Caxcan on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Caxcan are an
The Caxcan are an
 The Caxcan are an
The Caxcan are an ethnic group
An ethnicity or ethnic group is a group of people with shared attributes, which they collectively believe to have, and long-term endogamy. Ethnicities share attributes like language, culture, common sets of ancestry, traditions, society, re ...
who are Indigenous to western and north-central Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar ...
, particularly the regions corresponding to modern-day Zacatecas
Zacatecas, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Zacatecas, is one of the Political divisions of Mexico, 31 states of Mexico. It is divided into Municipalities of Zacatecas, 58 municipalities and its capital city is Zacatecas City, Zacatec ...
, southern Durango
Durango, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Durango, is one of the 31 states which make up the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 Federal Entities of Mexico, situated in the northwest portion of the country. With a population of 1,832,650 ...
, Jalisco
Jalisco, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Jalisco, is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. It is located in western Mexico and is bordered by s ...
, Colima
Colima, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Colima, is among the 31 states that make up the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It shares its name with its capital and main city, Colima.
Colima is a small state of western Mexico on the cen ...
, Aguascalientes
Aguascalientes, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Aguascalientes, is one of the 32 states which comprise the Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. At 22°N and with an average altitude of above sea level it is pre ...
, Nayarit
Nayarit, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Nayarit, is one of the 31 states that, along with Mexico City, comprise the Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in Municipalities of Nayarit, 20 municipalit ...
. The Caxcan language is most often documented as an ancient variant of Nahuatl
Nahuatl ( ; ), Aztec, or Mexicano is a language or, by some definitions, a group of languages of the Uto-Aztecan language family. Varieties of Nahuatl are spoken by about Nahuas, most of whom live mainly in Central Mexico and have smaller popul ...
and is a member of the Uto-Aztecan language family. The last generation of natively fluent Caxcan language speakers came to an end in the 1890s. Despite this having long been conflated by anthropologists with an extinction of the Caxcan people themselves, much of Caxcan culture has persisted via oral tradition
Oral tradition, or oral lore, is a form of human communication in which knowledge, art, ideas and culture are received, preserved, and transmitted orally from one generation to another.Jan Vansina, Vansina, Jan: ''Oral Tradition as History'' (19 ...
. There is currently an ongoing revitalization of Caxcan language, scholarship, and culture.
History
Pre-1550
The Caxcan were a partlynomadic
Nomads are communities without fixed habitation who regularly move to and from areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the population of nomadic pa ...
, partly sedentary people. Under their leader, Tenamaztle, the Caxcan were allied with the Zacatecos against the Spaniards
Spaniards, or Spanish people, are a Romance-speaking ethnic group native to the Iberian Peninsula, primarily associated with the modern nation-state of Spain. Genetically and ethnolinguistically, Spaniards belong to the broader Southern a ...
during the Mixtón Rebellion in 1540-42. During the rebellion, they were described as "the heart and the center of the Indian Rebellion". After the rebellion, they were a constant target of the Zacatecos and Guachichiles due to their ceasefire agreement with the Spaniards
Spaniards, or Spanish people, are a Romance-speaking ethnic group native to the Iberian Peninsula, primarily associated with the modern nation-state of Spain. Genetically and ethnolinguistically, Spaniards belong to the broader Southern a ...
. Their principal religious and population centers were at Teul, Tlaltenango, Juchipila, and Teocaltiche
Teocaltiche ( "place near the temple") is a town and municipality in the central-western Mexican state of Jalisco. It is located in the northeastern highlands region of Jalisco, commonly referred to in Spanish as "Los Altos de Jalisco". The grassh ...
.
Over time, the Caxcanes lost their culture due to warfare, disease, and marriage to non-Caxcanes. Also, most of the Caxcanes were sent into slavery by the Spanish to work in silver mines. During the colonial period, many Spanish (and some Basque settlers) had intermarried, or had relations, with the Caxcanes making many Caxcan descendants Mestizos. The allied tribes and Mestizos settled the Caxcan lands in Zacatecas and Jalisco.
Their elected rulers were called tlatoani. Caxcan society was divided up into several different city-states.
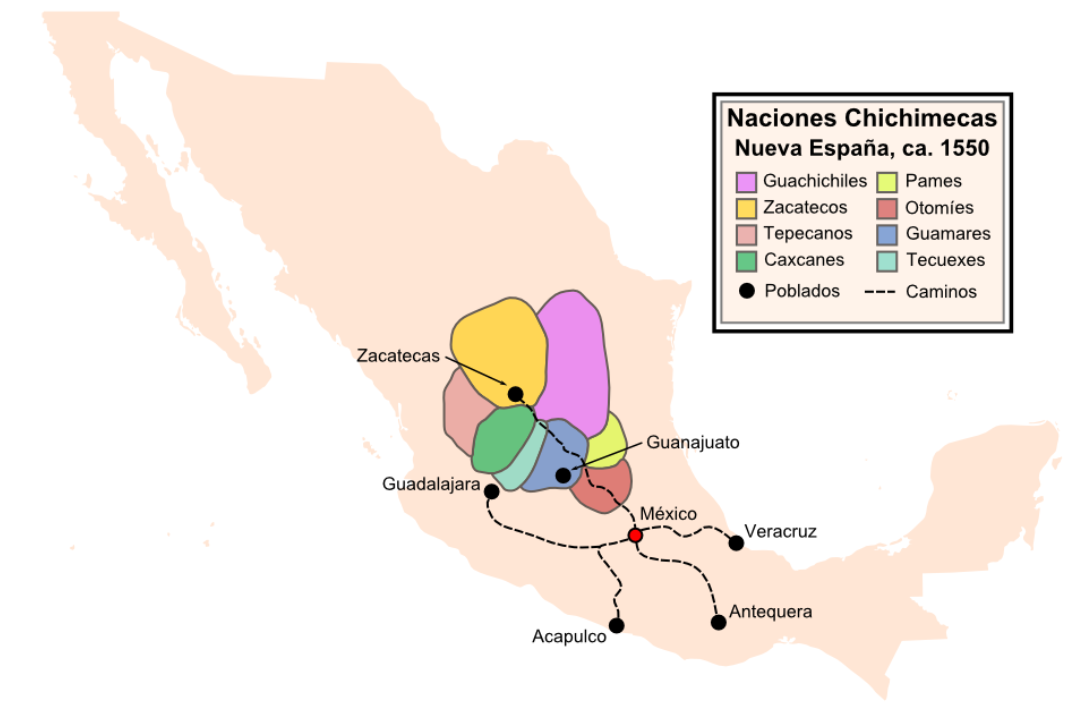
The Chichimeca War (1550-1590)
The Chichimeca War (1550–1590) was a military conflict waged between Spanish colonizers and their Indian allies against a confederation of Chichimeca Indians. It was the longest and most expensive conflict between Spaniards and the indigenous peoples ofNew Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( ; Nahuatl: ''Yankwik Kaxtillan Birreiyotl''), originally the Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain. It was one of several ...
in the history of the colony.
The Chichimeca wars began eight years after the Mixtón Rebellion (1540–1542). It can be considered as a continuation of that rebellion as the fighting did not come to a halt in the intervening years. Unlike in the Mixtón rebellion, the Caxcanes were now allied with the Spanish. The war was fought in the Bajío region known as La Gran Chichimeca
La Gran Chichimeca was a term used by the Spanish ''conquistadores'' of the 16th century to refer to an area of the northern central Mexican ''altiplano'' (plateau), a territory which today is encompassed by the modern Mexican states of Jalisco, ...
, specifically in the Mexican state
A Mexican State (), officially the Free and Sovereign State (), is a constituent federative entity of Mexico according to the Constitution of Mexico. Currently there are 31 states, each with its own constitution, government, state governor, a ...
s of Zacatecas
Zacatecas, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Zacatecas, is one of the Political divisions of Mexico, 31 states of Mexico. It is divided into Municipalities of Zacatecas, 58 municipalities and its capital city is Zacatecas City, Zacatec ...
, Guanajuato
Guanajuato, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Guanajuato, is one of the 32 states that make up the Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into Municipalities of Guanajuato, 46 municipalities and its cap ...
, Aguascalientes
Aguascalientes, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Aguascalientes, is one of the 32 states which comprise the Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. At 22°N and with an average altitude of above sea level it is pre ...
, Jalisco
Jalisco, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Jalisco, is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. It is located in western Mexico and is bordered by s ...
, and San Luis Potosi.
1900-2000
The Council of the Caxcan indigenous people was formed in the 1920s by Juana Belén Gutiérrez de Mendoza, a Caxcan from Durango.Pouwels, Joel Bollinger. Political Journalism by Mexican Women During the Age of Revolution 1876-1940. New York: Edwin Mellen P, 2006] She also published ''Alto!'', a book which stressed Mexican Nationalism through indigenous roots and, even after the alleged extinction of the Caxcan people, is quoted as saying "We do not recognize the right of any race to impose its civilization upon us" as a way to promote indigeneity.2000-Present
Caxcan people continue to live in Zacatecas and in diaspora. They are currently attempting to regain legal access to their sacred mountain, Tlachialoyantepec (El Cerro de las Ventanas).Notes
{{DEFAULTSORT:Caxcan Indigenous peoples of Aridoamerica Indigenous peoples in Mexico History of Zacatecas Uto-Aztecan peoples