Business Plan on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A business plan is a formal written document containing the goals of a
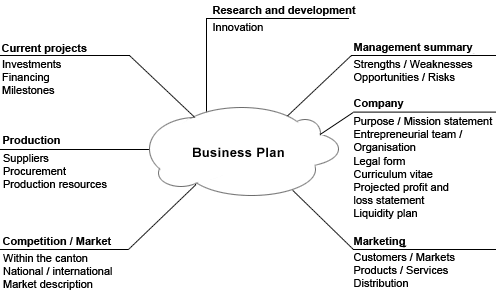 Typical structure for a business plan for a start-up venture
*cover page and table of contents
* executive summary
*
Typical structure for a business plan for a start-up venture
*cover page and table of contents
* executive summary
*
business
Business is the practice of making one's living or making money by producing or Trade, buying and selling Product (business), products (such as goods and Service (economics), services). It is also "any activity or enterprise entered into for ...
, the methods for attaining those goals, and the time-frame for the achievement of the goals. It also describes the nature of the business, background information on the organization
An organization or organisation (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English; American and British English spelling differences#-ise, -ize (-isation, -ization), see spelling differences) is an legal entity, entity—such as ...
, the organization's financial projections, and the strategies it intends to implement to achieve the stated targets. In its entirety, this document serves as a road-map (a plan
A plan is typically any diagram or list of steps with details of timing and resources, used to achieve an Goal, objective to do something. It is commonly understood as a modal logic, temporal set (mathematics), set of intended actions through wh ...
) that provides direction to the business.
Written business plans are often required to obtain a bank loan or other kind of financing. Templates and guides, such as the ones offered in the United States by the Small Business Administration can be used to facilitate producing a business plan.
Audience
Business plans may be internally or externally focused. Externally-focused plans draft goals that are important to outside stakeholders, particularly financial stakeholders. These plans typically have detailed information about the organization or the team making effort to reach its goals. With for-profit entities, external stakeholders include investors and customers, for non-profits, external stakeholders refer to donors and clients, for government agencies, external stakeholders are the tax-payers, higher-level government agencies, and international lending bodies such as theInternational Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution funded by 191 member countries, with headquarters in Washington, D.C. It is regarded as the global lender of las ...
, the World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and Grant (money), grants to the governments of Least developed countries, low- and Developing country, middle-income countries for the purposes of economic development ...
, various economic agencies of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
, and development banks.
Internally-focused business plans target intermediate goals required to reach the external goals. They may cover the development of a new product, a new service, a new IT system, a restructuring of finance, the refurbishing of a factory or the restructuring of an organization. An internally-focused business plan is often developed in conjunction with a balanced scorecard
A balanced scorecard is a strategy performance management tool – a well-structured report used to keep track of the execution of activities by staff and to monitor the consequences arising from these actions.
The term 'balanced scorecard' prim ...
or OGSM or a list of critical success factors. This allows the success of the plan to be measured using non-financial measures.
Business plans that identify and target internal goals, but provide only general guidance on how they will be met are called strategic plans.
Operational plans describe the goals of an internal organization, working group or department. Project plans, sometimes known as project frameworks, describe the goals of a particular project. They may also address the project's place within the organization's larger strategic goals.
Content
Business plans are essential decision-making tools. The content and format of a business plan depend on its goals and target audience. For example, a business plan for a non-profit organization might emphasize how it aligns with the organization's mission. Banks are particularly concerned about defaults, so a business plan created for a bank loan should convincingly demonstrate the organization’s ability to repay the loan. On the other hand, venture capitalists focus on initial investments, feasibility, and exit valuation. A business plan for a project that requires equity financing needs to explain why current resources, upcoming growth opportunities, and sustainable competitive advantages will contribute to a high exit valuation. Creating a business plan requires knowledge from various business disciplines, including finance, human resource management, intellectual property management, supply chain management, operations management, and marketing, among others. It can be helpful to view the business plan as a compilation of sub-plans, each addressing a key business discipline. A well-crafted business plan can help establish credibility, clarity, and appeal for individuals unfamiliar with the business. While writing a good business plan cannot guarantee success, it can significantly reduce the likelihood of failure. The process of creating a business plan involves five distinct steps. The first step is to clearly outline the main business concept. The second step is to gather data regarding the feasibility of your idea, including specific details about your business. The third step involves organizing the information you have collected and refining your plan. After that, you can start drafting an outline of your business plan, detailing the specifics of your business idea. The fifth and final step is to compile this information into a compelling format that will encourage potential investors to support your business.Presentation
The format of a business plan depends on its presentation context. It is common for businesses, especially start-ups, to have three or four formats for the same business plan. An " elevator pitch" is a short summary of the plan's executive summary. This is often used as a teaser to awaken the interest of potential investors, customers, or strategic partners. It is called an elevator pitch as it is supposed to be content that can be explained to someone else quickly in an elevator. The elevator pitch should be between 30 and 60 seconds. A pitch deck is a slide show and oral presentation that is meant to trigger discussion and interest potential investors in reading the written presentation. The content of the presentation is usually limited to the executive summary and a few key graphs showing financial trends and key decision-making benchmarks. If a new product is being proposed and time permits, a demonstration of the product may be included. A written presentation for external stakeholders is a detailed, well written, and pleasingly formatted plan targeted at external stakeholders. An internal operational plan is a detailed plan describing planning details that are needed by management but may not be of interest to external stakeholders. Such plans have a somewhat higher degree of candor and informality than the version targeted at external stakeholders and others.Business plans for start-ups
 Typical structure for a business plan for a start-up venture
*cover page and table of contents
* executive summary
*
Typical structure for a business plan for a start-up venture
*cover page and table of contents
* executive summary
*mission statement
A mission statement is a short statement of why an organization exists, what its overall goal is, the goal of its operations: what kind of product or service it provides, its primary customers or market, and its geographical region of operation ...
*business description
*business environment analysis
* SWOT analysis
*industry background
* competitor analysis
* market analysis
* marketing plan
* operations plan
*management summary
* financial plan
*achievements and milestones
Typical questions addressed by a business plan for a start-up venture
* What problem does the company's product or service solve? What niche will it fill?
* What is the company's solution to the problem?
* Who are the company's customers, and how will the company market and sell its products to them?
* What is the size of the market for this solution?
* What is the business model
A business model describes how a Company, business organization creates, delivers, and captures value creation, value,''Business Model Generation'', Alexander Osterwalder, Yves Pigneur, Alan Smith, and 470 practitioners from 45 countries, self-pub ...
for the business (how will it make money)?
* Who are the competitors and how will the company maintain a competitive advantage?
* How does the company plan to manage its operations as it grows?
* Who will run the company and what makes them qualified to do so?
* What are the risks and threats confronting the business, and what can be done to mitigate them?
* What are the company's capital and resource requirements?
* What are the company's historical and projected financial statements?
Revising the business plan
Cost overruns and revenue shortfalls
Cost andrevenue
In accounting, revenue is the total amount of income generated by the sale of product (business), goods and services related to the primary operations of a business.
Commercial revenue may also be referred to as sales or as turnover. Some compan ...
estimates are central to any business plan for deciding the viability of the planned venture. But costs are often underestimated and revenues overestimated resulting in later cost overruns, revenue shortfalls, and possibly non-viability. During the dot-com bubble 1997-2001 this was a problem for many technology start-ups. Reference class forecasting has been developed to reduce the risks of cost overruns and revenue shortfalls and thus generate more accurate business plans.
Uses
*Education
Education is the transmission of knowledge and skills and the development of character traits. Formal education occurs within a structured institutional framework, such as public schools, following a curriculum. Non-formal education als ...
**Business plans are used in some primary and secondary programs to teach economic principles.
:* Wikiversity has a Lunar Boom Town project where students of all ages can collaborate with designing and revising business models and practice evaluating them to learn practical business planning techniques and methodology
*Fundraising
Fundraising is the primary purpose of many business plans since they are related to the inherent probable success/failure of the company risk.
:*Angel investor
An angel investor (also known as a business angel, informal investor, angel funder, private investor, or seed investor) is an individual who provides capital to a business or businesses, including startups, usually in exchange for convertible de ...
s
:* Business loans
:* Grants
:*Startup company
A startup or start-up is a company or project undertaken by an Entrepreneurship, entrepreneur to seek, develop, and validate a scalable business model. While entrepreneurship includes all new businesses including self-employment and businesses tha ...
funding
:*Venture capital
Venture capital (VC) is a form of private equity financing provided by firms or funds to start-up company, startup, early-stage, and emerging companies, that have been deemed to have high growth potential or that have demonstrated high growth in ...
*Internal use
:* Management by objectives (MBO) is a process of agreeing upon objectives (as can be detailed within business plans) within an organization so that management and employees agree to the objectives and understand what they are in the organization.
:*Strategic planning
Strategic planning is the activity undertaken by an organization through which it seeks to define its future direction and makes decisions such as resource allocation aimed at achieving its intended goals. "Strategy" has many definitions, but it ...
is an organization's process of defining its strategy, or direction, and making decisions on allocating its resources to pursue this strategy, including its capital and people. Business plans can help decision-makers see how specific projects relate to the organization's strategic plan.
:* Total quality management (TQM) is a business management strategy aimed at embedding awareness of quality in all organizational processes. TQM has been widely used in manufacturing, education, call centers, government, and service industries, as well as NASA space and science programs.
Not for-profit businesses
Business goals can be defined for both non-profit and for-profit organizations. For-profit business plans typically emphasize financial objectives, such as generating profit and creating wealth. In contrast, non-profit organizations and government agencies often center their plans around their "organizational mission," which underpins their tax-exempt status or governmental role. However, non-profits may also seek to optimize their revenue. The primary distinction between for-profit and non-profit organizations lies in their fundamental objectives. For-profit organizations aim to maximize wealth, while non-profit organizations focus on serving the greater good of society. In non-profits, a creative tension often emerges as they try to balance their mission-driven goals with the need to generate revenue and maintain financial sustainability.Example
A notable real-life example of a business plan is the one created by Tesla Motors during its early days. Tesla's plan focused on revolutionizing the automotive industry by introducing electric vehicles (EVs) that were not only environmentally friendly but also high-performance and stylish. Key elements of their business plan included: # Vision: To accelerate the world's transition to sustainable energy. # Product Strategy: Starting with high-end EVs (like the Roadster) to establish credibility, then scaling down to more affordable models (like the Model S and Model 3). # Market Analysis: Highlighting the growing demand for sustainable transportation and the lack of competitive EVs in the market. # Revenue Model: Selling EVs directly to consumers and later expanding into energy products like solar panels and batteries. # Scalability: Emphasizing the potential for global expansion and partnerships with suppliers and governments. Tesla's business plan attracted significant investor interest and laid the foundation for its success as a leader in the EV market.See also
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Business Plan Business documents Business plan competitions Entrepreneurship Formal statements Strategic management Venture capital Business planning