Cervical effacement on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Cervical effacement or cervical ripening refers to the thinning and shortening of the cervix. This process occurs during labor to prepare the
Cervical effacement or cervical ripening refers to the thinning and shortening of the cervix. This process occurs during labor to prepare the

cervix
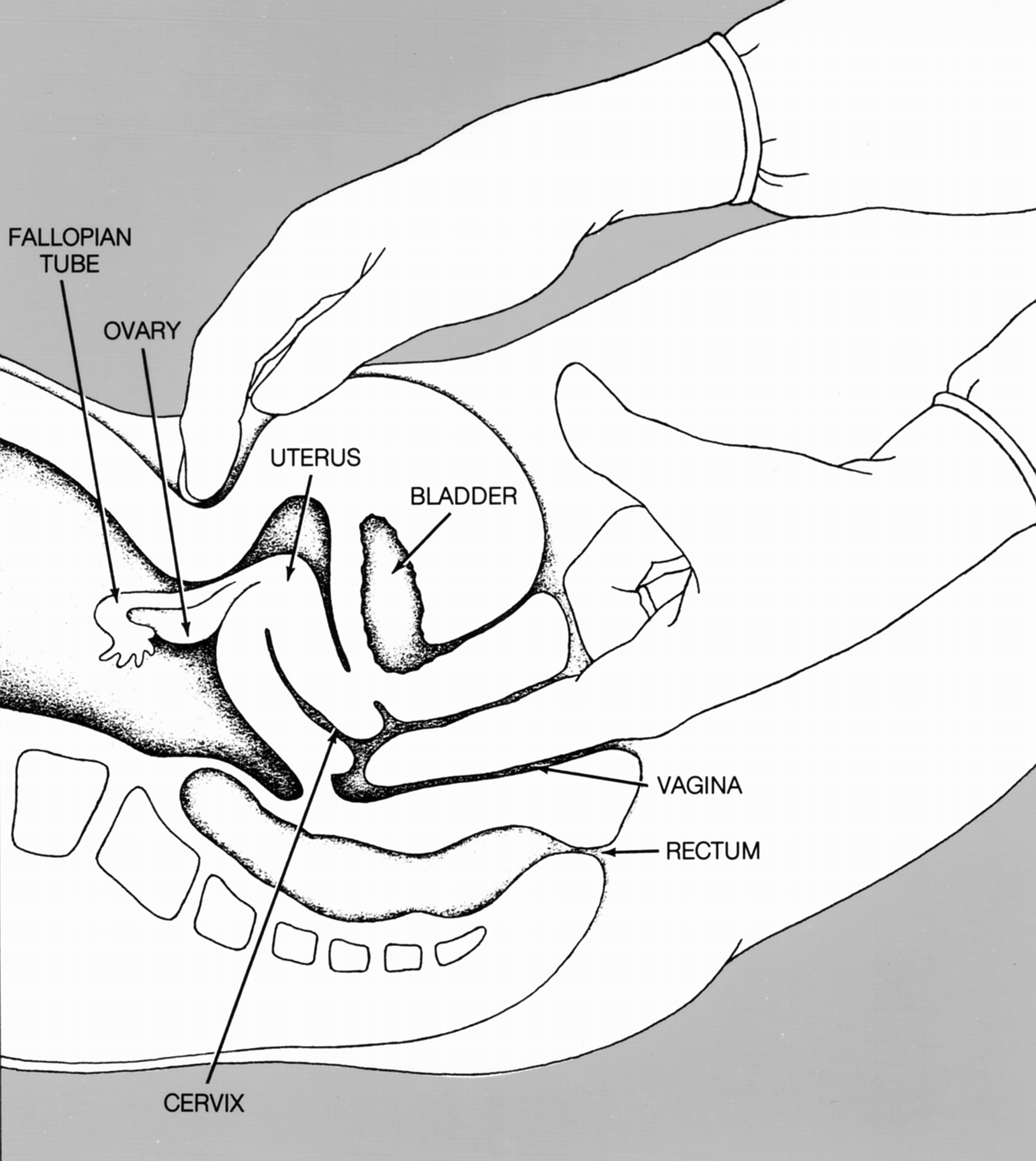
The cervix (: cervices) or cervix uteri is a dynamic fibromuscular sexual organ of the female reproductive system that connects the vagina with the uterine cavity. The human female cervix has been documented anatomically since at least the time ...
for dilation to allow the fetus to pass through the vagina. While this is a normal, physiological process that occurs at the later end of pregnancy, it can also be induced through medications and procedures.
During gestation
Gestation is the period of development during the carrying of an embryo, and later fetus, inside viviparous animals (the embryo develops within the parent). It is typical for mammals, but also occurs for some non-mammals. Mammals during pregn ...
, the cervix maintains pregnancy by increasing synthesis of various proteins
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, re ...
. These proteins have defined interactions that allow the formation of matrix proteins to help fortify the uterine cervix. Toward the end of pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring gestation, gestates inside a woman's uterus. A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Conception (biology), Conception usually occurs ...
, a series of hormone-mediated biochemical process takes place to degrade the collagen and fiber network to cause the cervix to ripen during labor. Failure to ripen the cervix during labor may delay its onset and cause complications. Current efforts to induce labor include pharmacologic, non-pharmacologic, mechanical and surgical methods.
Cervical ripening has primarily been performed in the inpatient setting. Due to a variety of reasons, such as cost and patient preference, the capacity to undergo outpatient cervical ripening is being explored.
Mechanism
Physiological
Prior to effacement, the cervix is like a long bottleneck, usually about four centimeters in length. Throughoutpregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring gestation, gestates inside a woman's uterus. A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Conception (biology), Conception usually occurs ...
, the cervix is tightly closed and protected by a plug of mucus
Mucus (, ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both Serous fluid, serous and muc ...
. Effacement is accompanied by cervical dilation
Cervical dilation (or cervical dilatation) is the opening of the cervix, the entrance to the uterus, during childbirth, miscarriage, induced abortion, or gynecological surgery. Cervical dilation may occur naturally, or may be induced surgically ...
. When the cervix effaces, the mucus plug is loosened and passes out of the vagina
In mammals and other animals, the vagina (: vaginas or vaginae) is the elastic, muscular sex organ, reproductive organ of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vulval vestibule to the cervix (neck of the uterus). The #Vag ...
. The mucus may be tinged with blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells.
Blood is com ...
and the passage of the mucus plug is called bloody show (or simply "show"). As effacement takes place, the cervix then shortens, or effaces, pulling up into the uterus and becoming part of the lower uterine wall.

Histological and biochemical
''Further Information:'Histologically, the cervix undergoes significant changes towards the end of gestation, allowing the ripening of cervix for the passage of birth delivery. First, there is an increase in the cervical synthesis of glycosaminoglycan hyaluronan (HA), which increases tissue hydration, thereby catalyzing the degradation of collagen and elastin-fibers. Second, there is an increase in the secretion of matrix metalloproteinases that also act to digest components of the extracellular matrix, including proteoglycans, laminin, and fibronectin, which are found in the cervical stroma ( parametrium). Third, due to the nature of the cervical effacement process, enzymes and other mediators that regulate allergic and inflammatory responses are also involved. One of the immunomodulating factors,
Signaling Pathways Regulating Human Cervical Ripening in Preterm and Term Delivery
ref name="Socha-2022">
mast cells
A mast cell (also known as a mastocyte or a labrocyte) is a resident cell of connective tissue that contains many granules rich in histamine and heparin. Specifically, it is a type of granulocyte derived from the myeloid stem cell that is a ...
, is known to secrete inflammatory mediators that modulate the process of cervical ripening through mast cell degranulation. Histamine
Histamine is an organic nitrogenous compound involved in local immune responses communication, as well as regulating physiological functions in the gut and acting as a neurotransmitter for the brain, spinal cord, and uterus. Discovered in 19 ...
, one of the allergenic mediators released by mast cells, has shown to have causative relationship with cervical smooth muscle contractility. However, the research is not complete.
Assessment and measurement

Bishop score
The Bishop score is the most common method of assessing the need for induction of labor. The scoring is based on a digital cervical exam and takes into considerationcervical dilation
Cervical dilation (or cervical dilatation) is the opening of the cervix, the entrance to the uterus, during childbirth, miscarriage, induced abortion, or gynecological surgery. Cervical dilation may occur naturally, or may be induced surgically ...
, position, effacement, consistency of the cervix
The cervix (: cervices) or cervix uteri is a dynamic fibromuscular sexual organ of the female reproductive system that connects the vagina with the uterine cavity. The human female cervix has been documented anatomically since at least the time ...
and fetal station.
* Cervical dilation measures how dilated the cervix is in centimeters
* Position refers to the position of the cervix relative to the fetal head and pelvis
* Effacement assesses the thinning and shortening of the cervix in comparison to the whole cervix length
* Consistency of the cervix refers to the firmness of the cervix
* Fetal station is the position of the fetal head relative to the pelvis
Cervical dilation, effacement and station are scored from 0 to 3. Cervical consistency and position are scored from 0 to 2. The total score ranges with a minimum of 0 and maximum of 13. A Bishop score of 6 and below indicates that induction is not favorable and no method of induction will be highly effective. In these cases, cervical ripening agents may be used. A score of 8 and above indicates induction of labor is favorable and the possibility of a vaginal delivery
In mammals and other animals, the vagina (: vaginas or vaginae) is the elastic, muscular sex organ, reproductive organ of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vulval vestibule to the cervix (neck of the uterus). The #Vag ...
with induction will be similar to spontaneous labor.
Cervical effacement is an important component of the Bishop score and is reported as a percentage. 0% indicates the cervix is at normal length, 50% indicates the cervix is half of the expected length and 100% effaced means the cervix is paper thin.
The Bishop score has been modified in current medical practice. The modified scoring method takes into consideration only 3 parameters: dilation, effacement, and fetal station. These are scored between the range of 0 to 3 each with a score of 5 or above being favorable for induction of labor.
Other methods
Given that cervical effacement is measured as a percentage, this method requires a consensus on a standard uneffaced cervix length. However, this can vary among physicians. This requirement presents itself as an opportunity for error, miscommunication and inappropriate care in the process of assessing cervical effacement. Other methods used in assessing and measuring cervical effacement may be more accurate than the Bishop score, such as the metric system of measuring the cervix. Integrating the metric system of measurement of the cervix may reduce and eliminate the risk of error and assumptions on cervical length. Imaging methods are also being considered to measure cervical effacement. Elastography measures the stiffness and ability of soft tissue and can be used to assess how the cervical tissue deforms under pressure. This cannot be assessed manually and can be a useful parameter in predicting a preterm or full term delivery. There are two methods of elastography. Static elastography measures the tissue displacement in response to manual compression or movement. Dynamic elastography measures speed of shear wave propagation. Both methods can provide useful information on the stiffness of the cervix in considering induction of labor.Contra-indications
Cervical ripening is contraindicated in pregnancies presenting with the following conditions: * Less than 39 weeks ofgestation
Gestation is the period of development during the carrying of an embryo, and later fetus, inside viviparous animals (the embryo develops within the parent). It is typical for mammals, but also occurs for some non-mammals. Mammals during pregn ...
, without medical indication
* Prior caesarean delivery
* Major uterine surgery
The contraindications for cervical ripening also include those of vaginal birth. Absolute contraindications can result in life-threatening events, and relative contraindications should be considered with caution. The absolute and relative contraindications to vaginal birth include, but are not limited to the following:
Absolute contraindications:
* Breech presentations (footling, frank, complete)
* Cord prolapse
Cord or CORD may refer to:
Common meanings
* String (structure), String
* Thin rope
* Twine
* Cord (unit) used for measuring wood
* Power cord
* Umbilical cord
Cord or CORD may also refer to:
Places
* Cord, Arkansas
People
* Alex Cord ( ...
* Fetus malposition
* Conjoined twins
Conjoined twins, popularly referred to as Siamese twins, are twins joined '' in utero''. It is a very rare phenomenon, estimated to occur in anywhere between one in 50,000 births to one in 200,000 births, with a somewhat higher incidence in south ...
* Mono-amniotic twins
* Placenta praevia
* History of uterine rupture
* Active genital herpes infection
Relative contraindications:
* Fetal weight greater than 5kg in an individual with diabetes
* Fetal weight greater than 4.5kg in an individual without diabetes
* Non-reassuring fetal heart rate patterns
Risks and complications
Labor induction poses different risks to the woman and fetus. As such, risks and complications relating to cervical effacement can be classified as being a risk to the woman or the fetus.Risk to woman
Infection
Cervical ripening via transcervical balloon catheter can increase the risk of infection to the woman. Approximately 11% of pregnancies develop an intrapartum infection, 3% a postpartum infection and 5% a neonatal infection. Only intrapartum infection was deemed a clinically significant risk.Uterine hyperstimulation
The risk of uterine hyperstimulation as it relates to labor induction is higher with dinoprostone and vaginally administered misoprostol than it is with oxytocin and mechanical methods. Postpartum Hemorrhage Postpartum Hemorrhage, or any blood loss over 1,000 mL, rarely occurs in outpatient and inpatient groups. However, women postpartum still are at risk of hemorrhage and should be monitored.Fetal risks
Autism
Oxytocin dysregulation has been linked to Autism or autism spectrum disorder. As oxytocin is one of the methods used for cervical ripening, the Committee on Obstetric Practice at theAmerican College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) is a professional association of physicians specializing in obstetrics and gynecology in the United States. Several Latin American countries are also represented within Districts of ...
conducted a review of existing research regarding this link, and concluded that there was insufficient evidence of a causal link between cervical effacement via oxytocin and autism/ASD.
Fetal distress or hyperstimulation
Low dose oral misoprostol for the purpose of labor induction, is associated with a lower risk of fetal distress than vaginally administered misoprostol. Vaginally administereddinoprostone
Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), also known as dinoprostone, is a naturally occurring prostaglandin with oxytocic properties that is used as a medication. Dinoprostone is used in labor induction, bleeding after delivery, termination of pregnanc ...
is associated with an increased risk of fetal hyperstimulation with or without fetal heart rate abnormalities.
Cervical ripening in the outpatient setting and the inpatient setting
Inpatient and outpatient cervical ripening done via vaginally administereddinoprostone
Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), also known as dinoprostone, is a naturally occurring prostaglandin with oxytocic properties that is used as a medication. Dinoprostone is used in labor induction, bleeding after delivery, termination of pregnanc ...
or balloon catheters in low risk pregnancies do not have different rates of caesarean section
Caesarean section, also known as C-section, cesarean, or caesarean delivery, is the Surgery, surgical procedure by which one or more babies are Childbirth, delivered through an incision in the mother's abdomen. It is often performed because va ...
. Cervical ripening using dinoprostone
Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), also known as dinoprostone, is a naturally occurring prostaglandin with oxytocic properties that is used as a medication. Dinoprostone is used in labor induction, bleeding after delivery, termination of pregnanc ...
vaginal inserts have the same rates of neonatal morbidity, caesarean section
Caesarean section, also known as C-section, cesarean, or caesarean delivery, is the Surgery, surgical procedure by which one or more babies are Childbirth, delivered through an incision in the mother's abdomen. It is often performed because va ...
, and labor onset when used in the outpatient setting and the inpatient setting. Evidence for use of misoprostol in the outpatient versus inpatient setting was insufficient to draw conclusions.
Methods
Pharmacologic
*Oxytocin
Oxytocin is a peptide hormone and neuropeptide normally produced in the hypothalamus and released by the posterior pituitary. Present in animals since early stages of evolution, in humans it plays roles in behavior that include Human bonding, ...
Oxytocin is one of the most commonly used medications for cervical effacement. It is given as an infusion to either start or increase uterine contractions. Epidurals are often used together for pain. Oxytocin may also be used in the setting of amniotomy as well as balloon catheters to further contractions in conjunction to these procedures.
* Misoprostol
Misoprostol is a medication that can cause contractions for cervical effacement. When used with balloon catheters, vaginal delivery was more likely to occur within the next 24 hours after initiation. It is known as a type of prostaglandin and available worldwide. It can also be used for early termination of pregnancy.
* Dinoprostone
Also in the class of prostaglandins, dinoprostone increases contractions. It is available in both gel and vaginal insert form and while both are safe and efficacious, one study has found that in those with a bishop score of less than or equal to 4, the vaginal insert seemed to be more effective in spontaneous vaginal delivery by about 20%.
Non-pharmacologic
* Red raspberry leaf Red raspberry leaf tea is an herbal option for cervical effacement. In a retrospective observational study conducted in 1999, while there was not significant difference in time for second and third stage of labour, the "mean time in first stage of labour is also substantially lower in the raspberry leaf group". The data, however, was not proven to be statistically significant. * Warm bath Warm bath is a common method used by midwives to ease labor pain and also induce labor. In a study conducted in 2019, "cervical dilation increased in all groups (p<.001), as well as the number of uterine contractions increased, mainly in the group that used combined bath and ball and also showed shorter labor time". Safety precautions should be taken to make sure that the water temperature is not too high as it can lead to fetal distress.Mechanical
* Balloon Catheter Balloon Catheters are catheters that can be inserted into the cervix in the setting of pregnancy to induce labor. Saline is used to inflate the balloon, causing increased pressure to the cervix. This is to imitate the pressure of a fetal head that would be pressing on the cervix during labor, which in turn speeds up the process. * Hygroscopic Dilator Hygroscopic dilator is a dilator that is inserted into the cervix and expands in size as it absorbs genital tract moisture. They can also be used for early termination of pregnancy. According to a study conducted in Japan from 2012-2014, the rate of delivery at term seemed to be equivalent between the group that used balloon catheter and that of the hygroscopic dilator.Surgical
* Amniotomy Amniotomy is a procedure where a hook is inserted into the amniotic membranes to puncture, causing the amniotic fluid to drain from the amniotic sac that holds the fetus. The reason for the surgical procedure could either be for cervical effacement or to look at fetal status as a device can be inserted into the amniotic sac for monitoring. The sign of successful procedure is when the amniotic fluid immediately comes out once the membrane is punctured. Certain amniotic fluid colors can indicate fetal distress, which is why it is important for the obstetrician or midwife to check the color. * Membrane Stripping Membrane stripping, otherwise known as membrane sweeping, is a procedure where the obstetrician inserts a finger into the cervix and moves in a sweeping motion to detach the amniotic membrane from the uterus. It is thought to be different from other procedures in that it is less costly compared to the other. While it may be an inexpensive procedure, it comes with its own risks. Membrane sweeping may rupture the amniotic sac for 1 out of 10 women who get this procedure done, which will then lead for the need to formally induce labor within 24 hours. Membrane sweeping can also be very painful and can cause bleeding and irregular contractions. Membrane sweeping is also not effective for 7 out of the 8 women that get this procedure done.References
{{Pregnancy Childbirth Midwifery Obstetrics