bypass capacitor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 In
In
 A bypass capacitor is often used to decouple a subcircuit from AC signals or
A bypass capacitor is often used to decouple a subcircuit from AC signals or
Capacitor Design Data, and Decoupling Placement, How-to
o
Leroy's Engineering Web Site
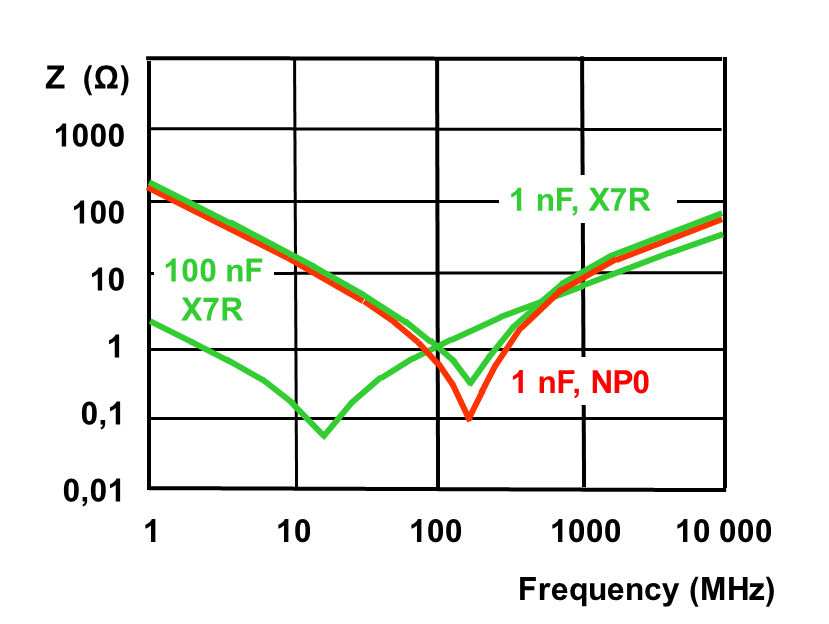
/ref> Since capacitors differ in their high-frequency characteristics, decoupling ideally involves the use of a combination of capacitors. For example in logic circuits, a common arrangement is ~100 nF ceramic per logic IC (multiple ones for complex ICs), combined with electrolytic or tantalum capacitor(s) up to a few hundred μF per board or board section.
File:0431 - C64 Mainboard ASSY250407 RevA.jpg, 1980s
Choosing and Using Bypass Capacitors
– application note from Intersil
– decoupling guide for various frequencies by Henry W. Ott
Power Supply Noise Reduction
– how to design effective supply bypassing and decoupling networks by Ken Kundert
ESR and Bypass Capacitor Self Resonant Behavior: How to Select Bypass Caps
– article written by Douglas Brooks
Circuit Board Decoupling Information
– decoupling guidelines for various types of circuit boards
Basic Principles of Signal Integrity
– Altera whitepaper
Bypass Capacitors, an Interview With Todd Hubing
– by Douglas Brooks Capacitors
 In
In electronics
Electronics is a scientific and engineering discipline that studies and applies the principles of physics to design, create, and operate devices that manipulate electrons and other Electric charge, electrically charged particles. It is a subfield ...
, a decoupling capacitor is a capacitor
In electrical engineering, a capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy by accumulating electric charges on two closely spaced surfaces that are insulated from each other. The capacitor was originally known as the condenser, a term st ...
used to decouple (i.e. prevent electrical energy
Electrical energy is the energy transferred as electric charges move between points with different electric potential, that is, as they move across a voltage, potential difference. As electric potential is lost or gained, work is done changing the ...
from transferring to) one part of a circuit from another. Noise
Noise is sound, chiefly unwanted, unintentional, or harmful sound considered unpleasant, loud, or disruptive to mental or hearing faculties. From a physics standpoint, there is no distinction between noise and desired sound, as both are vibrat ...
caused by other circuit elements is shunted through the capacitor, reducing its effect on the rest of the circuit. For higher frequencies, an alternative name is bypass capacitor as it is used to bypass the power supply
A power supply is an electrical device that supplies electric power to an electrical load. The main purpose of a power supply is to convert electric current from a source to the correct voltage, electric current, current, and frequency to power ...
or other high- impedance component of a circuit.
Discussion
Active devices of anelectronic system
Electronic may refer to:
*Electronics, the science of how to control electric energy in semiconductors
*Electronics (magazine), ''Electronics'' (magazine), a defunct American trade journal
*Electronic storage, the storage of data using an electron ...
(e.g. transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electric power, power. It is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semicondu ...
s, integrated circuit
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
s, vacuum tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, thermionic valve (British usage), or tube (North America) is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric voltage, potential difference has been applied. It ...
s) are connected to their power supplies
A power supply is an electrical device that supplies electric power to an electrical load. The main purpose of a power supply is to convert electric current from a source to the correct voltage, current, and frequency to power the load. As a r ...
through conductors with finite resistance and inductance
Inductance is the tendency of an electrical conductor to oppose a change in the electric current flowing through it. The electric current produces a magnetic field around the conductor. The magnetic field strength depends on the magnitude of the ...
. If the current drawn by an active device changes, the voltage drop
In electronics, voltage drop is the decrease of electric potential along the path of a current flowing in a circuit. Voltage drops in the internal resistance of the source, across conductors, across contacts, and across connectors are unde ...
from the power supply to the device will also change due to these impedances. If several active devices share a common path to the power supply, changes in the current drawn by one element may produce voltage changes large enough to affect the operation of others – voltage spike
In electrical engineering, spikes are fast, short duration electrical transients in voltage (voltage spikes), current (current spikes), or transferred energy (energy spikes) in an electrical circuit.
Fast, short duration electrical transients ...
s or ground bounce, for example – so the change of state of one device is coupled to others through the common impedance to the power supply. A decoupling capacitor provides a bypass path for transient currents, instead of flowing through the common impedance. Don Lancaster, ''TTL Cookbook', Howard W. Sams, 1975, no ISBN, pp.23-24
The decoupling capacitor works as the device’s local energy storage
Energy storage is the capture of energy produced at one time for use at a later time to reduce imbalances between energy demand and energy production. A device that stores energy is generally called an Accumulator (energy), accumulator or Batte ...
. The capacitor is placed between the power line and the ground to the circuit the current is to be provided. According to the capacitor current–voltage relation
:
a voltage drop between a power line and the ground results in a current drawn out from the capacitor to the circuit. When capacitance is large enough, sufficient current is supplied to maintain an acceptable range of voltage drop. The capacitor stores a small amount of energy that can compensate for the voltage drop in the power supply conductors to the capacitor. To reduce undesired parasitic equivalent series inductance
Equivalent series inductance (ESL) is an effective inductance that is used to describe the inductive part of the Electrical impedance, impedance of certain electrical components.
Overview
The theoretical treatment of devices such as capacitors a ...
, small and large capacitors are often placed in parallel, adjacent to individual integrated circuits (see § Placement).
In digital circuits, decoupling capacitors also help prevent radiation of electromagnetic interference from relatively long circuit traces due to rapidly changing power supply currents.
Decoupling capacitors alone may not suffice in such cases as a high-power amplifier stage with a low-level pre-amplifier coupled to it. Care must be taken in the layout of circuit conductors so that heavy current at one stage does not produce power supply voltage drops that affect other stages. This may require re-routing printed circuit board traces to segregate circuits, or the use of a ground plane
In electrical engineering, a ground plane is an electrically conductive surface, usually connected to electrical ground. Ground planes are typically made of copper or aluminum, and they are often located on the bottom of printed circuit boards ...
to improve the stability of power supply.
Decoupling
 A bypass capacitor is often used to decouple a subcircuit from AC signals or
A bypass capacitor is often used to decouple a subcircuit from AC signals or voltage spike
In electrical engineering, spikes are fast, short duration electrical transients in voltage (voltage spikes), current (current spikes), or transferred energy (energy spikes) in an electrical circuit.
Fast, short duration electrical transients ...
s on a power supply or other line. A bypass capacitor can shunt energy from those signals, or transients, past the subcircuit to be decoupled, right to the return path. For a power supply line, a bypass capacitor from the supply voltage line to the power supply return (neutral) would be used.
High frequencies and transient currents can flow through a capacitor to circuit ground instead of to the harder path of the decoupled circuit, but DC cannot go through the capacitor and continues to the decoupled circuit.
Another kind of decoupling is stopping a portion of a circuit from being affected by switching that occurs in another portion of the circuit. Switching in subcircuit A may cause fluctuations in the power supply or other electrical lines, but you do not want subcircuit B, which has nothing to do with that switching, to be affected. A decoupling capacitor can decouple subcircuits A and B so that B doesn't see any effects of the switching.
Switching subcircuits
In a subcircuit, switching will change the load current drawn from the source. Typical power supply lines show inherentinductance
Inductance is the tendency of an electrical conductor to oppose a change in the electric current flowing through it. The electric current produces a magnetic field around the conductor. The magnetic field strength depends on the magnitude of the ...
, which results in a slower response to changes in current. The supply voltage will drop across these parasitic inductances for as long as the switching event occurs. This transient voltage drop would be seen by other loads as well if the inductance between two loads is much lower compared to the inductance between the loads and the output of the power supply.
To decouple other subcircuits from the effect of the sudden current demand, a decoupling capacitor can be placed in parallel with the subcircuit, across its supply voltage lines. When switching occurs in the subcircuit, the capacitor supplies the transient current. Ideally, by the time the capacitor runs out of charge, the switching event has finished, so that the load can draw full current at normal voltage from the power supply and the capacitor can recharge. The best way to reduce switching noise is to design a PCB as a giant capacitor by sandwiching the power and ground planes across a dielectric
In electromagnetism, a dielectric (or dielectric medium) is an Insulator (electricity), electrical insulator that can be Polarisability, polarised by an applied electric field. When a dielectric material is placed in an electric field, electric ...
material.
Sometimes parallel combinations of capacitors are used to improve response. This is because real capacitors have parasitic inductance, which causes the impedance to deviate from that of an ideal capacitor at higher frequencies.
Transient load decoupling
Transient load decoupling as described above is needed when there is a large load that gets switched quickly. The parasitic inductance in every (decoupling) capacitor may limit the suitable capacity and influence the appropriate type if switching occurs very fast.Logic
Logic is the study of correct reasoning. It includes both formal and informal logic. Formal logic is the study of deductively valid inferences or logical truths. It examines how conclusions follow from premises based on the structure o ...
circuits tend to do sudden switching (an ideal logic circuit would switch from low voltage to high voltage instantaneously, with no middle voltage ever observable). So logic circuit boards often have a decoupling capacitor close to each logic IC connected from each power supply connection to a nearby ground. These capacitors decouple every IC from every other IC in terms of supply voltage dips.
These capacitors are often placed at each power source as well as at each analog component in order to ensure that the supplies are as steady as possible. Otherwise, an analog component with a poor power supply rejection ratio (PSRR) will copy fluctuations in the power supply onto its output.
In these applications, the decoupling capacitors are often called ''bypass capacitors'' to indicate that they provide an alternate path for high-frequency signals that would otherwise cause the normally steady supply voltage to change. Those components that require quick injections of current can ''bypass'' the power supply by receiving the current from the nearby capacitor. Hence, the slower power supply connection is used to charge these capacitors, and the capacitors actually provide large quantities of high-availability current.
Placement
A transient load decoupling capacitor is placed as close as possible to the device requiring the decoupled signal. This minimizes the amount of lineinductance
Inductance is the tendency of an electrical conductor to oppose a change in the electric current flowing through it. The electric current produces a magnetic field around the conductor. The magnetic field strength depends on the magnitude of the ...
and series resistance between the decoupling capacitor and the device. The longer the conductor between the capacitor and the device, the more inductance is present.o
Leroy's Engineering Web Site
/ref> Since capacitors differ in their high-frequency characteristics, decoupling ideally involves the use of a combination of capacitors. For example in logic circuits, a common arrangement is ~100 nF ceramic per logic IC (multiple ones for complex ICs), combined with electrolytic or tantalum capacitor(s) up to a few hundred μF per board or board section.
Example uses
These photos show oldprinted circuit board
A printed circuit board (PCB), also called printed wiring board (PWB), is a Lamination, laminated sandwich structure of electrical conduction, conductive and Insulator (electricity), insulating layers, each with a pattern of traces, planes ...
s with through-hole capacitors, where as modern boards typically have tiny surface-mount
Surface-mount technology (SMT), originally called planar mounting, is a method in which the electrical components are mounted directly onto the surface of a printed circuit board (PCB). An electrical component mounted in this manner is referred ...
capacitors.
Commodore 64
The Commodore 64, also known as the C64, is an 8-bit computing, 8-bit home computer introduced in January 1982 by Commodore International (first shown at the Consumer Electronics Show, January 7–10, 1982, in Las Vegas). It has been listed in ...
main board. Most of the "orange" round disc parts are decoupling capacitors.
File:Cromemco XXU 32-bit 68020 S-100 microcomputer CPU.jpg, 1980s Cromemco XXU, a Motorola
Motorola, Inc. () was an American multinational telecommunications company based in Schaumburg, Illinois. It was founded by brothers Paul and Joseph Galvin in 1928 and had been named Motorola since 1947. Many of Motorola's products had been ...
68020 processor S-100 bus
The S-100 bus or Altair bus, later standardized as IEEE 696-1983 ''(inactive-withdrawn)'', is an early computer bus designed in 1974 as a part of the Altair 8800. The bus was the first industry standard expansion bus for the microcomputer in ...
card. The axial parts between the ICs are decoupling capacitors.
File:Cromemco 16KZ S-100 Board.jpg, 1970s Cromemco 16KZ, a 16KB DRAM
Dram, DRAM, or drams may refer to:
Technology and engineering
* Dram (unit), a unit of mass and volume, and an informal name for a small amount of liquor, especially whisky or whiskey
* Dynamic random-access memory, a type of electronic semicondu ...
memory S-100 bus
The S-100 bus or Altair bus, later standardized as IEEE 696-1983 ''(inactive-withdrawn)'', is an early computer bus designed in 1974 as a part of the Altair 8800. The bus was the first industry standard expansion bus for the microcomputer in ...
card. The green round disc parts are decoupling capacitors.
File:Interface I1.JPG, 1970s I1 parallel interface board for Electronika 60. The green rectangular parts are decoupling capacitors.
See also
* Ceramic capacitor *Equivalent series inductance
Equivalent series inductance (ESL) is an effective inductance that is used to describe the inductive part of the Electrical impedance, impedance of certain electrical components.
Overview
The theoretical treatment of devices such as capacitors a ...
* Equivalent series resistance
* Film capacitor
* E-series of preferred numbers
References
{{ReflistExternal links
Choosing and Using Bypass Capacitors
– application note from Intersil
– decoupling guide for various frequencies by Henry W. Ott
Power Supply Noise Reduction
– how to design effective supply bypassing and decoupling networks by Ken Kundert
ESR and Bypass Capacitor Self Resonant Behavior: How to Select Bypass Caps
– article written by Douglas Brooks
Circuit Board Decoupling Information
– decoupling guidelines for various types of circuit boards
Basic Principles of Signal Integrity
– Altera whitepaper
Bypass Capacitors, an Interview With Todd Hubing
– by Douglas Brooks Capacitors