Celestial Poles on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The north and south celestial poles are the two points in the sky where
The north and south celestial poles are the two points in the sky where
 The north celestial pole currently is within one degree of the bright star
The north celestial pole currently is within one degree of the bright star
Visual representation of finding Polaris using the Big Dipper
{{Portal bar, Astronomy, Stars, Spaceflight, Outer space, Solar System Pole Articles containing video clips Ursa Minor Octans
 The north and south celestial poles are the two points in the sky where
The north and south celestial poles are the two points in the sky where Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
's axis of rotation
Rotation or rotational/rotary motion is the circular movement of an object around a central line, known as an ''axis of rotation''. A plane figure can rotate in either a clockwise or counterclockwise sense around a perpendicular axis intersect ...
, indefinitely extended, intersects the celestial sphere
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large radius and is concentric to Earth. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphere, ...
. The north and south celestial poles appear permanently directly overhead to observers at Earth's North Pole
The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is the point in the Northern Hemisphere where the Earth's rotation, Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface. It is called the True North Pole to distingu ...
and South Pole
The South Pole, also known as the Geographic South Pole or Terrestrial South Pole, is the point in the Southern Hemisphere where the Earth's rotation, Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface. It is called the True South Pole to distinguish ...
, respectively. As Earth spins on its axis, the two celestial poles remain fixed in the sky, and all other celestial points appear to rotate around them, completing one circuit per day (strictly, per sidereal day
Sidereal time ("sidereal" pronounced ) is a system of timekeeping used especially by astronomers. Using sidereal time and the celestial coordinate system, it is easy to locate the positions of celestial objects in the night sky. Sidereal t ...
).
The celestial poles are also the poles of the celestial equatorial coordinate system
The equatorial coordinate system is a celestial coordinate system widely used to specify the positions of astronomical object, celestial objects. It may be implemented in spherical coordinate system, spherical or Cartesian coordinate system, rect ...
, meaning they have declination
In astronomy, declination (abbreviated dec; symbol ''δ'') is one of the two angles that locate a point on the celestial sphere in the equatorial coordinate system, the other being hour angle. The declination angle is measured north (positive) or ...
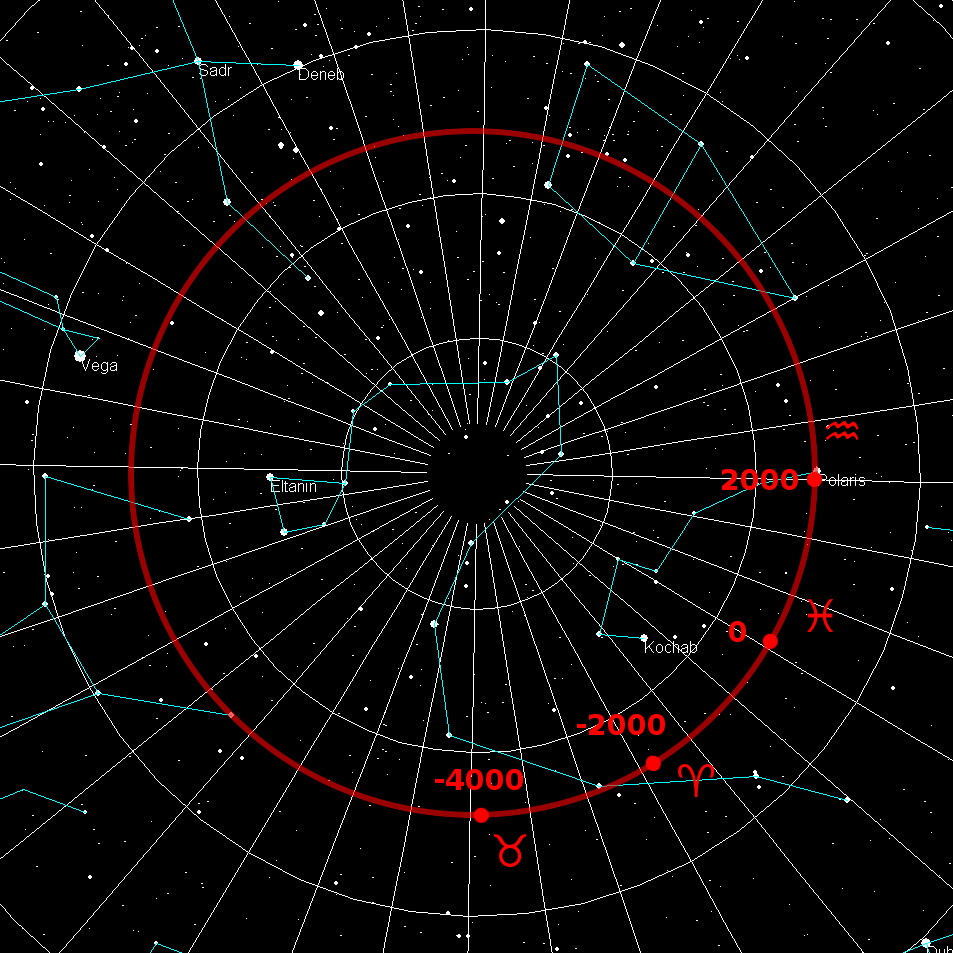
s of +90 degrees and −90 degrees (for the north and south celestial poles, respectively). Despite their apparently fixed positions, the celestial poles in the long term do not actually remain permanently fixed against the background of the stars. Because of a phenomenon known as the precession of the equinoxes
In astronomy, axial precession is a gravity-induced, slow, and continuous change in the orientation of an astronomical body's Rotation around a fixed axis, rotational axis. In the absence of precession, the astronomical body's orbit would show ...
, the poles trace out circles on the celestial sphere, with a period of about 25,700 years. The Earth's axis is also subject to other complex motions which cause the celestial poles to shift slightly over cycles of varying lengths (see nutation
Nutation () is a rocking, swaying, or nodding motion in the axis of rotation of a largely axially symmetric object, such as a gyroscope, planet, or bullet in flight, or as an intended behaviour of a mechanism. In an appropriate reference fra ...
, polar motion
Polar motion of the Earth is the motion of the Earth's rotation, Earth's rotational axis relative to its Earth's crust, crust. This is measured with respect to a reference frame in which the solid Earth is fixed (a so-called ''Earth-centered, Ea ...
and axial tilt
In astronomy, axial tilt, also known as obliquity, is the angle between an object's rotational axis and its orbital axis, which is the line perpendicular to its orbital plane; equivalently, it is the angle between its equatorial plane and orbita ...
). Finally, over very long periods the positions of the stars themselves change, because of the stars' proper motion
Proper motion is the astrometric measure of changes in the apparent places of stars or other celestial objects as they move relative to the center of mass of the Solar System. It is measured relative to the distant stars or a stable referenc ...
s. To take into account such movement, celestial pole definitions come with an epoch
In chronology and periodization, an epoch or reference epoch is an instant in time chosen as the origin of a particular calendar era. The "epoch" serves as a reference point from which time is measured.
The moment of epoch is usually decided b ...
to specify the date of the rotation axis; J2000.0 is the current standard.
An analogous concept applies to other planets: a planet's celestial poles are the points in the sky where the projection of the planet's axis of rotation intersects the celestial sphere. These points vary because different planets' axes are oriented differently (the apparent positions of the stars also change slightly because of parallax
Parallax is a displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object viewed along two different sightline, lines of sight and is measured by the angle or half-angle of inclination between those two lines. Due to perspective (graphica ...
effects).
Finding the north celestial pole
 The north celestial pole currently is within one degree of the bright star
The north celestial pole currently is within one degree of the bright star Polaris
Polaris is a star in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Minor. It is designated α Ursae Minoris (Latinisation of names, Latinized to ''Alpha Ursae Minoris'') and is commonly called the North Star or Pole Star. With an ...
(named from the Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
''stella polaris'', meaning "pole star
A pole star is a visible star that is approximately aligned with the axis of rotation of an astronomical body; that is, a star whose apparent position is close to one of the celestial poles. On Earth, a pole star would lie directly overhead when ...
"). This makes Polaris, colloquially known as the "North Star", useful for navigation in the Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined by humans as being in the same celestial sphere, celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the Solar ...
: not only is it always above the north point of the horizon, but its altitude angle
The horizontal coordinate system is a celestial coordinate system that uses the observer's local horizon as the fundamental plane to define two angles of a spherical coordinate system: altitude and ''azimuth''.
Therefore, the horizontal coordin ...
is always (nearly) equal to the observer's geographic latitude
In geography, latitude is a geographic coordinate system, geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from −90° at t ...
(though it can, of course, only be seen from locations in the Northern Hemisphere).
Polaris is near the north celestial pole for only a small fraction of the 25,700-year precession cycle. It will remain a good approximation for about 1,000 years, by which time the pole will have moved closer to Alrai (Gamma Cephei
Gamma Cephei (γ Cephei, abbreviated Gamma Cep, γ Cep) is a binary star system approximately 45 light-years away in the northern constellation of Cepheus (constellation), Cepheus. The primary (designated Gamma Cephei A, officially name ...
). In about 5,500 years, the pole will have moved near the position of the star Alderamin
Alpha Cephei (α Cephei, abbreviated Alpha Cep, α Cep), officially named Alderamin , is a second magnitude star in the constellation of Cepheus near the northern pole. The star is relatively close to Earth at 49 light years (''ly'') ...
(Alpha Cephei), and in 12,000 years, Vega
Vega is the brightest star in the northern constellation of Lyra. It has the Bayer designation α Lyrae, which is Latinised to Alpha Lyrae and abbreviated Alpha Lyr or α Lyr. This star is relatively close at only from the Sun, and ...
(Alpha Lyrae) will become the "North Star", though it will be about six degrees from the true north celestial pole.
To find Polaris, from a point in the Northern Hemisphere, face north and locate the Big Dipper
The Big Dipper (American English, US, Canadian English, Canada) or the Plough (British English, UK, Hiberno-English, Ireland) is an asterism (astronomy), asterism consisting of seven bright stars of the constellation Ursa Major; six of them ar ...
(Plough) and Little Dipper
Ursa Minor (, contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation located in the far northern sky. As with the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the North Amer ...
asterisms. Looking at the "cup" part of the Big Dipper, imagine that the two stars at the outside edge of the cup form a line pointing upward out of the cup. This line points directly at the star at the tip of the Little Dipper's handle. That star is Polaris, the North Star.
Finding the south celestial pole
The south celestial pole is visible only from the Southern Hemisphere. It lies in the dimconstellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The first constellati ...
Octans
Octans is a faint constellation located in the deep southern celestial hemisphere, Southern Sky. Its name is Latin for the eighth part of a circle, but it is named after the octant (instrument), octant, a navigational instrument. Devised by kingd ...
, the Octant. Sigma Octantis is identified as the south pole star, more than one degree away from the pole, but with a magnitude of 5.5 it is barely visible on a clear night.
Method one: The Southern Cross
The south celestial pole can be located from theSouthern Cross
CRUX is a lightweight x86-64 Linux distribution targeted at experienced Linux users and delivered by a tar.gz-based package system with BSD-style initscripts. It is not based on any other Linux distribution. It also utilizes a ports system to ...
(Crux) and its two "pointer" stars α Centauri and β Centauri. Draw an imaginary line from γ Crucis
Gacrux is the third-brightest star in the southern constellation of Crux, the Southern Cross. It has the Bayer designation Gamma Crucis, which is Latinised from γ Crucis and abbreviated Gamma Cru or γ Cru. With an apparent visual magn ...
to α Crucis
Acrux is the brightest star in the southern constellation of Crux. It has the Bayer designation α Crucis, which is Latinisation of names, Latinised to Alpha Crucis and abbreviated Alpha Cru or α Cru. With a combined visual magnitude o ...
—the two stars at the extreme ends of the long axis of the cross—and follow this line through the sky. Either go four-and-a-half times the distance of the long axis in the direction the narrow end of the cross points, or join the two pointer stars with a line, divide this line in half, then at right angles draw another imaginary line through the sky until it meets the line from the Southern Cross. This point is 5 or 6 degrees from the south celestial pole. Very few bright stars of importance lie between Crux and the pole itself, although the constellation Musca is fairly easily recognised immediately beneath Crux.
Method two: Canopus and Achernar
The second method usesCanopus
Canopus is the brightest star in the southern constellation of Carina (constellation), Carina and the list of brightest stars, second-brightest star in the night sky. It is also Bayer designation, designated α Carinae, which is Rom ...
(the second-brightest star in the sky) and Achernar
Achernar is the brightest star in the constellation of Eridanus and the ninth-brightest in the night sky. It has the Bayer designation Alpha Eridani, which is Latinized from α Eridani and abbreviated Alpha Eri or α Eri. The name Ac ...
. Make a large equilateral triangle
An equilateral triangle is a triangle in which all three sides have the same length, and all three angles are equal. Because of these properties, the equilateral triangle is a regular polygon, occasionally known as the regular triangle. It is the ...
using these stars for two of the corners. But where should the third corner go? It could be on either side of the line connecting Achernar and Canopus, and the wrong side will not lead to the pole. To find the correct side, imagine that Archernar and Canopus are both points on the circumference of a circle. The third corner of the equilateral triangle will also be on this circle. The corner should be placed clockwise from Achernar and anticlockwise from Canopus. The third imaginary corner will be the south celestial pole. If the opposite is done, the point will land in the middle of Eridanus, which isn't at the pole. If Canopus has not yet risen, the second-magnitude Alpha Pavonis can also be used to form the triangle with Achernar and the pole. In this case, go anticlockwise from Achernar instead of clockwise, form the triangle with Canopus, and the third point, the pole, will reveal itself. The wrong way will lead to Aquarius, which is very far away from the celestial pole.
Method three: The Magellanic Clouds
The third method is best for moonless and clear nights, as it uses two faint "clouds" in the Southern Sky. These are marked in astronomy books as theLarge
Large means of great size.
Large may also refer to:
Mathematics
* Arbitrarily large, a phrase in mathematics
* Large cardinal, a property of certain transfinite numbers
* Large category, a category with a proper class of objects and morphisms (o ...
and Small Magellanic Cloud
The Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC) is a dwarf galaxy near the Milky Way. Classified as a dwarf irregular galaxy, the SMC has a D25 isophotal diameter of about , and contains several hundred million stars. It has a total mass of approximately 7 bill ...
s (the LMC and the SMC). These "clouds" are actually dwarf galaxies near the Milky Way
The Milky Way or Milky Way Galaxy is the galaxy that includes the Solar System, with the name describing the #Appearance, galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars in other arms of the galax ...
. Make an equilateral triangle, the third point of which is the south celestial pole. Like before, the SMC, LMC, and the pole will all be points on an equilateral triangle on an imaginary circle. The pole should be placed clockwise from the SMC and anticlockwise from the LMC. Going in the wrong direction will land you in the constellation of Horologium instead.
Method four: Sirius and Canopus
A line fromSirius
Sirius is the brightest star in the night sky. Its name is derived from the Greek word (Latin script: ), meaning 'glowing' or 'scorching'. The star is designated Canis Majoris, Latinized to Alpha Canis Majoris, and abbr ...
, the brightest star in the sky, through Canopus, the second-brightest, continued for the same distance lands within a couple of degrees of the pole. In other words, Canopus is halfway between Sirius and the pole.
See also
*Celestial sphere
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large radius and is concentric to Earth. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphere, ...
*Celestial equator
The celestial equator is the great circle of the imaginary celestial sphere on the same plane as the equator of Earth. By extension, it is also a plane of reference in the equatorial coordinate system. Due to Earth's axial tilt, the celestial ...
*Circumpolar star
A circumpolar star is a star that, as viewed from a given latitude on Earth, never sets below the horizon due to its apparent proximity to one of the celestial poles. Circumpolar stars are therefore visible from said location toward the nearest p ...
*Orbital pole
An orbital pole is either point at the ends of the orbital normal, an imaginary line segment that runs through a Focus (geometry), focus of an orbit (of a revolving body like a planet, natural satellite, moon or satellite) and is perpendicular ...
*Polaris
Polaris is a star in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Minor. It is designated α Ursae Minoris (Latinisation of names, Latinized to ''Alpha Ursae Minoris'') and is commonly called the North Star or Pole Star. With an ...
*Pole star
A pole star is a visible star that is approximately aligned with the axis of rotation of an astronomical body; that is, a star whose apparent position is close to one of the celestial poles. On Earth, a pole star would lie directly overhead when ...
*Poles of astronomical bodies
The poles of astronomical bodies are determined based on their axis of rotation in relation to the celestial poles of the celestial sphere. Astronomical bodies include stars, planets, dwarf planets and small Solar System bodies such as comets a ...
References
External links
Visual representation of finding Polaris using the Big Dipper
{{Portal bar, Astronomy, Stars, Spaceflight, Outer space, Solar System Pole Articles containing video clips Ursa Minor Octans