Cantref Buellt on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Buellt or Builth was a
Buellt or Builth was a
 During the
During the
Builth Wells Castle
. 10 Dec 2012. Accessed 13 Feb 2013. In the 16th century, as part of

 Buellt or Builth was a
Buellt or Builth was a cantref
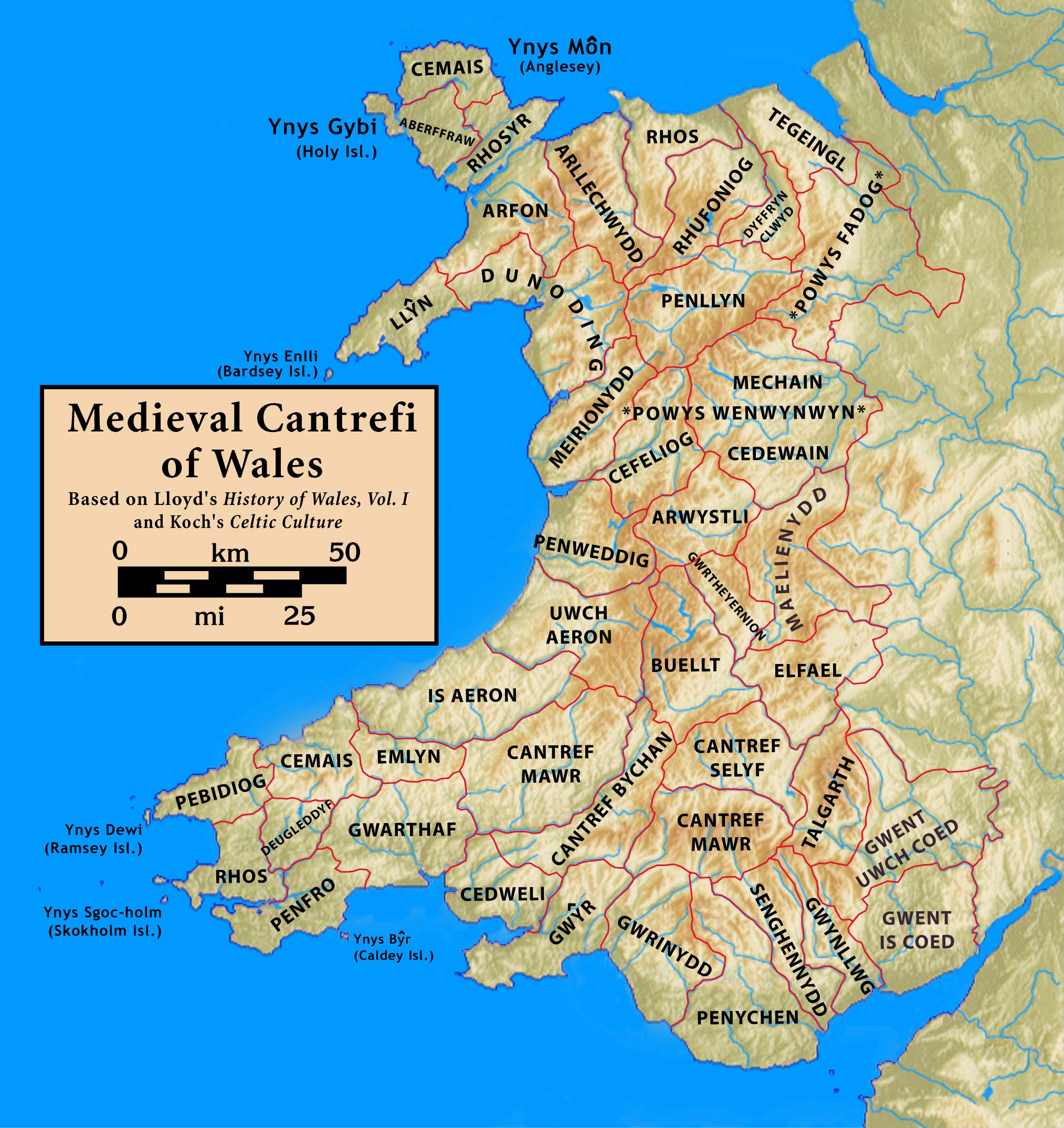
A cantref ( ; ; plural cantrefi or cantrefs; also rendered as ''cantred'') was a Wales in the Early Middle Ages, medieval Welsh land division, particularly important in the administration of Welsh law.
Description
Land in medieval Wales was divid ...
in medieval Wales
Wales ( ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by the Irish Sea to the north and west, England to the England–Wales border, east, the Bristol Channel to the south, and the Celtic ...
, located west of the River Wye
The River Wye (; ) is the Longest rivers of the United Kingdom, fourth-longest river in the UK, stretching some from its source on Plynlimon in mid Wales to the Severn Estuary. The lower reaches of the river forms part of Wales-England bor ...
. Unlike most cantrefs, it was not part of any of the major Welsh kingdoms for most of its history, but was instead ruled by an autonomous local dynasty. During the Norman era
Norman or Normans may refer to:
Ethnic and cultural identity
* The Normans, a people partly descended from Norse Vikings who settled in the territory of Normandy in France in the 9th and 10th centuries
** People or things connected with the Norma ...
it was associated with Rhwng Gwy a Hafren
was a region of medieval Wales, located in the Welsh Marches between Kingdom of Powys, Powys to the north and Brycheiniog to the south. It was bounded by the rivers River Wye, Wye () and River Severn, Severn (). It covered about the same territor ...
, a region independent of the Welsh monarchies and controlled by Norman Marcher Lords
A marcher lord () was a noble appointed by the king of England to guard the border (known as the Welsh Marches) between England and Wales.
A marcher lord was the English equivalent of a margrave (in the Holy Roman Empire) or a marquis (in France ...
. In the 16th century, it was reorganized as a hundred
100 or one hundred (Roman numerals, Roman numeral: C) is the natural number following 99 (number), 99 and preceding 101 (number), 101.
In mathematics
100 is the square of 10 (number), 10 (in scientific notation it is written as 102). The standar ...
and joined with the former kingdom of Brycheiniog
Brycheiniog was an independent kingdom in South Wales in the Early Middle Ages. It often acted as a buffer state between England to the east and the south Welsh kingdom of Deheubarth to the west. It was conquered and pacified by the Normans ...
to form the county of Brecknockshire
Brecknockshire ( or ), also known as the County of Brecknock, Breconshire, or the County of Brecon, was Historic counties of Wales, one of the thirteen counties of Wales that existed from 1536 until their abolishment in 1974. It was created in 1 ...
.
Description
The name ''Buellt'', also rendered ''Buallt'', comes from the Welsh words ''bu'', meaning " ox", and ''gellt'' (later ''gwellt''), meaningpasture
Pasture (from the Latin ''pastus'', past participle of ''pascere'', "to feed") is land used for grazing.
Types of pasture
Pasture lands in the narrow sense are enclosed tracts of farmland, grazed by domesticated livestock, such as horses, c ...
. This was later anglicized to ''Builth'', as in the modern town of Builth Wells
Builth Wells (; ) is a market town and community in the county of Powys and historic county of Brecknockshire (Breconshire), mid Wales, lying at the confluence of rivers Wye and Irfon, in the Welsh (or upper) part of the Wye Valley. In 20 ...
.
Situated in the valley of Afon Irfon
Afon Irfon (the River Irfon) is a river in Powys, Wales. It flows from the upper slopes of Bryn Garw in the Cambrian Mountains, through the Abergwesyn Valley, past the Nant Irfon National Nature Reserve in the hills above the village of Abergw ...
, Buellt's boundaries were roughly the Cambrian Mountains
The Cambrian Mountains (, in a narrower sense: ''Elenydd'') are a series of mountain ranges in Wales.
The term ''Cambrian Mountains'' used to apply to most of the upland of Wales, and comes from the country's Latin name . Since the 1950s, it ...
to the north, the River Wye
The River Wye (; ) is the Longest rivers of the United Kingdom, fourth-longest river in the UK, stretching some from its source on Plynlimon in mid Wales to the Severn Estuary. The lower reaches of the river forms part of Wales-England bor ...
to the east, the Mynydd Epynt
Mynydd Epynt () is an upland region of Mid Wales, within the county of Powys. It is bounded on the south by the upper stretch of the Usk Valley, on the north by the Irfon Valley, and on the east by the Wye Valley. Its western boundary is less ...
range to the south, and Ceredigion
Ceredigion (), historically Cardiganshire (, ), is a Principal areas of Wales, county in the West Wales, west of Wales. It borders Gwynedd across the River Dyfi, Dyfi estuary to the north, Powys to the east, Carmarthenshire and Pembrokeshire t ...
to the west. It was closely associated with the territories of Gwrtheyrnion
Gwrtheyrnion or Gwerthrynion was a commote in medieval Wales, located in Mid Wales on the north side of the River Wye; its historical centre was Rhayader. It is said to have taken its name from the legendary king Vortigern (). For most of the med ...
, Elfael
Elfael was one of a number of Welsh cantrefi occupying the region between the River Wye and river Severn, known as Rhwng Gwy a Hafren, in the early Middle Ages. It was divided into two commotes, Is Mynydd and Uwch Mynydd, separated by the chai ...
, and Maelienydd
Maelienydd, sometimes spelt Maeliennydd, was a cantref and lordship in east central Wales covering the area from the River Teme to Radnor Forest and the area around Llandrindod Wells. The area, which is mainly upland, is now in Powys. During th ...
, and as such was often considered part of the region known as Rhwng Gwy a Hafren
was a region of medieval Wales, located in the Welsh Marches between Kingdom of Powys, Powys to the north and Brycheiniog to the south. It was bounded by the rivers River Wye, Wye () and River Severn, Severn (). It covered about the same territor ...
() despite being west of the Wye.Lloyd, p. 253–254. The cantref
A cantref ( ; ; plural cantrefi or cantrefs; also rendered as ''cantred'') was a Wales in the Early Middle Ages, medieval Welsh land division, particularly important in the administration of Welsh law.
Description
Land in medieval Wales was divid ...
was divided into four major commote
A commote (, sometimes spelt in older documents as , plural , less frequently )'' Geiriadur Prifysgol Cymru'' (University of Wales Dictionary), p. 643 was a secular division of land in Medieval Wales. The word derives from the prefix ("together" ...
s, whose boundaries are unclear: Treflys, Pebuellt, Dinan, and Is Irfon. Most of Buellt's major sites were located along the Irfon, including the courts of the commotes and the major church at Llanafan Fawr
Llanafan Fawr is a village, community and ecclesiastical parish in Powys, Wales. Located in the former cantref of Buellt (Builth) and historic county of Brecknockshire, the community includes the former parish of Llanfihangel Bryn Pabuan.
The pa ...
, dedicated to Saint Afan Buellt
Afan of Builth (; ) was an early 6th-century Welsh people, Welsh bishop, Martyr of the Faith, martyr, and list of Welsh saints, saint. His Gŵyl Mabsant, feast day is generally placed on 17 November, although the Demetian Calendar formerly used i ...
, the cantref's chief saint.Lloyd, p. 253.
Early history
It is unknown when Buellt began to emerge as a distinct political unit. Its organization as a cantref seems to have developed along the earlier tribal boundaries of a '' gwlad'' ("people") or ''tud'' ("tribe"). During theEarly Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages (historiography), Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th to the 10th century. They marked the start o ...
, Buellt and Gwrtheyrnion
Gwrtheyrnion or Gwerthrynion was a commote in medieval Wales, located in Mid Wales on the north side of the River Wye; its historical centre was Rhayader. It is said to have taken its name from the legendary king Vortigern (). For most of the med ...
on the other side of the Wye formed a small regional kingdom. This kingdom's rulers traced their descent back to the legendary 5th-century warlord Vortigern
Vortigern (; , ; ; ; Old Breton: ''Gurdiern'', ''Gurthiern''; ; , , , etc.), also spelled Vortiger, Vortigan, Voertigern and Vortigen, was a 5th-century warlord in Sub-Roman Britain, Britain, known perhaps as a king of the Britons or at least ...
(, from which Gwrtheyrnion was named.)
The kingdom is known from the 9th-century ''Historia Brittonum
''The History of the Britons'' () is a purported history of early Britain written around 828 that survives in numerous recensions from after the 11th century. The ''Historia Brittonum'' is commonly attributed to Nennius, as some recensions ha ...
'', whose author, possibly a native of southeastern Wales, focused particular attention on it. The ''Historia'' recounts that after Vortigern had invited the Anglo-Saxons
The Anglo-Saxons, in some contexts simply called Saxons or the English, were a Cultural identity, cultural group who spoke Old English and inhabited much of what is now England and south-eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. They traced t ...
to Britain and then been forced west, his son Pascent
Pasgen ap Cadeyrn was an ancient king of Powys and the father of Mawgan ap Pasgen, according to the Harleian genealogies.Ben Guy (2018), "The earliest Welsh genealogies: textual layering and the phenomenon of 'pedigree growth'," ''Early Medieval ...
ruled Buellt and Gwrtheyrnion as a grant from Ambrosius Aurelianus
Ambrosius Aurelianus (; Anglicised as Ambrose Aurelian and called Aurelius Ambrosius in the ''Historia Regum Britanniae'' and elsewhere) was a war leader of the Romano-British who won an important battle against the Anglo-Saxons in the 5th c ...
. ''Historia Brittonum'', ch. 47–49. Whatever the reality of this story, another section attributes descent from Pascent and Vortigern to Ffernfael ap Tewdwr
Ffernfael ap Tewdwr (; ; fl. c. 830) was a king of Buellt and Gwrtheyrnion in medieval Wales. Little is known of him besides a pedigree included in the 9th-century ''Historia Brittonum'', which makes him a descendant of the ruler Vortigern.
Life
F ...
, a 9th-century ruler of Buellt and Gwrtheyrnion known from other sources.Lloyd, p. 224 and note; 253.
The ''Historia'' further includes Buellt in its '' mirabilia'' section, or list of marvels. According to the text, Buellt is the location of the "Carn Cabal", a (since lost) petrosomatoglyph
A petrosomatoglyph is a supposed image of parts of a human or animal body in rock. They occur all over the world, often functioning as an important form of symbolism, used in religious and secular ceremonies, such as the crowning of kings. Some ...
: the imprint of a dog's paw. This marvel is attributed to King Arthur
According to legends, King Arthur (; ; ; ) was a king of Great Britain, Britain. He is a folk hero and a central figure in the medieval literary tradition known as the Matter of Britain.
In Wales, Welsh sources, Arthur is portrayed as a le ...
's dog Cavall
Cavall (Middle RBH & WBR; modernized: ''Cafall''; ; ', var. ''Caball'' (ms.K)) was King Arthur's dog, used in the hunt for the great boar, Twrch Trwyth ().
Cavall was Arthur's "favourite dog", and during a stag hunt, he was customarily the las ...
, who supposedly left the print while chasing the boar Troyt. Afterward, Arthur placed this stone on top of a cairn
A cairn is a human-made pile (or stack) of stones raised for a purpose, usually as a marker or as a burial mound. The word ''cairn'' comes from the (plural ).
Cairns have been and are used for a broad variety of purposes. In prehistory, t ...
, and anyone who tried to move it would find it back in its place the next day. The placename survives as Carn Gafallt near Rhayader
Rhayader (; ; ) is a market town and community (Wales), community in Powys, Wales, within the Historic counties of Wales, historic county of Radnorshire. The town is from the source of the River Wye on Plynlimon, the highest point of the Cambri ...
, though it is unlikely the modern hill is the same one mentioned in the ''Historia''.Bromwich, p. lxvi and note The prose tale ''Culhwch and Olwen
''Culhwch and Olwen'' () is a Welsh tale that survives in only two manuscripts about a hero connected with Arthur and his warriors: a complete version in the Red Book of Hergest, , and a fragmented version in the White Book of Rhydderch, . It ...
'' contains a more elaborate version of Arthur's hunting of the divine boar, here known as ''Twrch Trwyth
Twrch Trwyth (; also ), is a fabulous wild boar from the Legend of King Arthur, of which a richly elaborate account of its hunt described in the Welsh prose romance '' Culhwch and Olwen'', probably written around 1100.
Its hunt involved King ...
'', however, in ''Culhwch'' the boar's detailed itinerary does not take him through Buellt.
By the 11th century, Buellt and the rest of the Rhwng Gwy a Hafren passed under the control of a different dynasty tracing its descent to Elystan Glodrydd
Elystan Glodrydd (or, occasionally, Elstan Glodrydd; died 1010), also known as "Æthelstan the Famous" and "The Renowned," was, according to Welsh genealogical tracts, the founder of the fifth Royal Tribe of Wales. He was the Prince of Buellt, ...
.Lloyd, p. 406 & note.
Norman era
 During the
During the High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the periodization, period of European history between and ; it was preceded by the Early Middle Ages and followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended according to historiographical convention ...
, several rulers from the surrounding kingdoms took control of Buellt, but it generally reverted to independence upon their death. During the Norman invasion of Wales
The Norman invasion of Wales began shortly after the Norman Conquest, Norman conquest of England under William the Conqueror, who believed England to be his birthright. Initially (1067–1081), the invasion of Wales was not undertaken with the fer ...
, the Marcher Lord
A marcher lord () was a noble appointed by the king of England to guard the border (known as the Welsh Marches) between England and Wales.
A marcher lord was the English equivalent of a margrave (in the Holy Roman Empire) or a marquis (in Fra ...
Philip de Braose
Philip de Braose, 2nd Lord of Bramber ( 1070 – c. 1134) was an Anglo-Norman nobleman and Marcher Lord.
Origins
Philip was born about 1070 to 1073, the son of William de Braose, 1st Lord of Bramber (d. 1093/96) by his wife Eve de Boissey or ...
conquered Buellt shortly after he took Rhwng Gwy a Hafren in 1095. Philip fortified the hill east of present-day Builth Wells with a wooden motte and bailey
A motte-and-bailey castle is a European fortification with a wooden or stone keep situated on a raised area of ground called a motte, accompanied by a walled courtyard, or bailey, surrounded by a protective ditch and palisade. Relatively easy ...
castle and held the area until his death in 1134, when it passed to his son William
William is a masculine given name of Germanic languages, Germanic origin. It became popular in England after the Norman Conquest, Norman conquest in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle ...
. Through this period, however, the representatives of the old Welsh dynasty descended from Elystan contested the Marcher Lords' rule. The area changed hands between multiple Norman and Welsh figures, including Roger Mortimer, Rhys ap Gruffudd
Rhys ap Gruffydd or ap Gruffudd (often anglicised to "Griffith"; c. 1132 – 28 April 1197) was the ruler of the kingdom of Deheubarth in south Wales from 1155 to 1197. Today, he is commonly known as The Lord Rhys, in Welsh ''Yr Arglwydd Rhys' ...
and Llywelyn the Great
Llywelyn ab Iorwerth (, – 11 April 1240), also known as Llywelyn the Great (, ; ), was a medieval Welsh ruler. He succeeded his uncle, Dafydd ab Owain Gwynedd, as King of Gwynedd in 1195. By a combination of war and diplomacy, he dominate ...
. Buellt passed to Llywelyn's grandson Llywelyn ap Gruffudd
Llywelyn ap Gruffudd ( – 11 December 1282), also known as Llywelyn II and Llywelyn the Last (), was List of rulers of Gwynedd, Prince of Gwynedd, and later was recognised as the Prince of Wales (; ) from 1258 until his death at Cilmeri in 128 ...
, whose rights to it (though not other parts of Rhwng Gwy a Hafren) were confirmed by King Henry III in the 1267 Treaty of Montgomery
The Treaty of Montgomery was an Anglo- Welsh treaty signed on 29 September 1267 in Montgomeryshire by which Llywelyn ap Gruffudd was acknowledged as Prince of Wales by King Henry III of England (r. 1216–1272). It was the only time an English ...
. In November 1282, Edward I
Edward I (17/18 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots (Latin: Malleus Scotorum), was King of England from 1272 to 1307. Concurrently, he was Lord of Ireland, and from 125 ...
overran Buellt as part of his final conquest of Wales
The conquest of Wales by Edward I took place between 1277 and 1283. It is sometimes referred to as the Edwardian conquest of Wales,Examples of historians using the term include Professor J. E. Lloyd, regarded as the founder of the modern academ ...
.
Edward ordered the construction of the stone Builth Castle
Builth Castle () was a castle built under Edward I of England, King Edward I, just outside Builth Wells, Powys, Wales. At one time it was an impressive stone-built castle but all the masonry has been removed over the years and all that remains ar ...
on the site of Braose's burnt fort, although construction was halted for lack of funds. The castle saw action during Madog ap Llywelyn
Madog ap Llywelyn (died after 1312) was the leader of the Welsh revolt of 1294–95 against English rule in Wales. The revolt was surpassed in longevity only by the revolt of Owain Glyndŵr in the 15th century. Madog belonged to a junior branch ...
and Owain Glyndŵr
Owain ap Gruffydd (28 May 135420 September 1415), commonly known as Owain Glyndŵr (Glyn Dŵr, , anglicised as Owen Glendower) was a Welsh people, Welsh leader, soldier and military commander in the Wales in the late Middle Ages, late Middle ...
's rebellions, but was subsequently abandoned. In the 17th century it was damaged by a fire and its stones were plundered; it has since almost entirely disappeared.''Gatehouse Gazetteer''.Builth Wells Castle
. 10 Dec 2012. Accessed 13 Feb 2013. In the 16th century, as part of
Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is known for his Wives of Henry VIII, six marriages and his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. ...
's Laws in Wales Acts, Buellt became a hundred
100 or one hundred (Roman numerals, Roman numeral: C) is the natural number following 99 (number), 99 and preceding 101 (number), 101.
In mathematics
100 is the square of 10 (number), 10 (in scientific notation it is written as 102). The standar ...
and merged with Brycheiniog
Brycheiniog was an independent kingdom in South Wales in the Early Middle Ages. It often acted as a buffer state between England to the east and the south Welsh kingdom of Deheubarth to the west. It was conquered and pacified by the Normans ...
into the new county of Brecknockshire
Brecknockshire ( or ), also known as the County of Brecknock, Breconshire, or the County of Brecon, was Historic counties of Wales, one of the thirteen counties of Wales that existed from 1536 until their abolishment in 1974. It was created in 1 ...
. In 1996 the area became part of the modern county of Powys
Powys ( , ) is a Principal areas of Wales, county and Preserved counties of Wales, preserved county in Wales. It borders Gwynedd, Denbighshire, and Wrexham County Borough, Wrexham to the north; the English Ceremonial counties of England, ceremo ...
. The cantref's name survives in the modern town of Builth Wells
Builth Wells (; ) is a market town and community in the county of Powys and historic county of Brecknockshire (Breconshire), mid Wales, lying at the confluence of rivers Wye and Irfon, in the Welsh (or upper) part of the Wye Valley. In 20 ...
and the site of nearby Builth Castle.Lloyd, p. 401.
Notes
References
* * * * * * * * * * * *{{cite encyclopedia , last=Thornton , first= David, year= 2003 , title = Fratricide, Filacentricity, and the Rise of the Second Dynasty of Gwynedd , encyclopedia= Kings, Chronicles and Genealogies: Studies in the Political History of Early Medieval Ireland and Wales , publisher= Unit for Prosopographical Research, Linacre College, Oxford , isbn= 1900934094, url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Xw_YySYSscQC, access-date=13 February 2012 Cantrefs History of Powys