C15orf39 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
C15orf39 is a

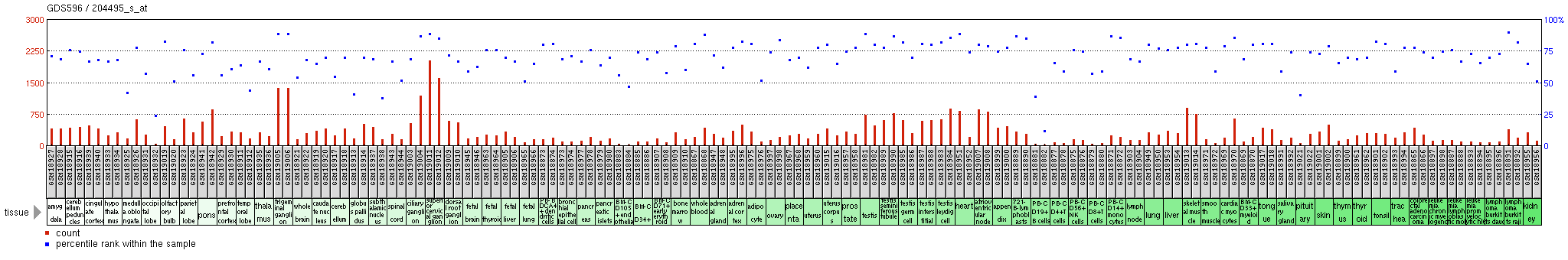 C15orf39 is highly expressed in the
C15orf39 is highly expressed in the 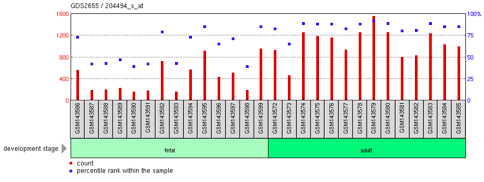 C15orf39 expression levels in
C15orf39 expression levels in
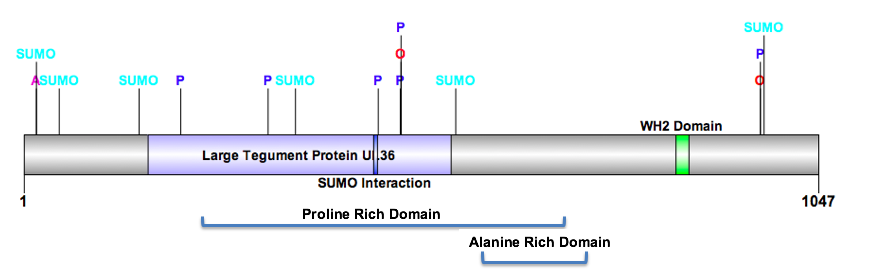 C15orf39 has four predicted domains. Two of which, are the
C15orf39 has four predicted domains. Two of which, are the
 .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.

 The graph displays that the C15orf39 protein is quickly
The graph displays that the C15orf39 protein is quickly
protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
that in humans is encoded by the Chromosome 15 open reading frame
In molecular biology, reading frames are defined as spans of DNA sequence between the start and stop codons. Usually, this is considered within a studied region of a prokaryotic DNA sequence, where only one of the six possible reading frames ...
15 (C15orf39) gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
.
Gene
Location
C15orf39 is located onchromosome 15
Chromosome 15 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 15 spans about 99.7 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents between 3% and 3.5% of the total DNA ...
(15q24.2), spanning 16.53kb from 75487985 to 75504515 on the plus DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
strand. C15orf39 has three exon
An exon is any part of a gene that will form a part of the final mature RNA produced by that gene after introns have been removed by RNA splicing. The term ''exon'' refers to both the DNA sequence within a gene and to the corresponding sequence ...
s, and seven intron
An intron is any nucleotide sequence within a gene that is not expressed or operative in the final RNA product. The word ''intron'' is derived from the term ''intragenic region'', i.e., a region inside a gene."The notion of the cistron .e., gen ...
s.
mRNA
Isoforms
The coding sequence for the C15orf39mRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of Protein biosynthesis, synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is ...
is 4443 base pair
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA ...
s long. The C15orf39 gene produces seven mRNA transcripts, with the longest coding isoform being 1047 amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
s long, and the shortest being 27 amino acids which has a truncated 3' end.
Expression
 C15orf39 is highly expressed in the
C15orf39 is highly expressed in the trigeminal ganglion
The trigeminal ganglion (also known as: Gasserian ganglion, semilunar ganglion, or Gasser's ganglion) is the sensory ganglion of each trigeminal nerve (CN V). The trigeminal ganglion is located within the trigeminal cave (Meckel's cave), a cav ...
, superior cervical ganglion
The superior cervical ganglion (SCG) is the upper-most and largest of the cervical sympathetic ganglia of the sympathetic trunk. It probably formed by the union of four sympathetic ganglia of the cervical spinal nerves C1–C4. It is the only ...
, whole blood
Whole blood (WB) is human blood from a standard blood donation. It is used in the treatment of massive bleeding, in exchange transfusion, and when people donate blood to themselves (autologous transfusion). One unit of whole blood (approxima ...
, and the heart
The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ found in humans and other animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. The heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrie ...
. Low expression levels of C15orf39 were found in the occipital lobe
The occipital lobe is one of the four Lobes of the brain, major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The name derives from its position at the back of the head, from the Latin , 'behind', and , 'head'.
The occipital lobe is the ...
and PB-CD19+ B-cells
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or inserted into the plasm ...
.
.
. C15orf39 expression levels in
C15orf39 expression levels in fetal
A fetus or foetus (; : fetuses, foetuses, rarely feti or foeti) is the unborn offspring of a viviparous animal that develops from an embryo. Following the embryonic stage, the fetal stage of development takes place. Prenatal development is a ...
and adult reticulocyte
In hematology, reticulocytes are immature red blood cells (RBCs). In the process of erythropoiesis (red blood cell formation), reticulocytes develop and mature in the bone marrow and then circulate for about a day in the blood stream before dev ...
s showed significantly different levels of expression (P < 0.0001), with adult reticulocytes expressing more C15orf39 than fetal cells.
.
.
.
.
Protein
General Properties
C15orf39 has an unmodifiedmolecular mass
The molecular mass () is the mass of a given molecule, often expressed in units of daltons (Da). Different molecules of the same compound may have different molecular masses because they contain different isotopes of an element. The derived quan ...
of 110.6 kDA. The modified molecular mass is 110.7 kDA. C15orf39 is composed of an above average level of proline
Proline (symbol Pro or P) is an organic acid classed as a proteinogenic amino acid (used in the biosynthesis of proteins), although it does not contain the amino group but is rather a secondary amine. The secondary amine nitrogen is in the p ...
(≈17%), and is deficient in isoleucine
Isoleucine (symbol Ile or I) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the depro ...
(≈1%) and asparagine
Asparagine (symbol Asn or N) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the depro ...
(≈1%). Both close (Thirteen-lined ground squirrel
The thirteen-lined ground squirrel (''Ictidomys tridecemlineatus''), also known as the striped gopher, leopard ground squirrel, and squinny (formerly known as the leopard-spermophile in the age of John James Audubon, Audubon), is a species of hib ...
) and distant ( Crested-Ibis) orthologs contained above average levels of proline, and low levels of isoleucine, and asparagine.
Domains and Motifs
 C15orf39 has four predicted domains. Two of which, are the
C15orf39 has four predicted domains. Two of which, are the proline
Proline (symbol Pro or P) is an organic acid classed as a proteinogenic amino acid (used in the biosynthesis of proteins), although it does not contain the amino group but is rather a secondary amine. The secondary amine nitrogen is in the p ...
rich and alanine
Alanine (symbol Ala or A), or α-alanine, is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an amine group and a carboxylic acid group, both attached to the central carbon atom which also carries a methyl group sid ...
rich domains. The large tegument protein UL36 domain is important in the regulation of the viral cycle of Human Herpes Virus 1 (HHV-1), including transporting the viral capsid
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or m ...
to the nuclear pore complex
The nuclear pore complex (NPC), is a large protein complex giving rise to the nuclear pore. A great number of nuclear pores are studded throughout the nuclear envelope that surrounds the eukaryote cell nucleus. The pores enable the nuclear tra ...
, and linking the inner and outer viral tegument capsids together. Lastly, the WH2 domain, WASP-homology domain 2, is approximately 18 amino acids long, and serves as an actin
Actin is a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of ...
binding domain. WH2 binds actin monomers enabling the production of actin filaments
Microfilaments, also called actin filaments, are protein filaments in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells that form part of the cytoskeleton. They are primarily composed of polymers of actin, but are modified by and interact with numerous other p ...
.
Post-Translational Modifications
The predictedpost-translational modification
In molecular biology, post-translational modification (PTM) is the covalent process of changing proteins following protein biosynthesis. PTMs may involve enzymes or occur spontaneously. Proteins are created by ribosomes, which translation (biolog ...
s for C15orf39 include phosphorylation
In biochemistry, phosphorylation is described as the "transfer of a phosphate group" from a donor to an acceptor. A common phosphorylating agent (phosphate donor) is ATP and a common family of acceptor are alcohols:
:
This equation can be writ ...
, acetylation
:
In chemistry, acetylation is an organic esterification reaction with acetic acid. It introduces an acetyl group into a chemical compound. Such compounds are termed ''acetate esters'' or simply ''acetates''. Deacetylation is the opposite react ...
, sumoylation
In molecular biology, SUMO (Small Ubiquitin-like Modifier) proteins are a family of small proteins that are covalently attached to and detached from other proteins in cells to modify their function. This process is called SUMOylation (pronounced ...
, and o-glycosylation
''O''-linked glycosylation is the attachment of a sugar molecule to the oxygen atom of serine (Ser) or threonine (Thr) residues in a protein. ''O''-glycosylation is a post-translational modification that occurs after the protein has been synthesis ...
. An amino acid of importance is K17, which has an acetyl and sumo-group covalently attached. Also, T970, which is phosphorylated and has an o-glycosyl group attached. All predicted post-translational modifications were conserved in distant and strict orthologs. .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
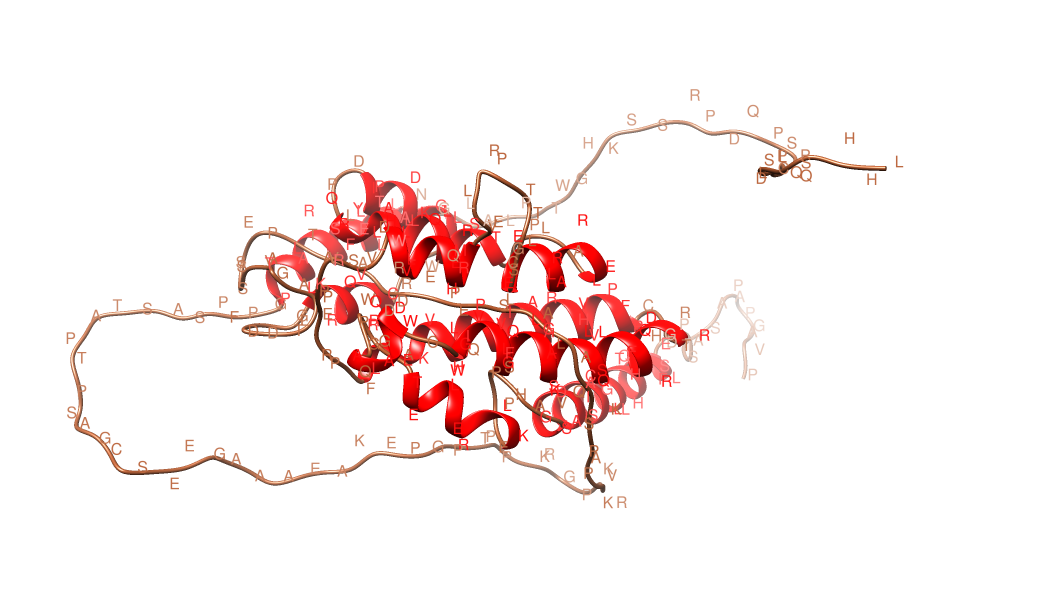
Structure
Alpha helices
An alpha helix (or α-helix) is a sequence of amino acids in a protein that are twisted into a coil (a helix).
The alpha helix is the most common structural arrangement in the secondary structure of proteins. It is also the most extreme type of l ...
predicted in the C15orf39 protein are colored red, and random coils are represented as tan. No beta sheet
The beta sheet (β-sheet, also β-pleated sheet) is a common motif of the regular protein secondary structure. Beta sheets consist of beta strands (β-strands) connected laterally by at least two or three backbone hydrogen bonds, forming a gene ...
s were predicted to be part of the secondary structure
Protein secondary structure is the local spatial conformation of the polypeptide backbone excluding the side chains. The two most common Protein structure#Secondary structure, secondary structural elements are alpha helix, alpha helices and beta ...
for C15orf39. The amino acids not modeled were predicted to be random coil
In polymer chemistry, a random coil is a conformation of polymers where the monomer subunits are oriented randomly while still being bonded to adjacent units. It is not one specific shape, but a statistical distribution of shapes for all the cha ...
s.
Sub-cellular Localization
C15orf39 is predicted to be located in thecytosol
The cytosol, also known as cytoplasmic matrix or groundplasm, is one of the liquids found inside cells ( intracellular fluid (ICF)). It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondri ...
of the cell.
Protein Interactions
Protein interaction screenings have shown C15orf39 to interact with many proteins, including RPLP1 and EIF4ENIF1. C15orf39 was discovered to interact withRPLP1
60S acidic ribosomal protein P1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''RPLP1'' gene.
Function
Ribosomes, the organelles that catalyze protein synthesis, consist of a small 40S subunit and a large 60S subunit. Together these subunits a ...
(Large Ribosomal Subunit Protein P1), a cytoplasm
The cytoplasm describes all the material within a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, including the organelles and excluding the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The material inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell a ...
ic protein, in a high-output yeast two-hybrid screening. RPLP1 is an acidic ribosomal
Ribosomes () are macromolecular machines, found within all cells, that perform biological protein synthesis (messenger RNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA molecules to fo ...
subunit that is important in the elongation step of transcription
Transcription refers to the process of converting sounds (voice, music etc.) into letters or musical notes, or producing a copy of something in another medium, including:
Genetics
* Transcription (biology), the copying of DNA into RNA, often th ...
. EIF4ENIF1 (Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor 4E Transporter), is a nucleocytoplasmic protein that shuttles the translation
Translation is the communication of the semantics, meaning of a #Source and target languages, source-language text by means of an Dynamic and formal equivalence, equivalent #Source and target languages, target-language text. The English la ...
initiation factor eIF4E between the nucleus
Nucleus (: nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucleu ...
and cytoplasm. The protein interaction between C15orf39 and EIF4ENIF1 was discovered through affinity capture.
Homology
Paralogs
There are no knownparalogs
Sequence homology is the biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences, defined in terms of shared ancestry in the evolutionary history of life. Two segments of DNA can have shared ancestry because of three phenomena: either a speci ...
for the human C15orf39 gene.
Orthologs
Theortholog
Sequence homology is the biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences, defined in terms of shared ancestry in the evolutionary history of life. Two segments of DNA can have shared ancestry because of three phenomena: either a speci ...
space for C15orf39 includes relatives as distant as the cartilaginous fish
Chondrichthyes (; ) is a class of jawed fish that contains the cartilaginous fish or chondrichthyans, which all have skeletons primarily composed of cartilage. They can be contrasted with the Osteichthyes or ''bony fish'', which have skeleto ...
like ''Rhincodon typus'' (whale shark
The whale shark (''Rhincodon typus'') is a slow-moving, filter feeder, filter-feeding carpet shark and the largest known Extant taxon, extant fish species. The largest confirmed individual had a length of . The whale shark holds many records for ...
), and as strict as closely related mammals like the Gorilla
Gorillas are primarily herbivorous, terrestrial great apes that inhabit the tropical forests of equatorial Africa. The genus ''Gorilla'' is divided into two species: the eastern gorilla and the western gorilla, and either four or five su ...
, which has 99% sequence identity to the human protein. The phylogenetic tree
A phylogenetic tree or phylogeny is a graphical representation which shows the evolutionary history between a set of species or taxa during a specific time.Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA. In ...
below, shows the evolution
Evolution is the change in the heritable Phenotypic trait, characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. It occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection and genetic drift act on genetic variation, re ...
ary relationship of the C15orf39 protein sequence in its orthologs.

Divergence
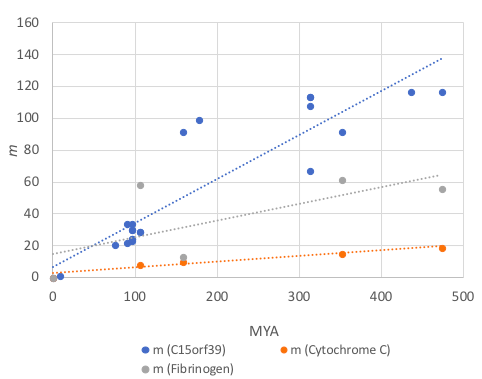
 The graph displays that the C15orf39 protein is quickly
The graph displays that the C15orf39 protein is quickly evolving
Evolution is the change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. It occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection and genetic drift act on genetic variation, resulting in certai ...
. C15orf39's sequence has diverged at a quicker rate than the quickly evolving fibrinogen
Fibrinogen (coagulation factor I) is a glycoprotein protein complex, complex, produced in the liver, that circulates in the blood of all vertebrates. During tissue and vascular injury, it is converted Enzyme, enzymatically by thrombin to fibrin ...
protein in humans.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.References