Chain code on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A chain code is a
 A related blob encoding method is crack code. Algorithms exist to convert between chain code, crack code, and run-length encoding.
A new trend of chain codes involve the utilization of biological behaviors. This started by the work of Mouring et al. who developed an algorithm that takes advantage of the pheromone of ants to track image information. An ant releases a pheromone when they find a piece of food. Other ants use the pheromone to track the food. In their algorithm, an image is transferred into a virtual environment that consists of food and paths according to the distribution of the pixels in the original image. Then, ants are distributed and their job is to move around while releasing pheromone when they encounter food items. This helps other ants identify information, and therefore, encode information.
A related blob encoding method is crack code. Algorithms exist to convert between chain code, crack code, and run-length encoding.
A new trend of chain codes involve the utilization of biological behaviors. This started by the work of Mouring et al. who developed an algorithm that takes advantage of the pheromone of ants to track image information. An ant releases a pheromone when they find a piece of food. Other ants use the pheromone to track the food. In their algorithm, an image is transferred into a virtual environment that consists of food and paths according to the distribution of the pixels in the original image. Then, ants are distributed and their job is to move around while releasing pheromone when they encounter food items. This helps other ants identify information, and therefore, encode information.
{{Compression methods
Lossless compression algorithms
Image compression
Data compression
lossless compression
Lossless compression is a class of data compression that allows the original data to be perfectly reconstructed from the compressed data with no loss of information. Lossless compression is possible because most real-world data exhibits statisti ...
based image segmentation
In digital image processing and computer vision, image segmentation is the process of partitioning a digital image into multiple image segments, also known as image regions or image objects (Set (mathematics), sets of pixels). The goal of segmen ...
method for binary image
A binary image is a digital image that consists of pixels that can have one of exactly two colors, usually black and white. Each pixel is stored as a single bit — i.e. either a 0 or 1.
A binary image can be stored in memory as a bitmap: a p ...
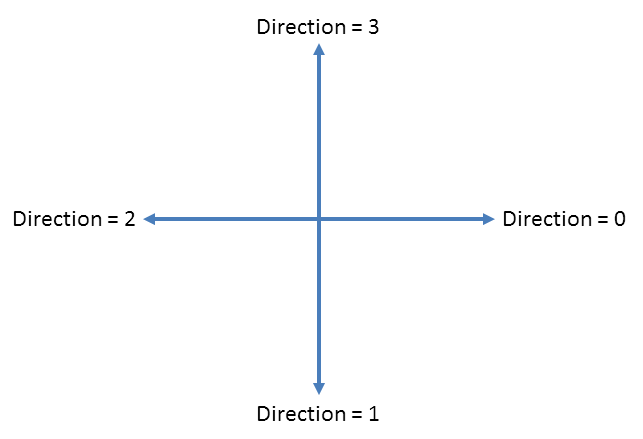
s based upon tracing image contours. The basic principle of chain coding, like other contour codings, is to separately encode each connected component, or "blob", in the image.
For each such region, a point on the boundary is selected and its coordinates are transmitted. The encoder then moves along the boundary of the region and, at each step, transmits a symbol representing the direction of this movement.
This continues until the encoder returns to the starting position, at which point the blob has been completely described, and encoding continues with the next blob in the image.
This encoding method is particularly effective for images consisting of a reasonably small number of large connected components.
Variations
Some popular chain codes include: * theFreeman
Freeman, free men, Freeman's or Freemans may refer to:
Places United States
* Freeman, Georgia, an unincorporated community
* Freeman, Illinois, an unincorporated community
* Freeman, Indiana, an unincorporated community
* Freeman, South Dako ...
Chain Code of Eight Directions (FCCE)
* Directional Freeman
Freeman, free men, Freeman's or Freemans may refer to:
Places United States
* Freeman, Georgia, an unincorporated community
* Freeman, Illinois, an unincorporated community
* Freeman, Indiana, an unincorporated community
* Freeman, South Dako ...
Chain Code of Eight Directions (DFCCE)
* Vertex Chain Code (VCC)
* Three OrThogonal symbol chain code (3OT)
* Unsigned Manhattan Chain Code (UMCC)
* Ant Colonies Chain Code (ACCC)
* Predator-Prey System Chain Code (PPSCC)
* Beaver Territories Chain Code (BTCC)
* Biological Reproduction Chain Code (BRCC)
* Agent-Based Modeling Chain Code (ABMCC)
In particular, FCCE, VCC, 3OT and DFCCE can be transformed from one to another
 A related blob encoding method is crack code. Algorithms exist to convert between chain code, crack code, and run-length encoding.
A new trend of chain codes involve the utilization of biological behaviors. This started by the work of Mouring et al. who developed an algorithm that takes advantage of the pheromone of ants to track image information. An ant releases a pheromone when they find a piece of food. Other ants use the pheromone to track the food. In their algorithm, an image is transferred into a virtual environment that consists of food and paths according to the distribution of the pixels in the original image. Then, ants are distributed and their job is to move around while releasing pheromone when they encounter food items. This helps other ants identify information, and therefore, encode information.
A related blob encoding method is crack code. Algorithms exist to convert between chain code, crack code, and run-length encoding.
A new trend of chain codes involve the utilization of biological behaviors. This started by the work of Mouring et al. who developed an algorithm that takes advantage of the pheromone of ants to track image information. An ant releases a pheromone when they find a piece of food. Other ants use the pheromone to track the food. In their algorithm, an image is transferred into a virtual environment that consists of food and paths according to the distribution of the pixels in the original image. Then, ants are distributed and their job is to move around while releasing pheromone when they encounter food items. This helps other ants identify information, and therefore, encode information.
In use
Recently, the combination ofmove-to-front transform
The move-to-front (MTF) transform is an encoding of data (typically a stream of bytes) designed to improve the performance of entropy encoding techniques of compression. When efficiently implemented, it is fast enough that its benefits usually ...
and adaptive run-length encoding
Run-length encoding (RLE) is a form of lossless data compression in which ''runs'' of data (consecutive occurrences of the same data value) are stored as a single occurrence of that data value and a count of its consecutive occurrences, rather th ...
accomplished efficient compression of the popular chain codes.
Chain codes also can be used to obtain high levels of compression for image documents, outperforming standards such as DjVu and JBIG2
JBIG2 is an image compression standard for bi-level images, developed by the Joint Bi-level Image Experts Group. It is suitable for both lossless and lossy compression. According to a press release from the Group, in its lossless mode JBIG2 typ ...
.
See also
*Image compression
Image compression is a type of data compression applied to digital images, to reduce their cost for computer data storage, storage or data transmission, transmission. Algorithms may take advantage of visual perception and the statistical properti ...
* Blob detection
In computer vision and image processing, blob detection methods are aimed at detecting regions in a digital image that differ in properties, such as brightness or color, compared to surrounding regions. Informally, a ''blob'' is a region of an ...
* Boundary tracing
Boundary tracing, also known as contour tracing, of a binary digital region can be thought of as a segmentation technique that identifies the boundary pixels of the digital region. Boundary tracing is an important first step in the analysis of ...
* Triangle strip
In computer graphics, a triangle strip is a subset of triangles in a triangle mesh with shared Vertex (geometry), vertices, and is a more Memory management, memory-efficient method of storing information about the mesh. They are more efficient tha ...
References