Check-up on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In a physical examination, medical examination, clinical examination, or medical checkup, a medical practitioner examines a
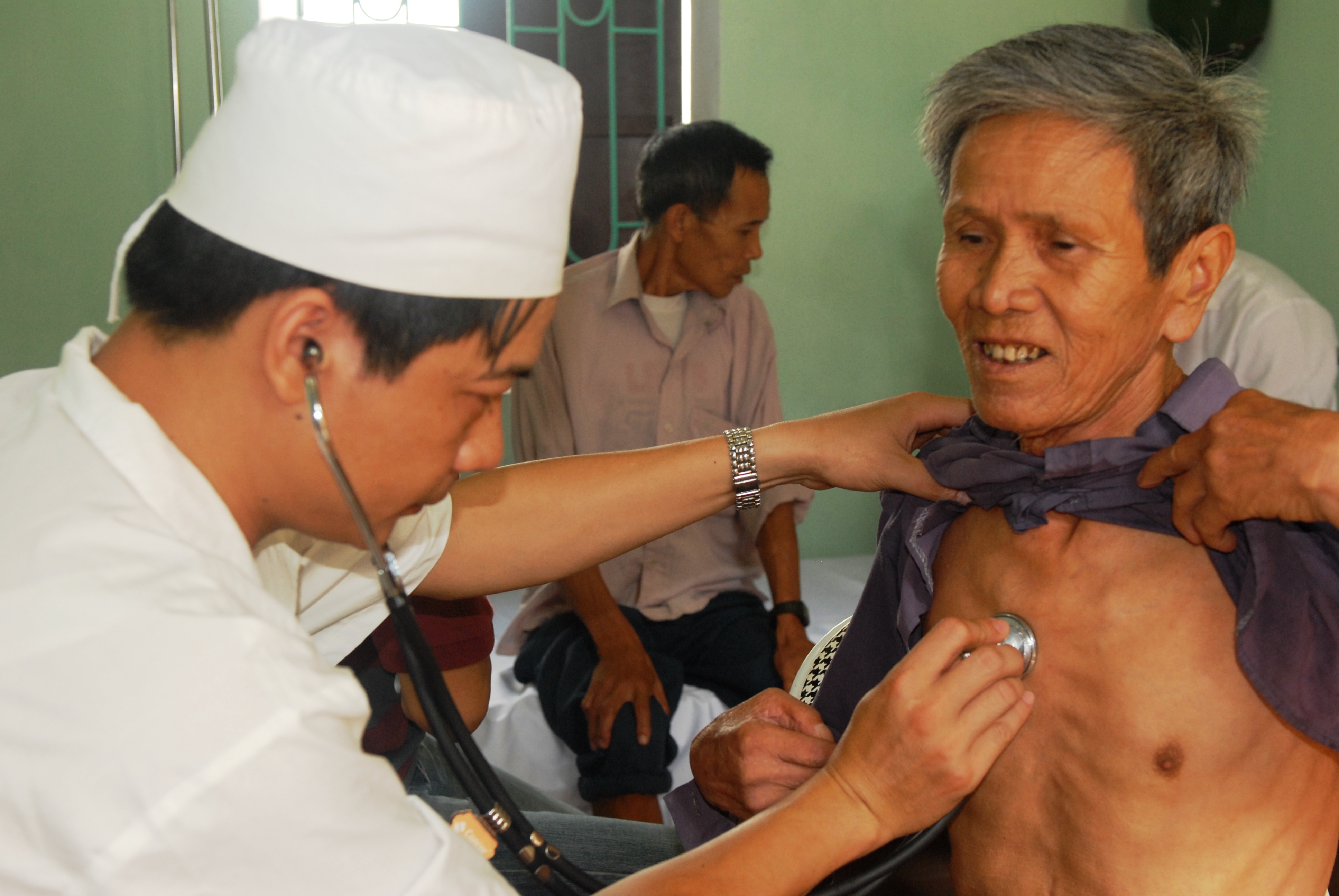 A physical examination may include checking vital signs, including temperature examination,
A physical examination may include checking vital signs, including temperature examination,
 While elective physical exams have become more elaborate, in routine use physical exams have become less complete. This has led to editorials in medical journals about the importance of an adequate physical examination. Physicians at Stanford University medical school have introduced a set of 25 key physical examination skills that were felt to be useful.
While elective physical exams have become more elaborate, in routine use physical exams have become less complete. This has led to editorials in medical journals about the importance of an adequate physical examination. Physicians at Stanford University medical school have introduced a set of 25 key physical examination skills that were felt to be useful.
patient
A patient is any recipient of health care services that are performed by Health professional, healthcare professionals. The patient is most often Disease, ill or Major trauma, injured and in need of therapy, treatment by a physician, nurse, op ...
for any possible medical signs or symptom
Signs and symptoms are diagnostic indications of an illness, injury, or condition.
Signs are objective and externally observable; symptoms are a person's reported subjective experiences.
A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature ...
s of a medical condition. It generally consists of a series of questions about the patient's medical history
The medical history, case history, or anamnesis (from Greek: ἀνά, ''aná'', "open", and μνήσις, ''mnesis'', "memory") of a patient is a set of information the physicians collect over medical interviews. It involves the patient, and ev ...
followed by an examination based on the reported symptoms. Together, the medical history and the physical examination help to determine a diagnosis
Diagnosis (: diagnoses) is the identification of the nature and cause of a certain phenomenon. Diagnosis is used in a lot of different academic discipline, disciplines, with variations in the use of logic, analytics, and experience, to determine " ...
and devise the treatment plan. These data then become part of the medical record.
Types
Routine
The ''routine physical'', also known as ''general medical examination'', ''periodic health evaluation'', ''annual physical'', ''comprehensive medical exam'', ''general health check'', ''preventive health examination'', ''medical check-up'', or simply ''medical'', is a physical examination performed on an asymptomatic patient for medical screening purposes. These are normally performed by a pediatrician, family practice physician, a physical therapist,physician assistant
A physician assistant or physician associate (PA) is a type of non-physician practitioner. While these job titles are used internationally, there is significant variation in training and scope of practice from country to country, and sometimes be ...
, a certified nurse practitioner
A nurse practitioner (NP) is an advanced practice registered nurse and a type of mid-level practitioner. NPs are trained to assess patient needs, order and interpret diagnostic and laboratory tests, diagnose disease, prescribe medications an ...
or other primary care provider. This routine physical exam usually includes the HEENT evaluation. Nursing professionals such as Registered Nurse
A registered nurse (RN) is a healthcare professional who has graduated or successfully passed a nursing program from a recognized nursing school and met the requirements outlined by a country, state, province or similar government-authorized ...
, Licensed Practical Nurses can develop a baseline assessment to identify normal versus abnormal findings. These are reported to the primary care provider. If necessary, the patient may be sent to a medical specialist
A medical specialty is a branch of medical practice that is focused on a defined group of patients, diseases, skills, or philosophy. Examples include those branches of medicine that deal exclusively with children (pediatrics), cancer ( oncology), ...
for further, more detailed examinations.
The term is generally ''not'' meant to include visits for the purpose of newborn checks, Pap smears for cervical cancer, or regular visits for people with certain chronic medical disorders (for example, diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of th ...
). The general medical examination generally involves a medical history
The medical history, case history, or anamnesis (from Greek: ἀνά, ''aná'', "open", and μνήσις, ''mnesis'', "memory") of a patient is a set of information the physicians collect over medical interviews. It involves the patient, and ev ...
, a (brief or complete) physical examination and sometimes laboratory
A laboratory (; ; colloquially lab) is a facility that provides controlled conditions in which scientific or technological research, experiments, and measurement may be performed. Laboratories are found in a variety of settings such as schools ...
tests. Some more advanced tests include ultrasound and mammography.
If done for a group of people the routine physical is a form of screening, as the aim of the examination is to detect early signs of diseases to prevent them.
Evidence
Although annual medical examinations are a routine practice in several countries, examinations performed on an asymptomatic patient are poorly supported byscientific evidence
Scientific evidence is evidence that serves to either support or counter a scientific theory or hypothesis, although scientists also use evidence in other ways, such as when applying theories to practical problems. "Discussions about empirical ev ...
in the majority of the population. A Cochrane Collaboration meta-study found that routine annual physicals did not measurably reduce the risk of illness or death, and conversely, could lead to overdiagnosis
Overdiagnosis is the diagnosis of disease that will never cause symptoms or death during a patient's ordinarily expected lifetime and thus presents no practical threat regardless of being pathologic. Overdiagnosis is a side effect of screening ...
and over-treatment; however, this article does not conclude that being in regular communication with a doctor is not important, simply that an actual physical examination may not be necessary.
Some notable general health organisations recommend against annual examinations, and propose a frequency adapted to age and previous examination results (risk factors
In epidemiology, a risk factor or determinant is a variable associated with an increased risk of disease or infection.
Due to a lack of harmonization across disciplines, determinant, in its more widely accepted scientific meaning, is often ...
).US Preventive Services Task Force. Guide to Clinical Preventive Services: Report of the Preventive Services Task Force 2nd ed. Baltimore, Md: Williams & Wilkins; 1996. The specialist American Cancer Society recommends a cancer-related health check-up annually in men and women older than 40, and every three years for those older than 20.
A systematic review
A systematic review is a scholarly synthesis of the evidence on a clearly presented topic using critical methods to identify, define and assess research on the topic. A systematic review extracts and interprets data from published studies on ...
of studies until September 2006 concluded that the examination does result in better delivery of some other screening interventions (such as Pap smears, cholesterol
Cholesterol is the principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body Tissue (biology), tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in Animal fat, animal fats and oils.
Cholesterol is biosynthesis, biosynthesized by all anima ...
screening, and faecal occult blood tests) and less patient worry. Evidence supports several of these individual screening interventions. The effects of annual check-ups on overall costs, patient disability
Disability is the experience of any condition that makes it more difficult for a person to do certain activities or have equitable access within a given society. Disabilities may be Cognitive disability, cognitive, Developmental disability, d ...
and mortality, disease detection, and intermediate end points such a blood pressure or cholesterol, are inconclusive. A recent study found that the examination is associated with increased participation in cancer screening.
Some employers require a mandatory health checkup before hiring a candidate, even though it is now well known that some of the components of the prophylactic annual visit may actually cause harm. For example, lab tests and exams that are performed on healthy patients (as opposed to people with symptoms or known illnesses) are statistically more likely to be "false positives"—that is, when test results suggest a problem that does not exist. Disadvantages cited include the time and money that could be saved by targeted screening (health economics
Health economics is a branch of economics concerned with issues related to Health care efficiency, efficiency, effectiveness, value and behavior in the production and consumption of health and healthcare. Health economics is important in dete ...
argument), increased anxiety over health risks ( medicalisation), overdiagnosis
Overdiagnosis is the diagnosis of disease that will never cause symptoms or death during a patient's ordinarily expected lifetime and thus presents no practical threat regardless of being pathologic. Overdiagnosis is a side effect of screening ...
, wrong diagnosis (for example athletic heart syndrome misdiagnosed as hypertrophic cardiomyopathy) and harm, or even death, resulting from unnecessary testing to detect or confirm, often non-existent, medical problems or while performing routine procedures as a followup after screening.
The lack of good evidence contrasts with population surveys showing that the general public is fond of these examinations, especially when they are free of charge. Despite guidelines recommending against routine annual examinations, many family physicians perform them. A fee-for-service
Fee-for-service (FFS) is a payment model where services are unbundled and paid for separately.
In health care, it gives an incentive for physicians to provide more treatments because payment is dependent on the quantity of care, rather than qualit ...
healthcare system has been suggested to promote this practice. An alternative would be to tailor the screening interval to the age, sex, medical conditions and risk factors of each patient. This means choosing between a wide variety of tests.
Prevalence
The routine physical is commonly performed in the United States and Japan, whereas the practice varies among South East Asia and mainland European countries. In Japan it is required by law for regular working employees to have a health check once a year.History
The roots of the periodic medical examination are not entirely clear. They have been referenced as early as 1671. They have also been advocated for since the 1920s. Some authors point to pleads from the 19th and early 20th century for the early detection of diseases liketuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can al ...
, and periodic school health examinations. The advent of medical insurance and related commercial influences seems to have promoted the examination, whereas this practice has been subject to controversy in the age of evidence-based medicine
Evidence-based medicine (EBM) is "the conscientious, explicit and judicious use of current best evidence in making decisions about the care of individual patients. It means integrating individual clinical expertise with the best available exte ...
. Several studies have been performed before current evidence-based recommendation for screening were formulated, limiting the applicability of these studies to current-day practice.
Comprehensive
Comprehensive physical exams, also known as executive physicals, typically include laboratory tests, chest x-rays, pulmonary function testing, audiograms, full body CAT scanning, EKGs, heart stress tests, vascular age tests, urinalysis, and mammograms or prostate exams depending on gender.Pre-employment
''Pre-employment examinations'' are screening tests which judge the suitability of a worker for hire based on the results of their physical examination. This is also called ''pre-employment medical clearance''. Some employers believe that by only hiring workers whose physical examination results pass certain exclusionary criteria, their employees collectively will have fewer absences due to sickness, fewer workplace injuries, and less occupational disease. A small amount of low-quality evidence in medical research supports this idea. Furthermore, the cost of staff health insurance will be lower. However, certain exams or tests that are requested by employers, such as a baseline low back x-ray, should not be performed, according to the American College of Occupational and Environmental Medicine. Reasons for this include the legality and medical necessity of the test as well as the inability of such testing to predict future problems, the radiation exposure to the worker, and the cost of the exam., which cites *Insurance
A physical examination may be provided underhealth insurance
Health insurance or medical insurance (also known as medical aid in South Africa) is a type of insurance that covers the whole or a part of the risk of a person incurring medical expenses. As with other types of insurance, risk is shared among ma ...
cover, required of new insurance customers. This is a part of insurance medicine. In the United States, physicals are also marketed to patients as a one-stop health review, avoiding the inconvenience of attending multiple appointments with different healthcare providers.
Uses
Diagnosis
Physical examinations are performed in most healthcare encounters. For example, a physical examination is performed when a patient visits complaining of flu-like symptoms. These diagnostic examinations usually focus on the patient's chief complaint.Screening
General health checks, including physical examinations performed when the patient reported no health concerns, often include medical screening for common conditions, such ashigh blood pressure
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms itself. It is, however, a major ri ...
. A Cochrane review found that general health checks did not reduce the risk of death from cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
, heart disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina pectoris, angina, myocardial infarction, heart attack), heart failure, ...
, or any other cause, and could not be proved to affect the patient's likelihood of being admitted to the hospital, becoming disabled, missing work, or needing additional office visits. The study found no effect on the risk of illness, but did find evidence suggesting that patients subject to routine physicals were diagnosed with hypertension
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a Chronic condition, long-term Disease, medical condition in which the blood pressure in the artery, arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms i ...
and other chronic conditions at a higher rate than those who were not. Its authors noted that studies often failed to consider or report possible harmful outcomes (such as unwarranted anxiety or unnecessary follow-up procedures), and concluded that routine health checks were "unlikely to be beneficial" in regards to lowering cardiovascular and cancer morbidity and mortality.
Doctor-patient relations
Physical examination has been described as aritual
A ritual is a repeated, structured sequence of actions or behaviors that alters the internal or external state of an individual, group, or environment, regardless of conscious understanding, emotional context, or symbolic meaning. Traditionally ...
that plays a significant role in the doctor-patient relationship that will provide benefits in other medical encounters. When a physical exam is expected by the patient but is not performed by the provider, patients may express concern for the lack of depth of investigation into their illness, the validity of treatment plans and exclusions, and the doctor-patient relationship.
Other uses
By extension, the term "health check" is also used for routing checks on the working of equipment or business operations orsolvency
Solvency, in finance or business, is the degree to which the current assets of an individual or entity exceed the current liabilities of that individual or entity. Solvency can also be described as the ability of a corporation to meet its long- ...
.
Format and interpretation
 A physical examination may include checking vital signs, including temperature examination,
A physical examination may include checking vital signs, including temperature examination, blood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of Circulatory system, circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term ...
, pulse, and respiratory rate. The healthcare provider uses the senses of sight, hearing, touch, and sometimes smell (e.g., in infection, uremia, diabetic ketoacidosis). Taste has been made redundant by the availability of modern lab tests. Four actions are taught as the basis of physical examination: inspection, palpation (feel), percussion
A percussion instrument is a musical instrument that is sounded by being struck or scraped by a percussion mallet, beater including attached or enclosed beaters or Rattle (percussion beater), rattles struck, scraped or rubbed by hand or ...
(tap to determine resonance characteristics), and auscultation
Auscultation (based on the Latin verb ''auscultare'' "to listen") is listening to the internal sounds of the body, usually using a stethoscope. Auscultation is performed for the purposes of examining the circulatory system, circulatory and resp ...
(listen).
Scope
Although providers have varying approaches as to the sequence of body parts, a systematic examination generally starts at thehead
A head is the part of an organism which usually includes the ears, brain, forehead, cheeks, chin, eyes, nose, and mouth, each of which aid in various sensory functions such as sight, hearing, smell, and taste. Some very simple ani ...
and finishes at the extremities and includes evaluation of general patient appearance and specific organ systems. After the main organ systems have been investigated by inspection, palpation, percussion
A percussion instrument is a musical instrument that is sounded by being struck or scraped by a percussion mallet, beater including attached or enclosed beaters or Rattle (percussion beater), rattles struck, scraped or rubbed by hand or ...
, and auscultation
Auscultation (based on the Latin verb ''auscultare'' "to listen") is listening to the internal sounds of the body, usually using a stethoscope. Auscultation is performed for the purposes of examining the circulatory system, circulatory and resp ...
, specific tests may follow (such as a neurological investigation, orthopedic
Orthopedic surgery or orthopedics ( alternative spelling orthopaedics) is the branch of surgery concerned with conditions involving the musculoskeletal system. Orthopedic surgeons use both surgical and nonsurgical means to treat musculoskeletal ...
examination) or specific tests when a particular disease is suspected (e.g. eliciting Trousseau's sign in hypocalcemia).
While the format of examination as listed below is largely as taught and expected of students, a specialist will focus on their particular field and the nature of the problem described by the patient. Hence a cardiologist will not in routine practice undertake neurological parts of the examination other than noting that the patient is able to use all four limbs on entering the consultation room and during the consultation become aware of their hearing, eyesight, and speech. Likewise an orthopaedic surgeon will examine the affected joint, but may only briefly check the heart sounds and chest to ensure that there is not likely to be any contraindication to surgery raised by the anaesthetist. A primary care physician
A primary care physician (PCP) is a physician who provides both the first contact for a person with an undiagnosed health concern as well as continuing care of varied medical conditions, not limited by cause, organ system, or diagnosis. The term ...
will also generally examine the male genitals but may leave the examination of the female genitalia to a gynecologist.
With the clues obtained during the ''history'' and ''physical examination'' the healthcare provider can now formulate a differential diagnosis, a list of potential causes of the symptoms. Specific diagnostic tests (or occasionally empirical therapy) generally confirm the cause, or shed light on other, previously overlooked, causes. The physical exam is then recorded in the medical record in a standard layout which facilitates billing and other providers later reading the notes.
 While elective physical exams have become more elaborate, in routine use physical exams have become less complete. This has led to editorials in medical journals about the importance of an adequate physical examination. Physicians at Stanford University medical school have introduced a set of 25 key physical examination skills that were felt to be useful.
While elective physical exams have become more elaborate, in routine use physical exams have become less complete. This has led to editorials in medical journals about the importance of an adequate physical examination. Physicians at Stanford University medical school have introduced a set of 25 key physical examination skills that were felt to be useful.
Recording
Depending upon the chief complaint, additional sections may be included. For example, hearing may be evaluated with a specific Weber test and Rinne test, or it may be more briefly addressed in a cranial nerve exam. To give another example, a neurological related complaint might be evaluated with a specific test, such as the Romberg maneuver.History
TheOld Testament
The Old Testament (OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible, or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew and occasionally Aramaic writings by the Isr ...
makes provision for persons in the Israelite community with leprosy
Leprosy, also known as Hansen's disease (HD), is a Chronic condition, long-term infection by the bacteria ''Mycobacterium leprae'' or ''Mycobacterium lepromatosis''. Infection can lead to damage of the Peripheral nervous system, nerves, respir ...
to be examined by a priest
A priest is a religious leader authorized to perform the sacred rituals of a religion, especially as a mediatory agent between humans and one or more deity, deities. They also have the authority or power to administer religious rites; in parti ...
: if the presenting sore was white and appeared to go beyond the depth of the skin, it was to be treated as a ritually defiling condition. A further examination was to take place seven days later.
The medical history
The medical history, case history, or anamnesis (from Greek: ἀνά, ''aná'', "open", and μνήσις, ''mnesis'', "memory") of a patient is a set of information the physicians collect over medical interviews. It involves the patient, and ev ...
and physical examination were supremely important to diagnosis before advanced health technology was developed, and even today, despite advances in medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to revea ...
and molecular medical tests, the history and physical remain indispensable steps in evaluating any patient. Before the 19th century, the history and physical examination were nearly the only diagnostic tools the physician had, which explains why tactile skill and ingenious appreciation in the exam were so highly valued in the definition of what made for a good physician. Even as late as 1890, the world had no radiography
Radiography is an imaging technology, imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical ("diagnostic" radiog ...
or fluoroscopy, only early and limited forms of electrophysiologic testing, and no molecular biology
Molecular biology is a branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecule, molecular basis of biological activity in and between Cell (biology), cells, including biomolecule, biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactio ...
as we know it today. Ever since this peak of the importance of the physical examination, reviewers have warned that clinical practice and medical education
Medical education is vocational education, education related to the practice of being a medical practitioner, including the initial training to become a physician (i.e., medical school and internship (medical), internship) and additional trainin ...
need to remain vigilant in appreciating the continuing need for physical examination and effectively teaching the skills to perform it; this call is ongoing, as the 21st-century literature shows.
Society and culture
People may request modesty in medical settings when the health care provider examines them. In many Western societies, a physical exam is required to participate in extracurricular sporting activities. During the physical examination, the doctor will examine the genitals, including the penis and testicles. The doctor may ask the teenager to cough while examining the scrotum. Although this can be embarrassing for an adolescent male, it is necessary to help evaluate the presence of inguinal hernias or tumors.See also
* * *References
{{Authority control Athletic training Practice of medicine General practice Prevention