Cascadia subduction zone on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Cascadia subduction zone is a convergent plate boundary, about off the Pacific coast of North America, that stretches from northern

 During low tide one day in March 1986, paleogeologist Brian Atwater dug along Neah Bay with a ''nejiri gama'', a small hand hoe. Under a top layer of sand, he uncovered a distinct plant— arrowgrass—that had grown in a layer of marsh soil. This finding was evidence that the ground had suddenly sunk under sea level, causing saltwater to kill the vegetation. The event had happened so quickly that the top layer of sand sealed away the air, thus preserving centuries-old plants.
In 1987, Atwater mounted another expedition paddling up the Copalis River with Dr. David Yamaguchi, who was then studying the eruptions of Mount St. Helens. The pair happened upon a section of "
During low tide one day in March 1986, paleogeologist Brian Atwater dug along Neah Bay with a ''nejiri gama'', a small hand hoe. Under a top layer of sand, he uncovered a distinct plant— arrowgrass—that had grown in a layer of marsh soil. This finding was evidence that the ground had suddenly sunk under sea level, causing saltwater to kill the vegetation. The event had happened so quickly that the top layer of sand sealed away the air, thus preserving centuries-old plants.
In 1987, Atwater mounted another expedition paddling up the Copalis River with Dr. David Yamaguchi, who was then studying the eruptions of Mount St. Helens. The pair happened upon a section of "
 The
The
"Cascadia Peril '09"
at dailywireless.org
9.0 Shakemap Scenario
The Really Big One
– University of California Television
Great Earthquakes of the Pacific Northwest
– Central Washington University
Toast, tsunamis and the really big one , Chris Goldfinger , TEDxMtHood
– TEDx {{Authority control Cascade Volcanoes Geologic provinces of California Geology of British Columbia Geology of Oregon Geology of Washington (state) Natural hazards in British Columbia Seismic zones of British Columbia Subduction zones
Vancouver Island
Vancouver Island is an island in the northeastern Pacific Ocean and part of the Canadian province of British Columbia. The island is in length, in width at its widest point, and in total area, while are of land. The island is the largest ...
in Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
to Northern California
Northern California (commonly shortened to NorCal) is a geocultural region that comprises the northern portion of the U.S. state of California, spanning the northernmost 48 of the state's List of counties in California, 58 counties. Northern Ca ...
in the United States. It is capable of producing 9.0+ magnitude
Magnitude may refer to:
Mathematics
*Euclidean vector, a quantity defined by both its magnitude and its direction
*Magnitude (mathematics), the relative size of an object
*Norm (mathematics), a term for the size or length of a vector
*Order of ...
earthquakes and tsunami
A tsunami ( ; from , ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and underwater explosions (including detonations, ...
s that could reach 30 m (100 ft) high. The Oregon Department of Emergency Management estimates shaking would last 5–7 minutes along the coast, with strength and intensity decreasing further from the epicenter. It is a very long, sloping subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere and some continental lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at the convergent boundaries between tectonic plates. Where one tectonic plate converges with a second p ...
zone where the Explorer
Exploration is the process of exploring, an activity which has some Expectation (epistemic), expectation of Discovery (observation), discovery. Organised exploration is largely a human activity, but exploratory activity is common to most organis ...
, Juan de Fuca, and Gorda plates move to the east and slide below the much larger mostly continental North American plate. The zone varies in width and lies offshore beginning near Cape Mendocino
Cape Mendocino ( Spanish: ''Cabo Mendocino'', meaning "Cape of Mendoza"), which is located approximately north of San Francisco, is located on the Lost Coast entirely within Humboldt County, California, United States. At 124° 24' 34" W longit ...
, Northern California, passing through Oregon
Oregon ( , ) is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is a part of the Western U.S., with the Columbia River delineating much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while t ...
and Washington, and terminating in Canada at about Vancouver Island
Vancouver Island is an island in the northeastern Pacific Ocean and part of the Canadian province of British Columbia. The island is in length, in width at its widest point, and in total area, while are of land. The island is the largest ...
in British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Situated in the Pacific Northwest between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains, the province has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that ...
.
The Explorer, Juan de Fuca, and Gorda plates are some of the remnants of the vast ancient Farallon plate which is now mostly subducted under the North American plate. The North American plate itself is moving slowly in a generally southwest direction, sliding over the smaller plates as well as the huge oceanic Pacific plate (which is moving in a northwest direction) in other locations such as the San Andreas Fault
The San Andreas Fault is a continental Fault (geology)#Strike-slip faults, right-lateral strike-slip transform fault that extends roughly through the U.S. state of California. It forms part of the tectonics, tectonic boundary between the Paci ...
in central and southern California.
Tectonic processes active in the Cascadia subduction zone region include accretion, subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere and some continental lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at the convergent boundaries between tectonic plates. Where one tectonic plate converges with a second p ...
, deep earthquake
An earthquakealso called a quake, tremor, or tembloris the shaking of the Earth's surface resulting from a sudden release of energy in the lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those so weak they ...
s, and active volcanism
Volcanism, vulcanism, volcanicity, or volcanic activity is the phenomenon where solids, liquids, gases, and their mixtures erupt to the surface of a solid-surface astronomical body such as a planet or a moon. It is caused by the presence of a he ...
of the Cascades. This volcanism has included such notable eruptions as Mount Mazama ( Crater Lake) about 7,500 years ago, the Mount Meager massif ( Bridge River Vent) about 2,350 years ago, and Mount St. Helens in 1980. USGS Major cities affected by a disturbance in this subduction zone include Vancouver
Vancouver is a major city in Western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the List of cities in British Columbia, most populous city in the province, the 2021 Canadian census recorded 662,248 people in the cit ...
and Victoria, British Columbia
Victoria is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of British Columbia, on the southern tip of Vancouver Island off Canada's Pacific Ocean, Pacific coast. The city has a population of 91,867, and the Gre ...
; Seattle
Seattle ( ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Washington and in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. With a population of 780,995 in 2024, it is the 18th-most populous city in the United States. The city is the cou ...
, Washington; and Portland, Oregon
Portland ( ) is the List of cities in Oregon, most populous city in the U.S. state of Oregon, located in the Pacific Northwest region. Situated close to northwest Oregon at the confluence of the Willamette River, Willamette and Columbia River, ...
.
History
Tradition
There are no contemporaneous written records of the 1700 Cascadia earthquake. Orally transmitted legends from theOlympic Peninsula
The Olympic Peninsula is a large peninsula in Western Washington that lies across Puget Sound from Seattle, and contains Olympic National Park. It is bounded on the west by the Pacific Ocean, the north by the Strait of Juan de Fuca, and the ...
area tell of an epic battle between a thunderbird and a whale. In 2005, seismologist Ruth Ludwin set out to collect and analyze anecdotes from various First Nations
First nations are indigenous settlers or bands.
First Nations, first nations, or first peoples may also refer to:
Indigenous groups
*List of Indigenous peoples
*First Nations in Canada, Indigenous peoples of Canada who are neither Inuit nor Mé ...
groups. Reports from the Huu-ay-aht, Makah
The Makah (; Makah: ') are an Indigenous people of the Pacific Northwest Coast living in Washington, in the northwestern part of the continental United States. They are enrolled in the federally recognized Makah Indian Tribe of the Makah I ...
, Hoh, Quileute, Yurok, and Duwamish peoples referred to earthquakes and saltwater floods. This collection of data allowed the researchers to come up with an estimated date range for the event; the midpoint was in the year 1701.
Ghost forests

 During low tide one day in March 1986, paleogeologist Brian Atwater dug along Neah Bay with a ''nejiri gama'', a small hand hoe. Under a top layer of sand, he uncovered a distinct plant— arrowgrass—that had grown in a layer of marsh soil. This finding was evidence that the ground had suddenly sunk under sea level, causing saltwater to kill the vegetation. The event had happened so quickly that the top layer of sand sealed away the air, thus preserving centuries-old plants.
In 1987, Atwater mounted another expedition paddling up the Copalis River with Dr. David Yamaguchi, who was then studying the eruptions of Mount St. Helens. The pair happened upon a section of "
During low tide one day in March 1986, paleogeologist Brian Atwater dug along Neah Bay with a ''nejiri gama'', a small hand hoe. Under a top layer of sand, he uncovered a distinct plant— arrowgrass—that had grown in a layer of marsh soil. This finding was evidence that the ground had suddenly sunk under sea level, causing saltwater to kill the vegetation. The event had happened so quickly that the top layer of sand sealed away the air, thus preserving centuries-old plants.
In 1987, Atwater mounted another expedition paddling up the Copalis River with Dr. David Yamaguchi, who was then studying the eruptions of Mount St. Helens. The pair happened upon a section of "ghost forest
Ghost forests are areas of dead trees in former forests, typically in coastal regions where Sea level rise, rising sea levels or tectonic shifts have altered the height of a land mass. Forests located near the coast or estuary, estuaries may also ...
", so-called due to the dead, gray stumps left standing after a sudden inundation of salt water had killed them hundreds of years ago. Originally thought to have died slowly due to a gradual rise in sea level, closer inspection yielded a different story: the land plummeted up to two meters during an earthquake. Having initially tested spruce
A spruce is a tree of the genus ''Picea'' ( ), a genus of about 40 species of coniferous evergreen trees in the family Pinaceae, found in the northern temperate and boreal ecosystem, boreal (taiga) regions of the Northern hemisphere. ''Picea'' ...
using tree-ring dating, they found that the stumps were too rotted to count all the outer rings. However, upon having examined those of the western red cedar and comparing them to the living specimens meters away from the banks, they were able to approximate their year of death. There were rings up until the year 1699, indicating that the incident had occurred shortly thereafter. Root samples confirmed their conclusion, narrowing the time frame to the winter of 1699 to 1700.
As with the arrowgrass site, the banks of the Copalis River are lined with a layer of marsh followed by a layer of sand. Jody Bourgeois and her team went on to demonstrate that the sand cover had originated with a tsunami surge rather than a storm surge.
In 1995, an international team led by Alan Nelson of the USGS
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), founded as the Geological Survey, is an government agency, agency of the United States Department of the Interior, U.S. Department of the Interior whose work spans the disciplines of biology, geograp ...
further corroborated these findings with 85 new samples from the rest of the Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (PNW; ) is a geographic region in Western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Though no official boundary exists, the most common ...
. All along British Columbia, Washington State, and Oregon, the coast had fallen due to a violent earthquake and been covered by sand from the subsequent tsunami.
A further ghost forest was identified by Gordon Jacoby, a dendrochronologist from Columbia University, underwater in Lake Washington
Lake Washington () is a large freshwater lake adjacent to the city of Seattle, Washington, United States.
It is the largest lake in King County, Washington, King County and the second largest natural lake in the state of Washington (state), Was ...
. Unlike the other trees, these suffered from a landslide rather than a dip in the fault during a separate event around 900 CE.
Activity
In the 1960s, underground fractures were uncovered by oil companies inPuget Sound
Puget Sound ( ; ) is a complex estuary, estuarine system of interconnected Marine habitat, marine waterways and basins located on the northwest coast of the U.S. state of Washington (state), Washington. As a part of the Salish Sea, the sound ...
. These were believed to be inactive through the 1990s.
In the 1980s, geophysicists Tom Heaton and Hiroo Kanamori of Caltech
The California Institute of Technology (branded as Caltech) is a private university, private research university in Pasadena, California, United States. The university is responsible for many modern scientific advancements and is among a small g ...
compared the generally quiet Cascadia to more active subduction zones elsewhere in the Ring of Fire
The Ring of Fire (also known as the Pacific Ring of Fire, the Rim of Fire, the Girdle of Fire or the Circum-Pacific belt) is a tectonic belt of volcanoes and earthquakes.
It is about long and up to about wide, and surrounds most of the Pa ...
. They found similarities to faults in Chile, Alaska, and Japan's Nankai Trough
The is a submarine trough located south of the Nankaidō region of Japan's island of Honshu, extending approximately offshore. The underlying fault, the ''Nankai megathrust,'' is the source of the devastating Nankai megathrust earthquakes, ...
, locations known for megathrust earthquake
Megathrust earthquakes occur at convergent plate boundaries, where one tectonic plate is forced underneath another. The earthquakes are caused by slip along the thrust fault that forms the contact between the two plates. These interplate earthq ...
s, a conclusion that was met with skepticism from other geophysicists at the time.
Orphan tsunami
A 1996 study published by seismologist Kenji Satake supplemented the research by Atwater et al. with tsunami evidence across the Pacific. Japanese annals, which have recorded natural disasters since approximately 600 CE, had reports of a sixteen-foot tsunami that struck the coast of Honshu Island during theGenroku
was a after Jōkyō and before Hōei. The Genroku period spanned the years from September 1688 to March 1704. The reigning emperor was .Titsingh, Isaac. (1834). ''Annales des empereurs du japon'', p. 415.
The period was known for its peace and ...
era. Since no earthquake had been observed to produce it, scholars dubbed it an " orphan tsunami". Translating the Japanese calendar
Japanese calendar types have included a range of official and unofficial systems. At present, Japan uses the Gregorian calendar together with year designations stating the Japanese era name, year of the reign of the current Emperor. The written f ...
, Satake found the incident had taken place around midnight of 27–28 January 1700, ten hours after the earthquake occurred. The original magnitude 9.0 earthquake in the Pacific Northwest had thus occurred around 9 pm Pacific Standard Time on 26 January 1700.
Geophysics
The Cascadia subduction zone is a long dipping fault that stretches from Northern Vancouver Island toCape Mendocino
Cape Mendocino ( Spanish: ''Cabo Mendocino'', meaning "Cape of Mendoza"), which is located approximately north of San Francisco, is located on the Lost Coast entirely within Humboldt County, California, United States. At 124° 24' 34" W longit ...
in northern California. It separates the Juan de Fuca and North America plates. New Juan de Fuca plate is created offshore along the Juan de Fuca Ridge
The Juan de Fuca Ridge is a Mid-ocean ridge, mid-ocean spreading center and divergent plate boundary located off the coast of the Pacific Northwest region of North America, named after Juan de Fuca. The ridge separates the Pacific Plate to the we ...
. USGS
The Juan de Fuca plate moves toward, and eventually is pushed under the continent (North American plate). The zone separates the Juan de Fuca plate, Explorer plate, Gorda plate, and North American plate. Here, the oceanic crust
Oceanic crust is the uppermost layer of the oceanic portion of the tectonic plates. It is composed of the upper oceanic crust, with pillow lavas and a dike complex, and the lower oceanic crust, composed of troctolite, gabbro and ultramaf ...
of the Pacific Ocean has been sinking beneath the continent for about 200 million years, and currently does so at a rate of approximately 40 mm/ yr.
At depths shallower than or so, the Cascadia zone is locked by friction while stress slowly builds up as the subduction forces act, until the fault's frictional strength is exceeded and the rocks slip past each other along the fault in a megathrust earthquake
Megathrust earthquakes occur at convergent plate boundaries, where one tectonic plate is forced underneath another. The earthquakes are caused by slip along the thrust fault that forms the contact between the two plates. These interplate earthq ...
. Below the plate interface exhibits episodic tremor and slip
Episodic tremor and slip (ETS) is a seismological phenomenon observed in some subduction zones that is characterized by non-earthquake seismic rumbling, or tremor, and slow slip along the plate interface. Slow slip events are distinguished from ...
.
The width of the Cascadia subduction zone varies along its length, depending on the angle of the subducted oceanic plate, which heats up as it is pushed deeper beneath the continent. As the edge of the plate sinks and becomes hotter and more molten, the subducting rock eventually loses the ability to store mechanical stress; earthquake
An earthquakealso called a quake, tremor, or tembloris the shaking of the Earth's surface resulting from a sudden release of energy in the lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those so weak they ...
s may result. On the Hyndman and Wang diagram (not shown, click on reference link below) the "locked" zone is storing up energy for an earthquake, and the "transition" zone, although somewhat plastic, could probably rupture.
The Cascadia subduction zone runs from triple junctions at its north and south ends. To the north, just below Haida Gwaii
Haida Gwaii (; / , literally "Islands of the Haida people"), previously known as the Queen Charlotte Islands, is an archipelago located between off the British Columbia Coast, northern Pacific coast in the Canadian province of British Columbia ...
, it intersects the Queen Charlotte Fault and the Explorer Ridge. To the south, just off Cape Mendocino in California, it intersects the San Andreas Fault
The San Andreas Fault is a continental Fault (geology)#Strike-slip faults, right-lateral strike-slip transform fault that extends roughly through the U.S. state of California. It forms part of the tectonics, tectonic boundary between the Paci ...
and the Mendocino fracture zone at the Mendocino triple junction.
Recent seismicity
Subduction zones experience various types of earthquakes (or seismicity); includingslow earthquake
A slow earthquake, also known as a silent earthquake, is a discontinuous, earthquake-like event that releases energy over a period of hours to months, rather than the seconds to minutes characteristic of a typical earthquake. First detected using ...
s, megathrust earthquake
Megathrust earthquakes occur at convergent plate boundaries, where one tectonic plate is forced underneath another. The earthquakes are caused by slip along the thrust fault that forms the contact between the two plates. These interplate earthq ...
s, interplate earthquake
An interplate earthquake occurs at the boundary between two tectonic plates. Earthquakes of this type account for more than 90 percent of the total seismic energy released around the world. If one plate is trying to move past the other, they will ...
s, and intraplate earthquake
An intraplate earthquake occurs in the ''interior'' of a Plate tectonics, tectonic plate, in contrast to an interplate earthquake on the ''boundary'' of a tectonic plate. They are relatively rare compared to the more familiar interplate earthqu ...
s. Unlike other subduction zones on Earth, Cascadia currently experiences low levels of seismicity and has not generated a megathrust earthquake
Megathrust earthquakes occur at convergent plate boundaries, where one tectonic plate is forced underneath another. The earthquakes are caused by slip along the thrust fault that forms the contact between the two plates. These interplate earthq ...
since January 26, 1700. Despite low levels of seismicity compared to other subduction zones, Cascadia hosts various types of earthquakes that are recorded by seismic and geodetic instruments, such as seismometer
A seismometer is an instrument that responds to ground displacement and shaking such as caused by quakes, volcanic eruptions, and explosions. They are usually combined with a timing device and a recording device to form a seismograph. The out ...
s and GNSS receivers.
Tremor, a type of slow fault slip, occurs along almost the entire length of Cascadia at regular intervals of 13–16 months. Tremor occurs deeper on the subduction interface than the locked area where megathrust earthquakes occur. The depth of tremor along the subduction interface in Cascadia ranges from 28 km to 45 km, and the motion is so slow that it is not felt at the surface by people or animals, but it can be measured geodetically. The highest density of tremor activity in Cascadia occurs from northern Washington into southern Vancouver Island, and in northern California. Tremor in Cascadia is monitored by the Pacific Northwest Seismic Network's semi-automatic tremor detection system.
The majority of interplate earthquake
An interplate earthquake occurs at the boundary between two tectonic plates. Earthquakes of this type account for more than 90 percent of the total seismic energy released around the world. If one plate is trying to move past the other, they will ...
s, or earthquakes that occur near the boundaries of tectonic plates, near the Cascadia subduction zone occur in the forearc
A forearc is a region in a subduction zone between an oceanic trench and the associated volcanic arc. Forearc regions are present along convergent margins and eponymously form 'in front of' the volcanic arcs that are characteristic of convergen ...
of the overriding North American plate in Washington, west of the Cascade Volcanic Arc
The Cascade Volcanoes (also known as the Cascade Volcanic Arc or the Cascade Arc) are a number of volcanoes in a continental volcanic arc in western North America, extending from southwestern British Columbia through Washington and Oregon to No ...
and east of where tremor occurs. These earthquakes are sometimes referred to as crustal earthquakes, and they are capable of causing significant damage due to their relatively shallow depths. A damaging magnitude 7 interplate earthquake occurred on the Seattle Fault around 900–930 CE that generated 3 meters of uplift and a 4-5 meter tsunami. A substantial number of forearc
A forearc is a region in a subduction zone between an oceanic trench and the associated volcanic arc. Forearc regions are present along convergent margins and eponymously form 'in front of' the volcanic arcs that are characteristic of convergen ...
interplate earthquake
An interplate earthquake occurs at the boundary between two tectonic plates. Earthquakes of this type account for more than 90 percent of the total seismic energy released around the world. If one plate is trying to move past the other, they will ...
s also occur in northern California. Much less interplate seismicity occurs in Oregon compared to Washington and northern California, although Oregon hosts more volcanic activity
Volcanism, vulcanism, volcanicity, or volcanic activity is the phenomenon where solids, liquids, gases, and their mixtures erupt to the surface of a solid-surface astronomical body such as a planet or a moon. It is caused by the presence of a he ...
than its neighboring states.
Intraslab earthquakes, frequently associated with stresses within the subducting plate in convergent margins, occur most frequently in northern Cascadia along the west coast of Vancouver Island and in Puget Sound, and in southern Cascadia within the subducting Gorda plate, near the Mendocino triple junction offshore of northern California. The 1949 Olympia earthquake was a damaging magnitude 6.7 intraslab earthquake that occurred at 52 km depth and caused eight deaths. Another notable intraslab earthquake in the Puget Sound
Puget Sound ( ; ) is a complex estuary, estuarine system of interconnected Marine habitat, marine waterways and basins located on the northwest coast of the U.S. state of Washington (state), Washington. As a part of the Salish Sea, the sound ...
region was the magnitude 6.8 2001 Nisqually earthquake. Intraslab earthquakes in Cascadia occur in areas where the subducting plate has high curvature
In mathematics, curvature is any of several strongly related concepts in geometry that intuitively measure the amount by which a curve deviates from being a straight line or by which a surface deviates from being a plane. If a curve or su ...
. Much of the seismicity that occurs off the coast of northern California is due to intraplate deformation within the Gorda plate. Similar to the distribution of interplate earthquakes in Cascadia, intraslab earthquakes are infrequent in Oregon, with its strongest earthquake since statehood being the 5.6 magnitude 1993 Scotts Mills earthquake, an oblique-slip quake.
Megathrust earthquakes
Earthquake effects
Megathrust earthquake
Megathrust earthquakes occur at convergent plate boundaries, where one tectonic plate is forced underneath another. The earthquakes are caused by slip along the thrust fault that forms the contact between the two plates. These interplate earthq ...
s are the most powerful earthquakes known to occur, and can exceed magnitude
Magnitude may refer to:
Mathematics
*Euclidean vector, a quantity defined by both its magnitude and its direction
*Magnitude (mathematics), the relative size of an object
*Norm (mathematics), a term for the size or length of a vector
*Order of ...
9.0, which releases 1,000 times more energy than magnitude 7.0 and 1 million times more energy than a magnitude 5.0. They occur when enough energy (stress) has accumulated in the "locked" zone of the fault to cause a rupture. The magnitude of a megathrust earthquake is proportional to length of the rupture along the fault. The Cascadia subduction zone, which forms the boundary between the Juan de Fuca and North American plates, is a very long sloping fault that stretches from mid-Vancouver Island to Northern California.
Because of the great length of the fault, the Cascadia subduction zone is capable of producing very large earthquakes if rupture occurs along its entire length. Thermal and deformation studies indicate that the region 60 kilometers (about 40 miles) downdip (east) of the deformation front (where plate deformation begins) is fully locked (the plates do not move past each other). Further downdip, there is a transition from fully locked to aseismic sliding.
In 1999, a group of Continuous Global Positioning System
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite-based hyperbolic navigation system owned by the United States Space Force and operated by Mission Delta 31. It is one of the global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) that provide ge ...
sites registered a brief reversal of motion of approximately 2 centimeters (0.8 inches) over a 50 kilometer by 300 kilometer (about 30 mile by 200 mile) area. The movement was the equivalent of a 6.7 magnitude earthquake. The motion did not trigger an earthquake and was only detectable as silent, non-earthquake seismic signatures.
In 2004, a study conducted by the Geological Society of America analyzed the potential for land subsidence along the Cascadia subduction zone. It postulated that several towns and cities on the west coast of Vancouver Island, such as Tofino
Tofino ( , Nuu-chah-nulth language, Nuu-chah-nulth: ''Načiks'') is a town of approximately 2,516 residents on the west coast of Vancouver Island in the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of British Columbia. The District ...
and Ucluelet, are at risk for a sudden, earthquake initiated, 1–2 m subsidence.
San Andreas Fault connection
Studies of past earthquake traces on both the northernSan Andreas Fault
The San Andreas Fault is a continental Fault (geology)#Strike-slip faults, right-lateral strike-slip transform fault that extends roughly through the U.S. state of California. It forms part of the tectonics, tectonic boundary between the Paci ...
and the southern Cascadia subduction zone indicate a correlation in time which may be evidence that quakes on the Cascadia subduction zone may have triggered most of the major quakes on the northern San Andreas during at least the past 3,000 years or so. The evidence also shows the rupture direction going from north to south in each of these time-correlated events. The 1906 San Francisco earthquake
At 05:12 AM Pacific Time Zone, Pacific Standard Time on Wednesday, April 18, 1906, the coast of Northern California was struck by a major earthquake with an estimated Moment magnitude scale, moment magnitude of 7.9 and a maximum Mercalli inte ...
seems to have been a major exception to this correlation, however, as it was not preceded by a major Cascadia quake.
Earthquake timing
The last known great earthquake in the northwest was the 1700 Cascadia earthquake, years ago.Geological
Geology (). is a branch of natural science concerned with the Earth and other astronomical objects, the rocks of which they are composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth s ...
evidence indicates that great earthquakes (> magnitude 8.0) may have occurred sporadically at least seven times in the last 3,500 years, suggesting a return time of about 500 years. Seafloor core evidence indicates that there have been forty-one subduction zone earthquakes on the Cascadia subduction zone in the past 10,000 years, suggesting a general average earthquake recurrence interval of only 243 years. Of these 41, nineteen have produced a "full margin rupture", wherein the entire fault opens up. By comparison, similar subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere and some continental lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at the convergent boundaries between tectonic plates. Where one tectonic plate converges with a second p ...
zones in the world usually have such earthquakes every 100 to 200 years; the longer interval here may indicate unusually large stress buildup and subsequent unusually large earthquake slip.
There is also evidence of accompanying tsunami
A tsunami ( ; from , ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and underwater explosions (including detonations, ...
s with every earthquake. One strong line of evidence for these earthquakes is convergent timings for fossil damage from tsunamis in the Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (PNW; ) is a geographic region in Western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Though no official boundary exists, the most common ...
and historical Japanese records of tsunamis. USGS Professional Paper 1707
The next rupture of the Cascadia subduction zone is anticipated to be capable of causing widespread destruction throughout the Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (PNW; ) is a geographic region in Western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Though no official boundary exists, the most common ...
.
Forecasts of the next major earthquake
Prior to the 1980s, scientists thought that the subduction zone did not generate earthquakes like other subduction zones around the world, but research by Brian Atwater and Kenji Satake tied together evidence of a large tsunami on the Washington coast with documentation of an orphan tsunami in Japan (a tsunami without an associated earthquake). The two pieces of the puzzle were linked, and they then realized that the subduction zone was more hazardous than previously suggested. In 2009, some geologists predicted a 10% to 14% probability that the Cascadia subduction zone will produce an event of magnitude 9.0 or higher in the next 50 years. In 2010, studies suggested that the risk could be as high as 37% for earthquakes of magnitude 8.0 or higher. Geologists and civil engineers have broadly determined that the Pacific Northwest region is not well prepared for such a colossal earthquake. The earthquake is expected to be similar to the2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami
On 11 March 2011, at 14:46:24 Japan Standard Time, JST (05:46:24 UTC), a 9.0–9.1 Submarine earthquake, undersea megathrust earthquake occurred in the Pacific Ocean, east of the Oshika Peninsula of the Tōhoku region. It lasted approx ...
, because the rupture is expected to be as long as the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami
On 26 December 2004, at 07:58:53 local time ( UTC+7), a major earthquake with a magnitude of 9.2–9.3 struck with an epicentre off the west coast of Aceh in northern Sumatra, Indonesia. The undersea megathrust earthquake, known in the sci ...
. The resulting tsunami
A tsunami ( ; from , ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and underwater explosions (including detonations, ...
might reach heights of approximately 30 meters (100 ft). FEMA estimates some 13,000 fatalities from such an event, with another 27,000 injured, which would make it the deadliest natural disaster in American, and North American, history. FEMA further predicts that a million people will be displaced, with yet another 2.5 million requiring food and water. An estimated 1/3 of public safety workers will not respond to the disaster due to a collapse in infrastructure and a desire to ensure the safety of themselves and their loved ones. Other analyses predict that even a magnitude 6.7 earthquake in Seattle would result in 7,700 dead and injured, $33 billion in damage, 39,000 buildings severely damaged or destroyed, and 130 simultaneous fires.
Cascade Volcanic Arc
 The
The Cascade Volcanic Arc
The Cascade Volcanoes (also known as the Cascade Volcanic Arc or the Cascade Arc) are a number of volcanoes in a continental volcanic arc in western North America, extending from southwestern British Columbia through Washington and Oregon to No ...
is a continental arc of volcanoes
A volcano is commonly defined as a vent or fissure in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often fo ...
that extends from northern California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
to the coastal peninsula of Alaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the north ...
. The arc consists of a series of Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), as well as the current and most recent of the twelve periods of the ...
age stratovolcanoes that grew on top of pre-existing geologic materials that ranged from Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and mea ...
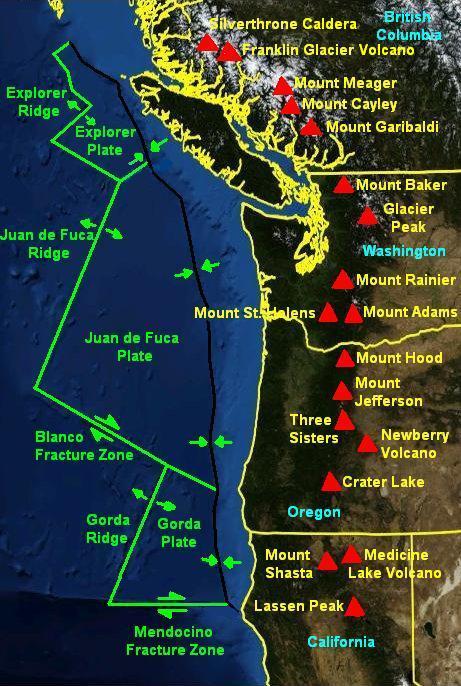
volcanics to glacial ice. The Cascade Volcanic arc is located approximately 100 km inland from the coast, and forms a north-to-south chain of peaks that average over 3,000 m (10,000 ft) in elevation. The major peaks from south to north include:
* Lassen Peak and Mount Shasta
Mount Shasta ( ; Shasta people, Shasta: ''Waka-nunee-Tuki-wuki''; Karuk language, Karuk: ''Úytaahkoo'') is a Volcano#Volcanic activity, potentially active stratovolcano at the southern end of the Cascade Range in Siskiyou County, California. A ...
(California)
* Crater Lake (Mazama), Three Sisters, Mount Jefferson, Mount Hood
Mount Hood, also known as Wy'east, is an active stratovolcano in the Cascade Range and is a member of the Cascade Volcanic Arc. It was formed by a subduction zone on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast and rests in the Pacific N ...
(Oregon)
* Mount Adams, Mount St. Helens, Mount Rainier
Mount Rainier ( ), also known as Tahoma, is a large active stratovolcano in the Cascade Range of the Pacific Northwest in the United States. The mountain is located in Mount Rainier National Park about south-southeast of Seattle. With an off ...
, Glacier Peak
Glacier Peak or Dakobed (known in the Sauk-Suiattle dialect of the Lushootseed language as "Tda-ko-buh-ba" or "Takobia") is the most isolated of the five major stratovolcanoes (composite volcanoes) of the Cascade Volcanoes, Cascade Volcanic Arc ...
, Mount Baker (Washington)
* Mount Garibaldi
Mount Garibaldi (, ) is a dormant stratovolcano in the Garibaldi Ranges of the Pacific Ranges in southwestern British Columbia, Canada. It has a maximum elevation of and rises above the surrounding landscape on the east side of the Cheakamus Ri ...
and Mount Meager massif (British Columbia)
The most active volcanoes in the chain include Mount St. Helens, Mount Baker, Lassen Peak, Mount Shasta, and Mount Hood. Mount St. Helens captured worldwide attention when it erupted catastrophically in 1980. St. Helens continues to rumble, albeit more quietly, emitting occasional steam plumes and experiencing small earthquakes, both signs of continuing magmatic activity.
Most of the volcanoes have a main, central vent from which the most recent eruptions have occurred. The peaks are composed of layers of solidified andesitic
Andesite () is a volcanic rock of intermediate composition. In a general sense, it is the intermediate type between silica-poor basalt and silica-rich rhyolite. It is fine-grained (aphanitic) to porphyritic in texture, and is composed predomina ...
to dacitic magma
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma (sometimes colloquially but incorrectly referred to as ''lava'') is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also ...
, and the more siliceous (and explosive) rhyolite
Rhyolite ( ) is the most silica-rich of volcanic rocks. It is generally glassy or fine-grained (aphanitic) in texture (geology), texture, but may be porphyritic, containing larger mineral crystals (phenocrysts) in an otherwise fine-grained matri ...
.
Volcanoes above the subduction zone
The volcanoes above the subduction zone include: * Silverthrone Caldera * Mount Meager massif * Mount Cayley *Mount Garibaldi
Mount Garibaldi (, ) is a dormant stratovolcano in the Garibaldi Ranges of the Pacific Ranges in southwestern British Columbia, Canada. It has a maximum elevation of and rises above the surrounding landscape on the east side of the Cheakamus Ri ...
* Mount Baker
* Glacier Peak
Glacier Peak or Dakobed (known in the Sauk-Suiattle dialect of the Lushootseed language as "Tda-ko-buh-ba" or "Takobia") is the most isolated of the five major stratovolcanoes (composite volcanoes) of the Cascade Volcanoes, Cascade Volcanic Arc ...
* Mount Rainier
Mount Rainier ( ), also known as Tahoma, is a large active stratovolcano in the Cascade Range of the Pacific Northwest in the United States. The mountain is located in Mount Rainier National Park about south-southeast of Seattle. With an off ...
* Mount St. Helens
* Mount Adams
* Mount Hood
Mount Hood, also known as Wy'east, is an active stratovolcano in the Cascade Range and is a member of the Cascade Volcanic Arc. It was formed by a subduction zone on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast and rests in the Pacific N ...
* Mount Jefferson
* Three Sisters
* Newberry Volcano
* Mount Mazama (Crater Lake)
* Mount McLoughlin
* Medicine Lake Volcano
* Mount Shasta
Mount Shasta ( ; Shasta people, Shasta: ''Waka-nunee-Tuki-wuki''; Karuk language, Karuk: ''Úytaahkoo'') is a Volcano#Volcanic activity, potentially active stratovolcano at the southern end of the Cascade Range in Siskiyou County, California. A ...
* Lassen Peak
* Black Butte
* Black Butte (California)
See also
* Astoria Fan *Cascade Range
The Cascade Range or Cascades is a major mountain range of western North America, extending from southern British Columbia through Washington (state), Washington and Oregon to Northern California. It includes both non-volcanic mountains, such as m ...
* Cascadia (region)
* Cascadia Channel
* Cascadia Region Earthquake Science Center (CRESCENT)
* Geology of the Pacific Northwest
* Neskowin Ghost Forest
The Neskowin Ghost Forest is the remnants of a Sitka spruce forest on the Oregon Coast of the United States. The stumps were likely created when an earthquake of the Cascadia subduction zone abruptly lowered the trees, that were then covered by mu ...
* North Cascades National Park
North Cascades National Park is a List of national parks of the United States, national park of the United States in Washington (state), Washington. At more than , it is the largest of the three National Park Service units that comprise the No ...
* Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (, ) is the scientific theory that the Earth's lithosphere comprises a number of large tectonic plates, which have been slowly moving since 3–4 billion years ago. The model builds on the concept of , an idea developed durin ...
References
Further reading
*Owen, R., 2024, A clearer picture of Cascadia emerges from modern mapping, Temblor,External links
* *"Cascadia Peril '09"
at dailywireless.org
9.0 Shakemap Scenario
The Really Big One
– University of California Television
Great Earthquakes of the Pacific Northwest
– Central Washington University
Toast, tsunamis and the really big one , Chris Goldfinger , TEDxMtHood
– TEDx {{Authority control Cascade Volcanoes Geologic provinces of California Geology of British Columbia Geology of Oregon Geology of Washington (state) Natural hazards in British Columbia Seismic zones of British Columbia Subduction zones