Census in Germany on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A national census in Germany (, ) was held every five years from 1875 to 1910. After the
A national census in Germany (, ) was held every five years from 1875 to 1910. After the
p. 272
/ref> held a census, to be prepared in case of a siege. Brandenburg-Prussia in 1683 began to count its rural population. The first systematic population survey on the European continent was taken in 1719 in the Mark Brandenburg of the
 When the
When the
Population density in Germany by district, 1925.svg, Population density in the 1925 census
Occupation in Germany by district, 1925.svg, Occupation in the 1925 census
Religion in Germany by district, 1925.svg, Religion in the 1925 census
The 1930 census was delayed until 1933 by the Depression, and another one was carried out in 1939, with both being affected by the bias of the 

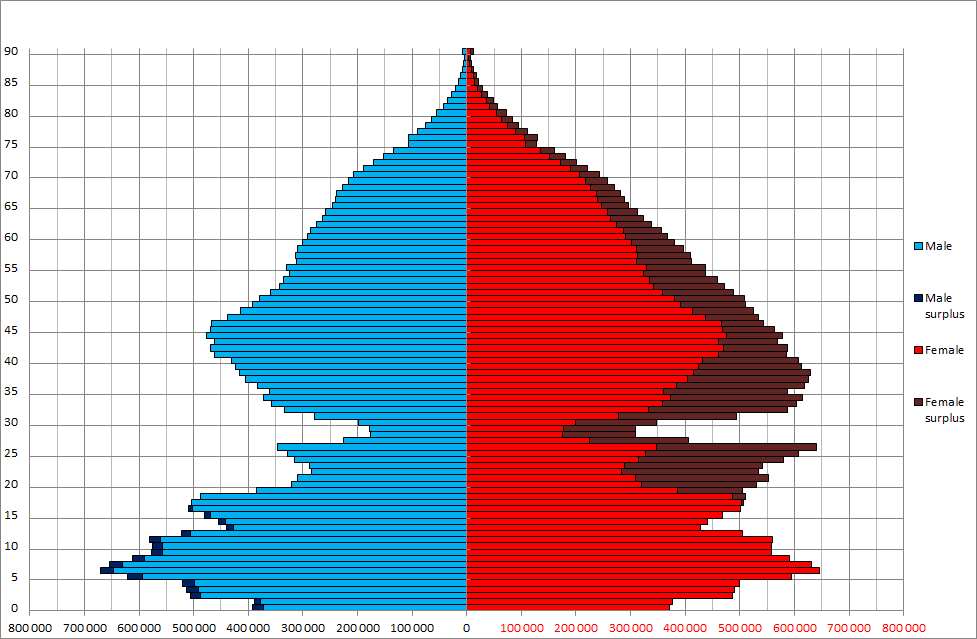

 In the 1980s, attempts at introducing a census in
In the 1980s, attempts at introducing a census in
The Census Enumeration in Prussia
. ''Publications of the American Statistical Association''. 2 (16): 407–420.
Destatis zum nächsten Zensus 2011
Historisch-Geographisches Informationssystem (HGIS)Historical facts about the German Minority Census of 1939
GeoHive mit Daten und Resultaten von Volkszählungen weltweit
Transkription der Volkszählungen in Schleswig-Holstein 1769 bis 1864
{{DEFAULTSORT:Census In Germany Government of Germany
World Wars
A world war is an international conflict that involves most or all of the world's major powers. Conventionally, the term is reserved for two major international conflicts that occurred during the first half of the 20th century, World War I (19 ...
, only a few full population census
A census (from Latin ''censere'', 'to assess') is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording, and calculating population information about the members of a given Statistical population, population, usually displayed in the form of stati ...
es have been held, the last in 1987. The most recent census, though not a national census, was the 2011 European Union census. A "micro census", with smaller samples has been held more frequently.
Early history
Nuremberg
Nuremberg (, ; ; in the local East Franconian dialect: ''Nämberch'' ) is the Franconia#Towns and cities, largest city in Franconia, the List of cities in Bavaria by population, second-largest city in the States of Germany, German state of Bav ...
in 1471Kersten Krüger: ''Historische Statistik'', in: ''Formung der frühen Moderne - Ausgewählte Aufsätze'', LIT Verlag Berlin-Hamburg-Münster, 2005 ,p. 272
/ref> held a census, to be prepared in case of a siege. Brandenburg-Prussia in 1683 began to count its rural population. The first systematic population survey on the European continent was taken in 1719 in the Mark Brandenburg of the
Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (, ) was a German state that existed from 1701 to 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It played a signif ...
, in order to prepare the first general census of 1725.
In Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (; ), also known as the House of Austria, was one of the most powerful dynasties in the history of Europe and Western civilization. They were best known for their inbreeding and for ruling vast realms throughout Europe d ...
ruled Austria, a population count had been introduced in 1754, but due to resistance by nobility and clerics, no full census was held after 1769. A century and many political changes later, census resumed in 1869, and were held also in 1880, 1890, 1900, 1910, in the same years as the German Empire
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperia ...
census. Between the wars, census were held in 1920, 1923, 1934 and 1939, to be resumed in 1951 with a ten-year occurrence.
For 1806, a population of 24,241,000 for several Imperial Circles is quoted in the "Statistik des deutschen Reiches", even though the old Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
had fallen apart, and a new German Empire did not exist yet as a political entity. By 1821, the population within the newly founded German Confederation
The German Confederation ( ) was an association of 39 predominantly German-speaking sovereign states in Central Europe. It was created by the Congress of Vienna in 1815 as a replacement of the former Holy Roman Empire, which had been dissolved ...
had grown to over 30 million.
German Zollverein (1834–1867)
German Confederation
The German Confederation ( ) was an association of 39 predominantly German-speaking sovereign states in Central Europe. It was created by the Congress of Vienna in 1815 as a replacement of the former Holy Roman Empire, which had been dissolved ...
had been founded in 1815, some states had been anxious to prove they had a small population in order to contribute fewer soldiers to the Federal Army. On the other hand, when the first custom union between southern states were formed, they wanted to show they had a large population in order to claim a larger share of the custom revenue. The German Customs Union, the Zollverein
The (), or German Customs Union, was a coalition of States of the German Confederation, German states formed to manage tariffs and economic policies within their territories. Organized by the 1833 treaties, it formally started on 1 January 1 ...
, conducted population counts from 1834 to 1867, every three years on 3 December, in order to share its revenue among the member states accordingly. The date of 3 December was chosen as most people of the „Zollabrechnungsbevölkerung“, the ''custom accounting population'', were expected to be at home then. The Eastern parts of Prussia remained outside of the Confederation for most of the time, but the whole of Prussia was part of the Zollverein. While most states joined the Zollverein sooner or later, the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire, officially known as the Empire of Austria, was a Multinational state, multinational European Great Powers, great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the Habsburg monarchy, realms of the Habsburgs. Duri ...
never did until the German Confederation and the Zollverein broke up in the civil war of 1866. The Zollverein regrouped and held another census in 1867, but the census of 1870 was postponed due to the ongoing Franco-German War
The Franco-Prussian War or Franco-German War, often referred to in France as the War of 1870, was a conflict between the Second French Empire and the North German Confederation led by the Kingdom of Prussia. Lasting from 19 July 1870 to 28 Jan ...
and the foundation of the German Empire.
German Empire, Weimar Republic and Nazi Germany (1871–1945)
Starting in 1871, the census resumed in the newly unitedGerman Empire
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperia ...
, continuing every five years from 1875 to 1910. The first large-scale census in the German Empire took place in 1895 (see German census of 1895). The last pre-war census was held on 1 December 1910. The 1915 census was canceled, but two war censuses were held on 5 December 1916 and 1917 to organize the sharing of food. Regular censuses resumed during the Weimar Republic
The Weimar Republic, officially known as the German Reich, was the German Reich, German state from 1918 to 1933, during which it was a constitutional republic for the first time in history; hence it is also referred to, and unofficially proclai ...
, being held on 8 October 1919 and 16 June 1925.
Nazi
Nazism (), formally named National Socialism (NS; , ), is the far-right politics, far-right Totalitarianism, totalitarian socio-political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Germany. During H ...
government. Initially planned for 1937, the 1939 census now also included the areas of Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
, Sudetenland
The Sudetenland ( , ; Czech and ) is a German name for the northern, southern, and western areas of former Czechoslovakia which were inhabited primarily by Sudeten Germans. These German speakers had predominated in the border districts of Bohe ...
and Memelland. About 750,000 counters covered 22 million households and roughly 80 million inhabitants. Made in an atmosphere of terror, attacks on members of the Polish minority, and the demolition of Polish businesses, the census resulted in many Poles living in Germany giving their nationality as German, out of fear of losing their lives or the well-being of their families being endangered.
After the Second World War, the occupying powers started to count the population in their zones, first the Soviets on 1 December 1945, then the French on 26 January 1946. On 29 October 1946, a census was held in all four zones.




Ethnic minorities in 1900
According to the census of 1900, among the total population of 56,367,178 there were 51,883,131 with theGerman language
German (, ) is a West Germanic language in the Indo-European language family, mainly spoken in Western Europe, Western and Central Europe. It is the majority and Official language, official (or co-official) language in Germany, Austria, Switze ...
as their first and only language, plus 252,918 bilingual Germans. The largest minority was the Polish, with 3,086,489 (not including 142,049 Masurians
The Masurians or Mazurs (; ; Masurian dialects, Masurian: ''Mazurÿ''), historically also known as Prussian Masurians (Polish language, Polish: ''Mazurzy pruscy''), are an ethnic group originating from the region of Masuria, within the Warmian- ...
and 100,213 Kashubians
The Kashubians (; ; ), also known as Cassubians or Kashubs, are a Lechitic ( West Slavic) ethnic group native to the historical region of Pomerania, including its eastern part called Pomerelia, in north-central Poland. Their settlement area is ...
). The census results also listed the districts with a minority larger than 5%, including many districts in which German speakers were a minority. Many of these areas would later become part of the Second Polish Republic
The Second Polish Republic, at the time officially known as the Republic of Poland, was a country in Central and Eastern Europe that existed between 7 October 1918 and 6 October 1939. The state was established in the final stage of World War I ...
as a result of German territorial losses in the Treaty of Versailles.
East Germany (1949–1990)
TheGerman Democratic Republic
East Germany, officially known as the German Democratic Republic (GDR), was a country in Central Europe from Foundation of East Germany, its formation on 7 October 1949 until German reunification, its reunification with West Germany (FRG) on ...
held four census during its existence, of which only the 1964 results were published in full. Unlike most European countries, which saw a significant growth of their populations, the GDR suffered a drop. Until the building of the Berlin Wall
The Berlin Wall (, ) was a guarded concrete Separation barrier, barrier that encircled West Berlin from 1961 to 1989, separating it from East Berlin and the East Germany, German Democratic Republic (GDR; East Germany). Construction of the B ...
in 1961, over three million Germans had defected from the GDR to West Germany
West Germany was the common English name for the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG) from its formation on 23 May 1949 until German reunification, its reunification with East Germany on 3 October 1990. It is sometimes known as the Bonn Republi ...
. As many young adults had chosen to leave, this also affected the numbers of babies born in the following decades.
Federal Republic of Germany (formerly known as West Germany) (since 1949)
West Germany
West Germany was the common English name for the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG) from its formation on 23 May 1949 until German reunification, its reunification with East Germany on 3 October 1990. It is sometimes known as the Bonn Republi ...
sparked strong popular resentment since some felt that the questions to be asked were quite personal. Comparisons to Orwell's ''1984'' were drawn. Some campaigned for a boycott, or for intentional false statements. The Constitutional Court
A constitutional court is a high court that deals primarily with constitutional law. Its main authority is to rule on whether laws that are challenged are in fact unconstitutional, i.e. whether they conflict with constitutionally established ru ...
stopped the census in 1983, and required a revision of the process. The modified census was eventually held in 1987.
For 1991 a concurrent census in both West and East Germany had been planned, but it was canceled due to reunification, and replaced by a "micro census" population sample among 1 percent of house holds. Due to reunification and immigration from former Eastern Bloc states and the war-torn Balkans, the population has grown to c. 82 million in the 1990s, but no census has been held since 1987. As of July 2017 The CIA Factbook
''The World Factbook'', also known as the ''CIA World Factbook'', is a reference resource produced by the United States' Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The official print ver ...
estimates the population at 80,159,662, and ranks Germany as 19th in the world.
Former population censuses in Germany were complete enumerations obtained directly from the entire population in personal interviews or by questionnaire. For the 1987 population census, some 500 000 enumerators were required and for 2011, a change in methodology was planned, and the costs of the largely register-based census were expected to be only about one third of the expenditure of a traditional population census. Mainly the data already stored in the registers of the administrative authorities, in the population registers of the municipalities and the registers of the Federal Employment Agency was used. Additional data, like information on education, training and occupation, would be collected by an interview-based sample survey. The data on buildings and dwellings, for which there are no registers in Germany, would be collected by mail from all owners.
See also
*Statistisches Bundesamt
The Federal Statistical Office (, shortened ''Destatis'') is a federal authority of Germany. It reports to the Federal Ministry of the Interior.
The Office is responsible for collecting, processing, presenting and analysing statistical informati ...
(Destatis)
* Demographics of Germany
The demography of Germany is monitored by the ''Statistisches Bundesamt'' (Federal Statistical Office of Germany). According to the most recent data, Germany's population is 83,456,045 (31 December 2023) making it the most populous country in ...
* Judenzählung
Literature
* Kaiserliches Statistisches Amt (Hrsg.): ''Statistisches Jahrbuch für das Deutsche Reich'', 1880–1918 * Statistisches Reichsamt (Hrsg.): ''Statistisches Jahrbuch für das Deutsche Reich'', 1919–1941/42 * Statistisches Bundesamt (Hrsg.): ''Statistisches Jahrbuch für die Bundesrepublik Deutschland'', 1952 ff. * Staatliche Zentralverwaltung für Statistik (Hrsg.): ''Statistisches Jahrbuch der Deutschen Demokratischen Republik'', 1955–1989Further reading
* Plehn, Carl C. (1891).The Census Enumeration in Prussia
. ''Publications of the American Statistical Association''. 2 (16): 407–420.
References
External links
Destatis zum nächsten Zensus 2011
Historisch-Geographisches Informationssystem (HGIS)
GeoHive mit Daten und Resultaten von Volkszählungen weltweit
Transkription der Volkszählungen in Schleswig-Holstein 1769 bis 1864
{{DEFAULTSORT:Census In Germany Government of Germany