C17orf98 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sperm microtubule associated protein 1 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''SPMAP1'' gene. The protein is derived from ''Homo sapiens'' chromosome 17. The ''SPMAP1'' gene consists of a 6,302 base sequence. Its mRNA has three exons and no alternative splice sites. The protein has 154 amino acids, with no abnormal amino acid levels. SPMAP1 has a
/ref> SPMAP1 does not belong to any other families nor does it have any isoforms. The protein has orthologs with high percent similarity in mammals and reptiles. The protein has additional distantly related orthologs across the
/ref> The protein has also been known to have elevated levels in cancer. The protein has been shown to be expressed in proximity to or within
/ref> Motif and transcription factor analysis points towards SPMAP1 playing a role in proliferation, specially in immune cell proliferation.

 Kinase finder at Cuckoo determined kinase binding sites for SPMAP1. There are many Serine/Threonine, and Tyrosine kinase phosphorylation sites. Serine and Threonine kinase binding sites are the most prevalent above the statistically significant threshold. There are no SUMOylation sites. ''SPMAP1'' gene has six sites on the sequence of possible O-GlcNAc sites. Highly conserved O-GlcNAc amino acid sites are 24, 32, 117, and 142. O-GlcNAc post-translational modification occurs on Ser/Thr residues, specifically on oncogenes, tumor suppressors, and proteins involved in growth factor signaling.
SPMAP1 has a Caspase3/7 motif, where either Caspase 3 or 7 would cleave. This supports the idea that SPMAP1 is involved in proliferation, as a proapoptotic caspase would want to destroy any protein driving proliferation. The protein also has a motif where peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase NIMA interacting 1 (Pin1) binds. Pin1 upregulation is involved in cancer and immune disorders. This supports the claim that SPMAP1 is involved in cancer, immune cells, and perhaps cancers of the immune system. Additionally, SPMAP1 protein has an IBM site, where inhibitors of apoptosis (IAPs) bind.Eukaryotic Linear Motif search on c17orf98 amino acid sequence
Kinase finder at Cuckoo determined kinase binding sites for SPMAP1. There are many Serine/Threonine, and Tyrosine kinase phosphorylation sites. Serine and Threonine kinase binding sites are the most prevalent above the statistically significant threshold. There are no SUMOylation sites. ''SPMAP1'' gene has six sites on the sequence of possible O-GlcNAc sites. Highly conserved O-GlcNAc amino acid sites are 24, 32, 117, and 142. O-GlcNAc post-translational modification occurs on Ser/Thr residues, specifically on oncogenes, tumor suppressors, and proteins involved in growth factor signaling.
SPMAP1 has a Caspase3/7 motif, where either Caspase 3 or 7 would cleave. This supports the idea that SPMAP1 is involved in proliferation, as a proapoptotic caspase would want to destroy any protein driving proliferation. The protein also has a motif where peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase NIMA interacting 1 (Pin1) binds. Pin1 upregulation is involved in cancer and immune disorders. This supports the claim that SPMAP1 is involved in cancer, immune cells, and perhaps cancers of the immune system. Additionally, SPMAP1 protein has an IBM site, where inhibitors of apoptosis (IAPs) bind.Eukaryotic Linear Motif search on c17orf98 amino acid sequence
/ref> This again supports the idea of SPMAP1 being involved in inhibiting apoptosis, and logically, driving cancer. Furthermore, SPMAP1 has motifs where
intermediate filaments and the nucleoli
A SPMAP1 antibody is available from Sigma-Aldrich. Additionally, SPMAP1 localizes in the cytoplasm. Distantly related SPMAP1 orthologs in organisms such as ''Macrostomum lignano'' and ''Amphimedon queenslandica'' exhibit nuclear expression.
domain of unknown function A domain of unknown function (DUF) is a protein domain that has no characterised function. These families have been collected together in the Pfam database using the prefix DUF followed by a number, with examples being DUF2992 and DUF1220. As of 201 ...
(DUF4542) and is 17.6kDa in weight.ENMBL-EBI SAPS entry on c17orf98/ref> SPMAP1 does not belong to any other families nor does it have any isoforms. The protein has orthologs with high percent similarity in mammals and reptiles. The protein has additional distantly related orthologs across the
metazoa
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, have myocytes and are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and grow from a hol ...
n kingdom, culminating with the sponge family.
Like most proteins, SPMAP1 is known to be highly expressed in the testes.Human protein atlas entry on c17orf98/ref> The protein has also been known to have elevated levels in cancer. The protein has been shown to be expressed in proximity to or within
intermediate filaments
Intermediate filaments (IFs) are cytoskeletal structural components found in the cells of vertebrates, and many invertebrates. Homologues of the IF protein have been noted in an invertebrate, the cephalochordate ''Branchiostoma''.
Intermedi ...
and the nucleolus
The nucleolus (; : nucleoli ) is the largest structure in the cell nucleus, nucleus of eukaryote, eukaryotic cell (biology), cells. It is best known as the site of ribosome biogenesis. The nucleolus also participates in the formation of signa ...
. Additionally, ''SPMAP1'' has transcription factors which are also active in hematopoietic stem cell
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are the stem cells that give rise to other blood cells. This process is called haematopoiesis. In vertebrates, the first definitive HSCs arise from the ventral endothelial wall of the embryonic aorta within the ...
s, the immune system
The immune system is a network of biological systems that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to bacteria, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells, Parasitic worm, parasitic ...
, and the cardiovascular system
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart a ...
, among others. The gene is over-expressed in many cancer types, including kidney renal clear cell carcinoma and lung squamous cell carcinoma.TissGDB entry on c17orf98/ref> Motif and transcription factor analysis points towards SPMAP1 playing a role in proliferation, specially in immune cell proliferation.
Gene
Background
The ''SPMAP1'' gene consists of 6,303 bases. It has three exons and two large introns. The gene has no alternative splice sites. The 5' UTR sequence of ''SPMAP1'' is highly conserved in primates. No non-mammalian 5' UTR matches were able to be determined. ''SPMAP1'' has 11 Alu repeats.Enhancers
GeneCards determined that ''SPMAP1'' has five enhancer sequences. The role of the sequences may provide insight into the function of SPMAP1. Four of the five enhancers are active in the thymus. All five enhancers are active in the H1 hESC. Additionally, all five enhancers are active in iPS DF 19.11 derived from foreskin fibroblasts.Transcription factors
The ''SPMAP1'' promoter has many transcription factors binding sites. SPMAP1's transcription factors are commonly found in hematopoietic cells, connective tissue, cardiovascular tissue, and the immune system. The presence of Krueppel Like Transcription Factors suggests a role for SPMAP1 in proliferation or apoptosis. The presence of SMAD indicates an involvement in the TGF-β pathway, while the presence ofMyc
''Myc'' is a family of regulator genes and proto-oncogenes that code for transcription factors. The ''Myc'' family consists of three related human genes: ''c-myc'' ( MYC), ''l-myc'' ( MYCL), and ''n-myc'' ( MYCN). ''c-myc'' (also sometimes r ...
related transcription factors indicates a potential proliferation function of the protein. Additionally, other ''SPMAP1'' transcription factors, like RBPJ-Kappa are involved in proliferation and signalling.
Variants
NumerousSNPs
In genetics and bioinformatics, a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP ; plural SNPs ) is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. Although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in ...
were found in the 5' UTR, 3' UTR, and coding region of ''SPMAP1''. Few SNPs were found in highly conserved regions. In all, four SNPs were found in the highly conserved amino acids. One SNP was found in the start codon sequence. Of these five, three had a SNP on the third position of the codon. Due to the wobble hypothesis
A wobble base pair is a pairing between two nucleotides in RNA molecules that does not follow Watson-Crick base pair rules. The four main wobble base pairs are guanine-uracil (G-U), hypoxanthine-uracil (I-U), hypoxanthine-adenine (I-A), and hypo ...
, three of the five SNPs would have no effect on the overall protein structure.
mRNA
''SPMAP1'' does not have any miRNA binding sites. Its mRNA has low abundance (0.44%). The mRNA sequence has three hexaloops, none of which are significant.Protein
Primary structure
SPMAP1 is a 17.6kDa protein. Distant orthologs are 5 to 6 kDa larger, but some of the discrepancies come from an added NLS sequence, which ''Homo sapiens'' does not have There are no positive or negative charge clusters. There are no transmembrane components. The isoelectric point is 9.80 / 17564.67 pI/Mw. SPMAP1 is hydrophobic and soluble.
Secondary and tertiary structure
Secondary structure of SPMAP1 consists of both beta sheets and alpha helices (see diagram on right). Results are confirmed in the tertiary structure, however, alpha helix and beta sheet numbers differ slightly (see diagram on right).Motifs and binding sites
There are no N-terminal signal peptides. Cleavage motifs were not found. There are no ER membrane retention signals, nor peroxisomal targeting signal. SKL2 is not present, thus a secondary peroxisome signal is not present. There are no vacuolar targeting signals. There are no RNA binding motifs or actinin type actin binding motifs. There are no N-myristoylation pattern or prenylation patterns. Kinase finder at Cuckoo determined kinase binding sites for SPMAP1. There are many Serine/Threonine, and Tyrosine kinase phosphorylation sites. Serine and Threonine kinase binding sites are the most prevalent above the statistically significant threshold. There are no SUMOylation sites. ''SPMAP1'' gene has six sites on the sequence of possible O-GlcNAc sites. Highly conserved O-GlcNAc amino acid sites are 24, 32, 117, and 142. O-GlcNAc post-translational modification occurs on Ser/Thr residues, specifically on oncogenes, tumor suppressors, and proteins involved in growth factor signaling.
SPMAP1 has a Caspase3/7 motif, where either Caspase 3 or 7 would cleave. This supports the idea that SPMAP1 is involved in proliferation, as a proapoptotic caspase would want to destroy any protein driving proliferation. The protein also has a motif where peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase NIMA interacting 1 (Pin1) binds. Pin1 upregulation is involved in cancer and immune disorders. This supports the claim that SPMAP1 is involved in cancer, immune cells, and perhaps cancers of the immune system. Additionally, SPMAP1 protein has an IBM site, where inhibitors of apoptosis (IAPs) bind.Eukaryotic Linear Motif search on c17orf98 amino acid sequence
Kinase finder at Cuckoo determined kinase binding sites for SPMAP1. There are many Serine/Threonine, and Tyrosine kinase phosphorylation sites. Serine and Threonine kinase binding sites are the most prevalent above the statistically significant threshold. There are no SUMOylation sites. ''SPMAP1'' gene has six sites on the sequence of possible O-GlcNAc sites. Highly conserved O-GlcNAc amino acid sites are 24, 32, 117, and 142. O-GlcNAc post-translational modification occurs on Ser/Thr residues, specifically on oncogenes, tumor suppressors, and proteins involved in growth factor signaling.
SPMAP1 has a Caspase3/7 motif, where either Caspase 3 or 7 would cleave. This supports the idea that SPMAP1 is involved in proliferation, as a proapoptotic caspase would want to destroy any protein driving proliferation. The protein also has a motif where peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase NIMA interacting 1 (Pin1) binds. Pin1 upregulation is involved in cancer and immune disorders. This supports the claim that SPMAP1 is involved in cancer, immune cells, and perhaps cancers of the immune system. Additionally, SPMAP1 protein has an IBM site, where inhibitors of apoptosis (IAPs) bind.Eukaryotic Linear Motif search on c17orf98 amino acid sequence/ref> This again supports the idea of SPMAP1 being involved in inhibiting apoptosis, and logically, driving cancer. Furthermore, SPMAP1 has motifs where
GRB2
Growth factor receptor-bound protein 2, also known as Grb2, is an adaptor protein involved in signal transduction/ cell communication. In humans, the GRB2 protein is encoded by the ''GRB2'' gene.
The protein encoded by this gene binds recepto ...
's SH2 domain binds. GRB2 is an adapter protein involved in the RAS signaling pathway, a pathway that when deregulated drives uncontrolled proliferation.
Amino acid sequence
A duplication may have occurred at positions 59–71. ''Homo sapiens''MAYLSECRLRLEKGFILDGVAVSTAARAYGRSRPKLWSAIPPYNAQQDYHARSYFQ SHVVPPLLRVVPPLLRKTDQDHGGTGRDGWIVDYIHIFGQGQRYLNRRNWAGTGHS LQQVTGHDHYNADLKPIDGFNGRFGYRRNTPALRQSTSVFGEVTHFPLF
Associated proteins
There are no known associated proteins.Expression
Protein abundance in ''Homo sapiens'' whole organism is quite low. No data is available for other species. Allen Brain Atlas yields no brain atlas for SPMAP1.Subcellular localization
SPMAP1 protein has been found to be expressed in thintermediate filaments and the nucleoli
A SPMAP1 antibody is available from Sigma-Aldrich. Additionally, SPMAP1 localizes in the cytoplasm. Distantly related SPMAP1 orthologs in organisms such as ''Macrostomum lignano'' and ''Amphimedon queenslandica'' exhibit nuclear expression.
Nuclear localization signals
A nuclear localization signal ''or'' sequence (NLS) is an amino acid sequence that 'tags' a protein for import into the cell nucleus by nuclear transport. Typically, this signal consists of one or more short sequences of positively charged lysines ...
are present in distantly related organisms in non-conserved sites. The results of the k-NN prediction is cytoplasmic localization. SPMAP1 is not a signal peptide. The protein is a soluble.
Tissue
Like most proteins, SPMAP1 protein is highly expressed in the testes. The protein is expressed on adult tissues as well as fetal tissue. The protein has been found to be mildly expressed in connective tissue. Additionally, expression has been seen in the sperm, breast epithelial cells, and various cells of the immune system.Clinical significance
Cancer
Protein expression is elevated in many cancer patients. Specifically, protein expression has been shown to be high on colorectal, breast, prostate, and lung. SPMAP1 is expressed in papillary thyroid cancer as well. Additionally, mutations were found in SPMAP1 in endometrial, stomach, coloratura, and kidney cancer. SPMAP1 expression is elevated in cancer patients with BRCA. In kidney renal clear cell carcinoma patients, SPMAP1 expression dramatically decreased compared to the non cancerous state. In 80% of chromophobe renal cell carcinoma patients, at least one gene duplication SPMAP1 was present.Other conditions
Protein expression is lower in males withteratozoospermia
Teratospermia or teratozoospermia is a condition characterized by the presence of sperm with abnormal morphology that affects fertility in males.
Causes
The causes of teratozoospermia are unknown in most cases. However, Hodgkin's disease, coeliac ...
as compared to those without. Many Geo Profile experiments have been conducted with SPMAP1, however, none yield data showing significant change in expression.
Evolution
SPMAP1 is a slow mutating protein. It resembles cytochrome c in its rate of divergence, as determined by the molecular clock equations.
Paralogs
There are no known ''Homo sapiens'' paralogs for SPMAP1.Blast entry on c17orf98 https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi?PAGE=ProteinsOrthologs
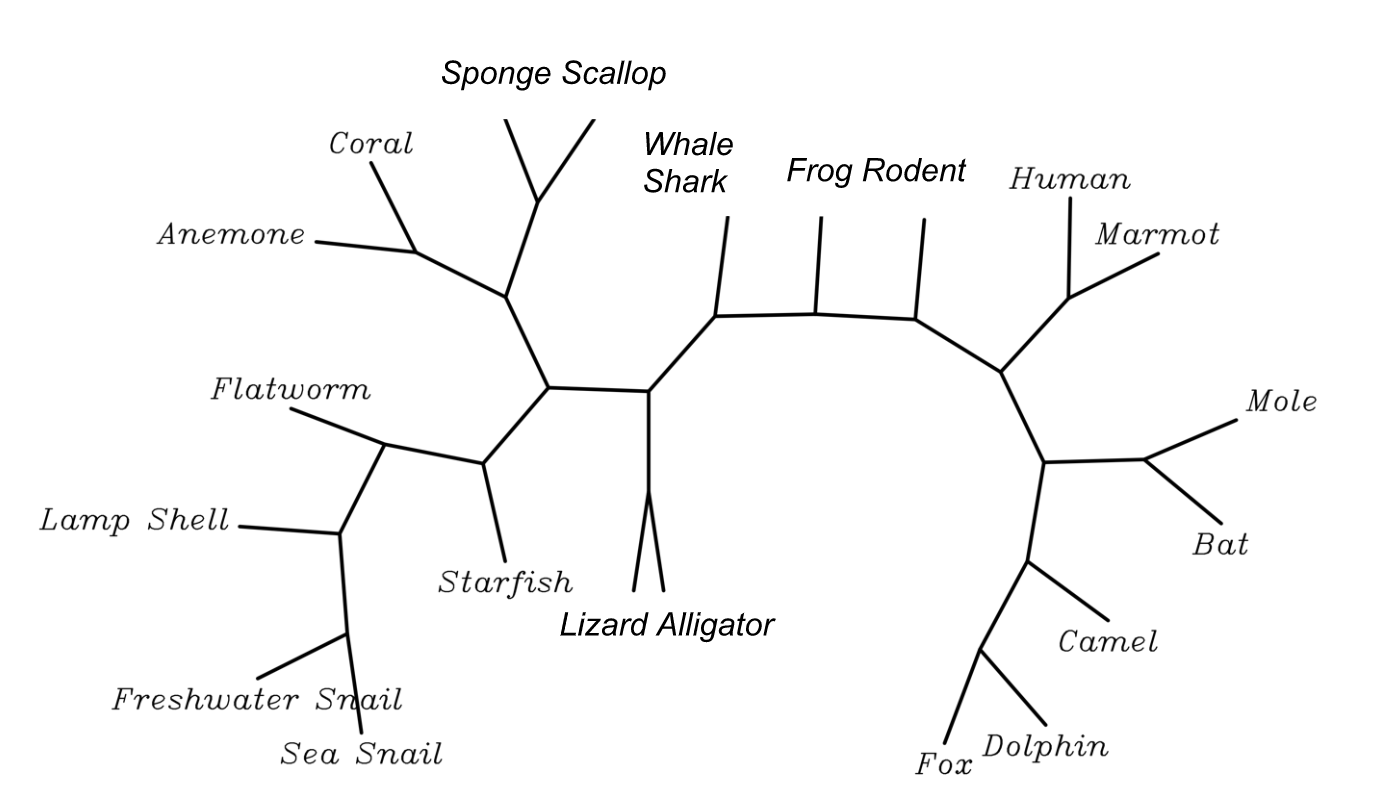
SPMAP1 protein has additional distantly related orthologs across the metazoan kingdom. Its most distant relative is in the sponge family. There is no known ortholog in ctenophores, nematodes, bacteria, fungus, plants, or zebrafish. There are only two fish with the ''SPMAP1'' gene. Model organisms such as ''Caenorhabditis elegans
''Caenorhabditis elegans'' () is a free-living transparent nematode about 1 mm in length that lives in temperate soil environments. It is the type species of its genus. The name is a Hybrid word, blend of the Greek ''caeno-'' (recent), ''r ...
'', and ''Drosophila melanogaster
''Drosophila melanogaster'' is a species of fly (an insect of the Order (biology), order Diptera) in the family Drosophilidae. The species is often referred to as the fruit fly or lesser fruit fly, or less commonly the "vinegar fly", "pomace fly" ...
'', do not have the gene.
SPMAP1 Orthologs
References
{{Reflist