Chernobyl Nuclear Power Station on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant (ChNPP) is a
 Electrical energy was generated by a pair of 2x500 MW hydrogen-cooled turbo generators per unit. These are located in the -long machine hall, adjacent to the reactor building. The turbines—the venerable five-cylinder K-500-65/3000 steam turbine were supplied by the
Electrical energy was generated by a pair of 2x500 MW hydrogen-cooled turbo generators per unit. These are located in the -long machine hall, adjacent to the reactor building. The turbines—the venerable five-cylinder K-500-65/3000 steam turbine were supplied by the
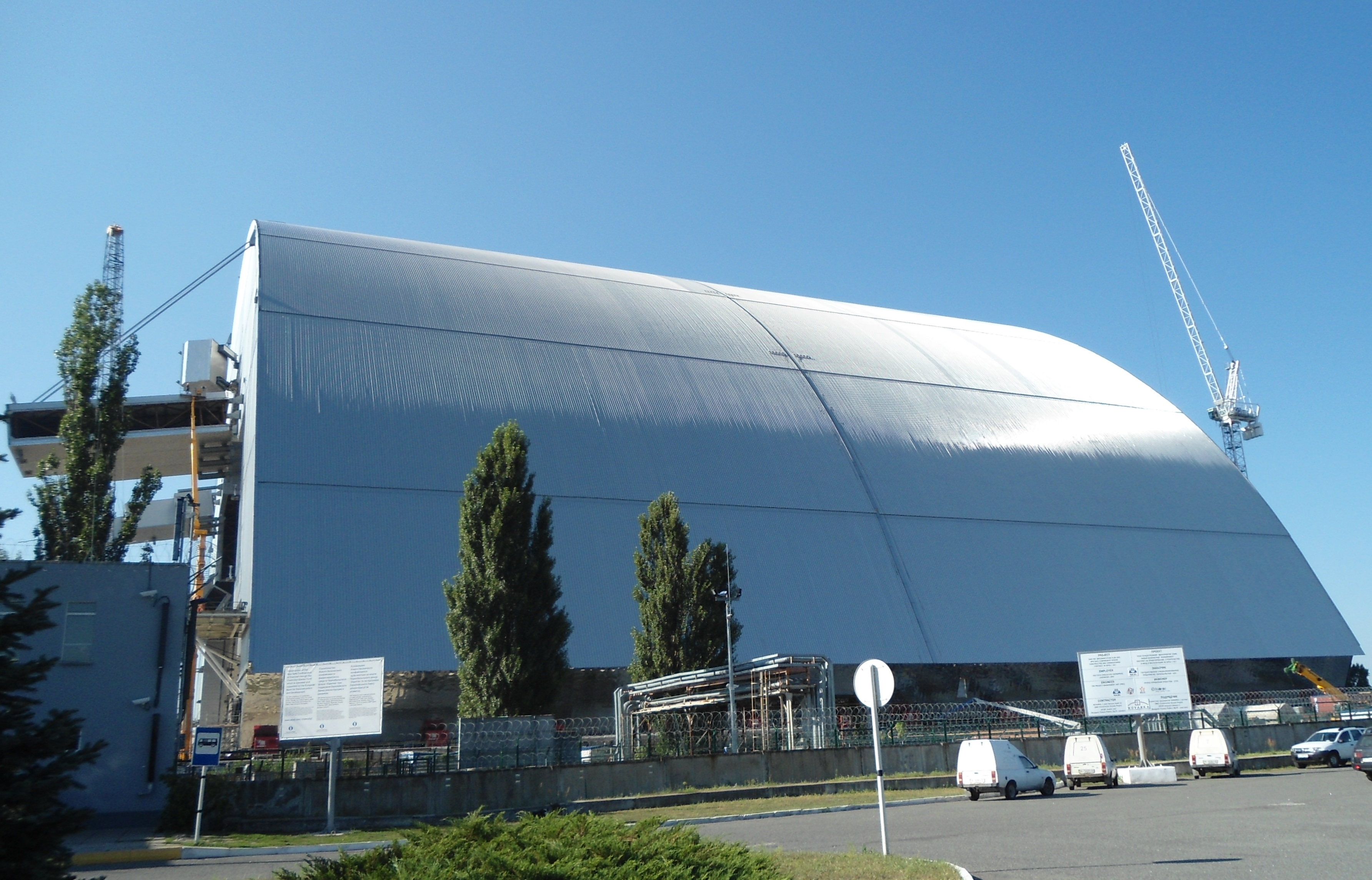 Originally announced in June 2003, a new steel containment structure named the New Safe Confinement was built to replace the aging and hastily built sarcophagus that protected ruined reactor No. 4. Though the project's development had been delayed several times, construction officially began in September 2010. The New Safe Confinement was financed by an international fund managed by the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development and was designed and built by the French-led consortium Novarka.
In February 2013, a portion of the roof and wall adjacent to the covered part of the turbine hall collapsed into the entombed area of the turbine hall. The collapse did not affect any other part of the Object Shelter (sarcophagus) or the New Safe Confinement. No variances in radiation levels as a result of the incident were detected. The collapsed roof was built after the Chernobyl disaster and was later repaired.
Novarka built a large arch-shaped structure out of steel wide, high, and long to cover the old crumbling concrete dome that was in use at the time. The structure was built in two segments which were joined in August 2015. In November 2016, the completed arch was placed over the existing sarcophagus. This steel casing project was expected to cost $1.4 billion, and was completed in 2017. The casing also meets the definition of a nuclear entombment device.
A separate deal has been made with the American firm Holtec International to build a storage facility within the exclusion zone for nuclear waste produced by Chernobyl. This facility, named the Interim Storage Facility 2, has storage for the 21,297 Spent Fuel assemblies currently at the power plant, which will be loaded into approximately 231 waste canisters, and stored in the ISF-2 for 100 years. In 2020, the storage facility was completed, and on November 18, 2020, the first canister of nuclear waste was loaded into the storage area.
Originally announced in June 2003, a new steel containment structure named the New Safe Confinement was built to replace the aging and hastily built sarcophagus that protected ruined reactor No. 4. Though the project's development had been delayed several times, construction officially began in September 2010. The New Safe Confinement was financed by an international fund managed by the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development and was designed and built by the French-led consortium Novarka.
In February 2013, a portion of the roof and wall adjacent to the covered part of the turbine hall collapsed into the entombed area of the turbine hall. The collapse did not affect any other part of the Object Shelter (sarcophagus) or the New Safe Confinement. No variances in radiation levels as a result of the incident were detected. The collapsed roof was built after the Chernobyl disaster and was later repaired.
Novarka built a large arch-shaped structure out of steel wide, high, and long to cover the old crumbling concrete dome that was in use at the time. The structure was built in two segments which were joined in August 2015. In November 2016, the completed arch was placed over the existing sarcophagus. This steel casing project was expected to cost $1.4 billion, and was completed in 2017. The casing also meets the definition of a nuclear entombment device.
A separate deal has been made with the American firm Holtec International to build a storage facility within the exclusion zone for nuclear waste produced by Chernobyl. This facility, named the Interim Storage Facility 2, has storage for the 21,297 Spent Fuel assemblies currently at the power plant, which will be loaded into approximately 231 waste canisters, and stored in the ISF-2 for 100 years. In 2020, the storage facility was completed, and on November 18, 2020, the first canister of nuclear waste was loaded into the storage area.
nuclear power plant
A nuclear power plant (NPP), also known as a nuclear power station (NPS), nuclear generating station (NGS) or atomic power station (APS) is a thermal power station in which the heat source is a nuclear reactor. As is typical of thermal power st ...
undergoing decommissioning. ChNPP is located near the abandoned city of Pripyat
Pripyat, also known as Prypiat, is an abandoned industrial city in Kyiv Oblast, Ukraine, located near the border with Belarus. Named after the nearby river, Pripyat (river), Pripyat, it was founded on 4 February 1970 as the ninth ''atomgrad'' ...
in northern Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
, northwest of the city of Chernobyl, from the Belarus–Ukraine border, and about north of Kyiv
Kyiv, also Kiev, is the capital and most populous List of cities in Ukraine, city of Ukraine. Located in the north-central part of the country, it straddles both sides of the Dnieper, Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2022, its population was 2, ...
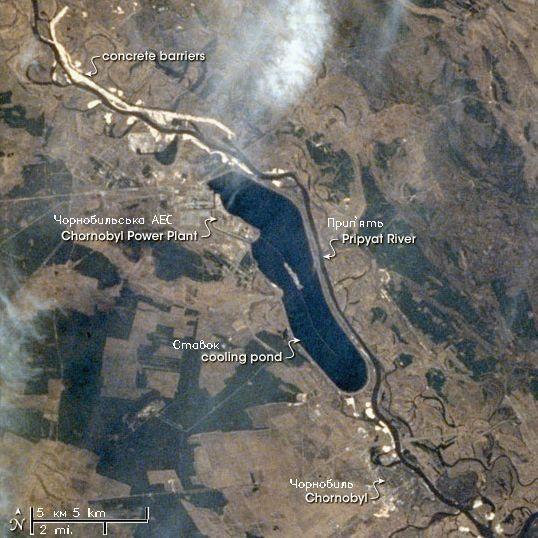
. The plant was cooled by an engineered pond, fed by the Pripyat River about northwest from its juncture with the Dnieper
The Dnieper or Dnepr ( ), also called Dnipro ( ), is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. Approximately long, with ...
River.
Originally named the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant of V. I. Lenin after the founding leader of the Soviet Union, the plant was commissioned in phases with the four reactors entering commercial operation between 1978 and 1984. In 1986, in what became known as the Chernobyl disaster
On 26 April 1986, the no. 4 reactor of the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, located near Pripyat, Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, Ukrainian SSR, Soviet Union (now Ukraine), exploded. With dozens of direct casualties, it is one of only ...
, reactor No. 4 suffered a catastrophic explosion and meltdown; as a result of this, the power plant is now within a large restricted area known as the Chernobyl Exclusion Zone
The Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant Zone of Alienation, also called the 30-Kilometre Zone or simply The Zone, was established shortly after the 1986 Chernobyl disaster in the Ukrainian SSR of the Soviet Union.
Initially, Soviet authorities declar ...
. Both the zone and the power plant are administered by the State Agency of Ukraine on Exclusion Zone Management. The three other reactors remained operational post-accident maintaining a capacity factor between 60 and 70%. In total, units 1 and 3 had supplied 98 terawatt-hours of electricity each, with unit 2 slightly less at 75 TWh. In 1991, unit 2 was placed into a permanent shutdown state by the plant's operator due to complications resulting from a turbine fire. This was followed by Unit 1 in 1996 and Unit 3 in 2000. Their closures were largely attributed to foreign pressures. In 2013, the plant's operator announced that units 1–3 were fully defueled, and in 2015 entered the decommissioning phase, during which equipment contaminated during the operational period of the power station will be removed. This process is expected to take until 2065 according to the plant's operator. Although the reactors have all ceased generation, Chernobyl maintains a large workforce as the ongoing decommissioning process requires constant management.
From 24 February to 31 March 2022, Russian troops occupied the plant as part of their invasion of Ukraine.
Construction
Construction of the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant began in 1972. The plant was meant to have 12 units, made up of six construction phases, and if completed would have been the largest nuclear power plant in the world. The plant would eventually consist of four RBMK-1000 reactors, each capable of producing 1,000megawatt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of Power (physics), power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantification (science), quantify the rate of Work ...
s (MW) of electric power (3,200 MW of thermal power), and the four together produced about 10% of Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
's electricity. Like other sites which housed multiple RBMK reactors such as Kursk, the construction of the plant was also accompanied by the construction of a nearby city to house workers and their families. In the case of the ChNPP, the new city was Pripyat
Pripyat, also known as Prypiat, is an abandoned industrial city in Kyiv Oblast, Ukraine, located near the border with Belarus. Named after the nearby river, Pripyat (river), Pripyat, it was founded on 4 February 1970 as the ninth ''atomgrad'' ...
. Construction of the station concluded in the late 1970s, with reactor No. 1 being commissioned in 1977. It was the third Soviet RBMK nuclear power plant, after the Leningrad
Saint Petersburg, formerly known as Petrograd and later Leningrad, is the List of cities and towns in Russia by population, second-largest city in Russia after Moscow. It is situated on the Neva, River Neva, at the head of the Gulf of Finland ...
and Kursk
Kursk (, ) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and the administrative center of Kursk Oblast, Russia, located at the confluence of the Kur (Kursk Oblast), Kur, Tuskar, and Seym (river), Seym rivers. It has a population of
Kursk ...
power plants, and the first plant on Ukrainian soil.
The completion of the first reactor in 1977 was followed by reactor No. 2 in 1978, No. 3 in 1981, and No. 4 in 1983. Two more blocks, numbered five and six, of more or less the same reactor design, were planned at a site roughly a kilometre from the contiguous buildings of the four older blocks. This is similar to the layout of units 5 and 6 at Kursk and shows the similarity in design between the RBMK sites. Reactor No. 5 was around 70% complete at the time of Reactor 4's explosion and was scheduled to come online approximately seven months later, in November 1986. In the aftermath of the disaster, construction on No. 5 and 6 was suspended, and eventually cancelled on April 20, 1989, days before the third anniversary of the 1986 explosion. At one point six other reactors were planned on the other side of the river, bringing the total to twelve.
Reactors No. 3 and 4 were second-generation units, whereas No. 1 and 2 were first-generation units, like those in operation at the Kursk power plant. Second-generation RBMK designs were fitted with a more secure containment structure, visible in photos of the facility.
Design

Electrical systems
The power plant is connected to the 330 kV and 750 kVelectrical grid
An electrical grid (or electricity network) is an interconnected network for electricity delivery from producers to consumers. Electrical grids consist of power stations, electrical substations to step voltage up or down, electric power tran ...
. The block has two electrical generator
In electricity generation, a generator, also called an ''electric generator'', ''electrical generator'', and ''electromagnetic generator'' is an electromechanical device that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy for use in an extern ...
s connected to the 750 kV grid by a single generator transformer. The generators are connected to their common transformer by two switches in series. Between them, the unit transformers are connected to supply power to the power plant's own systems; each generator can therefore be connected to the unit transformer to power the plant, or to the unit transformer and the generator transformer to also feed power to the grid.
The 330 kV line was normally not used, and served as an external power supply, connected to a station's transformer – meaning to the power plant's electrical systems. The plant was powered by its own generators, or at any event got power from the 750 kV national grid through the main grid backup feed in the transformer, or from the 330 kV level feed in grid transformer 2, or from the other power plant blocks via two reserve busbars. In case of total external power loss, the essential systems could be powered by diesel generators. Each unit's transformer is therefore connected to two 6 kV main power line switchboards, A and B (e.g., 7A, 7B, 8A, 8B for generators 7 and 8), powering principal essential systems and connected to even another transformer at 4 kV, which is backed up twice (4 kV reserve busbar).
The 7A, 7B, and 8B boards are also connected to the three essential power lines (for the coolant pumps), each also having its own diesel generator. In case of a coolant circuit failure with simultaneous loss of external power, the essential power can be supplied by spinning down turbogenerators for about 45 to 50 seconds, during which time the diesel generators should start. The generators were started automatically within 15 seconds at loss of off-site power.
Turbo generators
 Electrical energy was generated by a pair of 2x500 MW hydrogen-cooled turbo generators per unit. These are located in the -long machine hall, adjacent to the reactor building. The turbines—the venerable five-cylinder K-500-65/3000 steam turbine were supplied by the
Electrical energy was generated by a pair of 2x500 MW hydrogen-cooled turbo generators per unit. These are located in the -long machine hall, adjacent to the reactor building. The turbines—the venerable five-cylinder K-500-65/3000 steam turbine were supplied by the Kharkiv
Kharkiv, also known as Kharkov, is the second-largest List of cities in Ukraine, city in Ukraine.
turbine plant; the electrical generators are the TBB-500. The turbine and the generator rotors are mounted on the same shaft; the combined weight of the rotors is almost and their speed was 3,000 revolutions per minute
Revolutions per minute (abbreviated rpm, RPM, rev/min, r/min, or r⋅min−1) is a unit of rotational speed (or rotational frequency) for rotating machines.
One revolution per minute is equivalent to hertz.
Standards
ISO 80000-3:2019 de ...
.
The turbo generator is long and its total weight is . The coolant flow for each turbine is 82,880 t/h. The generator produced 20 kV 50 Hz AC power. The generator's stator was cooled by water while its rotor was cooled by hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
. The hydrogen for the generators was manufactured on-site by electrolysis
In chemistry and manufacturing, electrolysis is a technique that uses Direct current, direct electric current (DC) to drive an otherwise non-spontaneous chemical reaction. Electrolysis is commercially important as a stage in the separation of c ...
. The design and reliability of the turbines earned them the State Prize of Ukraine for 1979.
The Kharkiv turbine plant later developed a new version of the turbine, K-500-65/3000-2, in an attempt to reduce use of valuable metal. The Chernobyl plant was equipped with both types of turbines; block 4 had the newer ones. The newer turbines, however, turned out to be more sensitive to their operating parameters, and their bearings had frequent problems with vibrations.
Reactor fleet
The construction of two partially completed reactors, No. 5 and 6, were suspended immediately after the accident at reactor No. 4, and eventually cancelled in 1989. Reactors No. 1 and 3 continued to operate after the disaster. Reactor No. 2 was permanently shut down in 1991 after a fire broke out due to a faulty switch in a turbine. Reactors No. 1 and 3 were to be eventually closed due to a 1995 agreement Ukraine made with theEuropean Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
.
Ukraine agreed to close the remaining units in exchange for EU assistance in modernizing the shelter over reactor No. 4 and improving the energy sector of the country, including the completion of two new nuclear reactors, Khmelnytskyi 2 and Rivne 4. Reactor No. 1 was shut down in 1996 with No. 3 following in 2000.
Computer systems
SKALA (Russian: СКАЛА, система контроля аппарата Ленинградской Атомной; ''sistema kontrolya apparata Leningradskoj Atomnoj'', "Control system of the device of the Leningrad Nuclear ower Plant, lit. "rock") was the process computer for the RBMK nuclear reactor at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant prior to October 1995. Dating to the 1960s, it usedmagnetic-core memory
In computing, magnetic-core memory is a form of random-access memory. It predominated for roughly 20 years between 1955 and 1975, and is often just called core memory, or, informally, core.
Core memory uses toroids (rings) of a hard magneti ...
, magnetic tape data storage
Magnetic-tape data storage is a system for storing digital information on magnetic tape using digital recording.
Tape was an important medium for primary data storage in early computers, typically using large open reels of 7-track, later ...
, and punched tape
file:PaperTapes-5and8Hole.jpg, Five- and eight-hole wide punched paper tape
file:Harwell-dekatron-witch-10.jpg, Paper tape reader on the Harwell computer with a small piece of five-hole tape connected in a circle – creating a physical program ...
for loading software.
SKALA monitored and recorded reactor conditions and control board inputs. It was wired to accept 7200 analog signals and 6500 digital signals. The system continuously monitored the plant and displayed this information to operators. Additionally, a program called PRIZMA (Russian: ПРИЗМА, программа измерения мощности аппарата; ''programma izmereniya moshchnosti apparata'', "Device power measurement program", lit. "prism") processed plant conditions and made recommendations to guide plant operators. This program took 5 to 10 minutes to run, and could not directly control the reactor.
Known accidents and incidents
1982 reactor #1 partial meltdown
On 9 September 1982, a partial core meltdown occurred in reactor No. 1 due to a faulty cooling valve remaining closed following maintenance. Once the reactor came online, the uranium in the channel 13-44 overheated and ruptured. The extent of the damage was comparatively minor, and no one was killed during the accident. However, due to the negligence of the operators, the accident was not noticed until several hours later, resulting in significant release of radiation in the form of fragments of uranium oxide and several other radioactive isotopes escaping with steam from the reactor via the ventilation stack. This accident was somewhat similar to the 1975 Leningrad unit 1 accident. The accident was not made public until several years later, despite cleanups taking place in and around the power station and Pripyat. The reactor was repaired and put back into operation after eight months.1984 reactor #3 and #4 incident
According toKGB
The Committee for State Security (, ), abbreviated as KGB (, ; ) was the main security agency of the Soviet Union from 1954 to 1991. It was the direct successor of preceding Soviet secret police agencies including the Cheka, Joint State Polit ...
documents declassified in Ukraine on 26 April 2021, serious incidents occurred in the third and fourth reactors in 1984. According to these documents, the central government in Moscow knew as early as 1983 that the powerplant was "one of the most dangerous nuclear powerplants in the USSR". The reasoning behind this had to do with the building's structural integrity. The room which housed the steam separators would reach temperatures as high as 270 degrees Celsius. This excess heat caused the concrete of the building to shift its position, which made the building unsafe and could potentially result in the collapse of the steam separators, which would cause it to collapse onto the reactor hall, causing a meltdown.
1986 reactor #4 catastrophe (Chernobyl disaster)
On 26 April 1986, reactor No. 4 suffered catastrophic meltdown resulting in a core explosion and open-air fires. This caused large quantities of radioactive materials to be dispersed in the atmosphere and surrounding land. The disaster is regarded as the worst accident in the history of nuclear power. The destroyed reactor was encased in a concrete and lead sarcophagus, followed more recently by a large steel confinement shelter to prevent further escape of radioactivity. The radioactive cloud spread as far away as Norway.1991 reactor #2 turbine fire
Reactor No. 2 was permanently shut down shortly after October 1991 when a fire broke out due to a faulty switch in a turbine. On 11 October 1991, a fire broke out in the turbine hall of reactor No. 2. The fire began in reactor No. 2's fourth turbine, while the turbine was being idled for repairs. A faulty switch caused a surge of current to the generator, igniting insulating material on some electrical wiring. This subsequently led to hydrogen, used as a coolant in the synchronous generator, being leaked into the turbine hall "which apparently created the conditions for fire to start in the roof and for one of the trusses supporting the roof to collapse." The adjacent reactor hall and reactor were unaffected, but due to the political climate it was decided to shut down this reactor permanently after this incident.2017 cyberattack
The 2017 Petya cyberattack affected the radiation monitoring system and took down the power plant's official website, which hosts information about the incident and the area.2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine
The Chernobyl Exclusion Zone was the site of fighting between Russian and Ukrainian forces during the Battle of Chernobyl as part of theRussian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, , starting the largest and deadliest war in Europe since World War II, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, conflict between the two countries which began in 2014. The fighting has caused hundreds of thou ...
. On 24 February 2022, Russian forces captured the plant. The resulting activity reportedly led to a 20-fold increase of detected radiation levels in the area due to disturbance of contaminated soil.
On 9 March 2022, there was a power cut at the plant itself. No radiation leaks were reported at the time. However, Ukrainian authorities reported that there was a risk of a radiation leak due to spent fuel coolant being unable to circulate properly.
On 31 March 2022, Russian forces formally handed control of the plant back to its employees, and most occupying forces withdrew. Ukrainian National Guard personnel were moved to Belarus
Belarus, officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Russia to the east and northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Belarus spans an a ...
as prisoners of war
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person held captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold prisoners of war for a ...
. On 2 April 2022, Ukrainian media reported that the flag of Ukraine was raised at the plant.
Russian troops dug trenches and other fighting positions on the outskirts of the highly contaminated Red Forest, which attracted considerable media attention due to unconfirmed reports that soldiers were being treated for radiation sickness in Belarus
Belarus, officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Russia to the east and northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Belarus spans an a ...
. The IAEA later clarified that only modest radiation doses (6.5 mSv/year) could have resulted from such activities, and a tour guide in the Zone later acknowledged to the Washington Post that he had helped start these rumors in a "huge exaggeration."
On 14 February 2025, Ukrainian president Volodymyr Zelenskyy said that a Russian drone attack significantly damaged the Chernobyl New Safe Confinement, which covers the sarcophagus and Unit No. 4. The IAEA said that radiation levels at the site remained normal.
Decommissioning
After the explosion at reactor No. 4 and construction of the sarcophagus, the remaining three reactors were de-contaminated and re-launched (reactor No. 1 on 1 October 1986, reactor No. 2 on 5 November 1986, & reactor No. 3 on 4 December 1987) and continued to operate until the post-Soviet period. TheChernobyl New Safe Confinement
The New Safe Confinement (NSC or New Shelter; ) is a structure put in place in 2016 to confine the remains of the number 4 reactor unit at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, in Ukraine, which was destroyed during the Chernobyl disaster in 1986 ...
is equipped with two overhead main cranes, which will be used to remove unstable parts of the original sarcophagus. The majority of the external gamma radiation
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol ), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from high energy interactions like the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei or astronomical events like solar flares. It consists o ...
emissions at the site are from the isotope
Isotopes are distinct nuclear species (or ''nuclides'') of the same chemical element. They have the same atomic number (number of protons in their Atomic nucleus, nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemica ...
caesium-137, which has a half-life Half-life is a mathematical and scientific description of exponential or gradual decay.
Half-life, half life or halflife may also refer to:
Film
* Half-Life (film), ''Half-Life'' (film), a 2008 independent film by Jennifer Phang
* ''Half Life: ...
of 30.17 years. , the radiation exposure from that radionuclide has declined by half since the 1986 accident.
On 11 October 1991, reactor No. 2 caught fire, and was subsequently shut down. Ukraine's 1991 independence from the Soviet Union generated further discussion on the Chernobyl topic, because the Verkhovna Rada
The Verkhovna Rada ( ; VR), officially the Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine, is the unicameralism, unicameral parliament of Ukraine. It consists of 450 Deputy (legislator), deputies presided over by a speaker. The Verkhovna Rada meets in the Verkhovn ...
, Ukraine's new parliament, was composed largely of young reformers. Discussions about the future of nuclear energy in Ukraine ultimately moved the government toward a decision to decommission reactor No. 2.
On 30 November 1996, following pressure from foreign governments, reactor No. 1 was shut down. Dismantling and removal of equipment began at reactor No. 1 in 2007. The work is expected to be completed by 2028.
On 15 December 2000, reactor No. 3 was shut down after operating briefly since March 1999 following almost three months of repairs, and the plant as a whole ceased producing electricity. In April 2015, units 1 through 3 entered the decommissioning phase. Upon being shut down, the plant was re-classified as a 'State Special Enterprise,' while 'V. I. Lenin' was removed from the name following Ukraine's independence.
In 2013, the pump lifting river water into the cooling reservoir adjacent to the facility was powered down, with the thermal sink expected to slowly evaporate.
 Originally announced in June 2003, a new steel containment structure named the New Safe Confinement was built to replace the aging and hastily built sarcophagus that protected ruined reactor No. 4. Though the project's development had been delayed several times, construction officially began in September 2010. The New Safe Confinement was financed by an international fund managed by the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development and was designed and built by the French-led consortium Novarka.
In February 2013, a portion of the roof and wall adjacent to the covered part of the turbine hall collapsed into the entombed area of the turbine hall. The collapse did not affect any other part of the Object Shelter (sarcophagus) or the New Safe Confinement. No variances in radiation levels as a result of the incident were detected. The collapsed roof was built after the Chernobyl disaster and was later repaired.
Novarka built a large arch-shaped structure out of steel wide, high, and long to cover the old crumbling concrete dome that was in use at the time. The structure was built in two segments which were joined in August 2015. In November 2016, the completed arch was placed over the existing sarcophagus. This steel casing project was expected to cost $1.4 billion, and was completed in 2017. The casing also meets the definition of a nuclear entombment device.
A separate deal has been made with the American firm Holtec International to build a storage facility within the exclusion zone for nuclear waste produced by Chernobyl. This facility, named the Interim Storage Facility 2, has storage for the 21,297 Spent Fuel assemblies currently at the power plant, which will be loaded into approximately 231 waste canisters, and stored in the ISF-2 for 100 years. In 2020, the storage facility was completed, and on November 18, 2020, the first canister of nuclear waste was loaded into the storage area.
Originally announced in June 2003, a new steel containment structure named the New Safe Confinement was built to replace the aging and hastily built sarcophagus that protected ruined reactor No. 4. Though the project's development had been delayed several times, construction officially began in September 2010. The New Safe Confinement was financed by an international fund managed by the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development and was designed and built by the French-led consortium Novarka.
In February 2013, a portion of the roof and wall adjacent to the covered part of the turbine hall collapsed into the entombed area of the turbine hall. The collapse did not affect any other part of the Object Shelter (sarcophagus) or the New Safe Confinement. No variances in radiation levels as a result of the incident were detected. The collapsed roof was built after the Chernobyl disaster and was later repaired.
Novarka built a large arch-shaped structure out of steel wide, high, and long to cover the old crumbling concrete dome that was in use at the time. The structure was built in two segments which were joined in August 2015. In November 2016, the completed arch was placed over the existing sarcophagus. This steel casing project was expected to cost $1.4 billion, and was completed in 2017. The casing also meets the definition of a nuclear entombment device.
A separate deal has been made with the American firm Holtec International to build a storage facility within the exclusion zone for nuclear waste produced by Chernobyl. This facility, named the Interim Storage Facility 2, has storage for the 21,297 Spent Fuel assemblies currently at the power plant, which will be loaded into approximately 231 waste canisters, and stored in the ISF-2 for 100 years. In 2020, the storage facility was completed, and on November 18, 2020, the first canister of nuclear waste was loaded into the storage area.
See also
* List of Chernobyl-related articles * List of nuclear reactorsNotes
References
External links
* {{Authority control 1977 establishments in Ukraine Chernobyl disaster Chernobyl Exclusion Zone Nuclear power stations built in the Soviet Union Nuclear power stations using RBMK reactors Photovoltaic power stations in Ukraine Buildings and structures in Pripyat Buildings and structures completed in 1977 Energy infrastructure completed in 1977 Former nuclear power stations in Ukraine Energy infrastructure closed in the 1980s