to work in groups, to share, to negotiate, to resolve conflicts, and to learn self-advocacy skills. However, when play is controlled by adults, children acquiesce to adult rules and concerns and lose some of the benefits play offers them. This is especially true in developing creativity, leadership, and group skills.
 Play is considered to be very important to optimal child development that it has been recognized by the
Play is considered to be very important to optimal child development that it has been recognized by the United Nations Commission on Human Rights
The United Nations Commission on Human Rights (UNCHR) was a functional commission within the United Nations System, overall framework of the United Nations from 1946 until it was replaced by the United Nations Human Rights Council in 2006. It was a ...
as a right of every child. Children who are being raised in a hurried and pressured style may limit the protective benefits they would gain from child-driven play.
The initiation of play in a classroom setting allows teachers and students to interact through playfulness associated with a learning experience. Therefore, playfulness aids the interactions between adults and children in a learning environment. “Playful Structure” means to combine informal learning with formal learning to produce an effective learning experience for children at a young age.
Even though play is considered to be the most important to optimal child development, the environment affects their play and therefore their development. Poor children confront widespread environmental inequities as they experience less social support, and their parents are less responsive and more authoritarian. Children from low income families are less likely to have access to books and computers which would enhance their development.
Street culture
 Children's street culture refers to the cumulative
Children's street culture refers to the cumulative culture
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes ...
created by young children and is sometimes referred to as their ''secret world''. It is most common in children between the ages of seven and twelve. It is strongest in urban working class
The working class is a subset of employees who are compensated with wage or salary-based contracts, whose exact membership varies from definition to definition. Members of the working class rely primarily upon earnings from wage labour. Most c ...
industrial district
Industrial district (ID) is a place where workers and firms, specialised in a main industry and auxiliary industries, live and work. The concept was initially used by Alfred Marshall to describe some aspects of the industrial organisation of nat ...
s where children are traditionally free to play out in the streets for long periods without supervision. It is invented and largely sustained by children themselves with little adult interference.
Young children's street culture usually takes place on quiet backstreets and pavements, and along routes that venture out into local park
A park is an area of natural, semi-natural or planted space set aside for human enjoyment and recreation or for the protection of wildlife or natural habitats. Urban parks are urban green space, green spaces set aside for recreation inside t ...
s, playground
A playground, playpark, or play area is a place designed to provide an environment for children that facilitates play, typically outdoors. While a playground is usually designed for children, some are designed for other age groups, or people wi ...
s, scrub and wasteland, and to local shops. It often imposes imaginative status on certain sections of the urban realm (local buildings, kerbs, street objects, etc.). Children designate specific areas that serve as informal meeting and relaxation places (see: Sobel, 2001). An urban area that looks faceless or neglected to an adult may have deep 'spirit of place
Spirit of place (or soul) refers to the unique, distinctive and cherished aspects of a place; often those celebrated by artists and writers, but also those cherished in folk tales, festivals and celebrations. It is thus as much in the invisible w ...
' meanings in to children. Since the advent of indoor distractions such as video games
A video game or computer game is an electronic game that involves interaction with a user interface or input device (such as a joystick, game controller, controller, computer keyboard, keyboard, or motion sensing device) to generate visual fe ...
, and television
Television (TV) is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. Additionally, the term can refer to a physical television set rather than the medium of transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertising, ...
, concerns have been expressed about the vitality – or even the survival – of children's street culture.
Geographies of childhood
The geographies of childhood involves how (adult) society perceives the idea of childhood, the many ways adult attitudes and behaviors affect children's lives, including the environment which surrounds children and its implications. The geographies of childhood is similar in some respects tochildren's geographies
Children's geographies is an area of study within human geography and childhood studies which involves researching the places and spaces of children's lives.
Context
Children's geographies is the branch of human geography which deals with the stu ...
which examines the places and spaces in which children live.
Nature deficit disorder
Nature Deficit Disorder, a term coined byRichard Louv
Richard Louv (born 1949) is an American non-fiction author and journalist. He is best known for his seventh book, '' Last Child in the Woods: Saving Our Children From Nature-Deficit Disorder'' (first published in 2005 by Algonquin Books of Chapel ...
in his 2005 book '' Last Child in the Woods,'' refers to the trend in the United States and Canada towards less time for outdoor play, resulting in a wide range of behavioral problems.
With increasing use of cellphones, computers, video games and television, children have more reasons to stay inside rather than outdoors exploring. “The average American child spends 44 hours a week with electronic media”. Research in 2007 has drawn a correlation between the declining number of National Park
A national park is a nature park designated for conservation (ethic), conservation purposes because of unparalleled national natural, historic, or cultural significance. It is an area of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that is protecte ...
visits in the U.S. and increasing consumption of electronic media by children. The media has accelerated the trend for children's nature disconnection by deemphasizing views of nature, as in Disney films.
Age of responsibility
The age at which children are considered responsible for their society-bound actions (e. g. marriage, voting, etc.) has also changed over time, and this is reflected in the way they are treated in courts of law. In Roman times, children were regarded as not culpable for crimes, a position later adopted by the Church. In the 19th century, children younger than seven years old were believed incapable of crime. Children from the age of seven forward were considered responsible for their actions. Therefore, they could face criminal charges, be sent to adult prison, and be punished like adults by whipping, branding or hanging. However, courts at the time would consider the offender's age when deliberating sentencing. Minimum employment age and marriage age also vary. The age limit of voluntary/involuntary military service is also disputed at the international level.Education
Education, in the general sense, refers to the act or process of imparting or acquiring general knowledge, developing the powers of reasoning and judgment, and preparing intellectually for mature life. Formal education most often takes place throughschooling
A school is the educational institution (and, in the case of in-person learning, the building) designed to provide learning environments for the teaching of students, usually under the direction of teachers. Most countries have systems of fo ...
. A right to education
The right to education has been recognized as a human rights, human right in a number of international conventions, including the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights which recognizes a right to free education, free, pr ...
has been recognized by some governments. At the global level, Article 13 of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
' 1966 International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights
The International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (ICESCR) is a multilateral treaty adopted by the United Nations General Assembly (GA) on 16 December 1966 through GA. Resolution 2200A (XXI), and came into force on 3 January 197 ...
(ICESCR) recognizes the right of everyone to an education.''ICESCR'', Article 13.1 Education is compulsory in most places up to a certain age, but attendance at school
A school is the educational institution (and, in the case of in-person learning, the Educational architecture, building) designed to provide learning environments for the teaching of students, usually under the direction of teachers. Most co ...
may not be, with alternative options such as home-schooling
Homeschooling or home schooling (American English), also known as home education or elective home education (EHE) (British English), is the education of school-aged children at home or a variety of places other than a school. Usually conducted ...
or e-learning
Educational technology (commonly abbreviated as edutech, or edtech) is the combined use of computer hardware, software, and educational theory and practice to facilitate learning and teaching. When referred to with its abbreviation, "EdTech" ...
being recognized as valid forms of education in certain jurisdictions.
Children in some countries (especially in parts of Africa and Asia) are often kept out of school, or attend only for short periods. Data from UNICEF
UNICEF ( ), originally the United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund, officially United Nations Children's Fund since 1953, is an agency of the United Nations responsible for providing Humanitarianism, humanitarian and Development a ...
indicate that in 2011, 57 million children were out of school; and more than 20% of African children have never attended primary school or have left without completing primary education. According to a UN report, warfare
War is an armed conflict between the armed forces of State (polity), states, or between governmental forces and armed groups that are organized under a certain command structure and have the capacity to sustain military operations, or betwe ...
is preventing 28 million children worldwide from receiving an education, due to the risk of sexual violence and attacks in schools. Other factors that keep children out of school include poverty, child labor, social attitudes, and long distances to school.
Attitudes toward children
 Social attitudes toward children differ around the world in various cultures and change over time. A 1988 study on European attitudes toward the centrality of children found that Italy was more child-centric and the Netherlands less child-centric, with other countries, such as Austria, Great Britain, Ireland and
Social attitudes toward children differ around the world in various cultures and change over time. A 1988 study on European attitudes toward the centrality of children found that Italy was more child-centric and the Netherlands less child-centric, with other countries, such as Austria, Great Britain, Ireland and West Germany
West Germany was the common English name for the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG) from its formation on 23 May 1949 until German reunification, its reunification with East Germany on 3 October 1990. It is sometimes known as the Bonn Republi ...
falling in between.
Child marriage
In 2013,child marriage
Child marriage is a practice involving a marriage or domestic partnership, formal or informal, that includes an individual under 18 and an adult or other child.*
*
*
*
Research has found that child marriages have many long-term negative co ...
rates of female children under the age of 18 reached 75% in Niger, 68% in Central African Republic and Chad, 66% in Bangladesh, and 47% in India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
. According to a 2019 UNICEF
UNICEF ( ), originally the United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund, officially United Nations Children's Fund since 1953, is an agency of the United Nations responsible for providing Humanitarianism, humanitarian and Development a ...
report on child marriage, 37% of females were married before the age of 18 in sub-Saharan Africa, followed by South Asia at 30%. Lower levels were found in Latin America and Caribbean (25%), the Middle East and North Africa (18%), and Eastern Europe and Central Asia (11%), while rates in Western Europe and North America were minimal. Child marriage is more prevalent with girls, but also involves boys. A 2018 study in the journal Vulnerable Children and Youth Studies found that, worldwide, 4.5% of males are married before age 18, with the Central African Republic having the highest average rate at 27.9%.
Fertility and number of children per woman
Beforecontraception
Birth control, also known as contraception, anticonception, and fertility control, is the use of methods or devices to prevent pregnancy. Birth control has been used since ancient times, but effective and safe methods of birth control only be ...
became widely available in the 20th century, women had little choice other than abstinence
Abstinence is the practice of self-enforced restraint from indulging in bodily activities that are widely experienced as giving pleasure. Most frequently, the term refers to sexual abstinence, but it can also mean abstinence from alcohol (drug), ...
or having often many children. In fact, current population growth
Population growth is the increase in the number of people in a population or dispersed group. The World population, global population has grown from 1 billion in 1800 to 8.2 billion in 2025. Actual global human population growth amounts to aroun ...
concerns have only become possible with drastically reduced child mortality
Child mortality is the death of children under the age of five. The child mortality rate (also under-five mortality rate) refers to the probability of dying between birth and exactly five years of age expressed per 1,000 live births.
It encompa ...
and sustained fertility. In 2017 the global total fertility rate
The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that are born to a woman over her lifetime, if they were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates (ASFRs) through their lifetime, and they were t ...
was estimated to be 2.37 children per woman, adding about 80 million people to the world population per year. In order to measure the total number of children, scientists often prefer the completed cohort fertility at age 50 years (CCF50). Although the number of children is also influenced by cultural norms
A social norm is a shared standard of acceptable behavior by a group. Social norms can both be informal understandings that govern the behavior of members of a society, as well as be codified into rules and laws. Social normative influences or so ...
, religion
Religion is a range of social system, social-cultural systems, including designated religious behaviour, behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, religious text, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics in religion, ethics, or ...
, peer pressure
Peer pressure is a direct or indirect influence on peers, i.e., members of social groups with similar interests and experiences, or social statuses. Members of a peer group are more likely to influence a person's beliefs, values, religion and beh ...
and other social factors, the CCF50 appears to be most heavily dependent on the educational level of women, ranging from 5–8 children in women without education to less than 2 in women with 12 or more years of education.
Issues
Emergencies and conflicts
Emergencies and conflicts pose detrimental risks to thehealth
Health has a variety of definitions, which have been used for different purposes over time. In general, it refers to physical and emotional well-being, especially that associated with normal functioning of the human body, absent of disease, p ...
, safety, and well-being of children. There are many different kinds of conflicts and emergencies, e.g. war
War is an armed conflict between the armed forces of states, or between governmental forces and armed groups that are organized under a certain command structure and have the capacity to sustain military operations, or between such organi ...
s and natural disaster
A natural disaster is the very harmful impact on a society or community brought by natural phenomenon or Hazard#Natural hazard, hazard. Some examples of natural hazards include avalanches, droughts, earthquakes, floods, heat waves, landslides ...
s. As of 2010 approximately 13 million children are displaced by armed conflicts
War is an armed conflict between the armed forces of states, or between governmental forces and armed groups that are organized under a certain command structure and have the capacity to sustain military operations, or between such organize ...
and violence
Violence is characterized as the use of physical force by humans to cause harm to other living beings, or property, such as pain, injury, disablement, death, damage and destruction. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines violence a ...
around the world. Where violent conflicts are the norm, the lives of young children are significantly disrupted and their families have great difficulty in offering the sensitive and consistent care that young children need for their healthy development. Studies on the effect of emergencies and conflict on the physical and mental health
Mental health is often mistakenly equated with the absence of mental illness. However, mental health refers to a person's overall emotional, psychological, and social well-being. It influences how individuals think, feel, and behave, and how t ...
of children between birth and 8 years old show that where the disaster is natural, the rate of PTSD
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a mental disorder that develops from experiencing a traumatic event, such as sexual assault, domestic violence, child abuse, warfare and its associated traumas, natural disaster, traffic collision, ...
occurs in anywhere from 3 to 87 percent of affected children. However, rates of PTSD for children living in chronic conflict conditions varies from 15 to 50 percent.
Child protection
Child abuse and child labor
Protection of children fromabuse
Abuse is the act of improper usage or treatment of a person or thing, often to unfairly or improperly gain benefit. Abuse can come in many forms, such as: physical or verbal maltreatment, injury, assault, violation, rape, unjust practices, ...
is considered an important contemporary goal. This includes protecting children from exploitation such as child labor
Child labour is the exploitation of children through any form of work that interferes with their ability to attend regular school, or is mentally, physically, socially and morally harmful. Such exploitation is prohibited by legislation w ...
, child trafficking
Trafficking of children, also known as child trafficking, is a form of human trafficking and is defined by the United Nations as the "recruitment, transportation, harbouring, or receipt of a child" for the purpose of slavery, forced labour, and ...
and child selling
Child-selling is the practice of selling children, usually by parents, legal guardians, or subsequent custodians, including adoption agencies, orphanages and Mother and Baby Homes. Where the subsequent relationship with the child is essentia ...
, child sexual abuse
Child sexual abuse (CSA), also called child molestation, is a form of child abuse in which an adult or older adolescent uses a child for sexual stimulation. Forms of child sexual abuse include engaging in Human sexual activity, sexual activit ...
, including child prostitution
Child prostitution is prostitution involving a child, and it is a form of commercial sexual exploitation of children. The term normally refers to prostitution of a minor, or person under the legal age of consent.
In most jurisdictions, child ...
and child pornography
Child pornography (also abbreviated as CP, also called child porn or kiddie porn, and child sexual abuse material, known by the acronym CSAM (underscoring that children can not be deemed willing participants under law)), is Eroticism, erotic ma ...
, military use of children
Children in the military, including state armed forces, non-state armed groups, and other military organizations, may be trained for combat, assigned to support roles, such as cooks, porters/couriers, or messengers, or used for tactical adv ...
, and child laundering
Child laundering is a tactic used in illegal or fraudulent international adoptions. It may involve child trafficking and child acquisition through payment, deceit or force. The children may then be held in sham orphanages while formal adoption ...
in illegal adoption
Adoption is a process whereby a person assumes the parenting of another, usually a child, from that person's biological or legal parent or parents. Legal adoptions permanently transfer all rights and responsibilities, along with filiation, fro ...
s. There exist several international instruments for these purposes, such as:
* Worst Forms of Child Labour Convention
The Convention Concerning the Prohibition and Immediate Action for the Elimination of the Worst Forms of Child Labour, known in short as the Worst Forms of Child Labour Convention, was adopted by the International Labour Organization (ILO) in 1 ...
* Minimum Age Convention, 1973
The ILO Convention Concerning Minimum Age for Admission to Employment C138, is a convention adopted in 1973 by the International Labour Organization. It requires ratifying states to pursue a national policy designed to ensure the effective aboli ...
* Optional Protocol on the Sale of Children, Child Prostitution and Child Pornography
The Optional Protocol on the Sale of Children, Child Prostitution and Child Pornography is a protocol to the Convention on the Rights of the Child and requires parties to prohibit the sale of children, child prostitution and child pornography.
...
* Council of Europe Convention on the Protection of Children against Sexual Exploitation and Sexual Abuse
The Council of Europe Convention on the Protection of Children Against Sexual Exploitation and Sexual Abuse, also known as the Lanzarote Convention, is a Council of Europe multilateral treaty whereby states agree to criminalise certain forms of se ...
* Optional Protocol on the Involvement of Children in Armed Conflict
The Optional Protocol to the Convention on the Rights of the Child on the Involvement of Children in Armed Conflict (OPAC), also known as the child soldier treaty, is a multilateral treaty whereby states agree to: 1) prohibit the conscription ...
* Hague Adoption Convention
The Hague Convention on Protection of Children and Co-operation in Respect of Intercountry Adoption (or Hague Adoption Convention) is an international convention dealing with international adoption, child laundering, and child trafficking ...
Climate change
Health
Child mortality
During the early 17th century inEngland
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
, about two-thirds of all children died before the age of four. During the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succee ...
, the life expectancy of children increased dramatically. This has continued in England, and in the 21st century child mortality rates have fallen across the world. About 12.6 million under-five infants died worldwide in 1990, which declined to 6.6 million in 2012. The infant mortality rate dropped from 90 deaths per 1,000 live births in 1990, to 48 in 2012. The highest average infant mortality rates are in sub-Saharan Africa, at 98 deaths per 1,000 live births – over double the world's average.
See also
*Outline of childhood
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to childhood:
Children – biologically, a child (plural: children) is generally a human between the stages of birth and puberty. Some definitions include the unborn (termed ...
* Child slavery
Child slavery means that children have to work under slave-like conditions. Even though-slavery has been abolished, there are still many children with this fate. Many of them live in developing countries. The enslavement of children can be trac ...
* Childlessness
Childlessness is the state of not having children. Childlessness may have personal, social or political significance.
Childlessness, which may be by choice or circumstance, is distinguished from voluntary childlessness, also called being "childfr ...
* Depression in childhood and adolescence
Major depressive disorder, often simply referred to as depression, is a mental disorder characterized by prolonged unhappiness or irritability. It is accompanied by a constellation of somatic and cognitive signs and symptoms such as fatigue, ...
* One-child policy
The one-child policy ( zh, c=一孩政策, p=yī hái zhèngcè) was a population planning initiative in China implemented between 1979 and 2015 to curb the country's population growth by restricting many families to a single child. The progr ...
* Religion and children
Children often acquire religious views approximating those of their parents, although they may also be influenced by others they communicate with – such as peers and teachers. Matters relating the subject of children and religion may include r ...
* Youth rights
The youth rights movement (also known as youth liberation) seeks to grant the rights to Youth, young people that are traditionally reserved for adults. This is closely akin to the notion of evolving capacities within the children's rights mov ...
* Archaeology of childhood
The archaeology of childhood is an emerging field of study within archaeology that applied anthropology, ethnography, history, sociology, osteology and biological anthropology to the study of the development and lives of juvenile human individuals ...
References
Sources
* *Further reading
* Cook, Daniel Thomas. ''The moral project of childhood: Motherhood, material life, and early children's consumer culture'' (NYU Press, 2020)online book
see also
online review
* Fawcett, Barbara, Brid Featherstone, and Jim Goddard. ''Contemporary child care policy and practice'' (Bloomsbury Publishing, 2017
online
* Hutchison, Elizabeth D., and Leanne W. Charlesworth. "Securing the welfare of children: Policies past, present, and future." ''Families in Society'' 81.6 (2000): 576–585. * Fass, Paula S. ''The end of American childhood: A history of parenting from life on the frontier to the managed child'' (Princeton University Press, 2016). * Fass, Paula S. ed. ''The Routledge History of Childhood in the Western World'' (2012
online
* Klass, Perri. ''The Best Medicine: How Science and Public Health Gave Children a Future'' (WW Norton & Company, 2020
online
* Michail, Samia. "Understanding school responses to students’ challenging behaviour: A review of literature." ''Improving schools'' 14.2 (2011): 156–171
online
* Sorin, Reesa. ''Changing images of childhood: Reconceptualising early childhood practice'' (Faculty of Education, University of Melbourne, 2005
online
* Sorin, Reesa. "Childhood through the eyes of the child and parent." ''Journal of Australian Research in Early Childhood Education'' 14.1 (2007)
online
* Vissing, Yvonne. "History of Children’s Human Rights in the USA." in ''Children's Human Rights in the USA: Challenges and Opportunities'' (Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2023) pp. 181–212. * Yuen, Francis K.O. ''Social work practice with children and families: a family health approach'' (Routledge, 2014
online
{{Authority control * Developmental psychology Kinship and descent