Camboglanna on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
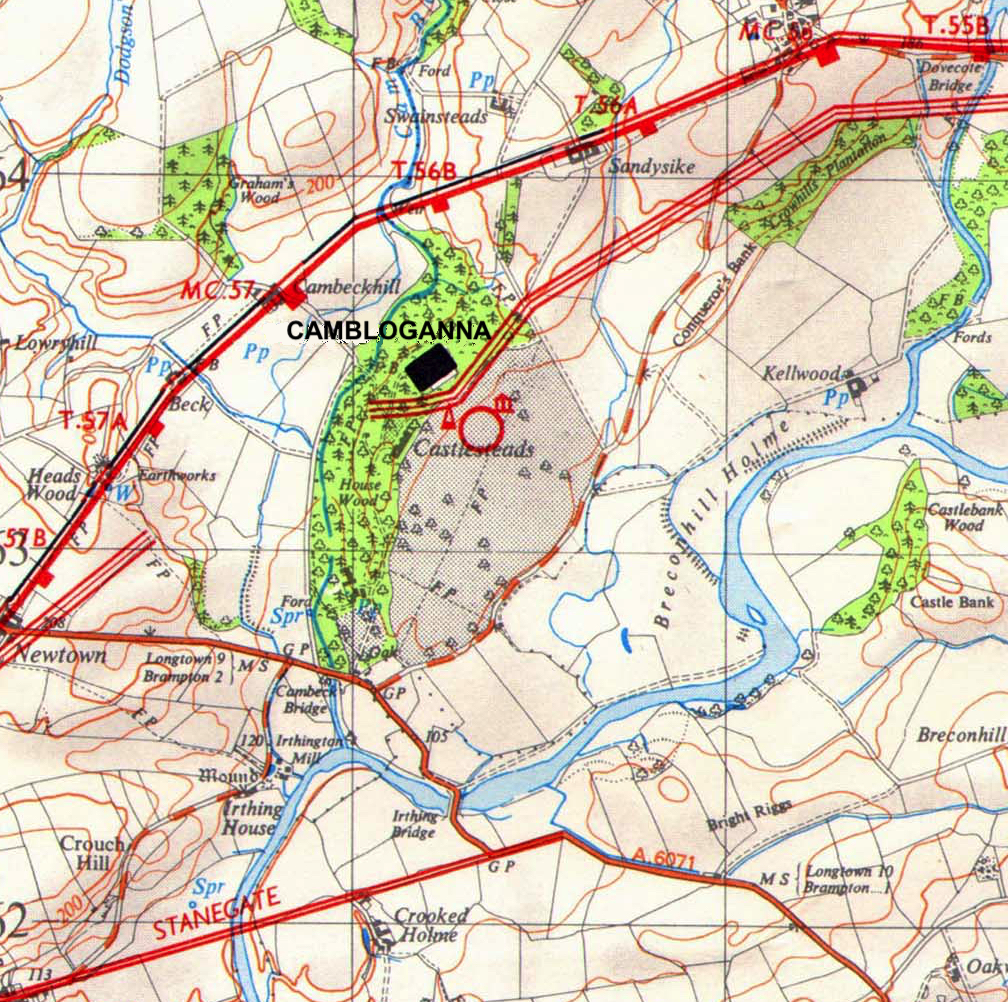
 Camboglanna (with the modern name of Castlesteads) was a Roman
Camboglanna (with the modern name of Castlesteads) was a Roman
Castlesteads (Camboglanna)
at www.Roman-Britain.co.uk {{coord, 54.965, N, 2.761, W, source:placeopedia, display=title Forts of Hadrian's Wall Roman fortifications in England Roman sites in Cumbria

 Camboglanna (with the modern name of Castlesteads) was a Roman
Camboglanna (with the modern name of Castlesteads) was a Roman fort
A fortification (also called a fort, fortress, fastness, or stronghold) is a military construction designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from La ...
. It was the twelfth fort on Hadrian's Wall
Hadrian's Wall (, also known as the ''Roman Wall'', Picts' Wall, or ''Vallum Aelium'' in Latin) is a former defensive fortification of the Roman province of Roman Britain, Britannia, begun in AD 122 in the reign of the Emperor Hadrian. Ru ...
counting from the east, between Banna ( Birdoswald) almost to the east and Uxelodunum ( Stanwix), 9 miles to the west. It was on a high bluff commanding the Cambeck Valley. It guarded an important approach to the Wall and also watched the east bank of the Cambeck against raiders from the Bewcastle area. The site was drastically levelled in 1791 when the gardens of Castlesteads House were laid over it. The name "Camboglanna" is believed to mean "Crook Bank", or "Bent Valley" because it overlooks a bend in the river Irthing; the name is Brythonic, made of cambo- "curved, bent, crooked" and glanna "steep bank, stream/river side, valley with a stream".
There was some confusion over the Roman name for the fort. At one time Camboglanna was the accepted name for Birdoswald, but this is now believed to be an error in the '' Notitia Dignitatum''. The Roman name for Birdoswald is now thought to be Banna.
Description
The fort was approximately square, measuring about and covering approximately . It faces roughly north-west by south-east and overlooks the gorge of the Cambeck. Erosion of the gorge has destroyed the north-west face of the fort. The fort lies within the Vallum, but is not adjacent to the Wall. It is the only fort on Hadrian's Wall in this position. It appears that the Wall had already been built at the most convenient point to cross the Cambeck and so, when the fort was built, the strongest point was chosen rather than one adjacent to the Wall.Garrison
The 2nd-century garrison was the Cohors IV Gallorum equitata. After it moved to Vindolanda, the 3rd-century garrison was the Cohors II Tungrorum, part-mounted.Vicus
The '' vicus'' (civilian settlement) next to the fort was seen in 1727 and was below the fort on the slope towards the River Irthing. After the levelling of the site for a walled garden in 1791 there are no remains visible and the area is now in woodland. A geophysical survey in 2007 showed the parts of the vicus around the south of the fort, with an east-west road. These parts of the vicus are to the south of the Vallum with a further ditch outside it. Buildings were generally stone-built, including four substantial buildings the larger of which is about 8 x 8 m, and were separated by a grid of streets. Some buildings were also between the vallum and the fort.Camlann?
Camboglanna is suspected by numerous authorities such as O. G. S. Crawford, Andrew Breeze, Michael Wood and Robin Collingwood of being the site of the infamous and semi-legendary sixth centuryBattle of Camlann
The Battle of Camlann ( or ''Brwydr Camlan'') is the legendary final battle of King Arthur, in which Arthur either died or was mortally wounded while fighting either alongside or against Mordred, who also perished. The original legend of Caml ...
between King Arthur
According to legends, King Arthur (; ; ; ) was a king of Great Britain, Britain. He is a folk hero and a central figure in the medieval literary tradition known as the Matter of Britain.
In Wales, Welsh sources, Arthur is portrayed as a le ...
and Mordred
Mordred or Modred ( or ; Welsh: ''Medraut'' or ''Medrawt'') is a major figure in the legend of King Arthur. The earliest known mention of a possibly historical Medraut is in the Welsh chronicle ''Annales Cambriae'', wherein he and Arthur are a ...
, a connection made at least as far back as 1935.
Excavations
In 1934 the fort was partly excavated and the walls, apart from the missing north-east wall, were uncovered. The north-east and south-west double gates, and the tower at the southern corner were also uncovered. It was also established that the fort was defended by a single ditch. Several altars have been found at the site and have been preserved. Previously, in 1741, an external bath-house was located and partly dug by Susanna Appleby, a local antiquarian.References
* J. Collingwood Bruce, Roman Wall (1863), Harold Hill & Son, * Frank Graham, The Roman Wall, Comprehensive History and Guide (1979), Frank Graham,External links
Castlesteads (Camboglanna)
at www.Roman-Britain.co.uk {{coord, 54.965, N, 2.761, W, source:placeopedia, display=title Forts of Hadrian's Wall Roman fortifications in England Roman sites in Cumbria