The Western Allied invasion of Germany was coordinated by the
Western Allies
Western Allies was a political and geographic grouping among the Allied Powers of the Second World War. It primarily refers to the leading Anglo-American Allied powers, namely the United States and the United Kingdom, although the term has also be ...
during the final months of hostilities in the
European theatre
The European theatre of World War II was one of the two main theatres of combat during World War II, taking place from September 1939 to May 1945. The Allied powers (including the United Kingdom, the United States, the Soviet Union and Franc ...
of
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
. In preparation for the Allied invasion of
Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
east of the
Rhine
The Rhine ( ) is one of the List of rivers of Europe, major rivers in Europe. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein border, then part of the Austria–Swit ...
, a series of offensive operations were designed to seize and capture its east and west banks:
Operation Veritable
Operation Veritable (also known as the Battle of the Reichswald) was the northern part of an Allies of World War II, Allied pincer movement that took place between 8 February and 11 March 1945 during the final stages of the World War II, Second ...
and
Operation Grenade
During World War II, Operation Grenade was the crossing of the Roer river between Roermond and Düren by the U.S. Ninth Army, commanded by Lieutenant General William Hood Simpson, in February 1945, which marked the beginning of the Allied inv ...
in February 1945, and
Operation Lumberjack
Operation Lumberjack was a military operation with the goal of capturing the west bank of the Rhine River and seizing key German cities, near the end of World War II in Europe. The First United States Army launched the operation in March 1945 ...
and
Operation Undertone
Operation Undertone, also known as the Saar-Palatinate Offensive, was a large assault by the Seventh United States Army, U.S. Seventh, United States Army Central, Third, and First Army (France), French First Armies of the Sixth United States Arm ...
in March 1945; these are considered separate from the main invasion operation. The Allied invasion of Germany east of the Rhine started with the Western Allies crossing the river on 22 March 1945 before fanning out and overrunning all of
western Germany
The old states of Germany () is a jargon referring to the ten of the sixteen states of the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG) that were part of West Germany and that unified with the eastern German Democratic Republic's 5 states, which are giv ...
from the
Baltic
Baltic may refer to:
Peoples and languages
*Baltic languages, a subfamily of Indo-European languages, including Lithuanian, Latvian and extinct Old Prussian
*Balts (or Baltic peoples), ethnic groups speaking the Baltic languages and/or originatin ...
in the north to the
Alpine passes in the south, where they linked up with troops of the
U.S. Fifth Army in Italy.
[Fifth Army History, Race to the Alps, Chapter VI : Conclusion](_blank)
/ref>[Wallace, Linnel, Lt. Col., Commanding Officer, ''Summary History of the 289th Engineer Combat Battalion – WW II'', 1990, U.S. Army Heritage and Education Center, Carlisle, PA] Combined with the capture of ''Berchtesgaden
Berchtesgaden () is a municipality in the district Berchtesgadener Land, Bavaria, in southeastern Germany, near the border with Austria, south of Salzburg and southeast of Munich. It lies in the Berchtesgaden Alps. South of the town, the Be ...
'', any hope of Nazi leadership continuing to wage war from a so-called "national redoubt
A national redoubt or national fortress is an area to which the (remnant) military forces of a nation can be withdrawn if the main battle has been lost or even earlier if defeat is considered inevitable. Typically, a region is chosen with a geogra ...
" or escape through the Alps was crushed, shortly followed by unconditional German surrender on 8 May 1945. This is known as the Central Europe Campaign in United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
military histories.
By early 1945, events favored the Allied forces in Europe. On the Western Front, the Allies had been fighting in Germany with campaigns against the Siegfried Line
The Siegfried Line, known in German as the ''Westwall (= western bulwark)'', was a German defensive line built during the late 1930s. Started in 1936, opposite the French Maginot Line, it stretched more than from Kleve on the border with the ...
since the Battle of Aachen
The Battle of Aachen was a battle of World War II, fought by American and German forces in and around Aachen, Germany, between 12 September and 21 October 1944. The city had been incorporated into the Siegfried Line, the main defensive network ...
, the Battle of Metz and the Battle of Hürtgen Forest
The Battle of Hürtgen Forest () was a series of battles fought from 19 September to 16 December 1944, between United States Armed Forces, American and Wehrmacht, German forces on the Western Front (World War II), Western Front during World War ...
in late 1944 and by January 1945, had pushed the Germans back to their starting points during the Battle of the Bulge
The Battle of the Bulge, also known as the Ardennes Offensive or Unternehmen Die Wacht am Rhein, Wacht am Rhein, was the last major German Offensive (military), offensive Military campaign, campaign on the Western Front (World War II), Western ...
. The failure of this offensive exhausted Germany's strategic reserve, leaving it ill-prepared to resist the final Allied campaigns in Europe. Additional losses in the Rhineland
The Rhineland ( ; ; ; ) is a loosely defined area of Western Germany along the Rhine, chiefly Middle Rhine, its middle section. It is the main industrial heartland of Germany because of its many factories, and it has historic ties to the Holy ...
further weakened the German Army
The German Army (, 'army') is the land component of the armed forces of Federal Republic of Germany, Germany. The present-day German Army was founded in 1955 as part of the newly formed West German together with the German Navy, ''Marine'' (G ...
, leaving shattered remnants of units to defend the east bank of the Rhine. On 7 March, the Allies seized the intact bridge across the Rhine at Remagen
Remagen () is a town in Germany in the state of Rhineland-Palatinate, in the district of Ahrweiler (district), Ahrweiler. It is about a one-hour drive from Cologne, just south of Bonn, the former West Germany, West German seat of government. It i ...
, and established a large bridgehead
In military strategy, a bridgehead (or bridge-head) is the strategically important area of ground around the end of a bridge or other place of possible crossing over a body of water which at time of conflict is sought to be defended or taken over ...
on the river's east bank. During Operation Lumberjack, Operation Plunder
Operation Plunder was a military operation to cross the Rhine on the night of 23 March 1945, launched by the 21st Army Group under Field Marshal Bernard Montgomery. The crossing of the river was at Rees, Wesel, and south of the river Lippe b ...
and Operation Undertone, German casualties during February–March 1945 are estimated at 400,000 men, including 280,000 men captured as prisoners of war
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person held captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold prisoners of war for a ...
.
On the Eastern Front, the Soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army, often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Republic and, from 1922, the Soviet Union. The army was established in January 1918 by a decree of the Council of People ...
(including the Polish Armed Forces in the East under Soviet command), had taken most of Poland, launched an offensive into East Prussia and began their invasion into Eastern Germany in February 1945, and by March were within striking distance of Berlin
Berlin ( ; ) is the Capital of Germany, capital and largest city of Germany, by both area and List of cities in Germany by population, population. With 3.7 million inhabitants, it has the List of cities in the European Union by population withi ...
. The initial advance into Romania, the First Jassy–Kishinev Offensive in April and May 1944 was a failure; the Second Jassy–Kishinev Offensive
The second (symbol: s) is a unit of time derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes, and finally to 60 seconds each (24 × 60 × 60 = 86400). The current and formal definition in the International System of U ...
in August succeeded. The Red Army also pushed deep into Hungary (the Budapest Offensive) and eastern Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia ( ; Czech language, Czech and , ''Česko-Slovensko'') was a landlocked country in Central Europe, created in 1918, when it declared its independence from Austria-Hungary. In 1938, after the Munich Agreement, the Sudetenland beca ...
and temporarily halted at what is now the modern Germany–Poland border
The Germany–Poland border (, ) is the state international border, border between Poland and Germany, mostly along the Oder–Neisse line, with a total length of . (Downloadable pdf file) It stretches from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Czec ...
on the Oder–Neisse line
The Oder–Neisse line (, ) is an unofficial term for the Germany–Poland border, modern border between Germany and Poland. The line generally follows the Oder and Lusatian Neisse rivers, meeting the Baltic Sea in the north. A small portion ...
. These rapid advances on the Eastern Front destroyed additional veteran German combat units and severely limited German Führer
( , spelled ''Fuehrer'' when the umlaut is unavailable) is a German word meaning "leader" or " guide". As a political title, it is strongly associated with Adolf Hitler, the dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 to 1945. Hitler officially cal ...
Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (20 April 1889 – 30 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was the dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his suicide in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the lea ...
's ability to reinforce his Rhine defenses. With the Soviets at the door of Berlin, the western Allies decided any attempt on their behalf to push that far east would be too costly, concentrating instead on mopping up resistance in the west German cities. Nazi Germany surrendered unconditionally on 8 May, leaving the western Allies in control of most of Germany.
Order of battle
Allied forces
At the very beginning of 1945, the Supreme Commander of the Allied Expeditionary Force on the Western Front, General
A general officer is an Officer (armed forces), officer of high rank in the army, armies, and in some nations' air force, air and space forces, marines or naval infantry.
In some usages, the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colone ...
Dwight D. Eisenhower
Dwight David "Ike" Eisenhower (born David Dwight Eisenhower; October 14, 1890 – March 28, 1969) was the 34th president of the United States, serving from 1953 to 1961. During World War II, he was Supreme Commander of the Allied Expeditionar ...
, had 73 divisions under his command in North-western Europe of which 49 were infantry divisions, 20 armored divisions and four airborne divisions. Forty-nine of these divisions were American, 12 British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
, eight French, three Canadian
Canadians () are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of their being ''C ...
and one Polish. Another seven American divisions arrived during February, along with the British 5th Infantry Division
The 5th Infantry Division was a regular army infantry Division (military), division of the British Army. It was established by Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington for service in the Peninsular War, as part of the Anglo-Portuguese Army, and ...
and I Canadian Corps (composed of two divisions, one infantry division and one armoured division), both of which had arrived from the fighting on the Italian front. As the invasion of Germany commenced, Eisenhower had a total of 90 full-strength divisions under his command, with the number of armored divisions now reaching 25. The Allied front along the Rhine stretched from the river's mouth at the North Sea in the Netherlands to the Swiss border in the south.
The Allied forces along this line were organized into three army groups. In the north, from the North Sea to a point about north of Cologne, was the 21st Army Group
The 21st Army Group was a British headquarters formation formed during the Second World War. It controlled two field armies and other supporting units, consisting primarily of the British Second Army and the First Canadian Army. Established ...
commanded by Field Marshal
Field marshal (or field-marshal, abbreviated as FM) is the most senior military rank, senior to the general officer ranks. Usually, it is the highest rank in an army (in countries without the rank of Generalissimo), and as such, few persons a ...
Sir Bernard Montgomery
Field Marshal Bernard Law Montgomery, 1st Viscount Montgomery of Alamein (; 17 November 1887 – 24 March 1976), nicknamed "Monty", was a senior British Army officer who served in the First World War, the Irish War of Independence and the ...
. Within 21st Army Group the Canadian First Army (under Harry Crerar) held the left flank of the Allied line, with the British Second Army
The British Second Army was a Field Army active during the World War I, First and World War II, Second World Wars. During the First World War the army was active on the Western Front (World War I), Western Front throughout most of the war and later ...
( Miles C. Dempsey) in the center and the U.S. 9th Army (William Hood Simpson
General William Hood Simpson (18 May 1888 – 15 August 1980) was a senior United States Army officer who served with distinction in both World War I and World War II. He is best known for being the commanding general of the Ninth United Sta ...
) to the south. Holding the middle of the Allied line from the 9th Army's right flank to a point about south of Mainz
Mainz (; #Names and etymology, see below) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate, and with around 223,000 inhabitants, it is List of cities in Germany by population, Germany's 35th-largest city. It lies in ...
was the 12th Army Group under the command of Lieutenant General
Lieutenant general (Lt Gen, LTG and similar) is a military rank used in many countries. The rank traces its origins to the Middle Ages, where the title of lieutenant general was held by the second-in-command on the battlefield, who was norma ...
Omar Bradley
Omar Nelson Bradley (12 February 1893 – 8 April 1981) was a senior Officer (armed forces), officer of the United States Army during and after World War II, rising to the rank of General of the Army (United States), General of the Army. He wa ...
. Bradley had three American armies, the U.S. 1st Army ( Courtney Hodges) on the left (north), the U.S. 3rd Army ( George S. Patton) on the right (south), and the U.S. 15th Army ( Leonard T. Gerow). Completing the Allied line to the Swiss border was the 6th Army Group commanded by Lieutenant General Jacob L. Devers, with the U.S. 7th Army (Alexander Patch
Alexander McCarrell Patch (23 November 1889 – 21 November 1945) was a senior United States Army Officer (armed forces), officer who fought in World war, both world wars, rising to rank of General (United States), general. During World War ...
) in the north and the French 1st Army (Jean de Lattre de Tassigny
Jean Joseph Marie Gabriel de Lattre de Tassigny (2 February 1889 – 11 January 1952) was a French ''général d'armée'' during World War II and the First Indochina War. He was posthumously elevated to the dignity of Marshal of France in 1952.
...
) on the Allied right, and southernmost, flank.
As these three army groups cleared out the ''Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the German Army (1935–1945), ''Heer'' (army), the ''Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmac ...
'' west of the Rhine, Eisenhower began to rethink his plans for the final drive across the Rhine and into the heart of Germany. Originally, Eisenhower had planned to draw all his forces up to the west bank of the Rhine, using the river as a natural barrier to help cover the inactive sections of his line. The main thrust beyond the river was to be made in the north by Montgomery's 21st Army Group, elements of which were to proceed east to a juncture with the U.S. 1st Army as it made a secondary advance northeast from below the Ruhr
The Ruhr ( ; , also ''Ruhrpott'' ), also referred to as the Ruhr Area, sometimes Ruhr District, Ruhr Region, or Ruhr Valley, is a polycentric urban area in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With a population density of 1,160/km2 and a populati ...
River. If successful, this pincer movement would envelop the industrial Ruhr area, neutralizing the largest concentration of German industrial capacity left.
German forces
Facing the Allies was ''Oberbefehlshaber West'' ("Army Command West") commanded by Generalfeldmarschall
''Generalfeldmarschall'' (; from Old High German ''marahscalc'', "marshal, stable master, groom"; ; often abbreviated to ''Feldmarschall'') was a rank in the armies of several German states and the Holy Roman Empire, (''Reichsgeneralfeldmarsch ...
Albert Kesselring
Albert Kesselring (30 November 1885 – 16 July 1960) was a German military officer and convicted war crime, war criminal who served in the ''Luftwaffe'' during World War II. In a career which spanned both world wars, Kesselring reached the ra ...
, who had taken over from Generalfeldmarschall Gerd von Rundstedt
Karl Rudolf Gerd von Rundstedt (12 December 1875 – 24 February 1953) was a German ''Generalfeldmarschall'' (Field Marshal) in the ''German Army (1935–1945), Heer'' (Army) of Nazi Germany and OB West, ''Oberbefehlshaber West'' (Commande ...
on 10 March. Although Kesselring brought an outstanding track record as a defensive strategist with him from the Italian campaign, he did not have the resources to make a coherent defense. During the fighting west of the Rhine up to March 1945, the German Army on the Western Front had been reduced to a strength of only 26 divisions, organized into three army groups ('' H'', '' B'' and '' G''). Little or no reinforcement was forthcoming as the (OKW) continued to concentrate most forces against the Soviets; it was estimated that the Germans had 214 divisions on the Eastern Front in April.
On 21 March, Army Group H headquarters became ''Oberbefehlshaber Nordwest'' ("Army Command Northwest") commanded by Ernst Busch leaving the former Army Group H commander—Johannes Blaskowitz
Johannes Albrecht Blaskowitz (10 July 1883 – 5 February 1948) was a German ''Generaloberst'' during World War II. After joining the Imperial German Army in 1901, Blaskowitz served throughout World War I, where he earned the Iron Cross for brav ...
—to lead "Army Command Netherlands" ( 25th Army) cut off in the Netherlands. Busch—whose main unit was the German 1st Parachute Army—was to form the right-wing of the German defenses. In the center of the front, defending the Ruhr, Kesselring had Field Marshal Walther Model commanding Army Group B ( 15th Army and 5th Panzer Army
5th Panzer Army () was the name of two different German armoured formations during World War II. The first of these was formed in 1942, during the North African campaign and surrendered to the Allies at Tunis in 1943. The army was re-formed in F ...
) and in the south Paul Hausser
Paul Hausser, also known by his birth name Paul Falk post war (7 October 1880 – 21 December 1972), was a German general and, together with Sepp Dietrich, one of the two highest ranking commanders in the Waffen-SS. He played a key role in the ...
's Army Group G ( 7th Army, 1st Army and 19th Army).
Eisenhower's plans
After capturing the Ruhr, Eisenhower planned to have the 21st Army Group continue its drive east across the plains of northern Germany to Berlin. The 12th and 6th Army Groups were to mount a subsidiary offensive to keep the Germans off balance and diminish their ability to stop the northern thrust. This secondary drive would also give Eisenhower a degree of flexibility in case the northern attack ran into difficulties.
For several reasons, Eisenhower began to readjust these plans toward the end of March. First, his headquarters received reports that Soviet forces held a bridgehead over the Oder River
The Oder ( ; Czech and ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and its largest tributary the Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows through west ...
, from Berlin. Since the Allied armies on the Rhine were more than from Berlin, with the Elbe River
The Elbe ( ; ; or ''Elv''; Upper and , ) is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Giant Mountains of the northern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia (western half of the Czech Republic), then Germany and flo ...
, ahead, still to be crossed it seemed clear that the Soviets would capture Berlin long before the Western Allies could reach it. Eisenhower thus turned his attention to other objectives, most notably a rapid meet-up with the Soviets to cut the German Army in two and prevent any possibility of a unified defense. Once this was accomplished the remaining German forces could be defeated in detail.
In addition, there was the matter of the Ruhr. Although the Ruhr area still contained a significant number of Axis troops and enough industry to retain its importance as a major objective, Allied intelligence reported that much of the region's armament industry was moving southeast, deeper into Germany. This increased the importance of the southern offensives across the Rhine.
Also focusing Eisenhower's attention on the southern drive was concern over the "National redoubt
A national redoubt or national fortress is an area to which the (remnant) military forces of a nation can be withdrawn if the main battle has been lost or even earlier if defeat is considered inevitable. Typically, a region is chosen with a geogra ...
." According to rumor, Hitler's most fanatically loyal troops were preparing to make a lengthy, last-ditch stand in the natural fortresses formed by the rugged alpine mountains of southern Germany and western Austria. If they held out for a year or more, dissension between the Soviet Union and the Western Allies might have given them political leverage for some kind of favorable peace settlement. In reality, the Nazi leadership had never seriously considered or made plans to implement any sort of "national redoubt" and as such the concept had been allowed to evolve into a ruse of war to cause misdirection of Allied units and resources. Moreover, by the time of the Allied Rhine crossings the ''Wehrmacht'' had suffered such severe defeats on both the Eastern and Western Fronts that it could barely manage to mount effective delaying actions, much less muster enough troops to establish a well-organized alpine resistance force. Still, Allied intelligence could not entirely discount the possibility that remnants of the German forces would attempt a suicidal last stand in the Alps. Denying this opportunity became another argument for rethinking the role of the southern drive through Germany.
Perhaps the most compelling reason for increasing the emphasis on this southern drive had more to do with the actions of Americans than those of Germans. While Montgomery was carefully and cautiously planning for the main thrust in the north, complete with massive artillery preparation and an airborne assault, American forces in the south were displaying the kind of basic aggressiveness that Eisenhower wanted to see. On 7 March, Hodges's U.S. 1st Army captured the last intact bridge over the Rhine at Remagen
Remagen () is a town in Germany in the state of Rhineland-Palatinate, in the district of Ahrweiler (district), Ahrweiler. It is about a one-hour drive from Cologne, just south of Bonn, the former West Germany, West German seat of government. It i ...
and steadily expanded the bridgehead
In military strategy, a bridgehead (or bridge-head) is the strategically important area of ground around the end of a bridge or other place of possible crossing over a body of water which at time of conflict is sought to be defended or taken over ...
.
To the south in the Saar-Palatinate region, Patton's U.S. 3rd Army had dealt a devastating blow to the German 7th Army and, in conjunction with the U.S. 7th Army, had nearly destroyed the German 1st Army. In five days of battle, from 18 to 22 March, Patton's forces captured over 68,000 Germans. These bold actions eliminated the last German positions west of the Rhine. Although Montgomery's drive was still planned as the main effort, Eisenhower believed that the momentum of the American forces to the south should not be squandered by having them merely hold the line at the Rhine or make only limited diversionary attacks beyond it. By the end of March, the Supreme Commander thus leaned toward a decision to place more responsibility on his southern forces. The events of the first few days of the final campaign would be enough to convince him that this was the proper course of action.
Occupation process
When Allied soldiers arrived in a town, its leaders and remaining residents typically used white flags, bedsheets, and tablecloths to signal surrender. The officer in charge of the unit capturing the area, typically a company or battalion, accepted responsibility over the town. Soldiers posted copies of General Eisenhower's '' Proclamation No. 1'', which began with "We come as a victorious army, not as oppressors." The proclamation demanded compliance with all orders by the commanding officer, instituted a strict curfew and limited travel and confiscated all communications equipment and weapons. After a day or two, specialized Office of Military Government, United States
The Office of Military Government, United States (OMGUS; ) was the United States military-established government created shortly after the end of hostilities in Allied-occupied Germany, occupied Germany in World War II. Under General Lucius D. Cla ...
(OMGUS) units took over. Soldiers requisitioned housing and office space as needed from residents. At first, this was done informally with occupants evicted immediately and taking with them few personal possessions, but the process became standardized, with three hours' notice and OMGUS personnel providing receipts for buildings' contents. The displaced residents nonetheless had to find housing on their own.
Operations
On 19 March, Eisenhower told Bradley to prepare the 1st Army for a breakout from the Remagen bridgehead any time after 22 March. The same day, in response to the 3rd Army's robust showing in the Saar-Palatinate region, and to have another strong force on the Rhine's east bank guarding the 1st Army's flank, Bradley gave Patton the go-ahead for an assault crossing of the Rhine as soon as possible.
These were exactly the orders Patton had hoped for; he felt that if a sufficiently strong force could be thrown across the river and significant gains made, then Eisenhower might transfer responsibility for the main drive through Germany from Montgomery's 21st Army Group to Bradley's 12th. Patton also appreciated the opportunity he now had to beat Montgomery across the river and win for the 3rd Army the coveted distinction of making the first assault crossing of the Rhine in modern history. To accomplish this, he had to move quickly.
On 21 March, Patton ordered his XII Corps to prepare for an assault over the Rhine on the following night, one day before Montgomery's scheduled crossing. While this was short notice, it did not catch the XII Corps completely unaware. As soon as Patton had received the orders on the 19th to make a crossing, he had begun sending assault boats, bridging equipment and other supplies forward from depots in Lorraine
Lorraine, also , ; ; Lorrain: ''Louréne''; Lorraine Franconian: ''Lottringe''; ; ; is a cultural and historical region in Eastern France, now located in the administrative region of Grand Est. Its name stems from the medieval kingdom of ...
where they had been stockpiled since autumn in the expectation of just such an opportunity. Seeing this equipment moving up, his frontline soldiers did not need any orders from higher headquarters to tell them what it meant.
The location of the river-crossing assault was critical. Patton knew that the most obvious place to jump the river was at Mainz or just downstream, north of the city. The choice was obvious because the Main River
The Main () is the longest tributary of the Rhine, one of the major European rivers. It rises as the White Main in the Fichtel Mountains of northeastern Bavaria and flows west through central Germany for to meet the Rhine below Rüsselsheim, ...
, flowing northward east of and parallel to the Rhine, turns west and empties into the Rhine at Mainz and an advance south of the city would involve crossing two rivers rather than one. However, Patton also realized that the Germans were aware of this difficulty and would expect his attack north of Mainz. Thus, he decided to feint at Mainz while making his real effort at Nierstein and Oppenheim, south of the city. Following this primary assault, which XII Corps would undertake, VIII Corps would execute supporting crossings at Boppard and St. Goar, northwest of Mainz.
The terrain in the vicinity of Nierstein and Oppenheim was conducive to artillery support, with high ground on the west bank overlooking relatively flat land to the east. However, the same flat east bank meant that the bridgehead would have to be rapidly and powerfully reinforced and expanded beyond the river since there was no high ground for a bridgehead defense. The importance of quickly obtaining a deep bridgehead was increased by the fact that the first access to a decent road network was over inland at the town of Groß-Gerau.
British 21st Army Group plans Operation Plunder
On the night of 23/24 March, after the XII Corps' assault of the Rhine, Bradley had announced his success. The 12th Army Group commander said that American troops could cross the Rhine anywhere, without aerial bombardment or airborne troops, a direct jab at Montgomery whose troops were at that very moment preparing to launch their own Rhine assault following an intense and elaborate aerial and artillery preparation and with the assistance of two airborne divisions, the American 17th and the British 6th. Montgomery was exhibiting his now-legendary meticulous and circumspect approach to such enterprises, a lesson he had learned early in the North African campaign
The North African campaign of World War II took place in North Africa from 10 June 1940 to 13 May 1943, fought between the Allies and the Axis Powers. It included campaigns in the Libyan and Egyptian deserts (Western Desert campaign, Desert Wa ...
. Thus, as his forces had approached the east bank of the river, Montgomery proceeded with one of the most intensive buildups of material and manpower of the war. His detailed plans, code-named Operation Plunder
Operation Plunder was a military operation to cross the Rhine on the night of 23 March 1945, launched by the 21st Army Group under Field Marshal Bernard Montgomery. The crossing of the river was at Rees, Wesel, and south of the river Lippe b ...
, were comparable to the Normandy invasion in terms of numbers of men and extent of equipment, supplies, and ammunition to be used. The 21st Army Group had 30 full-strength divisions, 11 each in the British Second and U.S. 9th Armies and eight in the Canadian First Army, providing Montgomery with more than 1,250,000 men.
Plunder called for the Second Army to cross at three locations along the 21st Army Group front—at Rees, Xanten
Xanten (, Low Rhenish: ''Santen'') is a town in the state of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is located in the district of Wesel.
Xanten is known for the Archaeological Park, one of the largest archaeological open air museums in the ...
and Rheinberg. The crossings would be preceded by several weeks of aerial bombing and final massive artillery preparation. A heavy bombing campaign by USAAF
The United States Army Air Forces (USAAF or AAF) was the major land-based aerial warfare service component of the United States Army and ''de facto'' aerial warfare service branch of the United States during and immediately after World War II ...
and RAF forces, known as the "Interdiction of Northwest Germany", designed primarily to destroy the lines of communication
A line of communication (or communications) is the route that connects an operating military unit with its supply base.
Supplies and reinforcements are transported along the line of communication. Therefore, a secure and open line of communicat ...
and supply connecting the Ruhr to the rest of Germany had been underway since February. The intention was to create a line from Bremen south to Neuwied. The main targets were rail yards, bridges, and communication centers, with a secondary focus on fuel processing and storage facilities and other important industrial sites. During the three days leading up to Montgomery's attack, targets in front of the 21st Army Group zone and in the Ruhr area to the southeast were pummeled by about 11,000 sorties, effectively sealing off the Ruhr while easing the burden on Montgomery's assault forces.
Montgomery had originally planned to attach one corps of the U.S. 9th Army to the British Second Army, which would use only two of the corps' divisions for the initial assault. The rest of the 9th Army would remain in reserve until the bridgehead was ready for exploitation. The 9th Army's commander, Lieutenant General William Hood Simpson and the Second Army's Lieutenant-General Dempsey took exception to this approach. Both believed that the plan squandered the great strength in men and equipment that the 9th Army had assembled and ignored the many logistical problems of placing the 9th Army's crossing sites within the Second Army's zone.
Montgomery responded to these concerns by making a few small adjustments to the plan. Although he declined to increase the size of the American crossing force beyond two divisions, he agreed to keep it under the 9th Army rather than Second Army control. To increase Simpson's ability to bring his army's strength to bear for exploitation, Montgomery also agreed to turn the bridges at Wesel
Wesel () is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, in western Germany. It is the capital of the Wesel (district), Wesel district.
Geography
Wesel is situated at the confluence of the Lippe River and the Rhine.
Division of the city
Suburbs of Wesel i ...
, just north of the inter-army boundary, over to the 9th Army once the bridgehead had been secured.
In the southernmost sector of the 21st Army Group's attack, the 9th Army's assault divisions were to cross the Rhine along an section of the front, south of Wesel and the Lippe River
The Lippe () is a river in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is a right tributary of the Rhine and in length with an elevation difference of 125 metres and a catchment area of 4.890 km².
The source is located at the edge of the Teutoburg ...
. This force would block any German counterattack from the Ruhr. Because of the poor road network on the east bank of this part of the Rhine, a second 9th Army corps was to cross over the promised Wesel bridges through the British zone north of the Lippe River, which had an abundance of good roads. After driving east nearly , this corps was to meet elements of the 1st Army near Paderborn
Paderborn (; Westphalian language, Westphalian: ''Patterbuorn'', also ''Paterboärn'') is a city in eastern North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, capital of the Paderborn (district), Paderborn district. The name of the city derives from the river Pade ...
, completing the encirclement of the Ruhr.
Another important aspect of Montgomery's plan was Operation Varsity, in which two divisions of Major General Matthew Ridgway
Matthew Bunker Ridgway (3 March 1895 – 26 July 1993) was a senior officer in the United States Army, who served as Supreme Allied Commander Europe (1952–1953) and the 19th Chief of Staff of the United States Army (1953–1955). Although he ...
's XVIII Airborne Corps
The XVIII Airborne Corps is a corps of the United States Army that has been in existence since 1942 and saw extensive service during World War II. The corps is designed for Rapid deployment force, rapid deployment anywhere in the world and is r ...
were to make an airborne assault over the Rhine. In a departure from standard airborne doctrine, which called for a jump deep behind enemy lines several hours prior to an amphibious assault, Varsity's drop zones were close behind the German front, within Allied artillery range. Additionally, to avoid being caught in the artillery preparation, the paratroopers would jump only after the amphibious troops had reached the Rhine's east bank. The wisdom of putting lightly armed paratroopers so close to the main battlefield was debated, and the plan for amphibious forces to cross the Rhine prior to the parachute drop raised questions as to the utility of making an airborne assault at all. However, Montgomery believed that the paratroopers would quickly link up with the advancing river assault forces, placing the strongest force within the bridgehead as rapidly as possible. Once the bridgehead was secured the British 6th Airborne Division would be transferred to Second Army control, while the U.S. 17th Airborne Division would revert to 9th Army control.
U.S. 12th Army Group crosses the Rhine (22 March)
 On 22 March, with a bright moon lighting the late-night sky, elements of U.S. XII Corps' 5th Infantry Division began the 3rd Army's Rhine crossing. At Nierstein assault troops did not meet any resistance. As the first boats reached the east bank, seven startled Germans surrendered and then paddled themselves unescorted to the west bank to be placed in custody. Upstream at Oppenheim, however, the effort did not proceed so casually. The first wave of boats was halfway across when the Germans began pouring machine-gun fire into their midst. An intense exchange of fire lasted for about thirty minutes as assault boats kept pushing across the river and those men who had already made it across mounted attacks against the scattered defensive strongpoints. Finally, the Germans surrendered, and by midnight units moved out laterally to consolidate the crossing sites and to attack the first villages beyond the river. German resistance everywhere was sporadic, and the hastily mounted counterattacks invariably burned out quickly, causing few casualties. The Germans lacked both the manpower and the heavy equipment to make a more determined defense.
By midafternoon on 23 March, all three regiments of the 5th Infantry Division were in the bridgehead, and an attached regiment from the
On 22 March, with a bright moon lighting the late-night sky, elements of U.S. XII Corps' 5th Infantry Division began the 3rd Army's Rhine crossing. At Nierstein assault troops did not meet any resistance. As the first boats reached the east bank, seven startled Germans surrendered and then paddled themselves unescorted to the west bank to be placed in custody. Upstream at Oppenheim, however, the effort did not proceed so casually. The first wave of boats was halfway across when the Germans began pouring machine-gun fire into their midst. An intense exchange of fire lasted for about thirty minutes as assault boats kept pushing across the river and those men who had already made it across mounted attacks against the scattered defensive strongpoints. Finally, the Germans surrendered, and by midnight units moved out laterally to consolidate the crossing sites and to attack the first villages beyond the river. German resistance everywhere was sporadic, and the hastily mounted counterattacks invariably burned out quickly, causing few casualties. The Germans lacked both the manpower and the heavy equipment to make a more determined defense.
By midafternoon on 23 March, all three regiments of the 5th Infantry Division were in the bridgehead, and an attached regiment from the 90th Infantry Division 90th Division may refer to:
;Infantry
* 90th Division (1st Formation) (People's Republic of China), 1949–1950
* 90th Division (2nd Formation) (People's Republic of China), 1950–1952
* 90th Light Infantry Division (Wehrmacht)
* 90th Infantry Di ...
was crossing. Tanks and tank destroyers had been ferried across all morning, and by evening a Treadway bridge was open to traffic. By midnight, infantry units had pushed the boundary of the bridgehead more than inland, ensuring the unqualified success of the first modern assault crossing of the Rhine.
Two more 3rd Army crossings—both by VIII Corps—quickly followed. In the early morning hours of 25 March, elements of the 87th Infantry Division crossed the Rhine to the north at Boppard, and then some 24 hours later elements of the 89th Infantry Division crossed south of Boppard at St. Goar. Although the defense of these sites was somewhat more determined than that XII Corps had faced, the difficulties of the Boppard and St. Goar crossings were compounded more by terrain than by German resistance. VIII Corps crossing sites were located along the Rhine Gorge, where the river had carved a deep chasm between two mountain ranges, creating precipitous canyon walls over high on both sides. In addition, the river flowed quickly and with unpredictable currents along this part of its course. Still, despite the terrain and German machine-gun and anti-aircraft
Anti-aircraft warfare (AAW) is the counter to aerial warfare and includes "all measures designed to nullify or reduce the effectiveness of hostile air action".AAP-6 It encompasses surface-based, subsurface ( submarine-launched), and air-ba ...
cannon
A cannon is a large-caliber gun classified as a type of artillery, which usually launches a projectile using explosive chemical propellant. Gunpowder ("black powder") was the primary propellant before the invention of smokeless powder during th ...
fire, VIII Corps troops managed to gain control of the east bank's heights, and by dark on 26 March, with German resistance crumbling all along the Rhine, they were preparing to continue the drive the next morning.
Operation Plunder (23 March)
 Plunder began on the evening of 23 March with the assault elements of the British 2nd Army massed against three main crossing sites: Rees in the north, Xanten in the center, and Wesel in the south. The two 9th Army divisions tasked for the assault concentrated in the Rheinberg area south of Wesel. At the northern crossing site, elements of British XXX Corps began the assault (Operation Turnscrew) about 21:00, attempting to distract the Germans from the main crossings at Xanten in the center and Rheinberg to the south. The initial assault waves crossed the river quickly, meeting only light opposition. Meanwhile, Operation Widgeon began north of Wesel as the 2nd Army's 1st Commando Brigade slipped across the river and waited within of the city while it was demolished by one thousand tons of bombs delivered by
Plunder began on the evening of 23 March with the assault elements of the British 2nd Army massed against three main crossing sites: Rees in the north, Xanten in the center, and Wesel in the south. The two 9th Army divisions tasked for the assault concentrated in the Rheinberg area south of Wesel. At the northern crossing site, elements of British XXX Corps began the assault (Operation Turnscrew) about 21:00, attempting to distract the Germans from the main crossings at Xanten in the center and Rheinberg to the south. The initial assault waves crossed the river quickly, meeting only light opposition. Meanwhile, Operation Widgeon began north of Wesel as the 2nd Army's 1st Commando Brigade slipped across the river and waited within of the city while it was demolished by one thousand tons of bombs delivered by RAF Bomber Command
RAF Bomber Command controlled the Royal Air Force's bomber forces from 1936 to 1968. Along with the United States Army Air Forces, it played the central role in the Strategic bombing during World War II#Europe, strategic bombing of Germany in W ...
. Entering in the night, the commandos secured the city late on the morning of 24 March, although scattered resistance continued until dawn on the 25th. The 2nd Army's XII Corps and the 9th Army's XVI Corps began the main effort about 02:00 on 24 March, following a massive artillery and air bombardment.
For the American crossing, Simpson had chosen the veteran 30th and 79th Infantry Divisions of the XVI Corps. The 30th was to cross between Wesel and Rheinberg while the 79th assaulted south of Rheinberg. In reserve were the XVI Corps' 8th Armored Division, and 35th and 75th Infantry Divisions, as well as the 9th Army's XIII and XIX Corps, each with three divisions. Simpson planned to commit the XIX Corps as soon as possible after the bridgehead had been secured, using the XIII Corps to hold the Rhine south of the crossing sites.
After an hour of extremely intense artillery preparation, which Eisenhower himself viewed from the front, the 30th Infantry Division began its assault. The artillery fire had been so effective and so perfectly timed that the assault battalions merely motored their storm boats across the river and claimed the east bank against almost no resistance. As subsequent waves of troops crossed, units fanned out to take the first villages beyond the river to only the weakest of opposition. An hour later, at 03:00, the 79th Infantry Division began its crossing upriver, achieving much the same results. As heavier equipment was ferried across the Rhine, both divisions began pushing east, penetrating into the German defensive line that day.
To the north, the British crossings had also gone well, with the ground and airborne troops linking up by nightfall. By then, the paratroopers had taken all their first day's objectives in addition to 3,500 prisoners.
 To the south, the discovery of a defensive gap in front of the 30th Infantry Division fostered the hope that a full-scale breakout would be possible on 25 March. When limited objective attacks provoked little response on the morning of the 25th, the division commander Major General Leland Hobbs formed two mobile task forces to make deeper thrusts with an eye toward punching through the defense altogether and breaking deep into the German rear. However, Hobbs had not fully taken into account the nearly nonexistent road network in front of the XVI Corps bridgehead. Faced with trying to make rapid advances through dense forest on rutted dirt roads and muddy trails, which could be strongly defended by a few determined soldiers and well-placed roadblocks, the task forces advanced only about on the 25th. The next day they gained some more ground, and one even seized its objective, having slogged a total of , but the limited progress forced Hobbs to abandon the hope for a quick breakout.
In addition to the poor roads, the 30th Division's breakout attempts were also hampered by the German 116th Panzer Division. The only potent unit left for commitment against the Allied Rhine crossings in the north, the 116th began moving south from the Dutch-German border on 25 March against what the Germans considered their most dangerous threat, the U.S. 9th Army. The enemy armored unit began making its presence felt almost immediately, and by the end of 26 March, the combination of the ''panzer'' division and the rough terrain had conspired to sharply limit the 30th Division's forward progress. With the 79th Infantry Division meeting fierce resistance to the south, Simpson's only recourse was to commit some of his forces waiting on the west bank of the Rhine. Late on 26 March, the 8th Armored Division began moving into the bridgehead.
Although the armored division bolstered his offensive capacity within the bridgehead, Simpson was more interested in sending the XIX Corps across the Wesel bridges, as Montgomery had agreed, and using the better roads north of the Lippe to outflank the enemy in front of the 30th Division. Unfortunately, because of pressure from the Germans in the northern part of the 2nd Army bridgehead, the British were having trouble completing their bridges at Xanten and were, therefore, bringing most of their traffic across the river at Wesel. With Montgomery allowing use of the Wesel bridges to the 9th Army for only five out of every 24 hours, and with the road network north of the Lippe under 2nd Army control, General Simpson was unable to commit or maneuver sufficient forces to make a rapid flanking drive.
To the south, the discovery of a defensive gap in front of the 30th Infantry Division fostered the hope that a full-scale breakout would be possible on 25 March. When limited objective attacks provoked little response on the morning of the 25th, the division commander Major General Leland Hobbs formed two mobile task forces to make deeper thrusts with an eye toward punching through the defense altogether and breaking deep into the German rear. However, Hobbs had not fully taken into account the nearly nonexistent road network in front of the XVI Corps bridgehead. Faced with trying to make rapid advances through dense forest on rutted dirt roads and muddy trails, which could be strongly defended by a few determined soldiers and well-placed roadblocks, the task forces advanced only about on the 25th. The next day they gained some more ground, and one even seized its objective, having slogged a total of , but the limited progress forced Hobbs to abandon the hope for a quick breakout.
In addition to the poor roads, the 30th Division's breakout attempts were also hampered by the German 116th Panzer Division. The only potent unit left for commitment against the Allied Rhine crossings in the north, the 116th began moving south from the Dutch-German border on 25 March against what the Germans considered their most dangerous threat, the U.S. 9th Army. The enemy armored unit began making its presence felt almost immediately, and by the end of 26 March, the combination of the ''panzer'' division and the rough terrain had conspired to sharply limit the 30th Division's forward progress. With the 79th Infantry Division meeting fierce resistance to the south, Simpson's only recourse was to commit some of his forces waiting on the west bank of the Rhine. Late on 26 March, the 8th Armored Division began moving into the bridgehead.
Although the armored division bolstered his offensive capacity within the bridgehead, Simpson was more interested in sending the XIX Corps across the Wesel bridges, as Montgomery had agreed, and using the better roads north of the Lippe to outflank the enemy in front of the 30th Division. Unfortunately, because of pressure from the Germans in the northern part of the 2nd Army bridgehead, the British were having trouble completing their bridges at Xanten and were, therefore, bringing most of their traffic across the river at Wesel. With Montgomery allowing use of the Wesel bridges to the 9th Army for only five out of every 24 hours, and with the road network north of the Lippe under 2nd Army control, General Simpson was unable to commit or maneuver sufficient forces to make a rapid flanking drive.
U.S. 6th Army Group crosses the Rhine (26 March)
Adding to the Germans' woes, the 6th Army Group made an assault across the Rhine on 26 March. At Worms
The World Register of Marine Species (WoRMS) is a taxonomic database that aims to provide an authoritative and comprehensive catalogue and list of names of marine organisms.
Content
The content of the registry is edited and maintained by scien ...
, about south of Mainz, the 7th Army's XV Corps established a bridgehead, which it consolidated with the southern shoulder of the 3rd Army's bridgehead early the next day. After overcoming stiff initial resistance, XV Corps also advanced beyond the Rhine, opposed primarily by small German strongpoints sited in roadside villages.
German Army Group B surrounded in the Ruhr pocket (1 April)
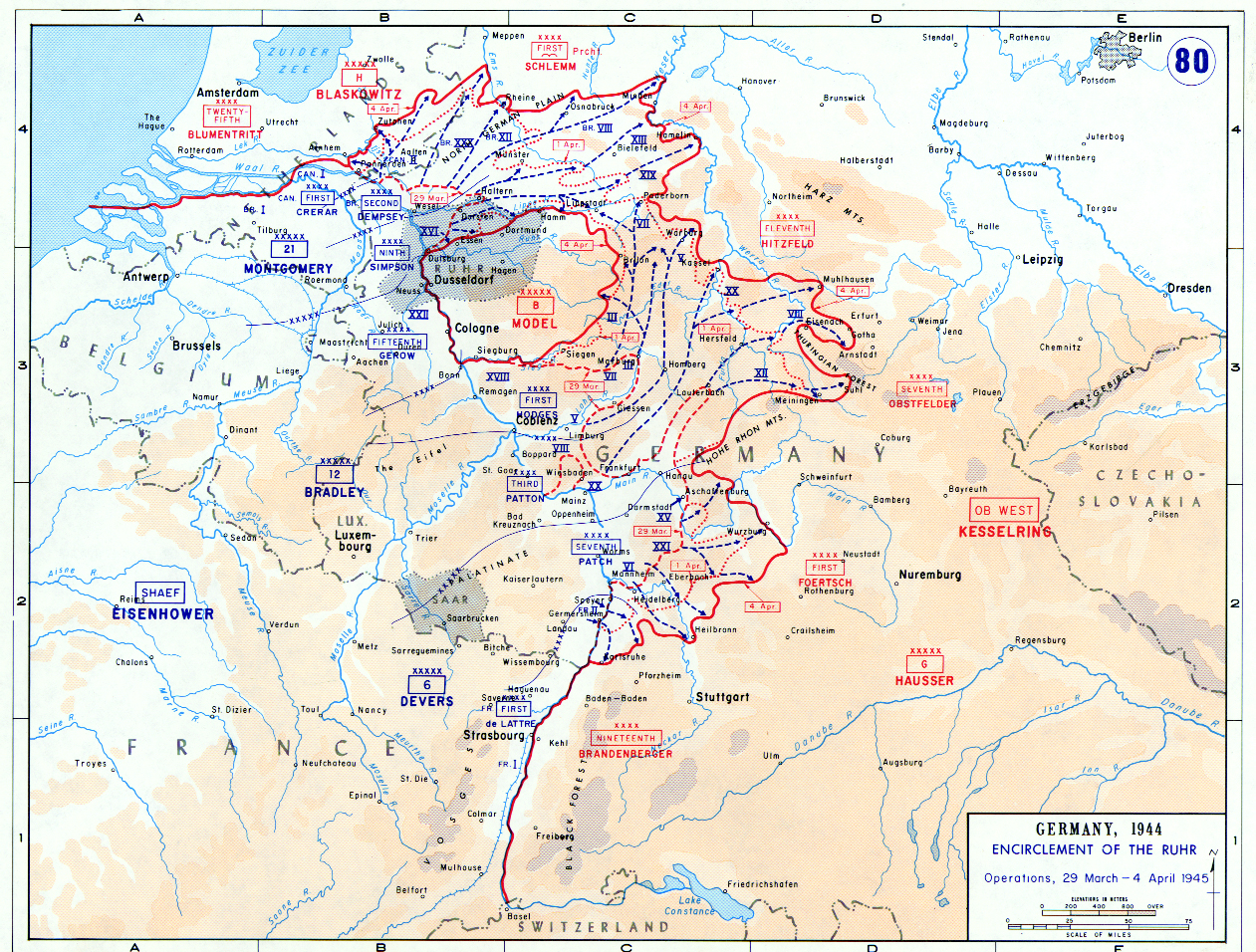 By 28 March, the 8th Armored Division had expanded the bridgehead by only about and still had not reached
By 28 March, the 8th Armored Division had expanded the bridgehead by only about and still had not reached Dorsten
Dorsten (; Westphalian: ''Dössen'') is a town in the district of Recklinghausen in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany and has a population of about 75,000.
Dorsten is situated on the western rim of Westphalia bordering the Rhineland. Its histori ...
, a town about east of the Rhine, whose road junction promised to expand the XVI Corps' offensive options. On the same day, however, Montgomery announced that the eastbound roads out of Wesel would be turned over to the 9th Army on 30 March with the Rhine bridges leading into that city changing hands a day later. Also on 28 March, elements of the U.S. 17th Airborne Division operating north of the Lippe River in conjunction with British armored forces—dashed to a point some east of Wesel, opening a corridor for the XIX Corps and handily outflanking Dorsten and the enemy to the south. Simpson now had both the opportunity and the means to unleash the power of the 9th Army and begin in earnest the northern drive to surround the Ruhr.
Simpson began by moving elements of the XIX Corps' 2nd Armored Division into the XVI Corps bridgehead on 28 March with orders to cross the Lippe east of Wesel, thereby avoiding that city's traffic jams. After passing north of the Lippe on 29 March, the 2nd Armored Division broke out late that night from the forward position that the XVIII Airborne Corps had established around Haltern
Haltern am See (''Haltern at the lake'', before December 2001 only Haltern) is a medium-sized town in the northern part of the district of Recklinghausen in the ''Regierungsbezirk'' Münster in North Rhine-Westphalia. The town is located in the n ...
, northeast of Dorsten. On the 30th and 31st, the 2nd Armored made an uninterrupted drive east to Beckum, cutting two of the Ruhr's three remaining rail lines and severing the autobahn
The (; German , ) is the federal controlled-access highway system in Germany. The official term is (abbreviated ''BAB''), which translates as 'federal motorway'. The literal meaning of the word is 'Federal Auto(mobile) Track'.
Much of t ...
to Berlin. As the rest of the XIX Corps flowed into the wake of this spectacular drive, the 1st Army was completing its equally remarkable thrust around the southern and eastern edges of the Ruhr.
The 1st Army's drive from the Remagen bridgehead began with a breakout before dawn on 25 March. German Field Marshal Walter Model, whose ''Army Group B'' was charged with the defense of the Ruhr, had deployed his troops heavily along the east–west Sieg River south of Cologne
Cologne ( ; ; ) is the largest city of the States of Germany, German state of North Rhine-Westphalia and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with nearly 1.1 million inhabitants in the city pr ...
, thinking that the Americans would attack directly north from the Remagen bridgehead. Instead, the 1st Army struck eastward, heading for Giessen
Giessen, spelled in German (), is a town in the Germany, German States of Germany, state () of Hesse, capital of both the Giessen (district), district of Giessen and the Giessen (region), administrative region of Giessen. The population is appro ...
and the Lahn River, beyond Remagen, before turning north toward Paderborn and linking up with the 9th Army. All three corps of the 1st Army participated in the breakout, which on the first day employed five infantry and two armored divisions. The U.S. VII Corps, on the left, had the hardest going due to the German concentration north of the bridgehead, yet its armored columns managed to advance beyond their line of departure. The U.S. III Corps, in the center, did not commit its armor on the first day of the breakout, but still made a gain of . The U.S. V Corps on the right advanced , incurring minimal casualties.
Beginning the next day, 26 March, the armored divisions of all three corps turned these initial gains into a complete breakout, shattering all opposition and roaming at will throughout the enemy's rear areas. By the end of 28 March, Hodges' 1st Army had crossed the Lahn, having driven at least beyond the original line of departure, capturing thousands of German soldiers in the process. Nowhere, it seemed, were the Germans able to resist in strength. On 29 March, the 1st Army turned toward Paderborn, about north of Giessen, its right flank covered by the 3rd Army, which had broken out of its own bridgeheads and was headed northeast toward Kassel
Kassel (; in Germany, spelled Cassel until 1926) is a city on the Fulda River in North Hesse, northern Hesse, in Central Germany (geography), central Germany. It is the administrative seat of the Regierungsbezirk Kassel (region), Kassel and the d ...
.
A task force of the VII Corps' 3rd Armored Division, which included some of the new M26 Pershing heavy tanks, spearheaded the drive for Paderborn on 29 March. By attaching an infantry regiment of the 104th Infantry Division to the armored division and following the drive closely with the rest of the 104th Division, the VII Corps was well prepared to hold any territory gained. Rolling northward without casualties, the mobile force stopped for the night from its objective. Taking up the advance again the next day, it immediately ran into stiff opposition from students of an SS ''panzer'' replacement training center located near Paderborn. Equipped with about 60 tanks, the students put up a fanatical resistance, stalling the American armor all day. When the task force failed to advance on 31 March, Maj. Gen. J. Lawton Collins, commander of the VII Corps, asked Simpson if his 9th Army, driving eastward north of the Ruhr, could provide assistance. Simpson, in turn, ordered a combat command of the 2nd Armored Division, which had just reached Beckum, to make a advance southeast to Lippstadt
Lippstadt () is a town in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is the largest town within the district of Soest. Lippstadt is situated about 60 kilometres east of Dortmund, 40 kilometres south of Bielefeld and 30 kilometres west of Paderborn.
Geo ...
, midway between Beckum and the stalled 3rd Armored Division spearhead. Early in the afternoon of 1 April elements of the 2nd and 3rd Armored Divisions met at Lippstadt, linking the 9th and 1st Armies and sealing the prized Ruhr industrial complex, along with Model's ''Army Group B'', within American lines.
As March turned to April the offensive east of the Rhine was progressing in close accordance with Allied plans. All the armies assigned to cross the Rhine had elements east of the river, including the Canadian 1st Army in the north, which sent a division through the British bridgehead at Rees, and the French 1st Army in the south, which on 31 March established its own bridgehead by assault crossings at Germersheim
Germersheim () is a town in the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate, of around 20,000 inhabitants. It is also the seat of the Germersheim (district), Germersheim district. The neighboring towns and cities are Speyer, Landau, Philippsburg, Karlsru ...
and Speyer
Speyer (, older spelling ; ; ), historically known in English as Spires, is a city in Rhineland-Palatinate in the western part of the Germany, Federal Republic of Germany with approximately 50,000 inhabitants. Located on the left bank of the r ...
, about south of Mainz. With spectacular thrusts being made beyond the Rhine nearly every day and the enemy's capacity to resist fading at an ever-accelerating rate, the campaign to finish Germany was transitioning into a general pursuit.
In the center of the Allied line, Eisenhower inserted the new 15th Army, under U.S. 12th Army Group control to hold the western edge of the Ruhr Pocket along the Rhine while the 9th and 1st Armies squeezed the remaining German defenders there from the north, east, and south. Following the reduction of the Ruhr, the 15th Army was to take over occupation duties in the region as the 9th, 1st and 3rd Armies pushed farther into Germany.
Eisenhower switches his main thrust to U.S. 12th Army Group front (28 March)
On 28 March, as these developments unfolded, Eisenhower announced his decision to adjust his plans governing the future course of the offensive. Once the Ruhr was surrounded, he wanted the 9th Army transferred from the British 21st Army Group to the U.S. 12th Army Group. After the reduction of the Ruhr Pocket, the main thrust east would be made by Bradley's 12th Army Group in the center, rather than by Montgomery's 21st Army Group in the north as originally planned. Montgomery's forces were to secure Bradley's northern flank while Devers' 6th U.S. Army Group covered Bradley's southern shoulder. Furthermore, the main objective was no longer Berlin, but Leipzig
Leipzig (, ; ; Upper Saxon: ; ) is the most populous city in the States of Germany, German state of Saxony. The city has a population of 628,718 inhabitants as of 2023. It is the List of cities in Germany by population, eighth-largest city in Ge ...
where a juncture with the Soviet Army would split the remaining German forces in two. Once this was done, the 21st Army Group would take Lübeck
Lübeck (; or ; Latin: ), officially the Hanseatic League, Hanseatic City of Lübeck (), is a city in Northern Germany. With around 220,000 inhabitants, it is the second-largest city on the German Baltic Sea, Baltic coast and the second-larg ...
and Wismar
Wismar (; ), officially the Hanseatic City of Wismar () is, with around 43,000 inhabitants, the sixth-largest city of the northeastern German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, and the fourth-largest city of Mecklenburg after Rostock, Schwerin and ...
on the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the ...
, cutting off the Germans remaining in the Jutland
Jutland (; , ''Jyske Halvø'' or ''Cimbriske Halvø''; , ''Kimbrische Halbinsel'' or ''Jütische Halbinsel'') is a peninsula of Northern Europe that forms the continental portion of Denmark and part of northern Germany (Schleswig-Holstein). It ...
peninsula of Denmark
Denmark is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe. It is the metropole and most populous constituent of the Kingdom of Denmark,, . also known as the Danish Realm, a constitutionally unitary state that includes the Autonomous a ...
, while the 6th U.S. Army Group and the 3rd Army drove south into Austria.
The British Prime Minister and Chiefs of Staff strongly opposed the new plan. Despite the Russian proximity to Berlin, they argued that the city was still a critical political, if not military, objective. Eisenhower, supported by the American Chiefs of Staff, disagreed. His overriding objective was the swiftest military victory possible. Should the U.S. political leadership direct him to take Berlin, or if a situation arose in which it became militarily advisable to seize the German capital, Eisenhower would do so. Otherwise, he would pursue those objectives that would end the war soonest. In addition, since Berlin and the rest of Germany had already been divided into occupation zones by representatives of the Allied governments at the Yalta Conference
The Yalta Conference (), held 4–11 February 1945, was the World War II meeting of the heads of government of the United States, the United Kingdom, and the Soviet Union to discuss the postwar reorganization of Germany and Europe. The three sta ...
, Eisenhower saw no political advantage in a race for Berlin. Any ground the Western Allies gained in the future Soviet zone would merely be relinquished to the Soviets after the war. In the end, the campaign proceeded as Eisenhower had planned it.
Ruhr pocket cleared (18 April)
 The first step in realizing Eisenhower's plan was the eradication of the Ruhr Pocket. Even before the encirclement had been completed, the Germans in the Ruhr had begun making attempts at a breakout to the east. All had been unceremoniously repulsed by the vastly superior Allied forces. Meanwhile, the 9th and 1st Armies began preparing converging attacks using the east-west Ruhr River as a boundary line. The 9th Army's XVI Corps, which had taken up position north of the Ruhr area after crossing the Rhine, would be assisted in its southward drive by two divisions of the XIX Corps, the rest of which would continue to press eastward along with the XIII Corps. South of the Ruhr River, the 1st Army's northward attack was to be executed by the XVIII Airborne Corps, which had been transferred to Hodges after Operation Varsity, and the III Corps, with the 1st Army's V and VII Corps continuing the offensive east. The 9th Army's sector of the Ruhr Pocket, although only about 1/3 the size of the 1st Army's sector south of the river, contained the majority of the densely urbanized industrial area within the encirclement. The 1st Army's area, on the other hand, was composed of rough, heavily forested terrain with a poor road network.
By 1 April, when the trap closed around the Germans in the Ruhr, their fate was sealed. In a matter of days, they would all be killed or captured. On 4 April, the day it shifted to Bradley's control, the 9th Army began its attack south toward the Ruhr River. In the south, the 1st Army's III Corps launched its strike on the 5th and the XVIII Airborne Corps joined in on the 6th, both pushing generally northward. German resistance, initially rather determined, dwindled rapidly. By 13 April, the 9th Army had cleared the northern part of the pocket, while elements of the XVIII Airborne Corps' 8th Infantry Division reached the southern bank of the Ruhr, splitting the southern section of the pocket in two. Thousands of prisoners were being taken every day; from 16 to 18 April, when all opposition ended and the remnants of German ''Army Group B'' formally surrendered, German troops had been surrendering in droves throughout the region. Army Group B commander Model committed suicide on 21 April.
The final tally of prisoners taken in the Ruhr reached 325,000, far beyond anything the Americans had anticipated. Tactical commanders hastily enclosed huge open fields with barbed wire creating makeshift prisoner of war camps, where the inmates awaited the end of the war and their chance to return home. Also looking forward to going home, tens of thousands of freed forced laborers and Allied prisoners of war further strained the American logistical system.
The first step in realizing Eisenhower's plan was the eradication of the Ruhr Pocket. Even before the encirclement had been completed, the Germans in the Ruhr had begun making attempts at a breakout to the east. All had been unceremoniously repulsed by the vastly superior Allied forces. Meanwhile, the 9th and 1st Armies began preparing converging attacks using the east-west Ruhr River as a boundary line. The 9th Army's XVI Corps, which had taken up position north of the Ruhr area after crossing the Rhine, would be assisted in its southward drive by two divisions of the XIX Corps, the rest of which would continue to press eastward along with the XIII Corps. South of the Ruhr River, the 1st Army's northward attack was to be executed by the XVIII Airborne Corps, which had been transferred to Hodges after Operation Varsity, and the III Corps, with the 1st Army's V and VII Corps continuing the offensive east. The 9th Army's sector of the Ruhr Pocket, although only about 1/3 the size of the 1st Army's sector south of the river, contained the majority of the densely urbanized industrial area within the encirclement. The 1st Army's area, on the other hand, was composed of rough, heavily forested terrain with a poor road network.
By 1 April, when the trap closed around the Germans in the Ruhr, their fate was sealed. In a matter of days, they would all be killed or captured. On 4 April, the day it shifted to Bradley's control, the 9th Army began its attack south toward the Ruhr River. In the south, the 1st Army's III Corps launched its strike on the 5th and the XVIII Airborne Corps joined in on the 6th, both pushing generally northward. German resistance, initially rather determined, dwindled rapidly. By 13 April, the 9th Army had cleared the northern part of the pocket, while elements of the XVIII Airborne Corps' 8th Infantry Division reached the southern bank of the Ruhr, splitting the southern section of the pocket in two. Thousands of prisoners were being taken every day; from 16 to 18 April, when all opposition ended and the remnants of German ''Army Group B'' formally surrendered, German troops had been surrendering in droves throughout the region. Army Group B commander Model committed suicide on 21 April.
The final tally of prisoners taken in the Ruhr reached 325,000, far beyond anything the Americans had anticipated. Tactical commanders hastily enclosed huge open fields with barbed wire creating makeshift prisoner of war camps, where the inmates awaited the end of the war and their chance to return home. Also looking forward to going home, tens of thousands of freed forced laborers and Allied prisoners of war further strained the American logistical system.
U.S. 12th Army Group prepares its final thrust
Meanwhile, the remaining Allied forces north, south, and east of the Ruhr had been adjusting their lines in preparation for the final advance through Germany. Under the new concept, Bradley's 12th U.S. Army Group would make the main effort, with Hodges' 1st Army in the center heading east for about toward the city of Leipzig and the Elbe River. To the north, the 9th Army's XIX and XIII Corps would also drive for the Elbe, toward Magdeburg
Magdeburg (; ) is the Capital city, capital of the Germany, German States of Germany, state Saxony-Anhalt. The city is on the Elbe river.
Otto I, Holy Roman Emperor, Otto I, the first Holy Roman Emperor and founder of the Archbishopric of Mag ...
, about north of Leipzig, although the army commander, General Simpson, hoped he would be allowed to go all the way to Berlin. To the south, Patton's 3rd Army was to drive east to Chemnitz
Chemnitz (; from 1953 to 1990: Karl-Marx-Stadt (); ; ) is the third-largest city in the Germany, German States of Germany, state of Saxony after Leipzig and Dresden, and the fourth-largest city in the area of former East Germany after (East Be ...
, about southeast of Leipzig, but well short of the Elbe, and then turn southeast into Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
. At the same time, General Devers' 6th U.S. Army Group would move south through Bavaria
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a States of Germany, state in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the list of German states by area, largest German state by land area, comprising approximately 1/5 of the total l ...
and the Black Forest
The Black Forest ( ) is a large forested mountain range in the States of Germany, state of Baden-Württemberg in southwest Germany, bounded by the Rhine Valley to the west and south and close to the borders with France and Switzerland. It is th ...
to Austria and the Alps
The Alps () are some of the highest and most extensive mountain ranges in Europe, stretching approximately across eight Alpine countries (from west to east): Monaco, France, Switzerland, Italy, Liechtenstein, Germany, Austria and Slovenia.
...
, ending the threat of any Nazi last-ditch stand there.
On 4 April, as it paused to allow the rest of the 12th U.S. Army Group to catch up, the 3rd Army made two notable discoveries. Near the town of Merkers, elements of the 90th Infantry Division found a sealed salt mine containing a large portion of the German national treasure. The hoard included vast quantities of German paper currency, stacks of priceless paintings, piles of looted gold and silver jewelry and household objects, and an estimated $250,000,000 worth of gold bars and coins of various nations. But the other discovery made by the 3rd Army on 4 April horrified and angered those who saw it. When the 4th Armored Division and elements of the 89th Infantry Division captured the small town of Ohrdruf, a few miles south of Gotha
Gotha () is the fifth-largest city in Thuringia, Germany, west of Erfurt and east of Eisenach with a population of 44,000. The city is the capital of the district of Gotha and was also a residence of the Ernestine Wettins from 1640 until the ...
, they found the first concentration camp taken by the Western Allies.
U.S. 12th Army Group advances to the Elbe (9 April)
The 4 April pause in the 3rd Army advance allowed the other armies under Bradley's command to reach the Leine
The Leine (; Old Saxon ''Lagina'') is a river in Thuringia and Lower Saxony, Germany. It is a left tributary of the Aller and the Weser and is long.
The river's source is located close to the town of Leinefelde in Thuringia. About downriver ...
River, about east of Paderborn. Thus all three armies of the 12th U.S. Army Group were in a fairly even north–south line, enabling them to advance abreast of each other to the Elbe. By 9 April, both the 9th and 1st Armies had seized bridgeheads over the Leine, prompting Bradley to order an unrestricted eastward advance. On the morning of 10 April, the 12th U.S. Army Group's drive to the Elbe began in earnest.
 The Elbe River was the official eastward objective, but many American commanders still eyed Berlin. By the evening of 11 April, elements of the 9th Army's 2nd Armored Division—seemingly intent on demonstrating how easily their army could take that coveted prize—had dashed to reach the Elbe southeast of Magdeburg, just short of the German capital. On 12 April, additional 9th Army elements attained the Elbe and by the next day were on the opposite bank hopefully awaiting permission to drive on to Berlin. But two days later, on 15 April, they had to abandon these hopes. Eisenhower sent Bradley his final word on the matter: the 9th Army was to stay put—there would be no effort to take Berlin. Simpson subsequently turned his troops' attention to mopping up pockets of local resistance.
In the center of the 12th U.S. Army Group, Hodges' 1st Army faced somewhat stiffer opposition, though it hardly slowed the pace. As its forces approached Leipzig, about south of Magdeburg and short of the Mulde River, the 1st Army ran into one of the few remaining centers of organized resistance. Here the Germans turned a thick defense belt of antiaircraft guns against the American ground troops with devastating effects. Through a combination of flanking movements and night attacks, First Army troops were able to destroy or bypass the guns, moving finally into Leipzig, which formally surrendered on the morning of 20 April. By the end of the day, the units that had taken Leipzig joined the rest of the 1st Army on the
The Elbe River was the official eastward objective, but many American commanders still eyed Berlin. By the evening of 11 April, elements of the 9th Army's 2nd Armored Division—seemingly intent on demonstrating how easily their army could take that coveted prize—had dashed to reach the Elbe southeast of Magdeburg, just short of the German capital. On 12 April, additional 9th Army elements attained the Elbe and by the next day were on the opposite bank hopefully awaiting permission to drive on to Berlin. But two days later, on 15 April, they had to abandon these hopes. Eisenhower sent Bradley his final word on the matter: the 9th Army was to stay put—there would be no effort to take Berlin. Simpson subsequently turned his troops' attention to mopping up pockets of local resistance.
In the center of the 12th U.S. Army Group, Hodges' 1st Army faced somewhat stiffer opposition, though it hardly slowed the pace. As its forces approached Leipzig, about south of Magdeburg and short of the Mulde River, the 1st Army ran into one of the few remaining centers of organized resistance. Here the Germans turned a thick defense belt of antiaircraft guns against the American ground troops with devastating effects. Through a combination of flanking movements and night attacks, First Army troops were able to destroy or bypass the guns, moving finally into Leipzig, which formally surrendered on the morning of 20 April. By the end of the day, the units that had taken Leipzig joined the rest of the 1st Army on the Mulde
The Mulde () is a river in Saxony and Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. It is a left tributary of the Elbe and is long.
The river is formed by the confluence, near Colditz, of the Zwickauer Mulde (running through Zwickau) and the Freiberger Mulde (wit ...
, where it had been ordered to halt.
Meanwhile, on the 12th U.S. Army Group's southern flank, the 3rd Army had advanced apace, moving eastward to take Erfurt
Erfurt () is the capital (political), capital and largest city of the Central Germany (cultural area), Central German state of Thuringia, with a population of around 216,000. It lies in the wide valley of the Gera (river), River Gera, in the so ...
and Weimar
Weimar is a city in the state (Germany), German state of Thuringia, in Central Germany (cultural area), Central Germany between Erfurt to the west and Jena to the east, southwest of Leipzig, north of Nuremberg and west of Dresden. Together w ...
, and then, by 12 April, another through the old 1806 Jena Napoleonic battlefield area. On that day, Eisenhower instructed Patton to halt the 3rd Army at the Mulde River, about short of its original objective, Chemnitz. The change resulted from an agreement between the American and Soviet military leadership based on the need to establish a readily identifiable geographical line to avoid accidental clashes between the converging Allied forces. However, as the 3rd Army began pulling up to the Mulde on 13 April, the XII Corps—Patton's southernmost force—continued moving southeast alongside the 6th U.S. Army Group to clear southern Germany and move into Austria. After taking Coburg
Coburg ( , ) is a Town#Germany, town located on the Itz (river), Itz river in the Upper Franconia region of Bavaria, Germany. Long part of one of the Thuringian states of the Ernestine duchies, Wettin line, it joined Bavaria by popular vote only ...
, about south of Erfurt, on 11 April, XII Corps troops captured Bayreuth
Bayreuth ( or ; High Franconian German, Upper Franconian: Bareid, ) is a Town#Germany, town in northern Bavaria, Germany, on the Red Main river in a valley between the Franconian Jura and the Fichtel Mountains. The town's roots date back to 11 ...
, farther southeast, on 14 April.
As was the case throughout the campaign, the German ability to fight was sporadic and unpredictable during the drive to the Elbe–Mulde line. Some areas were stoutly defended while in others the enemy surrendered after little more than token resistance. By sending armored spearheads around hotly contested areas, isolating them for reduction by subsequent waves of infantry, Eisenhower's forces maintained their eastward momentum. A German holdout force of 70,000 in the Harz
The Harz (), also called the Harz Mountains, is a highland area in northern Germany. It has the highest elevations for that region, and its rugged terrain extends across parts of Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Thuringia. The name ''Harz'' der ...
Mountains— north of Erfurt—was neutralized in this way, as were the towns of Erfurt, Jena
Jena (; ) is a List of cities and towns in Germany, city in Germany and the second largest city in Thuringia. Together with the nearby cities of Erfurt and Weimar, it forms the central metropolitan area of Thuringia with approximately 500,000 in ...
, and Leipzig.
U.S. First Army makes first contact with the advancing Soviets (25 April)
Every unit along the Elbe–Mulde line was anxious to be the first to meet the Red Army. By the last week of April, it was well known that the Soviets were close, and dozens of American patrols were probing beyond the east bank of the Mulde, hoping to meet them. Elements of the 1st Army's V Corps made first contact. At 11:30 on 25 April, a small patrol from the 69th Infantry Division met a lone Soviet horseman in the village of Leckwitz. Several other patrols from the 69th had similar encounters later that day, and on 26 April the division commander, Maj. Gen. Emil F. Reinhardt, met Maj. Gen. Vladimir Rusakov of the Soviet 58th Guards Rifle Division at Torgau
Torgau () is a town on the banks of the Elbe in northwestern Saxony, Germany. It is the capital of the district Nordsachsen.
Outside Germany, the town is best known as where on 25 April 1945, the United States and Soviet Armies first met near ...
in the first official link-up ceremony.
25 April is known as Elbe Day
Elbe Day, April 25, 1945, is the day Soviet and American troops met at the Elbe River, near Torgau in Germany, marking an important step toward the end of World War II in Europe. This contact between the Soviets, advancing from the east, and ...
.
U.S. 6th Army Group heads for Austria
While the 12th U.S. Army Group made its eastward thrust, Devers' 6th U.S. Army Group to the south had the dual mission of protecting the 12th U.S. Army Group's right flank and eliminating any German attempt to make a last stand in the Alps of southern Germany and western Austria. To accomplish both objectives, Patch's 7th Army on Devers' left was to make a great arc, first driving northeastward alongside Bradley's flank, then turning south with the 3rd Army to take Nuremberg
Nuremberg (, ; ; in the local East Franconian dialect: ''Nämberch'' ) is the Franconia#Towns and cities, largest city in Franconia, the List of cities in Bavaria by population, second-largest city in the States of Germany, German state of Bav ...
and Munich
Munich is the capital and most populous city of Bavaria, Germany. As of 30 November 2024, its population was 1,604,384, making it the third-largest city in Germany after Berlin and Hamburg. Munich is the largest city in Germany that is no ...
, ultimately continuing into Austria. The French 1st Army, under de Lattre de Tassigny, was to attack to the south and southeast, taking Stuttgart
Stuttgart (; ; Swabian German, Swabian: ; Alemannic German, Alemannic: ; Italian language, Italian: ; ) is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Baden-Württemberg by population, largest city of the States of Germany, German state of ...
before moving to the Swiss border and into Austria.
Initially, the opposition in the 6th U.S. Army Group's sector was stiffer than that facing the 12th U.S. Army Group. The German forces there were simply in less disarray than those to the north. Nevertheless, the 7th Army broke out of its Rhine bridgehead, just south of Frankfurt
Frankfurt am Main () is the most populous city in the States of Germany, German state of Hesse. Its 773,068 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the List of cities in Germany by population, fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located in the forela ...
, on 28 March, employing elements of three corps—the XV Corps to the north, the XXI Corps in the center, and the VI Corps to the south. The XV Corps' 45th Infantry Division fought for six days before taking the city of Aschaffenburg
Aschaffenburg (; Hessian: ''Aschebersch'', ) is a town in northwest Bavaria, Germany. The town of Aschaffenburg, despite being its administrative seat, is not part of the district of Aschaffenburg.
Aschaffenburg belonged to the Archbishopric ...
, east of the Rhine, on 3 April. To the south, elements of the VI Corps met unexpectedly fierce resistance at Heilbronn
Heilbronn () is a List of cities and towns in Germany, city in northern Baden-Württemberg, Germany, surrounded by Heilbronn (district), Heilbronn District.
From the late Middle Ages on, it developed into an important trading centre. At the begi ...
, into the German rear. Despite a wide armored thrust to envelop the enemy defenses, it took nine days of intense fighting to bring Heilbronn fully under American control. Still, by 11 April 7 Army had penetrated the German defenses in-depth, especially in the north, and was ready to begin its wheeling movement southeast and south. Thus, on 15 April when Eisenhower ordered Patton's entire 3rd Army to drive southeast down the Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest sou ...
River valley to Linz
Linz (Pronunciation: , ; ) is the capital of Upper Austria and List of cities and towns in Austria, third-largest city in Austria. Located on the river Danube, the city is in the far north of Austria, south of the border with the Czech Repub ...
, and south to Salzburg
Salzburg is the List of cities and towns in Austria, fourth-largest city in Austria. In 2020 its population was 156,852. The city lies on the Salzach, Salzach River, near the border with Germany and at the foot of the Austrian Alps, Alps moun ...
and central Austria, he also instructed the 6th U.S. Army Group to make a similar turn into southern Germany and western Austria.
Advancing along this new axis the Seventh Army's left rapidly overran Bamberg
Bamberg (, , ; East Franconian German, East Franconian: ''Bambärch'') is a town in Upper Franconia district in Bavaria, Germany, on the river Regnitz close to its confluence with the river Main (river), Main. Bamberg had 79,000 inhabitants in ...
, over east of the Rhine, on its way to Nuremberg, about to the south. As its forces reached Nuremberg on 16 April, the Seventh Army ran into the same type of anti-aircraft gun defense that the 1st Army was facing at Leipzig. Only on 20 April, after breaching the ring of anti-aircraft guns and fighting house-to-house for the city, did its forces take Nuremberg.
Following the capture of Nuremberg, the 7th Army discovered little resistance as the XXI Corps' 12th Armored Division dashed to the Danube, crossing it on 22 April, followed several days later by the rest of the corps and the XV Corps as well.
Meanwhile, on the 7th Army's right, the VI Corps had moved southeast alongside the French 1st Army. In a double envelopment, the French captured Stuttgart on 21 April, and by the next day, both the French and the VI Corps had elements on the Danube. Similarly, the 3rd Army on the 6th U.S. Army Group's left flank had advanced rapidly against very little resistance, its lead elements reaching the river on 24 April.
As the 6th U.S. Army Group and the 3rd Army finished clearing southern Germany and approached Austria, it was clear to most observers, Allied and German alike, that the war was nearly over. Many towns flew white flags of surrender to spare themselves the otherwise inevitable destruction suffered by those that resisted, while German troops surrendered by the tens of thousands, sometimes as entire units.
Link-up of U.S. forces in Germany and Italy (4 May)
On 30 April, elements of 7th Army's XV and XXI Corps captured Munich, south of the Danube, while the first elements of its VI Corps had already entered Austria two days earlier. On 4 May, the 3rd Army's V Corps and XII Corps advanced into Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia ( ; Czech language, Czech and , ''Česko-Slovensko'') was a landlocked country in Central Europe, created in 1918, when it declared its independence from Austria-Hungary. In 1938, after the Munich Agreement, the Sudetenland beca ...
, and units of the VI Corps met elements of Lieutenant General Lucian Truscott
General (United States), General Lucian King Truscott Jr. (9 January 1895 – 12 September 1965) was a highly decorated senior United States Army Officer (armed forces), officer, who saw distinguished Active duty, active service during World War ...
's U.S. 5th Army on the Italian frontier, linking the European and Mediterranean Theaters.[ Also on 4 May, after a shift in inter-army boundaries that placed Salzburg in the 7th Army sector, that city surrendered to elements of the XV Corps. The XV Corps also captured ]Berchtesgaden
Berchtesgaden () is a municipality in the district Berchtesgadener Land, Bavaria, in southeastern Germany, near the border with Austria, south of Salzburg and southeast of Munich. It lies in the Berchtesgaden Alps. South of the town, the Be ...
, the town that would have been Hitler's command post in the National Redoubt
A national redoubt or national fortress is an area to which the (remnant) military forces of a nation can be withdrawn if the main battle has been lost or even earlier if defeat is considered inevitable. Typically, a region is chosen with a geogra ...
. With all passes to the Alps now sealed, however, there would be no final redoubt in Austria or anywhere else. In a few days the war in Europe would be over.
British 21st Army Group crosses the Elbe (29 April)
 While the Allied armies in the south marched to the Alps, the 21st Army Group drove north and northeast. At the same time, a part of the 21st Army Group (British and Canadian units) adnanced in the Netherlands. During 12–16 April 1945 Operation Anger was conducted, resulting in the liberation of
While the Allied armies in the south marched to the Alps, the 21st Army Group drove north and northeast. At the same time, a part of the 21st Army Group (British and Canadian units) adnanced in the Netherlands. During 12–16 April 1945 Operation Anger was conducted, resulting in the liberation of Arnhem
Arnhem ( ; ; Central Dutch dialects, Ernems: ''Èrnem'') is a Cities of the Netherlands, city and List of municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality situated in the eastern part of the Netherlands, near the German border. It is the capita ...
. Two days later Groningen was liberated.
The right-wing of the British Second Army reached the Elbe southeast of Hamburg
Hamburg (, ; ), officially the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg,. is the List of cities in Germany by population, second-largest city in Germany after Berlin and List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, 7th-lar ...
on 19 April. Its left fought for a week to capture Bremen
Bremen (Low German also: ''Breem'' or ''Bräm''), officially the City Municipality of Bremen (, ), is the capital of the States of Germany, German state of the Bremen (state), Free Hanseatic City of Bremen (), a two-city-state consisting of the c ...
, which fell on 26 April. On 29 April, the British made an assault crossing of the Elbe, supported on the following day by the recently reattached XVIII Airborne Corps. The bridgehead expanded rapidly, and by 2 May Lübeck
Lübeck (; or ; Latin: ), officially the Hanseatic League, Hanseatic City of Lübeck (), is a city in Northern Germany. With around 220,000 inhabitants, it is the second-largest city on the German Baltic Sea, Baltic coast and the second-larg ...
and Wismar
Wismar (; ), officially the Hanseatic City of Wismar () is, with around 43,000 inhabitants, the sixth-largest city of the northeastern German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, and the fourth-largest city of Mecklenburg after Rostock, Schwerin and ...
, beyond the river, were in Allied hands, sealing off the Germans in the Jutland Peninsula
Jutland (; , ''Jyske Halvø'' or ''Cimbriske Halvø''; , ''Kimbrische Halbinsel'' or ''Jütische Halbinsel'') is a peninsula of Northern Europe that forms the continental portion of Denmark and part of northern Germany (Schleswig-Holstein). It ...
.
On the 21st Army Group's left, one corps of the Canadian First Army reached the North Sea near the Dutch-German border on 16 April, while another drove through the central Netherlands, trapping the German forces remaining in that country. However, concerned that the bypassed Germans would flood much of the nation and cause complete famine among a Dutch population already near starvation, Eisenhower approved an agreement with the local German commanders to allow the Allies to air-drop food into the country in return for a local ceasefire on the battlefield. The ensuing airdrops, which began on 29 April, marked the beginning of what was to become a colossal effort to put war-torn Europe back together again.
Hamburg was the last remaining pocket of German resistance in the north, it was captured on 3 May.
On 6 May, the Polish 1st Armoured Division seized the Kriegsmarine
The (, ) was the navy of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It superseded the Imperial German Navy of the German Empire (1871–1918) and the inter-war (1919–1935) of the Weimar Republic. The was one of three official military branch, branche ...
naval base in Wilhelmshaven
Wilhelmshaven (, ''Wilhelm's Harbour''; Northern Low Saxon: ''Willemshaven'') is a coastal town in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is situated on the western side of the Jade Bight, a bay of the North Sea, and has a population of 76,089. Wilhelmsha ...
, where General Maczek accepted the capitulation of the fortress, naval base, East Frisian Fleet and more than 10 infantry divisions.
Final moves by the western Allies
Eisenhower's armies were facing resistance that varied from almost non-existent to fanatical as they advanced toward Berlin, which was located from their positions in early April 1945. Britain's Prime Minister
A prime minister or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. A prime minister is not the head of state, but r ...
, Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 1874 – 24 January 1965) was a British statesman, military officer, and writer who was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1940 to 1945 (Winston Churchill in the Second World War, ...
, urged Eisenhower to continue the advance toward Berlin by the 21st Army Group, under the command of Montgomery with the intention of capturing the city. Even Patton agreed with Churchill that he should order the attack on the city since Montgomery's troops could reach Berlin within three days.[Eisenhower Commission]
Eisenhower Memorial
The British and Americans contemplated an airborne operation before the attack. In Operation Eclipse, the 17th Airborne Division, 82d Airborne Division
The 82nd Airborne Division is an Airborne forces, airborne infantry division (military), division of the United States Army specializing in Paratrooper, parachute assault operations into hostile areasSof, Eric"82nd Airborne Division" ''Spec Ops ...
, 101st Airborne Division
The 101st Airborne Division (Air Assault) ("Screaming Eagles") is a light infantry division (military), division of the United States Army that specializes in air assault military operation, operations. The 101st is designed to plan, coordinat ...
, and a British brigade were to seize the Tempelhof
Tempelhof () is a locality of Berlin within the borough of Tempelhof-Schöneberg. It is the location of the former Tempelhof Airport, one of the earliest commercial airports in the world. The former airport and surroundings are now a park call ...
, Rangsdorf, Gatow, Staaken
Staaken () is a locality at the western rim of Berlin within the borough of Spandau.
History
First mentioned in a 1273 deed as ''Stakene'' (from Middle Low German: ''staken'', "stakes") in the Mittelmark region of the Margraviate of Brandenbur ...
, and Oranienburg
Oranienburg () is a town in Brandenburg, Germany. It is the capital of the district of Oberhavel.
Geography
Oranienburg is on the banks of the River Havel, 35 km north of the centre of Berlin.
Division of the town
Oranienburg consists of ni ...
airfields. In Berlin, the Reichsbanner resistance organization identified possible drop zones for Allied paratroopers and planned to guide them past German defenses into the city.Bremen
Bremen (Low German also: ''Breem'' or ''Bräm''), officially the City Municipality of Bremen (, ), is the capital of the States of Germany, German state of the Bremen (state), Free Hanseatic City of Bremen (), a two-city-state consisting of the c ...
and Hamburg
Hamburg (, ; ), officially the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg,. is the List of cities in Germany by population, second-largest city in Germany after Berlin and List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, 7th-lar ...
. While the U.S. Ninth and First Armies held their ground from Magdeburg through Leipzig to western Czechoslovakia, Eisenhower ordered three Allied field armies (1st French, and the U.S. Seventh and Third Armies) into southeastern Germany and Austria. Advancing from northern Italy, the British Eighth Army pushed to the borders of Yugoslavia
, common_name = Yugoslavia
, life_span = 1918–19921941–1945: World War II in Yugoslavia#Axis invasion and dismemberment of Yugoslavia, Axis occupation
, p1 = Kingdom of SerbiaSerbia
, flag_p ...
to defeat the remaining ''Wehrmacht'' elements there.[ This later caused some friction with the Yugoslav forces, notably around ]Trieste
Trieste ( , ; ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital and largest city of the Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with special statute, autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, as well as of the Province of Trieste, ...
.
German surrender (8 May)
 By the end of April, the
By the end of April, the Third Reich
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a totalitarian dictat ...
was in tatters. Of the land still under Nazi control, almost none was actually in Germany. With his escape route to the south severed by the 12th Army Group's eastward drive and Berlin surrounded by the Soviets, Hitler committed suicide on 30 April, leaving to his successor, Grand Admiral
Grand admiral is a historic naval rank, the highest rank in the several European navies that used it. It is best known for its use in Germany as . A comparable rank in modern navies is that of admiral of the fleet.
Grand admirals in individual ...
Karl Dönitz
Karl Dönitz (; 16 September 1891 – 24 December 1980) was a German grand admiral and convicted war criminal who, following Adolf Hitler's Death of Adolf Hitler, suicide, succeeded him as head of state of Nazi Germany during the Second World ...
, the task of capitulation. After attempting to strike a deal whereby he would surrender only to the Western Allies, a proposal that was summarily rejected on 7 May, Dönitz granted his representative, Alfred Jodl
Alfred Josef Ferdinand Jodl (; born Alfred Josef Baumgärtler; 10 May 1890 – 16 October 1946) was a German Wehrmacht Heer, Army ''Generaloberst'' (the rank was equal to a four-star full general) and War crime, war criminal, who served as th ...
, permission to effect a complete surrender on all fronts. The appropriate documents were signed on the same day and became effective on 8 May. Despite scattered resistance from a few isolated units, the war in Europe was over.
Analysis
 By the beginning of 1945, Allied victory in Europe was inevitable. Having gambled his future ability to defend Germany on the
By the beginning of 1945, Allied victory in Europe was inevitable. Having gambled his future ability to defend Germany on the Ardennes offensive
The Ardennes ( ; ; ; ; ), also known as the Ardennes Forest or Forest of Ardennes, is a region of extensive forests, rough terrain, rolling hills and ridges primarily in Belgium and Luxembourg, extending into Germany and France.
Geological ...
and lost, Hitler had no real strength left to stop the powerful Allied armies. The Western Allies still had to fight, often bitterly, for victory. Even when the hopelessness of the German situation became obvious to his most loyal subordinates, Hitler refused to admit defeat. Only when Soviet artillery was falling around his Berlin headquarters bunker did he begin to perceive the outcome.
The crossing of the Rhine, the encirclement and reduction of the Ruhr, and the sweep to the Elbe–Mulde line and the Alps all established the final campaign on the Western Front as a showcase for Western Allied superiority over the Germans in maneuver warfare. Drawing on the experience gained during the campaign in Normandy and the Allied advance from Paris to the Rhine
The Siegfried Line campaign was a phase in the Western Front (World War II)#1944–1945: The Second Front, Western European campaign of World War II, which involved engagments near the German defensive Siegfried Line.
This campaign spanned from ...
, the Western Allies demonstrated in western Germany and Austria their capability of absorbing the lessons of the past. By attaching mechanized infantry
Mechanized infantry are infantry units equipped with Armoured personnel carrier, armored personnel carriers (APCs) or infantry fighting vehicles (IFVs) for transport and combat (see also armoured corps).
As defined by the United States Army, me ...
units to armored divisions, they created a hybrid of strength and mobility that served them well in the pursuit of warfare through Germany. Key to the effort was the logistical support that kept these forces fueled, and the determination to maintain the forward momentum at all costs. These mobile forces made great thrusts to isolate pockets of German troops, which were mopped up by additional infantry following close behind. The Western Allies rapidly eroded any remaining ability to resist.
For their part, captured German soldiers often claimed to be most impressed not by American armor or infantry but by the artillery. They frequently remarked on its accuracy and the swiftness of its target acquisition—and especially the prodigious amount of artillery ammunition expended. On the whole, Western Allied plans were considered effective as demonstrated by how rapidly they met their objectives.
Legacy
Several German political leaders have described the invasion as "liberation", including President Richard von Weizsäcker
Richard Karl Freiherr von Weizsäcker (; 15 April 1920 – 31 January 2015) was a German politician ( CDU), who served as President of Germany from 1984 to 1994. Born into the aristocratic Weizsäcker family, who were part of the German nobili ...
in 1985 and Chancellor Angela Merkel
Angela Dorothea Merkel (; ; born 17 July 1954) is a German retired politician who served as Chancellor of Germany from 2005 to 2021. She is the only woman to have held the office. She was Leader of the Opposition from 2002 to 2005 and Leade ...
in 2019. According to the ''Chicago Tribune
The ''Chicago Tribune'' is an American daily newspaper based in Chicago, Illinois, United States. Founded in 1847, it was formerly self-styled as the "World's Greatest Newspaper", a slogan from which its once integrated WGN (AM), WGN radio and ...
'', "over the decades, Germans' attitudes toward the war have evolved from a sense of defeat to something far more complex".
Notes
References
Bibliography
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Attribution:
*
Further reading
*Ellis, L.F. et al. ''Victory in the West'', Volume 2: Defeat of Germany, London: HMSO, 1968
*Russell, J "Theirs The Strife" Helion & Company 2020. ISBN 978-1-913118-56-3
External links
{{World War II
1945 in Germany
Conflicts in 1945
March 1945 in Europe
April 1945 in Europe
May 1945 in Europe
World War II invasions
World War II operations and battles of the Western European Theatre
Invasions of Germany
Battles and operations of World War II involving Canada
Military history of Canada during World War II
Invasions by Canada
Battles and operations of World War II involving the United Kingdom
Battles and operations of World War II involving the United States
Battles and operations of World War II involving France
Battles and operations of World War II involving Poland
Battles and operations of World War II involving Belgium
Battles and operations of World War II involving the Netherlands
Battles and operations of World War II involving Hungary
Allies of World War II
Battles of World War II involving the United States
 On 22 March, with a bright moon lighting the late-night sky, elements of U.S. XII Corps' 5th Infantry Division began the 3rd Army's Rhine crossing. At Nierstein assault troops did not meet any resistance. As the first boats reached the east bank, seven startled Germans surrendered and then paddled themselves unescorted to the west bank to be placed in custody. Upstream at Oppenheim, however, the effort did not proceed so casually. The first wave of boats was halfway across when the Germans began pouring machine-gun fire into their midst. An intense exchange of fire lasted for about thirty minutes as assault boats kept pushing across the river and those men who had already made it across mounted attacks against the scattered defensive strongpoints. Finally, the Germans surrendered, and by midnight units moved out laterally to consolidate the crossing sites and to attack the first villages beyond the river. German resistance everywhere was sporadic, and the hastily mounted counterattacks invariably burned out quickly, causing few casualties. The Germans lacked both the manpower and the heavy equipment to make a more determined defense.
By midafternoon on 23 March, all three regiments of the 5th Infantry Division were in the bridgehead, and an attached regiment from the
On 22 March, with a bright moon lighting the late-night sky, elements of U.S. XII Corps' 5th Infantry Division began the 3rd Army's Rhine crossing. At Nierstein assault troops did not meet any resistance. As the first boats reached the east bank, seven startled Germans surrendered and then paddled themselves unescorted to the west bank to be placed in custody. Upstream at Oppenheim, however, the effort did not proceed so casually. The first wave of boats was halfway across when the Germans began pouring machine-gun fire into their midst. An intense exchange of fire lasted for about thirty minutes as assault boats kept pushing across the river and those men who had already made it across mounted attacks against the scattered defensive strongpoints. Finally, the Germans surrendered, and by midnight units moved out laterally to consolidate the crossing sites and to attack the first villages beyond the river. German resistance everywhere was sporadic, and the hastily mounted counterattacks invariably burned out quickly, causing few casualties. The Germans lacked both the manpower and the heavy equipment to make a more determined defense.
By midafternoon on 23 March, all three regiments of the 5th Infantry Division were in the bridgehead, and an attached regiment from the  Plunder began on the evening of 23 March with the assault elements of the British 2nd Army massed against three main crossing sites: Rees in the north, Xanten in the center, and Wesel in the south. The two 9th Army divisions tasked for the assault concentrated in the Rheinberg area south of Wesel. At the northern crossing site, elements of British XXX Corps began the assault (Operation Turnscrew) about 21:00, attempting to distract the Germans from the main crossings at Xanten in the center and Rheinberg to the south. The initial assault waves crossed the river quickly, meeting only light opposition. Meanwhile, Operation Widgeon began north of Wesel as the 2nd Army's 1st Commando Brigade slipped across the river and waited within of the city while it was demolished by one thousand tons of bombs delivered by
Plunder began on the evening of 23 March with the assault elements of the British 2nd Army massed against three main crossing sites: Rees in the north, Xanten in the center, and Wesel in the south. The two 9th Army divisions tasked for the assault concentrated in the Rheinberg area south of Wesel. At the northern crossing site, elements of British XXX Corps began the assault (Operation Turnscrew) about 21:00, attempting to distract the Germans from the main crossings at Xanten in the center and Rheinberg to the south. The initial assault waves crossed the river quickly, meeting only light opposition. Meanwhile, Operation Widgeon began north of Wesel as the 2nd Army's 1st Commando Brigade slipped across the river and waited within of the city while it was demolished by one thousand tons of bombs delivered by  To the south, the discovery of a defensive gap in front of the 30th Infantry Division fostered the hope that a full-scale breakout would be possible on 25 March. When limited objective attacks provoked little response on the morning of the 25th, the division commander Major General Leland Hobbs formed two mobile task forces to make deeper thrusts with an eye toward punching through the defense altogether and breaking deep into the German rear. However, Hobbs had not fully taken into account the nearly nonexistent road network in front of the XVI Corps bridgehead. Faced with trying to make rapid advances through dense forest on rutted dirt roads and muddy trails, which could be strongly defended by a few determined soldiers and well-placed roadblocks, the task forces advanced only about on the 25th. The next day they gained some more ground, and one even seized its objective, having slogged a total of , but the limited progress forced Hobbs to abandon the hope for a quick breakout.
In addition to the poor roads, the 30th Division's breakout attempts were also hampered by the German 116th Panzer Division. The only potent unit left for commitment against the Allied Rhine crossings in the north, the 116th began moving south from the Dutch-German border on 25 March against what the Germans considered their most dangerous threat, the U.S. 9th Army. The enemy armored unit began making its presence felt almost immediately, and by the end of 26 March, the combination of the ''panzer'' division and the rough terrain had conspired to sharply limit the 30th Division's forward progress. With the 79th Infantry Division meeting fierce resistance to the south, Simpson's only recourse was to commit some of his forces waiting on the west bank of the Rhine. Late on 26 March, the 8th Armored Division began moving into the bridgehead.
Although the armored division bolstered his offensive capacity within the bridgehead, Simpson was more interested in sending the XIX Corps across the Wesel bridges, as Montgomery had agreed, and using the better roads north of the Lippe to outflank the enemy in front of the 30th Division. Unfortunately, because of pressure from the Germans in the northern part of the 2nd Army bridgehead, the British were having trouble completing their bridges at Xanten and were, therefore, bringing most of their traffic across the river at Wesel. With Montgomery allowing use of the Wesel bridges to the 9th Army for only five out of every 24 hours, and with the road network north of the Lippe under 2nd Army control, General Simpson was unable to commit or maneuver sufficient forces to make a rapid flanking drive.
To the south, the discovery of a defensive gap in front of the 30th Infantry Division fostered the hope that a full-scale breakout would be possible on 25 March. When limited objective attacks provoked little response on the morning of the 25th, the division commander Major General Leland Hobbs formed two mobile task forces to make deeper thrusts with an eye toward punching through the defense altogether and breaking deep into the German rear. However, Hobbs had not fully taken into account the nearly nonexistent road network in front of the XVI Corps bridgehead. Faced with trying to make rapid advances through dense forest on rutted dirt roads and muddy trails, which could be strongly defended by a few determined soldiers and well-placed roadblocks, the task forces advanced only about on the 25th. The next day they gained some more ground, and one even seized its objective, having slogged a total of , but the limited progress forced Hobbs to abandon the hope for a quick breakout.
In addition to the poor roads, the 30th Division's breakout attempts were also hampered by the German 116th Panzer Division. The only potent unit left for commitment against the Allied Rhine crossings in the north, the 116th began moving south from the Dutch-German border on 25 March against what the Germans considered their most dangerous threat, the U.S. 9th Army. The enemy armored unit began making its presence felt almost immediately, and by the end of 26 March, the combination of the ''panzer'' division and the rough terrain had conspired to sharply limit the 30th Division's forward progress. With the 79th Infantry Division meeting fierce resistance to the south, Simpson's only recourse was to commit some of his forces waiting on the west bank of the Rhine. Late on 26 March, the 8th Armored Division began moving into the bridgehead.
Although the armored division bolstered his offensive capacity within the bridgehead, Simpson was more interested in sending the XIX Corps across the Wesel bridges, as Montgomery had agreed, and using the better roads north of the Lippe to outflank the enemy in front of the 30th Division. Unfortunately, because of pressure from the Germans in the northern part of the 2nd Army bridgehead, the British were having trouble completing their bridges at Xanten and were, therefore, bringing most of their traffic across the river at Wesel. With Montgomery allowing use of the Wesel bridges to the 9th Army for only five out of every 24 hours, and with the road network north of the Lippe under 2nd Army control, General Simpson was unable to commit or maneuver sufficient forces to make a rapid flanking drive.
 By 28 March, the 8th Armored Division had expanded the bridgehead by only about and still had not reached
By 28 March, the 8th Armored Division had expanded the bridgehead by only about and still had not reached  The first step in realizing Eisenhower's plan was the eradication of the Ruhr Pocket. Even before the encirclement had been completed, the Germans in the Ruhr had begun making attempts at a breakout to the east. All had been unceremoniously repulsed by the vastly superior Allied forces. Meanwhile, the 9th and 1st Armies began preparing converging attacks using the east-west Ruhr River as a boundary line. The 9th Army's XVI Corps, which had taken up position north of the Ruhr area after crossing the Rhine, would be assisted in its southward drive by two divisions of the XIX Corps, the rest of which would continue to press eastward along with the XIII Corps. South of the Ruhr River, the 1st Army's northward attack was to be executed by the XVIII Airborne Corps, which had been transferred to Hodges after Operation Varsity, and the III Corps, with the 1st Army's V and VII Corps continuing the offensive east. The 9th Army's sector of the Ruhr Pocket, although only about 1/3 the size of the 1st Army's sector south of the river, contained the majority of the densely urbanized industrial area within the encirclement. The 1st Army's area, on the other hand, was composed of rough, heavily forested terrain with a poor road network.
By 1 April, when the trap closed around the Germans in the Ruhr, their fate was sealed. In a matter of days, they would all be killed or captured. On 4 April, the day it shifted to Bradley's control, the 9th Army began its attack south toward the Ruhr River. In the south, the 1st Army's III Corps launched its strike on the 5th and the XVIII Airborne Corps joined in on the 6th, both pushing generally northward. German resistance, initially rather determined, dwindled rapidly. By 13 April, the 9th Army had cleared the northern part of the pocket, while elements of the XVIII Airborne Corps' 8th Infantry Division reached the southern bank of the Ruhr, splitting the southern section of the pocket in two. Thousands of prisoners were being taken every day; from 16 to 18 April, when all opposition ended and the remnants of German ''Army Group B'' formally surrendered, German troops had been surrendering in droves throughout the region. Army Group B commander Model committed suicide on 21 April.
The final tally of prisoners taken in the Ruhr reached 325,000, far beyond anything the Americans had anticipated. Tactical commanders hastily enclosed huge open fields with barbed wire creating makeshift prisoner of war camps, where the inmates awaited the end of the war and their chance to return home. Also looking forward to going home, tens of thousands of freed forced laborers and Allied prisoners of war further strained the American logistical system.
The first step in realizing Eisenhower's plan was the eradication of the Ruhr Pocket. Even before the encirclement had been completed, the Germans in the Ruhr had begun making attempts at a breakout to the east. All had been unceremoniously repulsed by the vastly superior Allied forces. Meanwhile, the 9th and 1st Armies began preparing converging attacks using the east-west Ruhr River as a boundary line. The 9th Army's XVI Corps, which had taken up position north of the Ruhr area after crossing the Rhine, would be assisted in its southward drive by two divisions of the XIX Corps, the rest of which would continue to press eastward along with the XIII Corps. South of the Ruhr River, the 1st Army's northward attack was to be executed by the XVIII Airborne Corps, which had been transferred to Hodges after Operation Varsity, and the III Corps, with the 1st Army's V and VII Corps continuing the offensive east. The 9th Army's sector of the Ruhr Pocket, although only about 1/3 the size of the 1st Army's sector south of the river, contained the majority of the densely urbanized industrial area within the encirclement. The 1st Army's area, on the other hand, was composed of rough, heavily forested terrain with a poor road network.
By 1 April, when the trap closed around the Germans in the Ruhr, their fate was sealed. In a matter of days, they would all be killed or captured. On 4 April, the day it shifted to Bradley's control, the 9th Army began its attack south toward the Ruhr River. In the south, the 1st Army's III Corps launched its strike on the 5th and the XVIII Airborne Corps joined in on the 6th, both pushing generally northward. German resistance, initially rather determined, dwindled rapidly. By 13 April, the 9th Army had cleared the northern part of the pocket, while elements of the XVIII Airborne Corps' 8th Infantry Division reached the southern bank of the Ruhr, splitting the southern section of the pocket in two. Thousands of prisoners were being taken every day; from 16 to 18 April, when all opposition ended and the remnants of German ''Army Group B'' formally surrendered, German troops had been surrendering in droves throughout the region. Army Group B commander Model committed suicide on 21 April.
The final tally of prisoners taken in the Ruhr reached 325,000, far beyond anything the Americans had anticipated. Tactical commanders hastily enclosed huge open fields with barbed wire creating makeshift prisoner of war camps, where the inmates awaited the end of the war and their chance to return home. Also looking forward to going home, tens of thousands of freed forced laborers and Allied prisoners of war further strained the American logistical system.
 The Elbe River was the official eastward objective, but many American commanders still eyed Berlin. By the evening of 11 April, elements of the 9th Army's 2nd Armored Division—seemingly intent on demonstrating how easily their army could take that coveted prize—had dashed to reach the Elbe southeast of Magdeburg, just short of the German capital. On 12 April, additional 9th Army elements attained the Elbe and by the next day were on the opposite bank hopefully awaiting permission to drive on to Berlin. But two days later, on 15 April, they had to abandon these hopes. Eisenhower sent Bradley his final word on the matter: the 9th Army was to stay put—there would be no effort to take Berlin. Simpson subsequently turned his troops' attention to mopping up pockets of local resistance.
In the center of the 12th U.S. Army Group, Hodges' 1st Army faced somewhat stiffer opposition, though it hardly slowed the pace. As its forces approached Leipzig, about south of Magdeburg and short of the Mulde River, the 1st Army ran into one of the few remaining centers of organized resistance. Here the Germans turned a thick defense belt of antiaircraft guns against the American ground troops with devastating effects. Through a combination of flanking movements and night attacks, First Army troops were able to destroy or bypass the guns, moving finally into Leipzig, which formally surrendered on the morning of 20 April. By the end of the day, the units that had taken Leipzig joined the rest of the 1st Army on the
The Elbe River was the official eastward objective, but many American commanders still eyed Berlin. By the evening of 11 April, elements of the 9th Army's 2nd Armored Division—seemingly intent on demonstrating how easily their army could take that coveted prize—had dashed to reach the Elbe southeast of Magdeburg, just short of the German capital. On 12 April, additional 9th Army elements attained the Elbe and by the next day were on the opposite bank hopefully awaiting permission to drive on to Berlin. But two days later, on 15 April, they had to abandon these hopes. Eisenhower sent Bradley his final word on the matter: the 9th Army was to stay put—there would be no effort to take Berlin. Simpson subsequently turned his troops' attention to mopping up pockets of local resistance.
In the center of the 12th U.S. Army Group, Hodges' 1st Army faced somewhat stiffer opposition, though it hardly slowed the pace. As its forces approached Leipzig, about south of Magdeburg and short of the Mulde River, the 1st Army ran into one of the few remaining centers of organized resistance. Here the Germans turned a thick defense belt of antiaircraft guns against the American ground troops with devastating effects. Through a combination of flanking movements and night attacks, First Army troops were able to destroy or bypass the guns, moving finally into Leipzig, which formally surrendered on the morning of 20 April. By the end of the day, the units that had taken Leipzig joined the rest of the 1st Army on the  While the Allied armies in the south marched to the Alps, the 21st Army Group drove north and northeast. At the same time, a part of the 21st Army Group (British and Canadian units) adnanced in the Netherlands. During 12–16 April 1945 Operation Anger was conducted, resulting in the liberation of
While the Allied armies in the south marched to the Alps, the 21st Army Group drove north and northeast. At the same time, a part of the 21st Army Group (British and Canadian units) adnanced in the Netherlands. During 12–16 April 1945 Operation Anger was conducted, resulting in the liberation of  By the end of April, the
By the end of April, the  By the beginning of 1945, Allied victory in Europe was inevitable. Having gambled his future ability to defend Germany on the
By the beginning of 1945, Allied victory in Europe was inevitable. Having gambled his future ability to defend Germany on the