Caminha on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Caminha () is a municipality in the north-west of
/ref> in an area of 136.52 km². Caminha is subdivided into 14

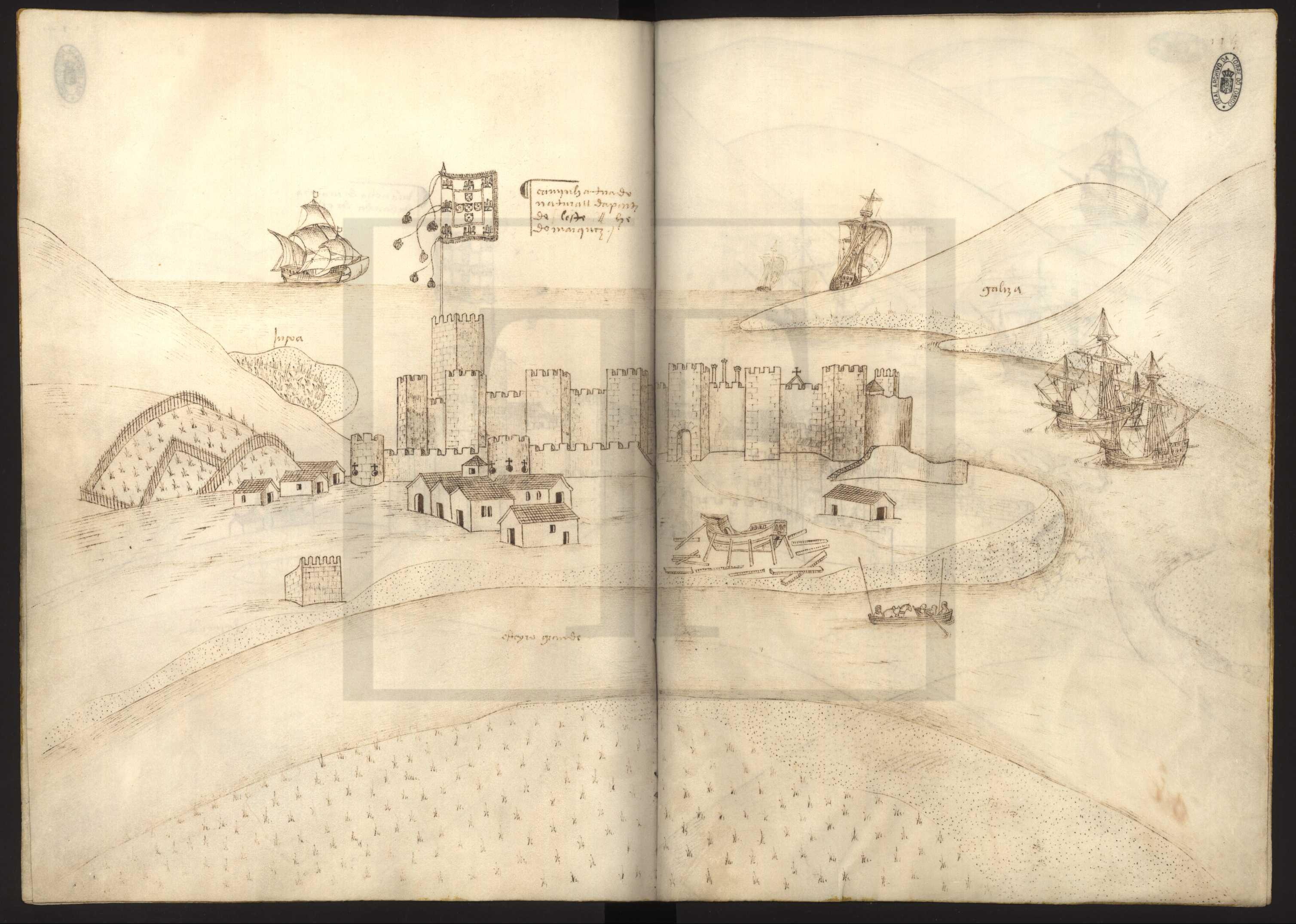 The first letter of feudal rights (
The first letter of feudal rights (
Municipality official website
{{Authority control Municipalities of Viana do Castelo District
Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, is a country on the Iberian Peninsula in Southwestern Europe. Featuring Cabo da Roca, the westernmost point in continental Europe, Portugal borders Spain to its north and east, with which it share ...
, 21 km north from Viana do Castelo, located in the Viana do Castelo District. The population in 2011 was 16,684,Instituto Nacional de Estatística/ref> in an area of 136.52 km². Caminha is subdivided into 14
civil parishes
In England, a civil parish is a type of Parish (administrative division), administrative parish used for Local government in England, local government. It is a territorial designation which is the lowest tier of local government. Civil parishe ...
. The parish Vilar de Mouros is well known for the oldest rock festival in Portugal. The seat of the municipality is the town (or ''vila'' in Portuguese) of Caminha, with 2,500 inhabitants.
The town is on the coastal part of the Portuguese Way path of the Camino de Santiago
The Camino de Santiago (, ; ), or the Way of St. James in English, is a network of pilgrims' ways or pilgrimages leading to the shrine of the apostle James in the cathedral of Santiago de Compostela in Galicia in northwestern Spain, where tra ...
.
The present Mayor is Luís Miguel da Silva Mendonça Alves. The municipal holiday is Easter Monday.
General information
Caminha is located 2 km from theAtlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
, on the southern side of the Minho Minho or Miño may refer to:
People
* Miño (surname)
* Choi Min-ho, South Korean singer and actor known mononymously as Minho
Places
* Minho (river) or Miño, in Portugal and Spain
Jamaica
* Rio Minho, a river
Portugal
* Minho Province
...
estuary, where this river is met by the smaller and meandering Coura. Here the Minho reaches its widest point (about 2 km) and marks the border between Portugal and Galiza. The highly scenic area, with the wide estuary marked by low-tide sandbar
In oceanography, geomorphology, and geoscience, a shoal is a natural submerged ridge, bank, or bar that consists of, or is covered by, sand or other unconsolidated material, and rises from the bed of a body of water close to the surface or ...
s, a pastoral and green rural landscape, and pine forests on the slopes of the granitic mountains is increasingly popular for second homes and as a summer resort.
History
Despite Strabo's reference toPhoenicia
Phoenicians were an Ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient Semitic group of people who lived in the Phoenician city-states along a coastal strip in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily modern Lebanon and the Syria, Syrian ...
n docks in the mouth of the Minho, no further evidence was found. An islet
An islet ( ) is generally a small island. Definitions vary, and are not precise, but some suggest that an islet is a very small, often unnamed, island with little or no vegetation to support human habitation. It may be made of rock, sand and/ ...
at the confluence of the Minho and Coura, now connected to the mainland, was the site of a small military settlement in Roman Gallaecia
Gallaecia, also known as Hispania Gallaecia, was the name of a Roman province in the north-west of Hispania, approximately present-day Galicia, northern Portugal, Asturias and Leon and the later Kingdom of Gallaecia. The Roman cities inclu ...
. Caminha was called ''Camenae'' or ''Camina'' during the period of part of the Kingdom of Galicia
The Kingdom of Galicia was a political entity located in southwestern Europe, which at its territorial zenith occupied the entire northwest of the Iberian Peninsula. In the early 10th century, the Kingdom of Galicia was formed following the div ...
in the 5th century. The area was depopulated due to Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years ...
and Norman raids, and slowly reoccupied after the 10th century. Around 1060, during the reign of Ferdinand I of Galicia and León, Caminha was briefly a county
A county () is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesL. Brookes (ed.) '' Chambers Dictionary''. Edinburgh: Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, 2005. in some nations. The term is derived from the Old French denoti ...
and it is known that a castle existed in the area.
In the 13th century, Caminha was just a fishing village until King Afonso III decided to build a modern castle and a fortified village following the '' bastide'' model, finished in 1260. At that time, the region was of great military importance, since it was located at the border with Galicia. The castle was later reinforced by Kings Dinis I, when reclaimed land finally connected the original island to the shore, and Ferdinand I. Although most of the walls and towers were torn down or built over, the oval shape of the castle is still clearly visible in the design of some streets, and the keep
A keep is a type of fortified tower built within castles during the Middle Ages by European nobility. Scholars have debated the scope of the word ''keep'', but usually consider it to refer to large towers in castles that were fortified residen ...
tower is still intact and serves as entrance to the historical centre. The pinewood of ''Camarido'', stabilizing the sandbars at the mouth of the Minho, was another important initiative of Dinis I.

 The first letter of feudal rights (
The first letter of feudal rights (foral
200px, Foral of Castro Verde - Portugal
The ''Carta de Foral'', or simply ''Foral'', was a royal document in Portugal and its former empire, whose purpose was to establish a ''concelho'' (Council) and regulate its administration, borders and priv ...
) dates from 1284. Caminha belonged to the crown until King Ferdinand I established in 1371 the County of Caminha, whose first count was Álvaro Pires de Castro. In 1390, King John I granted much freedom to the town (creating a ''póvoa marítima''), leading maritime commerce to flourish. In the 15th and 16th centuries, it became one of the main ports in Northern Portugal, trading extensively with Northern Europe, Africa and India. A witness of this golden age is the main church (''Igreja Matriz''), built between the 15th and 16th centuries in an exuberant late Gothic-Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
mixed style. King Manuel I granted Caminha a new foral
200px, Foral of Castro Verde - Portugal
The ''Carta de Foral'', or simply ''Foral'', was a royal document in Portugal and its former empire, whose purpose was to establish a ''concelho'' (Council) and regulate its administration, borders and priv ...
in 1512. King Manuel also rebuilt the Ínsua Fort (''Forte da Ínsua''), located in an island at sea and close to the village of Moledo.
After Portugal regained its independence from Spain in 1640, King John IV remodeled the fortifications of Caminha following modern ballistic advances. The Ínsua Fort was also remodeled. Together with the fortifications of Viana do Castelo, Valença, and Monção, the castle of Caminha was part of the defence line against the Castilians in the North.
With time, Caminha was superseded by Viana do Castelo in dominating maritime trade in Northern Portugal. Now Caminha lives from trade and tourism and it is connected to Galiza by a car ferry and to the rest of the country by rail and highways.
Attractions
The large Parish Church (begun 1488) is one of the most significant buildings illustrating the transition from Gothic toRenaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
in Portugal, with Manueline
The Manueline (, ), occasionally known as Portuguese late Gothic, is the sumptuous, composite Portuguese architectural style originating in the 16th century, during the Portuguese Renaissance and Age of Discoveries. Manueline architecture inco ...
influence. Several architects from Northern Spain participated in its long construction. The outstanding timber roof in the interior has rich decoration showing Moorish influences (Mudéjar
Mudéjar were Muslims who remained in Iberia in the late medieval period following the Christian reconquest. It is also a term for Mudéjar art, which was greatly influenced by Islamic art, but produced typically by Christian craftsmen for C ...
style).
Other major points of interest include the main square (Renaissance fountain of 1551), several Gothic and Renaissance houses in the old core and main square, and remains of medieval and 17th-century fortifications. Some pre-Roman archeological findings and ethnographic pieces are shown in the modest Municipal Museum.
The marshes along the Coura are protected and good for birdwatching.
The Atlantic beaches in the area are wide and have good sand but tend to be windy for part of the day; the Moledo beach (4 km south) attracts surfers. River and sea excursions can be arranged with local fishermen.
South of the Coura, the small granitic range ("Serra") of Arga (823 m) provides ample opportunities for hiking, cyclocross and canyoning. In the wooded northern slopes is the small monastery of S. João de Arga (popular place for picnics, camping and exploring peaks and streams; also venue for a religious festival) and the village of Castanheira (scenic terraced fields and natural pools).
A weekly market is held every Wednesday. Work from local coppersmiths and lacemakers can be found around town.
Parishes
Administratively, the municipality is divided into 14 civil parishes ('' freguesias''): * Âncora * Arga (Baixo, Cima e São João) * Argela * Caminha (Matriz) e Vilarelho * Dem * Gondar e Orbacém * Lanhelas * Moledo e Cristelo * Riba de Âncora * Seixas * Venade e Azevedo * Vila Praia de Âncora * Vilar de Mouros * VilePopulation
Notable people
* João Lourenço Rebelo (1610–1661) a composer who adopted the Venetian polychoral style. *Sidónio Pais
Sidónio Bernardino Cardoso da Silva Pais (1 May 1872 – 14 December 1918) nicknamed "the President-King" (), was the 4th president of Portugal, serving in 1918. A Portuguese people, Portuguese politician, Officer (armed forces), militar ...
(1872–1918) a politician, military officer and diplomat. The fourth President of the First Portuguese Republic in 1918. A charismatic, controversial and divisive figure.
; and
* José Vieira (born 1932) & Rui Valença (born 1932) & Ilídio Silva (born 1932) & José Porto (born 1933) & Jorge Cravinho (born 1933) are Portuguese rowers who competed in the Rowing at the 1960 Summer Olympics – Men's coxed four event.
References
External links
Municipality official website
{{Authority control Municipalities of Viana do Castelo District