Caulkin on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

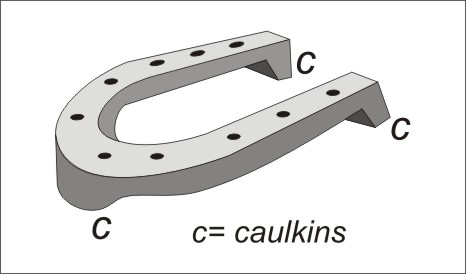
 A caulkin is a blunt projection on a
A caulkin is a blunt projection on a

Historical development of the horseshoe
1891

horseshoe
A horseshoe is a product designed to protect a horse hoof from wear. Shoes are attached on the palmar surface (ground side) of the hooves, usually nailed through the insensitive hoof wall that is anatomically akin to the human toenail, altho ...
or oxshoe that is often forged, welded or brazed onto the shoe. The term may also refer to traction devices screwed into the bottom of a horseshoe, also commonly called shoe studs or screw-in calks. These are usually a blunt spiked cleat, usually placed at the sides of the shoe.
Use
Caulkins or studs improve a horse's balance and grip over uneven or slippery terrain, allowing the animal to move better and jump more confidently in poor footing. Screw in calks are most often seen in speed sports, such aseventing
Eventing (also known as three-day eventing or horse trials) is an equestrian event where the same horse and rider combination compete against other competitors across the three disciplines of dressage, cross-country, and show jumping. This ...
, polo
Polo is a stick and ball game that is played on horseback as a traditional field sport. It is one of the world's oldest known team sports, having been adopted in the Western world from the game of Chovgan (), which originated in ancient ...
, and show jumping
Show jumping is a part of a group of English riding equestrian events that also includes eventing, hunters, and equitation. Jumping classes are commonly seen at horse shows throughout the world, including the Olympics. Sometimes shows ar ...
, although they are sometimes used for dressage
Dressage ( or ; , most commonly translated as "training") is a form of horse riding performed in exhibition and competition, as well as an art sometimes pursued solely for the sake of mastery. As an equestrianism, equestrian sport defined by th ...
. Forged caulks of various styles are more often seen on race horses and working animals
Working may refer to:
* Work (human activity), intentional activity people perform to support themselves, others, or the community
Arts and media
* ''Working'' (musical), a 1978 musical
* ''Working'' (TV series), an American sitcom
* ''Workin ...
such as draft horse
A draft horse (US) or draught horse (UK), also known as dray horse, carthorse, work horse or heavy horse, is a large horse bred to be a working animal hauling freight and doing heavy agricultural tasks such as plowing. There are a number o ...
s and some packhorse
A packhorse, pack horse, or sumpter refers to a horse, mule, donkey, or pony used to carry goods on its back, usually in sidebags or panniers. Typically packhorses are used to cross difficult terrain, where the absence of roads prevents the use of ...
s and trail horses, though in some areas they are still seen on field hunter
A field hunter, or a fox hunter, is a type of horse used in the hunt field for fox hunting and stag hunting.
Characteristics
The field hunter may be of any breed, but should possess stamina, a level head, and bravery. The horse should have a ...
s and other riding horses that have to work in all weather and require extra traction, such as police horses.
Designs

Permanent designs
Traditionally, the prongs of an elongated horseshoe (commonly not more than ) have tips bent at anacute angle
In Euclidean geometry, an angle can refer to a number of concepts relating to the intersection of two straight lines at a point. Formally, an angle is a figure lying in a plane formed by two rays, called the '' sides'' of the angle, sharing ...
opposite to the surface attached to the horses' hoof
The hoof (: hooves) is the tip of a toe of an ungulate mammal, which is covered and strengthened with a thick and horny keratin covering. Artiodactyls are even-toed ungulates, species whose feet have an even number of digits; the ruminants with ...
. Traditionally, a farrier
A farrier is a specialist in equine hoof care, including the trimming and balancing of horses' hooves and the placing of shoes on their hooves, if necessary. A farrier combines some blacksmith's skills (fabricating, adapting, and adju ...
employs a forge
A forge is a type of hearth used for heating metals, or the workplace (smithy) where such a hearth is located. The forge is used by the smith to heat a piece of metal to a temperature at which it becomes easier to shape by forging, or to the ...
in hot-shoeing to heat the two heel prongs to red hot and bends them by hammering prongs over a right-angle to bend into an acute angle
In Euclidean geometry, an angle can refer to a number of concepts relating to the intersection of two straight lines at a point. Formally, an angle is a figure lying in a plane formed by two rays, called the '' sides'' of the angle, sharing ...
. Occasionally, another caulkin is on the toe of the shoe and integrally formed in the initial forging process.
For a horseshoe built as a concave caulk and wedge shoe, the 2 prongs differ: one prong ends with a caulkin, and the other prong ends with a wedge (with both facing downward to the ground). That caulk/wedge horseshoe is a traditional British hunting shoe, and it has been used to provide the horse with a sure-footed grip when working at a fast pace over uneven ground. The shapes of the caulkin and the wedge have been designed to provide hoof traction, meanwhile ensuring the horse's safety is not compromised. The caulk/wedge horseshoe design has been recognised by the Worshipful Company of Farriers as being an appropriate specimen horseshoe to be used for the diploma exam.
Another way caulkins are applied is for borium to be brazed onto the surface of the shoe. Usually borium is placed at the heels and toe, either in small knobs for maximum grip, or in small rough patches for extra traction and to prevent wear on the shoe.
Screw-in calks
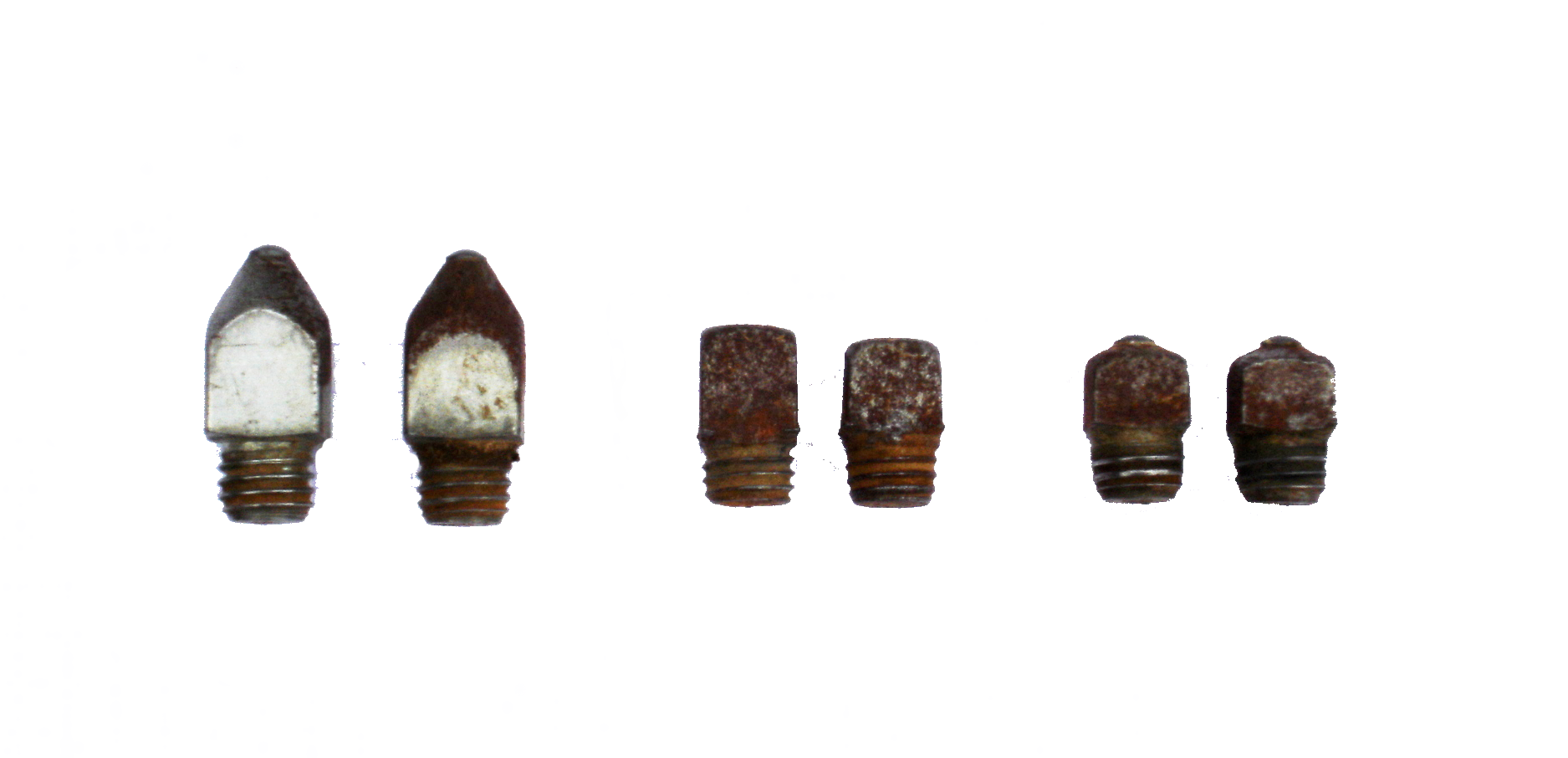
For use of screw-in calks or studs, horseshoes are "tapped", or drilled, on either heel of the shoe, so that different studs may be applied as needed and changed according to the footing conditions and the type of work performed by the horse. Therefore, a horse may have a maximum of 8 studs (2 per foot). Studs come in several sizes and types. Screw-in calks or studs are popular in sport competition because they can be changed to adapt to different terrain. However, the size and design of stud must be carefully selected, as the wrong stud will be useless and can damage the horse's legs. Too little traction, and the horse may slip and possibly fall. Too much, and the horse is jarred, as his feet cannot naturally slip (which is a shock-absorption mechanism). Additionally, the more stud used, the greater chance the shoe may be pulled off. Usually, if there is doubt, it is considered best to slightly under-stud. In general, the faster the pace, the larger the stud will be used. Therefore, small studs are used for dressage and lower-level jumping or eventing, and larger studs are used for polo and upper-level eventing. Studs with more of a point are used for hard ground, and those that have more circumference are used in "heavier" footing, such as thick mud. A hoof pick or horseshoe nail can help remove the plug prior to insertion of a screw-in stud. A special instrument called a T-tap is used to clean out the stud holes before the stud is screwed in, or it can be used to re-tap the stud hole if the threads are damaged. Additionally, a small metal brush can be used to help clean threads which are especially dirty. A wrench is used to tighten or loosen the studs.
Frost nails
Frost nails can be used in the place of studs for a few different reasons. Originally they were created to be used in icy conditions for extra traction and stability. However, they can also be used in various equine competitions for better traction on footing such as wet and slippery conditions. The head of the nail is sharper than regular nails and is wedge shaped.Safety
Caulkins forged into the shoe which are not removable pose an increased risk of injury to handler or horse should the horse step on or kick a person, itself, or another animal. Whenstable
A stable is a building in which working animals are kept, especially horses or oxen. The building is usually divided into stalls, and may include storage for equipment and feed.
Styles
There are many different types of stables in use tod ...
d, animals wearing caulkins need extra bedding to avoid abrasion when lying down and for protection while moving about in a confined area. When working, leg protection in the form of bell boots and splint boots or exercise bandages may minimize the risk of injury.
Screw-in studs are often longer and sharper than permanent caulkins and thus are removed when the horse is not working. The hole for the stud is plugged with cotton, rubber plugs, or a stud blank so dirt does not ruin the threads of the hole. Due to risk of injury, horses are not shipped in studs or left unattended with studs screwed in.
Pointed studs, such as grass studs or pointed bullets are generally placed only on the outside of the shoe, so the horse is less likely to cut himself should his foot hit one of his legs. Road stud can be used on the inside or outside of a shoe. However, the shoe should have some stud on the inside of the shoe; without it, there will be a twisting motion on the foot, which can cause a loss of shoe, and possibly strain the legs. Most riders place smaller studs on the front feet, because the horse's hind legs are stronger and generally require more traction.
See also
*Farrier
A farrier is a specialist in equine hoof care, including the trimming and balancing of horses' hooves and the placing of shoes on their hooves, if necessary. A farrier combines some blacksmith's skills (fabricating, adapting, and adju ...
* Horse hoof
A horse hoof is the lower extremity of each leg of a horse, the part that makes contact with the ground and carries the weight of the animal. It is both hard and flexible. It is a complex structure surrounding the distal Phalanx bones, phalanx o ...
Notes
References
More reading
* * *External links
Historical development of the horseshoe
1891
Scientific American
''Scientific American'', informally abbreviated ''SciAm'' or sometimes ''SA'', is an American popular science magazine. Many scientists, including Albert Einstein and Nikola Tesla, have contributed articles to it, with more than 150 Nobel Pri ...
article from Project Gutenberg
Project Gutenberg (PG) is a volunteer effort to digitize and archive cultural works, as well as to "encourage the creation and distribution of eBooks."
It was founded in 1971 by American writer Michael S. Hart and is the oldest digital li ...
{{Horse equipment
Equine hoof
Horseshoes
Farriery
bg:Подкова
cs:Podkova
da:Hestesko
de:Hufeisen
es:Herradura
eo:Hufumo
eu:Perra
fr:Fer à cheval
gd:Crudha
id:Sepatu kuda
it:Ferro di cavallo
nl:Hoefijzer
ja:蹄鉄
pt:Ferradura
ru:Подкова
simple:Horseshoe
sr:Потковица
fi:Hevosenkenkä
sv:Hästsko
zh:马蹄铁