Cell-free fetal DNA on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cell-free fetal DNA (cffDNA) is
cffDNA may also be used to diagnose genetic disorder, single gene disorders. Developments in laboratory processes using cffDNA may allow prenatal diagnosis of aneuploidies such as
 ;Trisomy 21
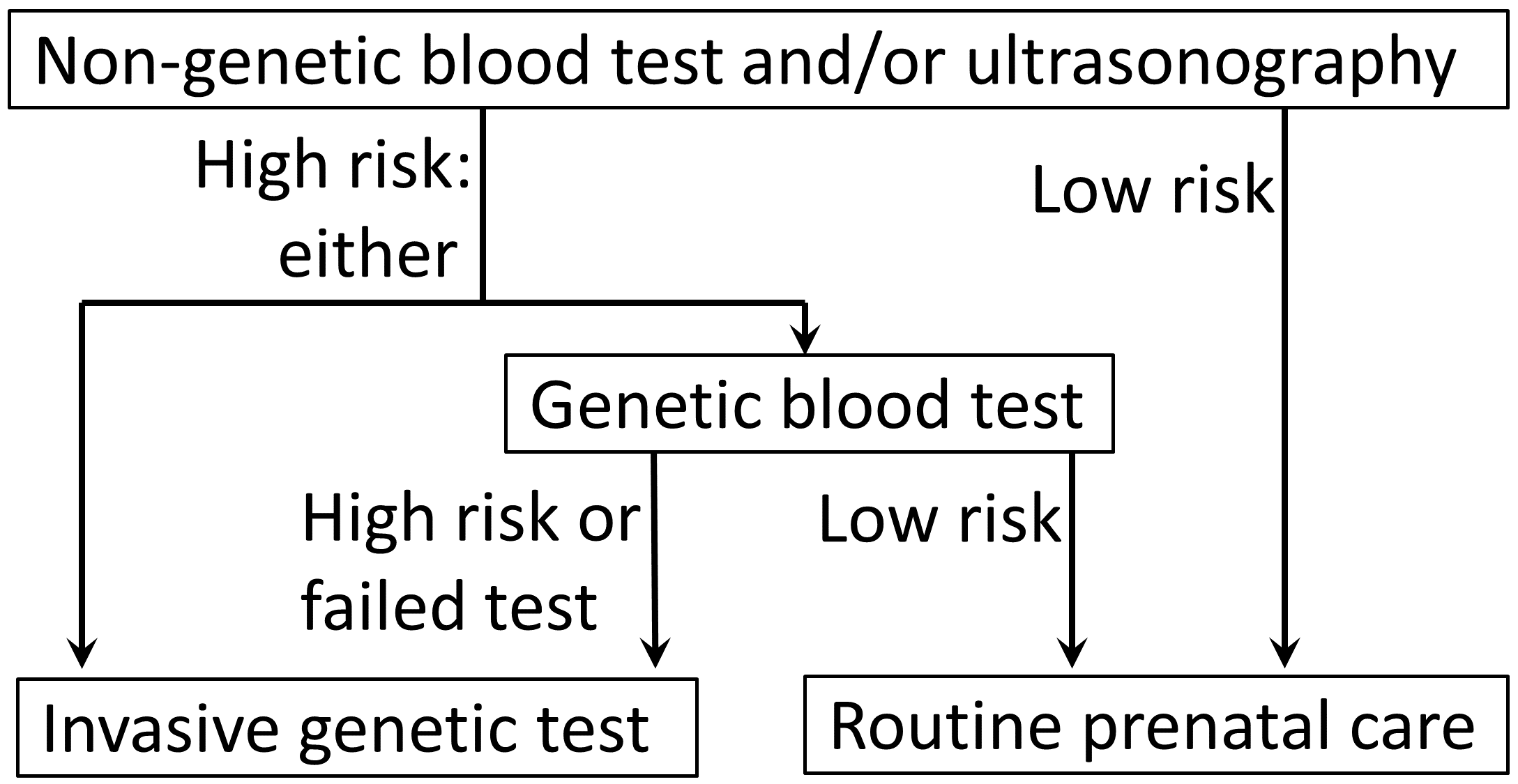
Fetal trisomy of chromosome 21 is the cause of Down's syndrome. This trisomy can be detected by analysis of cffDNA from maternal blood by massively parallel shotgun sequencing (MPSS). Another technique is digital analysis of selected regions (DANSR). Such tests show a sensitivity of about 99% and a specificity of more than 99.9%. Therefore, they cannot be regarded as diagnostic procedures but may be used to confirm a positive maternal screening test such as a first trimester screening or ultrasound markers of the condition.
;Trisomy 13 and 18
Analysis of cffDNA from maternal plasma with MPSS looking for trisomy 13 or 18 is possible
Factors limiting sensitivity and specificity include the levels of cffDNA in the maternal plasma; maternal chromosomes may have mosaicism.
A number of fetal nucleic acid molecules derived from aneuploid chromosomes can be detected including SERPINEB2 mRNA, clad B, hypomethylated SERPINB5 from chromosome 18, placenta-specific 4 (PLAC4), hypermethylated holocarboxylase synthetase (HLCS) and c21orf105 mRNA from chromosome 12. With complete trisomy, the mRNA alleles in maternal plasma isn't the normal 1:1 ratio, but is in fact 2:1. Allelic ratios determined by epigenetic markers can also be used to detect the complete trisomies. Massive parallel sequencing and digital PCR for fetal aneuploidy detection can be used without restriction to fetal-specific nucleic acid molecules. (MPSS) is estimated to have a sensitivity of between 96 and 100%, and a specificity between 94 and 100% for detecting Down syndrome. It can be performed at 10 weeks of gestational age.Noninvasive Prenatal Diagnosis of Fetal Aneuploidy Using Cell-Free Fetal Nucleic Acids in Maternal Blood: Clinical Policy (Effective 05/01/2013)
;Trisomy 21
Fetal trisomy of chromosome 21 is the cause of Down's syndrome. This trisomy can be detected by analysis of cffDNA from maternal blood by massively parallel shotgun sequencing (MPSS). Another technique is digital analysis of selected regions (DANSR). Such tests show a sensitivity of about 99% and a specificity of more than 99.9%. Therefore, they cannot be regarded as diagnostic procedures but may be used to confirm a positive maternal screening test such as a first trimester screening or ultrasound markers of the condition.
;Trisomy 13 and 18
Analysis of cffDNA from maternal plasma with MPSS looking for trisomy 13 or 18 is possible
Factors limiting sensitivity and specificity include the levels of cffDNA in the maternal plasma; maternal chromosomes may have mosaicism.
A number of fetal nucleic acid molecules derived from aneuploid chromosomes can be detected including SERPINEB2 mRNA, clad B, hypomethylated SERPINB5 from chromosome 18, placenta-specific 4 (PLAC4), hypermethylated holocarboxylase synthetase (HLCS) and c21orf105 mRNA from chromosome 12. With complete trisomy, the mRNA alleles in maternal plasma isn't the normal 1:1 ratio, but is in fact 2:1. Allelic ratios determined by epigenetic markers can also be used to detect the complete trisomies. Massive parallel sequencing and digital PCR for fetal aneuploidy detection can be used without restriction to fetal-specific nucleic acid molecules. (MPSS) is estimated to have a sensitivity of between 96 and 100%, and a specificity between 94 and 100% for detecting Down syndrome. It can be performed at 10 weeks of gestational age.Noninvasive Prenatal Diagnosis of Fetal Aneuploidy Using Cell-Free Fetal Nucleic Acids in Maternal Blood: Clinical Policy (Effective 05/01/2013)
from Oxford Health Plans One study in the United States estimated a false positive rate of 0.3% and a positive predictive value of 80% when using cffDNA to detect Down syndrome.. A recent study in th
New England Journal of Medicine
demonstrated the feasibility of usin
NIPT
in a low risk population.
fetal
A fetus or foetus (; : fetuses, foetuses, rarely feti or foeti) is the unborn offspring of a viviparous animal that develops from an embryo. Following the embryonic stage, the fetal stage of development takes place. Prenatal development is a ...
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
that circulates freely in the maternal blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells.
Blood is com ...
. Maternal blood is sampled by venipuncture
In medicine, venipuncture or venepuncture is the process of obtaining intravenous access for the purpose of venous Sampling (medicine)#blood, blood sampling (also called ''phlebotomy'') or intravenous therapy. In healthcare, this procedure is p ...
. Analysis of cffDNA is a method of non-invasive prenatal diagnosis frequently ordered for pregnant women of advanced age. Two hours after delivery, cffDNA is no longer detectable in maternal blood.
Background
cffDNA originates fromplacenta
The placenta (: placentas or placentae) is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas, and waste exchange between ...
l trophoblast
The trophoblast (from Greek language, Greek : to feed; and : germinator) is the outer layer of cells of the blastocyst. Trophoblasts are present four days after Human fertilization, fertilization in humans. They provide nutrients to the embryo an ...
s. Fetal DNA is fragmented when placental microparticles are shed into the maternal blood circulation.
cffDNA fragments are approximately 200 base pairs (bp) in length. They are significantly smaller than maternal DNA fragments. The difference in size allows cffDNA to be distinguished from maternal DNA fragments.
Approximately 11 to 13.4 percent of the cell-free DNA in maternal blood is of fetal origin. The amount varies widely from one pregnant woman to another. cffDNA is present after five to seven weeks gestation. The amount of cffDNA increases as the pregnancy progresses. The quantity of cffDNA in maternal blood diminishes rapidly after childbirth. Two hours after delivery, cffDNA is no longer detectable in maternal blood.
Analysis of cffDNA may provide earlier diagnosis of fetal conditions than current techniques. As cffDNA is found in maternal blood, sampling carries no associated risk of spontaneous abortion. cffDNA analysis has the same ethical and practical issues as other techniques such as amniocentesis
Amniocentesis is a medical procedure used primarily in the prenatal diagnosis of genetic conditions. It has other uses such as in the assessment of infection and fetal lung maturity. Prenatal diagnostic testing, which includes amniocentesis, is ...
and chorionic villus sampling.
Some disadvantages of sampling cffDNA include a low concentration of cffDNA in maternal blood; variation in the quantity of cffDNA between individuals; a high concentration of maternal cell free DNA compared to the cffDNA in maternal blood.
New evidence shows that cffDNA test failure rate is higher, fetal fraction (proportion of fetal versus maternal DNA in the maternal blood sample) is lower and PPV for trisomies 18, 13 and SCA is decreased in IVF pregnancies compared to those conceived spontaneously.
Laboratory methods
A number of laboratory methods have been developed for cell-free fetal DNA screening for genetic defects have been developed. The main ones are (1) massively parallel shotgun sequencing (MPSS), (2) targeted massive parallel sequencing (t-MPS) and (3)single nucleotide polymorphism
In genetics and bioinformatics, a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP ; plural SNPs ) is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. Although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in ...
(SNP) based approach.
A maternal peripheral blood sample is taken by venesection at about ten weeks gestation.
Separation of cffDNA
Blood plasma
Blood plasma is a light Amber (color), amber-colored liquid component of blood in which blood cells are absent, but which contains Blood protein, proteins and other constituents of whole blood in Suspension (chemistry), suspension. It makes up ...
is separated from the maternal blood sample using a laboratory centrifuge. The cffDNA is then isolated and purified. A standardized protocol for doing this was written through an evaluation of the scientific literature
Scientific literature encompasses a vast body of academic papers that spans various disciplines within the natural and social sciences. It primarily consists of academic papers that present original empirical research and theoretical ...
. The highest yield in cffDNA extraction was obtained with the "QIAamp DSP Virus Kit".
Addition of formaldehyde to maternal blood samples increases the yield of cffDNA. Formaldehyde stabilizes intact cells, and therefore inhibits the further release of maternal DNA. With the addition of formaldehyde, the percentage of cffDNA recovered from a maternal blood sample varies between 0.32 percent and 40 percent with a mean of 7.7 percent. Without the addition of formaldehyde, the mean percentage of cffDNA recovered has been measured at 20.2 percent. However, other figures vary between 5 and 96 percent.
Recovery of cffDNA may be related to the length of the DNA fragments. Another way to increase the fetal DNA is based on physical length of DNA fragments. Smaller fragments can represent up to seventy percent of the total cell free DNA in the maternal blood sample.
Analysis of cffDNA
In real-time PCR, fluorescent probes are used to monitor the accumulation of amplicons. The reporter fluorescent signal is proportional to the number of amplicons generated. The most appropriate real time PCR protocol is designed according to the particular mutation or genotype to be detected. Point mutations are analysed with qualitative real time PCR with the use ofallele
An allele is a variant of the sequence of nucleotides at a particular location, or Locus (genetics), locus, on a DNA molecule.
Alleles can differ at a single position through Single-nucleotide polymorphism, single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP), ...
specific probes. insertions and deletions are analyzed by dosage measurements using quantitative real time PCR.
cffDNA may be detected by finding paternally inherited DNA sequences via polymerase chain reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to make millions to billions of copies of a specific DNA sample rapidly, allowing scientists to amplify a very small sample of DNA (or a part of it) sufficiently to enable detailed st ...
(PCR).
Quantitative real-time PCR
sex-determining region Y gene (SRY) and Y chromosome short tandem repeat "DYS14" in cffDNA from 511 pregnancies were analyzed using quantitative real-time PCR (RT-qPCR). In 401 of 403 pregnancies where maternal blood was drawn at seven weeks gestation or more, both segments of DNA were found.Nested PCR
The use of nested polymerase chain reaction (nested PCR) was evaluated to determine sex by detecting a Y chromosome specific signal in the cffDNA from maternal plasma. Nested PCR detected 53 of 55 male fetuses. The cffDNA from the plasma of 3 of 25 women with female fetuses contained the Y chromosome-specific signal. The sensitivity of nested PCR in this experiment was 96 percent. The specificity was 88 percent.Digital PCR
Microfluidic devices allow the quantification of cffDNA segments in maternal plasma with accuracy beyond that of real-time PCR.Point mutation
A point mutation is a genetic mutation where a single nucleotide base is changed, inserted or deleted from a DNA or RNA sequence of an organism's genome. Point mutations have a variety of effects on the downstream protein product—consequences ...
s, loss of heterozygosity
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism.
Mos ...
and aneuploidy
Aneuploidy is the presence of an abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell (biology), cell, for example a human somatic (biology), somatic cell having 45 or 47 chromosomes instead of the usual 46. It does not include a difference of one or more plo ...
can be detected in a single PCR step. Digital PCR can differentiate between maternal blood plasma and fetal DNA in a multiplex
Multiplex may refer to:
Science and technology
* Multiplex communication, combining many signals into one transmission circuit or channel
** Multiplex (television), a group of digital television or radio channels that are combined for broadcast
* ...
fashion.
Shotgun sequencing
High throughput shotgun sequencing using tools such as Solexa or Illumina, yields approximately 5 million sequence tags per sample of maternal serum. Aneuploid pregnancies such as trisomy were identified when testing at the fourteenth week of gestation. Fetal whole of genome mapping by parentalhaplotype
A haplotype (haploid genotype) is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent.
Many organisms contain genetic material (DNA) which is inherited from two parents. Normally these organisms have their DNA orga ...
analysis was completed using sequencing of cffDNA from maternal serum. Pregnant females were studied using a 2-plex massively parallel maternal plasma DNA sequencing and trisomy was diagnosed with z-score greater than 3. The sequencing gave sensitivity of 100 percent, specificity of 97.9 percent, a positive predictive value of 96.6 percent and a negative predictive value of 100 percent.
Mass spectrometry
Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization- time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) combined with single-base extension after PCR allows cffDNA detection with single base specificity and single DNA molecule sensitivity. DNA is amplified by PCR. Then, linear amplification with base extension reaction (with a third primer) is designed to anneal to the region upstream from themutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, ...
site. One or two bases are added to the extension primer to produce two extension products from wild-type DNA and mutant DNA. Single base specificity provides advantages over hybridization-based techniques using TaqMan hydrolysis probes. When assessing the technique, no false positives or negatives were found when looking for cffDNA to determine fetal sex in sixteen maternal plasma samples. The sex of ninety-one male foetuses were correctly detected using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. The technique had accuracy, sensitivity and specificity of over 99 percent.
Epigenetic modifications
Differences in gene activation between maternal and fetal DNA can be exploited. Epigenetic modifications (heritable modifications that change gene function without changing DNA sequence) can be used to detect cffDNA. The hypermethylated RASSF1A promoter is a universal fetal marker used to confirm the presence of cffDNA. A technique was described where cffDNA was extracted from maternal plasma and then digested with methylation-sensitive and insensitiverestriction enzyme
A restriction enzyme, restriction endonuclease, REase, ENase or'' restrictase '' is an enzyme that cleaves DNA into fragments at or near specific recognition sites within molecules known as restriction sites. Restriction enzymes are one class o ...
s. Then, real-time PCR analysis of RASSF1A, SRY, and DYS14 was done. The procedure detected 79 out of 90 (88 percent) maternal blood samples where hypermethylated RASSF1A was present.
mRNA
mRNA transcripts from genes expressed in the placenta are detectable in maternal plasma. In this procedure, plasma is centrifuged so an aqueous layer appears. This layer is transferred and from itRNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule that is essential for most biological functions, either by performing the function itself (non-coding RNA) or by forming a template for the production of proteins (messenger RNA). RNA and deoxyrib ...
is extracted. RT-PCR is used to detect a selected expression of RNA. For example, Human placental lactogen (hPL) and beta-hCG mRNA are stable in maternal plasma and can be detected. (Ng et al. 2002). This can help to confirm the presence of cffDNA in maternal plasma.
Applications
Prenatal sex discernment
The analysis of cffDNA from a sample of maternal plasma allows forprenatal sex discernment
Prenatal sex discernment is the prenatal testing for discerning the sex of a fetus before birth.
Methods
Prenatal sex discernment can be performed by preimplantation genetic diagnosis before conception, but this method may not always be classifi ...
. Applications of prenatal sex discernment include:
* Disease testing: Whether the sex of the fetus is male or female allows the determination of the risk of a particular X-linked recessive genetic disorder in a particular pregnancy, especially where the mother is a genetic carrier
A hereditary carrier (genetic carrier or just carrier), is a person or other organism that has inherited a recessive allele for a genetic trait or mutation but usually does not display that trait or show symptoms of the disease. Carriers are, ho ...
of the disorder.
* Preparation, for any sex-dependent aspects of parenting.
* Sex selection, which after preimplantation genetic diagnosis may be performed by selecting only embryos of the preferred sex, or, after post-implantation methods by performing sex-selective abortion depending on the test result and personal preference.
In comparison to obstetric ultrasonography
Obstetric ultrasonography, or prenatal ultrasound, is the use of medical ultrasonography in pregnancy, in which sound waves are used to create real-time visual images of the developing embryo or fetus in the uterus (womb). The procedure is a stand ...
which is unreliable for sex determination in the first trimester and amniocentesis which carries a small risk of miscarriage
Miscarriage, also known in medical terms as a spontaneous abortion, is an end to pregnancy resulting in the loss and expulsion of an embryo or fetus from the womb before it can fetal viability, survive independently. Miscarriage before 6 weeks ...
, sampling of maternal plasma for analysis of cffDNA is without risk. The main targets in the cffDNA analysis are the gene responsible for the sex-determining region Y protein (SRY) on the Y chromosome
The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes in therian mammals and other organisms. Along with the X chromosome, it is part of the XY sex-determination system, in which the Y is the sex-determining chromosome because the presence of the ...
and the DYS14 sequence.
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Incongenital adrenal hyperplasia
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) is a group of Genetic disorder#Autosomal recessive, autosomal recessive disorders characterized by impaired cortisol synthesis. It results from the deficiency of one of the five enzymes required for the Biosy ...
, the adrenal cortex lacks appropriate corticosteroid synthesis, leading to excess adrenal androgens and affects female fetuses. There is an external masculinization of the genitalia in the female fetuses. Mothers of at risk fetuses are given dexamethasone at 6 weeks gestation to suppress pituitary gland
The pituitary gland or hypophysis is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, the pituitary gland is located at the base of the human brain, brain, protruding off the bottom of the hypothalamus. The pituitary gland and the hypothalamus contr ...
release of androgen
An androgen (from Greek ''andr-'', the stem of the word meaning ) is any natural or synthetic steroid hormone that regulates the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors. This includes ...
s.
If analysis of cffDNA obtained from a sample of maternal plasma lacks genetic markers found only on the Y chromosome, it is suggestive of a female fetus. However, it might also indicate a failure of the analysis itself (a false negative result). Paternal genetic polymorphisms and sex-independent markers may be used to detect cffDNA. A high degree of heterozygosity of these markers must be present for this application.
Paternity testing
PrenatalDNA paternity testing
DNA paternity testing uses DNA profiling, DNA profiles to determine whether an individual is the biology, biological parent of another individual. Paternity testing can be essential when the rights and duties of the father are in issue, and a ch ...
is commercially available. The test can be performed at nine weeks gestation.
Single gene disorders
Autosomal dominant and recessive
An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same Morphology (biology), morphology, unlike those in allosome, allosomal (sex chromosome) pairs, which may have different str ...
single gene disorders which have been diagnosed prenatally by analysing paternally inherited DNA include cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disorder inherited in an autosomal recessive manner that impairs the normal clearance of Sputum, mucus from the lungs, which facilitates the colonization and infection of the lungs by bacteria, notably ''Staphy ...
, beta thalassemia, sickle cell anemia
Sickle cell disease (SCD), also simply called sickle cell, is a group of inherited haemoglobin-related blood disorders. The most common type is known as sickle cell anemia. Sickle cell anemia results in an abnormality in the oxygen-carrying ...
, spinal muscular atrophy, and myotonic dystrophy. Prenatal diagnosis of single gene disorders which are due to an autosomal recessive mutation, a maternally inherited autosomal dominant mutation or large sequence mutations that include duplication, expansion or insertion of DNA sequences is more difficult.
In cffDNA, fragments of 200 300 bp length involved in single gene disorders are more difficult to detect.
For example, the autosomal dominant condition, achondroplasia
Achondroplasia is a genetic disorder with an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance whose primary feature is dwarfism. It is the most common cause of dwarfism and affects about 1 in 27,500 people. In those with the condition, the Rhizomeli ...
is caused by the FGFR3 gene point mutation. In two pregnancies with a fetus with achondroplasia was found a paternally inherited G1138A mutation from cffDNA from a maternal plasma sample in one and a G1138A de novo mutation from the other.
In studies of the genetics of Huntington's chorea using qRT-PCR of cffDNA from maternal plasma samples, CAG repeats have been detected at normal levels (17, 20 and 24).cffDNA may also be used to diagnose genetic disorder, single gene disorders. Developments in laboratory processes using cffDNA may allow prenatal diagnosis of aneuploidies such as
trisomy 21
A trisomy is a type of polysomy in which there are three instances of a particular chromosome, instead of the normal two. A trisomy is a type of aneuploidy (an abnormal number of chromosomes).
Description and causes
Most organisms that repro ...
(Down's syndrome) in the fetus.
Hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn
Incompatibility of fetal and maternal RhD antigens is the main cause ofHemolytic disease of the newborn
Hemolytic disease of the newborn, also known as hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn, HDN, HDFN, or erythroblastosis fetalis, is an alloimmune condition that develops in a fetus at or around birth, when the IgG molecules (one of the five ...
. Approximately 15 percent of Caucasian women, 3 to 5 percent of black Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
women and less than 3 percent of Asia
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which ...
n women are RhD negative.
Accurate prenatal diagnosis is important because the disease can be fatal to the newborn and because treatment including intramuscular immunoglobulin
An antibody (Ab) or immunoglobulin (Ig) is a large, Y-shaped protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as pathogenic bacteria, bacteria and viruses, includin ...
(Anti-D) or intravenous immunoglobulin
An antibody (Ab) or immunoglobulin (Ig) is a large, Y-shaped protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as pathogenic bacteria, bacteria and viruses, includin ...
can be administered to mothers at risk.
PCR to detect RHD (gene) gene exon
An exon is any part of a gene that will form a part of the final mature RNA produced by that gene after introns have been removed by RNA splicing. The term ''exon'' refers to both the DNA sequence within a gene and to the corresponding sequence ...
s 5 and 7 from cffDNA obtained from maternal plasma between 9 and 13 weeks gestation gives a high degree of specificity, sensitivity and diagnostic accuracy (>90 percent) when compared to RhD determination from newborn cord blood serum. Similar results were obtained targeting exons 7 and 10. Droplet digital PCR in fetal RhD determination was comparable to a routine real-time PCR technique.
Routine determination of fetal RhD status from cffDNA in maternal serum allows early management of at risk pregnancies while decreasing unnecessary use of Anti-D by over 25 percent.
Aneuploidy
;Sex chromosomes Analysis of maternal serum cffDNA by high-throughput sequencing can detect common fetal sex chromosome aneuploidies such as Turner's syndrome, Klinefelter's syndrome and triple X syndrome but the procedure's positive predictive value is low. ;Trisomy 21
Fetal trisomy of chromosome 21 is the cause of Down's syndrome. This trisomy can be detected by analysis of cffDNA from maternal blood by massively parallel shotgun sequencing (MPSS). Another technique is digital analysis of selected regions (DANSR). Such tests show a sensitivity of about 99% and a specificity of more than 99.9%. Therefore, they cannot be regarded as diagnostic procedures but may be used to confirm a positive maternal screening test such as a first trimester screening or ultrasound markers of the condition.
;Trisomy 13 and 18
Analysis of cffDNA from maternal plasma with MPSS looking for trisomy 13 or 18 is possible
Factors limiting sensitivity and specificity include the levels of cffDNA in the maternal plasma; maternal chromosomes may have mosaicism.
A number of fetal nucleic acid molecules derived from aneuploid chromosomes can be detected including SERPINEB2 mRNA, clad B, hypomethylated SERPINB5 from chromosome 18, placenta-specific 4 (PLAC4), hypermethylated holocarboxylase synthetase (HLCS) and c21orf105 mRNA from chromosome 12. With complete trisomy, the mRNA alleles in maternal plasma isn't the normal 1:1 ratio, but is in fact 2:1. Allelic ratios determined by epigenetic markers can also be used to detect the complete trisomies. Massive parallel sequencing and digital PCR for fetal aneuploidy detection can be used without restriction to fetal-specific nucleic acid molecules. (MPSS) is estimated to have a sensitivity of between 96 and 100%, and a specificity between 94 and 100% for detecting Down syndrome. It can be performed at 10 weeks of gestational age.Noninvasive Prenatal Diagnosis of Fetal Aneuploidy Using Cell-Free Fetal Nucleic Acids in Maternal Blood: Clinical Policy (Effective 05/01/2013)
;Trisomy 21
Fetal trisomy of chromosome 21 is the cause of Down's syndrome. This trisomy can be detected by analysis of cffDNA from maternal blood by massively parallel shotgun sequencing (MPSS). Another technique is digital analysis of selected regions (DANSR). Such tests show a sensitivity of about 99% and a specificity of more than 99.9%. Therefore, they cannot be regarded as diagnostic procedures but may be used to confirm a positive maternal screening test such as a first trimester screening or ultrasound markers of the condition.
;Trisomy 13 and 18
Analysis of cffDNA from maternal plasma with MPSS looking for trisomy 13 or 18 is possible
Factors limiting sensitivity and specificity include the levels of cffDNA in the maternal plasma; maternal chromosomes may have mosaicism.
A number of fetal nucleic acid molecules derived from aneuploid chromosomes can be detected including SERPINEB2 mRNA, clad B, hypomethylated SERPINB5 from chromosome 18, placenta-specific 4 (PLAC4), hypermethylated holocarboxylase synthetase (HLCS) and c21orf105 mRNA from chromosome 12. With complete trisomy, the mRNA alleles in maternal plasma isn't the normal 1:1 ratio, but is in fact 2:1. Allelic ratios determined by epigenetic markers can also be used to detect the complete trisomies. Massive parallel sequencing and digital PCR for fetal aneuploidy detection can be used without restriction to fetal-specific nucleic acid molecules. (MPSS) is estimated to have a sensitivity of between 96 and 100%, and a specificity between 94 and 100% for detecting Down syndrome. It can be performed at 10 weeks of gestational age.Noninvasive Prenatal Diagnosis of Fetal Aneuploidy Using Cell-Free Fetal Nucleic Acids in Maternal Blood: Clinical Policy (Effective 05/01/2013)from Oxford Health Plans One study in the United States estimated a false positive rate of 0.3% and a positive predictive value of 80% when using cffDNA to detect Down syndrome.. A recent study in th
New England Journal of Medicine
demonstrated the feasibility of usin
NIPT
in a low risk population.
Preeclampsia
Preeclampsia is a complex condition of pregnancy involvinghypertension
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a Chronic condition, long-term Disease, medical condition in which the blood pressure in the artery, arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms i ...
and proteinuria usually after 20 weeks gestation. It is associated with poor cytotrophoblastic invasion of the myometrium. Onset of the condition between 20 and 34 weeks gestation, is considered "early". Maternal plasma samples in pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia have significantly higher levels of cffDNA that those in normal pregnancies. This holds true for early onset preeclampsia.
History
In 1997, Hong Kong molecular biologist Dennis Lo and his team first employed the Y-PCR assay to identify fetal Y chromosome sequences (because Y-specific sequences are genetic sequences of the fetus not in the maternal genome) in maternal plasma samples. For this groundbreaking work, Lo was honored with the 2022 Lasker DeBakey Clinical Medical Research Award.Future perspectives
New generation sequencing may be used to yield a whole genome sequence from cffDNA. This raises ethical questions. However, the utility of the procedure may increase as clear associations between specific genetic variants and disease states are discovered.See also
* Microchimerism * Quad test * Triple testReferences
{{reflist, 30em Blood DNA Obstetrical procedures