CDK inhibitor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A CDK (cyclin-dependent kinase) inhibitor is any chemical that inhibits the function of CDKs. They are used to treat
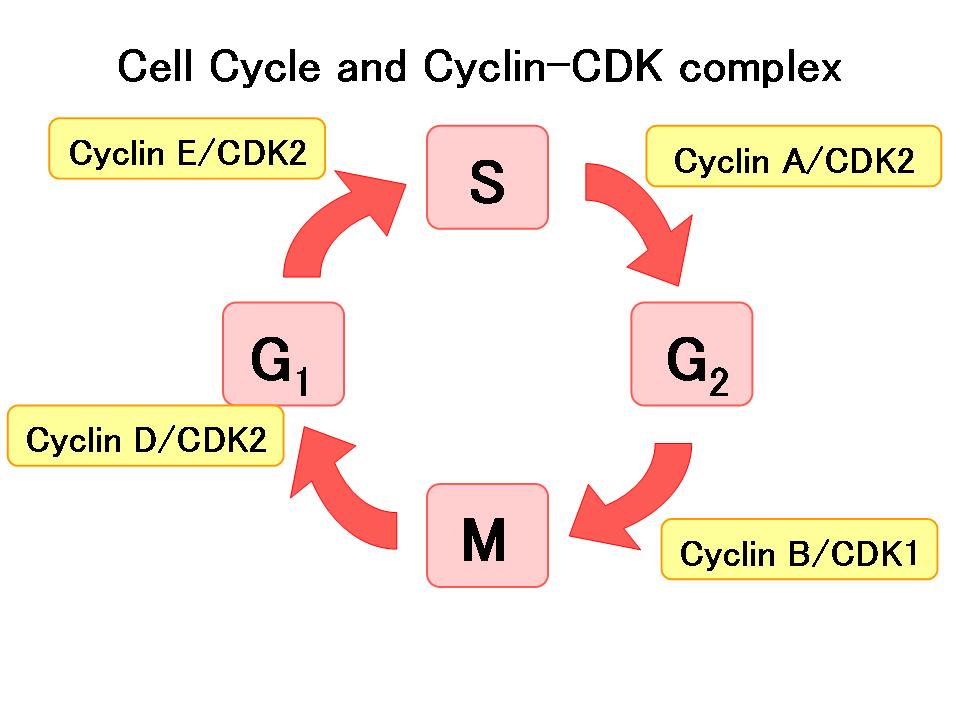 The
The
Purvalanol A, Olomoucine II and Roscovitine Inhibit ABCB1 Transporter and Synergistically Potentiate Cytotoxic Effects of Daunorubicin In Vitro.
/ref> Based on molecular docking results, Ligands-3, 5, 14, and 16 were screened among 17 different Pyrrolone-fused benzosuberene compounds as potent and specific inhibitors without any cross-reactivity against different CDK isoforms. Analysis of MD simulations and MM-PBSA studies, revealed the binding energy profiles of all the selected complexes. Selected ligands performed better than the experimental drug candidate (Roscovitine). Ligands-3 and 14 show specificity for CDK7 and Ligands-5 and 16 were specific against CDK9. These ligands are expected to possess lower risk of side effects due to their natural origin. Interpretation of dynamic simulations and binding free energy studies unveiled that Ligand2 (Out of 17 in-house synthesized pyrrolone-fused benzosuberene (PBS) compounds) has a stable and equivalent free energy to Flavopiridol, SU9516, and CVT-313 inhibitors. Ligand2 scrutinized as a selective inhibitor of CDK2 without off-target binding (CDK1 and CDK9) based on ligand efficiency and binding affinity.
cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
s by preventing overproliferation of cancer cells. The US FDA approved the first drug of this type, palbociclib
Palbociclib, sold under the brand name Ibrance among others, is a medication developed by Pfizer for the treatment of HR-positive and HER2-negative breast cancer. It is a selective inhibitor of the cyclin-dependent kinases CDK4 and CDK6. Palb ...
(Ibrance), a CDK4
Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4), also known as cell division protein kinase 4, is an enzyme that is encoded by the ''CDK4'' gene in humans. CDK4 is a member of the cyclin-dependent kinase family, a group of serine/threonine kinases which regula ...
/ 6 inhibitor, in February 2015, for use in postmenopausal women with breast cancer that is estrogen receptor
Estrogen receptors (ERs) are proteins found in cell (biology), cells that function as receptor (biochemistry), receptors for the hormone estrogen (17β-estradiol). There are two main classes of ERs. The first includes the intracellular estrogen ...
positive and HER2 negative. While there are multiple cyclin/CDK complexes regulating the cell cycle, CDK inhibitors targeting CDK4/6 have been the most successful; four CDK4/6 inhibitors have been FDA approved. No inhibitors targeting other CDKs have been FDA approved, but several compounds are in clinical trials.
CDKs as cancer target
:''See also Ribociclib#Mechanism of action re: CDK4'' The
The cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the sequential series of events that take place in a cell (biology), cell that causes it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the growth of the cell, duplication of its DNA (DNA re ...
is a highly regulated process governing cell division and is controlled by several cyclins and CDKs. Cyclins phosphorylate CDKs, forming complexes that stabilize them and allow them to enact their function. While cyclins activate CDKs, there are other regulatory molecules that can inhibit their function. Under normal conditions, the activation and inhibition of CDK complexes controls the behavior of the cell at many important cell cycle checkpoints to regulate healthy division. However, this process can become dysregulated, leading to the uncontrolled division of cells known as cancer. In fact, in many human cancers, CDKs are overactive or CDK-inhibiting proteins are not functional. CDK inhibitors as a therapy emerged from the idea that order could be restored to an overreactive cell cycle by inhibiting the CDKs whose activation drives the cell cycle forward. Therefore, it is rational to target CDK function to prevent unregulated proliferation of cancer cells.
However, the validity of CDK as a cancer target should be carefully assessed because genetic studies have revealed that knockout of one specific type of CDK often does not affect proliferation of cells or has an effect only in specific tissue types. For example, most adult cells in mice proliferate normally even without both CDK4
Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4), also known as cell division protein kinase 4, is an enzyme that is encoded by the ''CDK4'' gene in humans. CDK4 is a member of the cyclin-dependent kinase family, a group of serine/threonine kinases which regula ...
and CDK2
Cyclin-dependent kinase 2, also known as cell division protein kinase 2, or Cdk2, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''CDK2'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the cyclin-dependent kinase family of serine/threonine ...
.
Furthermore, specific CDKs are only active in certain periods of the cell cycle. Therefore, the pharmacokinetics and dosing schedule of the candidate compound must be carefully evaluated to maintain active concentration of the drug throughout the entire cell cycle.
Limitations
Another remaining question surrounding CDK inhibitors as a therapy is if certain cancers will evade or be resistant to treatment. One study showed that 20% of the patients being treated for metastatic ER+ HER2-breast cancer did not respond at all to treatment with a CDK4/6 inhibitor due to preexisting mutations allowing the cancer cells to continue proliferating despite treatment with the drug. Other studies have shown this number to be as high as 30%. Another study notes that the usefulness of CDK4/6 in the clinical may be limited by acquired drug resistance. In this study, treatment with CDK4/6 inhibitors in ER+ breast cancer and non-small cell lung carcinoma harboring KRAS mutations resulted in upregulation of cyclin D1, CDK4, and cyclin E1, negating the effects of administering the drug.Types
Malumbres et al., categorized CDK inhibitors based on their target specificity:Broad CDK inhibitors
* Compounds targeting a broad spectrum of CDKs * Also known as pan-CDK inhibitors * Many of the initial CDK inhibitor drugs that entered clinical trials were pan-CDK inhibitors * These initial drugs exhibited high levels of toxicity and off-target effects due to a lack of specificity, so many were discontinued * There are still ongoing efforts to bring pan-CDK inhibitors to clinical useSpecific CDK inhibitors
* Compounds targeting a specific type of CDK * Shown to decrease off-target effects * Developed in response to issues implementing pan-CDK inhibitors * Evidence shows that different tumor types express different levels of CDKs, necessitating that specific CDK inhibitors be tested for clinical effectiveness in each cancer typeMultiple Target Inhibitors
* Compounds targeting CDKs as well as additional kinases such as VEGFR or PDGFRApproved
CDK4/CDK6 inhibitors
The current FDA approved drugs are all CDK4/6 inhibitors targeting CDK4 and CDK6, two enzymes that control the cell cycle checkpoint transition checkpoint from the G1 to the S phase of the cell cycle. These cell cycle inhibitors work by inducing cell cycle arrest at G1. Several drugs have been approved by theUS FDA
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food ...
for HR-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer
Breast cancer is a cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a Breast lump, lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, Milk-rejection sign, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipp ...
.
Palbociclib
Palbociclib, sold under the brand name Ibrance among others, is a medication developed by Pfizer for the treatment of HR-positive and HER2-negative breast cancer. It is a selective inhibitor of the cyclin-dependent kinases CDK4 and CDK6. Palb ...
(PD-033299, trade name Ibrance) gave encouraging results in a phase II clinical trial on patients with HR-positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer. The addition of PD-0332991 to letrozole
Letrozole, sold under the brand name Femara among others, is an aromatase inhibitor medication that is used in the treatment of breast cancer for post-menopausal women.
It was patented in 1986 and approved for medical use in 1996. In 2021, ...
trebled median time to disease progression to 26.1 months compared with 7.5 months for letrozole alone. The FDA granted it Accelerated Approval The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) initiated the FDA Accelerated Approval Program in 1992 to allow faster approval of drugs for serious conditions that fill an unmet medical need. The faster approval relies on use of surrogate end ...
in Feb 2015.
Ribociclib (LEE011, trade names Kisqali and Kryxana), is US FDA approved in combination with letrozole for treatment of breast cancer in patients with HR-positive, HER2-negative advanced metastatic breast cancer. A phase three clinical trial found that ribociclib administered in combination with letrozole increased the likelihood of progression free survival to 63% in the first 18 months of therapy versus 42% for letrozole alone. Subsequent analysis demonstrated that patients treated with ribociclib and letrozole showed a median progression-free survival of 25.3 months.
Abemaciclib (LY2835219, trade name Verzenio) was approved in September 2017 by the FDA for "adult patients who have hormone receptor (HR)-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer that has progressed after taking therapy that alters a patient's hormones".
One drug has been FDA approved for mediating chemotherapy-induced side effects.
Trilaciclib (V03AF12, trade name Cosela) was approved in February 2021 to reduce chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression in patients with late-stage small-cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC). However, there are active clinical trials evaluating the use of trilaciclib in other forms of cancer, including small cell lung cancer, breast cancer, and colorectal cancer.
Dalpiciclib is approved in China for use in combination with fulvestrant for treatment of HR-positive, HER2-negative recurrent, or metastatic breast cancer
Metastatic breast cancer, also referred to as metastases, advanced breast cancer, secondary tumors, secondaries or stage IV breast cancer, is a stage of breast cancer where the breast cancer cells have spread to distant sites beyond the axillary l ...
in patients who have progressed after previous endocrine therapy.
In clinical trials
There are more than 10 CDK inhibitor compounds that have gone through or currently ongoing clinical trials, as of 2009. Most of them are targeting multiple CDKs, but some are targeting specific CDKs. For example, P1446A-05 targets CDK4. Various types of cancers includingleukemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia; pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and produce high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or '' ...
, melanoma
Melanoma is the most dangerous type of skin cancer; it develops from the melanin-producing cells known as melanocytes. It typically occurs in the skin, but may rarely occur in the mouth, intestines, or eye (uveal melanoma). In very rare case ...
, solid tumors, and other types are being targeted. In some cases, very specific cancer types, such as 'melanoma positive for cyclin D1 expression' are targeted to maximize the efficacy.
, trilaciclib (G1T28, CDK4/6 inhibitor, G1 Therapeutics) is in multiple phase II clinical trials. The drug is being tested as a method for reducing the adverse effects of chemotherapy. In August 2019, trilaciclib received breakthrough therapy
Breakthrough therapy is a United States Food and Drug Administration designation that expedites drug development that was created by Congress under Section 902 of the 9 July 2012 Food and Drug Administration Safety and Innovation Act. The FDA's "b ...
designation for its ability to minimize chemotherapy-induced bone marrow suppression. , the drug was under Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respo ...
(FDA) priority review
Priority review is a program of the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to expedite the review process for drugs that are expected to have a particularly great impact on the treatment of a disease. The priority review voucher program ...
for small-cell lung cancer
Small-cell carcinoma, also known as oat cell carcinoma, is a type of highly malignant cancer that most commonly arises within the lung, although it can occasionally arise in other body sites, such as the cervix, prostate, and gastrointestinal tr ...
with an application decision date of February 15, 2021.
Although CDK4/6 inhibitors have had the most success, CDK inhibitors targeting other CDKs are also undergoing clinical trials.
* Milciclib- a pan-CDK inhibitor targeting CDK1, CDK2, CDK4, and CDK7. It is currently being evaluated in phase II trials for hepatocellular carcinoma.
* Dinaciclib- a pan-CDK inhibitor against CDK1, CDK2, CDK5, and CDK9. As of December 2023, it is on the market as an orphan drug
An orphan drug is a medication, pharmaceutical agent that is developed to treat certain rare medical conditions. An orphan drug would not be profitable to produce without government assistance, due to the small population of patients affected by th ...
for treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
* Roscovitine- a pan-CDK inhibitor against CDK2, CDK7, CDK9. It is currently in phase II clinical trials for pituitary cushing disease.
Combination Therapies
Due to recurrent issues with CDK inhibitor resistance and non-responders, the current focus of many clinical trials includes examining the outcomes of administering CDK inhibitors in combination with other existing therapies. The interest in combined therapies is also in part due to the fact that CDK inhibitors halt the cell cycle to stop cancer growth, but they do not induce apoptosis to reduce tumor size. Therefore, many clinical trials are interested in observing if there are better health outcomes by combining CDK inhibitors with other forms of therapy. For example, using a combination ofPalbociclib
Palbociclib, sold under the brand name Ibrance among others, is a medication developed by Pfizer for the treatment of HR-positive and HER2-negative breast cancer. It is a selective inhibitor of the cyclin-dependent kinases CDK4 and CDK6. Palb ...
(CDK4/6 inhibitor), Fulvestrant (estrogen receptor antagonist), and Avelumab (monoclonal antibody) for the treatment of metastatic ER+ HER- breast cancer is currently undergoing Phase II clinical trials.
Other
* Purvalanol A, Olomoucine II./ref> Based on molecular docking results, Ligands-3, 5, 14, and 16 were screened among 17 different Pyrrolone-fused benzosuberene compounds as potent and specific inhibitors without any cross-reactivity against different CDK isoforms. Analysis of MD simulations and MM-PBSA studies, revealed the binding energy profiles of all the selected complexes. Selected ligands performed better than the experimental drug candidate (Roscovitine). Ligands-3 and 14 show specificity for CDK7 and Ligands-5 and 16 were specific against CDK9. These ligands are expected to possess lower risk of side effects due to their natural origin. Interpretation of dynamic simulations and binding free energy studies unveiled that Ligand2 (Out of 17 in-house synthesized pyrrolone-fused benzosuberene (PBS) compounds) has a stable and equivalent free energy to Flavopiridol, SU9516, and CVT-313 inhibitors. Ligand2 scrutinized as a selective inhibitor of CDK2 without off-target binding (CDK1 and CDK9) based on ligand efficiency and binding affinity.

See also
* * ZotiraciclibReferences
{{DEFAULTSORT:Cdk Inhibitor