Calcitonin Gene Related Peptide on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) is a
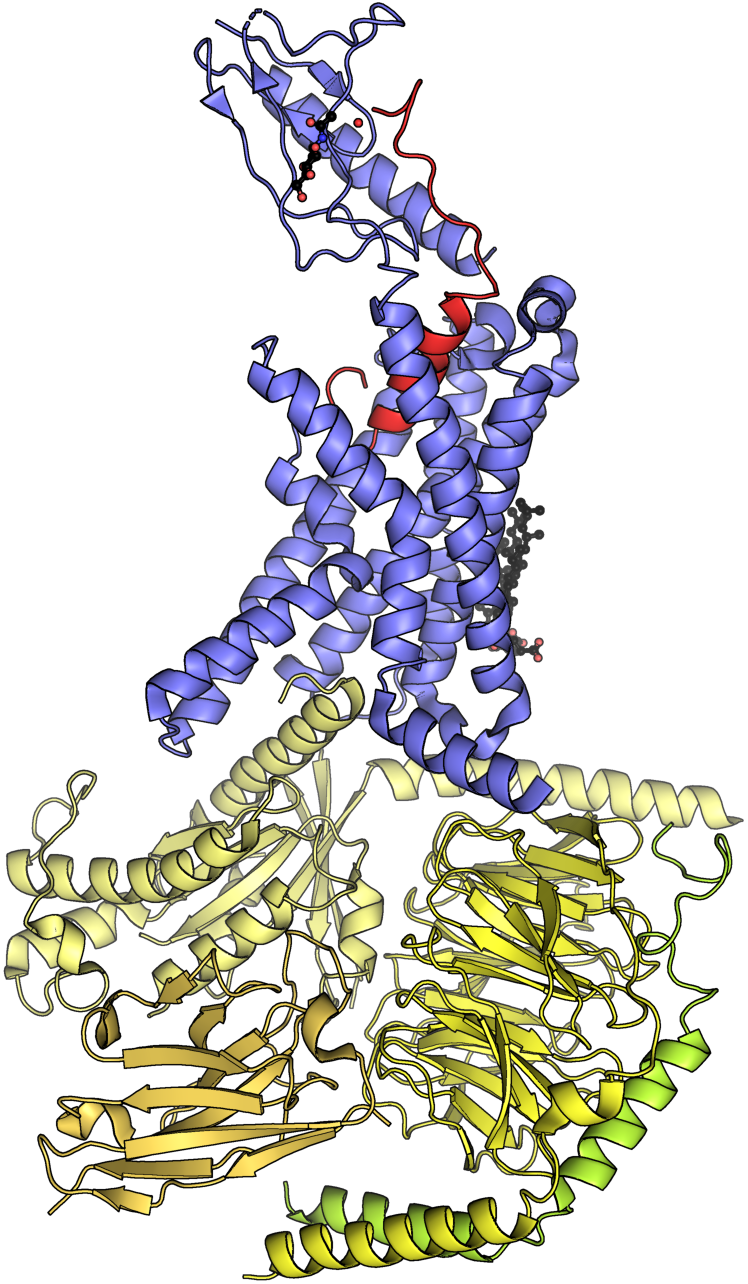 CGRP mediates its effects through a
CGRP mediates its effects through a
neuropeptide
Neuropeptides are chemical messengers made up of small chains of amino acids that are synthesized and released by neurons. Neuropeptides typically bind to G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) to modulate neural activity and other tissues like the ...
that belongs to the calcitonin
Calcitonin is a 32 amino acid peptide hormone secreted by parafollicular cells (also known as C cells) of the thyroid (or endostyle) in humans and other chordates in the ultimopharyngeal body. It acts to reduce blood calcium (Ca2+), opposing the ...
family. Human CGRP consists of two isoforms
A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar proteins that originate from a single gene and are the result of genetic differences. While many perform the same or similar biological roles, some isoforms have uniqu ...
, CGRP alpha (α-CGRP, also known as CGRP I) and CGRP beta (β-CGRP, also known as CGRP II). α-CGRP is a 37-amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
neuropeptide formed by alternative splicing
Alternative splicing, alternative RNA splicing, or differential splicing, is an alternative RNA splicing, splicing process during gene expression that allows a single gene to produce different splice variants. For example, some exons of a gene ma ...
of the calcitonin/CGRP gene located on chromosome 11
Chromosome 11 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. Humans normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 11 spans about 135 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents between 4 and 4.5 percent of the tota ...
. β-CGRP is less studied. In humans, β-CGRP differs from α-CGRP by three amino acids and is encoded in a separate, nearby gene. The CGRP family includes calcitonin (CT), adrenomedullin
Adrenomedullin (ADM) is a peptide hormone that plays an important role in various physiological processes throughout the human body. Initially discovered in 1993 from a pheochromocytoma, a tumor of the adrenal medulla, this 52-amino acid peptid ...
(AM), and amylin
Amylin, or islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP), is a 37-residue peptide hormone. It is co-secreted with insulin from the pancreatic β-cells in the ratio of approximately 100:1 (insulin:amylin). Amylin plays a role in glycemic regulation by slo ...
(AMY).
Function
CGRP is produced in both peripheral and centralneuron
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural net ...
s. It is a potent peptide vasodilator
Vasodilation, also known as vasorelaxation, is the widening of blood vessels. It results from relaxation of smooth muscle cells within the vessel walls, in particular in the large veins, large arteries, and smaller arterioles. Blood vessel wal ...
and can function in the transmission of nociception
In physiology, nociception , also nocioception; ) is the Somatosensory system, sensory nervous system's process of encoding Noxious stimulus, noxious stimuli. It deals with a series of events and processes required for an organism to receive a pai ...
. In the spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal c ...
, the function and expression of CGRP may differ depending on the location of synthesis. CGRP is derived mainly from the cell bodies of motor neuron
A motor neuron (or motoneuron), also known as efferent neuron is a neuron whose cell body is located in the motor cortex, brainstem or the spinal cord, and whose axon (fiber) projects to the spinal cord or outside of the spinal cord to directly o ...
s when synthesized in the ventral horn of the spinal cord and may contribute to the regeneration of nervous tissue after injury. Conversely, CGRP is derived from dorsal root ganglion
A dorsal root ganglion (or spinal ganglion; also known as a posterior root ganglion) is a cluster of neurons (a ganglion) in a dorsal root of a spinal nerve. The cell bodies of sensory neurons known as first-order neurons are located in the do ...
when synthesized in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord
The grey columns are three regions of the somewhat ridge-shaped mass of grey matter in the spinal cord. These regions present as three columns: the anterior grey column, the posterior grey column, and the lateral grey column, all of which are ...
and may be linked to the transmission of pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging Stimulus (physiology), stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sense, sensory and emotional experience associated with, or res ...
. In the trigeminal vascular system, the cell bodies of the trigeminal ganglion
The trigeminal ganglion (also known as: Gasserian ganglion, semilunar ganglion, or Gasser's ganglion) is the sensory ganglion of each trigeminal nerve (CN V). The trigeminal ganglion is located within the trigeminal cave (Meckel's cave), a cav ...
are the main source of CGRP. CGRP is thought to play a role in cardiovascular homeostasis and nociception. In the heart, CGRP acts as a chronotrope by increasing heart rate
Heart rate is the frequency of the cardiac cycle, heartbeat measured by the number of contractions of the heart per minute (''beats per minute'', or bpm). The heart rate varies according to the body's Human body, physical needs, including the nee ...
. Apart from these attributes, CGRP is known to modulate the autonomic nervous system
The autonomic nervous system (ANS), sometimes called the visceral nervous system and formerly the vegetative nervous system, is a division of the nervous system that operates viscera, internal organs, smooth muscle and glands. The autonomic nervo ...
and plays a role in ingestion.
CGRP has moderate effects on calcium homeostasis compared to its extensive actions in other areas, such as the autonomic nervous system.
Appetite
As a neuropeptide, CGRP acts as anappetite suppressant
An anorectic is a drug that reduces appetite, resulting in lower food consumption, leading to weight loss. These substances work by affecting the central nervous system or certain neurotransmitters to create a feeling of fullness or reduce the desi ...
and contributes to gastric acid
Gastric acid or stomach acid is the acidic component – hydrochloric acid – of gastric juice, produced by parietal cells in the gastric glands of the stomach lining. In humans, the pH is between one and three, much lower than most other a ...
secretion. It also functions in temperature homeostasis
Thermoregulation is the ability of an organism to keep its body temperature within certain boundaries, even when the surrounding temperature is very different. A thermoconforming organism, by contrast, simply adopts the surrounding temperature ...
, increases heart rate, and plays a role in the release of the pituitary hormones
The pituitary gland or hypophysis is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, the pituitary gland is located at the base of the brain, protruding off the bottom of the hypothalamus. The pituitary gland and the hypothalamus control much of th ...
in a paracrine
In cellular biology, paracrine signaling is a form of cell signaling, a type of cellular communication (biology), cellular communication in which a Cell (biology), cell produces a signal to induce changes in nearby cells, altering the behaviour of ...
manner. Because of these characteristics, it has been said that CGRP functions more as a neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a Chemical synapse, synapse. The cell receiving the signal, or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neurotra ...
than a hormone.
Stem cell mobilization
CGRP has a role in humanstem cell
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can change into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of cell ...
(HSC) mobilization. In investigations carried out in 2021, treatment with CGRP resulted in significantly increased CGRP levels in the bone marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid biological tissue, tissue found within the Spongy bone, spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It i ...
extracellular fluid and substantially increased the number of HSCs mobilized by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor
Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF or GCSF), also known as colony-stimulating factor 3 (CSF 3), is a glycoprotein that stimulates the bone marrow to produce granulocytes and stem cells and release them into the bloodstream.
Function ...
(G-CSF). The authors of the 2021 study concluded that G-CSF-induced HSC mobilization is regulated by the nociceptor nerve-derived neuropeptide CGRP. This peptide exerts its effect on HSC mobilization via the receptor activity-modifying protein 1 (RAMP1) pathway.
Receptors
 CGRP mediates its effects through a
CGRP mediates its effects through a heteromeric A heteromer is something that consists of different parts; the antonym of homomeric. Examples are:
Biology
* Spinal neurons that pass over to the opposite side of the spinal cord.
* A protein complex that contains two or more different polypeptid ...
receptor composed of a G protein-coupled receptor
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily related ...
called calcitonin receptor-like receptor (CALCRL
Calcitonin receptor-like (CALCRL), also known as the calcitonin receptor-like receptor (CRLR), is a human protein; it is a receptor for calcitonin gene-related peptide.
Function
The protein encoded by the CALCRL gene is a G protein-coupled rece ...
) and RAMP1. CGRP receptors are found throughout all the body, suggesting that the protein may modulate a variety of physiological functions in all major systems (e.g., respiratory
The respiratory system (also respiratory apparatus, ventilatory system) is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in animals and plants. The anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies gr ...
, endocrine
The endocrine system is a messenger system in an organism comprising feedback loops of hormones that are released by internal glands directly into the circulatory system and that target and regulate distant organs. In vertebrates, the hypotha ...
, gastrointestinal
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascular system. ...
, immune
In biology, immunity is the state of being insusceptible or resistant to a noxious agent or process, especially a pathogen or infectious disease. Immunity may occur naturally or be produced by prior exposure or immunization.
Innate and adaptive ...
, and cardiovascular
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart a ...
). These transmembrane receptors
Cell surface receptors (membrane receptors, transmembrane receptors) are receptors that are embedded in the plasma membrane of cells. They act in cell signaling by receiving (binding to) extracellular molecules. They are specialized integral ...
form folded accordion-like structures embedded in the cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extr ...
with loops of protein on the inside (intracellular loops) and outside (extracellular loops) of the membrane. The second extracellular loop is fundamental for ligand-induced activation, with key interactions of R274/Y278/D280/W283.
Regulation
Regulation of the CGRP gene is in part controlled by the expression of themitogen-activated protein kinase
A mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK or MAP kinase) is a type of serine/threonine-specific protein kinases involved in directing cellular responses to a diverse array of stimuli, such as mitogens, osmotic stress, heat shock and proinflamma ...
(MAPK) signaling pathway
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) is the process by which a cell interacts with itself, other cells, and the environment. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all cellular life in both prokaryotes and eukary ...
and cytokine
Cytokines () are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling.
Cytokines are produced by a broad range of cells, including immune cells like macrophages, B cell, B lymphocytes, T cell, T lymphocytes ...
s like TNFα
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF), formerly known as TNF-α, is a chemical messenger produced by the immune system that induces inflammation. TNF is produced primarily by activated macrophages, and induces inflammation by binding to its receptors o ...
and iNOS
Nitric oxide synthases (NOSs) are a family of enzymes catalyzing the production of nitric oxide (NO) from L-arginine. NO is an important cellular signaling molecule. It helps modulate vascular tone, insulin secretion, airway tone, and perist ...
. 5HT1 receptor agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a Receptor (biochemistry), receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are Cell (biology), cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an R ...
s like sumatriptan
Sumatriptan, sold under the brand name Imitrex among others, is a medication used to treat migraine headaches and cluster headaches. It is taken Oral administration, orally, Nasal administration, intranasally, or by Subcutaneous injection, su ...
increase intracellular calcium, which causes decreases in CGRP promoter activity.
CGRP receptors are found in myelinated A-fiber axons which is required for ligand specificity and function of the receptor. The CGRP receptor has three subunits: receptor activity-modifying protein 1 (RAMP1), calcitonin-like receptor (CLR) and receptor component protein (RCP). The complex central receptor is the G protein-coupled receptor calcitonin receptor-like receptor (CALCRL) which is necessary for CGRP and adrenomedullin (AM receptors). For function CGRP, CALCRL must coincide with RAMP1 where the ligand-binding domain of CGRP is located. It also includes two cytoplasmic proteins that associate with the CALCRL-RAMP1 to form signal transduction. CALCRL contains the Gα subunit, which activates adenylyl cyclase and cAMP-dependent signaling pathways. Receptor-mediated transduction elevates in intracellular cAMP activate protein kinase A, which results in the phosphorylation of multiple targets, including potassium- sensitive ATP channels (KATP channels), extracellular signal-related kinases and transcription factors such as cAMP-responsive element-binding protein (CREB). In smooth muscle of neurovascular region, the elevation of cAMP upon CGRP activation results in vasodilation of the blood vessel. Chronic exposure to CGRP causes degradation of lysosomes.
Research
Increased levels of CGRP have been reported inmigraine
Migraine (, ) is a complex neurological disorder characterized by episodes of moderate-to-severe headache, most often unilateral and generally associated with nausea, and light and sound sensitivity. Other characterizing symptoms may includ ...
and temporomandibular joint disorder
Temporomandibular joint dysfunction (TMD, TMJD) is an umbrella term covering pain and dysfunction of the muscles of mastication (the muscles that move the jaw) and the temporomandibular joints (the joints which connect the mandible to the skul ...
patients as well as a variety of other diseases such as cardiac failure, hypertension, and sepsis.
There is mounting evidence to suggest that CGRP may be beneficial in preventing the development of hypertension and cardiovascular pathologies associated with hypertension. Prophylactic therapy with calcitonin gene-related peptides (CGRPs) may have unknown fertility consequences for women of childbearing age. This is of particular concern, as females (16.6%) are more genetically predisposed to migraine than are males (7.5%).
Preclinical evidence suggests that, during a migraine
Migraine (, ) is a complex neurological disorder characterized by episodes of moderate-to-severe headache, most often unilateral and generally associated with nausea, and light and sound sensitivity. Other characterizing symptoms may includ ...
, activated primary sensory neurons (meningeal nociceptors) in the trigeminal ganglion
The trigeminal ganglion (also known as: Gasserian ganglion, semilunar ganglion, or Gasser's ganglion) is the sensory ganglion of each trigeminal nerve (CN V). The trigeminal ganglion is located within the trigeminal cave (Meckel's cave), a cav ...
release CGRP from their peripherally projecting nerve endings located within the meninges
In anatomy, the meninges (; meninx ; ) are the three membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord. In mammals, the meninges are the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater. Cerebrospinal fluid is located in the subarachnoid spac ...
. This CGRP then binds to and activates CGRP receptors located around meningeal vessels, causing vasodilation, mast cell
A mast cell (also known as a mastocyte or a labrocyte) is a resident cell of connective tissue that contains many granules rich in histamine and heparin. Specifically, it is a type of granulocyte derived from the myeloid stem cell that is a p ...
degranulation, and plasma extravasation
Extravasation is the leakage of a fluid out of its contained space into the surrounding area, especially blood or blood cells from vessels. In the case of inflammation, it refers to the movement of white blood cells through the capillary wall, ...
. Human observations have further implicated the role of CGRP in the pathophysiology of migraine. Activation of primary sensory neurons in the trigeminal vascular system in humans can cause the release of CGRP. During some migraine attacks, increased concentrations of CGRP can be found in both saliva and in plasma drawn from the external jugular vein. Furthermore, intravenous administration of alpha-CGRP is able to induce headache in individuals susceptible to migraine.
Medicines
Treatments based onmonoclonal antibodies
A monoclonal antibody (mAb, more rarely called moAb) is an antibody produced from a Lineage (evolution), cell lineage made by cloning a unique white blood cell. All subsequent antibodies derived this way trace back to a unique parent cell.
Mon ...
have been produced related to CGRP or CGRP receptors. They have been shown to be effective in patients who experience migraine headaches, both with and without aura, and both episodic and chronic cluster headache. These are the first class of preventive medications originally designed and approved for people with migraine. Due to the nature of the monoclonal antibodies, they must be administered parenterally, preferably by injection.
The first CGRP related medication approved by the FDA is called Erenumab
Erenumab, sold under the brand name Aimovig, is a medication which blocks the calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor (CGRPR) for the prevention of migraine. It is administered by subcutaneous injection.
Erenumab, which was developed by Amgen ...
(trade name Aimovig), produced by pharmaceutical company Amgen and Novartis. It interacts with the CGRP receptor. It is injected once monthly with a dose of 70 or 140 mg. Few adverse effects were reported (most related to injection site reactions) and patients had a significant reduction in migraines.
The second approved by the FDA is called Fremanezumab
Fremanezumab, sold under the brand name Ajovy, is a medication used to prevent migraines in adults. It is given by subcutaneous injection (injection under the skin).
The most common side effect is pain and redness at the site of injection. O ...
(trade name Ajovy), produced by the Teva pharmaceutical company. It interacts with the CGRP protein, whose expression is related to migraine attacks. It may be administered monthly or every three months, giving options for users. Trials have shown a reduction of greater than 50% of migraine days for those who responded. There were few significant side effects during trials, most related to injection site reactions.
The third approved by the FDA is called Galcanezumab
Galcanezumab, sold under the brand name Emgality, is a humanized monoclonal antibody used for the prevention of migraine. It is also used for the treatment of cluster headaches.
A substance called calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) has ...
(trade name Emgality), produced by the Eli Lilly Company. It interacts with the CGRP protein, whose expression is related to migraine attacks. It is injected once a month, after the first month having a double dose. The main side effects are injection site reactions.
Approved by the FDA in February 2020, ubrogepant
Ubrogepant, sold under the brand name Ubrelvy, is a medication used for the acute (immediate) treatment of migraine with or without aura (a sensory phenomenon or visual disturbance) in adults. It is not indicated for the preventive treatment of ...
(Ubrelvy) is an oral medication manufactured by AbbVie.
Also FDA approved in February 2020, Eptinezumab
Eptinezumab, sold under the brand name Vyepti, is a medication used for the preventive treatment of migraine in adults. It is a monoclonal antibody that targets calcitonin gene-related peptides (CGRP) alpha and beta. It is administered by intra ...
(Vyapti), is an intravenous migraine prophylactic medication manufactured by Lundbeck.
In September 2021 the FDA approved Qulipta
Atogepant, sold under the brand name Qulipta among others, is a medication used to prevent migraines. It is a gepant, a calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor antagonist administered orally.
The most common side effects include nausea, co ...
(atogepant), the first oral CGRP receptor antagonist approved to prevent chronic migraine.
The phytocannabinoids
Cannabinoids () are several structural classes of compounds found primarily in the ''Cannabis'' plant or as synthetic compounds. The most notable cannabinoid is the phytocannabinoid tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) (delta-9-THC), the primary psychoact ...
delta-9 tetrahydrocannabinol
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is a cannabinoid found in cannabis. It is the principal psychoactive constituent of ''Cannabis'' and one of at least 113 total cannabinoids identified on the plant. Although the chemical formula for THC (C21H30O2) de ...
(Δ9-THC) and its oxidative
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is ...
byproduct cannabinol
Cannabinol (CBN) is a mildly psychoactive phytocannabinoid that acts as a low affinity partial agonist at both CB1 and CB2 receptors. This activity at CB1 and CB2 receptors constitutes interaction of CBN with the endocannabinoid system (ECS) ...
(CBN) are found to induce a CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptor
Cannabinoid receptors, located throughout the body, are part of the endocannabinoid system of vertebrates a class of cell membrane receptors in the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily. As is typical of G protein-coupled receptors, the cann ...
-independent release of calcitonin gene-related peptide from capsaicin
Capsaicin (8-methyl-''N''-vanillyl-6-nonenamide) (, rarely ) is an active component of chili peppers, which are plants belonging to the genus ''Capsicum''. It is a potent Irritation, irritant for Mammal, mammals, including humans, and produces ...
-sensitive perivascular
Mural cells are the generalized name of cell population in the microcirculation that is comprised of vascular smooth muscle cells (vSMCs), and pericytes. Both types are in close contact with the endothelial cells lining the capillaries, and are i ...
sensory nerve
A sensory nerve, or afferent nerve, is a nerve that contains exclusively afferent nerve fibers. Nerves containing also motor fibers are called mixed nerve, mixed. Afferent nerve fibers in a sensory nerve carry sensory system, sensory information ...
s, an action that other psychotropic cannabinoids cannot do.
References
External links
* {{Sigma receptor modulators Neuropeptides