Chester Cathedral on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Chester Cathedral is a
 *
*
Chester Cathedral & its Historic Links with New York
* ttps://archive.today/20121224033929/http://www.npor.org.uk/cgi-bin/Rsearch.cgi?Fn=Rsearch&rec_index=K00226 Details of organ
British History Online
* ttps://www.british-towns.net/england/midland/cheshire-west-and-chester/chester/album/plan-of-chester-cathedral Plan of the cathedral
Medieval stained glass from CVMA
Photographs and panorama
Chester Cathedral Quarter — development project
Chester Cathedral Nave Choir Website
{{Authority control Anglican cathedrals in England Grade I listed cathedrals Grade I listed monasteries Tourist attractions in Cheshire Church of England church buildings in Cheshire Grade I listed buildings in Chester English churches with Norman architecture English Gothic architecture in Cheshire Buildings and structures in Chester Diocese of Chester Thomas Harrison buildings Arthur Blomfield buildings Churches in Chester Pre-Reformation Roman Catholic cathedrals Monasteries dissolved under the English Reformation 13th-century church buildings in England
Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the State religion#State churches, established List of Christian denominations, Christian church in England and the Crown Dependencies. It is the mother church of the Anglicanism, Anglican Christian tradition, ...
cathedral
A cathedral is a church (building), church that contains the of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, Annual conferences within Methodism, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually s ...
and the mother church
Mother church or matrice is a term depicting the Christian Church as a mother in her functions of nourishing and protecting the believer. It may also refer to the primary church of a Christian denomination or diocese, i.e. a cathedral church, or ...
of the Diocese of Chester. It is located in the city of Chester
Chester is a cathedral city in Cheshire, England, on the River Dee, Wales, River Dee, close to the England–Wales border. With a built-up area population of 92,760 in 2021, it is the most populous settlement in the borough of Cheshire West an ...
, Cheshire
Cheshire ( ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in North West England. It is bordered by Merseyside to the north-west, Greater Manchester to the north-east, Derbyshire to the east, Staffordshire to the south-east, and Shrop ...
, England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
. The cathedral, formerly the abbey
An abbey is a type of monastery used by members of a religious order under the governance of an abbot or abbess. Abbeys provide a complex of buildings and land for religious activities, work, and housing of Christians, Christian monks and nun ...
church of a Benedictine
The Benedictines, officially the Order of Saint Benedict (, abbreviated as O.S.B. or OSB), are a mainly contemplative monastic order of the Catholic Church for men and for women who follow the Rule of Saint Benedict. Initiated in 529, th ...
monastery dedicated to Saint Werburgh, is dedicated to Christ and the Blessed Virgin Mary
Mary was a first-century Jewish woman of Nazareth, the wife of Saint Joseph, Joseph and the mother of Jesus. She is an important figure of Christianity, venerated under titles of Mary, mother of Jesus, various titles such as Perpetual virginity ...
. Since 1541, it has been the seat of the bishop of Chester
The Bishop of Chester is the Ordinary of the Church of England Diocese of Chester in the Province of York.
The diocese extends across most of the historic county boundaries of Cheshire, including the Wirral Peninsula and has its see in the ...
.
The cathedral is a Grade I listed building
In the United Kingdom, a listed building is a structure of particular architectural or historic interest deserving of special protection. Such buildings are placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Hi ...
, and part of a heritage site that also includes the former monastic
Monasticism (; ), also called monachism or monkhood, is a religious way of life in which one renounces worldly pursuits to devote oneself fully to spiritual activities. Monastic life plays an important role in many Christian churches, especially ...
buildings to the north, which are also listed Grade I. The cathedral's construction dates from between the 10th century and the early 16th century, having been modified a number of times throughout history, a typical characteristic of English cathedrals; however, the site itself may have been used for Christian worship since Roman times. All the major styles of English medieval architecture, from Norman to Perpendicular
In geometry, two geometric objects are perpendicular if they intersect at right angles, i.e. at an angle of 90 degrees or π/2 radians. The condition of perpendicularity may be represented graphically using the '' perpendicular symbol'', � ...
, are represented in the present building.
The cathedral and former monastic buildings were extensively restored during the 19th century (amidst some controversy), and a free standing bell tower was added in the 20th century. In addition to holding services for Christian worship, the buildings are a major tourist attraction in Chester and the cathedral is used as a venue for concerts and exhibitions.
History
The city of Chester was an important Roman stronghold. There may have been a Christianbasilica
In Ancient Roman architecture, a basilica (Greek Basiliké) was a large public building with multiple functions that was typically built alongside the town's forum. The basilica was in the Latin West equivalent to a stoa in the Greek Eas ...
on the site of the present cathedral in the late Roman era
In modern historiography, ancient Rome is the Roman people, Roman civilisation from the founding of Rome, founding of the Italian city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, collapse of the Western Roman Em ...
, while Chester was controlled by Legio XX Valeria Victrix. Legend holds that the basilica was dedicated to Saint Paul and Saint Peter
Saint Peter (born Shimon Bar Yonah; 1 BC – AD 64/68), also known as Peter the Apostle, Simon Peter, Simeon, Simon, or Cephas, was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus and one of the first leaders of the Jewish Christian#Jerusalem ekklēsia, e ...
. This is supported by evidence that in Saxon
The Saxons, sometimes called the Old Saxons or Continental Saxons, were a Germanic people of early medieval "Old" Saxony () which became a Carolingian " stem duchy" in 804, in what is now northern Germany. Many of their neighbours were, like th ...
times the dedication of an early chapel on this site was changed from Saint Peter to Saint Werburgh. In 958 King Edgar
Edgar is a commonly used masculine English given name, from an Anglo-Saxon name ''Edgar'' (composed of ''wikt:en:ead, ead'' "rich, prosperous" and ''Gar (spear), gar'' "spear").
Like most Anglo-Saxon names, it fell out of use by the Late Midd ...
granted land to the Minster of St Werburgh in Chester.
During the Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages (historiography), Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th to the 10th century. They marked the start o ...
Barloc of Norbury, a Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
*Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Foot ...
saint
In Christianity, Christian belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of sanctification in Christianity, holiness, imitation of God, likeness, or closeness to God in Christianity, God. However, the use of the ...
and hermit
A hermit, also known as an eremite (adjectival form: hermitic or eremitic) or solitary, is a person who lives in seclusion. Eremitism plays a role in a variety of religions.
Description
In Christianity, the term was originally applied to a Chr ...
, was venerated
Veneration (; ), or veneration of saints, is the act of honoring a saint, a person who has been identified as having a high degree of sanctity or holiness. Angels are shown similar veneration in many religions. Veneration of saints is practiced, ...
at Chester Cathedral with a feast day
The calendar of saints is the traditional Christian method of organizing a liturgical year by associating each day with one or more saints and referring to the day as the feast day or feast of said saint. The word "feast" in this context does n ...
on 10 September. He is known to history mainly through the hagiography
A hagiography (; ) is a biography of a saint or an ecclesiastical leader, as well as, by extension, an adulatory and idealized biography of a preacher, priest, founder, saint, monk, nun or icon in any of the world's religions. Early Christian ...
of the Secgan manuscript; he also occurs in a litany in MS Tanner 169* of the Bodleian Library
The Bodleian Library () is the main research library of the University of Oxford. Founded in 1602 by Sir Thomas Bodley, it is one of the oldest libraries in Europe. With over 13 million printed items, it is the second-largest library in ...
, Oxford
Oxford () is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and non-metropolitan district in Oxfordshire, England, of which it is the county town.
The city is home to the University of Oxford, the List of oldest universities in continuou ...
.
In 907 Chester was refortified against the threat from the Vikings, and shortly afterwards the minster was founded or refounded, and Werburgh's remains were transferred there from Hanbury, probably by Æthelflæd
Æthelflæd ( – 12 June 918) ruled as Lady of the Mercians in the English Midlands from 911 until her death in 918. She was the eldest child of Alfred the Great, king of the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of Wessex, and his wife Ealhswith.
Æthelflæd ...
, Lady of the Mercians. The collegiate church
In Christianity, a collegiate church is a church where the daily office of worship is maintained by a college of canons, a non-monastic or "secular" community of clergy, organised as a self-governing corporate body, headed by a dignitary bearing ...
, as it was then, was restored in 1057 by Leofric, Earl of Mercia
Leofric (died 31 August or 30 September 1057) was an Earl of Mercia. He founded monasteries at Coventry and Much Wenlock and was a very powerful earl under King Cnut and his successors. Leofric was the husband of Lady Godiva.
Life
Leofric was ...
, and Lady Godiva
Lady Godiva (; died between 1066 and 1086), in Old English , was a late Anglo-Saxon noblewoman who is relatively well documented as the wife of Leofric, Earl of Mercia, and a patron of various churches and monasteries.
She is mainly remembere ...
. This church was razed to the ground around 1090, with the secular canons evicted, and no known trace of it remains.
In 1093 a Benedictine
The Benedictines, officially the Order of Saint Benedict (, abbreviated as O.S.B. or OSB), are a mainly contemplative monastic order of the Catholic Church for men and for women who follow the Rule of Saint Benedict. Initiated in 529, th ...
abbey
An abbey is a type of monastery used by members of a religious order under the governance of an abbot or abbess. Abbeys provide a complex of buildings and land for religious activities, work, and housing of Christians, Christian monks and nun ...
was established on the site by Hugh Lupus, Earl of Chester
The Earldom of Chester () was one of the most powerful earldoms in medieval England, extending principally over the counties of Cheshire and Flintshire. Since 1301 the title has generally been granted to heirs apparent to the English throne, ...
, with the assistance of St Anselm and other monks from Bec in Normandy. The earliest surviving parts of the structure date from that time. The abbey church was not at that time the cathedral of Chester; from 1075 to 1082 the cathedral of the diocese was the nearby church of St John the Baptist, after which the see was transferred to Coventry
Coventry ( or rarely ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and metropolitan borough in the West Midlands (county), West Midlands county, in England, on the River Sherbourne. Coventry had been a large settlement for centurie ...
. In 1538, during the dissolution of the monasteries, the monastery was disbanded and the shrine of Saint Werburgh was desecrated. In 1541 St Werburgh's abbey became a cathedral of the Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the State religion#State churches, established List of Christian denominations, Christian church in England and the Crown Dependencies. It is the mother church of the Anglicanism, Anglican Christian tradition, ...
, by order of Henry VIII. At the same time, the dedication was changed to Christ and the Blessed Virgin. The last abbot
Abbot is an ecclesiastical title given to the head of an independent monastery for men in various Western Christian traditions. The name is derived from ''abba'', the Aramaic form of the Hebrew ''ab'', and means "father". The female equivale ...
of St Werburgh's Abbey, Thomas Clarke, became the first dean of the new cathedral, at the head of a secular chapter.
Although little trace of the 10th-century church has been discovered, save possibly some Saxon masonry found during a 1997 excavation of the nave, there is much evidence of the monastery of 1093. This work in the Norman style may be seen in the northwest tower, the north transept
A transept (with two semitransepts) is a transverse part of any building, which lies across the main body of the building. In cruciform ("cross-shaped") cruciform plan, churches, in particular within the Romanesque architecture, Romanesque a ...
and in remaining parts of the monastic buildings. The abbey church, beginning with the Lady Chapel at the eastern end, was extensively rebuilt in Gothic style during the 13th and 14th centuries. At the time of the dissolution of the monasteries, the cloister
A cloister (from Latin , "enclosure") is a covered walk, open gallery, or open Arcade (architecture), arcade running along the walls of buildings and forming a quadrangle (architecture), quadrangle or garth. The attachment of a cloister to a cat ...
, the central tower, a new south transept, the large west window and a new entrance porch to the south had just been built in the Perpendicular
In geometry, two geometric objects are perpendicular if they intersect at right angles, i.e. at an angle of 90 degrees or π/2 radians. The condition of perpendicularity may be represented graphically using the '' perpendicular symbol'', � ...
style, and the southwest tower of the façade had been begun. The west front was given a Tudor entrance, but the tower was never completed.
In 1636 the space beneath the south west tower became a bishop's consistory court. It was furnished as such at that time, and is now a unique survival in England, hearing its last case, that of an attempted suicide of a priest, in the 1930s. Until 1881, the south transept, which is unusually large, also took on a separate function as an independent ecclesiastical entity: the parish church
A parish church (or parochial church) in Christianity is the Church (building), church which acts as the religious centre of a parish. In many parts of the world, especially in rural areas, the parish church may play a significant role in com ...
of St Oswald. Although the 17th century saw additions to the furnishings and fittings, there was no further building work for several centuries. By the 19th century, the building was badly in need of restoration. The present homogeneous appearance that the cathedral presents from many exterior angles is largely the work of Victorian restorers, particularly George Gilbert Scott
Sir George Gilbert Scott (13 July 1811 – 27 March 1878), largely known as Sir Gilbert Scott, was a prolific English Gothic Revival architect, chiefly associated with the design, building and renovation of churches and cathedrals, although he ...
.
The 20th century has seen continued maintenance and restoration. In 1922, the Chester War Memorial was installed in the cathedral grounds and dedicated to the fallen soldiers of the First World War and later the Second World War. In 1973–75 a detached belfry, the Addleshaw Tower, designed by George Pace, was erected in the grounds of the cathedral. In 2005 a new Song School was added to the cathedral. During the 2000s, the cathedral library was refurbished and relocated. It was officially reopened in September 2007. The cathedral and the former monastic buildings were designated as Grade I listed buildings on 28 July 1955.
In October 2021, the abbey's gateway was one of 142 sites across England to receive part of a £35-million injection into the government's Culture Recovery Fund.
Architecture
Cathedral
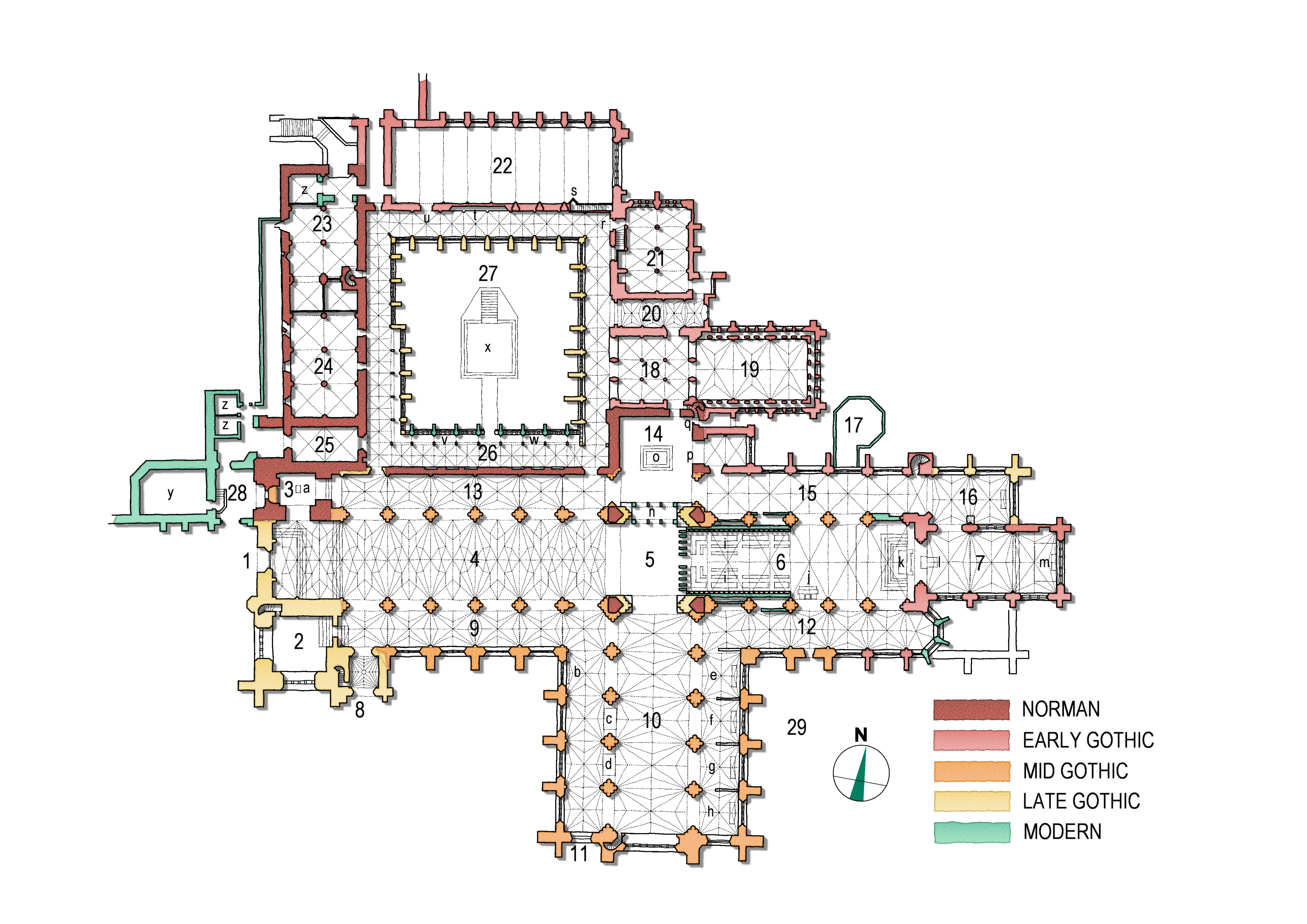
Plan
Chester Cathedral has an east–west axis, common to many cathedrals, with the chancel at the eastern end, and the façade to the west. The plan iscruciform
A cruciform is a physical manifestation resembling a common cross or Christian cross. These include architectural shapes, biology, art, and design.
Cruciform architectural plan
Christian churches are commonly described as having a cruciform ...
, with a central tower (as is usual in English monastic churches), but is asymmetrical, having a small transept
A transept (with two semitransepts) is a transverse part of any building, which lies across the main body of the building. In cruciform ("cross-shaped") cruciform plan, churches, in particular within the Romanesque architecture, Romanesque a ...
on the north side remaining from an earlier building, and an unusually large south transept. As the plan shows, the asymmetry extends to the west front, where the north tower remains from the Norman building, and the south tower is of the early 16th century. At the eastern end, the symmetrical arrangement of the aisles was lost when the end of the south aisle was demolished and rebuilt in an apsidal shape. The nave, choir and south transept have wide aisles on either side, and are lit by clerestory
A clerestory ( ; , also clearstory, clearstorey, or overstorey; from Old French ''cler estor'') is a high section of wall that contains windows above eye-level. Its purpose is to admit light, fresh air, or both.
Historically, a ''clerestory' ...
windows and large multi-light windows in each of the three cliff-like ends. To the north of the cathedral are monastic buildings, including the cloister
A cloister (from Latin , "enclosure") is a covered walk, open gallery, or open Arcade (architecture), arcade running along the walls of buildings and forming a quadrangle (architecture), quadrangle or garth. The attachment of a cloister to a cat ...
, refectory
A refectory (also frater, frater house, fratery) is a dining room, especially in monastery, monasteries, boarding schools and academic institutions. One of the places the term is most often used today is in graduate seminary, seminaries. The name ...
and a rectangular chapter house
A chapter house or chapterhouse is a building or room that is part of a cathedral, monastery or collegiate church in which meetings are held. When attached to a cathedral, the cathedral chapter meets there. In monasteries, the whole communi ...
. The façade of the building is abutted on the north by later buildings.

External appearance
Like the cathedrals ofCarlisle
Carlisle ( , ; from ) is a city in the Cumberland district of Cumbria, England.
Carlisle's early history is marked by the establishment of a settlement called Luguvalium to serve forts along Hadrian's Wall in Roman Britain. Due to its pro ...
, Lichfield
Lichfield () is a city status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and Civil parishes in England, civil parish in Staffordshire, England. Lichfield is situated south-east of the county town of Stafford, north-east of Walsall, north-west of ...
and Worcester, Chester Cathedral is built of New Red Sandstone
The New Red Sandstone, chiefly in United Kingdom, British geology, is composed of beds of red sandstone and associated rocks laid down throughout the Permian (300 million years ago) to the end of the Triassic (about 200 million years a ...
, in this case Keuper Sandstone from the Cheshire Basin. The stone lends itself to detailed carving, but is also friable, easily eroded by rain and wind, and is badly affected by pollution. With the other red sandstone buildings, Chester is one of the most heavily restored of England's cathedrals. The restoration, which included much refacing and many new details, took place mainly in the 19th century.
Because the south transept is similar in dimension to the nave and choir, views of the building from the south-east and south-west give the impression of a building balanced around a central axis, with its tower as the hub. The tower is of the late 15th century Perpendicular
In geometry, two geometric objects are perpendicular if they intersect at right angles, i.e. at an angle of 90 degrees or π/2 radians. The condition of perpendicularity may be represented graphically using the '' perpendicular symbol'', � ...
style, but its four large battlement
A battlement, in defensive architecture, such as that of city walls or castles, comprises a parapet (a defensive low wall between chest-height and head-height), in which gaps or indentations, which are often rectangular, occur at intervals ...
ed turret
Turret may refer to:
* Turret (architecture), a small tower that projects above the wall of a building
* Gun turret, a mechanism of a projectile-firing weapon
* Optical microscope#Objective turret (revolver or revolving nose piece), Objective turre ...
s are the work of the restoration architect George Gilbert Scott
Sir George Gilbert Scott (13 July 1811 – 27 March 1878), largely known as Sir Gilbert Scott, was a prolific English Gothic Revival architect, chiefly associated with the design, building and renovation of churches and cathedrals, although he ...
.
With its rhythmic arrangement of large, traceried windows, pinnacle
A pinnacle is an architectural element originally forming the cap or crown of a buttress or small turret, but afterwards used on parapets at the corners of towers and in many other situations. The pinnacle looks like a small spire. It was main ...
s, battlements and buttress
A buttress is an architectural structure built against or projecting from a wall which serves to support or reinforce the wall. Buttresses are fairly common on more ancient (typically Gothic) buildings, as a means of providing support to act ...
es, the exterior of Chester Cathedral from the south presents a fairly homogeneous character, which is an unusual feature as England's cathedrals are in general noted for their stylistic diversity. Close examination reveals window tracery
Tracery is an architectural device by which windows (or screens, panels, and vaults) are divided into sections of various proportions by stone ''bars'' or ''ribs'' of moulding. Most commonly, it refers to the stonework elements that support th ...
of several building stages from the 13th to the early 16th century. The richness of the 13th-century tracery is accentuated by the presence of ornate, crocketted drip-mouldings around the windows; those around the perpendicular windows are of simpler form.
The façade of the cathedral is dominated by a large deeply recessed eight-light window in the Perpendicular style, above a recessed doorway set in a screen-like porch designed, probably by Seth and George Derwall, in the early 1500s. This porch formed part of the same late 15th-century building programme as the south transept, central and southwest towers, and cloister. Neither of the west towers was completed. To the north is the lower stage of a Norman tower, while to the south is the lower stage of a tower designed and begun, probably by Seth and George Derwall, in 1508, but left incomplete following the dissolution of the monastery in 1538. The cathedral's façade is abutted on the north by a Victorian building housing the education centre and largely obscured from view by the building previously used as the King's School and the Choir School which was until 2024 a branch of Barclays Bank. The door of the west front is not used as the normal entrance to the cathedral, which is through the southwest porch which is in an ornate Tudor style.
Interior
The interior of Chester Cathedral gives a warm and mellow appearance because of the pinkish colour of the sandstone. The proportions appear spacious because the view from the west end of the nave to the east end is unimpeded by a pulpitum and the nave, although not long, is both wide and high compared with many of England's cathedrals. The piers of the nave and choir are widely spaced, those of the nave carrying only the clerestory of large windows with notriforium
A triforium is an interior Gallery (theatre), gallery, opening onto the tall central space of a building at an upper level. In a church, it opens onto the nave from above the side aisles; it may occur at the level of the clerestory windows, o ...
gallery. The proportions are made possible partly because the ornate stellar vault, like that at York Minster
York Minster, formally the Cathedral and Metropolitical Church of Saint Peter in York, is an Anglicanism, Anglican cathedral in the city of York, North Yorkshire, England. The minster is the seat of the archbishop of York, the second-highest of ...
, is of wood, not stone.
Norman remnants
The present building, dating from around 1283 to 1537, mostly replaced the earlier monastic church founded in 1093 which was built in the Norman style. It is believed that the newer church was built around the older one. That the few remaining parts of the Norman church are of small proportions, while the height and width of the Gothic church are generous would seem to confirm this belief. Aspects of the design of the Norman interior are still visible in the north transept, which retains wall arcading and a broadly moulded arch leading to thesacristy
A sacristy, also known as a vestry or preparation room, is a room in Christianity, Christian churches for the keeping of vestments (such as the alb and chasuble) and other church furnishings, sacred vessels, and parish records.
The sacristy is us ...
, which was formerly a chapel. The transept has retained an early 16th-century coffered ceiling with decorated bosses, two of which are carved with the arms
Arms or ARMS may refer to:
*Arm or arms, the upper limbs of the body
Arm, Arms, or ARMS may also refer to:
People
* Ida A. T. Arms (1856–1931), American missionary-educator, temperance leader
Coat of arms or weapons
*Armaments or weapons
**Fi ...
of Henry VIII and Cardinal Wolsey
Thomas Wolsey ( ; – 29 November 1530) was an English statesman and Catholic cardinal. When Henry VIII became King of England in 1509, Wolsey became the king's almoner. Wolsey's affairs prospered and by 1514 he had become the controlling f ...
.
The north west tower is also of Norman construction. It serves as the baptistry and houses a black marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock consisting of carbonate minerals (most commonly calcite (CaCO3) or Dolomite (mineral), dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2) that have recrystallized under the influence of heat and pressure. It has a crystalline texture, and is ty ...
font
In metal typesetting, a font is a particular size, weight and style of a ''typeface'', defined as the set of fonts that share an overall design.
For instance, the typeface Bauer Bodoni (shown in the figure) includes fonts " Roman" (or "regul ...
, consisting of a bowl on a large baluster
A baluster () is an upright support, often a vertical moulded shaft, square, or lathe-turned form found in stairways, parapets, and other architectural features. In furniture construction it is known as a spindle. Common materials used in its ...
dating from 1697. The lower part of the north wall of the nave is also from the Norman building, but can only be viewed from the cloister
A cloister (from Latin , "enclosure") is a covered walk, open gallery, or open Arcade (architecture), arcade running along the walls of buildings and forming a quadrangle (architecture), quadrangle or garth. The attachment of a cloister to a cat ...
because the interior has been decorated with mosaic
A mosaic () is a pattern or image made of small regular or irregular pieces of colored stone, glass or ceramic, held in place by plaster/Mortar (masonry), mortar, and covering a surface. Mosaics are often used as floor and wall decoration, and ...
.
Early English
TheEarly English Gothic
English Gothic is an architectural style that flourished from the late 12th until the mid-17th century. The style was most prominently used in the construction of cathedrals and churches. Gothic architecture's defining features are pointed a ...
chapter house, built between 1230 and 1265, is rectangular and opens off a "charming" vestibule leading from the north transept. The chapter house has grouped windows of simple untraceried form. Alec Clifton-Taylor describes the exterior of this building as a "modest but rather elegant example of composition in lancets" while Nikolaus Pevsner
Sir Nikolaus Bernhard Leon Pevsner (30 January 1902 – 18 August 1983) was a German-British art historian and architectural historian best known for his monumental 46-volume series of county-by-county guides, ''The Buildings of England'' (195 ...
says of the interior "It is a wonderfully noble room" which is the "aesthetic climax of the cathedral". To the north of the chapter house is the slype, also Early English in style, and the warming room, which contains two large former fireplaces. The monastic refectory to the north of the cloister is of about the same date as the chapter house.
The Lady Chapel to the eastern end of the choir dates from between 1265 and 1290. It is of three bays, and contains the Shrine of St Werburgh, dating from the 14th century. The vault of the Lady Chapel is the only one in the cathedral that is of stone. It is decorated with carved roof bosses representing the Trinity
The Trinity (, from 'threefold') is the Christian doctrine concerning the nature of God, which defines one God existing in three, , consubstantial divine persons: God the Father, God the Son (Jesus Christ) and God the Holy Spirit, thr ...
, the Madonna and Child
In Christian art, a Madonna () is a religious depiction of the Blessed Virgin Mary in a singular form or sometimes accompanied by the Child Jesus. These images are central icons for both the Roman Catholic and Orthodox churches. The word ...
, and the murder of Thomas Becket
Thomas Becket (), also known as Saint Thomas of Canterbury, Thomas of London and later Thomas à Becket (21 December 1119 or 1120 – 29 December 1170), served as Lord Chancellor from 1155 to 1162, and then as Archbishop of Canterbury fr ...
. The chapel also has a sedilia
In church architecture, sedilia (plural of Latin ''sedīle'', "seat") are seats, typically made of stone, located on the liturgical south side of the altar—often within the chancel—intended for use by the officiating priest, deacon, an ...
and a piscina
A piscina is a shallow basin placed near the altar of a church, or else in the vestry or sacristy, used for washing the communion vessels. The sacrarium is the drain itself. Lutherans and Anglicans usually refer to the basin, calling it a pisci ...
.
Decorated Gothic
The choir, of five bays, was built between 1283 and 1315 to the design of Richard Lenginour, and is an early example of Decorated Gothic architecture. The piers have strongly modelled attached shafts, supporting deeply moulded arches. There is a triforium gallery with four cusped arches to each bay. The sexpartite vault, which is a 19th-century restoration, is supported by clusters of three shafts which spring from energetic figurativecorbel
In architecture, a corbel is a structural piece of stone, wood or metal keyed into and projecting from a wall to carry a wikt:superincumbent, bearing weight, a type of bracket (architecture), bracket. A corbel is a solid piece of material in t ...
s. The overall effect is robust, and contrasts with the delicacy of the pinnacled choir stalls, the tracery of the windows and the rich decoration of the vault which was carried out by the ecclesiastical designers, Clayton and Bell
Clayton and Bell was one of the most prolific and proficient British workshops of stained-glass windows during the latter half of the 19th century and early 20th century. The partners were John Richard Clayton (1827–1913) and Alfred Bell (1832� ...
. The choir stalls, dating from about 1380, are one of the glories of the cathedral.
The aisles of the choir previously both extended on either side of the Lady Chapel. The south aisle was shortened in about 1870 by George Gilbert Scott, and given an apsidal east end, becoming the chapel of St Erasmus. The eastern end of the north aisle contains the chapel of St Werburgh.
The nave of six bays, and the large, aisled south transept were begun in about 1323, probably to the design of Nicholas de Derneford. There are a number of windows containing fine Flowing Decorated tracery of this period. The work ceased in 1375, in which year there was a severe outbreak of plague in England. The building of the nave was recommenced in 1485, more than 150 years after it was begun. The architect was probably William Rediche. Remarkably, for an English medieval architect, he maintained the original form, changing only the details. The nave was roofed with a stellar vault rather like that of the Lady Chapel at Ely and the choir at York Minster
York Minster, formally the Cathedral and Metropolitical Church of Saint Peter in York, is an Anglicanism, Anglican cathedral in the city of York, North Yorkshire, England. The minster is the seat of the archbishop of York, the second-highest of ...
, both of which date from the 1370s. Like that at York, the vault is of wood, imitating stone.
Perpendicular Gothic
From about 1493 until 1525 the architect appears to have been Seth Derwall, succeeded by George Derwall until 1537. Seth Derwall completed the south transept to aPerpendicular Gothic
Perpendicular Gothic (also Perpendicular, Rectilinear, or Third Pointed) architecture was the third and final style of English Gothic architecture developed in the Kingdom of England during the Late Middle Ages, typified by large windows, four-ce ...
design, as seen in the transomed windows of the clerestory. He also built the central tower, southwest porch and cloisters. Work commenced on the south west tower in 1508, but it had not risen above the roofline at the time of the dissolution of the monasteries, and has never been completed. The central tower, rising to , is a lantern tower with large windows letting light into the crossing. Its external appearance has been altered by the addition of four battlemented turrets by George Gilbert Scott in the 19th century.
Former monastic buildings
The Perpendicular Gothiccloister
A cloister (from Latin , "enclosure") is a covered walk, open gallery, or open Arcade (architecture), arcade running along the walls of buildings and forming a quadrangle (architecture), quadrangle or garth. The attachment of a cloister to a cat ...
is entered from the cathedral through a Norman doorway in the north aisle. The cloister is part of the building programme that commenced in the 1490s and is probably the work of Seth Derwall. The south wall of the cloister, dating from the later part of the Norman period, forms the north wall of the nave of the cathedral, and includes blind arcading. Among the earliest remaining structures on the site is an undercroft
An undercroft is traditionally a cellar or storage room, often brick-lined and Vault (architecture), vaulted, and used for storage in buildings since medieval times. In modern usage, an undercroft is generally a ground (street-level) area whi ...
off the west range of the cloisters, which dates from the early 12th century, and which was originally used by the monks for storing food. It consists of two naves with groin vaults and short round piers with round scalloped capitals.
Leading from the south of the undercroft is the abbot's passage which dates from around 1150 and consists of two bays with rib-vaulting. Above the abbot's passage, approached by a stairway from the west cloister, is St Anselm's Chapel which also dates from the 12th century. It is in three bays and has a 19th century Gothic-style plaster vault. The chancel is in one bay and was remodelled in the early 17th century. The screen, altar rails, holy table and plaster ceiling of the chancel date from the 17th century. The north range of the cloister gives access to a refectory, built by Simon de Whitchurch in the 13th century. It contains an Early English pulpit
A pulpit is a raised stand for preachers in a Christian church. The origin of the word is the Latin ''pulpitum'' (platform or staging). The traditional pulpit is raised well above the surrounding floor for audibility and visibility, accesse ...
, approached by a staircase with an ascending arcade. The only other similar pulpit in England is in Beaulieu Abbey
Beaulieu Abbey was a Cistercian abbey in Hampshire, England. It was founded in 1203–1204 by John of England, King John and (uniquely in England in the Middle Ages, Britain) populated by 30 monks sent from the abbey of Cîteaux in France, the ...
.
Restoration
By the 19th century the fabric of the building had become badly weathered, with Charles Hiatt writing that "the surface rot of the very perishable red sandstone, of which the cathedral was built, was positively unsightly" and that the "whole place previous to restoration struck one as woebegone and neglected; it perpetually seemed to hover on the verge of collapse, and yet was without a trace of the romance of the average ruin". Between 1818 and 1820 the architect Thomas Harrison restored the south transept, adding corner turrets. This part of the building served until 1881 as the parish church of St Oswald, and it was ecclesiastically separate. From 1844 R. C. Hussey carried out a limited restoration including work on the south side of the nave. The most extensive restoration was carried out by theGothic Revival
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic or neo-Gothic) is an Architectural style, architectural movement that after a gradual build-up beginning in the second half of the 17th century became a widespread movement in the first half ...
architect Sir Gilbert Scott, who between 1868 and 1876 "almost entirely re-cased" the cathedral. The current building is acknowledged to be mainly the product of this Victorian restoration commissioned by the Dean, John Saul Howson. In addition to extensive additions and alterations to the body of the church, Scott remodelled the tower, adding turret
Turret may refer to:
* Turret (architecture), a small tower that projects above the wall of a building
* Gun turret, a mechanism of a projectile-firing weapon
* Optical microscope#Objective turret (revolver or revolving nose piece), Objective turre ...
s and crenellations. Scott chose sandstone
Sandstone is a Clastic rock#Sedimentary clastic rocks, clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of grain size, sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate mineral, silicate grains, Cementation (geology), cemented together by another mineral. Sand ...
from the quarries at Runcorn
Runcorn is an industrial town and Runcorn Docks, cargo port in the Borough of Halton, Cheshire, England. Runcorn is on the south bank of the River Mersey, where the estuary narrows to form the Runcorn Gap. It is upstream from the port of Live ...
for his restoration work. In addition to the restoration of the fabric of the building, Scott designed internal fittings such as the choir screen to replace those destroyed during the Civil War
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
; the roof had also been melted down to make musket balls. He built the fan vault of the south porch, renewed the wooden vault of the choir and added a great many decorative features to the interior.
Scott's restorations were not without their critics and caused much debate in architectural circles. Scott claimed to have archaeological evidence for his work, but the Liverpool architect, Samuel Huggins, argued in an 1868 address to the Liverpool Architectural Society that the alterations were less like restoration and more like rebuilding. One of the larger changes was to shorten the south aisle and restyle it as an apse. The changes also proposed the addition of a spire above the existing tower, but this proposal was later rejected. Samuel's further paper of 1871 entitled ''On so-called restorations of our cathedral and abbey churches'' compelled the Dean to attempt to answer the criticism. The debate contributed to the establishment of the Society for the Protection of Ancient Buildings
The Society for the Protection of Ancient Buildings (SPAB) (also known as Anti-Scrape) is an amenity society founded by William Morris, Philip Webb, and others in 1877 to oppose the Victorian restoration, destructive 'restoration' of ancient bu ...
. ()
Later in the century, from 1882, Arthur Blomfield and his son Charles made further additions and modifications, including restoring and reinstating the Shrine of St Werburgh. More work was carried out in the 20th century by Giles Gilbert Scott between 1891 and 1913, and by F. H. Crossley in 1939.
Bell tower
Towards the end of 1963 the cathedral bells, which were housed in the central tower, were in need of an overhaul and ringing was suspended. In 1965 the Dean asked George Pace, architect toYork Minster
York Minster, formally the Cathedral and Metropolitical Church of Saint Peter in York, is an Anglicanism, Anglican cathedral in the city of York, North Yorkshire, England. The minster is the seat of the archbishop of York, the second-highest of ...
, to prepare specifications for a new bell frame and for electrification of the clock and tolling mechanism. Due to structural difficulties and the cost of replacing the bells in the central tower it was advised that consideration should be given to building a detached bell and clock tower in the southeast corner of the churchyard. It was decided to proceed with that plan, and in 1969 an announcement was made that the first detached cathedral bell tower was to be erected since the building of the campanile at Chichester Cathedral in the 15th century. In February 1969, nine of the ten bells in the central tower were removed to be recast by John Taylor & Co
John Taylor Bell Foundry (Loughborough) Limited, trading as John Taylor & Co and commonly known as Taylor's Bell Foundry, Taylor's of Loughborough, or simply Taylor's, is the world's largest working bell (instrument), bell foundry. It is locat ...
as a ring of twelve bells with a flat sixth. The new bells were cast in 1973. Work on the new bell-tower began in February 1973. Two old bells dating from 1606 and 1626 were left in the tower. On 26 February 1975 the bells were rung for the first time to celebrate the wedding of a member of the Grosvenor family. The official opening on 25 June 1975 was performed by the Duke of Gloucester
Duke of Gloucester ( ) is a British royal title (after Gloucester), often conferred on one of the sons of the reigning monarch. The first four creations were in the Peerage of England and the last in the Peerage of the United Kingdom; the curre ...
. The belfry is known as the Dean Addleshaw Tower, after the dean of the cathedral responsible for its construction. The tower is built in concrete, faced with sandstone at its base. It is the first detached bell tower to be built for a cathedral in this country since the Reformation
The Reformation, also known as the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation, was a time of major Theology, theological movement in Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the p ...
. Between the bell tower and the south transept is a garden in remembrance of the Cheshire Regiment
The Cheshire Regiment was a line infantry regiment of the British Army, part of the Prince of Wales' Division. The 22nd Regiment of Foot was raised by the Henry Howard, 7th Duke of Norfolk in 1689 and was able to boast an independent existence ...
(originally the 22nd Regiment of Foot).
Fittings and glass
The treasures of Chester Cathedral are its rare fittings, specifically its choir stalls and the 17th-century furnishing of the bishop's Consistory Court in the south tower, which is a unique survival.Choir stalls
The choir stalls date from about 1380. They have high, spiky, closely set canopies, with crocketed arches and spirelets. The stall ends have poppyheads and are rich with figurative carving. The stalls include 48misericord
A misericord (sometimes named mercy seat, like the biblical object) is a small wooden structure formed on the underside of a folding seat in a church which, when the seat is folded up, is intended to act as a shelf to support a person in a p ...
s, all but five of which are original, depicting a variety of subjects, some humorous and some grotesque. Pevsner states that they are "one of the finest sets in the country", while Alec Clifton-Taylor calls them "exquisite" and says of the misericords that "for delicacy and grace they surpass even those at Lincoln and Beverley".
Organ
In 1844, an organ by Gray & Davison of London was installed in the cathedral, replacing an instrument with parts dating back to 1626. The organ was rebuilt and enlarged by Whiteley Bros of Chester in 1876, to include harmonic flutes and reeds by Cavaillé-Coll. It was later moved to its present position at the front of the north transept. In 1910 William Hill and Son of London extensively rebuilt and revoiced the organ, replacing the Cavaillé-Coll reeds with new pipes of their own. The choir division of the organ was enlarged and moved behind the choirstalls on the south side. The instrument was again overhauled by Rushworth and Dreaper of Liverpool in 1969, when a new mechanism and some new pipework made to a design by the organist, Roger Fisher, was installed. Since 1991 the organ has been in the care of David Wells of Liverpool.Stained glass
:'' See Gallery below'' Chester suffered badly at the hands of theParliamentary
In modern politics and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
troops. As a consequence, its stained glass dates mainly from the 19th and 20th centuries and has representative examples the significant trends in stained glass design from the 1850s onwards. Of the earlier Victorian firms, William Wailes is the best represented, in the south aisle (1862), as well as Hardman & Co. and Michael O'Connor. Glass from the High Victorian period is well represented by two leading London firms, Clayton and Bell
Clayton and Bell was one of the most prolific and proficient British workshops of stained-glass windows during the latter half of the 19th century and early 20th century. The partners were John Richard Clayton (1827–1913) and Alfred Bell (1832� ...
and Heaton, Butler and Bayne. The Aesthetic style is represented by Charles Eamer Kempe
Charles Eamer Kempe (29 June 1837 – 29 April 1907) was a British Victorian era designer and manufacturer of stained glass. His studios produced over 4,000 windows and also designs for altars and altar frontals, furniture and furnishings, lychg ...
. Early 20th century windows include several commemorating those who died in World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
.
There are also several notable modern windows, the most recent being the refectory window of 2001 by Ros Grimshaw which depicts the Creation. The eight-light Perpendicular window of the west end contains mid-20th century glass representing the Holy Family and Saints, by W. T. Carter Shapland. Three modern windows in the south aisle, designed and made by Alan Younger to replace windows damaged in the Second World War. They were donated by the 6th Duke of Westminster to celebrate the 900th anniversary of the cathedral and contain the dates 1092 and 1992 to reflect the theme of "continuity and change".
Features
Nave
The west end of the nave is dominated by an eight-light window in the Perpendicular Gothic style which almost fills the upper part of the west wall. It contains stained glass designed by W. T. Carter Shapland dating from 1961 and depicts theHoly Family
The Holy Family consists of the Child Jesus, the Virgin Mary and Saint Joseph. The subject became popular in art from the 1490s on,Ainsworth, 122 but veneration of the Holy Family was formally begun in the 17th century by Saint François de La ...
in the middle two lights, flanked by the northern saints Werburgh, Oswald, Aidan, Chad
Chad, officially the Republic of Chad, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of North Africa, North and Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to Chad–Libya border, the north, Sudan to Chad–Sudan border, the east, the Central Afric ...
and Wilfrid
Wilfrid ( – 709 or 710) was an English bishop and saint. Born a Northumbrian noble, he entered religious life as a teenager and studied at Lindisfarne, at Canterbury, in Francia, and at Rome; he returned to Northumbria in about 660, and beca ...
, and Queen Ethelfleda.
The stone nave pulpit
A pulpit is a raised stand for preachers in a Christian church. The origin of the word is the Latin ''pulpitum'' (platform or staging). The traditional pulpit is raised well above the surrounding floor for audibility and visibility, accesse ...
was designed by the restorer R. C. Hussey and the lectern
A lectern is a standing reading desk with a slanted top, on which documents or books are placed as support for reading aloud, as in a scripture reading, lecture, or sermon. A lectern is usually attached to a stand or affixed to some other form of ...
, dated 1876, is by Skidmore. The mosaic
A mosaic () is a pattern or image made of small regular or irregular pieces of colored stone, glass or ceramic, held in place by plaster/Mortar (masonry), mortar, and covering a surface. Mosaics are often used as floor and wall decoration, and ...
floor of the tower bay was designed by John Howson (Dean, 1867–1885) and executed by Burke and Co. The same firm installed the mosaics which decorate the wall of the north aisle, depicting the patriarchs and prophets Abraham
Abraham (originally Abram) is the common Hebrews, Hebrew Patriarchs (Bible), patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father who began the Covenant (biblical), covenanta ...
, Moses
In Abrahamic religions, Moses was the Hebrews, Hebrew prophet who led the Israelites out of slavery in the The Exodus, Exodus from ancient Egypt, Egypt. He is considered the most important Prophets in Judaism, prophet in Judaism and Samaritani ...
, David
David (; , "beloved one") was a king of ancient Israel and Judah and the third king of the United Monarchy, according to the Hebrew Bible and Old Testament.
The Tel Dan stele, an Aramaic-inscribed stone erected by a king of Aram-Dam ...
and Elijah
Elijah ( ) or Elias was a prophet and miracle worker who lived in the northern kingdom of Israel during the reign of King Ahab (9th century BC), according to the Books of Kings in the Hebrew Bible.
In 1 Kings 18, Elijah defended the worsh ...
. They were designed by J. R. Clayton of Clayton and Bell, and date from 1883 to 86.
Monuments in the nave include those to Roger Barnston, dated 1838, by John Blayney, to Nicholas Stratford (Bishop, 1689–1707), dated 1708, to George Hall (Bishop, 1662–1668 (d.)), to Edmund Entwistle, dated 1712, to John and Thomas Wainwright who died respectively in 1686 and 1720, to Robert Bickerstaff who died in 1841 by Blayney, to William Smith (Dean, 1758–1787 (d.)) by Thomas Banks, and to William Mainwaring, dated 1671.
Quire
The most famous feature of the quire is the set of choir stalls, dating from about 1380, and described above. The lectern, in the form of a wooden eagle, symbol ofJohn the Evangelist
John the Evangelist ( – ) is the name traditionally given to the author of the Gospel of John. Christians have traditionally identified him with John the Apostle, John of Patmos, and John the Presbyter, although there is no consensus on how ...
, dates from the first half of the 17th century. The candlesticks also date from the 17th century and are by Censore of Bologna
Bologna ( , , ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the Emilia-Romagna region in northern Italy. It is the List of cities in Italy, seventh most populous city in Italy, with about 400,000 inhabitants and 150 different nationalities. Its M ...
who died in 1662.
With these exceptions, most of the decoration and the fittings of the quire date from the 19th century and are in keeping with the Gothic Revival
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic or neo-Gothic) is an Architectural style, architectural movement that after a gradual build-up beginning in the second half of the 17th century became a widespread movement in the first half ...
promoted by the Oxford Movement
The Oxford Movement was a theological movement of high-church members of the Church of England which began in the 1830s and eventually developed into Anglo-Catholicism. The movement, whose original devotees were mostly associated with the Un ...
and Augustus Welby Pugin. The restored vault of the quire is typical of the period, having been designed by Scott and decorated and gilded by Clayton and Bell.
The quire is entered through a screen designed by George Gilbert Scott, with gates made by Skidmore. The rood
A rood or rood cross, sometimes known as a triumphal cross, is a cross or crucifix, especially the large crucifix set above the entrance to the chancel of a medieval church. Alternatively, it is a large sculpture or painting of the crucifixio ...
was designed by Scott, and was made by F. Stuflesser. The bishop's throne or "cathedra
A ''cathedra'' is the throne of a bishop in the early Christian basilica. When used with this meaning, it may also be called the bishop's throne. With time, the related term ''cathedral'' became synonymous with the "seat", or principa ...
" was designed by Scott to complement the choir stalls. It was constructed by Farmer and Brindley in 1876. The reredos
A reredos ( , , ) is a large altarpiece, a screen, or decoration placed behind the altar in a Church (building), church. It often includes religious images.
The term ''reredos'' may also be used for similar structures, if elaborate, in secular a ...
and the floor mosaic
A mosaic () is a pattern or image made of small regular or irregular pieces of colored stone, glass or ceramic, held in place by plaster/Mortar (masonry), mortar, and covering a surface. Mosaics are often used as floor and wall decoration, and ...
date from 1876, and were designed by J. R. Clayton. The east window has tracery of an elegant Decorated Gothic design which is filled with stained glass of 1884 by Heaton, Butler and Bayne.
Lady Chapel
The 13th-century Lady Chapel contains the stone shrine of Saint Werburgh which dates from the 14th century and which used to contain her relics. The shrine, of similar red sandstone as the cathedral, has a base pierced with deep niches. The upper part takes the form of a miniature chapel containing statuettes. During the Dissolution of the Monasteries it was dismantled. Some of the parts were found during the 1873 restoration of the cathedral and the shrine was reassembled in 1888 by Blomfield. A carving of St Werburgh by Joseph Pyrz was added in 1993. Also in the chapel are asedilia
In church architecture, sedilia (plural of Latin ''sedīle'', "seat") are seats, typically made of stone, located on the liturgical south side of the altar—often within the chancel—intended for use by the officiating priest, deacon, an ...
and a piscina
A piscina is a shallow basin placed near the altar of a church, or else in the vestry or sacristy, used for washing the communion vessels. The sacrarium is the drain itself. Lutherans and Anglicans usually refer to the basin, calling it a pisci ...
. The stained glass of 1859, is by William Wailes. The chapel contains a monument to Archdeacon Francis Wrangham, made by Hardman & Co. and dating from 1846. In 1555, George Marsh, Martyr stood trial here accused of heresy.
North quire aisle
The north quire aisle has a stone screen by R. C. Hussey and an iron gate dated 1558 that came fromGuadalajara
Guadalajara ( ; ) is the capital and the most populous city in the western Mexican List of states of Mexico, state of Jalisco, as well as the most densely populated municipality in Jalisco. According to the 2020 census, the city has a population ...
. At the east end of the aisle is the chapel of St Werburgh which has a vault of two bays, and an east window depicting the Nativity by Michael O'Connor, dated 1857. Other stained glass windows in the north aisle are by William Wailes, by Heaton, Butler and Bayne, and by Clayton and Bell. The chapel contains a piscina dating from the 14th century, and monuments to John Graham (Bishop, 1848–1865) dated 1867, and to William Bispham who died in 1685, Other monuments in the north aisle include a tablet to William Jacobson (Bishop, 1865–1884), dated 1887, by Boehm to a design by Blomfield.
North transept, sacristy and chapter house
The small Norman transept has clerestory windows containing stained glass by William Wailes, installed in 1853. The sacristy, of 1200, has an east window depicting St Anselm, and designed by A. K. Nicholson. In the north transept is a freestanding tomb chest monument to John Pearson who died in 1686, designed by Arthur Blomfield and carved by Nicholas Earp, with a recumbent effigy by Matthew Noble. Other monuments in the transept include one to Samuel Peploe, dating from about 1784, by Joseph Nollekens. The wall monuments includecenotaph
A cenotaph is an empty grave, tomb or a monument erected in honor of a person or group of people whose remains are elsewhere or have been lost. It can also be the initial tomb for a person who has since been reinterred elsewhere. Although t ...
s to members of the Cheshire (Earl of Chester's) Yeomanry killed in the Boer War
The Second Boer War (, , 11 October 189931 May 1902), also known as the Boer War, Transvaal War, Anglo–Boer War, or South African War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer republics (the South African Republic an ...
and in the First and Second World Wars. At the corner of the transept with the north aisle is a 17th-century Tree of Jesse carved in whale ivory. A niche contains a rare example of a " cobweb picture", painted on the web of a caterpillar. Originating in the Austrian Tyrol
Tyrol ( ; historically the Tyrole; ; ) is a historical region in the Alps of Northern Italy and western Austria. The area was historically the core of the County of Tyrol, part of the Holy Roman Empire, Austrian Empire and Austria-Hungary, f ...
, it depicts Mary and the Christ-Child, and is based on a painting by Lucas Cranach the Elder
Lucas Cranach the Elder ( ; – 16 October 1553) was a German Renaissance painter and printmaker in woodcut and engraving. He was court painter to the Electors of Saxony for most of his career, and is known for his portraits, both of German ...
.
The chapter house has stained glass in its east window by Heaton, Butler and Bayne and grisaille
Grisaille ( or ; , from ''gris'' 'grey') means in general any European painting that is painted in grey.
History
Giotto used grisaille in the lower registers of his frescoes in the Scrovegni Chapel in Padua () and Robert Campin, Jan van Ey ...
windows in the north and south walls, dated 1882–83, by Blomfield. It contains an oak cope
A cope ( ("rain coat") or ("cape")) is a liturgical long mantle or cloak, open at the front and fastened at the breast with a band or clasp. It may be of any liturgical colour.
A cope may be worn by any rank of the Catholic or Anglican clerg ...
cupboard from the late 13th century. The front of the chapter house was rebuilt to a design by Hussey.
South choir aisle
The south aisle was shortened in about 1870 by Scott, and given an apsidal east end, becoming the chapel of St Erasmus. The stained glass in the apse window is dated 1872 and is by Clayton and Bell. Below this is a mosaic designed by J. R. Clayton and made by Salviati, and afresco
Fresco ( or frescoes) is a technique of mural painting executed upon freshly laid ("wet") lime plaster. Water is used as the vehicle for the dry-powder pigment to merge with the plaster, and with the setting of the plaster, the painting become ...
painting by Clayton and Bell, dated 1874. Elsewhere the stained glass in the aisle is by Wailes, and by Hardman & Co. to a design by Pugin. The aisle contains the tomb of Ranulf Higdon, a monk at St Werburgh's Abbey in the 12th century who wrote a major work of history entitled ''Polychronicon'', a monument to Thomas Brassey (a civil engineering contractor who died in 1870), designed by Blomfield and made by Wagmuller, a monument to Samuel Peploe (Bishop, 1726–1752) who died in 1752, and three painted monuments by a member of the Randle Holme family.
South transept
The south transept, formerly the parish church of St Oswald contains apiscina
A piscina is a shallow basin placed near the altar of a church, or else in the vestry or sacristy, used for washing the communion vessels. The sacrarium is the drain itself. Lutherans and Anglicans usually refer to the basin, calling it a pisci ...
and sedilia
In church architecture, sedilia (plural of Latin ''sedīle'', "seat") are seats, typically made of stone, located on the liturgical south side of the altar—often within the chancel—intended for use by the officiating priest, deacon, an ...
in the south wall. On the east wall are four chapels, each with a reredos
A reredos ( , , ) is a large altarpiece, a screen, or decoration placed behind the altar in a Church (building), church. It often includes religious images.
The term ''reredos'' may also be used for similar structures, if elaborate, in secular a ...
, two of which were designed by Giles Gilbert Scott, one by Kempe and the other by his successor, W. E. Tower. The south window is dated 1887 and was made by Heaton, Butler and Bayne to a design by R. C. Hussey. Other stained glass in the transept is by Clayton and Bell
Clayton and Bell was one of the most prolific and proficient British workshops of stained-glass windows during the latter half of the 19th century and early 20th century. The partners were John Richard Clayton (1827–1913) and Alfred Bell (1832� ...
, by C. E. Kempe and by Powell.
The monuments include those to George Ogden who died in 1781, by Hayward, to Anne Matthews who died in 1793, by Thomas Banks, to John Philips Buchanan who died at Waterloo in 1815, to the first Duke of Westminster, designed by C. J. Blomfield, and two memorial plaques to members of the Egerton family. On the wall of the southwest crossing pier are monuments which include a cenotaph
A cenotaph is an empty grave, tomb or a monument erected in honor of a person or group of people whose remains are elsewhere or have been lost. It can also be the initial tomb for a person who has since been reinterred elsewhere. Although t ...
to the casualties in HMS ''Chester'' in the Battle of Jutland
The Battle of Jutland () was a naval battle between Britain's Royal Navy Grand Fleet, under Admiral John Jellicoe, 1st Earl Jellicoe, Sir John Jellicoe, and the Imperial German Navy's High Seas Fleet, under Vice-Admiral Reinhard Scheer, durin ...
in 1916 who included the 16-year-old John Cornwell VC. The west wall of the south transept has many memorials, including cenotaphs to the Cheshire Regiment
The Cheshire Regiment was a line infantry regiment of the British Army, part of the Prince of Wales' Division. The 22nd Regiment of Foot was raised by the Henry Howard, 7th Duke of Norfolk in 1689 and was able to boast an independent existence ...
, the Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the Air force, air and space force of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies. It was formed towards the end of the World War I, First World War on 1 April 1918, on the merger of t ...
and the Free Czech Forces.
Cloisters and refectory
The cloisters were restored in the 20th century, and the stained glass windows contain the images of some 130 saints. The cloister garth contains a modern sculpture entitled ''The water of life'' by Stephen Broadbent. The refectory roof is dated 1939 and was designed by F. H. Crossley. The east window with reticulatedtracery
Tracery is an architectural device by which windows (or screens, panels, and vaults) are divided into sections of various proportions by stone ''bars'' or ''ribs'' of moulding. Most commonly, it refers to the stonework elements that support th ...
was designed by Giles Gilbert Scott and is dated 1913. The stained glass in the west window, depicting the Creation, was designed by Ros Grimshaw and installed in 2001 to celebrate the Millennium
A millennium () is a period of one thousand years, one hundred decades, or ten centuries, sometimes called a kiloannum (ka), or kiloyear (ky). Normally, the word is used specifically for periods of a thousand years that begin at the starting ...
. On the refectory's west wall there is a tapestry
Tapestry is a form of Textile arts, textile art which was traditionally Weaving, woven by hand on a loom. Normally it is used to create images rather than patterns. Tapestry is relatively fragile, and difficult to make, so most historical piece ...
depicting Elymas being struck with blindness which was woven at the Mortlake Tapestry Works in the 17th century from one of the Raphael Cartoons
The Raphael Cartoons are seven large cartoon paintings on paper for tapestries, surviving from a set of ten cartoons, designed by the High Renaissance painter Raphael in 1515–1516. Commissioned by Pope Leo X for the Sistine Chapel in the ...
. The heraldic paintings on the north wall represent the arms of the Earls of Chester.
Library
A library has been present since the time of St Werburgh's Abbey, and following the dissolution of the monasteries it became the cathedral library. It continued to grow over the centuries, but by the 19th century it had become neglected. Between 1867 and 1885 it was enlarged and in the 1890s new bookcases were added. A further reorganisation took place in the 1920s but by the 1980s the contents were contained in five separate sites around the cathedral. A programme of repair and re-cataloguing of the contents was instituted. During the 2000s more work was carried out and the refurbished library, housed in three rooms, opened in 2007. The library is available for research and for organised visits by groups.Ministry
Dean and chapter
As of 3 January 2024: * Dean — Tim Stratford (since 8 September 2018) *Canon Missioner & Vice Dean — Jane Brooke (since 11 September 2010 installation; Acting Dean, 2017–2018) *Canon for Worship and Spirituality – Rosie Woodall (since 20 May 2023 licensing)Services
The cathedral is a place of Christian worship, with two services held daily, and four or five each Sunday. There is Holy Communion each day, and Choral Evensong each day except Wednesday. There is a sung service of cathedral Eucharist every Sunday.Music
The Organist and Master of the Choristers is Philip Rushforth, Head of Music Outreach and Assistant Organist, Dan Mathieson and Sub-Organist, Alexander Palotai. There are lunchtime organ recitals weekly on Thursday at 1:10pm, immediately following Holy Communion. The monthly program of music is available on the cathedral's website. The hymn-writer William Cooke (1821–1894) was a canon of Chester.Organists
The earliest recorded appointment of an organist is of John Brycheley in 1541. Notable organists include the composers Robert White and John Sanders, conductor George Guest and the recording artist Roger Fisher.Cathedral Organists. John E West. 1899The Succession of Organists. Watkins Shaw. 1991Choirs
The choral tradition at Chester is 900 years old, dating from the foundation of the Benedictine monastery. In 1741Handel
George Frideric (or Frederick) Handel ( ; baptised , ; 23 February 1685 – 14 April 1759) was a German-British Baroque composer well-known for his operas, oratorios, anthems, concerti grossi, and organ concerti.
Born in Halle, Germany, H ...
heard the first recital of his Messiah
In Abrahamic religions, a messiah or messias (; ,
; ,
; ) is a saviour or liberator of a group of people. The concepts of '' mashiach'', messianism, and of a Messianic Age originated in Judaism, and in the Hebrew Bible, in which a ''mashiach ...
at Chester. There are usually eight choral services in the cathedral each week. Chester has a cathedral choir of male lay clerk
A lay clerk, also known as a lay vicar, song man or a vicar choral, is a professional adult singer in an Anglican cathedral and often Roman Catholic cathedral in the UK, or (occasionally) college choir in Britain and Ireland. The vicars choral w ...
s, choral scholars, boy and girl choristers and a Nave Choir which is of mixed voice. They rehearse in the Song School, built on the site of the former Monks' Dormitory. In addition to singing at services, the choir perform in concerts, tour abroad, and make recording on CDs. There was a choir school at the cathedral until 1975 but since that time choristers come from local schools. The Nave Choir, which sings Compline
Compline ( ), also known as Complin, Night Prayer, or the Prayers at the End of the Day, is the final prayer liturgy (or office) of the day in the Christian tradition of canonical hours, which are prayed at fixed prayer times.
The English wor ...
on Sunday evenings and in other services, also takes part in concerts, and undertakes tours. Having been founded during the 1860s, it is the longest-running voluntary cathedral choir in Britain.
Activities
Apart from services, a variety of events such as concerts, recitals, exhibitions and tours are held at the cathedral. There are weekly lunchtime organ recitals each Thursday, and concerts by the Chester Cathedral Nave Choir. The cathedral and precinct are open to visits both by individuals and by groups. The former Refectory of the abbey is used as a café. The Refectory, the Cloister Room, the Chapter House, and the Vestibule can be hired for meetings, receptions and other purposes.Burials
Hugh d'Avranches, 1st Earl of Chester
Hugh d'Avranches ( 1047 – 27 July 1101), nicknamed ''le Gros'' (the Large) or ''Lupus'' (the Wolf), was from 1071 the second Norman Earl of Chester and one of the great magnates of early Norman England.
Early life and career
Hugh d'A ...
(27 July 1101), first in the cemetery of Saint Werberg, reburied in the Chapter House
A chapter house or chapterhouse is a building or room that is part of a cathedral, monastery or collegiate church in which meetings are held. When attached to a cathedral, the cathedral chapter meets there. In monasteries, the whole communi ...
* Ranulf le Meschin, 3rd Earl of Chester (1070–1129)
* Ranulf de Gernon, 4th Earl of Chester, and his wife Maud of Gloucester, Countess of Chester
* Hugh de Kevelioc, 5th Earl of Chester
* Ranulf de Blondeville, 6th Earl of Chester (1170–1232)
* Ranulf Higden (c. 1280–1364), chronicler
* John Pearson, Bishop of Chester
The Bishop of Chester is the Ordinary of the Church of England Diocese of Chester in the Province of York.
The diocese extends across most of the historic county boundaries of Cheshire, including the Wirral Peninsula and has its see in the ...
(1673–1686)
* Samuel Peploe, Bishop of Chester (1725–1752)
* John Graham, Bishop of Chester (1845–1865) — in the cemetery
* George Clarke of Hyde, former Colonial Governor of New York, America between 1736 and 1743
* Frederick Philipse III, a wealthy landowner from New York, America, who was loyal to the British Colonial Government and forced to quit his estates.
Gallery
See also
* Architecture of the medieval cathedrals of England *English Gothic architecture
English Gothic is an architectural style that flourished from the late 12th until the mid-17th century. The style was most prominently used in the construction of Gothic cathedrals and churches, cathedrals and churches. Gothic architecture, Got ...
* Grade I listed buildings in Cheshire West and Chester
* Grade I listed churches in Cheshire
* Norman architecture in Cheshire
* List of works by Thomas Harrison
* List of works by George Pace
* Three hares
* Chester Cathedral Choir
* Chester Cathedral Choir School
References and notes
Notes Citations Sources * * * * * . * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Chester Cathedral & its Historic Links with New York
* ttps://archive.today/20121224033929/http://www.npor.org.uk/cgi-bin/Rsearch.cgi?Fn=Rsearch&rec_index=K00226 Details of organ
British History Online
* ttps://www.british-towns.net/england/midland/cheshire-west-and-chester/chester/album/plan-of-chester-cathedral Plan of the cathedral
Medieval stained glass from CVMA
Photographs and panorama
Chester Cathedral Quarter — development project
Chester Cathedral Nave Choir Website
{{Authority control Anglican cathedrals in England Grade I listed cathedrals Grade I listed monasteries Tourist attractions in Cheshire Church of England church buildings in Cheshire Grade I listed buildings in Chester English churches with Norman architecture English Gothic architecture in Cheshire Buildings and structures in Chester Diocese of Chester Thomas Harrison buildings Arthur Blomfield buildings Churches in Chester Pre-Reformation Roman Catholic cathedrals Monasteries dissolved under the English Reformation 13th-century church buildings in England