Carboxylate anions on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 In
In
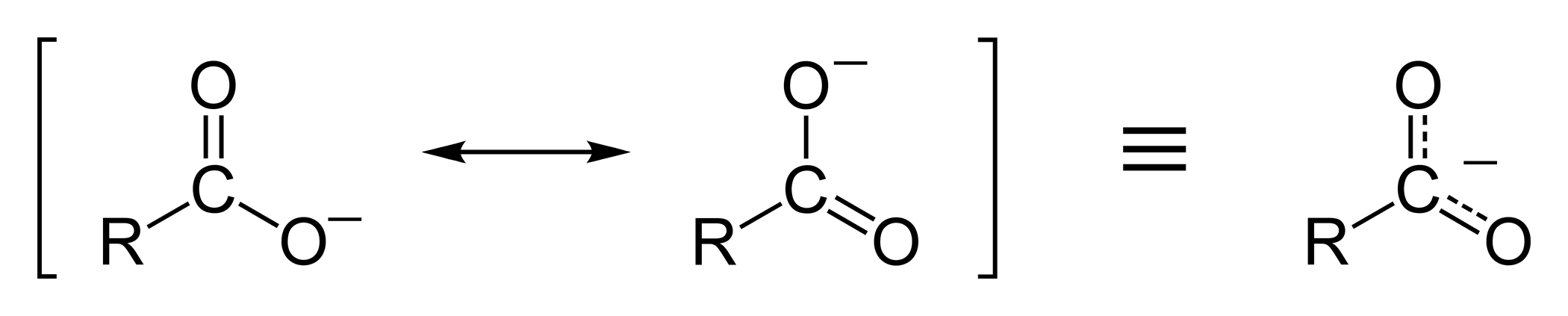 This
This
 The nucleophilicity of carboxylate ions is much weaker than that of
The nucleophilicity of carboxylate ions is much weaker than that of



 In
In organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the science, scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic matter, organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain ...
, a carboxylate is the conjugate base
A conjugate acid, within the Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, is a chemical compound formed when an acid gives a proton () to a base—in other words, it is a base with a hydrogen ion added to it, as it loses a hydrogen ion in the reve ...
of a carboxylic acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an Substituent, R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is often written as or , sometimes as with R referring to an organyl ...
, (or ). It is an anion, an ion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
with negative charge.
Carboxylate salts are salts
In chemistry, a salt or ionic compound is a chemical compound consisting of an assembly of positively charged ions ( cations) and negatively charged ions (anions), which results in a compound with no net electric charge (electrically neutral). ...
that have the general formula , where M is a metal and ''n'' is 1, 2,.... Carboxylate esters have the general formula (also written as ), where R and R′ are organic groups.
Synthesis
Carboxylate ions can be formed by deprotonation of carboxylic acids. Such acids typically have p''K''a of less than 5, meaning that they can be deprotonated by many bases, such assodium hydroxide
Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations and hydroxide anions .
Sodium hydroxide is a highly corrosive base (chemistry), ...
or sodium bicarbonate
Sodium bicarbonate ( IUPAC name: sodium hydrogencarbonate), commonly known as baking soda or bicarbonate of soda (or simply “bicarb” especially in the UK) is a chemical compound with the formula NaHCO3. It is a salt composed of a sodium cat ...
.
:
Resonance stabilization of the carboxylate ion
Carboxylic acids easily dissociate into a carboxylate anion and a positively charged hydrogen ion (proton), much more readily than alcohols do (into analkoxide
In chemistry, an alkoxide is the conjugate base of an alcohol and therefore consists of an organic group bonded to a negatively charged oxygen atom. They are written as , where R is the organyl substituent. Alkoxides are strong bases and, whe ...
ion and a proton), because the carboxylate ion is stabilized by resonance
Resonance is a phenomenon that occurs when an object or system is subjected to an external force or vibration whose frequency matches a resonant frequency (or resonance frequency) of the system, defined as a frequency that generates a maximu ...
. The negative charge that is left after deprotonation
Deprotonation (or dehydronation) is the removal (transfer) of a proton (or hydron, or hydrogen cation), (H+) from a Brønsted–Lowry acid in an acid–base reaction.Henry Jakubowski, Biochemistry Online Chapter 2A3, https://employees.csbsju.ed ...
of the carboxyl group is delocalized between the two electronegative
Electronegativity, symbolized as , is the tendency for an atom of a given chemical element to attract shared electrons (or electron density) when forming a chemical bond. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the d ...
oxygen atoms in a resonance structure. If the R group is an electron-withdrawing group (such as –CF3), the basicity of the carboxylate will be further weakened.
: This
This delocalization
In chemistry, delocalized electrons are electrons in a molecule, ion or solid metal that are not associated with a single atom or a covalent bond.IUPAC Gold Boo''delocalization''/ref>
The term delocalization is general and can have slightly diff ...
of the electron means that both of the oxygen atoms are less strongly negatively charged: the positive proton is therefore less strongly attracted back to the carboxylate group once it has left; hence, the carboxylate ion is more stable and less basic as a result of resonance stabilization
In chemistry, resonance, also called mesomerism, is a way of describing bonding in certain molecules or polyatomic ions by the combination of several contributing structures (or ''forms'', also variously known as ''resonance structures'' or '' ...
of the negative charge. In contrast, an alkoxide
In chemistry, an alkoxide is the conjugate base of an alcohol and therefore consists of an organic group bonded to a negatively charged oxygen atom. They are written as , where R is the organyl substituent. Alkoxides are strong bases and, whe ...
ion, once formed, would have a strong negative charge localized on its lone oxygen atom, which would strongly attract any nearby protons (indeed, alkoxides are very strong bases). Because of resonance stabilization, carboxylic acids have much lower p''K''a values (and are therefore stronger acids) than alcohols
In chemistry, an alcohol (), is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a Saturated and unsaturated compounds, saturated carbon atom. Alcohols range from the simple, like methanol and ethanol ...
. For example, the p''K''a value of acetic acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main compone ...
is 4.8, while ethanol
Ethanol (also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with its formula also written as , or EtOH, where Et is the ps ...
has a p''K''a of 16. Hence acetic acid is a much stronger acid than ethanol. This in turn means that for equimolar solutions of a carboxylic acid or an alcohol in water, the carboxylic acid would have a much lower pH.
Reactions
Alkyation
Carboxylic acid salts with a hydrogen atom in the ''alpha'' position next to the carboxylate group can be converted to dianions with strong bases like lithium diisopropylamide. These react with alkyl halides to give derivatives: : :Nucleophilic substitution
Carboxylate ions are good nucleophiles. They react with alkyl halides to formester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid (either organic or inorganic) in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group () of that acid is replaced by an organyl group (R). These compounds contain a distin ...
s. The following reaction shows the reaction mechanism.
 The nucleophilicity of carboxylate ions is much weaker than that of
The nucleophilicity of carboxylate ions is much weaker than that of hydroxide
Hydroxide is a diatomic anion with chemical formula OH−. It consists of an oxygen and hydrogen atom held together by a single covalent bond, and carries a negative electric charge. It is an important but usually minor constituent of water. It ...
and alkoxide
In chemistry, an alkoxide is the conjugate base of an alcohol and therefore consists of an organic group bonded to a negatively charged oxygen atom. They are written as , where R is the organyl substituent. Alkoxides are strong bases and, whe ...
ions, but stronger than that of halide
In chemistry, a halide (rarely halogenide) is a binary chemical compound, of which one part is a halogen atom and the other part is an element or radical that is less electronegative (or more electropositive) than the halogen, to make a fl ...
anions (in a polar aprotic solvent, though there are other effects such as solubility
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a chemical substance, substance, the solute, to form a solution (chemistry), solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form su ...
of the ion).
Reduction
Unlike the reduction of ester, the reduction of carboxylate is different, due to the lack of theleaving group
In organic chemistry, a leaving group typically means a Chemical species, molecular fragment that departs with an electron, electron pair during a reaction step with heterolysis (chemistry), heterolytic bond cleavage. In this usage, a ''leaving gr ...
and the relatively electron-rich carbon atom (due to the negative charge on the oxygen atoms). With a small amount of acid, the reaction occurs with lithium aluminium hydride
Lithium aluminium hydride, commonly abbreviated to LAH, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula or . It is a white solid, discovered by Finholt, Bond and Schlesinger in 1947. This compound is used as a reducing agent in organic synthe ...
by changing the LAH into the Lewis acid
A Lewis acid (named for the American physical chemist Gilbert N. Lewis) is a chemical species that contains an empty orbital which is capable of accepting an electron pair from a Lewis base to form a Lewis adduct. A Lewis base, then, is any ...
AlH3 in the process, converting the oxyanion to 4 Al–O bonds.
Examples
This list is for cases where there is a separate article for the anion or its derivatives. All other organic acids should be found at their parent carboxylic acid. *Formate
Formate (IUPAC name: methanoate) is the conjugate base of formic acid. Formate is an anion () or its derivatives such as ester of formic acid. The salts and esters are generally colorless.
Fundamentals
When dissolved in water, formic acid co ...
ion, HCOO−
* Acetate
An acetate is a salt formed by the combination of acetic acid with a base (e.g. alkaline, earthy, metallic, nonmetallic, or radical base). "Acetate" also describes the conjugate base or ion (specifically, the negatively charged ion called ...
ion, CH3COO−
* Methanetetracarboxylate ion, C(COO−)4
* Oxalate
Oxalate (systematic IUPAC name: ethanedioate) is an anion with the chemical formula . This dianion is colorless. It occurs naturally, including in some foods. It forms a variety of salts, for example sodium oxalate (), and several esters such as ...
ion,
See also
*Carboxylic acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an Substituent, R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is often written as or , sometimes as with R referring to an organyl ...
References
{{Reflist Anions