Chemical Hazards on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Chemical hazards are
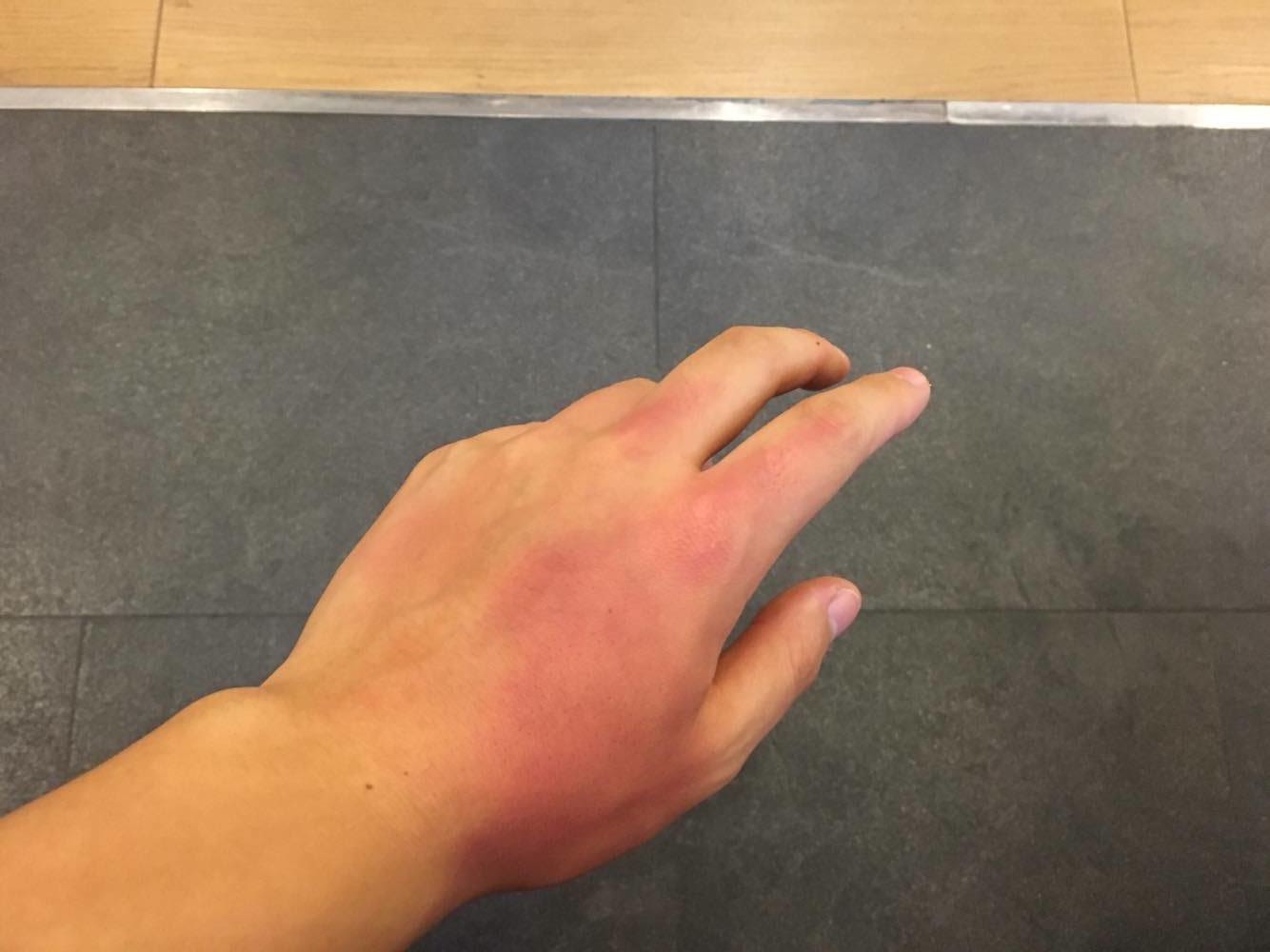 Chemical exposure to the skin is a common workplace injury and may also occur in domestic situations with chemicals such as bleach or drain-cleaners. The exposure of chemicals to the skin most often results in local irritation to the exposed area. In some exposures, the chemical will be absorbed through the skin and will result in poisoning. The eyes have a strong sensitivity to chemicals, and are consequently an area of high concern for chemical exposure. Chemical exposure to the eyes results in irritation and may result in burns and vision loss.
Injection is an uncommon method of chemical exposure in the workplace. Chemicals can be injected into the skin when a worker is punctured by a sharp object, such as a needle. Chemical exposure through injection may result in the chemical entering directly into the bloodstream.
Chemical exposure to the skin is a common workplace injury and may also occur in domestic situations with chemicals such as bleach or drain-cleaners. The exposure of chemicals to the skin most often results in local irritation to the exposed area. In some exposures, the chemical will be absorbed through the skin and will result in poisoning. The eyes have a strong sensitivity to chemicals, and are consequently an area of high concern for chemical exposure. Chemical exposure to the eyes results in irritation and may result in burns and vision loss.
Injection is an uncommon method of chemical exposure in the workplace. Chemicals can be injected into the skin when a worker is punctured by a sharp object, such as a needle. Chemical exposure through injection may result in the chemical entering directly into the bloodstream.
 Hazard pictograms are a type of labeling system that alerts people at a glance that there are hazardous chemicals present. The symbols help identify whether the chemicals that are going to be in use may potentially cause physical harm, or harm to the environment. The 9 symbols are:
* Explosive (exploding bomb)
* Flammable (flame)
* Oxidizing (flame above a circle)
* Corrosive (corrosion of table and hand)
* Acute toxicity ( skull and crossbones)
* Hazardous to environment (dead tree and fish)
* Health hazard/hazardous to the ozone layer (
Hazard pictograms are a type of labeling system that alerts people at a glance that there are hazardous chemicals present. The symbols help identify whether the chemicals that are going to be in use may potentially cause physical harm, or harm to the environment. The 9 symbols are:
* Explosive (exploding bomb)
* Flammable (flame)
* Oxidizing (flame above a circle)
* Corrosive (corrosion of table and hand)
* Acute toxicity ( skull and crossbones)
* Hazardous to environment (dead tree and fish)
* Health hazard/hazardous to the ozone layer (
hazards
A hazard is a potential source of harm. Substances, events, or circumstances can constitute hazards when their nature would potentially allow them to cause damage to health, life, property, or any other interest of value. The probability of that ...
present in hazardous chemicals and hazardous materials. Exposure to certain chemicals can cause acute or long-term adverse health effects. Chemical hazards are usually classified separately from biological hazard
A biological hazard, or biohazard, is a biological substance that poses a threat (or is a hazard) to the health of living organisms, primarily humans. This could include a sample of a microorganism, virus or toxin that can adversely affect huma ...
s (biohazards). Chemical hazards are classified into groups that include asphyxiants, corrosives, irritants, sensitizers Sensitizer or sensitiser may refer to:
* Chemical sensitizer, a chemical that causes allergic reaction in normal tissue after exposure
* Explosive sensitizer, a chemical that promotes the rate of propagation of an explosive; see Chemical explosiv ...
, carcinogen
A carcinogen () is any agent that promotes the development of cancer. Carcinogens can include synthetic chemicals, naturally occurring substances, physical agents such as ionizing and non-ionizing radiation, and biologic agents such as viruse ...
s, mutagen
In genetics, a mutagen is a physical or chemical agent that permanently changes genetic material, usually DNA, in an organism and thus increases the frequency of mutations above the natural background level. As many mutations can cause cancer in ...
s, teratogens
Teratology is the study of abnormalities of physiological development in organisms during their life span. It is a sub-discipline in medical genetics which focuses on the classification of congenital abnormalities in Dysmorphic feature, dysmor ...
, reactants
In chemistry, a reagent ( ) or analytical reagent is a substance or compound added to a system to cause a chemical reaction, or test if one occurs. The terms ''reactant'' and ''reagent'' are often used interchangeably, but reactant specifies a ...
, and flammables. In the workplace, exposure to chemical hazards is a type of occupational hazard
An occupational hazard is a hazard experienced in the workplace. This encompasses many types of hazards, including chemical hazards, biological hazards (biohazards), psychosocial hazards, and physical hazards. In the United States, the Nation ...
. The use of personal protective equipment
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is protective clothing, helmets, goggles, or other garments or equipment designed to protect the wearer's body from injury or infection. The hazards addressed by protective equipment include physical, elect ...
may substantially reduce the risk of adverse health effects from contact with hazardous materials.
Long-term exposure to chemical hazards such as silica dust, engine exhausts, tobacco smoke
Tobacco smoke is a sooty aerosol produced by the incomplete combustion of tobacco during the smoking of cigarettes and other tobacco products. Temperatures in burning cigarettes range from about 400 °C between puffs to about 900 °C ...
, and lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleabl ...
(among others) have been shown to increase risk of heart disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina pectoris, angina, myocardial infarction, heart attack), heart failure, ...
, stroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemor ...
, and high blood pressure
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms itself. It is, however, a major ri ...
.
Types of chemical hazard
Routes of exposure
The most common exposure route to chemicals in the work environment is throughinhalation
Inhalation (or inspiration) happens when air or other gases enter the lungs.
Inhalation of air
Inhalation of air, as part of the cycle of breathing, is a vital process for all human life. The process is autonomic (though there are exceptions ...
. Gas, vapour
In physics, a vapor (American English) or vapour (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences) is a substance in the gas phase at a temperature lower than its critical temperature,R. H. Petrucci, W. S. Harwood, and F. G. Herring, ''General ...
, mist, dust, fumes, and smoke
Smoke is an aerosol (a suspension of airborne particulates and gases) emitted when a material undergoes combustion or pyrolysis, together with the quantity of air that is entrained or otherwise mixed into the mass. It is commonly an unwante ...
can all be inhaled. Those with occupations involving physical work may inhale higher levels of chemicals if working in an area with contaminated air. This is because workers who do physical work will exchange over 10,000 litres of air over an 8-hour day, while workers who do not do physical work will exchange only 2,800 litres. If the air is contaminated in the workplace, more air exchange will lead to the inhalation of higher amounts of chemicals.
Chemicals may be ingested when food or drink is contaminated by unwashed hands or from clothing or poor handling practices. When ingestion of a chemical hazard occurs it comes from when those said chemicals are absorbed while in the digestive tract of the body. Ingestion
Ingestion is the consumption of a substance by an organism. In animals, it normally is accomplished by taking in a substance through the mouth into the gastrointestinal tract, such as through eating or drinking. In single-celled organisms, inge ...
only occurs when food or drink has contact with the toxic chemical
A chemical substance is a unique form of matter with constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Chemical substances may take the form of a single element or chemical compounds. If two or more chemical substances can be combin ...
. This can happen through direct or indirect ingestion. When food or drink is brought into an environment where harmful chemicals are unsealed there is the possibility of those chemical vapors or particles contaminating the food or the drink. A more direct form of chemical ingestion is the possibility of consuming the chemical directly. This rarely happens but, it is possible, that if there is little to no labeling on the chemical containers and if they are not secured properly an accident can occur which could lead to someone mistakenly assuming the chemical was something it was not.
 Chemical exposure to the skin is a common workplace injury and may also occur in domestic situations with chemicals such as bleach or drain-cleaners. The exposure of chemicals to the skin most often results in local irritation to the exposed area. In some exposures, the chemical will be absorbed through the skin and will result in poisoning. The eyes have a strong sensitivity to chemicals, and are consequently an area of high concern for chemical exposure. Chemical exposure to the eyes results in irritation and may result in burns and vision loss.
Injection is an uncommon method of chemical exposure in the workplace. Chemicals can be injected into the skin when a worker is punctured by a sharp object, such as a needle. Chemical exposure through injection may result in the chemical entering directly into the bloodstream.
Chemical exposure to the skin is a common workplace injury and may also occur in domestic situations with chemicals such as bleach or drain-cleaners. The exposure of chemicals to the skin most often results in local irritation to the exposed area. In some exposures, the chemical will be absorbed through the skin and will result in poisoning. The eyes have a strong sensitivity to chemicals, and are consequently an area of high concern for chemical exposure. Chemical exposure to the eyes results in irritation and may result in burns and vision loss.
Injection is an uncommon method of chemical exposure in the workplace. Chemicals can be injected into the skin when a worker is punctured by a sharp object, such as a needle. Chemical exposure through injection may result in the chemical entering directly into the bloodstream.
Symbols of chemical hazards
 Hazard pictograms are a type of labeling system that alerts people at a glance that there are hazardous chemicals present. The symbols help identify whether the chemicals that are going to be in use may potentially cause physical harm, or harm to the environment. The 9 symbols are:
* Explosive (exploding bomb)
* Flammable (flame)
* Oxidizing (flame above a circle)
* Corrosive (corrosion of table and hand)
* Acute toxicity ( skull and crossbones)
* Hazardous to environment (dead tree and fish)
* Health hazard/hazardous to the ozone layer (
Hazard pictograms are a type of labeling system that alerts people at a glance that there are hazardous chemicals present. The symbols help identify whether the chemicals that are going to be in use may potentially cause physical harm, or harm to the environment. The 9 symbols are:
* Explosive (exploding bomb)
* Flammable (flame)
* Oxidizing (flame above a circle)
* Corrosive (corrosion of table and hand)
* Acute toxicity ( skull and crossbones)
* Hazardous to environment (dead tree and fish)
* Health hazard/hazardous to the ozone layer (exclamation mark
The exclamation mark (also known as exclamation point in American English) is a punctuation mark usually used after an interjection or exclamation to indicate strong feelings or to show wikt:emphasis, emphasis. The exclamation mark often marks ...
)
* Serious health hazard (cross on a human silhouette)
* Gas under pressure (gas cylinder)
These pictographs are also subdivided into class and categories for each classification. The assignments for each chemical depends on their type and their severity. The standard set of 9 hazard pictograms was published and distributed as a regulatory requirement through the efforts of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
via the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals
The Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) is an internationally agreed-upon standard managed by the United Nations that was set up to replace the assortment of hazardous material classification and labellin ...
.
Controlling chemical exposure
Elimination and substitution
Chemical exposure is estimated to have caused approximately 190,000 illnesses and 50,000 deaths of workers annually. There exists an unknown link between chemical exposure and subsequent illness or death. Therefore, the majority of these illnesses and deaths are thought to be caused by a lack of knowledge or awareness concerning the dangers of chemicals. The best method of controlling chemical exposure within the workplace is through the elimination or the substitution of all chemicals that are thought or known to cause illness or death.Engineering controls
Although elimination and substitution of harmful chemicals is the best known method for controlling chemical exposure, there are other methods that can be implemented to diminish exposure. The implementation ofengineering controls
Engineering is the practice of using natural science, mathematics, and the engineering design process to solve problems within technology, increase efficiency and productivity, and improve systems. Modern engineering comprises many subfi ...
is an example of another method for controlling chemical exposures. When engineering controls are implemented, there is a physical change made to the work environment that will eliminate or reduce the risk to chemical exposure. An example of engineering controls is the enclosure or isolation of the process that creates the chemical hazard.
Administrative controls and safe work practices
If the process that creates the chemical hazard cannot be enclosed or isolated, the next best method is the implementation ofadministrative controls
Administrative controls are training, procedure, policy, or shift designs that lessen the threat of a hazard to an individual. Administrative controls typically change the behavior of people (e.g., factory workers) rather than removing the act ...
and work practices controls. This is the establishment of administrative and work practices that will reduce the amount of time and how often the workers will be exposed to the chemical hazard. An example of administrative and work practices controls is the establishment of work schedules in which workers have rotating job assignments. This will ensure that all workers have limited exposure to chemical hazards.
Personal protective equipment
Employers should providepersonal protective equipment
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is protective clothing, helmets, goggles, or other garments or equipment designed to protect the wearer's body from injury or infection. The hazards addressed by protective equipment include physical, elect ...
(PPE) to protect their workers from chemicals used within the workplace. The use of PPE prevents workers from being exposed to chemicals through the routes of exposure—inhalation, absorption through skin or eyes, ingestion, and injection. One example of how PPE usage can prevent chemical exposure concerns respirators. If workers wear respirators, they will prevent the exposure of chemicals through inhalation.
First aid
In case of an emergency, it is recommended to understand first aid procedures in order to minimize any damage. Different types of chemicals can cause a variety of damage. Most sources agree that it is best to rinse any contacted skin or eye with water immediately. Currently, there is insufficient evidence of how long the rinsing should be done, as the degree of impacts will vary for substances such as corrosive chemicals. Transporting the affected person to a health care facility may be important, depending on condition. If the victim needs to be transported before the recommended flush time, then flushing should be done during the transportation process. Some chemical manufacturers may state the specific type of cleansing agent that is recommended.Long-term risks
Cancers
Cardiovascular disease
A 2017 SBU report found evidence that workplace exposure to silica dust, engine exhaust orwelding fumes
Welding is a fabrication (metal), fabrication process that joins materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, primarily by using high temperature to melting, melt the parts together and allow them to cool, causing Fusion welding, fusion. Co ...
is associated with heart disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina pectoris, angina, myocardial infarction, heart attack), heart failure, ...
. Associations exist for exposure to arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol As and atomic number 33. It is a metalloid and one of the pnictogens, and therefore shares many properties with its group 15 neighbors phosphorus and antimony. Arsenic is not ...
, benzopyrenes, lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleabl ...
, dynamite
Dynamite is an explosive made of nitroglycerin, sorbents (such as powdered shells or clay), and Stabilizer (chemistry), stabilizers. It was invented by the Swedish people, Swedish chemist and engineer Alfred Nobel in Geesthacht, Northern German ...
, carbon disulfide
Carbon disulfide (also spelled as carbon disulphide) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula and structure . It is also considered as the anhydride of thiocarbonic acid. It is a colorless, flammable, neurotoxic liquid that is used as ...
, carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a poisonous, flammable gas that is colorless, odorless, tasteless, and slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the si ...
, metalworking fluids and occupational exposure to tobacco smoke
Tobacco smoke is a sooty aerosol produced by the incomplete combustion of tobacco during the smoking of cigarettes and other tobacco products. Temperatures in burning cigarettes range from about 400 °C between puffs to about 900 °C ...
. Working with the electrolytic production of aluminium, or the production of paper when the sulfate pulping process is used, is associated with heart disease. An association was found between heart disease and exposure to compounds which are no longer permitted in certain work environments, such as phenoxy acids containing TCDD (dioxin) or asbestos
Asbestos ( ) is a group of naturally occurring, Toxicity, toxic, carcinogenic and fibrous silicate minerals. There are six types, all of which are composed of long and thin fibrous Crystal habit, crystals, each fibre (particulate with length su ...
.
Workplace exposure to silica dust or asbestos is also associated with pulmonary heart disease. There is evidence that workplace exposure to lead, carbon disulfide, or phenoxy acids containing TCDD, as well as working in an environment where aluminium is being electrolytically produced, are associated with stroke.
Reproductive and developmental disorders
Pesticide
Pesticides are substances that are used to control pests. They include herbicides, insecticides, nematicides, fungicides, and many others (see table). The most common of these are herbicides, which account for approximately 50% of all p ...
s and carbon disulfide
Carbon disulfide (also spelled as carbon disulphide) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula and structure . It is also considered as the anhydride of thiocarbonic acid. It is a colorless, flammable, neurotoxic liquid that is used as ...
, amongst many other chemical species have been linked to disruptions of endocrine
The endocrine system is a messenger system in an organism comprising feedback loops of hormones that are released by internal glands directly into the circulatory system and that target and regulate distant organs. In vertebrates, the hypotha ...
balances in the brain and ovaries
The ovary () is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are endocr ...
. Any contact with harmful chemicals during the first few months of pregnancy or even after has been connected to some miscarriages
Miscarriage, also known in medical terms as a spontaneous abortion, is an end to pregnancy resulting in the loss and expulsion of an embryo or fetus from the womb before it can survive independently. Miscarriage before 6 weeks of gestation i ...
and has affected the menstrual cycle
The menstrual cycle is a series of natural changes in hormone production and the structures of the uterus and ovaries of the female reproductive system that makes pregnancy possible. The ovarian cycle controls the production and release of eg ...
to the point that it has been able to block ovulation
Ovulation is an important part of the menstrual cycle in female vertebrates where the egg cells are released from the ovaries as part of the ovarian cycle. In female humans ovulation typically occurs near the midpoint in the menstrual cycle and ...
. Chemicals inducing health issues during pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring gestation, gestates inside a woman's uterus. A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Conception (biology), Conception usually occurs ...
may also affect infants
In common terminology, a baby is the very young offspring of adult human beings, while infant (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'baby' or 'child') is a formal or specialised synonym. The terms may also be used to refer to juveniles of ...
or fetuses
A fetus or foetus (; : fetuses, foetuses, rarely feti or foeti) is the unborn offspring of a viviparous animal that develops from an embryo. Following the embryonic stage, the fetal stage of development takes place. Prenatal development is a ...
.
See also
* * * * *Health hazard
A hazard is a potential source of harm. Substances, events, or circumstances can constitute hazards when their nature would potentially allow them to cause damage to health, life, property, or any other interest of value. The probability of that ...
Hazards that would affect the health of exposed persons.
*
*
*
*
* Process safety
Process safety is an interdisciplinary engineering domain focusing on the study, prevention, and management of large-scale fires, explosions and chemical accidents (such as toxic gas clouds) in process plants or other facilities dealing with haza ...
– Discipline dealing with the study and management of fires, explosions and toxic gas clouds from hazardous materials in process plants.
*
References
{{Portal bar, Chemistry