Central Experimental Farm on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Central Experimental Farm (CEF), commonly known as the Experimental Farm, is an agricultural facility, working farm, and research centre of the Science and Technology Branch, formerly the Research Branch, of
 The
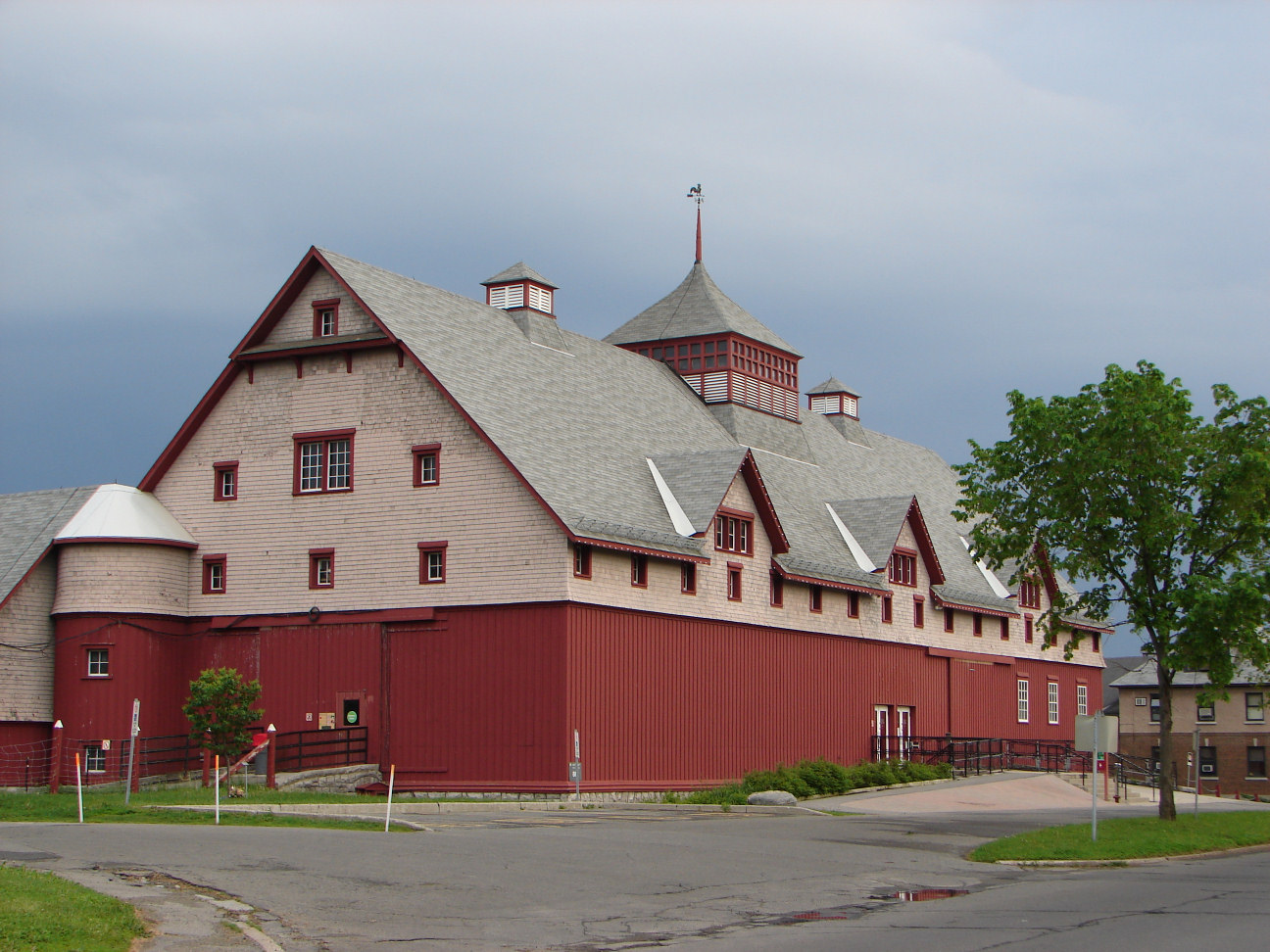
The  In 1887–1888, Chief Dominion Architect Thomas Fuller designed the Museum, laboratories, barn, stables, and Staff Residences on Prince of Wales Drive In 1887, Charles F. Cox lay out of the site and design of farm buildings. In 1887–1888, William John Beckett, a contractor, served as foreman during the building of the residences, offices and barns.
In 1887–1888, Chief Dominion Architect Thomas Fuller designed the Museum, laboratories, barn, stables, and Staff Residences on Prince of Wales Drive In 1887, Charles F. Cox lay out of the site and design of farm buildings. In 1887–1888, William John Beckett, a contractor, served as foreman during the building of the residences, offices and barns.
 In 1889, livestock was introduced to the CEF.
Chief Dominion Architect
In 1889, livestock was introduced to the CEF.
Chief Dominion Architect  John Bethune Roper designed the Administration Building, Carling Avenue, 1934. William James Abra designed the Biological Building, 1935.
John Bethune Roper designed the Administration Building, Carling Avenue, 1934. William James Abra designed the Biological Building, 1935.
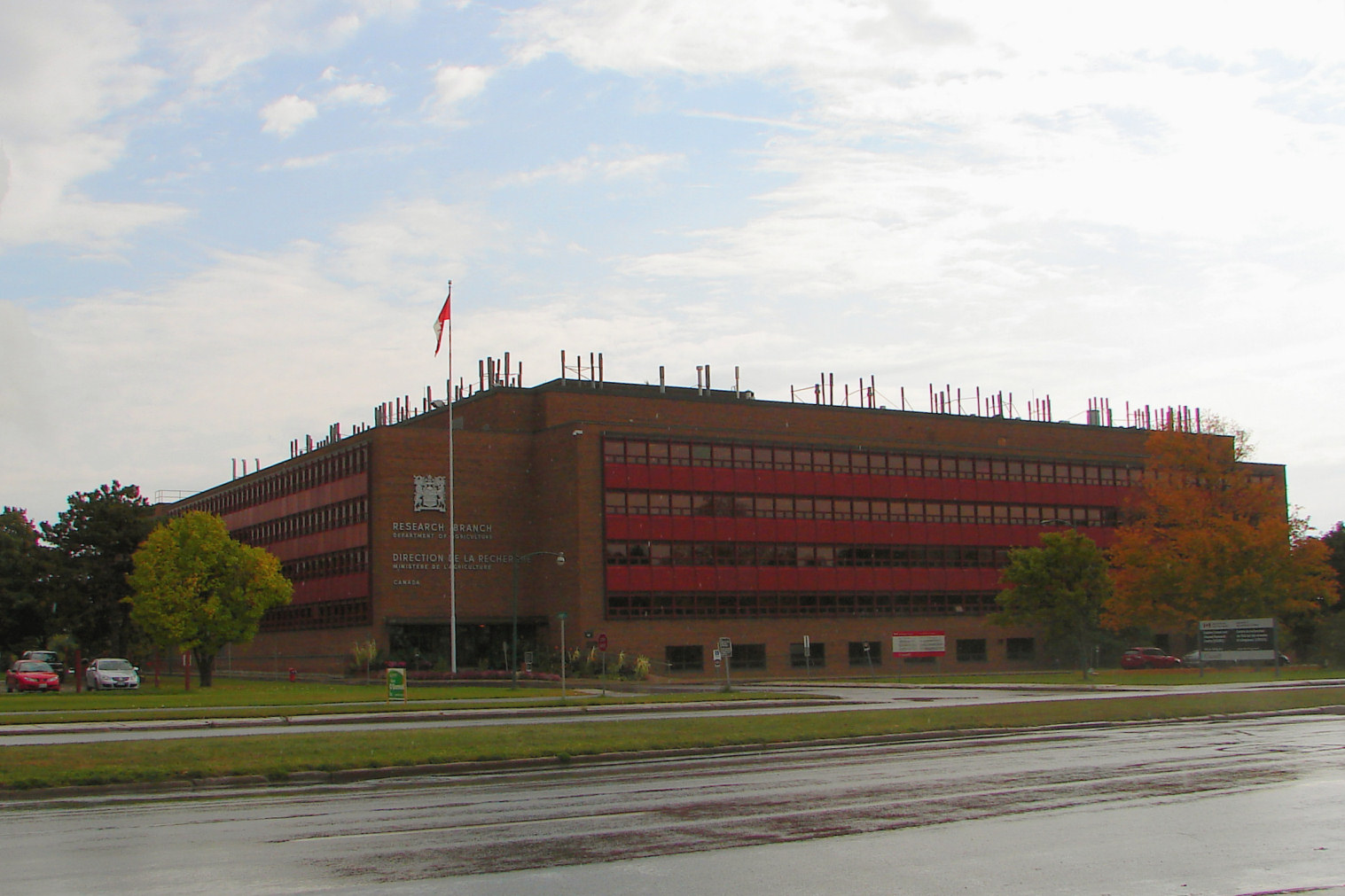 Over the years the scope of research grew and changed, prompting a need to increase the farm's lands and buildings. The Horticulturalist's house and staff residences were removed by the 1930s (they were no longer needed since the city had grown around the farm), the forest belt gradually disappeared, and new larger centralized facilities were built, starting with the Saunders Building in 1935, followed by the Neatby Building, Geophysical Lab, Laboratory Services Building, and the Carling Building.
From 1940 to 1947, building 136 operated as a high frequency Naval Radio Station-CFF which frequently intercepted enemy transmissions. On May 1, 1993, a memorial was erected by NOAC and Royal Canadian Naval Association Ottawa and dedicated to the Naval Veterans and those who served at this station which provided a link during World War II between Canadian naval headquarters and ships at sea, allied naval headquarters and operational naval authorities.
The CEF was the site of a large scale
Over the years the scope of research grew and changed, prompting a need to increase the farm's lands and buildings. The Horticulturalist's house and staff residences were removed by the 1930s (they were no longer needed since the city had grown around the farm), the forest belt gradually disappeared, and new larger centralized facilities were built, starting with the Saunders Building in 1935, followed by the Neatby Building, Geophysical Lab, Laboratory Services Building, and the Carling Building.
From 1940 to 1947, building 136 operated as a high frequency Naval Radio Station-CFF which frequently intercepted enemy transmissions. On May 1, 1993, a memorial was erected by NOAC and Royal Canadian Naval Association Ottawa and dedicated to the Naval Veterans and those who served at this station which provided a link during World War II between Canadian naval headquarters and ships at sea, allied naval headquarters and operational naval authorities.
The CEF was the site of a large scale
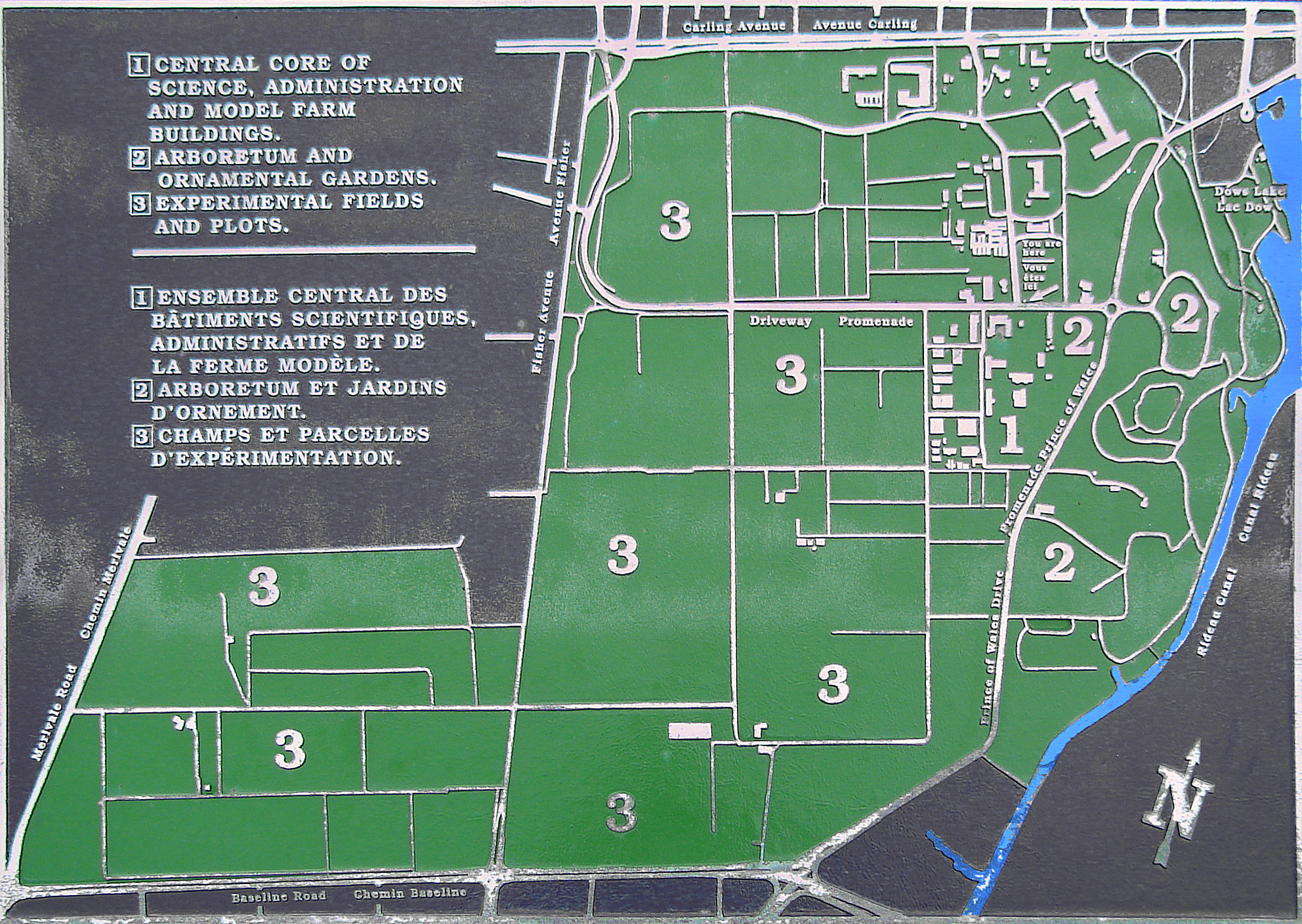
 ;Major features:
* Dominion Observatory
* Canada Agriculture and Food Museum
* Dominion Arboretum
* Ornamental Gardens, consisting of:
**the perennial collection
**the rock garden
**the rose garden
**the annuals garden
**the Macoun Memorial Garden
**the hedge collection
* Fletcher Wildlife Garden
;Notable office and research buildings:
* Sir John Carling Building (demolished 2014)
*Ottawa Research and Development Centre, formerly the Eastern Cereal and Oilseed Research Centre (ECORC) / K.W. Neatby Building
*Skyline Building, 1341 Baseline Road.
*The Canadian 4-H Council and Canadian 4-H Foundation
;Major features:
* Dominion Observatory
* Canada Agriculture and Food Museum
* Dominion Arboretum
* Ornamental Gardens, consisting of:
**the perennial collection
**the rock garden
**the rose garden
**the annuals garden
**the Macoun Memorial Garden
**the hedge collection
* Fletcher Wildlife Garden
;Notable office and research buildings:
* Sir John Carling Building (demolished 2014)
*Ottawa Research and Development Centre, formerly the Eastern Cereal and Oilseed Research Centre (ECORC) / K.W. Neatby Building
*Skyline Building, 1341 Baseline Road.
*The Canadian 4-H Council and Canadian 4-H Foundation
Parks Canada 3-D Tour of Central Experimental FarmCanadian 4-H Council
"One Hundred Harvests Research Branch Agriculture Canada 1886-1986"
{{Authority control Experimental farms in Canada Federal government buildings in Ottawa National Historic Sites in Ontario Tourist attractions in Ottawa Arboreta in Canada Agriculture in Ontario Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada 1886 establishments in Ontario
Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada
Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada (AAFC; sometimes Ag-Canada; )''Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada'' is the applied title under the Federal Identity Program; the legal title is Department of Agriculture and Agri-Food (). is the Structure of the Can ...
. As the name indicates, this farm is centrally located in and now surrounded by the City of Ottawa
Ottawa is the capital city of Canada. It is located in the southern Ontario, southern portion of the province of Ontario, at the confluence of the Ottawa River and the Rideau River. Ottawa borders Gatineau, Gatineau, Quebec, and forms the cor ...
, Ontario
Ontario is the southernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Located in Central Canada, Ontario is the Population of Canada by province and territory, country's most populous province. As of the 2021 Canadian census, it ...
, Canada. Located on of land, the farm is a National Historic Site of Canada
National Historic Sites of Canada () are places that have been designated by the federal Minister of the Environment on the advice of the Historic Sites and Monuments Board of Canada (HSMBC), as being of national historic significance. Parks C ...
and most buildings are protected and preserved as heritage buildings.
The CEF's original intent was to perform scientific research for improvement in agricultural methods and crops. While such research is still being conducted, the park-like atmosphere of the CEF has become an important place of recreation and education for the residents of Ottawa. Furthermore, over the years several other departments and agencies have encroached onto the CEF property, such as Natural Resources Canada
Natural Resources Canada (NRCan; ; )Natural Resources Canada is the applied title under the Federal Identity Program; the legal title is Department of Natural Resources (). is the department of the Government of Canada responsible for natural r ...
, National Defence ( HMCS ''Carleton'' on Dow's Lake), and the Ottawa Civic Hospital
The Ottawa Civic Hospital is one of three main campuses of The Ottawa Hospital – along with the General and Riverside campuses. With 549 beds (including the Heart Institute), the Civic Campus has the region's only adult-care trauma centre, servin ...
(helicopter pad).
The CEF is bordered by the Rideau Canal
The Rideau Canal is a 202-kilometre long canal that links the Ottawa River at Ottawa with the Cataraqui River and Lake Ontario at Kingston, Ontario, Canada. Its 46 Lock (water navigation), locks raise boats from the Ottawa River 83 metres (272 ...
(a National Historic Site as well) to the east, Prince of Wales Drive to the South-East, Baseline Road to the south, and Merivale and Fisher Roads to the west, and Carling Avenue to the north.
History
 The
The Victorian era
In the history of the United Kingdom and the British Empire, the Victorian era was the reign of Queen Victoria, from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. Slightly different definitions are sometimes used. The era followed the ...
was a time of great interest in the advancement of natural sciences and many nations built zoos, observatories
An observatory is a location used for observing terrestrial, marine, or celestial events. Astronomy, climatology/meteorology, geophysics, oceanography and volcanology are examples of disciplines for which observatories have been constructed.
Th ...
, botanical garden
A botanical garden or botanic gardenThe terms ''botanic'' and ''botanical'' and ''garden'' or ''gardens'' are used more-or-less interchangeably, although the word ''botanic'' is generally reserved for the earlier, more traditional gardens. is ...
s, and experimental farms. Canada followed suit and as the result of lobbying by John Carling
Sir John Carling, (January 23, 1828 – November 6, 1911) was a Canadian politician and prominent businessman who was associated with the Carling Brewery in London, Ontario. The Carling family and its descendants later resided in Ottawa, M ...
, the Minister of Agriculture, and William Saunders, the first director of the research branch, the "Act Respecting Experimental Stations" came into force in 1886. The land owned by local Ottawa farmers including John Mulligan (1799–1886) was sold to the government to create the experimental farm. The CEF started out with 188 hectares, chosen because of their proximity to Parliament Hill
Parliament Hill (), colloquially known as The Hill, is an area of Crown land on the southern bank of the Ottawa River that houses the Parliament of Canada in downtown Ottawa, Ontario. It accommodates a suite of Gothic revival buildings whose ...
but (at that time) outside the city. Over the next few years the site was prepared by improving the land, building the facilities, and planting the Arboretum
An arboretum (: arboreta) is a botanical collection composed exclusively of trees and shrubs of a variety of species. Originally mostly created as a section in a larger garden or park for specimens of mostly non-local species, many modern arbor ...
and forest belt. The CEF was established as the centre piece of the Dominion Experimental Farms, which would also have a series of sub stations located in other Canadian provinces. Early research projects focused only on entomology
Entomology (from Ancient Greek ἔντομον (''éntomon''), meaning "insect", and -logy from λόγος (''lógos''), meaning "study") is the branch of zoology that focuses on insects. Those who study entomology are known as entomologists. In ...
, botany
Botany, also called plant science, is the branch of natural science and biology studying plants, especially Plant anatomy, their anatomy, Plant taxonomy, taxonomy, and Plant ecology, ecology. A botanist or plant scientist is a scientist who s ...
, and horticulture
Horticulture (from ) is the art and science of growing fruits, vegetables, flowers, trees, shrubs and ornamental plants. Horticulture is commonly associated with the more professional and technical aspects of plant cultivation on a smaller and mo ...
.
The Chief Dominion Architect(s) designed a number of prominent public buildings in Canada including those at the CEF: Thomas Seaton Scott (1871–1881); Thomas Fuller (architect) (1880–1897); David Ewart
David Ewart, Imperial Service Order, ISO (18 February 1841 – 6 June 1921) was a Canadians, Canadian architect who served as Chief Dominion Architect from 1896 to 1914.
As chief government architect he was responsible for many of the federal bu ...
(1897–1914); Edgar Lewis Horwood (1914–1918); Richard Cotsman Wright (1918–1927); Thomas W. Fuller (1927–1936), Charles D. Sutherland (1936–1947); Joseph Charles Gustave Brault (1947–1952)
Thomas Seaton Scott and Thomas Fuller adopted the Neo-Gothic style. David Ewart embraced the Scottish baronial style.
 In 1889, livestock was introduced to the CEF.
Chief Dominion Architect
In 1889, livestock was introduced to the CEF.
Chief Dominion Architect David Ewart
David Ewart, Imperial Service Order, ISO (18 February 1841 – 6 June 1921) was a Canadians, Canadian architect who served as Chief Dominion Architect from 1896 to 1914.
As chief government architect he was responsible for many of the federal bu ...
designed the Dominion Observatory, Carling Avenue in 1902; Chief Astronomer's Residence, 1909; and the Geodetic Survey Building, 1914. Chief Dominion Architect Edgar Lewis Horwood designed the Cereal and Agrostology Building, 1915–16; Agricultural Building, 1915; and records storage building, 1937. Chief Dominion Architect Richard Cotsman Wright designed a number of buildings including: the Poultry Office Building, 1920; and the Botanical Laboratory Building, 1924–25.
cannabis
''Cannabis'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cannabaceae that is widely accepted as being indigenous to and originating from the continent of Asia. However, the number of species is disputed, with as many as three species be ...
grow operation in the 1970s, producing tonnes of crop from plants standing 20 feet tall. It was intended to provide Canadian scientists with reliable samples for research in response to an interim report of the Le Dain Commission
The Commission of Inquiry into the Non-Medical Use of Drugs, often referred to as the Le Dain Commission after its chair Dean Gerald Le Dain, was a Canadian government commission that was begun in 1969 and completed its work in 1972.
The recommen ...
. The plants were near Ash Lane, earning it the nickname " Hash Lane"; combined with the secrecy around the project, it became a local legend among area youth.
In 1983, the agricultural museum was created in the former Dairy Barn.
The Federal Heritage Buildings Review Office recognized or classified a number of CEF buildings on the Register of the Government of Canada Heritage Buildings between 1984 and 1997. The Cereal Barn Building 76 was classified in 1984. The Victoria Memorial Museum was classified in 1986. The Main Dairy Barn Building 88 was classified in 1987. In 1988, the Botanical Laboratory / Horticulture Building 74 and the Sheep Showcase / Small Dairy Barn Building 95 were recognized. The Nutrition Building 59 was recognized in 1992. In 1993, Heritage House, Building 60 was recognized. The William Saunders Building 49 was recognized in 1994. In 1995, Heritage House, Building 54; K. W. Neatby Building 20 and the Main Piggery, Building 91 were recognized. In 1996, the Main Greenhouse Range, Building 50 was recognized. In 1997, a number of buildings were recognized: ARC Biotech, Building 34; Carpenter Shed, Building 98; Cereal Crops Building 75; Dairy Technology Building 57; Engineering Research Building 94; Horticulture Building 55; Laboratory Services Building 22; Pottery Shed, Building 77; and Service Building 56.
The CEF was designated as a National Historic Site in 1998.
In 2003, Public Works and Government Services Canada
Public Services and Procurement Canada (PSPC; ),''Public Services and Procurement Canada'' is the applied title under the Federal Identity Program; the legal title is Department of Public Works and Government Services (). formerly Public Works ...
bought the Skyline office complex on the corner of Merivale and Baseline Roads from Nortel Networks. The complex has been renamed to "NHCAP" (= National Headquarters Complex for the Agriculture Portfolio). The head offices of Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada
Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada (AAFC; sometimes Ag-Canada; )''Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada'' is the applied title under the Federal Identity Program; the legal title is Department of Agriculture and Agri-Food (). is the Structure of the Can ...
have been relocated to this facility from the Sir John Carling Building, which was demolished on July 13, 2014.
The CEF housed, prior to its disestablishment on 29 September 2006 by the Harper government, the Canadian Agri-Food Research Council.
Features
 ;Major features:
* Dominion Observatory
* Canada Agriculture and Food Museum
* Dominion Arboretum
* Ornamental Gardens, consisting of:
**the perennial collection
**the rock garden
**the rose garden
**the annuals garden
**the Macoun Memorial Garden
**the hedge collection
* Fletcher Wildlife Garden
;Notable office and research buildings:
* Sir John Carling Building (demolished 2014)
*Ottawa Research and Development Centre, formerly the Eastern Cereal and Oilseed Research Centre (ECORC) / K.W. Neatby Building
*Skyline Building, 1341 Baseline Road.
*The Canadian 4-H Council and Canadian 4-H Foundation
;Major features:
* Dominion Observatory
* Canada Agriculture and Food Museum
* Dominion Arboretum
* Ornamental Gardens, consisting of:
**the perennial collection
**the rock garden
**the rose garden
**the annuals garden
**the Macoun Memorial Garden
**the hedge collection
* Fletcher Wildlife Garden
;Notable office and research buildings:
* Sir John Carling Building (demolished 2014)
*Ottawa Research and Development Centre, formerly the Eastern Cereal and Oilseed Research Centre (ECORC) / K.W. Neatby Building
*Skyline Building, 1341 Baseline Road.
*The Canadian 4-H Council and Canadian 4-H Foundation
See also
*Agriculture in Canada
Canada is one of the largest agricultural producers and exporters in the world. As with other developed nations, the proportion of the population agriculture employed and agricultural GDP as a percentage of the national GDP fell dramatically ...
*Demonstration farm
A demonstration farm, experimental farm or model farm, is a farm which is used primarily to research or demonstrate various agricultural techniques, with any economic gains being an added bonus. Demonstration farms are often owned and operated by ...
* List of Ottawa, Ontario parks
* Manitoba Agricultural Museum
* Ontario Agricultural Museum
*Ross Farm Museum
The Ross Farm Museum is an agricultural museum located in New Ross, Nova Scotia, New Ross, Nova Scotia. It is about an hour's drive from Halifax Urban Area, Halifax.
Museum
The exhibits feature working artisans, live animals, historic building ...
References
Further reading
;Bibliography * * *External links
Parks Canada 3-D Tour of Central Experimental Farm
"One Hundred Harvests Research Branch Agriculture Canada 1886-1986"
{{Authority control Experimental farms in Canada Federal government buildings in Ottawa National Historic Sites in Ontario Tourist attractions in Ottawa Arboreta in Canada Agriculture in Ontario Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada 1886 establishments in Ontario